
Import Export Business Plan Template
Written by Dave Lavinsky
Trade Global Business Plan
You’ve come to the right place to create your Trade Global business plan.
We have helped over 1,000 entrepreneurs and business owners create business plans and many have used them to start or grow their Trade Global businesses.
Below is a template to help you create each section of your Trade Global business plan.
Executive Summary
Business overview.
Trade Global is a startup Import/Export company located in Houston, Texas. The company was founded by Ted Rogers, who has deep experience as a wholesale distribution executive. Ted has long aspired to work for himself, and has been systematically acquiring the tools and knowledge necessary to successfully operate an import/export business. The combination of his skills and drive positions him to succeed. What’s more, he has an extensive network of contacts across the globe, which will provide an edge in acquiring clientele.
Product Offering
Trade Global has acquired a warehouse in Hong Kong, and has entered into contracts with five Asian manufacturers to export goods to the United States. As the company gains credibility and grows its client base, it has plans to begin building its own fleet of cargo ships that will carry goods both into and out of the United States.
Customer Focus
Trade Global will procure products from manufacturers and wholesale products to distributors throughout the United States, Southeast Asia, and Europe.
Management Team
Trade Global will be owned and operated by Ted Rogers. Ted has a background as a wholesaler, and is a graduate of Michigan State University’s Supply Chain Management program, and subsequently earned an Export/Import Certificate from the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC).
Success Factors
Trade Global will be able to achieve success by offering the following competitive advantages:
- Friendly, knowledgeable, and highly qualified owner
- An ideal warehouse location in Hong Kong, with ample room for expansion
- FTZ status with Port Houston
Financial Highlights
Trade Global is seeking $750,000 in debt financing to launch its import/export operation. The funding will be dedicated towards procuring, packing, and shopping products, and payroll of the staff until the firm reaches break even. The breakout of the funding is below:
- Inventory: $250,000
- Shipping costs: $250,000
- Office equipment, supplies, and materials: $10,000
- Overhead expenses (payroll, rent, utilities): $200,000
- Marketing costs: $20,000
- Working capital: $20,000
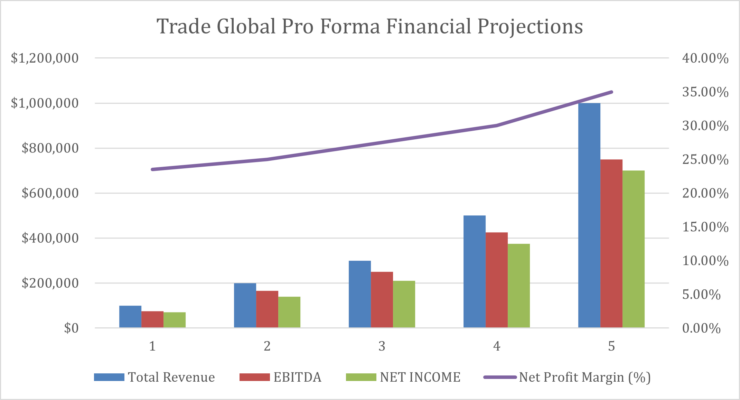
The following graph below outlines the pro forma financial projections for Trade Global.
Company Overview
Who is trade global.
Trade Global is a startup import/export company located in Hong Kong and Houston, Texas. The company was founded by Ted Rogers, who has deep experience as a wholesale distribution executive. Ted has long aspired to work for himself, and has been systematically acquiring the tools and knowledge necessary to successfully operate an import/export business. The combination of his skills and drive positions him to succeed. What’s more, he has an extensive network of contacts across the globe, which will provide an edge in acquiring clientele.
Trade Global aims to deliver a wide variety of goods both into and out of the United States. The team is highly qualified and experienced in sales and supply chain management.
Trade Global History
Trade Global is owned and operated by Ted Rogers, a former distribution executive and ICC certified Importer/Exporter. Ted has worked for a large wholesale company and oversaw a wide variety of accounts from around the world. Derek’s tenure with the wholesale distribution company, as well as his education in Supply Chain Management has given him the skills and knowledge required to venture out and start his own company. Ted has been awarded contracts with two large Chinese manufacturers, which guarantees Trade Global stability while it works to increase its reach.
Since incorporation, Trade Global has achieved the following milestones:
- Registered Trade Global, LLC to transact business in the state of Texas.
- Acquired an import license from US Customs and Border Protection (CBP)
- Has acquired an existing warehouse in Hong Kong.
- Reached out to numerous manufacturers to apply for wholesale contracts.
- Entered into a contract with a deep sea cargo transportation company.
- Began recruiting warehouse workers, and office personnel to work at Trade Global.
Trade Global Services
Trade Global has signed contracts with two manufacturers, to export goods from China to the US. It will begin as a small exporter, with ample warehouse space for growth. The company will keep abreast of logistics technology innovations as it grows.
Industry Analysis
The US import/export industry is significant in terms of revenue. According to the United States International Trade Commission (USITC), the total value of US goods and services exports in 2022 was approximately $2.09 trillion, and the value of imports was approximately $3.0 trillion. This resulted in a trade deficit of roughly $948.1 billion for the year. The revenue generated by the industry is a combination of goods and services exported and imported by the United States.
Over the last few decades, the US import/export industry has seen consistent growth. The USITC data indicates that the total value of US exports and imports has grown substantially since the 1980s. This growth is influenced by factors such as globalization, trade agreements, technological advancements, and evolving consumer demands.
The trade deficit, which occurs when the value of imports exceeds exports, has been a subject of concern for policymakers. Reducing the trade deficit has been a goal of various US administrations.
Several trends have shaped the US import/export industry:
- Globalization: Increased globalization has allowed US businesses to access international markets and global supply chains. This trend has led to an expansion in both exports and imports, as well as an interconnected global economy.
- E-commerce: The growth of e-commerce has had a substantial impact on the industry. Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) have easier access to international markets through online platforms, leading to a boost in exports of services and goods.
- Trade Policies: Trade policies, such as tariffs and trade agreements, have a significant impact on the industry. The US has experienced trade tensions with several countries, notably China. These policies can influence the types of goods and services that are imported and exported.
- Technology: Advancements in technology have made it easier for businesses to engage in international trade. Technologies like blockchain, logistics software, and automation have improved efficiency and tracking in the import/export process.
- Environmental and Ethical Concerns: There is a growing focus on sustainable and ethical trade practices. Consumers and businesses are increasingly concerned about the environmental impact of products, leading to changes in supply chain management and the types of goods being imported and exported.
- Geopolitical Factors: Geopolitical factors, such as trade relations with China, Brexit, and tensions in the Middle East, can affect trade patterns and the stability of the import/export industry.
Customer Analysis
Profile of target market.
Trade Global will initially target manufacturing companies in China, and wholesale companies in the US.
The precise data for these target markets are:
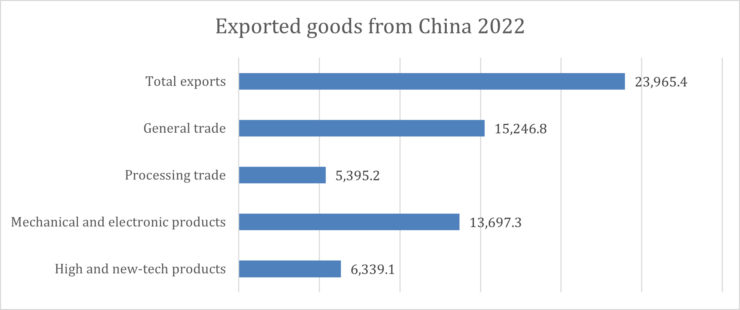
China In 2022, the total merchandise exports from China amounted to around 24 trillion yuan. This included 6.3 trillion yuan worth of high and new-tech products and over 13.6 trillion yuan worth of mechanical and electronic products.
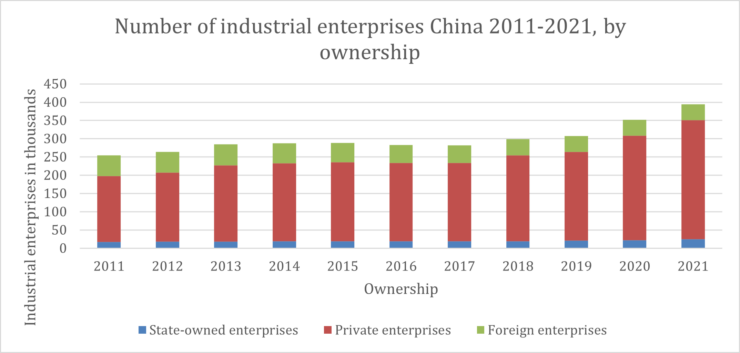
As of 2021, there were around 25,200 state-owned industrial enterprises above designated size in China.
United States The Wholesale Trade sector is an intermediary step in the supply chain process. Companies in the sector distribute goods from agriculture, mining, manufacturing and information industries to downstream markets, typically without any transformation. In 2023, the US Wholesale sector is valued at $11.3 trillion.

Customer Segmentation
Trade Global will primarily target the following customer profiles:
- Small to medium manufacturers of FMCG in China
- Wholesale distributors of FMCG in US
Competitive Analysis
Direct and indirect competitors.
Trade Global will face competition from other companies with similar business models. A description of each competitor company is below.
Global Electronic Imports & Exports, Inc.
Established in 1990, Global Electronic Imports & Exports specializes in the import and export of consumer electronics, including smartphones, tablets, and audio equipment. They also deal in a range of accessories and components related to consumer electronics.
Global Electronic Imports & Exports has long-standing partnerships with major electronics manufacturers in Asia, including Samsung, LG, and Panasonic. They also collaborate with major US-based retailers for distribution.
Global Electronic Imports & Exports reported an annual trade volume of approximately $150 million in consumer electronics and related products last year.
Natural Foods International
Established in 2005, Natural Foods International specializes in the import and export of food products, with a focus on organic and non-GMO items. They deal in a wide range of commodities, including grains, nuts, and dried fruits.
The company has established partnerships with a network of international organic farms and cooperatives. They also have distribution agreements with major US grocery chains, such as Whole Foods Market and Trader Joe’s.
Last year, Natural Foods International reported a trade volume of approximately $85 million in organic and non-GMO food products.
Titan Heavy Machinery, Inc.
Established in 1998, Titan Heavy Machinery is a specialized import/export company focusing on the heavy equipment and construction industry. Their product range includes excavators, bulldozers, and industrial vehicles.
The company has close partnerships with leading heavy machinery manufacturers, particularly in Japan and Germany. They also collaborate with construction and mining companies in the US and overseas.
Last year, Titan Heavy Machinery reported a trade volume of approximately $60 million in heavy equipment and machinery, serving the construction and infrastructure development sectors.
Competitive Advantage
Trade Global will be able to offer the following advantages over their competition:
- Smaller, more personal operation, with highly-qualified supply chain experts
- Trade Global stays abreast of all technology developments, constantly seeks to improve the supply chain, and delivers an accurate and complete shipment to each customer.
- Trade Global offers competitive pricing for its services. Their pricing structure is the most cost effective compared to the competition.
Marketing Plan
Brand & value proposition.
Trade Global will offer the unique value proposition to its clientele:
- Highly-qualified team of supply chain experts that provide a comprehensive suite of export/import services (sales, packaging, shipping, customs, tariff/financial, marketing, expedient delivery).
- Unbeatable pricing to its clients – Trade Global does not mark up its services at a large percentage, offering competitive pricing.
Promotions Strategy
Flexibility and adaptability are key in marketing, as the import/export industry is subject to changes in international trade policies, global economic conditions, and shifting market dynamics.
The promotions strategy for Trade Global is as follows:
Create a Strong Online Presence:
Trade Global will build a professional, user-friendly website that showcases the company’s services, products, and expertise. The site will be optimized for search engines (SEO) to improve its visibility in online search results.
Network and Build Relationships:
Trade Global will make a point of attending a variety of trade shows and industry events to meet potential clients, suppliers, and partners, since building and maintaining relationships in the import/export industry is often critical to success.
Trade Global will also join industry-specific associations and chambers of commerce to gain credibility and access a network of contacts.
Online Marketing:
Trade Global will list products or services on established online B2B marketplaces like Alibaba, Global Sources, or TradeIndia to reach a global audience.
Trade Global will launch an email marketing campaign to reach potential clients, partners, and suppliers. Share industry news, company updates, and promotional offers.
The company will use online advertising platforms such as Google Ads and social media advertising to deliver targeted ads that promote import/export services.
Trade Publications and Directories:
Trade Global will advertise the business in relevant industry directories and advertise in trade publications specific to each product niche.
Trade Global’s pricing will be moderate and on par with competitors so clients feel they receive value when purchasing their goods and services.
Operations Plan
The following will be the operations plan for Trade Global. Operation Functions:
- Ted Rogers will initially handle all procurement, finding goods, buyers for goods, negotiating prices, and arranging logistics.
- The company will employ an administrative assistant, who will handle all documentation and answer non-urgent communications.
- The company will employ three warehouse managers to oversee logistics operations.
Milestones:
Trade Global will have the following milestones complete in the next eight months.
- 5/1/202X – Finalize construction of warehouse space
- 6/1/202X – Complete recruitment process for warehouse management
- 6/15/202X – Finalize shipping partnerships
- 8/1/202X – Finalize wholesale contracts
- 11/15/202X – Complete hiring of warehouse team
- 12/1/202X – Receive first products intended for export
Trade Global will be owned and operated by Ted Rogers, who will oversee the procurement and logistical operations.
Ted Rogers has a background in wholesale, and is a graduate of Michigan State University’s Supply Chain Management program, and subsequently earned an Export/Import Certificate from the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC).
Trade Global has begun the recruitment process for experienced Warehouse Managers in Hong Kong, and expects to complete the hiring process within one month.
Financial Plan
Key revenue & costs.
The revenue drivers for Trade Global will largely rely on finding the best buyers for products being imported/exported. In addition, negotiating the lowest shipping costs will be a significant factor in revenue realized.
The cost drivers will be the overhead costs required to procure goods, and operate the warehouse. The major expenses will be payroll, and shipping costs.
Funding Requirements and Use of Funds
Key assumptions.
The following outlines the key assumptions required to achieve the revenue and cost numbers in the financials and to pay off the startup business loan.
- Sales Revenue: Projected sales revenue will be broken down by product or service, region, and customer segments.
- Gross Margin: Profit projections will account for variations in costs, such as shipping, import duties, and currency fluctuations.
- Cost of Goods Sold (COGS): This includes the cost of acquiring the goods for import or export.
- Currency Exchange Rates: Exchange rates can significantly impact the financial performance of an importer/exporter.
- Credit Terms: Credit terms offered to customers and suppliers impact cash flow and working capital requirements.
- Inventory Turnover: Carrying costs and storage expenses will impact profit; therefore, an accurate forecast of how quickly inventory will need to be replenished is important
- Taxes and Duties: Import/export duties, taxes, and customs fees based on the countries involved in the trade
- Economic Conditions: inflation rates, interest rates, and political stability can affect profitability
Financial Projections
Income statement, balance sheet, cash flow statement, trade global business plan faqs, what is an import export business plan.
An import export business plan is a plan to start and/or grow your import export business. Among other things, it outlines your business concept, identifies your target customers, presents your marketing plan and details your financial projections.
You can easily complete your Import Export business plan using our Import Export Business Plan Template here .
What are the Main Types of Import Export Businesses?
There are a number of different kinds of import export businesses , some examples include: Export management company, Export trading company, and Import-export merchant (or free agent).
How Do You Get Funding for Your Import Export Business Plan?
Import Export businesses are often funded through small business loans. Personal savings, credit card financing and angel investors are also popular forms of funding.
What are the Steps To Start an Import Export Business?
Starting an import export business can be an exciting endeavor. Having a clear roadmap of the steps to start a business will help you stay focused on your goals and get started faster.
1. Develop An Import Export Business Plan - The first step in starting a business is to create a detailed import export business plan that outlines all aspects of the venture. This should include potential market size and target customers, the services or products you will offer, pricing strategies and a detailed financial forecast.
2. Choose Your Legal Structure - It's important to select an appropriate legal entity for your import export business. This could be a limited liability company (LLC), corporation, partnership, or sole proprietorship. Each type has its own benefits and drawbacks so it’s important to do research and choose wisely so that your import export business is in compliance with local laws.
3. Register Your Import Export Business - Once you have chosen a legal structure, the next step is to register your import export business with the government or state where you’re operating from. This includes obtaining licenses and permits as required by federal, state, and local laws.
4. Identify Financing Options - It’s likely that you’ll need some capital to start your import export business, so take some time to identify what financing options are available such as bank loans, investor funding, grants, or crowdfunding platforms.
5. Choose a Location - Whether you plan on operating out of a physical location or not, you should always have an idea of where you’ll be based should it become necessary in the future as well as what kind of space would be suitable for your operations.
6. Hire Employees - There are several ways to find qualified employees including job boards like LinkedIn or Indeed as well as hiring agencies if needed – depending on what type of employees you need it might also be more effective to reach out directly through networking events.
7. Acquire Necessary Import Export Equipment & Supplies - In order to start your import export business, you'll need to purchase all of the necessary equipment and supplies to run a successful operation.
8. Market & Promote Your Business - Once you have all the necessary pieces in place, it’s time to start promoting and marketing your import export business. This includes creating a website, utilizing social media platforms like Facebook or Twitter, and having an effective Search Engine Optimization (SEO) strategy. You should also consider traditional marketing techniques such as radio or print advertising.

Researched by Consultants from Top-Tier Management Companies

Powerpoint Templates
Icon Bundle
Kpi Dashboard
Professional
Business Plans
Swot Analysis
Gantt Chart
Business Proposal
- Marketing Plan
Project Management
Business Case
Business Model
Cyber Security
Business PPT
Digital Marketing
Digital Transformation
Human Resources
Product Management
Artificial Intelligence
Company Profile
Acknowledgement PPT
PPT Presentation
Reports Brochures
One Page Pitch
Interview PPT
All Categories
Top 10 Export Business Plan Templates with Examples and Samples (Editable Word Doc, Excel and PDF Included)

Samradni Pradhan
Export business is pivotal in a country's economic growth and stability. It offers numerous advantages, including job creation, foreign exchange earnings, economic diversification, and global market exposure.
Success in the export business, however, is not guaranteed. It requires a well-thought-out business plan considering market research, logistics, regulatory compliance, and financial management. We offer comprehensive and customizable export business plan templates to assist entrepreneurs in this endeavor.
The business plan ppt templates provide a structured framework for outlining your business goals, strategies, and financial projections, ensuring a smooth path to export success. With the right plan and these templates, you can capitalize on the immense opportunities the global market offers and contribute to your country's economic global market development.
Table of Contents
- Executive Summary
- Company Overview
- Industry Analysis
- Customer Analysis
- Competitor Landscape
- SWOT Analysis
- Porter's Framework
- Operational Plan
- Financial Plan
Our business plan template bundles are crafted with precision, keeping in mind all of the nitty-gritty of the export business. These templates use the best graphics to ensure your business idea shines through. When you download this business plan template, you will get access to a 65-page template document. These are completely editable as per your needs and requirements. However, for the ease of this blog, we will only highlight the top 10 templates from this entire deck.
1. Executive Summary
This is the initial section of your export business plan, serving as a concise roadmap for the reader. It should encapsulate the essential aspects of your export strategy, including identifying target markets, primary objectives, a summary of key strategies, and a brief overview of financial projections and timelines. This summary sets the stage for the entire plan, looking at what the audience can expect to find in more detail further in the document.
In our Executive Summary section, you will get templates for
1.1 The Quick Pitch: A concise and compelling overview of your export business, capturing its essence and potential in a few sentences.
1.2 The Entity: Describing your business's legal structure and core identity, ensuring clarity regarding its nature and organization for international trade .
1.3 Company Overview: Offering a comprehensive introduction to your cross-border commerce , including its history, mission, and the core values that drive your international endeavors.
1.4 Products and Services: Detailing the range of export products and services you offer, emphasizing their unique features and how they meet the needs of international customers.

Download this business plan
(Do you have a trading business and wish to scale it up? We have a suitable template for a multinational trading business plan; you can download it here )
2. Company Overview
The company overview delves into the core aspects of your business. It provides information about your company's history, experience in international trade, certifications (such as ISO standards or export-related qualifications), and financial stability. This section aims to build confidence in your company's ability to operate successfully in the export market, demonstrating your credibility as an export partner.
In our Company Overview section, you will get templates for
2.1 Mission and Vision: Your export business's overarching purpose and long-term aspirations define your commitment to international success.
2.2 Goals and Objectives: The specific targets and milestones that steer your import-export business towards accomplishment in global markets.
2.3 Start-up Summary: A concise outline of the initial financial and operational aspects required to launch and establish your export operations.
2.4 Market Gap and Solution: Identifying a void in international markets and how your products or services provide a solution, ensuring a clear value proposition.
2.5 Product and Services Offered: Detailing the range of products and services of your export business offers, emphasizing their uniqueness and relevance in global markets.
2.6 Key Success Factors: The critical elements that underpin your export business's success, serving as the foundation for sustainable growth in foreign trade .

(Looking for something more generic that caters to international business ? Well, you are in luck! We have a business plan template that caters to international business !)
3. Industry Analysis
The industry analysis explores the global market where you intend to export your products or services. It should examine market trends, regulatory environments, and trade policies affecting your industry. This analysis helps you identify potential growth areas, challenges, and opportunities that can improve your import strategy.
In our Industry Analysis section, you will get templates for
3.1 Market Analysis: A comprehensive examination of international markets to identify opportunities and assess the export potential of your products.
3.2 Market Trends: Tracking global trade dynamics and consumer behavior shifts ensures your export strategies align with current and future market trends.
3.3 Major Challenges: Identifying the key hurdles and obstacles your export business may encounter in international markets and formulating strategies to overcome them.
3.4 Growth Drivers: Recognizing the factors that stimulate expansion and success in global markets, leveraging them to propel your export venture forward.
3.5 Geographical Analysis: Examining specific regions and countries to determine the most promising export destinations, tailoring your approach to each market's unique demands and opportunities.
(Is your business strategy driven? You need a template that focuses on the target market and global expansion. Get the best of both through this template )
4. Customer Analysis
In the customer analysis section, you must define and understand your target international customers. This involves delving into their demographics, preferences, behaviors, and cultural factors that may impact their purchasing decisions. A thorough customer analysis will guide you in tailoring your products, services, and marketing approaches to align with the needs and expectations of your global clientele.
In our Customer Analysis section, we offer comprehensive templates for:
4.1 Target Market: Defining the specific countries or regions where your export business aims to sell products, narrowing down the global focus.
4.2 Buyer Persona: Creating a detailed profile of the ideal international customer, understanding their needs and preferences to tailor export strategies better.
4.3 Market Sizing: Assessing the potential of the export market by determining its size in terms of customers, demand, and revenue, providing a clear understanding of the export opportunity.

5. Competitor Analysis
Analyzing the competitive landscape in your target markets is crucial for developing effective export strategies. This section should identify key competitors in the international market, evaluate their strengths and weaknesses, and provide insights into their market share. Understanding the competitive dynamics will help you position your products or services effectively and gain a competitive advantage.
In our Competitive Landscape section, we provide templates for:
5.1 Major Players: Identifying and analyzing key competitors and influential entities in the international market who impact your business.
5.2 Attributes Comparison: Evaluate the specific characteristics and features of your export products or services compared to those offered by competitors to determine your unique selling points and competitive advantages.
6. SWOT Analysis
A SWOT analysis is considered to be a strategic tool that assesses your export venture's internal strengths and weaknesses, also external opportunities and threats. This analysis provides a holistic perspective of your business and the export environment. By identifying internal advantages and challenges and external market opportunities and threats, you can make informed decisions, create mitigation plans, and better position your company for international success.

7. Porter's Framework
Porter's Five Forces framework is considered an excellent tool for analyzing the competitive forces within your industry. It examines the power of suppliers, the bargaining of buyers, the threat of new brands and substitutes, and the intensity of competitive rivalry. This analysis helps you understand the competitive dynamics of the export market, identify potential challenges, and develop strategies to address them effectively. You can make informed decisions about market entry and competition mitigation strategies using Porter's framework.
8. Marketing Plan
The marketing plan in an export business outlines the strategies for promoting and selling your products or services in international markets. It should include details about your international marketing mix, pricing strategies, distribution channels, and promotional efforts. A robust marketing plan is essential for gaining market share and building brand recognition in your target export markets.
In our Marketing Plan section, we provide templates for:
8.1 Sales and Distribution Strategy: Outlining the plan for leveraging international sales and distribution platforms to enhance brand visibility and engage with international customers in the export market.
8.2 Promotional Strategy: A comprehensive plan designed to increase brand visibility, engage international audiences, and drive sales in the global export market.
8.3 Pricing Strategy: Defining the approach for setting competitive and profitable prices for your export products or services, considering international market dynamics and customer expectations.
8.4 Sales Funnel: Describing the step-by-step process that international customers go through, from initial awareness to purchasing, facilitating efficient lead conversion in your export business.

9. Operational Plan
The operational plan defines how your company will execute its export strategy. This section should cover logistics, production, supply chain management, quality control, and international regulations and standards compliance. It's essential to provide a clear and organized operational plan to ensure a smooth flow of goods or services to your international customers.
In our Operational Plan section, we provide templates for:
9.1 Business Model: The blueprint of your export enterprise, elucidating how you create, deliver, and capture value in international markets, ensuring a clear understanding of your global trade approach.
9.2 Goals to be achieved: The specific, measurable objectives guiding your export business, ensuring a defined path to international success and a framework for tracking your progress.
10. Financial Plan
The financial plan is a critical section of the export business plan, detailing the expected costs, revenue projections, and financial forecasts related to your international expansion. It should include budgets, cash flow statements, break-even analysis, and return on investment calculations. This information helps stakeholders, including investors and lenders, understand your export business's financial viability and sustainability.
In our Financial Plan section, we provide templates for:
10.1 Financial Assumptions: Highlighting the critical assumptions underpinning the export venture's financial projections.
10.2 Revenue Model and Sales Forecast: Defining the approach for generating revenue from international markets and providing a sales forecast for export operations.
10.3 Break-Even Analysis: Identifying the point at which export revenues cover costs, indicating when the business becomes profitable.
10.4 Projected Profit and Loss Account: Summarizing expected revenues, expenses, and profitability for the export business over a specified period.
10.5 Projected Cash Flow Statement: Outlining the expected cash inflows and outflows related to export activities, ensuring cash liquidity for international operations.
10.6 Projected Balance Sheet: Present a snapshot of the export business's financial position, including assets, liabilities, and equity, specific to international trade.
10.7 Scenario Analysis: Assessing various scenarios to understand the impact of various elements on the financial performance of the export business.
10.8 DCF Valuation: Applying the Discounted Cash Flow process to determine the present value of future cash flows, assisting in the valuation of the export business in the international market.
We have so much more to offer
An export business plan considers many elements, and we know you are the expert to manage it all! However, we can only help you with the best base to get started. By downloading these templates, you are not only creating the right start for your business, but also creating a lasting impression for your investors. This 65-pager template deck has everything you will need for your business; what more can you ask for? For easy access and editability, you can download the PowerPoint file of this deck from here ! Happy business planning.
Related posts:
- Must-have Restaurant Business Plan Templates with Samples and Examples
- Must-have Advertising Agency Business Plan Templates with Examples and Samples
- Top 10 Bar Business Plan Templates with Examples and Samples (Editable Word Doc, Excel and PDF Included)
- Top 10 Law Firm Business Plan Templates with Samples and Examples (Editable Word Doc, Excel, and PDF Included)
Liked this blog? Please recommend us

Top 5 Goal Board Templates With Samples And Examples

Top 7 Data Quality Dashboard Samples with Templates and Examples
This form is protected by reCAPTCHA - the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.

Digital revolution powerpoint presentation slides

Sales funnel results presentation layouts
3d men joinning circular jigsaw puzzles ppt graphics icons

Business Strategic Planning Template For Organizations Powerpoint Presentation Slides

Future plan powerpoint template slide

Project Management Team Powerpoint Presentation Slides

Brand marketing powerpoint presentation slides

Launching a new service powerpoint presentation with slides go to market

Agenda powerpoint slide show

Four key metrics donut chart with percentage

Engineering and technology ppt inspiration example introduction continuous process improvement

Meet our team representing in circular format

Upmetrics AI Assistant: Simplifying Business Planning through AI-Powered Insights. Learn How
Entrepreneurs & Small Business
Accelerators & Incubators
Business Consultants & Advisors
Educators & Business Schools
Students & Scholars
AI Business Plan Generator
Financial Forecasting
AI Assistance
Ai Pitch Deck Generator
Strategic Planning
See How Upmetrics Works →
- Sample Plans
- WHY UPMETRICS?
Customers Success Stories
Business Plan Course
Small Business Tools
Strategic Canvas Templates
E-books, Guides & More
How to Start an Import Export Business in 9 Easy Steps

Free How to Write an Import Export Business Plan + Free Template Template
Matthew Khalili
16 Min Read

The import and export game in the U.S. is skyrocketing! Government numbers tell us that in just December 2021, imports and exports jumped by a whopping $7 billion each. Americans are craving new and exciting products from all corners of the globe.
So, starting an import/export business might be a gold mine waiting to be discovered. But before you jump in, let’s unpack different types of “import” and “export” businesses, how to get your international business started in the USA, and if it’s really the profitable venture you imagine.
Types of Import Export Businesses
Importers and exporters” – that’s the primary cast of characters in the international market trade. There are more exciting players, each with their role in global trade. Let’s meet the crew:
Import Export Merchants
These independent people don’t stick to just one product or market. They either make or buy products and then sell them to other countries. This way of doing business can be risky, but you might earn more money.
Export Trading Company (ETC)
This is like being a go-between or a distributor. Instead of making their products, ETCs find foreign buyers for goods and then look for someone in their home country to send these goods abroad. Sometimes, they might even own the goods they’re exporting and make money through commission.
Export Management Company (EMC)
An EMC manages all the export stuff for a company. If a company in your country wants to sell its products in other countries, an EMC will take care of everything needed to make that happen. This includes finding people to sell the products, creating ads, and arranging for the products to be shipped.
Now that you’ve learned about the various types of business, let’s explore how to start an import export business in nine easy steps.
Steps to starting an Import-export business
- Identify products to import or export
- Explore shipping options
- Source your suppliers
- Write an Import-export business plan
- Register your business
- Obtain necessary licenses & permits
- Figure out financing
- Get a business insurance
- Market your business
1. Identify products to import or export
Starting a successful import-export business means determining what products or services you want to trade.
You need to look into different items and industries to find out what’s in demand worldwide and see if importing or exporting them is practical.
Here’s how you can find out:
Learn What Customers Want
You can ask people directly through surveys or group discussions. Look at what’s selling well in foreign markets by checking sales data and market reports. Also, watch social media and import-export industry websites to stay updated on trends and what people like.
Doing this makes you more likely to sell products that people will want to buy.
Is the Product a Good Fit? After conducting market research, consider whether your export products will work well. This means looking at things like how much they’ll cost to make and send, how unique they are, and how much people need or want them.
Check Out Your Competitors
You need to know what your competitors are offering to pick the right products.
- Look at their prices and what their customers are saying. Websites like Alibaba can give you a good idea of global prices.
- Watch their ads and marketing to see how they’re selling their products.
Learning from your competitors can show you what might work or not in your target markets, helping you choose profitable products.
Costs and Profits
Consider the costs of making and shipping your products, including extra expenses like taxes. Then, think about how much profit you could make. A simple way to compare costs and profits is to use a spreadsheet.
Rules for Your Products
Before you start exporting or importing, know the rules for the products you want to send. This includes safety certifications, what needs to be on labels, and any export restrictions.
Different countries have different requirements for things like safety and environmental impact. Know these rules for the countries you’re targeting.
How you label and package your products can also vary by country. Ensure you know things like language requirements and what information must be on the label.
Now that you know your product, it’s time to make sure it will make money. You can look at the following studies:
- GlobalEdge’s Market Potential Index (MPI): This study by Michigan State University has been done since 1996. It looks at how good different countries are for business each year and ranks them from 1 to 100.
- International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) : This group helps trade and teaches businesses how to do things better.
- U.S. Census Bureau, Foreign Trade : This is the official place for U.S. export and import numbers. They also make sure exports follow the rules.
- Local Government Officials and Websites: You can also talk to local Commerce Departments for insights on what products and services are popular or needed in your area.
2. Explore shipping options
This step can be complex because there’s a lot to think about. You must decide how to ship your products – by land, sea, or air. You also have to figure out the right way to package them for shipping.
Plus, you need to plan how to store them so they’re easy to get to and arrange transport to and from places.
It’s usually a smart move to hire a global freight forwarder for any import/export business. They act like a shipping agent, taking a big load off your shoulders.
You tell them about your business and what you want to do with your products, and they handle the shipping plans, insurance, and often the paperwork like licenses, permits, taxes, and limits for trading in another country. This can make starting an import/export business much less stressful.
3. Source your suppliers
Once you’ve chosen a product to trade internationally, your next step is to find a local maker or supplier who can work well with you. Here’s how to do it:
Start by searching on Google for suppliers or makers of the product you’re interested in. If you want to buy from local sources, look for local wholesalers and distributors.
Remember, buying directly from foreign manufacturers or their agents usually gives you better prices than local sources. Once you find a supplier’s website, go to their “Contact Us” page and send them your questions.
Online Marketplaces
Many online marketplaces can help you find suppliers. One of the biggest is Alibaba, which is based in China and is great for finding Asian products. Global Sources, D.H. Gate, and All.Biz are also well-known if you’re looking for other options.
Use Import/Export Port Data
Look for suppliers and makers by getting import/export data from companies that sell this information. Companies like IHS Piers gather data from ports worldwide and sell it.
This data might not have direct contact info, so you should look up suppliers on Google.
Visit Trade Shows
Despite the shift to online business, meeting suppliers and seeing the products yourself can be valuable.
Trade shows are great for this, especially for high-tech or expensive products. Meeting sellers in person can build trust and add much to your business relationship.
4. Write an Import-export business plan
An Import-export business plan lets you understand the facts, limits, and goals of selling internationally. You can use it to set clear targets, plan when to do things, and track your progress. It can also help your team stay focused on reaching these goals.
A written plan outlines the steps you must take to commit to exporting. Without a plan, you might miss opportunities to grow your business beyond your country.
Usually, a business plan has parts like:
- A quick summary
- Info about your company
- Market Research
- Details about your products or services
- How you’ll market and sell
- Predictions for money coming in and going out
- Funding Request
Not very good at writing? Need help with your plan?
Write your business plan 10X faster with Upmetrics AI
Plans starting from $7/month

5. Register your business
After deciding on your product and suppliers, it’s time to make your import-export business official!
Here’s how you can do that:
Step 1: business registration:
Think of this as getting your official passport for your global target market. It makes your business legit and separate from you personally, which is suitable for legal purposes and taxes.
Most small import-export companies in the U.S. need to head to their state or local government office and tell them:
- Your business name
- Where your international trade H.Q. is located
- Who’s in charge (you, your partner, or your LLC crew)
- Your unique “Doing Business As” name, if you have one
Step 2: Pick your team structure:
Do you want to start your import export business solo, grab a partner, or have whole LLC members? This choice affects your taxes, money, and paperwork. Conduct market research and find what fits your goals best.
Step 3: Get your I.D. numbers:
- CIN: This is like your international trade license. It lets the Department of Commerce track your trades across borders. You can quickly get it on their website.
- EIN: This is your business tax I.D., like a social security number for your company. Get it online, by mail, or fax from the IRS.
If you want to bring products from other countries into the U.S., you must register with Customs and Border Protection. This makes you an Importer of Record (IOR) .
As an IOR, you ensure all the import rules for your products are followed. This includes filling out customs forms, paying duties and tariffs, and other tasks.
To be an IOR, you must fill out the Importer Identity Form, also known as CBP Form 5106.
6. Obtain necessary licenses & permits
Licenses and permits are the gatekeepers of the import/export world. The good news is most products in the U.S. don’t need them!
Here’s what you need to know about these licenses:
Importing Licenses
CBP doesn’t have a complete list of “import license needed” items, but they have some guidelines . Some special items do need licenses, which include:
- Dairy products
- Radioactive materials
- Wildlife and pets
- Biological Drugs
- Biological Materials and Vectors
If you’re importing one of these, double-check with CBP before your shipment gets stuck at the border.
Exporting Licenses
It’s your job to determine if your item needs a license to leave the country—usually, the Bureau of Industry and Security or the U.S. Department of State handles these permits.
So, how do you know if you need a license?
Four things matter:
- The item itself
- Where it’s going
- What is it used for
- Who’s getting it
In this case, the Export Administration Regulations (EAR) is your handbook for export licenses. Think of it like a map showing which items need permission to leave. It lists stuff under the Commerce Control List (CCL) in 10 categories, like nuclear materials, chemicals, computers, and airplanes.
However, not everything on the CCL needs a license. If your item isn’t listed, it’s probably EAR99 – mostly license-free. But be careful; some EAR99 products still need permission.
You can also find out if your product needs an export license by looking at its Export Control Classification Number (ECCN).
Here are three ways to find the ECCN
- Check it yourself using the CCL
- Ask your supplier
- Request it from the Bureau of Industry and Security.
7. Figure out financing
Starting an import/export business is exciting, but it takes some real money to get going. The good news? You can start small, even from home, without much inventory or employees. Starting an export-import business from your house would cost around $5000 to $25000.
But if your import export business takes off and you need more fuel, here are some options:
Export-Import Bank: They help American import export businesses like yours by offering loans, guarantees, and insurance.
SBA Export Loan Programs : The Small Business Administration has special programs to help you develop and grow your exports. They offer loans for different stages, from starting up to expanding.
Here are three loans that they offer:
- Export Express Program: Up to $500,000 for inventory, receivables, and development activities.
- International Trade Loan Program: Grow or expand your exports or fight against import competition.
- Export Working Capital Program: Get working capital for production, receivables, inventory, or even standby letters of credit.
- Import/Export Line of Credit: This is a flexible credit card for your import/export needs, helping you manage cash flow and pay suppliers or customers over time.
- Ex-Im Working Capital Guarantee Program: Need help before you even start exporting? This program can secure financing for things like raw materials and equipment for your export goods.
8. Get a business insurance
Shipping products across borders can be risky! But fear not; import-export business insurance is here to save the day. It’s like a superhero cape for your goods, protecting them from financial harm.
Here’s what you need to know:
Export Credit Insurance: Worried buyers won’t pay? This covers you if they skip out, reimbursing 80-90% of the loss.
Marine Insurance: Covers your goods from the moment they leave the supplier until they reach your buyer, no matter where they travel (not just the ocean!).
Political Risk Insurance: If you’re doing import export business in shaky countries, this insurance shields you from government seizures, payment delays, and even wars or riots.
International Product Liability: Even if you do your market research, sometimes goods get rejected at customs. This covers you if regulations change or your product doesn’t meet the mark.
Remember, research and preparation are essential, even with insurance. But with these options in your arsenal, you can trade internationally with more confidence and peace of mind!
9. Market your import export business
In your job as an international trader, your main goal is to sell yourself, your company, and the products you offer. You have to get companies to trust you to sell their products in foreign countries (export) or to bring in products from abroad to sell here (import).
The better you do in either exporting or importing, the easier it gets to do well in the other. Say you help a company sell many products in overseas markets; you can show that success to other companies to get more business.
Many import-export businesses don’t export or import, even though it could earn them more money. Your job is to find these companies and persuade them to let you help them sell abroad.
Before you reach out to a company, do your homework:
- Find out what products are hot in the U.S. Think about stuff you use or things certain groups love.
- Are these products also wanted in your target market countries?
- If they’re not popular, could they be if people knew about them?
- Who makes these products?
- How much does selling them, both here and in the target countries, cost?
Using this info, you can contact companies with your sales pitch through direct-mail campaigns.
Direct-Mail Campaigns
Pick a company that makes one of the products you’ve looked into. Find the right person to talk to, like their president or sales manager.
Your letter should explain:
- Who you are and what your company does.
- How exporting or importing could benefit them.
- Why is your company the best choice for this?
You have contacts with foreign distributors ready to sell their products.
Finish the letter by asking for a meeting. Keep sending out letters to other companies until you’ve covered your list.
Wait a week or two, then follow up with a phone call to request a meeting.
Cold-calling
You can also try calling companies directly. It might save money, but it’s tougher to nail.
Before you call, plan out what you want to say. You can even write a script but don’t stick to it too rigidly.
Be ready for rejections. It’s all part of the job.
Build an SEO-friendly website
Imagine this: someone searches for your products, and your website appears first. That’s what SEO can do. Make your website more accessible, and you’ll attract more customers.
Social media accounts
Use platforms like Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn, and Twitter. They’re great for connecting with potential customers, showing off your products, and building trust.
You can post interesting stuff, answer questions, and join industry chats. People will start seeing you as the expert.
Work with local pros
Team up with local agents in the countries you’re targeting. They know the local scene, language, and rules, helping you avoid mistakes.
Let your happy customers speak for you
Satisfied customers are like free salespeople. Ask them for referrals and testimonials, and put these on your website and social media.
The import export business brings products from one place to another, meets people’s desires, and makes money. Have you ever wondered how to get stuff that’s made far away? Or how do you share something cool with people in other countries while ensuring it’s suitable for everyone involved, from the makers to the transporters?
If you’re thinking about this, don’t worry about how big the task seems. With the proper research, a solid import-export business plan, and paperwork, you can start your own import-export business and make it work.
The Quickest Way to turn a Business Idea into a Business Plan
Fill-in-the-blanks, AI-assistance, and automatic financials make it easy.

Frequently Asked Questions
Is the import-export business profitable.
Like any business, making money in import-export depends on a few things. Your prices, how much it costs to make and ship products, and how big you can grow your business all matter for your profits.
People starting in import-export often make around $80,000 . If things go well, you might make hundreds of thousands; a few people even make millions.
How Much Should You Charge for Imports and Exports?
Your prices will depend on what you’re selling and the costs of making and shipping them. A standard pricing strategy is to add 10 to 15 percent to your costs.
How to Get an Import-Export License?
After making a business plan, check if you need any import-export licenses.
Most products coming into the U.S. don’t need an import export license. The U.S. Customs and Border Protection has guidelines for what requires a permit.
What Does It Cost to Start an Import-Export Business from Home?
Startup costs can vary. Usually, you spend between $5,000 – $7,000. Here’s a rough breakdown:
- Registering an import export business costs around $300 and can vary by state.
- Setting up phone, internet, and a website: Plan for ongoing costs of about $250-300.
- Buying your first products: Expect to use 17% – 25% of your budget.
What's the Best Business for Import-Export?
Based on U.S. Census Bureau data , the top imports in 2020-21 were:
- Computers and electronics
- Transportation equipment
- Non-electrical machinery
- Electrical equipment and appliances
The top exports were:
- Oil and gas
About the Author

Matthew Khalili is an experienced business planning expert and the founder of The Plan Writers. With over a decade of experience in the field, he has helped numerous entrepreneurs in creating investor-ready pitch decks and business plans. Matt has enabled 5000+ startups to raise over $1 billion through his business plan, market research, and financial modeling services. Read more
Reach Your Goals with Accurate Planning
No Risk – Cancel at Any Time – 15 Day Money Back Guarantee
Popular Templates
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
BorderBuddy
Orders Without Borders
- PARS Tracker
- Importing into Canada
- Exporting from Canada
- Customs Brokerage
- Customs Clearance
- Import a Car
- Customs for E-Commerce
Home » How to Write a Business Plan for Your Import-Export Business
How to Write a Business Plan for Your Import-Export Business

January 20, 2021
The world is more interconnected than it’s ever been. This provides a perfect opportunity for you to create your own import-export business. Whether it’s importing beautiful textiles from another continent or exporting local Canadian products abroad, all you need is passion and drive to get started.
You probably have plenty of ideas swirling around in your head, but the only way to make your business a reality and ensure your success is to write a winning business plan. Business plans are notoriously long and complex but don’t be disheartened. Here are 6 steps to writing the perfect business plan for your import-export company:
1. Start with an Executive Summary.
Think of this as the ultimate introduction to your business. It should concisely delineate exactly what you want as a business owner. Remember, you need to know where your business is going. It’s up to you to clarify your vision. No one is going to be as passionate about your import-export storefront as you are.
Your executive summary should have:
- Your business concept : what you’ll sell, who will purchase it, and why your business will work
- Financial points : your sales, profits, cash flows, and ROI
- Required finances : what capital is needed and how it will be used
- Current business state : a short history of your business including key members of staff
- Achievements : may include test marketing, facility locations, important contracts, etc.
Keep it short and sweet. Ideally, your executive summary will be no more than half a page. The rest of your business plan is where you’ll go into greater detail about these components.
It might be helpful to go through How to Start an Import Export Business before you create your executive summary to ensure everything is carefully thought out before you present it in your business plan.

2. Include a Business Description.
This is your opportunity to describe exactly what you’re importing or exporting and how it will succeed. Are you importing Congolese avocados? Show how you can guarantee perfect ripeness when they reach stores. Are you exporting blenders to Bolivia? Demonstrate you’ve found the perfect blender to suit the demand of that market.
Here are some questions to consider and incorporate:
- How does the industry look now and how might it change in the future?
- Is your business brand new or already established?
- What kind of business is it (e.g. partnership, corporation)?
- What are the ins and outs of the distribution of your product?
- How is your business better than your competitors?
- What exactly makes your business profitable?
Don’t forget insurance. Investors and lenders need to see you’re responsible and won’t lose money from major oversights. You might think skipping product insurance will help you make more money, but this is a huge mistake in the long run. Find a premium insurance company and include that information in your business description.
3. Conduct a Market Analysis.
Roll up your sleeves—this part takes a lot of effort. If you put the work in and do the research, it will pay off. The point of your market analysis is to demonstrate your knowledge of the market and your ability to claim a significant share of it.
A great market analysis can look like this:
- Define the market : talk about size, trends, rules and regulations, prospective growth areas, and sales potential
- Nail down the total feasible market : specifically address the portion of the market your business can realistically capture
- Estimate market share : take into consideration industry growth and your product’s life cycle
- Determine pricing : discuss your reasons for pricing and how you will cover costs
- Explain your promotion strategy : this includes advertising, packaging, PR, etc.
Factor in exchange rates. As you’re figuring out your price, be sure to include exchange rates in your calculations. Neglecting this could sink your business. You might want to consider using the local currency of the country you’re working with, especially if they use an international currency such as euros or US dollars. Are you planning on exporting to the EU? Don’t miss this helpful guide .

4. Summarize a Competitive Analysis.
Not quite the same as your market analysis, your competitive analysis focuses mainly on the strengths and weaknesses of your competitors. Planning to import Italian cars? Put yourself in your buyer’s shoes. What options do they have for purchasing an Italian car? What are the strengths and weaknesses of each option?
After you make a list of all your potential competitors, you’ll want to organize all the information in a competitive strength grid, which outlines which competitors are strong in each skill category and which ones are weak (e.g. price, product quality).
Lastly, you’ll need to clearly define your competitive advantage. Do you have a lower price point? Are your cars of better quality? Do you have a more solid advertising plan? Can you break into a new market?
Your price equates to your product’s value. If you price your product too far below your competitors, it may cheapen your product in the eyes of consumers. There’s nothing wrong with trying to outpace your competitors in pricing, but make sure you don’t overdo it and cause your customers to overlook your product due to a lower perceived quality.
5. Create a Design & Development Plan.
This is where you focus on details, details, details. How are you going to make your business a reality? Now is your opportunity to get it all on paper.
Here are some questions to answer in this section:
- What are your goals for product development?
- Which procedures will you have in place for product review, marketing, and distribution?
- What is your exact production schedule?
- What’s in your detailed development budget?
- How many employees need to be recruited and in what areas?
- What possible risks are apparent?
- How will your business function on a continuing basis?
- What is the organizational structure of your business?
If you’ve left any of these questions unanswered, you’ll need to add more details.
Don’t go it alone. You might prefer to do everything on your own, but that will only leave you overworked and exhausted. There are so many specifics in the import-export world that you can easily get overwhelmed. Do yourself a favor and hire a team to help.
Are you planning on selling your product on Amazon? Check out these useful logistical tips .

6. Don’t Forget the Financial Data.
When it comes down to it, this is what investors really want to see. This is how they’ll determine whether your business – anything from exporting dresses to importing sailboats – will succeed or not.
You’ll need to include three statements in the financial section:
- Income statement : a simple report on monthly sales and expenses
- Cash flow statement : a schedule of what money is needed and where it will come from
- Balance sheet : a summary of your business’s assets, liabilities, and equity
Let your words be few. You should include a short analysis statement after the income statement, but resist the temptation to ramble. The idea is to let the financial statements in this portion speak for themselves.
Once you’ve finished your business plan, send it out to investors and lenders you’ve already established a connection with. Make big asks—you never know who might say yes! With an excellent import export business plan at your disposal, you’re well on your way to becoming a successful business owner.
BorderBuddy creates importing and exporting solutions for any size of business. We specialize in smoothing the process for you—handling the paperwork and logistics so you can focus on growing your company. We love supporting small businesses and are proud of the success stories we’ve been a part of. Give us a call and let us help you create a unique and sustainable import-export business today.
Importing and Exporting in a COVID-19 World:
Smart Ways to Ensure Compliance, Prevent Contamination, and Save Money in the Process
DOWNLOAD FREE EBOOK
- Import/Export
- Testimonials
- © 2023 BorderBuddy, All Rights Reserved |
- Legal Terms
- Who Designed This Website?
How To Start An Export Business: From Local To Global
Figuring out how to start an export business is essential for motivated individuals that want to begin a new enterprise. Companies like these can earn high revenue streams by selling American-made products to buyers overseas. However, there are many regulatory concerns and market research that must be completed before you can get a company off the ground.
The U.S. Commercial Service, a government organization that helps U.S. exporters, recommends these steps when starting an export business:
- Determine your market
- Learn legal requirements
- Craft business plan
- Secure financing
- Source products
- Set up logistics network
Following these steps will ensure goods travel abroad without incident.
Learn how to start an export business with a guide crafted with the expertise of our specialists.
How To Start An Export Business from Home
The idea of taking a business from a local market to the global stage can be both exhilarating and daunting. In today’s interconnected world, starting an export business from the comfort of your home is more feasible than ever. By breaking the process down into simple steps, it’s possible to start shipping goods in no time.
We’ll break down the steps that you can follow to make this your reality.
1. Determining Your Market
Determining the right market for an export business is a crucial step that can dictate the success of a company. Fortunately, there are numerous ways aspiring entrepreneurs can find a viable market.
According to the International Trade Administration , businesses should research the following:
- Country market conditions
- Free trade agreements (FTA)
- Industry research
- Market intelligence
- Trade stats
- Export market ranking
- Foreign trade remedy actions
Researching country market conditions is essential for exporters. It will help them understand the economic health and consumer behavior in a potential market.
FTAs between the U.S. and other countries significantly influence the decision-making process for various export businesses. The U.S. has FTA’s with 14 countries as of the writing of this article. These agreements have many benefits, such as reduced or eliminated tariffs, improved intellectual property regulations, and ease of investment rules.
Popular U.S. FTA nations for exports include:
- Mexico, Canada Agreement (USMCA)
- Central America — Dominican Republic Free Trade Agreement (CAFTA-DR)
- Australia Free Trade Agreement (AUFTA)
- Israel Free Trade Agreement (ILFTA)
- Chile Free Trade Agreement (CLFTA)
Conducting industry-specific research can uncover the demand for products and the competitiveness of the sector within a market. This ensures exporters will be able to sell the goods they have.
Market intelligence requires gathering different types of information and data, such as:
- Competitors
- Overall market conditions
Armed with this information, businesses can set up timely updates about opportunities and conditions in certain markets.
Trade statistics offer quantitative insights into the flow of goods and services between countries. With this kind of raw data, business owners can find trends and determine which markets are growing the fastest.
Rankings can provide a starting point for exporters by giving them a better way to compare opportunities in different sectors. Each rank will highlight leading markets and future chances to earn profit.
Finally, exporters should check which countries have foreign trade remedies. This includes determining if a nation has antidumping and countervailing duties imposed on any incoming products. It may be harder to enter markets in nations that have these in place.

2. Legal Requirements
Now that a target market has been identified, businesses will need to handle certain legal requirements. The first thing an entrepreneur will have to do is register their business with the government. This can be done by filing for a federal tax ID .
For most companies, this is all that has to be done to become a legal entity. However, certain businesses may register with the federal government for trademark protection or to obtain a tax-exempt status.
Next, it’s necessary to determine the legal requirements for selling goods to other countries. While most products don’t need an export license, there are certain items that do.
To determine if one is needed, business owners will need to consider three government bodies that regulate U.S. exports:
- U.S. Department of Commerce
- U.S. State Department
- U.S. Treasury Department
The U.S. Department of Commerce, through their Bureau of Industry and Security (BIS), administers the U.S. Export Administration Regulations (EAR). These rules set export control guidelines for products that have a military or dual military use.
Exporters will need to determine if their items are on the Commerce Control List (CCL). This is done by checking the list and seeing if their product has an Export Control Classification Number (ECCN) .
If an exporter’s goods are on the list and has an ECCN, exporters will need to determine the following:
- Destination of goods
- End-use
ECCN information will determine if an export license is required or not. The U.S. State Department administers the International Trade in Arms (ITAR) Program. These guidelines apply to exports that are designed, modified, or upgraded for military purposes.
Businesses that plan to sell these goods to buyers in other countries will need to consult the U.S. Munitions List. This will let exporters determine if ITAR licensing is required.
The Office of Foreign Assets Control (OFAC) under the U.S. Treasury Department has regulations as well. They maintain a denied parties list, which contains individual, organizations, and entities that cannot be sold exported goods.
Finally, company owners should consult the Consolidated Screening List (CSL). This is a compilation of different screening lists from various federal agencies . The CSL is a list of parties the U.S. government places export restrictions on.
Learn more about ITAR and EAR compliance in our article on these two important U.S. export laws.
3. Crafting A Business Plan
The next part of starting an export business is formulating a plan. This will act as a blueprint for a company to follow. Exporters will need to work out a few details to formulate their business plan.
This includes:
- Determine product or service
- Use market research
- Decide on a pricing strategy
- Determine how to find buyers
The initial step in the process is selecting an appropriate product or service to export. The goods offered by a business should be in demand from buyers in a foreign country.
The market research analysis you should have conducted at this point will help. Using it, you can evaluate whether your chosen product(s) should be modified to align with different market regulations and consumer preferences.
When it comes to building out an effective pricing strategy, a business needs to strike a balance between covering their costs and offering a competitive price.
To figure out the right amount to charge, companies should consider:
- Foreign market objectives
- Product-related costs
- Market demand
- Competition
The last part of formulating an export business plan is buyer acquisition. Companies need customers that will purchase their products to thrive and grow. When just starting out, there are a few strategies available to find potential buyers.
This includes:
- Attending international trade fairs
- Engaging with promotion programs
- Leveraging online marketplaces
- Joining a sales channel
- Winning foreign government contracts
Entrepreneurs that find buyers early on will start earning money fast once their business launches.
4. Financing Your Business
Financing is another important step that goes into starting an export business. Without start-up capital of some kind, options are very limited. Fortunately, company owners can obtain loans from the SBA to help them with this financial support.
Funding includes:
- Export Express Program
- International Trade Loan Program
- Export Working Capital
The Export Express Loan program provides entrepreneurs with small term loans that will help them develop the export side of their business. Maximum funding can be as high as $500,000, which can be used to buy goods or produce services that a company can export.
The International Trade Loan Program is used to improve the competitive position of businesses that are engaged in or are preparing to engage in international trade. Funding for this program has a maximum of $5 million that can be used to upgrade tools and facilities.
Another option available to entrepreneurs is the Export Working Capital Program. This system provides short-term, transaction specific capital loans given to companies that can generate export sales, but need additional support. Funds for this program also have a limit of $5 million.
Entrepreneurs that don’t want to pursue these loans can seek out financing support from the Export-Import Bank (EXIM Bank) of the United States. There are two financing options provided by the EXIM Bank.
These include:
- Limited Recourse Project Finance
- Structured Financing
Limited Recourse Project Finance is an option that’s great for newly created companies. With this plan, businesses can repay the loan using their future cash-flows.
Benefits of this program include:
- Mitigated risk
- Legitimacy thanks to EXIM involvement
- Long-term finance assistance
For U.S. exporters, the Structured Finance program can make their bids more competitive on large international projects by providing their buyers with access to long-term financing.

5. Source Products
Sourcing products is the next critical step for entrepreneurs that want to start an export business. Knowing what you want to export and having it readily available are different goals. Company owners will need to identify a manufacturer that can provide the goods they want to sell.
Fortunately, there are a few resources that entrepreneurs can use, including:
- Trade shows
- Online directories
- Business network
- Industry contacts
Regardless of where you find a supplier, they should ensure they have a proven track record and a history of reliability. It’s important to ensure the products meet the quality standards expected by the target market. Exporters can check the quality of goods at a trade show or by requesting samples.
6. Set Up Logistics Operations
Setting up logistics and operations is the last, though not least, concern that needs to be taken care of when starting an export business.
There are three elements to this part of export operations:
- Product preparation
- Shipping basics
- Shipping documents
During product preparation, goods may require alteration to be operable, marketable, or legally compliant. Every country has unique standards, regulations, or certifications that products must adhere by to make entry. For example, goods going to the EU will require the European Conformity (CE) Mark.
Certain electronic equipment might need alteration to be operable. This could mean swapping out old plugs for new ones that will fit the wall sockets in a foreign country. Correct labels and marks are essential as well. Any words on a label should be in the foreign county’s native language.
Researching the local customs practiced by a certain nation is a good precaution to take. Certain colors might be associate with darker topics, such as death. Therefore, exporters will want to keep these off their labels.
Entrepreneurs should also check to ensure their company name and the products they’re selling don’t translate to something completely different in the native language of a foreign nation.
Now that the necessary preparations have been made, exporters can start focusing on how they will ship their goods. First, they’ll need to consider their transportation options.
Among these are:
- International air
- Ocean freight
- Truck
It’s likely that exporters will have to use some combination of these shipping options to deliver goods to their foreign buyers. Numerous carriers are available to provide their services. Connecting with a freight forwarding service is a great way to research your options for international shipping.
Exporters should also get familiar with Incoterms™ before shipping their goods. These are internationally recognized agreements between buyers and sellers that dictate responsibilities to each party in the shipping process. These agreements can impact how much responsibility an exporter may have over things such as shipping.
After taking care of transport, entrepreneurs will need to obtain the correct information and documents required for export .
- Schedule B number
- Pro forma invoice
- Commercial invoice
- Packing list
- Certificate of origin
- Certificate of conformity
- Air waybill/bill of lading
Some documents will need to be submitted electronically, such as the Automated Export System (AES). Depending on the shipment, a license might be required . Each document is essential for goods to be successfully exported to another country. Therefore, it’s imperative that exporters obtain them all before shipping.
How Much Does It Cost To Start An Export Business?
Startup costs for an export business can be somewhere between $4,000 and $26,000. Numerous factors will influence the expenses entrepreneurs can incur.
- Initial setup costs
- Market research and planing
- Product sourcing and inventory
- Marketing and promotion
- Logistics and shipping
Registering the business entity might include state and local registration fees. While most export licenses are generally free, there may be certain ones that have a specific expense. Opening an office space and obtaining supplies will also inflict costs on exporters.
Conducting thorough market research is essential and might include expenses for accessing detailed reports, market analysis tools, or consultancy fees. Entrepreneurs might need professional assistance to put together a comprehensive business plan, which can be costly.
Initial product procurement can be a significant expense, depending on the nature of the items and the quantities required. Inventory costs include not just the price of goods, but also storage and insurance.
Marketing expenses to promote the products in international markets can vary widely. This might include digital marketing, attending trade shows, or creating promotional materials. Developing a website and maintaining an online presence is also essential in today’s market. This will include web development and hosting costs.
Shipping is a major expense for export businesses. This includes freight charges, insurance, and packaging costs. Exporters will have to consider the costs from duties, taxes, and compliance with shipping regulations before they move their cargo as well.
Use our article on Schedule B numbers and HS codes to avoid confusion between the two.

What Are the Best Countries To Export To?
There are many foreign buyers willing to purchase a variety of U.S. goods, which means exporters won’t have much difficulty finding customers. According to the United States Trade Register (USTR), there are five countries that import U.S. products more than other nations around the world.
- United Kingdom
While these are great markets to get into, there are other nations that make for great export opportunities. Keep in mind, the U.S. has FTAs with numerous countries. Any of these nations will be good to conduct business in. We’ve listed some data of nations engaged in FTAs with the U.S. and how many goods they purchase.
Amount of U.S. Goods Exported To FTA Countries (2022)
Provided by the USTR , ITA , and Trading Economics
We’ve excluded Mexico and Canada, as these countries have already been mentioned. That said, the other nations on this list make for great export opportunities. Entrepreneurs will need to research the specific FTAs the U.S. shares with these countries to determine the extent of the agreement.
Start Your Business with Cargo Export USA In Your Corner
Cargo Export USA can guide you through the startup of your business. The team we have will give you the tools you need to be successful. With our plethora of skills and offerings, your business will be running efficiently.
Services offered by Cargo Export USA include:
- Product Classification: Ensuring your products are correctly classified for international shipping.
- Certificate of Origin: This documentation is essential for many FTAs. It will verify where your goods are from.
- Export Licensing: Assistance with obtaining the required licenses for your export products.
Starting an export business doesn’t have to be difficult. With the help of Cargo Export USA, your business will be operational and earning money at a rapid pace.
Let us help you unlock the door to international success. Connect with us through the site or call our team at (866) 301-0635 .
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.


Import Export Business Plan Template
Written by Dave Lavinsky
Import-Export Business Plan
Over the past 20+ years, we have helped over 1,000 entrepreneurs and business owners create business plans to start and grow their import-export businesses. On this page, we will first give you some background information with regards to the importance of business planning. We will then go through an import-export business plan template step-by-step so you can create your plan today.
Download our Ultimate Business Plan Template here >
What Is a Business Plan?
A business plan provides a snapshot of your import-export business as it stands today, and lays out your growth plan for the next five years. It explains your business goals and your strategy for reaching them. It also includes market research to support your plans.
Why You Need a Business Plan
If you’re looking to start an import-export business, or grow your existing business, you need a business plan. A business plan will help you raise funding, if needed, and plan out the growth of your import-export business in order to improve your chances of success. Your import-export business plan is a living document that should be updated annually as your company grows and changes.
Sources of Funding for Import-Export Businesses
With regards to funding, the main sources of funding for an import-export business are personal savings, credit cards, bank loans and angel investors. With regards to bank loans, banks will want to review your business plan and gain confidence that you will be able to repay your loan and interest. To acquire this confidence, the lender will not only want to confirm that your financials are reasonable, but they will also want to see a professional plan. Such a plan will give them the confidence that you can successfully and professionally operate a business. Personal savings and bank loans are the most common funding paths for social media marketing businesses.
Finish Your Business Plan Today!
How to write a business plan for an import-export company.
If you want to start an import-export business or expand your current one, you need a business plan. Below are links to each section of your import-export business plan template:
Executive Summary
Your executive summary provides an introduction to your business plan, but it is normally the last section you write because it provides a summary of each key section of your plan.
The goal of your Executive Summary is to quickly engage the reader. Explain to them the type of import-export business you are operating and its status. For example, are you a startup, do you have an import-export business that you would like to grow, or are you operating import-export companies in multiple markets?
Next, provide an overview of each of the subsequent sections of your plan. For example, give a brief overview of the import-export industry. Discuss the type of import-export business you are operating. Detail your direct competitors. Give an overview of your target market. Provide a snapshot of your marketing plan. Identify the key members of your team. And offer an overview of your financial plan.
Company Analysis
In your company analysis, you will detail the type of import-export business you are operating.
For example, you might operate one of the following types of import-export companies:
- Export management company – these types of businesses handle all the details (hiring distributors, handling logistics, creating marketing materials, etc) for companies wishing to export a product.
- Export trading company – these types of businesses determine what products foreign buyers want, and then find domestic companies who make the product.
- Import-export merchant (or free agent) – this type of business buys merchandise from a manufacturer, and resells that merchandise around the world.
In addition to explaining the type of import-export business you will operate, the Company Analysis section of your business plan needs to provide background on the business.
Include answers to question such as:
- When and why did you start the business?
- What milestones have you achieved to date? Milestones could include the volume of products you have exported or imported, number of import-export contracts signed, etc.
- Your legal structure. Are you incorporated as an S-Corp? An LLC? A sole proprietorship? Explain your legal structure here.
Industry Analysis
In your industry analysis, you need to provide an overview of the import-export industry.
While this may seem unnecessary, it serves multiple purposes.
First, researching the import-export industry educates you. It helps you understand the market in which you are operating.
Secondly, market research can improve your strategy, particularly if your research identifies market trends.
The third reason for market research is to prove to readers that you are an expert in your industry. By conducting the research and presenting it in your plan, you achieve just that.
The following questions should be answered in the industry analysis section of your import-export business plan:
- How big is the import-export industry (in dollars)?
- Is the market declining or increasing?
- Who are the key competitors in the market?
- Who are the key suppliers in the market?
- What trends are affecting the industry?
- What is the industry’s growth forecast over the next 5 – 10 years?
- What is the relevant market size? That is, how big is the potential market for your import-export business? You can extrapolate such a figure by assessing the size of the market in the entire country and then applying that figure to your local population.
Customer Analysis
The customer analysis section of your import-export business plan must detail the customers you serve and/or expect to serve.
The following are examples of customer segments: manufacturers, wholesalers, retailers, and consumers.
As you can imagine, the customer segment(s) you choose will have a great impact on the type of import-export business you operate. Clearly, individuals looking to purchase coffee beans online would respond to different marketing promotions than mobile phone manufacturers, for example.
Try to break out your target market in terms of their demographic and psychographic profiles. With regards to demographics, include a discussion of the ages, genders, locations and income levels of the customers you seek to serve. Because most import-export companies primarily serve customers living in their same city or town, such demographic information is easy to find on government websites.
Psychographic profiles explain the wants and needs of your target customers. The more you can understand and define these needs, the better you will do in attracting and retaining your customers.
Finish Your Import Export Business Plan in 1 Day!
Don’t you wish there was a faster, easier way to finish your business plan?
With Growthink’s Ultimate Business Plan Template you can finish your plan in just 8 hours or less!
Competitive Analysis
Your competitive analysis should identify the indirect and direct competitors your business faces and then focus on the latter.
Direct competitors are other import-export companies.
Indirect competitors are other options that customers have to purchase from that aren’t direct competitors. This includes manufacturers with vertically integrated distribution operations, or consumers who prefer to purchase similar products made domestically.
With regards to direct competition, you want to describe the other import-export companies with which you compete. Most likely, your direct competitors will be import-export businesses located very close to your location.
For each such competitor, provide an overview of their businesses and document their strengths and weaknesses. Unless you once worked at your competitors’ businesses, it will be impossible to know everything about them. But you should be able to find out key things about them such as:
- What types of customers do they serve?
- Do they specialize in specific products, or in imports from a specific country or region?
- What is their pricing (premium, low, etc.)?
- What are they good at?
- What are their weaknesses?
With regards to the last two questions, think about your answers from the customers’ perspective. And don’t be afraid to ask your competitors’ customers what they like most and least about them.
The final part of your competitive analysis section is to document your areas of competitive advantage. For example:
- Will you provide a wider variety of products or maintain distribution contracts with more manufacturers?
- Will you offer extra services, such as brokerage?
- Will you provide better customer service?
- Will you offer better pricing?
Think about ways you will outperform your competition and document them in this section of your plan.
Marketing Plan
Traditionally, a marketing plan includes the four P’s: Product, Price, Place, and Promotion. For an import-export business plan, your marketing plan should include the following:
Product : In the product section, you should reiterate the type of import-export company that you documented in your Company Analysis. Then, detail the specific products you will be offering. For example, in addition to mobile phones, will your import-export business offer other consumer electronics such as laptops or wireless headphones?
Price : Document the prices you will offer and how they compare to your competitors. Essentially in the product and price sub-sections of your marketing plan, you are presenting the services you offer and their prices.
Place : Place refers to the location through which you will sell your imported/exported goods. For example, will you distribute your goods directly to consumers online, or will you maintain supply contracts with retailers and wholesalers? In this section, document each method by which you will sell your products.
Promotions : The final part of your import-export marketing plan is the promotions section. Here you will document how you will drive customers to your business. The following are some promotional methods you might consider:
- Advertising in trade papers and magazines
- Direct contact with potential clients (cold calling)
- Social media marketing
- Exhibits at Trade Shows
Operations Plan
While the earlier sections of your business plan explained your goals, your operations plan describes how you will meet them. Your operations plan should have two distinct sections as follows.
Everyday short-term processes include all of the tasks involved in running your import-export business, including determining which products are needed, sourcing product manufacturers, securing and maintaining all necessary licenses and permits, arranging logistics, etc.
Long-term goals are the milestones you hope to achieve. These could include the dates when you expect to sign your 100 th supply contract, or when you hope to reach $X in revenue. It could also be when you expect to expand your import-export business to a new market.
Management Team
To demonstrate your import-export business’ ability to succeed, a strong management team is essential. Highlight your key players’ backgrounds, emphasizing those skills and experiences that prove their ability to grow a company.
Ideally you and/or your team members have direct experience in managing import-export companies. If so, highlight this experience and expertise. But also highlight any experience that you think will help your business succeed.
If your team is lacking, consider assembling an advisory board. An advisory board would include 2 to 8 individuals who would act like mentors to your business. They would help answer questions and provide strategic guidance. If needed, look for advisory board members with experience in logistics, or successfully running small businesses.
Financial Plan
Your financial plan should include your 5-year financial statement broken out both monthly or quarterly for the first year and then annually. Your financial statements include your income statement, balance sheet and cash flow statements.
Income Statement
An income statement is more commonly called a Profit and Loss statement or P&L. It shows your revenues and then subtracts your costs to show whether you turned a profit or not.
In developing your income statement, you need to devise assumptions. For example, will you import from one country, or will you operate globally? And will sales grow by 2% or 10% per year? As you can imagine, your choice of assumptions will greatly impact the financial forecasts for your business. As much as possible, conduct research to try to root your assumptions in reality.
Balance Sheets
Balance sheets show your assets and liabilities. While balance sheets can include much information, try to simplify them to the key items you need to know about. For instance, if you spend $50,000 on building out your import-export business, this will not give you immediate profits. Rather it is an asset that will hopefully help you generate profits for years to come. Likewise, if a bank writes you a check for $50,000, you don’t need to pay it back immediately. Rather, that is a liability you will pay back over time.
Cash Flow Statement
Your cash flow statement will help determine how much money you need to start or grow your business, and make sure you never run out of money. What most entrepreneurs and business owners don’t realize is that you can turn a profit but run out of money and go bankrupt.
In developing your Income Statement and Balance Sheets be sure to include several of the key costs needed in starting or growing an import-export business:
- Warehouse build-out including fixtures, construction, etc.
- Cost of buying or leasing the necessary transportation equipment (containers, cargo ship / airplane, etc.), or otherwise securing the means of transporting your goods
- Payroll or salaries paid to staff
- Business insurance
- Taxes and permits
- Legal expenses
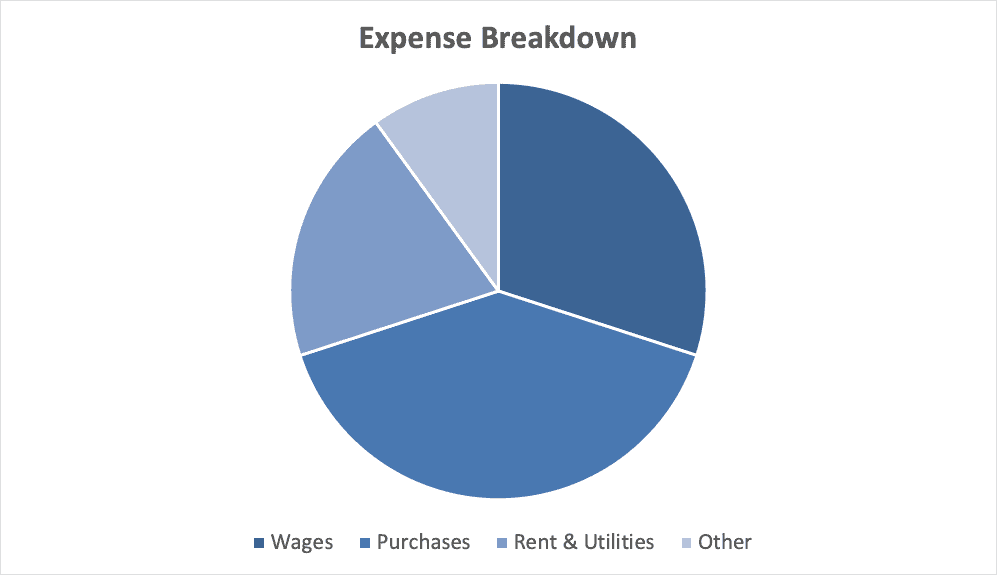
Attach your full financial projections in the appendix of your plan along with any supporting documents that make your plan more compelling. For example, you might include your warehouse lease, or contracts with manufacturers and distributors.
Putting together a business plan for your import-export business is a worthwhile endeavor. If you follow the template above, by the time you are done, you will truly be an expert. You will really understand the import-export industry, your competition, and your customers. You will have developed a marketing plan and will really understand what it takes to launch and grow a successful import-export business.
Import Export Business Plan FAQs
What is the easiest way to complete my import export business plan.
Growthink's Ultimate Business Plan Template allows you to quickly and easily complete your Import Export Business Plan.
What is the Goal of a Business Plan's Executive Summary?
The goal of your Executive Summary is to quickly engage the reader. Explain to them the type of import export business you are operating and the status; for example, are you a startup, do you have an import export business that you would like to grow, or are you operating a chain of import export businesses?
Don’t you wish there was a faster, easier way to finish your Import Export business plan?
OR, Let Us Develop Your Plan For You
Since 1999, Growthink has developed business plans for thousands of companies who have gone on to achieve tremendous success. Click here to see how Growthink’s professional business plan consulting services can create your business plan for you.
Other Helpful Business Plan Articles & Templates

Business Plan Template for Import Export Companies
- Great for beginners
- Ready-to-use, fully customizable Subcategory
- Get started in seconds

Starting an import-export business can be an exciting venture, but it requires careful planning and strategy to succeed in the global trade industry. That's where ClickUp's Business Plan Template for Import Export Companies comes in!
With this template, you can create a comprehensive business plan that covers all aspects of your import-export operations, including:
- Outlining your strategies and goals for entering and expanding in international markets
- Identifying target markets and customers to effectively position your products or services
- Assessing financial projections and budgets to ensure profitability and sustainability
- Determining logistics and supply chain management to streamline your operations
- Analyzing risks and competition to develop strategies for market penetration and differentiation
Don't miss out on the opportunity to create a roadmap for success in the import-export industry. Get started with ClickUp's Business Plan Template today!
Business Plan Template for Import Export Companies Benefits
Import and export companies can benefit greatly from using a business plan template specifically designed for their industry. Here are some of the advantages:
- Streamlining the strategic planning process by providing a structured framework for outlining goals and objectives
- Identifying target markets and customers, allowing for targeted marketing and sales efforts
- Assessing financial projections and forecasting revenue, expenses, and profitability
- Determining logistics and supply chain management strategies to optimize operations and minimize costs
- Analyzing risks and competition to develop effective risk management and competitive advantage strategies
- Creating a roadmap for success in the global trade industry, guiding the company's growth and expansion plans.
Main Elements of Import Export Companies Business Plan Template
ClickUp's Business Plan Template for Import Export Companies is specifically designed to help import and export companies create a comprehensive roadmap for success in the global trade industry. Here are the main elements of this template:
- Custom Statuses: Use the "Complete," "In Progress," "Needs Revision," and "To Do" statuses to track the progress of each section of your business plan and ensure that all tasks are completed on time.
- Custom Fields: Utilize the "Reference," "Approved," and "Section" custom fields to add important information to your business plan, such as references, approval status, and specific sections.
- Custom Views: Access different views, including "Topics," "Status," "Timeline," "Business Plan," and "Getting Started Guide," to easily navigate through your business plan and analyze different aspects, such as goals, progress, timelines, and overall plan structure.
- Collaboration: Collaborate with your team in real-time by assigning tasks, setting due dates, leaving comments, and attaching files within each section of your business plan.
- Integration: Seamlessly integrate with other tools, such as Google Drive, to import and export relevant documents and data, ensuring all your information is centralized and easily accessible.
How To Use Business Plan Template for Import Export Companies
If you're in the import-export business, having a well-thought-out business plan is crucial for success. Here are six steps to help you effectively use the Business Plan Template for Import Export Companies in ClickUp:
1. Define your mission and vision
Start by clearly defining the mission and vision of your import-export company. What do you aim to achieve? What values do you want to uphold? This will serve as the foundation for your business plan and guide your decision-making process.
Use a Doc in ClickUp to articulate your mission and vision statement and share it with your team for feedback.
2. Conduct market research
Before diving into the import-export industry, it's essential to conduct thorough market research. Identify potential target markets, assess competition, and analyze trends and opportunities. This step will help you understand the demand for your products and identify strategies to stay ahead.
Utilize custom fields in ClickUp to track key market research data, such as market size, competitors, and consumer behavior.
3. Define your products and services
Next, outline the specific products and services your import-export company will offer. Clearly define the unique selling points and advantages of your offerings. Additionally, identify potential suppliers and partners to ensure a smooth supply chain.
Create tasks in ClickUp to categorize and track your products and services, including details like pricing, sourcing, and quality control.
4. Develop a marketing and sales strategy
To attract customers and generate revenue, you'll need a robust marketing and sales strategy. Determine the most effective channels to reach your target audience, whether it's through digital marketing, trade shows, or partnerships. Additionally, outline your pricing strategy, sales targets, and promotional activities.
Use the Gantt chart in ClickUp to create a timeline for your marketing campaigns and track their progress.
5. Create a financial plan
A comprehensive financial plan is essential for the success of any business. Estimate your startup costs, projected revenue, and expenses. Determine your pricing structure, profit margins, and cash flow projections. Additionally, consider any financing options or investment opportunities that may be available.
Utilize the Table view in ClickUp to create financial projections, track expenses, and monitor your company's financial health.
6. Monitor and adapt
Once your business plan is in place, it's important to regularly monitor your progress and adapt as needed. Keep track of key performance indicators, such as sales volume, customer satisfaction, and market share. Review your plan periodically and make adjustments based on new information or changing market conditions.
Set up recurring tasks in ClickUp to review and update your business plan regularly, ensuring that it remains relevant and aligned with your goals.
By following these six steps and utilizing the Business Plan Template for Import Export Companies in ClickUp, you'll be well-equipped to navigate the import-export industry and achieve long-term success.
Get Started with ClickUp’s Business Plan Template for Import Export Companies
Import and export companies can use this Business Plan Template for Import Export Companies to streamline their planning process and ensure a successful global trade strategy.
First, hit “Add Template” to sign up for ClickUp and add the template to your Workspace. Make sure you designate which Space or location in your Workspace you’d like this template applied.
Next, invite relevant members or guests to your Workspace to start collaborating.
Now you can take advantage of the full potential of this template to create a comprehensive business plan:
- Use the Topics View to organize your business plan into different sections, such as market analysis, financial projections, and logistics
- The Status View will help you track the progress of each section, with statuses like Complete, In Progress, Needs Revision, and To Do
- Utilize the Timeline View to set deadlines and milestones for each section of your business plan
- The Business Plan View provides a holistic overview of your entire plan, allowing you to easily navigate and make updates
- Use the Getting Started Guide View to access helpful resources and tips for creating a successful business plan
- Customize the template by adding custom fields like Reference, Approved, and Section to track additional information and make your plan more organized
- Monitor and analyze your business plan to ensure it aligns with your goals and objectives
- Business Plan Template for Waitstaff
- Business Plan Template for Dominos
- Business Plan Template for Mobile UX/UI Specialists
- Business Plan Template for Market Analysts
- Business Plan Template for Ice Cream Business
Template details
Free forever with 100mb storage.
Free training & 24-hours support
Serious about security & privacy
Highest levels of uptime the last 12 months
- Product Roadmap
- Affiliate & Referrals
- On-Demand Demo
- Integrations
- Consultants
- Gantt Chart
- Native Time Tracking
- Automations
- Kanban Board
- vs Airtable
- vs Basecamp
- vs MS Project
- vs Smartsheet
- Software Team Hub
- PM Software Guide

A Comprehensive Guide: How to Create a Business Plan for Importing or Exporting Goods

Creating a well-structured business plan is essential for success in the import/export industry. Whether you are looking to import goods from overseas or export products to international markets, a carefully crafted business plan will serve as your roadmap and provide a solid foundation for your venture. In this article, we will walk you through the key steps and components to consider when developing a business plan for importing or exporting goods.
- Executive Summary: Start your business plan with a concise executive summary that provides an overview of your import/export venture. Clearly define your business goals, target market, competitive advantage, and a brief description of the products or services you intend to import or export.
- Market Analysis: Conduct a thorough market analysis to identify the demand for your products or services in the target market. Understand market trends, customer preferences, competition, and regulatory requirements. Analyze potential risks and opportunities, and showcase your understanding of the market dynamics.
- Product Selection and Sourcing: Define the specific products or services you plan to import or export. Research potential suppliers or manufacturers and evaluate their reliability, quality standards, pricing, and delivery capabilities. Outline your sourcing strategy and any exclusivity agreements or partnerships you may have.
- Competitive Analysis: Assess the competitive landscape in your target market. Identify direct and indirect competitors, their strengths and weaknesses, pricing strategies, distribution channels, and market positioning. Highlight how your unique selling proposition (USP) sets you apart from competitors and positions your business for success.
- Marketing and Sales Strategy: Develop a comprehensive marketing and sales strategy to reach your target customers effectively. Define your target audience, channels of distribution, pricing strategy, and promotional activities. Outline your sales forecast and customer acquisition plans, including any partnerships or collaborations that can help expand your reach.
- Operational Plan: Detail the operational aspects of your import/export business. Outline your supply chain management strategy, including transportation, logistics, and warehousing. Discuss any required licenses, permits, or certifications necessary for import/export operations. Provide insights into your order fulfillment process, quality control measures, and customer service strategy.
- Financial Projections: Create a detailed financial projection for your import/export business. Include revenue forecasts, cost analysis, pricing strategies, and projected profitability. Outline your startup costs, working capital requirements, and potential funding sources. Discuss your financial strategies, such as pricing structures, payment terms, and risk management techniques.
- Risk Assessment and Contingency Plans: Identify potential risks and challenges associated with importing or exporting goods. Develop contingency plans to mitigate risks, such as currency fluctuations, regulatory changes, supply chain disruptions, or geopolitical factors. Demonstrate your ability to adapt and navigate uncertainties in the international trade landscape.
- Implementation Timeline: Create a realistic timeline for the implementation of your import/export business plan. Break down the key milestones, activities, and deadlines necessary to launch and grow your venture. Include specific action plans for product sourcing, market entry, marketing campaigns, and operational setup.
- Monitoring and Evaluation: Establish mechanisms to monitor and evaluate the progress of your import/export business. Define key performance indicators (KPIs) to track your business’s performance against the set goals. Regularly review and update your business plan based on market feedback, industry trends, and internal analysis.
Conclusion: Crafting a comprehensive business plan is vital for importing or exporting goods successfully. By following the steps outlined above and addressing key components such as market analysis, product selection, marketing strategy, financial projections, and risk assessment, you can create a robust roadmap for your import/export business. A well-designed business plan will guide your decision-making process, attract potential investors or partners, and set the stage for a thriving venture in the global trade.
Import & Export Business Plans
Artificial flowers import business plan.
Fantastic Florals, Inc. imports exclusively handmade flowers by artisans from Indonesia.
Coffee Export Business Plan
Silvera & Sons is an ongoing manufacturing company which prepares green Arabica coffee beans grown in Brazil for exportation to American specialty roasters.
Ethnic Food Import Business Plan
Aztec Food Imports will supply authentic Mexican food imports to Richmond area retail stores and supermarkets.
Export Automobile Parts Business Plan
D.A.P. Exports is an automobile parts and lubricant exporter to Latin American countries.
Export Watch Manufacturer Business Plan
Grutzen Watches will build and import to the U.S. high-quality watches designed by the best German engineers.
Fitness Equipment Business Plan
Circuit Fitness Importing is a start-up business that has been formed to become the exclusive importer of the Wega Corporation’s innovative Esercitazione Diritta fitness equipment.
Furniture Import Business Plan
Poppi Designs' mission is to supply imported Spanish chairs and other furniture items to certain market niches which are not well served by the large domestic manufacturers.
Import Export Business Plan
Visigoth Imports will provide complete import/export brokerage services including purchase contracts, shipping, warehousing, and delivery scheduling.
Vending Services Business Plan
Chef Vending is a start-up vending machine and commercial food and beverage dispensing equipment company.
Give your import/export business a leg up on the competition by writing a winning business plan. Get a head start by checking out these sample business plans for fitness equipment importers, artificial flowers importing, ethnic food imports, furniture importers, and other import/export businesses.

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software

Item added to your cart
Here is a free business plan sample for an import/export company.

If you're considering entering the dynamic world of international trade but are unsure how to start, you've landed on the right page.
In the content that follows, we will present to you a comprehensive sample business plan tailored for an import/export company.
As you might be aware, a meticulously developed business plan is a cornerstone of success for any entrepreneur. It serves as a roadmap, enabling you to outline your business objectives, strategies, and the intricate details of your operations.
To streamline your planning process and get started on a solid foundation, you can utilize our import/export business plan template. Additionally, our team of experts is available to review and refine your plan at no extra cost.

How to draft a great business plan for your import/export company?
A good business plan for an import/export company must be tailored to the intricacies of international trade.
To start, it is crucial to provide a comprehensive overview of the global market you intend to operate in. This includes analyzing trade volumes, growth trends, and the economic climate, similar to what we have outlined in our import/export business plan template .
Your business plan should clearly articulate your company's vision, define your target markets (such as specific countries or regions), and describe your unique value proposition (competitive pricing, specialized products, etc.).
Market analysis is paramount. You need to thoroughly understand the regulatory environment, tariffs, and trade agreements that affect your business, as well as the competitive landscape and demand in your chosen markets.
For an import/export business, it is essential to detail your product or service offerings. Explain what you are importing or exporting, the benefits of these products or services, and how they fulfill the needs of your target market.
The operational plan should cover your logistics and supply chain strategy, including the selection of freight forwarders, customs brokers, and methods of transportation. It should also outline your approach to managing international payments and currency risks.
Quality control, compliance with international standards, and adherence to trade regulations are critical points to emphasize in your business plan.
Marketing and sales strategies must be adapted to the international context. Discuss how you will build relationships with foreign distributors, utilize trade shows, and leverage digital marketing to reach a global audience.
Given the digital age, having a robust online presence, including a professional website and active engagement on relevant B2B platforms, is indispensable.
The financial section should include your startup costs, projected revenues, cost of goods sold, and operational expenses. It is also important to analyze the financial risks associated with exchange rate fluctuations and international transactions. For assistance with this, consider using our financial forecast for an import/export business .
Compared to other business plans, an import/export business plan must pay special attention to international market analysis, logistics, customs regulations, and currency management.
A well-crafted business plan will not only help you clarify your strategy and operations but also serve as a tool to attract investors or secure loans.
Lenders and investors will be looking for a comprehensive understanding of international markets, a solid financial plan, and a clear operational strategy for managing the complexities of global trade.
By presenting a thorough and substantiated plan, you showcase your expertise and dedication to the success of your import/export venture.
To streamline the process and ensure you cover all necessary aspects, you can start with our import/export business plan template .

A free example of business plan for an import/export company
Here, we will provide a concise and illustrative example of a business plan for a specific project.
This example aims to provide an overview of the essential components of a business plan. It is important to note that this version is only a summary. As it stands, this business plan is not sufficiently developed to support a profitability strategy or convince a bank to provide financing.
To be effective, the business plan should be significantly more detailed, including up-to-date market data, more persuasive arguments, a thorough market study, a three-year action plan, as well as detailed financial tables such as a projected income statement, projected balance sheet, cash flow budget, and break-even analysis.
All these elements have been thoroughly included by our experts in the business plan template they have designed for an import/export company .
Here, we will follow the same structure as in our business plan template.

Market Opportunity
Market overview and statistics.
The import/export industry is a critical component of global trade, facilitating the movement of goods across international borders.
According to recent data, the global import/export market is valued in the trillions of dollars, highlighting its immense scale and impact on the world economy. In the United States alone, the total value of imports and exports amounted to over 5 trillion dollars in recent years.
This industry is vital for connecting producers and consumers worldwide, allowing for the distribution of a diverse range of products, from raw materials to finished goods.
These statistics underscore the significant role that the import/export sector plays in global commerce and its potential for lucrative business opportunities.
Industry Trends
The import/export sector is influenced by several key trends that shape the way trade is conducted.
Globalization continues to drive the expansion of international trade, with businesses sourcing products from and selling to markets around the world. E-commerce is also transforming the industry, as more companies leverage online platforms to reach global customers and streamline their operations.
Supply chain optimization is a major focus, with companies investing in logistics and technology to improve efficiency and reduce costs. Additionally, there is a growing emphasis on sustainability, as businesses seek to minimize their environmental impact and meet consumer demand for eco-friendly practices.
Trade agreements and regulatory changes also play a significant role in the industry, affecting tariffs, trade barriers, and market access.
These trends highlight the dynamic nature of the import/export business and the need for companies to stay informed and adaptable to succeed.
Key Success Factors
Success in the import/export industry hinges on several critical factors.
First and foremost, a deep understanding of international markets and regulations is essential. Companies must navigate complex trade laws and customs procedures to ensure compliance and avoid costly delays.
Building strong relationships with reliable suppliers and customers is also crucial for establishing trust and securing repeat business.
Strategic location and logistics capabilities are vital for efficient transportation and distribution of goods. Proximity to major ports, airports, and transportation networks can provide a competitive edge.
Exceptional customer service and communication are important for managing transactions and resolving any issues that may arise during the import/export process.
Lastly, effective risk management and the ability to adapt to changing market conditions are key to maintaining profitability and growth in the face of economic fluctuations and trade disputes.
The Project
Project presentation.
Our import/export company project is designed to bridge the gap between global markets and local businesses by providing a reliable and efficient trade channel. Strategically located to access major shipping routes and transportation hubs, our company will specialize in the import and export of high-demand commodities such as electronics, consumer goods, agricultural products, and textiles.
We will leverage advanced logistics, customs expertise, and a deep understanding of international trade regulations to ensure smooth and timely delivery of goods. Our services will cater to small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) looking to expand their market reach without the complexities of global trade.
Our import/export business aspires to be a trusted partner for companies aiming to navigate the complexities of international trade, thereby fostering global business growth and diversification.
Value Proposition
The value proposition of our import/export company lies in our ability to connect businesses with international markets, providing a seamless and cost-effective solution for trading goods across borders.
Our commitment to reliability, transparency, and customer service offers our clients peace of mind, knowing their international trade needs are managed by experts. We aim to simplify the import/export process, allowing businesses to focus on their core operations while we handle the intricacies of global logistics.
We are dedicated to empowering businesses to reach new markets, offering tailored solutions that align with their strategic goals, and contributing to their growth and success in the global marketplace.
Our company strives to be a catalyst for international trade, enabling businesses to leverage global opportunities and driving economic development in the communities we serve.
Project Owner
The project owner is an experienced entrepreneur with a robust background in international trade and logistics.
With a track record of successful trade negotiations and a vast network of global contacts, he is well-equipped to establish an import/export company that stands out for its efficiency, reliability, and customer-focused approach.
Driven by a vision of connecting markets and facilitating global commerce, he is committed to providing top-tier import/export services that support the growth of businesses and contribute to the dynamism of the global economy.
His dedication to excellence and his strategic insight into the world of international trade make him the driving force behind this project, aiming to create new opportunities for businesses and enhance the flow of goods across international borders.
The Market Study
Market segments.
The market segments for this import/export company are diverse and cater to various industries and consumer needs.
Firstly, there are businesses seeking to import goods and raw materials that are not readily available in the local market, such as specialized machinery, electronics, or unique consumer products.
Secondly, domestic manufacturers and producers looking to expand their market reach by exporting goods to international markets form another significant segment.
The market also includes retailers and e-commerce platforms that require a steady flow of imported products to satisfy consumer demand for variety and quality.
Finally, trade consultants and logistics companies can be key partners, as they may require the services of an import/export company to facilitate their operations.
SWOT Analysis
A SWOT analysis of this import/export company project reveals several aspects.
Strengths include a robust network of international suppliers and buyers, expertise in logistics and customs regulations, and the ability to offer competitive pricing due to economies of scale.
Weaknesses might involve currency exchange risks, dependency on international trade policies, and the challenge of maintaining quality control across borders.
Opportunities can be found in the increasing globalization of trade, the rise of e-commerce, and the potential to enter emerging markets with high demand for imported goods.
Threats could include geopolitical tensions affecting trade routes, sudden changes in import/export regulations, and the volatility of international shipping costs.
Competitor Analysis
Competitor analysis in the import/export industry indicates a highly competitive environment.
Direct competitors include other import/export companies, both large multinational corporations and smaller niche firms.
These competitors strive to establish strong relationships with suppliers and buyers, offer cost-effective solutions, and ensure timely delivery of goods.
Potential competitive advantages include a comprehensive understanding of market trends, superior customer service, and the agility to adapt to changing trade environments.
Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of competitors is crucial for carving out a unique market position and for strategic planning.
Competitive Advantages
Our import/export company's competitive edge lies in our extensive global network and our commitment to providing personalized service to each client.
We have established strong partnerships with reliable suppliers and logistics providers to ensure a seamless supply chain from source to destination.
Moreover, our expertise in navigating complex trade agreements and customs regulations allows us to minimize delays and reduce costs for our clients.
We are dedicated to transparency in our operations, providing clients with real-time updates on their shipments and ensuring that all transactions comply with international trade laws.
You can also read our articles about: - the customer segments of an import/export company - the competition study for an import/export company
The Strategy
Development plan.
Our three-year development plan for the import/export company is designed to establish a strong foothold in the international trade market.
In the first year, we will concentrate on building a robust network of suppliers and buyers, focusing on high-demand products and ensuring compliance with trade regulations.
The second year will be dedicated to expanding our market reach by entering new territories and diversifying our product portfolio to cater to a broader audience.
In the third year, we aim to solidify our presence in the industry by enhancing our logistics, customer service, and exploring strategic partnerships with local and international businesses.
Throughout this period, we will prioritize efficiency, customer satisfaction, and adaptability to the dynamic global market conditions to secure our growth and success.
Business Model Canvas
The Business Model Canvas for our import/export company targets businesses seeking reliable access to international markets for their products, as well as those looking to source goods from abroad.
Our value proposition is centered on providing seamless trade solutions, competitive pricing, and ensuring product quality and compliance.
We conduct our operations through direct sales channels, online platforms, and through partnerships with local distributors, utilizing our key resources such as our global trade network and logistics expertise.
Key activities include market research, negotiation, logistics management, and customer support.
Our revenue streams are generated from service fees, commissions on transactions, and margins on products traded, while our costs are mainly associated with logistics, operations, and marketing.
Access a comprehensive and editable real Business Model Canvas in our business plan template .
Marketing Strategy
Our marketing strategy is built on establishing trust and demonstrating expertise in the import/export field.
We aim to educate potential clients about the advantages of our services and the efficiency of our trade processes. Our approach includes targeted online campaigns, participation in trade shows, and the creation of informative content on international trade regulations and trends.
We will also develop partnerships with industry leaders to enhance our credibility and reach.
Additionally, we will leverage social media and professional networking platforms to connect with businesses worldwide, while emphasizing our commitment to providing exceptional trade services.
Risk Policy
The risk policy of our import/export company is designed to mitigate risks associated with international trade, such as currency fluctuations, compliance with trade laws, and supply chain disruptions.
We employ rigorous due diligence procedures, engage in hedging strategies to manage currency risks, and maintain strong relationships with logistics providers to ensure supply chain reliability.
Regular audits and compliance checks are conducted to adhere to international trade regulations. We also maintain a conservative financial strategy to manage operational costs effectively.
Furthermore, we have comprehensive insurance coverage to protect against unforeseen events and liabilities. Our priority is to conduct secure and efficient trade operations while safeguarding the interests of our clients and our business.
Why Our Project is Viable
We envision establishing an import/export company that serves as a bridge between markets, facilitating the flow of goods and contributing to global commerce.
With our strategic approach to market entry, commitment to service excellence, and adaptability to market trends, we are confident in our ability to thrive in the competitive world of international trade.
We are excited about the opportunity to foster global business connections and drive growth for our clients and our company.
We remain open to innovation and strategic shifts to navigate the complexities of global trade, and we look forward to the prosperous future of our import/export venture.
You can also read our articles about: - the Business Model Canvas of an import/export company - the marketing strategy for an import/export company
The Financial Plan
Of course, the text presented below is far from sufficient to serve as a solid and credible financial analysis for a bank or potential investor. They expect specific numbers, financial statements, and charts demonstrating the profitability of your project.
All these elements are available in our business plan template for an import/export company and our financial plan for an import/export company .
Initial expenses for our import/export company include setting up a robust logistics network, securing partnerships with reliable suppliers and distributors, obtaining the necessary licenses and permits for international trade, investing in a customer relationship management (CRM) system, and costs related to brand creation and launching targeted marketing campaigns to establish our presence in the market.
Our revenue assumptions are based on a comprehensive analysis of global market trends, the demand for specific products in various regions, and the potential for competitive pricing.
We anticipate a steady increase in trade volume, starting conservatively and expanding as our network and reputation in the import/export industry grow.
The projected income statement indicates expected revenues from our trading activities, cost of goods sold (including freight, tariffs, and insurance), and operating expenses (office rent, marketing, salaries, etc.).
This results in a forecasted net profit essential for assessing the long-term viability of our business.
The projected balance sheet reflects assets specific to our business, such as inventory, accounts receivable, and liabilities including debts and anticipated operational expenses.
It shows the overall financial health of our import/export company at the end of each fiscal period.
Our projected cash flow statement details incoming and outgoing cash flows, allowing us to anticipate our cash needs at any given time. This will enable us to effectively manage our finances and avoid liquidity issues.
The projected financing plan lists the specific financing sources we plan to use to cover our startup and operational expenses.
The working capital requirement for our import/export company will be closely monitored to ensure we have the necessary liquidity to finance our daily operations, including purchasing inventory, managing supplier payments, and covering overhead costs.
The break-even point specific to our project is the level of sales needed to cover all our costs, including startup expenses, and begin generating a profit.
It will indicate when our business will become financially sustainable.
Performance indicators we will track include the gross margin on our traded goods, the inventory turnover ratio to assess the efficiency of our stock management, and the return on investment to measure the profitability of the capital invested in our business.
These indicators will help us evaluate the financial health and overall success of our import/export company.
If you want to know more about the financial analysis of this type of activity, please read our article about the financial plan for an import/export company .
- Choosing a selection results in a full page refresh.
- Opens in a new window.
Get Ready to Export: Are You Export Ready Export Plan Development
U.s. exporting.
[Download the full video (16 MB))] Quick Links: Next Video | Get Ready to Export Video Set | How to Export Video Series | Subscribe to our Email Updates and Tips .
Qualities of an Export-Ready Company
Export-ready companies possess certain qualities that increase the likelihood that their exporting efforts will be successful:
- Have commitment from ownership and are prepared to fund exporting activities.
- Understand the added demands international business can place on key resources.
- Have realistic expectations regarding return on investments from international activities.
- Are prepared to modify products and services by market as well as provide training and after-sales service.
- Have an awareness of U.S. government export promotion and compliance resources.
Assess Your Company’s Export Readiness
Are you ready to make that first export sale or expand into new markets? Start by selecting one of our export assessments to help determine your company's current level of export readiness and any gaps in your export planning. Then, view the U.S. Commercial Service Market Destination videos . Each of the 20 video shorts provides in-depth insight into market opportunities and trends by in-country trade experts at U.S. embassies abroad; destinations which range from entry-level to more challenging export markets. Most businesses that haven’t yet exported will need to take steps to become export ready, and current exporters will need to research and strategize in targeting new markets. The key is developing an exporting business plan, as outlined below.
Export Plan Basics
Once you’ve decided to sell abroad or pursue new export markets, a well-thought out export plan increases your chances that the best options will be chosen, resources will be used wisely, and execution will lead to a successful result. Ready to get started? View My Export Plan , the third of the three-video Get Ready to Export set.
Export.gov , the U.S. federal government’s export portal, also links to many resources, including the following:
- If your business is just getting started, contact your nearest Small Business Development Center (SBDC ) or Score representative for help in developing an overall business plan.
- If you are an established firm with a record of domestic or overseas sales and are looking to export, your local U.S. Commercial Service office can assist.
- Country Commercial Guides provide the latest market intelligence on more than 140 countries from U.S. embassies worldwide.
- A Basic Guide to Exporting provides a roadmap for developing an export plan. See Chapter 1: Introduction: The World is Open for Your Business, and Chapter 2: Developing an Export Strategy.
Get Ready to Export: Are You Export Ready
Pick a board, create a board.
Owner: Beta Community Site Guest User
Create Cancel
Get Ready to Export: Are You Export Ready Export Plan Development
U.s. exporting.
[Download the full video (16 MB))] Quick Links: Next Video | Get Ready to Export Video Set | How to Export Video Series | Subscribe to our Email Updates and Tips .
Qualities of an Export-Ready Company
Export-ready companies possess certain qualities that increase the likelihood that their exporting efforts will be successful:
- Have commitment from ownership and are prepared to fund exporting activities.
- Understand the added demands international business can place on key resources.
- Have realistic expectations regarding return on investments from international activities.
- Are prepared to modify products and services by market as well as provide training and after-sales service.
- Have an awareness of U.S. government export promotion and compliance resources.
Assess Your Company’s Export Readiness
Are you ready to make that first export sale or expand into new markets? Start by selecting one of our export assessments to help determine your company's current level of export readiness and any gaps in your export planning. Then, view the U.S. Commercial Service Market Destination videos . Each of the 20 video shorts provides in-depth insight into market opportunities and trends by in-country trade experts at U.S. embassies abroad; destinations which range from entry-level to more challenging export markets. Most businesses that haven’t yet exported will need to take steps to become export ready, and current exporters will need to research and strategize in targeting new markets. The key is developing an exporting business plan, as outlined below.
Export Plan Basics
Once you’ve decided to sell abroad or pursue new export markets, a well-thought out export plan increases your chances that the best options will be chosen, resources will be used wisely, and execution will lead to a successful result. Ready to get started? View My Export Plan , the third of the three-video Get Ready to Export set.
Export.gov , the U.S. federal government’s export portal, also links to many resources, including the following:
- If your business is just getting started, contact your nearest Small Business Development Center (SBDC ) or Score representative for help in developing an overall business plan.
- If you are an established firm with a record of domestic or overseas sales and are looking to export, your local U.S. Commercial Service office can assist.
- Country Commercial Guides provide the latest market intelligence on more than 140 countries from U.S. embassies worldwide.
- A Basic Guide to Exporting provides a roadmap for developing an export plan. See Chapter 1: Introduction: The World is Open for Your Business, and Chapter 2: Developing an Export Strategy.
More Information
Get ready to export: are you export ready, pick a board, create a board.
Owner: Trade Community Site Guest User
Create Cancel
- Credit cards
- View all credit cards
- Banking guide
- Loans guide
- Insurance guide
- Personal finance
- View all personal finance
- Small business
- Small business guide
- View all taxes
You’re our first priority. Every time.
We believe everyone should be able to make financial decisions with confidence. And while our site doesn’t feature every company or financial product available on the market, we’re proud that the guidance we offer, the information we provide and the tools we create are objective, independent, straightforward — and free.
So how do we make money? Our partners compensate us. This may influence which products we review and write about (and where those products appear on the site), but it in no way affects our recommendations or advice, which are grounded in thousands of hours of research. Our partners cannot pay us to guarantee favorable reviews of their products or services. Here is a list of our partners .
How to Start an Import/Export Business in 6 Steps

Many or all of the products featured here are from our partners who compensate us. This influences which products we write about and where and how the product appears on a page. However, this does not influence our evaluations. Our opinions are our own. Here is a list of our partners and here's how we make money .
For nearly as long as there’s been people, there’s been trade. Imports and exports are how the potato came to Ireland, and in a more modern sense, it's how we’re able to buy food, drinks, furniture, clothes, and nearly everything else, from all around the world today.
Imports are any good or service brought in from one country to another, while exports are goods and services produced in the home country for sale to other markets. Thus, whether you’re importing or exporting a product (or both) depends on your orientation to the transaction.

The modern system of international trade is a complex web of import/export businesses that handle the sale, distribution, and delivery of goods from one nation to another. If you're interested in starting a business in this industry, know that there is more than one type of import/export business. You could focus just on importing or just on exporting. You could be a manufacturer’s representative, specializing in a certain industry, or you could be an import/export merchant or agent, which is more of a freelance broker.
Starting an import/export business
If you’re interested in starting an import/export business, there are a ton of considerations you need to make — just as you would for any business. For an import/export business, specifically, it’s helpful to have a background in business, international relations, or global finance. This should give you an understanding of the myriad hoops one must jump through to sell or buy a product from an overseas supplier.
“The compliances make it so complex that even if you did know how to do it, you’re still going to have to keep in mind a lot of random considerations,” says Selena Cuffe, co-founder of Heritage Link Brands, a company that imports, exports, and produces wine, and other high-end products like tea and honey.
Cuffe worked for years in brand management for Procter & Gamble, among other trade-related positions, before starting her company in 2005. She was inspired after going to South Africa, where she attended the first Soweto Wine Festival.
Heritage Link Brands now operates within the wine industry in different ways: It imports wine from South Africa into the U.S. wine market, and it exports grapes from its own South African vineyard to the U.S. as well as the Philippines and Hong Kong. It also exports wine to airlines for use on international flights.
Keep reading for the steps you need to take to start an import/export business, as well as tips from Cuffe.
How much do you need?
with Fundera by NerdWallet
We’ll start with a brief questionnaire to better understand the unique needs of your business.
Once we uncover your personalized matches, our team will consult you on the process moving forward.
1. Get your business basics in order
Anyone starting a business in the 21st century needs to cover certain bases, like creating a website as well as social media channels like Facebook, Twitter, and a host of others.
So here's your first step: Get the basics in order. This means registering your business with the state in which your headquarters will be located, registering a domain name, getting any business licenses you need to legally operate, and so on.
You'll need a business plan, too. Part of that business plan needs to cover how to handle the rules and regulations of the markets you want to work in. For example, to bring alcohol and tobacco products into the U.S., you need an Alcohol and Tobacco Trade and Tax Bureau permit, which is free but can take months to acquire. Similar research needs to be done when doing business with other countries, taking into account everything from various legal back label requirements in each nation to insurance.
Perhaps most importantly, you need access to capital. Startup costs can vary greatly depending on the type of imports/exports business you start.
“The first thing I recommend for anyone is to have your capital upfront,” says Cuffe. “That’s so you can protect your business from not only a legal standpoint but also the equity of the brand that you create and to make sure you invest in the quality of whatever you launch. Test a market, or test a city, then a state, then a region. Then I think that there are greater chances for success and sustainability long term.”
The ratio that Cuffe cited for success in the wine industry — "In order to make $1 million, you need to invest $7 million” — demonstrates the kind of capital needed to start a business comfortably (if one can ever be “comfortable” as an entrepreneur) and be prepared for whatever occurs, from issues with sourcing to changes in trade regulations.
2. Pick a product to import or export
The next step in starting an import/export business is to find a product or industry you are passionate about and that you think could sell in international markets.
For Cuffe, that product turned out to be wine. She felt a connection to the product not just from a quality and taste standpoint but from a social justice standpoint as well.
“When I first entered the industry in 2005, there was just one Black winemaker and five Black-owned brands," she says. "Today there are 17 Black winemakers and 31 Black-owned brands.”
Though the South African wine industry still deals with injustices like poor working conditions and unequal access to capital, Cuffe says things have improved since the previous decade thanks to the increased sales and notoriety of South African wines worldwide.
“The biggest thing that we’ve enabled is the financing of Black businesses. When we first got started, in order for even these brands to create their own wine, they had to source it from existing white wineries, because they didn’t own any land,” Cuffe says.
Once you find your product, you also need to identify the right market for it. After all, you need someone to sell it to. This is where your trend-spotting skills come into play. The best products for an import/export business are products that are just starting to become popular, or show some promise to being so in the future.
You can conduct research with resources like GlobalEDGE’s Market Potential Index or by checking with local government officials and websites, such as the Department of Commerce International Trade Administration’s Data and Analysis. You can also find reports on the state of the imports/exports industry with the Census Bureau Foreign Trade .
From there, it’s best to start “slow and steady.”
“Test your ideas,” says Cuffe. “Don’t assume that what you think will sell because you love it will catch fire in the market. What catches fire in the market is more than just the way it tastes — it’s who you know, and the packaging and serendipity of timing, and all of the indirect soft stuff that makes the difference.”
3. Source your suppliers
Once you have a product you’d like to trade internationally, you need to find a local manufacturer or other producer that makes your product and can lead to a strong partnership. A good relationship with a supplier is crucial to long-running success in an imports/exports business.
Generally, you can find suppliers through companies like Alibaba, Global Sources, and Thomas Register. You will need to convince the supplier of the benefits of entering the U.S. market (or another market you wish to sell to), and figure out the logistics of taking their product from their local warehouse or production facility to another one, potentially on the other side of the globe.
You might also be your own supplier — in some cases, as Cuffe occasionally is for herself.
“We own an interest in a vineyard in South Africa called Silkbush ," she says. "My orientation when I do business to them is, 80% of the grapes that we pick we send off to domestic wineries who use our grapes to produce their own proprietary high-end wine. The remaining 20% is used to create our proprietary label Silkbush, which we export to foreign markets.”
4. Price your product
You know what product you want to work with and you've identified your target market. Next up, figuring out how much to charge.
Typically, the business model on an imports/exports business includes two key understandings: the volume of units sold, and the commission made on that volume.
Be sure to price your product such that your markup on the product (what ends up being your commission) doesn't exceed what a customer is willing to pay. But you don't want to make it too low such that you aren't ever going to make a profit.
In the imports/exports industry, importers and exporters typically take 10% to 15% markup above what the manufacturer charges you when you buy the raw product.
5. Find your customers
Next up on how to start an imports/exports business? Finding customers to sell to.
Deciding on a market is not the same as finding your customers. You can’t just send your products to the Port of New York and start selling your wares on the docks to whoever walks by. You usually need to find distributors and clients who will take on your product and sell to others.
If you have a quality website that includes digital marketing campaigns, your customers may end up finding you. But to get started, Cuffe suggests doing things the old-fashioned way — by cold-calling. Check with any local contacts you have in the area, contact the area's Chamber of Commerce, trade consulates, embassies, and so on. These entities might be able to give you a local contact list that could be a vital help in starting a imports/exports business.
“I cold-called the local Cambridge, Massachusetts, Whole Foods store, and they gave me a chance. And now we do display programs and regional programs with Whole Foods,” says Cuffe. “A lot of what I did in the beginning and even today involves cold calls.”
6. Get the logistics down
Perhaps the most complex aspect of importing and exporting is the logistics of taking a product created somewhere and selling it somewhere else. How does the product make the trip from the vineyard of South Africa to the wine glasses of drinkers in California, for example?
“When you are operating within a supply chain where your customer is different than your client, which is different than your consumer, it requires an extraordinary amount of coordination,” says Cuffe. “I use a freight forwarder that on my behalf reaches out to shipping lines, like Maersk.”
Hiring a global freight forwarder is generally a good idea for all imports/exports businesses, as they'll serve as a transport agent for moving cargo — saving you a lot of time and worry about getting your products from the factory to a warehouse. Essentially, you'll give them information about your business and your intentions for the product, and they'll arrange the shipping agreements, insurance, and oftentimes the licenses, permits, tariffs, and quotas of working within another country. This can remove a lot of the headache associated with starting an imports/exports business in an international trade market.
Frequently asked questions
Is an import/export business profitable.
Many import/export businesses are very profitable. To improve your company's chances of profitability, it's important to conduct the required research on your industry and have a well-documented business plan. Understanding all of the costs associated with an imports/exports business and determining your profit margins when pricing your products is also essential.
How do import/export companies make money?
As an import/export company, you'll make a profit by selling products at a higher rate than you paid for them from the vendor or source.
What is an export license?
An export license is a government-issued document authorizing your company to complete certain export transactions. An export license is issued by the appropriate agency once the export transaction has been reviewed.
What documents do I need to import goods?
The types of documents you'll need to import goods will vary depending on the country you're importing the product into. In the United States, import licenses and permits may be required, but a Customs and Border Protection entry form is always required.

Start Your Dream Business
The bottom line
The world of importing and exporting is a dazzling, complex system that balances both emotional and economic needs. If we want something that is grown or produced in another part of the world, how can we get our hands on it? How can we give others the opportunity to enjoy it, while still creating a sustainable lifestyle for those producing it and for those who transport it from point A to B?
If you’re interested in answering these questions, don’t let the enormity of the task overwhelm you. With the proper research, planning, and documentation, you can launch a successful imports/exports business of your own.
On a similar note...

Export Finance Solutions Where Businesses Come to Grow: Official Blog of the Export-Import Bank
- Export Credit Insurance
- Working Capital
- Success Stories
- Additional Resources
The U.S. Small Business Administration (SBA) has created a hands-on exporting preparation guide and innovative tool called the Export Business Planner . It is designed to serve as a roadmap for creating an export business plan, exploring foreign markets and financing, developing a marketing plan, and more. But unlike a traditional printed manual, this Planner is a “living document”, ready to be customized and continually updated by you. The document can be updated and referenced time and again as your export business grows. If you have a successful product or service, you may be able to increase sales and profit by following your plan.
Export planning entails a fair amount of research. But with the Planner , there’s no need to remember and/or compile these resources yourself – they are all embedded in appropriate topical locations. As such, you are given a “head start” on conducting export research, as the step of finding the best sources of further information has already been done for you. All you need to do is complete the worksheets and then save them – and your Export Business Plan will be underway.
The Export Business Planner is a downloadable tool to save and customize:
- How to determine your export readiness
- Training and counseling information
- Worksheets for global market research
- Financing information and options
- Customizable export business plan and marketing plan templates
- Helpful resources for exporters
- Glossary of Export terms
If you are looking for more information on financing options for your exports and how export credit insurance can help your business mitigate risk and increase competitiveness, the Export-Import Bank of the U.S. has trade finance specialists located in your area that you can speak to. To get a FREE consultation, click below:

- International Trade
- International Negotiations
- International Contracts
- Business Etiquette
- Emerging Markets
- Business Guides
Global Negotiator Blog
What is an export business plan.
Posted by: Olegario Llamazares on 15 September, 2020 in International Trade Comments Off on What is an export business plan?
The purpose of the Export Business Plan is to prepare companies, specially middle and small, to enter the international marketplace or to better organize their existing international business activity. The Plan will serve as a step-by-step guide to lead the company through the process of exporting products and services to international markets. The purpose of the Plan is to address the main issues that arise in the development and implementation of international marketing strategy:
- Assessment of export potential and capabilities.
- Identify target markets.
- Choose the best market entry strategy.
- Selection of most suitable marketing actions.
- Better management of international business operations.
- Evaluate the financial resources, sales goals and profits.
The Export Business Plan is divided into six sections following a time sequence. Each section helps to plan international business strategies and take effective export decisions. The Plan provides worksheets with corresponding explanatory notes so that the user does not have difficulty developing and completing the Plan. It also offers a case study that is used as an example to apply the methodology. Below we develop briefly the contents of an Export Business Plan in six sections. Complete information on the Export Business Plan methodology with worksheets, explanatory texts and case study can be found on the link Export Business Plan.

SECTION 1: EXPORT DIAGNOSTICS
In order to make the most of your company’s strengths and improve your weaknesses, the internationalisation plan begins with an analysis of the competitive capacities of the company in relation to the foreign markets in order to achieve profit maximisation. The Export Business Plan analysis leads to an identification of the economic, policies and social trends etc, which may affect the international evolution of the sector where the company plans to develop its activity. Once the principal strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats are identified you must extract some conclusions and at the same time decide which actions you wish to proceed successfully in the foreign markets. These conclusions are double-sided: business strategy and resources.
SECTION 2: MARKET SELECTION
Before initiating the process of market selection, the company should decide whether a concentration or a diversification strategy is better to approach the foreign markets:
- Concentration: a limited number of markets are selected to focus commercial efforts on them and achieve a certain level of penetration.
- Diversification: the company operates in a large number of markets. The growth strategy is based on selling to these markets to achieve a high level of penetration in each one of them.
In the first pre-selection of the markets, it is not suitable to just consider the individual countries. It is advisable to consider them in groups or combinations of countries. Following the initial filter, you should select areas or markets which complete the basic criteria and these countries will subsequently be analysed in depth. It is not about selecting the most favourable countries; the most important is to eliminate those countries which do not comply with the basic criteria. Once that most favorable geographic areas, have been chosen, the next step is to select countries belonging to those geographic areas. Finally, it comes to selecting target countries for the following stages of the Plan (Stage 3: Marker Entry Methods and Stage 4: International Offer).
Export Business Plan Methodology
SECTION 3: MARKET ENTRY METHODS
The entry form chosen for foreign markets will be a critical decision in the Export Plan. The main alternatives to market products abroad are:
- Direct exports.
- Commercial Agent.
- Importer/Distributor.
- Trading companies.
- Piggyback agreement.
- Franchise agreement.
- Licence agreement.
- Joint venture agreement.
- Sales Branch.
Once the form of entry is chosen it is advisable to develop the company´s profile –even if you have final clients, intermediaries or partners– through those you will efficiently penetrate the market. The aspects that must be defined in this role are the following: Size of the company; business culture; product range; solvency; international experience; and commercial practices.
SECTION 4: INTERNATIONAL OFFER
At this section of the Plan it comes to choosing products or services offered by the company, mainly those that have more export capacity. Companies who have a very wide range of products should not select products but strategic units that will consist of products that have the same characteristics. With regards to the product´s policy it is advisable to define the characteristics of each one of their attributes and the necessary adaptations for its sale in foreign markets. There exist two alternatives:
- Standardization: to sell the same product in all foreign markets.
- Adaptation: consists in adapting the main attributes of the products for each market. In a double sense: on one side the legal normative of the country and on the other side the needs of the client in each country.
In this section it should also be designed a pricing strategy for the products in the target countries.
SECTION 5: COMMUNICATION STRATEGY
Section 5 starts verifying if the brand which the company uses in the domestic market adapts appropriately to the foreign markets or if it is advisable to create a new brand. The tools required to promote the product in foreign markets are basically the same tools employed in the domestic market. You can classify them into two groups: promotion tools and publicity tools. Between the first ones you can choose advertising as a means of communication and publicity through the internet while the promotion includes the elaboration of the documentation and promotional videos, the assistance to trade fairs, promotion at the point of sale etc. The activities of communication imply some necessarily some financial resources which should not be considered as an expense but as an investment. The SME with export vocation, no matter how small the company may be, it should dedicate some amount of the budget to promote their products in foreign markets.
SECTION 6: BUSINESS PLAN
The evaluation of the success of the Export Business Plan should be done in relation to certain objectives, between them, target sales are the most common. In the international activity these objectives should be accomplished at least with regards to the following three requirements:
- Geographic delimitation: this should be determined for each one of the selected markets.
- Precision: refer to a concrete concept, something which is easily calculated by the exporting company.
- Time: establish a period of time. Plans are generally annual.
The international operating account is the instrument that gathers, in a provisional form, the costs and economic contributions of the contemplated actions in the plan. This determines the cost to evaluate, the cost of implantation of the plan and the expected economic output (commercial margin and operating balance). The concepts included in this account are:
- Foreign sales: target sales established for each foreign market.
- Gross margin: the average margin that applies to the foreign sales.
- Structural costs: these are the functioning costs of the department of foreign trade classified by concepts.
- Selling costs: costs which are directly related to the activity of the sales for each one of the established concepts.
- Operating balance: this is the difference between the gross margin and the structure and sales costs.
In conclusion, planning is essential for any business. Before venturing into international markets companies have to draft an Export Business Plan as this document will help them set their goals, effectively allocate their resources and determine which countries offer the most potential for their products as well as how to reach the clients and how to make competitive offers.


Tagged with: business business plan Export export business plan
About Olegario Llamazares
Related Articles

International Trade Documents Templates Used for Exporting and Importing
21 December, 2022

Incoterms FCA – Free Carrier: The Most Used Incoterms
6 November, 2022

CMR Consignment Note: meaning and template
31 December, 2021
- Global Negotiator
- Chinese Contracts
- Country Guides
- Business Letters
- Trade Documents
Everything that you need to know to start your own business. From business ideas to researching the competition.
Practical and real-world advice on how to run your business — from managing employees to keeping the books.
Our best expert advice on how to grow your business — from attracting new customers to keeping existing customers happy and having the capital to do it.
Entrepreneurs and industry leaders share their best advice on how to take your company to the next level.
- Business Ideas
- Human Resources
- Business Financing
- Growth Studio
- Ask the Board
Looking for your local chamber?
Interested in partnering with us?
Start » strategy, a complete guide to small business exporting.
Exporting overseas is challenging but rewarding for small businesses.

Small- and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) accounted for $460 billion of the known export value in 2019. Yet, e-commerce skyrocketed in 2020, providing more chances for international sales. Global growth offers many benefits. It could even give a lifeline to small businesses in rural areas.
But selling products globally isn't without risk. It requires research and a plan. Below are answers to the top questions U.S. small business owners ask about exporting. Plus, you'll find an array of resources to help you sell and ship around the world.
What are the benefits of exporting for small businesses?
The U.S. Small Business Administration (SBA) says, “Two-thirds of the world’s purchasing power is in foreign countries.” International trade helps small businesses access new markets and consumers.
U.S. exporters, on average, grow faster than non-exporting businesses. They also benefit from market diversity. Indeed, investing in foreign markets may reduce dependence on the U.S. economy or any single region.
Exporting goods and services give small businesses several benefits:
- Expand your customer base: The United States represents only 4% of the world population. Targeting international markets helps companies access the other 96%.
- Reduce risk to your company: Broad geographic reach insulates small companies during an economic downturn, political unrest or natural disasters.
- Build resilience: Small businesses that export are “ 8.5% less likely to go out of business than non-exporting companies.”
- Increase profits: Exporting is a crucial part of any company's growth strategy. It boosts revenue and creates jobs.
- Extend product life cycles: Companies time product rollouts to increase their life cycles—launch, growth, maturity and decline.
- Decrease production costs: Growing businesses order higher quantities of materials and supplies, leading to cost reductions.
Are there risks when exporting internationally?
Global expansion isn't without its challenges. Regulations, freight networks and other factors expose small business owners to risk. Moreover, tariffs and logistics delays worry entrepreneurs. Other barriers encountered by small businesses include:
- Developing a tech stack that supports customers and payments across the world.
- Adjusting to cultural differences and language barriers.
- Securing financing for exporting worldwide.
- Estimating transportation and shipping costs.
- Navigating problems with global freight networks.
- Adhering to local and international laws.
- Complying with trade agreements and regulations.
- Finding foreign partners to address local commerce issues.
- Learning how to advertise and market internationally .
- Staying abreast of international disruptions.
- Understanding individual markets and demographics.
What goods or services should I export?
Many countries allow U.S. small businesses to export most goods and services. But there are exceptions. Certain regions may limit or prohibit sales. Others aren't financially workable. However, almost “40% of the known export value of SME exporters” stems from merchant wholesalers selling durable and nondurable goods, according to the U.S. Census Bureau .
Before choosing products to export:
- Read through U.S. business export regulations on the International Trade Administration's (ITA) site. Doing so will give you an idea of the rules and methods involved.
- Contact the U.S. Department of Commerce's Bureau of Industry and Security to see if your small business needs an export license.
- Learn about your intellectual property (IP) rights when exporting to foreign countries on STOPfakes.gov .
- Perform international market research at Export.gov to determine market viability.
- Use the SBA’s Trade Tools for International Sales to develop an export plan, including product selection.
What country or countries should I export to?
Certain areas have greater trade or market-related barriers, and picking the right market can make the difference between exporting success or failure. An estimated 45% of American SMEs do business in 11 or more countries. Nearly 13% export to six to 10 and just over 19% sell goods and services in two to five countries.
Start your search by using the U.S. Census Bureau's interactive Global Market Finder . Next, explore the ITA's Country Commercial Guides . Here, you can learn about business customs and market conditions.
Often, small businesses begin with international markets covered under Free Trade Agreements (FTAs). There are 14 FTAs comprising 20 countries, including Australia, Mexico, Canada and Singapore. Exporting to countries that fall under U.S. trade agreements may reduce business export barriers and costs. Accordingly, in 2019, 43% of U.S. exports went to Mexico, Canada, the United Kingdom and Japan.
Once you put in the work, nearly any small business can be competitive overseas.
How can a small business reach foreign consumers?
Pre-pandemic, "average monthly online sales represented 37% of total revenue," according to American Express . By February 2021, this number rose to 57%. Thanks to the internet, a U.S. small business has many ways to connect with people worldwide. Large marketplaces, such as eBay, Etsy and Amazon, also offer U.S. trade opportunities.
Increase export sales by using free and low-cost services, such as:
- The Single Company Promotion (SCP): The SCP helps U.S.-based small businesses increase brand awareness through a promotional event.
- Think with Google: Use Google’s free tool to discover potential markets and get tailored recommendations.
- Trade specialist: Find your local U.S. Commercial Service office or U.S. Export Assistance Center for help selling online to overseas customers.
- Website Globalization Review (WGR): Use the WGR Gap Analysis service to assess your e-commerce channels and improve search engine optimization (SEO).
- State Trade Expansion Program (STEP): Leverage STEP to access website assistance, design marketing campaigns and explore foreign trade shows.
Can small- and medium-sized companies get export financing?
U.S. banks are wary about lending to exporters, but the Small Business Association offers several export loan programs . Your local SBA Export Finance Manager or the SBA's Office of International Trade can go over your options and help you take advantage of resources, which may include:
- Export Express loans, which may be approved in about 36 hours for up to $500,000.
- Export Working Capital loans, which take roughly five to 10 days for up to $5 million.
- International Trade Loans, which provide access to up to $5 million for fixed assets, working capital financing and debt refinancing.
How will I ship my product overseas?
Shipping and logistics can be simple for some entrepreneurs. The U.S. Postal Service or third-party shippers such as DHL or FedEx provide shipping tools and resources. But certain exporters may need extra support.
Federal agencies provide information about the international shipping process. Details may include shipping options, export documentation protocols and insurance. Since shipping costs can eat away at your profits, small businesses should compare figures and price products accordingly.
Can a small business be competitive overseas?
Once you put in the work, nearly any small business can be competitive overseas. However, success depends on your strategy and market choice. Furthermore, picking the right mix of technologies is essential.
An estimated 66% of small business owners believe technology can help subdue the top three barriers to exporting, according to a report by Google and the U.S. Chamber of Commerce. Digital tools assist with:
- Communications challenges.
- Finance and payment collection.
- Tariffs and customs issues.
Sell your product and service around the world
International trade could be the key to overcoming challenges in today's economy. Moreover, it could help small businesses that live outside major cities. In fact, exports increased 5.6% during the first quarter of 2021. Almost 98% of exporters are small- to medium-sized companies, so selling goods and services worldwide is an excellent way to create a sustainable business model.
Take advantage of support from your local SBA office and invest in digital technology to access international consumers and markets.
CO— aims to bring you inspiration from leading respected experts. However, before making any business decision, you should consult a professional who can advise you based on your individual situation.
Follow us on Instagram for more expert tips & business owners’ stories.
CO—is committed to helping you start, run and grow your small business. Learn more about the benefits of small business membership in the U.S. Chamber of Commerce, here .
Join us for our Small Business Day event!
Join us at our next event on Wednesday, May 1, at 12:00 p.m., where we’ll be kicking off Small Business Month alongside business experts and entrepreneurs. Register to attend in person at our Washington, D.C., headquarters, or join us virtually!
Subscribe to our newsletter, Midnight Oil
Expert business advice, news, and trends, delivered weekly
By signing up you agree to the CO— Privacy Policy. You can opt out anytime.
For more business strategies
How startups contribute to innovation in emerging industries, how entrepreneurs can find a business mentor, 5 business metrics you should analyze every year.
By continuing on our website, you agree to our use of cookies for statistical and personalisation purposes. Know More
Welcome to CO—
Designed for business owners, CO— is a site that connects like minds and delivers actionable insights for next-level growth.
U.S. Chamber of Commerce 1615 H Street, NW Washington, DC 20062
Social links
Looking for local chamber, stay in touch.
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( A locked padlock ) or https:// means you’ve safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
- Search ITA Search

Learn How To Export
Are you looking to grow your business through exporting? Assess your company’s readiness to enter your first markets, expand into additional markets, or take on more challenging, high-growth export markets.
Understand the Export Process

How to Start an Import/Export Business
Main Sections In This Post Steps To Starting An Import/Export Business Points to Consider Knowledge Is Power Featured Video
Embarking on Import/Export Business
A step-by-step guide to launch, along with practical examples. Leverage “Knowledge Is Power” for current insights—resources for startup and ongoing success.
Let’s get started with the steps.

Steps to Starting an Import/Export Business
Below are the steps to starting an Import/Export business.
Each step is linked to a specific section, allowing you to jump to your desired section or scroll to follow the steps in order.
- An Overview of What You’re Getting Into
- Import/Export Business Overview
- Researching Your Import/Export Business
- Looking at Financials
- Choosing A Business Location
- Creating Your Mission Statement
- Creating A Unique Selling Proposition (USP)
- Choose an Import/Export Business Name
- Register Your Company
- Create Your Corporate Identity
- Writing a Business Plan
- Banking Considerations
- Getting the Funds for Your Operation
- Software Setup
- Business Insurance Considerations
- Supplier and Service Provider Considerations
- Physical Setup
- Creating a Website
- Create an External Support Team
- Hiring Employees
1. An Overview of What You’re Getting Into
Is Starting an Import/Export Business the Right Step for You?
There is a key factor to succeeding in business, and that factor is you!
Understanding Your Passion
Understanding how you feel about owning and running an Import/Export business is important.
The Power of Passion
Passion is a crucial element for success in your own business.
The Driving Force
Passion is the driving force you need.
When you’re passionate about your business and problems, arise, you look for solutions. On the other hand, without it, you’ll look for a way out.
Assessing Your Passion
How passionate are you about owning your own Import/Export business?
Let’s go through a short exercise. Take a few minutes to think about this. It’s important before moving forward.
Imagine you won the lottery, quit your job, traveled the world, and bought your dream home, cars, and everything you ever wanted. You have given to charity and causes you believe in. You have helped your friends and family with more than enough money to live a better life.
It’s been three years since you won the lottery, and you still have 10 million dollars left in cash and investments that provide more than enough income flowing in every month.
Passion’s Litmus Test
Here is an important question to think about!
Now that you have achieved everything you have ever wanted, would you still start an Import/Export business?
If your answer is yes, it shows that you are passionate about owning and operating an Import/Export business and are heading in the right direction.
However, if your answer is no, it prompts another question:
Alternative Paths
What would you prefer to do instead? Perhaps, you should pursue that path instead.
The Sum of It
In summary, you need to be passionate about the business you plan to start because it’s something you want to do!
When your only concern is the money generated, you won’t be as successful as starting a business you are passionate about.
For More, See How Passion Affects Your Business . Also, see, Considerations Before You Start Your Business to identify key points for a new business owner.
2. Gaining an Overview of Owning an Import/Export Business
Next, let’s spend some time on key issues to give you an overview of what to expect from owning and running your business.
a.) A Quick Overview of Owning an Import/Export Business
An Import/Export business operates at the heart of international trade, facilitating the exchange of products between countries.
This dynamic venture involves sourcing products from one country and distributing them in another, creating a bridge between different markets and cultures.
Inward and Outward Flow
In the import aspect, the business identifies products in foreign markets holding local demand, negotiates deals with manufacturers and suppliers, and manages the logistics to bring these products to the home market.
On the export side, the business identifies local products with potential appeal in foreign markets, connects with buyers, and oversees delivering products to international customers.
Driving Global Economy
This type of commerce plays a pivotal role in diversifying markets and supporting economic growth.
It introduces products that might not be available otherwise, enriching consumer choices globally.
Moreover, it creates opportunities for manufacturers and producers to tap into wider markets, expanding their reach beyond national borders.

Navigating Challenges
Running an Import/Export business requires navigating intricate regulations, customs procedures, currency fluctuations, and cultural differences.
Adaptability, cultural sensitivity, and strong logistical planning are crucial to success.
In essence, this venture isn’t just about moving products—it’s about fostering connections and contributing to the intricate web of global trade.
Daily Operations in Import/Export Business
- Market Research: Identifying demand, trends, and potential markets.
- Supplier Outreach: Connecting with manufacturers and suppliers.
- Negotiations: Securing favorable terms, including pricing and quantities.
- Logistics: Organizing shipping, customs, and warehousing.
- Documentation: Managing permits, licenses, and trade regulations.
- Quality Control: Ensuring products meet standards.
- Sales and Marketing: Attracting clients, promoting products.
- Financial Management: Budgeting, pricing, and payment handling.
- Relationship Building: Cultivating partnerships globally.
- Staying Updated: Adapting to evolving regulations and markets.
Running an Import/Export business demands adaptability, negotiation skills, market awareness, and logistical efficiency. It’s a dynamic venture with potential for growth in the global marketplace.
b.) Import/Export Business Models
Variety of Import/Export Business Models
1. Trading Company: Acting as an intermediary, trading companies buy products from manufacturers and sell them to foreign markets. They don’t alter products significantly.
2. Distributorship: These businesses secure exclusive distribution rights within a specific region. They focus on building a strong local presence and managing distribution networks.
3. Export Management Company (EMC): EMCs work on behalf of manufacturers, handling all aspects of exporting. They earn commission based on sales.
4. Import/Export Agent: Agents connect buyers and sellers, earning a commission for successful transactions. They’re valuable for those with limited resources.
5. Dropshipping: This model involves selling products without holding inventory. When a sale occurs, products are shipped directly from the supplier to the customer.
6. Licensing and Franchising: Foreign companies can produce and sell products using your brand. Franchising involves replicating your business model in other countries.
Strategic Decision
Choosing the right business model from the beginning is crucial, as switching later is challenging. Identifying a profitable and high-demand niche is equally vital.
Research extensively, analyze market trends, and align your strengths with the chosen model. Success in the import/export realm hinges on astute planning and a clear strategic direction.
c.) Pros and Cons of Owning an Import/Export Business
Pros of Owning an Import/Export Business
- Entrepreneurial Freedom: You can be your own boss, making independent decisions to shape your business.
- Creativity Unleashed: Your business is a canvas for innovation and new ideas.
- Potential for High Revenue: A successful venture can yield substantial profits.
- Flexibility: Successful operations and a capable team can afford you flexible work hours.
- Control Over Environment: You have the power to create a work environment that suits you.
- Global Reach: Connecting with diverse markets opens expansive opportunities.
- Learning Opportunity: Navigating international trade sharpens your skills.
- Cultural Exposure: Engaging with different cultures enriches your perspective.
Cons of Running an Import/Export Business
- Accountability: Problems and challenges rest on your shoulders.
- Irregular Income: Earnings can be unpredictable in the initial stages.
- Tough Start-Up: The beginning can be financially and operationally demanding.
- Customer Acquisition: Gaining and retaining customers requires dedicated efforts.
- Long Work Hours: Expectations of dedication may lead to extended workdays.
- Pressure to Thrive: Success pressure is always present in a competitive landscape.
- Significant Investment: Starting often demands substantial capital outlay.
- Adaptation Challenges: Constant changes in regulations and markets require adaptability.
- Inherent Risks: Business ownership comes with financial and operational risks.
Navigating the Journey
Owning an Import/Export business offers remarkable potential, but embracing both its rewards and challenges is vital.
Careful planning, resilience, and a willingness to learn are key to thriving in this dynamic domain.
For more, see Pros and Cons of Starting a Small Business.
d.) Questions You Need to Consider for Your Import/Export Business
Preparing for Your Import/Export Business Journey
Addressing the following inquiries prepare you for potential challenges in your Import/Export venture.
Before You Begin: Key Considerations
- Business Model: What Import/Export model resonates with your goals?
- Work Dynamics: Will you handle tasks solo or hire a team?
- Management Approach: Do you plan to lead or hire a manager?
- Customer Acquisition: How will you attract your initial customers?
- Customer Retention: What strategies ensure customer loyalty?
- Partnerships: Are partnerships or investors on your radar?
- Physical or Digital: Will your business be brick-and-mortar or online?
- Growth Contemplation: Have you envisioned your business’s long-term expansion?
Insightful Planning for Success
As you contemplate these questions, you pave the way for a more informed and strategic approach to your Import/Export enterprise.
Navigating the intricacies of global trade demands thoughtful consideration, ensuring your business is primed for success and sustainability.
3. Research
Import/export business research.
Essential Research for Your Import/Export Business
Conducting thorough research before embarking on your venture is paramount. Quality information will illuminate your path, preventing unexpected hurdles.
Leveraging Expertise
Engage with experienced professionals in the Import/Export realm. Their insights provide dependable guidance honed by practical experience.
Invaluable Learning
Time spent with these experts is an invaluable opportunity. Their knowledge and seasoned experience offer priceless insights.
Guidance for Your Journey
I’ve crafted an article outlining methods to identify and approach these knowledgeable individuals.
These steps extend beyond this post. Reading the article via the link below will provide a comprehensive understanding of your forthcoming endeavor.
Empower yourself with the wisdom of those who’ve walked the path.
This approach ensures you’re well-prepared to navigate the complexities of the Import/Export landscape.
See An Inside Look Into the Business You Want To Start for all the details.
Target Audience
Understanding Your Target Audience in Import/Export Business
Knowing your target market is key. Tailoring your offerings to their preferences and needs enhances your Import/Export business’s appeal.

Identifying Potential Interest: Target Market Ideas
- Small Businesses: Seeking diverse product sourcing.
- Manufacturers: Exploring global markets for distribution.
- Entrepreneurs: Launching unique foreign products domestically.
- Online Retailers: Accessing unique goods for e-commerce.
- Wholesalers: Sourcing bulk products at competitive rates.
- Artisans: Seeking unique materials or components.
- Boutiques: Curating distinct products for niche markets.
- Global Brands: Expanding market presence through diversification.
- Trade Shows: Participants interested in product variety.
- Startups: Seeking cost-effective inventory solutions.
Catering to Success
Identifying your potential customers paves the way for strategic marketing and product offerings.
Knowing who values your Import/Export business’s offerings strengthens your competitive edge and positions you for growth.
For more, see How To Understand Your Target Market.
4. Looking at Financials:
Financial Overview of Your Import/Export Startup
Gain insights into startup costs, monthly outlays, revenues, and potential profits to steer your Import/Export venture toward success.
Startup Costs: Planning for a Smooth Launch
Accurate estimation of startup expenses is pivotal for a seamless launch.
Underestimation risks funds depletion, hindering your opening. Overestimation might deter potential investors.
Your expenses hinge on factors like scale, location, hiring, equipment, and leasing.
List your needs, gather prices, and anticipate unexpected costs during research.
For more detailed information, refer to my article on Estimating Startup Costs.
Sales and Profit: Foundations of Financial Success
Sales depend on product appeal, demand, and strategic marketing. To ensure profitability:
- Develop sought-after products.
- Address market needs.
- Skillfully promote your business.
Profit Calculation: Delving Beyond Revenue
Profitability entails more than direct sales earnings. It involves considering rent, payroll, overhead, and other costs.
For More, See Estimating Profitability and Revenue.
Sufficient sales must cover monthly expenses and yield personal income. A well-balanced equation ensures a prosperous journey in the Import/Export domain.
Simple Sample: Financial Lists to Consider As a Starting Point
Note: Focus on the issues more than the numbers. The numbers are samples. Your estimates will differ due to how you set up your business, location, expenses, and revenues.
Sample List of Estimated Costs to Start a New Import/Export Business in the USA (lower and upper values):
- Business Registration and Licensing: $500 – $1,000
- Office Space (Deposit and Initial Setup): $5,000 – $10,000
- Initial Inventory Purchase: $10,000 – $50,000
- Import/Export Documentation and Compliance: $1,000 – $5,000
- Marketing and Branding: $2,000 – $7,000
- Transportation and Shipping Equipment: $5,000 – $20,000
- Website Development: $1,000 – $5,000
- Legal and Professional Consultation: $2,000 – $10,000
- Total Estimated Starting Costs: $26,500 – $108,000
Sample List of Estimated Monthly Expenses for an Import/Export Business in the USA:
- Rent for Office Space: $1,500 – $3,000
- Utilities (Electricity, Water, Internet): $200 – $500
- Salaries and Wages: $5,000 – $15,000
- Insurance: $300 – $800
- Loan Payments: $1,000 – $3,000
- Marketing and Advertising: $500 – $2,000
- Transportation and Shipping Costs: $2,000 – $6,000
- Legal and Compliance Fees: $300 – $1,000
- Total Monthly Expenses: $10,800 – $31,300
3. Sample of a Few Examples of Profit per Sale:
- Low-End Product: Profit of $10 – $50 per unit
- Mid-Range Product: Profit of $50 – $200 per unit
- High-End Product: Profit of $200 – $1,000 per unit
Finish Note: Your overall profit will depend on the monthly sales you can generate and your actual profit per sale.
These are samples so you can understand the issues to consider when planning to start your Import/Export business. So focus on the list and not the numbers.
Adjusting costs makes a significant difference in whether the business will be successful.
A slight shift in profit per sale on high-volume sales will make a difference in your overall profits.
Also, note many new businesses take time to become profitable because it takes building a customer base, building a reputation, and fine-tuning operations.
Your figures will be different. Every situation is different, and many factors come into play.
Research and Consider getting professional advice when calculating your business’s startup costs, expenses, and potential revenues and profits.
5. Choosing The Right Business Location
Strategic Location: Key to Business Success
The fate of your local brick-and-mortar business hinges heavily on your chosen site.
Demand Dynamics: A Decisive Factor
Operating where demand for your offerings is scarce spells failure even before launch.
Competitive Landscape: Finding the Sweet Spot
Overcrowded locales make market share acquisition a challenge.
Ideal Scenario: Balancing Act
Locate where demand and competition strike equilibrium.
Cost Considerations: Financial Prudence
Affordability is vital. A high population brings exposure, but expenses must not outweigh gains.
Balance Affordability and Sales Potential
Inexpensive sites need ample customer flow for sustainability.
Online Realm’s Flexibility
Even for online models, assess demand and rivalry closely.

Ultimate Influence on Success
In sum, location selection steers business destiny. Thoroughly research and analyze options. Your decision shapes your venture’s triumph.
For more about business locations, see Choosing The Best Location for Your Business.
6. Create Your Mission Statement
Guiding Your Business’s Purpose: The Role of a Mission Statement
A mission statement serves as a compass, aiding you in identifying your business’s core purpose.
It’s a reminder of the primary value you bring to customers and the community, ensuring you stay on track.
Mission Statement Examples for an Import/Export Business
- “Empowering Global Commerce: Connecting businesses worldwide, enriching markets with diverse products.”
- “Navigating Boundaries, Enhancing Lives: Bridging nations, offering quality goods to uplift lives globally.”
- “Driving Trade Diversity: Facilitating cross-cultural trade, fostering economic growth, one partnership at a time.”
- “Catalyzing Global Business: Facilitating seamless exchange, propelling businesses towards international success.”
- “Enriching Connections, Empowering Economies: Uniting markets through unparalleled import/export solutions.”
Steering Purpose and Value
These mission statement samples exemplify how your business’s fundamental aim can be succinctly captured. Such a statement keeps your endeavors aligned, ensuring the provision of exceptional value to both clientele and the community at large.
For more, see, How To Create a Mission Statement.
7. Creating A Unique Selling Proposition (USP)
Crafting Distinction: The Power of Unique Selling Proposition
A Unique Selling Proposition (USP) aids in discerning and crafting elements that set your business apart.
It’s a potent tool for creating something distinctive that resonates with customers.
Examples of USP for an Import/Export Business
- “Global Discovery Hub: Unearth unique products from every corner of the world, tailored for your market’s cravings.”
- “Seamless Sourcing Solutions: Our network guarantees streamlined access to the globe’s most sought-after products.”
- “Cultural Connection Catalyst: Bridging gaps with products that celebrate diversity, fostering international camaraderie.”
- “Reliable Worldwide Reach: Empowering businesses with consistent access to global markets, ensuring growth.”
- “Tailored Treasures, Globally Delivered: Transforming international products into local treasures, delivered at your doorstep.”
Carving Identity, Sustaining Success
These USP samples exemplify how to carve a unique business identity.
USP underscores your distinct value, magnetizing customers and cultivating lasting success.
8. Choose a Business Name
Crafting an Exceptional Business Name: A Vital Choice
Your business name plays a pivotal role in brand recognition.
Opt for a catchy, apt name that’s both easy to recall and pronounce. It’s a long-lasting decision that holds significance throughout your business journey.
Incorporating Factors for a Striking Name
Ensure your chosen name aligns with your venture’s essence.
It’s advisable to have a matching domain for an online presence. Verify name availability to avoid legal complications.
30 Import/Export Business Name Ideas: Fueling Creativity
- GlobalLink Commerce
- Horizon Trade Co.
- EchoCommerce
- MarketFusion Export
- Nexus Imports
- TerraTrade Connections
- WorldBridge Traders
- Aegis International
- SpectrumExports
- EchoSphere Imports
- PrimeWorld Traders
- TradeMosaic
- Echelon Global Goods
- Unity Exporters
- GlobeGlide Imports
- VentureHaven Traders
- EnrichGlobal Commerce
- InterLoom Trading Co.
- Skylight Exports
- ZenithCross Imports
- NexusSphere Trade
- VirtuTrade Global
- Infinite Horizons Commerce
- TerraTrek Traders
- PinnacleExports
- TradePulse International
- EnvisionEdge Imports
- SummitWorld Commerce
- EquiTrade Global
Igniting Brand Identity
These name suggestions spark your imaginative process, assisting you in forging a distinct business identity.
Pick a name resonating with your venture’s essence, securing a memorable position in the global business landscape.
For more, see the following articles:
- How To Register a Business Name
- Registering a Domain Name For Your Business
9. Register Your Company
Legal Foundations for Your Import/Export Business
Ensuring Compliance: An Imperative Step
Establishing your business on legal grounds is paramount.
Professional Consultation: A Wise Move
Consulting professional aids in legal assurance, optimal tax strategies, and liability management.
Common Business Registrations for an Import/Export Venture
- Sole Proprietorship: Individual ownership simplicity.
- Partnership: Shared responsibility and resources.
- Limited Liability Company (LLC): Personal liability protection.
- Corporation: Legal entity status, distinct from owners.
Permits and Licenses: Navigating Legal Terrain
- Business License: Operational legitimacy.
- Importer/Exporter License: Compliance for global trade.
- Sales Tax Permit: Tax collection eligibility.
- Customs Bond: Assurance for customs compliance.
- EIN (Employer Identification Number): Tax identification for businesses with employees.
Prioritizing Legal Adherence
By comprehending these legal aspects, your Import/Export business gains firm legal footing. Seek professional guidance, ensuring a compliant and thriving journey.
Registration:
- How to Register Your Business
- How To Register a DBA
- How to Register a Trademark
- How to Get a Business License
Business Structures:
- How to Choose a Business Structure
- Pros & Cons of a Sole Proprietorship
- How To Form an LLC
- How To Register a Business Partnership
- How To Form a Corporation
- How To Choose a Business Registration Service
10. Create Your Corporate Identity
Building a Strong Corporate Identity: A Design Emblem

Defining Corporate ID: Visual Business Representation
A Corporate ID encapsulates your business essence in design.
Key Elements of Corporate ID: Crafting Visual Cohesion
Components encompass logo, business cards, website, signage, stationery, and promotional materials.
Consistency is King: Leaving a Lasting Impression
A uniform, professional design resonates with both new and loyal customers.
Crafting Visual Excellence
Crafting a cohesive Corporate ID leaves an indelible mark.
A seamless design across mediums elevates your business presence, engaging customers and building brand loyalty.
You can see our page for an overview of your logo , business cards , website , and business sign , or see A Complete Introduction to Corporate Identity Packages.
11. Writing a Business Plan
Strategic Roadmap: The Significance of a Business Plan
Pivotal Document: Navigating Growth and Investment
A business plan serves dual roles: securing funding and guiding operations. It outlines your business’s course from inception to full operation.
Vision in Ink: Cultivating Your Business’s Blueprint
Creating a business plan is a meticulous process. It encapsulates your envisioned business reality, demanding time and consideration.
Comprehensive Vision: A Path to Clarity and Success
Crafting a business plan reaps the rewards. It unveils your business’s essentials, ensuring a clear roadmap for commencement and operation.
Approaches to Formulating Your Plan
Options abound: crafting from scratch, seeking professional assistance, employing templates, or using business plan software.
Personal Involvement: A Touch of Distinctiveness
Active engagement is vital, particularly when collaborating with a professional. Distinctiveness and effective communication are paramount.
Adaptability and Optimization: An Evolving Blueprint
Your business plan evolves alongside the experience. Regular review and optimization ensure congruence with operational realities.
Business Plan Template for an Import/Export Business
I. Executive Summary:
- Overview: Briefly describe your Import/Export business, mission, and vision.
- Objectives: Key business goals and milestones to achieve.
- Ownership Structure: Information on the business’s ownership, whether a sole proprietorship, partnership, or corporation.
II. Business Description:
- Industry Background: Description of the import/export industry and current market trends.
- Business Offering: Detailed explanation of the products or services you import or export.
- Target Market: Outline your primary target markets, including geographic locations and demographics.
III. Market Analysis:
- Market Needs: Identify the needs of your target market and how your business will meet those needs.
- Competitive Analysis: Analyze your main competitors, their strengths and weaknesses, and your competitive edge.
IV. Marketing and Sales Strategy:
- Marketing Plan: Detail your marketing strategies, channels, and tools.
- Sales Strategy: Outline your sales techniques, processes, and targets.
V. Operations Plan:
- Location: Description of the business location, considering logistics and accessibility.
- Technology Needs: Outline the technology required for operations, including software for tracking shipments.
- Supply Chain Management: Detail your strategies for sourcing products, managing suppliers, and maintaining inventory.
VI. Financial Plan:
- Start-up Costs: Detailed estimate of the initial investment required.
- Revenue Projections: Monthly and yearly revenue forecasts.
- Expense Projections: Estimation of ongoing operational expenses, including loan payments.
- Break-even Analysis: Calculation of the point at which revenues equal expenses.
VII. Legal and Compliance:
- Licenses and Permits: List necessary licenses and permits for the import/export business.
- Regulations: Outline applicable international and domestic regulations and how you plan to comply.
VIII. Risk Management:
- Risk Assessment: Identify potential risks, such as currency fluctuations or regulatory changes.
- Mitigation Strategies: Outline strategies to mitigate those risks.
IX. Management and Personnel:
- Management Team: Profiles of the key management team members, including qualifications and experience.
- Organizational Structure: Description of the company’s organizational structure, including departments and roles.
X. Appendices and Supporting Documents:
- Financial Statements: Include any necessary financial statements, charts, or graphs.
- Legal Documents: Copies of relevant legal agreements, patents, or other intellectual property documentation.
XI. Conclusion:
- Summary: Concluding remarks summarizing the critical aspects of the business plan.
- Next Steps: Clearly outline the next steps and actions required to implement the plan.
Remember, this template is a starting point, and it should be customized to fit the unique needs and regulations related to your specific import/export business.
Conduct thorough research and consider seeking professional advice to ensure that all aspects are covered comprehensively.
For information on creating your business plan, see, How to Write a Business Plan.
12. Banking Considerations
Financial Foundations: Choosing the Right Banking Partner
Strategic Banking Choice: Empowering Small Businesses
Opt for a local bank with a strong small business focus for optimal support.
Distinct Account, Streamlined Finances
A dedicated business account segregates expenses vital for sole proprietorships: precise expense tracking, seamless bookkeeping, and audit protection result.

Building Banking Relationships: Advantages Beyond Transactions
Foster a rapport with your banker. Access advice, financial services, and simplified application procedures.
Embrace Digital Transactions: Amplify Sales
Merchant accounts and online services boost sales by facilitating credit and debit card payments—convenience and higher sales potential benefit both business and customers.
For more, see, How to Open a Business Bank Account. You may also want to look at, What Is a Merchant Account and How to Get One.
13. Getting the Funds for Your Operation
Financial Launchpad: Navigating Business Loans
Crucial Tips for Loan Seekers
Exploring Funding Avenues: Options for Import/Export Ventures
Consider diverse funding paths: traditional lenders, private loans, investors, asset sales, and collateral usage.
Meeting with a Loan Officer: Essential Points
- Preparation: Understand your business needs and loan purpose.
- Research: Know the lender’s criteria and offerings.
- Documentation: Compile necessary financial and business documents.
- Business Plan: Present a well-structured plan highlighting profitability and repayment strategies.
- Clarity: Articulate your business’s strengths, market viability, and repayment certainty.
Required Documents for New Business Loan Application
- Business Plan
- Personal and Business Credit History
- Financial Statements
- Income Tax Returns
- Legal Documents (Incorporation, Contracts, etc.)
- Collateral Details (if applicable)
Empowering Your Business’s Financial Journey
These insights facilitate informed loan pursuit.
Thorough preparation, diligent research, and organized documentation enhance your Import/Export venture’s financial foundations.
See, Getting a Small Business Loan for more.
14. Software Setup
Software Selection: Strategic Insights for Import/Export Ventures
Informed Software Choice: A Prudent Step
Thoroughly researching software options is paramount.
Opting for a robust system from the outset minimizes the need for future transitions, preserving data integrity.
Dependability Matters: A Proven Track Record
Prioritize software companies with a strong history, ensuring ongoing support and reliability.
Exploring Demos and Reviews: Insights from Users
Assess software through demos, reviews, and forums. Gaining firsthand experiences of others aids informed decision-making.
Comprehensive Software Considerations
- Import/Export Management Software
- Supply Chain Management (SCM) Software
- Customs Broker Software
- International Trade Compliance Software
- Logistics and Freight Management Software
- Inventory Management Software
- Financial Software (Accounting and Bookkeeping)
- E-commerce Platform
- Communication Tools (Email, Video Conferencing)
- Data Analytics Tools
- CRM (Customer Relationship Management) Software
- Language Translation Software
Accounting Software: Expert Counsel
For financial management, consult your bookkeeper or accountant to select suitable accounting software, ensuring compliance and streamlined tax filing.
By diligently researching software, you pave the way for efficient operations and lasting success in your import/export business.
Check out Google’s latest search results for software packages for an Import/Export business.
15. Get The Right Business Insurance
Safeguarding Your Business: Insurance Essentials
Proactive Protection: Prioritize Insurance
Secure appropriate insurance coverage before commencing any business activities to shield against unforeseen incidents.
Comprehensive Protection: Addressing Diverse Risks
Consider insurance covering customers, employees, property, and potential legal liabilities.
Professional Liability Shield: Navigating Legal Claims
Professional liability insurance guards against potential lawsuits and legal claims.
Operational Continuity: Embrace Interruption Insurance
Interruption insurance provides crucial support during involuntary shutdowns, ensuring operational continuity.
Home-Based Business Alert: Maintain Insurance Validity
If operating from home, inform your home insurance agent to prevent nullifying your existing policy.
Insurance Expertise: Navigating Coverage Adequacy
Leverage a competent insurance broker’s guidance to ensure comprehensive coverage, protecting your business interests effectively.
For more, see What to Know About Business Insurance . You can also browse the latest Google Import/Export business insurance search results.

16. Suppliers, Service Providers and Inventory
Strategic Supplier Relations: Fueling Business Success
Essential Supplier Partnerships: Items and Services
Enumerate essential items and services your Import/Export business may source from suppliers.
Supplier Bonds: Cornerstone of Operational Success
Forge strong connections with suppliers and service providers to underpin your business triumph. Trustworthiness and reliability are paramount.
Cost-Efficient Collaborations: Competitive Prices and Margins
A dependable supplier allows cost-effective pricing, facilitating customer savings and bolstering profit margins.
Seamless Operations: Ensuring Adequate Supplies
Reliable suppliers guarantee smooth business operations by providing essential supplies consistently.
Mutually Beneficial Ties: Respect and Shared Gains
Nurturing a mutually advantageous relationship with suppliers enhances cooperation and rapport.
Strategic Inventory Management: Customer-Centric Approach
Product Mix and Variety: Customer-Centric Focus
Curate your inventory based on customer preferences and include variety for broad customer appeal, augmenting value.
Inventory Control: Balance and Efficiency
Strike a balance in inventory volume to prevent tied-up funds or lost sales, optimizing resource allocation.
Expiry Date Vigilance: Mitigating Loss
Mitigate losses by managing expiration dates meticulously, ensuring inventory freshness and value.
By cultivating robust supplier relationships and strategic inventory management, your Import/Export business thrives with efficiency and customer-centricity.
For More See, How To Choose a Supplier.
17. Physical Setup
Strategic Setup: Physical Arrangement for Success
Optimized Layout: A Blueprint for Efficiency
Designing an effective physical setup for your Import/Export business is pivotal. A streamlined layout enhances operational efficiency.
Strategic Signage: Guiding the Way
Strategically placed signage is vital for customer guidance and professional presentation.
Beyond the main business sign, ensure directional and informational signs in key areas like parking lots, exits, and special zones.
Office Harmony: A Productive Workspace
Your office plays a crucial role in managing your business. A well-organized office is a hub of productivity, fostering efficient business management.
Functional Equipping: Necessities for Effectiveness
Equip your office comprehensively to facilitate smooth business operations. Essential tools, technology, and resources should be at your fingertips.
Space Optimization: Productivity and Professionalism
Effective physical setup and signage guide customers seamlessly and reflect professionalism, while an organized office empowers efficient business management.
Maximize your potential by laying a strong foundation for operational success.
See, Here are Considerations for The Setup of Your Office, for tips and ideas to make your office work for you. Also, have a look at our article About Company Signs.
18. Creating a Website
Virtual Presence: Your Digital Storefront
Essential Website: Gateway to Your Business
A website is an indispensable asset for business owners, serving as a primary interface for sharing information with existing and potential clients.
Ownership Advantage: Your Virtual Territory
Unlike social media platforms, your website offers autonomy and control.
When you host your site and secure a domain name, you dictate the rules.
Marketing Potential: Showcasing Expertise
Your website doubles as a marketing powerhouse.
By sharing industry insights and valuable tips through blogs, you position yourself as an authority, fostering customer trust and bolstering sales potential.
A website isn’t just a digital address; it’s a dynamic tool that strengthens your brand, reinforces credibility, and expands your reach in the competitive landscape.
For more, see How to Build a Website for Your Business .
19. Create an External Support Team
External Support Network: Your Advisory Allies
An external support team comprises non-payroll professionals providing advice and services.
Their expertise aids projects, contracts, or on a retainer basis.
While some members might already be collaborators, embracing them as your core team enhances their role.
Strategic Approach: Building a Resilient Network
You needn’t assemble the complete team before launch; fostering these relationships takes time.
However, nurturing this network is an ongoing endeavor for enduring success.
Team Synergy: Collaborative Powerhouse
Your team may encompass an accountant, lawyer, financial advisor, marketing specialist, technical advisor, and consultant.
Their collective prowess fortifies your business, providing insights, solutions, and guidance when needed.
This collaborative network safeguards your business journey.
For more, see, Building a Team of Professional Advisors for Your Business.
20. Hiring Employees
Growing Workforce: Hiring Right for Expansion
In the initial phases, handling tasks single-handedly can curb costs, especially considering the significant payroll expense during startup.
As the business flourishes, your ability to manage all aspects may dwindle, prompting the need for new hires.
Strategic Hiring: Building a Competent Team
When recruiting, prioritize qualified individuals with strong work ethics for each role.
Properly fitting employees enhance productivity and streamline operations, facilitating business growth.
Essential Roles: Structuring Your Team
The following are job positions or outsourced services you may want to consider as your Import/Export business grows:
- Sales and Marketing Specialist
- Logistics Coordinator
- Customs Compliance Manager
- Financial Analyst
- Customer Service Representative
- Inventory Manager
- Data Analyst
- Shipping Coordinator
- Legal Advisor
- Graphic Designer
- Content Writer
As you scale, assembling the right team becomes pivotal to sustaining success and expanding your import/export enterprise.
For more, see, How and When to Hire a New Employee.
Points To Consider
Hours of operation:.
Operating Hours for Import/Export Business
Consider these hours of operation for your Import/Export business:
- Weekdays: Standard business hours, 9 AM to 5 PM
- Saturdays: Half-day, 9 AM to 1 PM
- Sundays: Closed
- Holidays: Closed, unless essential for trade
Adapting operational hours to global time zones and clients’ needs is vital for international commerce. Flexibility can enhance customer satisfaction and streamline communication.
A List of Equipment and Supplies to Consider for an Import/Export Business:
- Computers and Laptops: For communication, research, and documentation.
- High-Speed Internet Connection: Essential for online transactions and communication.
- Smartphones: Stay connected on the go and manage business emails.
- Printer and Scanner: For printing contracts, invoices, and scanning documents.
- Office Furniture: Desks, chairs, and storage for a comfortable workspace.
- Communication Tools: Landline phones, mobiles, and headsets.
- Shipping Supplies: Packaging materials, boxes, tape, and labels.
- Inventory Management System: Software to track stock and orders.
- Security Measures: Surveillance cameras and alarm systems for asset protection.
- Transportation: Vehicles for local pickups and deliveries.
- Warehousing Equipment: Shelving, pallets, and forklifts for storage.
- Global Positioning System (GPS): For efficient navigation during shipments.
- Customs Documentation Tools: Software to manage international paperwork.
- Currency Conversion Tools: To handle multi-currency transactions.
- Backup Systems: Data backup solutions to prevent data loss.
Customize this list based on your business scale and specific needs.
Key Points To Succeeding in an Import/Export Business
Successfully operating an Import/Export business requires attention to several crucial points:
- Building Customer Base: Establishing a customer base is challenging during startup. Develop strong relationships with customers, suppliers, and employees.
- Supplying Demand: Offer products and services that customers desire, adapting to their needs and preferences.
- Customer Feedback: Use customer feedback to improve your business operations.
- Exceptional Customer Service: Prioritize exceptional customer service, as your customers are the heart of your business.
- Team Building: Assemble the right team for various positions, fostering a positive work environment.
- Cash Flow Management: Efficiently manage cash flow to sustain operations and growth.
- Cost Control: Keep costs low without compromising quality or service.
- Adaptation to Change: Stay updated and adapt to industry, process, and technological changes.
- Fluctuations and Competition: Handle revenue fluctuations and navigate competition, focusing on differentiation.
- Effective Marketing: Invest in effective advertising and marketing to boost awareness and attract customers.
Remember these factors to drive your Import/Export business towards success.
Making Your Import/Export Business stand out
Making Your Import/Export Business Stand Out
Setting your Import/Export business apart in a competitive market is crucial for success.
Here are some ideas to make your business stand out:
- Niche Specialization: Focus on a specific niche within the Import/Export industry. Specializing allows you to become an expert in a particular area, catering to a targeted customer base.
- Exceptional Customer Experience: Provide an unparalleled customer experience from start to finish. Prompt communication, transparency, and going the extra mile can leave a lasting impression.
- Unique Product Offerings: Source and offer unique, high-quality products that aren’t widely available. This exclusivity can attract customers seeking something different.
- Sustainable Practices: Embrace environmentally-friendly practices in your operations, appealing to eco-conscious customers.
- Technology Integration: Utilize cutting-edge technology to streamline processes, enhance customer service, and improve efficiency.
- Customization: Offer personalized solutions that cater to individual customer needs and preferences.
- Partnerships: Collaborate with complementary businesses to expand your reach and offer bundled services.
- Online Presence: Develop a user-friendly, informative website and leverage social media to connect with potential customers globally.
- Transparent Pricing: Provide clear and transparent pricing structures, instilling trust in customers.
- Educational Resources: Share industry insights, how-tos, and resources through blogs, videos, and webinars, positioning your business as an industry authority.
Add on Ideas for an Import/Export Business
Diversifying your offerings with add-ons can enhance your business value and attract a broader clientele. Consider these add-on ideas:
- Consulting Services: Provide expert advice to clients seeking guidance on navigating the import/export landscape.
- Customs Clearance Assistance: Help clients navigate the complexities of customs regulations and paperwork.
- Supply Chain Management: Offer end-to-end supply chain solutions, ensuring smooth operations for your clients.
- Trade Compliance Training: Provide training sessions on trade compliance and regulations, empowering businesses to handle import/export processes more effectively.
- Market Research Reports: Offer market research reports to clients looking to expand into new markets, providing valuable insights.
- Freight and Logistics Services: Partner with logistics providers to offer seamless shipping and delivery solutions.
- Trade Show Representation: Represent clients’ products at international trade shows to expand their reach.
- Packaging Solutions: Provide customized packaging solutions that protect goods during transit and enhance brand identity.
- Sourcing Tours: Offer guided sourcing tours to help clients discover suppliers and products in different regions.
- Language and Cultural Consulting: Assist clients in understanding language and cultural nuances when dealing with international partners.
By incorporating these ideas and add-ons, you can make your Import/Export business unique, appealing, and positioned for success in a competitive global market.
Marketing Considerations
Attracting Customers for Your Import/Export Business
To succeed in the Import/Export industry, customer attraction is paramount. Initially challenging due to being new, it becomes easier as your reputation grows.
Marketing remains an ongoing process, driving revenue growth through effective strategies.
While you don’t always need a professional agency, investing in marketing yields significant returns.
Simple Methods to Promote Your Import/Export Business:
- Networking: Attend industry events, trade shows, and conferences to connect with potential clients and partners.
- Social Media: Leverage platforms like LinkedIn, Instagram, and X to showcase your services, share industry insights, and engage with your audience.
- Content Marketing: Create informative blogs, videos, and guides related to the import/export field to establish yourself as an expert.
- Referral Programs: Encourage satisfied customers to refer your services to others in exchange for incentives.
- Cold Calling/Emailing: Reach out to potential clients directly with tailored messages highlighting your services’ value.
- Collaborations: Partner with related businesses for joint promotions, broadening your reach.
- Localized SEO: Optimize your online content for local search terms to attract customers in your area.
- Testimonials and Reviews: Display positive feedback from satisfied clients on your website and social media.
- Webinars and Workshops: Host online sessions to educate potential clients about import/export processes and benefits.
- Free Resources: Offer downloadable resources like e-books, checklists, or templates to entice potential clients to engage with your brand.
- Direct Mail: Send informative brochures or postcards to targeted businesses that could benefit from your services.
- Participate in Forums: Engage in online forums and discussion boards related to import/export to share insights and build credibility.
- Google My Business: Create and optimize your Google My Business listing to improve local visibility.
- Video Marketing: Create informative videos explaining import/export procedures, highlighting your expertise.
- Local Networking: Attend local business networking events to connect with potential clients in your area.
- Industry Associations: Join relevant trade associations and actively participate in expanding your network.
Remember, effective marketing is about consistency and persistence.
As you invest time and effort into these simple methods, your Import/Export business’s visibility will grow, attracting a steady stream of interested customers.
We have an article on How To Get Customers Through the Door and a marketing section that will provide ideas to help you bring awareness to your business.
Sample Ad Ideas:
Headline: Unlock Global Opportunities with Our Import/Export Expertise!
Expand your business horizons with our seamless import/export solutions.
From customs clearance to logistics, we handle it all, ensuring your goods reach destinations hassle-free.
Tap into new markets, increase profits, and establish a global presence. Let us be your gateway to international success.
Headline: Navigate International Trade Effortlessly with Us!
Ad Copy: Breaking barriers in international trade is our forte.
Seamlessly import/export your goods with our expert guidance.
Our team ensures compliance, swift deliveries, and cost-effective solutions. Don’t let logistics hold you back – let us be your trade partner.
Headline: Your Bridge to Global Markets Starts Here!
Dreaming of tapping into overseas markets? Our import/export expertise is your ticket to success.
We handle every step, from documentation to delivery. Let’s make your business go global together.
Headline: Expand Borders, Increase Profits – Start Now!
Ad Copy: Why limit your business to local shores? Our import/export services open doors to endless possibilities.
Seamlessly move goods worldwide, conquer new markets, and elevate profits. Your journey to international success begins here.
Headline: Unleash Growth Potential – Import/Export Made Easy!
Ad Copy: Want to skyrocket your business growth? Our import/export solutions simplify global trade.
Seamlessly ship your products, ensure compliance, and boost profitability. Get started today and watch your business thrive on the global stage.
Potential Businesses for Referral Partnerships:
- Logistics Companies: Collaborate with freight forwarders, shipping companies, and logistics providers. They can refer clients who need assistance with importing/exporting goods.
- Customs Brokers: Build relationships with customs brokerage firms. They can refer clients looking to import or export products.
- International Trade Consultants: Partner with consultants who provide advice on global trade. You can complement each other’s services and refer clients back and forth.
- Trade Associations: Join industry-specific trade associations and chambers of commerce. Network with members and establish referral partnerships.
- E-commerce Platforms: If you specialize in importing/exporting goods related to e-commerce, collaborate with online marketplaces that could refer their sellers to your services.
- Business Consultants: Business consultants often work with companies looking to expand globally. They can refer clients in need of import/export expertise.
- Legal Firms: Attorneys specializing in international trade law can refer clients needing assistance with compliance, contracts, and legal aspects of import/export.
- Manufacturers: Manufacturers seeking to export their products can refer you to their network for assistance with the logistics and export processes.
- Financial Institutions: Establish partnerships with banks that offer international business services. They can refer clients who need assistance with cross-border transactions.
- Export Development Agencies: Collaborate with government agencies focused on promoting exports. They may refer companies looking to expand their overseas market presence.
Remember, building a strong relationship with your referral partners is key.
Offer them value in return through referral fees, reciprocal referrals, or other mutually beneficial arrangements.
- Assessing your skill set for running an Import/Export business is crucial. Your skills influence your business’s success.
- Evaluate your abilities in negotiation, communication, market analysis, logistics, and customer relationship management.
- If you lack a necessary skill, consider learning it through training or hiring professionals.
Essential Skills for an Import/Export Business Owner:
- Market Research: Understanding global market trends and demands is vital.
- Negotiation: Negotiating deals with suppliers, distributors, and customers.
- Logistics Management: Efficiently coordinating shipments, customs clearance, and delivery.
- Financial Acumen: Managing finances, calculating costs, and analyzing profitability.
- Networking: Building relationships with industry professionals, suppliers, and customers.
- Communication: Effective communication across cultures and languages.
- Problem-Solving: Addressing unexpected challenges in international trade.
- Risk Management: Mitigating potential risks, such as currency fluctuations and geopolitical uncertainties.
- Legal Awareness: Understanding international trade regulations and compliance.
- Adaptability: Navigating changing market dynamics and adapting strategies.
- Leadership: Managing a team if your business grows.
- Technology Proficiency: Utilizing software for inventory, logistics, and communication.
These skills can lead to informed decision-making, efficient operations, and successful business expansion.
Knowledge Is Power if You Use It!
Knowledge Empowers: Industry Insights Await
Unveil valuable industry insights online.
These sections offer vital information for your research, startup, and operational phases. Dive in and harness the power of knowledge!
Trends and Statistics
Unveiling Industry Trends: Your Business Advantage
Explore industry trends and statistics for your Import/Export venture. Unlock valuable insights to steer your business toward success.
See the latest search results for trends and statistics related to the Import/Export industry.
Import/Export Associations
Empowerment Through Trade Associations
Trade associations offer vital industry insights, networking, and events that keep you informed and connected.
Maximize your business potential with these valuable resources.
See the search results related to Import/Export associations.
The Top Import/Export Companies
Learning From Successful Models
Studying established Import/Export businesses can reveal innovative gaps in the industry or overlooked opportunities in your own venture.
See the latest search results for the top Import/Export companies.
The Future of the Import/Export Industry
Anticipating Industry Evolution
Researching the industry’s future is crucial for aspiring Import/Export business owners to prepare for upcoming trends, changes, and opportunities.
See the search results for the future of the Import/Export industry.
Import/Export Businesses for Sale
Buying vs. Starting: Weighing Your Options
When considering an existing Import/Export business for purchase, weigh the benefits:
- Immediate Revenue Generation.
- Skips Startup Phase.
- Proven Business Model.
- Known Financials & Customer Base.
- Established Reputation.
However, note the downsides:
- Higher Cost due to Goodwill.
- Potential Customer Loss with Changes.
- Inheriting Both Positive and Negative Reputation.
While an exact match might not be available, exploring the industry’s existing businesses can provide valuable insights for your decision-making process. Check out the link to learn more.
See the latest search results for a Import/Export business for sale and others closely related.
Franchise Opportunities Related to an Import/Export
Exploring Import/Export Franchises: A Balanced View
Considering an Import/Export franchise? Understand the benefits and drawbacks before you decide:
- Proven Business Model: Follow a successful blueprint from the corporate office.
- Leverage Existing Reputation and Marketing.
- Comprehensive Pre-Knowledge of the Business.
- Corporate Support and Guidance.
- Higher Initial Investment.
- Limited Freedom for Major Changes.
- Restricted to Approved Products/Services.
- Bound by Franchise Agreement Terms.
- Ongoing Franchise Fees.
Exploring franchise opportunities could uncover aspects of your Import/Export venture that you hadn’t considered.
While an exact match may not be available, browsing franchises in the same industry can provide valuable insights. Check out the link to learn more.
See the latest search results for franchise opportunities related to this industry.
Import/Export Business Insights
Valuable Insights for Your Import/Export Business
Exploring tips and insights offers a wealth of knowledge. Discover brilliant ideas, avoid pitfalls, and enrich your understanding of the industry.
See the latest search results about insights into running an Import/Export business.
Import/Export Publications
Staying Informed: The Power of Publications
Publications serve as a dynamic resource for staying updated on the latest trends and insights within the Import/Export business landscape.
See the search results for Import/Export publications.
Import/Export Forums
Forums: Connecting and Learning in Import/Export
Participating in Import/Export forums offers a unique opportunity to engage in discussions, connect with industry peers, and gain valuable customer insights, enriching your perspective.
See the latest search results related to Import/Export forums.
Courses: Expanding Expertise for Import/Export Success
Enroll in online or local courses to enhance your skills, broaden your knowledge, and ensure ongoing professional growth within the Import/Export field.
See the latest courses on Import/Export and our management articles to provide insights and tips on managing Your business.
Import/Export Blogs
Stay Informed: Subscribing to Import/Export Blogs
Subscribe to relevant Import/Export blogs to receive up-to-date insights and ideas.
Over time, curate your list by focusing on blogs that consistently providing valuable and current information for your business journey.
Look at the latest search results for Import/Export blogs to follow.
Import/Export News
Stay Current with Industry News
Regularly check industry news sources to stay informed about trends, developments, and updates in the Import/Export field.
See the latest results for Import/Export news.
YouTube for Insights
Explore YouTube for videos related to Import/Export business.
Many creators share valuable insights, tips, and tutorials that can enhance your knowledge and understanding of the industry.
See the links to YouTube Videos Below.
Videos related to starting an Import/Export business can be found here.

Privacy Overview
Why you’ll never succeed online.
This controversial report may shock you but the truth needs to be told. If you’ve been struggling online this report will open your eyes.
The Truth May Shock You!

We respect your email privacy
Powered by AWeber Email Marketing
Export Business Plan and Exporter's Roadmap

If the export business plan is planned comprehensively, the chance of being successful in the target market increases. Poor planning or lack of planning can lead to major failures and harm the exporter. Therefore, an important question should be how the export plan should be made for an exporter.
Companies that have just started exporting or that aim to enter a different foreign market for the first time can benefit from companies that provide export consultancy services before carrying out their export business plan.
The steps of the export business plan are as follows;
-Approval of Top Management Must Be Obtained
Before the research is done and the plan is written, the person or department responsible for the target market entry strategy should inform the senior management about this and get approval. By doing this, it can be understood whether the key people in the company are willing to meet the challenges and meet the financial requirements for export. All departments, including the head of the company, must know and adopt the firm's export plan.
-Market Research Should Be Done
The company that will conduct market research should follow the country's export potential and product information, marketing guides, political and socio-economic conditions of the countries.
-Market Research Should Be Analyzed
Market research is the process of collecting information about the sales conditions, price range and potential customers of a product in the market. Features such as the design, size and color of the product should be determined by studying the target consumer in the selected region to determine consumer preferences. In addition, the expectations and purchasing behaviors of potential customers can be learned by sending product samples to sales channels in the relevant market.
-Export Flow Should Be Determined
For an exporter to be successful, it is very important to determine whether the product can compete in this market. Such data can be obtained from the Statistical Institute of the relevant country, the Undersecretariat of Foreign Trade.
-The Most Appropriate Export Price Should Be Determined
Determining the price of a product is the most important factor that will affect the financial projections within the export plan. Therefore, cost-increasing factors should be considered while exporting. These factors are sales commissions, fees paid for shipping companies, costs for necessary documents, financing costs, letters of credit, packaging, labeling, marking, transportation within the country, insurance and storage costs, translation costs of product documents, and loan terms. It should be ensured that each of these factors is clearly expressed in the financial projections and the price of the product should be determined accordingly.
-The capacity of the firm should be clearly revealed
Pricing is not the only factor that influences a buyer's decision to purchase a product or service. The company's management capability, production capacity, quality control system, technical cooperation with foreign companies, order fulfillment system, references of the company and credibility related to financial stability are also important factors that can affect the purchase decision of the buyer.
- Matters that will affect the buyer's decision should be addressed
It should be researched which issues the buyer attaches importance to in the purchasing process and methods and procedures should be developed accordingly. Thus, those who read the business plan come to the conclusion that the company knows the issues that are important to foreign buyers. The factors that affect the purchase are as follows, from the most important to the least important; Quality, deadline, price, warranty, commitment to compensate for complaints or damage, protection of patents and prevention of infringement, technical support, confidentiality, packaging, payment methods, mode of transportation and correct follow-up of customer demands.
Some of the methods such as doing research on the internet for marketing, participating in international fairs, promoting products and services on websites that are used effectively in a particular country, getting support from effective consultancy companies for international marketing should be investigated. Then, marketing activities should be started with methods suitable for the firm's budget, the structure of the product and the determined market.
-Checking a Buyer's Creditworthiness
Before the exporter enters into a business deal, the potential buyer must check the credibility of the distributor or external partner. The best sources for this are the foreign credit services in the relevant country and the Chambers of Commerce and Industry in the buyer's country.
-Selection of Distribution Type
Companies should choose one of the distribution methods suitable for them. This can be direct or indirect export by finding a sales agent or sales representative.
EXPORTER'S ROADMAP
An exporter without a roadmap may encounter some unexpected problems in business life. These problems can cause additional business loss, loss of time and some cost issues. It is necessary to be sensitive about a subject such as export, which has many variables and risks. For this, exporters should plan what they will do step by step and draw up a road map.
First of all, the company that wants to start exporting should revise its official web page, product and promotional catalogues, brochures, corporate social media accounts for export in order to create a sense of trust and reputation. For this, if the company does not have a public relations and promotion department, it should apply to export consultancy companies that offer these services.
In the next step, the company that wants to export should optimize the work of its export department and, if necessary, encourage its employees to train in order to make up for their deficiencies. Considering that this is a long process, the company can benefit from the services of the external export department. Foreign trade consultancy institutions that provide external export department services will gain new customers to the company by carrying out transactions such as market research and potential market analyzes in a shorter period of time.
In the next step, in order to start export activities, a deep market analysis for the target product should be made. This analysis should be carried out by an experienced foreign trade expert or by the institution providing the relevant service. Thanks to market analysis, target markets are determined and detailed research on these markets are carried out. Thus, the current market value in the market, price policies for the target product, potential competitors, market density, supply-demand ratios and potential risks are determined.
After the potential market analysis is prepared and evaluated, the sectoral markets to be entered are determined. Additional information may be needed after this stage. For this, the trade attachés, foreign trade institutions and B2B trade platforms operating in the relevant region should be consulted.
If these preparations and preliminary studies for export are carried out meticulously, the probability of the company's failure in export will be reduced to a minimum.
It is very easy to reach importers and exporters all over the world directly with TradeAtlas! TradeAtlas is a global importer and exporter search engine that contains 1.8 billion bills of lading and shipment details data of 20 million importer companies in more than 230 countries around the world. TradeAtlas is with you to accompany you in taking steps towards becoming a more important part of global trade! To become part of the global ecosystem, you can register and search for free by clicking here .
RECENT BLOG ARTICLES

Target Markets

The Russia Ukraine Crisis and the Effects on the Global Economy

The European Green Deal and Its Effects on Export

DIFFERENCES BETWEEN GENERAL TRADE SYSTEM AND SPECIAL TRADE SYSTEM

Supply Chain 4.0

Resolution of Disputes in International Trade and Arbitration

Transportation Insurances

Packing List

United Nations Convention on Contracts for the International Sale of Goods (CISG)

The Impact of Chip Shortage on World Trade
What is Import? How to Become an Importer?

What is Blockchain and How Does Blockchain Work?

What is Origin?

Regional Economic Integrations

What is Export? How to Become an Exporter?

Target Market Selection in Export

Types of Companies and Establishment Stages in Turkey

Things to Consider in Export Contracts

What is a Free Zone and What are its Benefits?

Trademark Registration in International Markets

Social Media Marketing and Its Effects on Commerce

National and International Institutions Regarding Foreign Trade

Making a Difference in Trade Fairs
What is Cross Trade? How to Do it?

Useful Databases For Conducting Market Research

Free Trade Agreements and Contributions to Countries

What is a letter of credit and what are the types of letters of credit?

OFFICIAL DOCUMENTS USED IN FOREIGN TRADE

Digitalization of International Trade

Technical Barriers to Trade

What are the Risks that can be Encountered in Foreign Trade?

What is Commercial Intelligence?

What are the Incoterms Used in International Trade?

What are the Payment Methods in Foreign Trade?

What is Bill of Lading? How to Fill Out Bill of Lading?

Container Crisis

10 Global Trade Products in 2021

What is The Impact of Influencers on B2B Marketing?

How to Establish Export and Import Companies?

What is HS Code? What is it for? How to find a HS Code?

How to Find Importers in 4 Steps?

The Ratio of Exports to Imports

Transportation Methods Used in Turkey's Foreign Trade
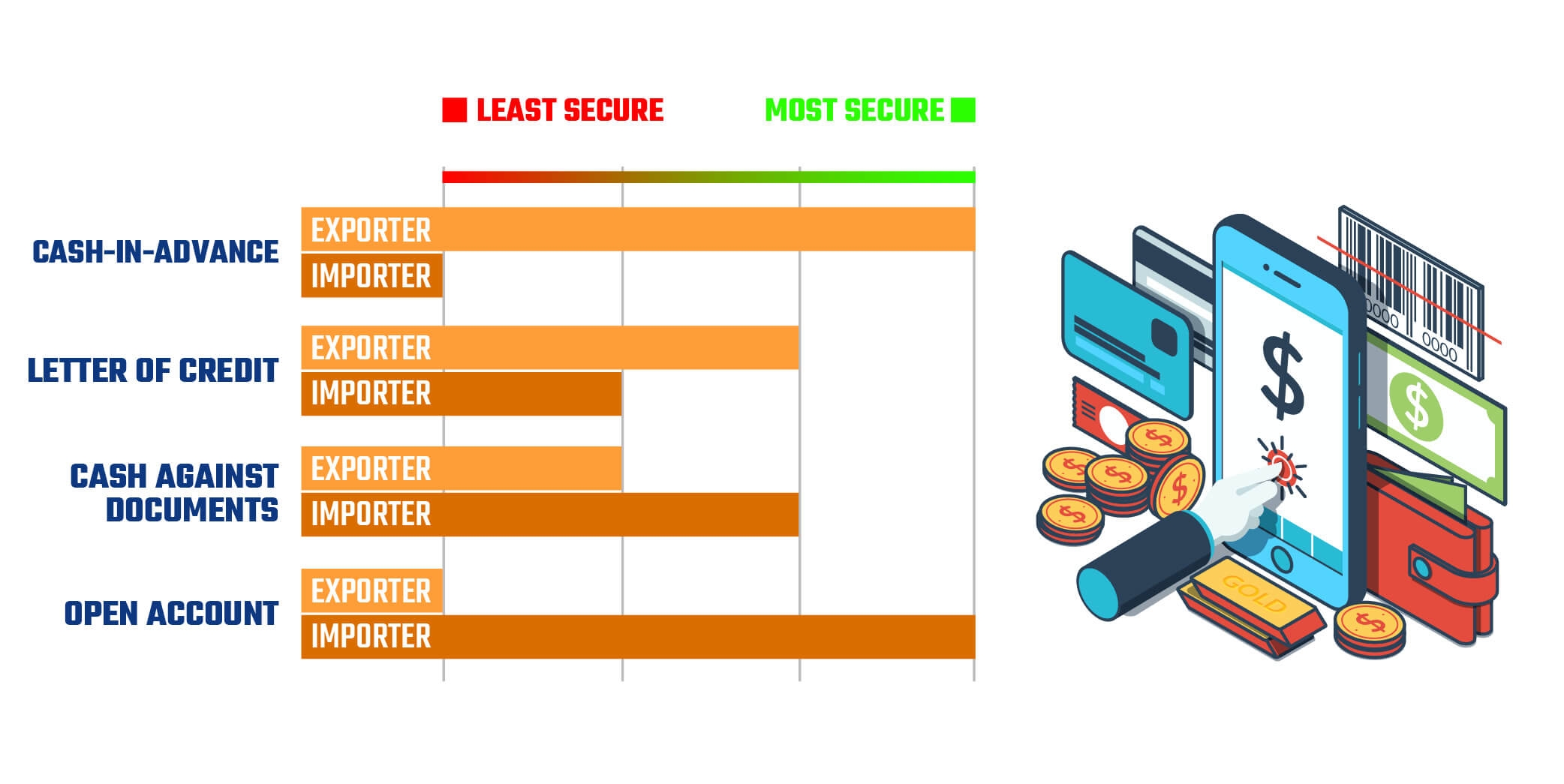
Payment Methods Turkey Uses in Foreign Trade

This website uses cookies.
As TradeAtlas, we use cookies for various purposes on our website and process your personal data through these cookies.
Cookies settings
For more detailed information about the processing of your personal data by the Company, we recommend you visit TicaretAtlası Bilgi Sistemleri San. ve Tic. Ltd. Sti. cookies policy and read the Personal Data Protection and Processing Policy.
The use of certain cookies is mandatory for our website to function properly. For example, authentication cookies, which are activated when you log in to our site, ensure that your active session continues when you switch from one page to another on our website.
These cookies allow us to personalize the services offered on our website by remembering your preferences and choices on the site. For example, it allows us to remember your language selection on our website or the font size you have chosen when reading a text.
These cookies allow us to collect information about your use of social media. For example, cookies can be used to use the information of your Facebook/Twitter accounts to create personalized advertisements or to conduct market research.
Thanks to these cookies, we can improve the services we provide to you by analyzing your use of our website and the performance of our website. For example, thanks to these cookies, we can detect which pages our visitors view the most, whether our website is working properly and possible problems.
We use cookies to promote products and services to you on our website or in channels other than our website. In addition, we may cooperate with some of our business partners to advertise and promote you within or outside of our website. For example, cookies can be used to track whether you click on an ad that you see on our website, and if you benefit from the service on the website to which that ad is directed after the ad has attracted your attention.
Register now for the Small Business Academy and attend free workshops to start or grow your business.
View this page for information on the We're All In Small Business Grant.

- Ambassadors
- Success Stories
- Small Business Programs
- Small Business Academy
- Green Ribbon Commission
- Industry Programs
- Industry Resource Center
- Industry Stories
- COVID-19 Business Resources
- Attracting Business
- Growing Business
- Partnership for Your Success (PaYS)
- Diverse Business Development
- Cost of Doing Business
- Certified Sites
- Locate In Wisconsin
- INsource Newsletters
- Business Development Stories
- Entrepreneur Programs
- Innovation Investment Portfolio
- Start In Wisconsin
- Entrepreneur Stories
- Launch Blog
- Export Programs
- Getting Started
- Global Navigation Network
- Market Intelligence
- Wisconsin Export Data
- Export Stories
- Community Programs
- INtersections Newsletter
- Environmental Equity
- Places Blog
- Community Stories
- RURAL PROSPERITY
- WEDC Programs
- Program Goals and Budget
- WEDC Public Records Request
- WEDC Ethics Hotline
- Program Outcomes
- Working at WEDC
- Request for Proposals
- Talent Attraction Co-Op Initiative
GETTING STARTED
Begin your exporting journey with guidance from wisconsin's experts., opening global doors for business in wisconsin.
For hands-on exporting assistance, tools and resources—plus in-market representatives covering 96 countries and territories around the world—look to WEDC. WEDC can help you with research and planning to successfully launch or expand an exporting strategy. And with more than 600 global, national, regional and local business development partners, WEDC provides tools and resources to help you identify and pursue the global market opportunities that are right for you.
EXPORTING 101
Exporting q&a, inside exporting.
Subscribe to receive information on upcoming trade ventures and information on how to reach new global markets.
GLOBAL MARKET REPORTS
Find data, insights and information on industry-specific and country-specific export opportunities worldwide.
UPCOMING TRADE VENTURES
Expand your company’s global reach by participating in a global trade venture. Find a list of upcoming trade ventures here.
GOVERNOR'S EXPORT AWARDS
Wedc success stories, badger technology group, aiq solutions, gamber-johnson, hydro-thermal.
Badger Technology Group’s export success helped it grow from 10 employees to 39 and increase sales by 400% since 2020.
The goal of AIQ Solutions is to create a new, faster, and more comprehensive way to analyze multiple radiological images at one time.

With assistance from WEDC, Gamber-Johnson has become a leading supplier of rugged computer mounting systems and vehicle mounting components used in consumer, law enforcement and military applications.

Although Hydro-Thermal was already an experienced exporter, the company chose to take part in the ExporTech™ Program for guidance in refining its export strategy.

STAY CONNECTED TO WEDC
Receive up-to-date information regarding Wisconsin’s economic development, export data, investment activity and more.
Small Business Trends
65 innovative import export business ideas for small businesses.
The world is getting smaller every day as global trade becomes easier and more attainable. This opens up avenues for even small businesses to venture globally. While the import and export sectors are dotted with hurdles, they’re also teeming with a multitude of business prospects in international commerce. This article will provide a collection of top import-export business ideas to ponder over as you seek new entrepreneurial opportunities .
Table of Contents
Understanding the Basics of the Import and Export Business
The import-export business idea, at its core, involves trading goods and services across national boundaries. While it sounds straightforward, the actual process can be quite intricate, with considerations such as tariffs, trade agreements, customs regulations, and logistics playing significant roles.
Take, for example, a small toy manufacturer based in Ohio. If this business decides to export its toys to a country like Japan, it will have to first understand the demand for its toys in the Japanese market. Then, they will need to navigate customs regulations, tariffs, and international shipping logistics. This is the export side of the business.
On the flip side, consider a boutique coffee shop in London that wants to serve authentic Colombian coffee. They would need to import beans from a Colombian supplier. This means understanding how to get coffee from Colombia to the UK, handling international payment methods, and complying with UK import regulations. This is the import side of the business.
In both scenarios, businesses must also consider cultural nuances and market preferences to ensure their products or services resonate with the foreign market. Understanding these basics is the first step to success in the import-export business.
Here’s a word from Murat Oztturjer on the basics of starting an import-export business from home:
What is an import business?
Importing is all about buying goods or services from another country and bringing them into the home country. In simple terms, if a product or service is made in one country and bought in another, it’s considered an import.
What is an export business?
An export business, quite simply, is a business that makes goods or services in its home country and sells them to customers in other countries. In other words, if a product or service is produced domestically and sold internationally, it’s considered an export.

How to Start Your Own Import-Export Business
Starting your own import-export business can be an exciting endeavor. Here are some general steps to guide you:
- Research and Plan: Start by researching markets that interest you and where you see a demand for certain goods that you can supply. Create a business plan outlining your import-export business idea, target market, business structure, and strategies for operations, marketing, and finances.
- Understand Legal Requirements: Familiarize yourself with your country’s import-export business laws and regulations and the countries you’ll be trading with. This includes duties, taxes, licenses, and customs procedures.
- Establish Your Business: Once your plan is in place, you can formally establish your import-export business idea. This could involve registering your business name, obtaining necessary licenses or permits, and setting up your business accounts.
- Build Relationships: Establish strong relationships with manufacturers, suppliers, and buyers. Networking is key in the import-export business, and strong relationships can lead to better deals and partnerships.
- Organize Logistics: Decide on the logistics of how your goods will be transported, stored, and distributed. This might involve partnering with freight forwarders or shipping companies.
- Market Your Business: Market your import-export business to your target audience. This could involve creating a website, leveraging social media, attending trade shows, or even cold-calling potential clients.
Remember, every business is unique, and these import-export business steps might vary based on your specific circumstances and business model.
Choosing the Right Import Business Ideas
Finding the perfect import business idea requires careful thought and research. Here are some factors to consider:
- Examine market demand: Start by discovering the products in high demand in your local market. Research the latest trends and consumer needs. This data-driven approach guides you to potential winning goods for your import business.
- Harness Your Product Knowledge: Select products that resonate with you or align with your expertise. This depth of understanding boosts your marketing efforts and helps you cater to your customers’ needs more effectively.
- Check for Reliable Suppliers: Confirm the availability of reputable suppliers for your chosen product. Establishing connections with trustworthy suppliers ensures a stable, high-quality supply for your import business.
- Calculate Profit Margin: Calculate the cost of your product, taking into account import duties, shipping, and overhead expenses. This calculation gives you an insight into a reasonable selling price in your local market and your potential profit margin.
- Understand Legal Regulations: Check import regulations to confirm the legal status of your chosen goods. Not all products can be legally imported, so this step safeguards your import business from potential legal pitfalls.
- Study your competition: Understand the competitive landscape for your product in your local market. High saturation of a particular product might pose difficulties in carving out your niche.
Selecting Profitable Export Business Ideas
Choosing the right export business ideas requires a keen understanding of both your local market and potential foreign markets. Here are some factors to consider:
- Market Trends: Keep an eye on international market trends and consumer preferences. The success of your export business idea significantly depends on the current trends and demands in your target market.
- The uniqueness of the product: If your product has a unique aspect or a special feature that’s not available in the target market, it will have a better chance of standing out and being successful.
- Manufacturing Capacity: Ensure that you have the capacity to produce the goods for your export business. This involves not just production but also storage, packaging, and transport.
- Cost and Profit Margin: Determine the total cost of producing and exporting your product, and then compare it with the price it can fetch in the international market. Remember to include all costs such as production, packaging, shipping, and export duties.
- Legal Regulations and Standards: Understand the export business regulations of your home country and the import regulations of your target country. Also, consider the safety and quality standards that your product must meet.
- Competitor Analysis: Study your competitors in the export business target market. Understanding who your competitors are and how they operate will help you position your product more effectively.
65 Innovative Import-Export Business Ideas

Whether you’re fascinated by the idea of sourcing unique products from abroad or excited about sharing local goods with the world, the right import-export business ideas can set you on the path to success. In this section, we’ll explore 65 innovative import and export business ideas, each with its own unique potential.
1. Importing fine teas

Import fine teas from renowned tea-producing regions like China, India, and Sri Lanka. This import business could tap into a growing global interest in tea culture and varieties, catering to tea connoisseurs and health-conscious consumers.
2. Exporting handmade jewelry
Showcase the craftsmanship of local artisans on a global scale by exporting unique handmade jewelry. The demand for such personalized and intricate pieces spans the globe, catering to consumers seeking distinctive and meaningful accessories.
3. Importing specialty coffee beans
Feed the global coffee obsession by importing specialty coffee beans from famed regions like Ethiopia, Colombia, and Brazil. With a rising coffee culture and consumers valuing quality and uniqueness, there’s a robust market for distinct coffee experiences.
4. Exporting Organic Skincare Products
In your import-export business, capitalize on the escalating demand for organic skincare products. Exporting a range of top-quality, natural cosmetics free of chemicals targets health-conscious consumers seeking sustainable beauty solutions. This is one of many lucrative import-export business ideas that cater to the eco-friendly market.
5. Importing Gourmet Cheeses

As part of your import and export business strategy, introduce the exceptional flavors of gourmet cheeses to refined taste buds globally. Importing a selection of artisanal cheeses from famous cheese-producing regions will cater to food enthusiasts, restaurants, and specialty shops in search of superior and unique cheese options.
6. Exporting Artisanal Chocolates
Treat global chocolate connoisseurs by exporting artisanal chocolates crafted from premium ingredients and innovative flavors. In the export business, the demand for unique and high-quality chocolates is burgeoning, making this a profitable venture.
7. Importing Premium Olive Oil
In the import-export business, consider importing top-quality olive oil varieties from countries such as Italy, Greece, or Spain. This strategy introduces rich, flavorful oils to health-conscious consumers and culinary enthusiasts seeking exquisite and healthy cooking oils.
8. Exporting Custom Furniture
Demonstrate local craftsmanship and distinct designs by exporting custom-made furniture as part of your import-export business ideas. This strategy targets customers who value bespoke furniture, providing them with personalized and outstanding interior solutions.
9. Importing exotic spices
In your import business, consider importing an array of exotic spices from diverse global regions. This strategy spices up international cuisine and caters to culinary enthusiasts, restaurants, and specialty food stores in search of authentic flavors and unique spice blends.
10. Exporting Local Artworks

Promote your region’s artistic talent by exporting local artworks, such as paintings, sculptures, or handmade crafts. This export business idea targets art collectors, interior designers, and galleries, showcasing the cultural and artistic expressions of your home country.
11. Importing luxury textiles
Introduce the elegance of luxury textiles into your import and export business by importing high-quality fabrics like silk, cashmere, or fine linens. This approach targets fashion designers, upscale boutiques, and home decor enthusiasts seeking exclusive textiles for their designs or interiors.
12. Exporting Craft Beers
Join the growing craft beer movement in your export business by exporting a range of unique artisanal beers. This approach targets beer enthusiasts, pubs, and craft beer retailers globally, offering them distinctive brewing styles that highlight the creativity and quality of your local breweries.
13. Importing Unique Wines
As an import-export business idea, import unique wines from renowned wine regions to introduce wine enthusiasts to a realm of distinctive flavors. Curate a selection of exceptional vintages and varietals for wine connoisseurs, fine dining establishments, and specialty wine shops in search of exclusive wine options.
14. Exporting homemade sauces
Spice up the global market with your delicious homemade sauces, crafted with secret family recipes and premium ingredients. Target food enthusiasts, specialty food stores, and international culinary scenes crave unique flavors and exceptional-quality sauces that elevate their dishes and set them apart from mass-produced options.
15. Importing fashionable eyewear
Introduce the latest trends in fashionable eyewear to consumers by importing a diverse range of stylish glasses and sunglasses. Target fashion-conscious individuals, boutiques, and eyewear retailers seeking unique and on-trend eyewear options, offering them a selection of high-quality and fashion-forward frames that enhance their style.
16. Exporting leather goods

Showcase the craftsmanship of your region by exporting a range of high-quality leather goods. Target fashion enthusiasts, luxury boutiques, and discerning consumers who appreciate the durability, sophistication, and timeless appeal of genuine leather products. Offer a selection of handcrafted bags, wallets, belts, and accessories that exude elegance and quality.
17. Importing electronic gadgets
Embrace the tech-savvy demand by importing a wide array of innovative electronic gadgets. Target gadget enthusiasts, electronics retailers, and tech-savvy consumers who seek cutting-edge devices, offering them the latest technology trends and unique features that enhance their digital experiences.
18. Exporting musical instruments
Share the joy of music worldwide by exporting a diverse range of high-quality musical instruments. Target music enthusiasts, music stores, and educational institutions seeking exceptional sound quality and craftsmanship. Offer a variety of instruments, including guitars, pianos, drums, and more, catering to musicians of all skill levels and genres.
19. Importing designer handbags
Bring the allure of luxury and style to fashion-conscious consumers by importing designer handbags from renowned fashion capitals. Target fashionistas, upscale boutiques, and department stores seeking high-end, meticulously crafted handbags from prestigious fashion brands, offering them exclusive and coveted accessories that exude elegance and sophistication.
20. Exporting eco-friendly products
Cater to the growing demand for sustainable and environmentally conscious products by exporting a wide range of eco-friendly goods. Target eco-conscious consumers, green retailers, and eco-friendly businesses worldwide, offering them a variety of sustainable alternatives, such as biodegradable packaging, organic personal care products, renewable energy solutions, or recycled home goods.
21. Importing handcrafted ceramics

Import exquisite handcrafted ceramics from skilled artisans. Target home decor enthusiasts, interior designers, and specialty retailers seeking unique and visually appealing ceramic pieces.
22. Exporting digital software
Tap into the thriving digital market by exporting cutting-edge software solutions. Target businesses, organizations, and tech enthusiasts seeking innovative software applications that streamline processes, enhance productivity, or provide unique functionalities. Offer a range of digital software solutions, such as productivity tools, creative software, project management systems, or specialized industry-specific applications.
23. Importing antique furniture
Unearth the timeless charm of antique furniture by importing carefully curated pieces from different eras. Target antique collectors, interior designers, and vintage furniture enthusiasts who appreciate the historical significance and unique craftsmanship of antique furniture. Offer a diverse selection of restored and well-preserved furniture, showcasing the elegance, character, and authenticity that antique pieces bring to both residential and commercial spaces.
24. Exporting fitness equipment
Promote an active and healthy lifestyle by exporting a range of high-quality fitness equipment. Target fitness enthusiasts, gyms, and health clubs seeking durable and performance-driven equipment. Offer a variety of fitness gear, including cardio machines, strength training equipment, yoga accessories, and wearable fitness technology.
25. Importing natural sweeteners
Satiate the demand for healthier alternatives to traditional sweeteners by importing a range of natural sweeteners. Target health-conscious consumers, organic food stores, and specialty bakeries looking for natural and sustainable sweetening options. Offer a selection of natural sweeteners like stevia, coconut sugar, or honey.
26. Exporting e-books
Embrace the digital age by exporting a diverse range of e-books, catering to the growing demand for digital reading materials. Target avid readers, online bookstores, and e-book platforms seeking a wide selection of genres and topics. Offer a range of engaging e-books, including fiction, non-fiction, self-help, and educational content, providing convenient access to captivating stories, valuable knowledge, and literary works in digital format.
27. Importing innovative toys
Ignite the imagination of children and parents alike by importing a selection of innovative and engaging toys. Target parents, toy stores, and educational institutions searching for unique and educational playthings. Offer a range of toys that stimulate creativity, problem-solving skills, and learning.
28. Exporting 3D-printed items
Export a diverse range of customized and precise 3D-printed items. Target industries like architecture, healthcare, engineering, and design that demand tailored solutions, showcasing the efficiency and versatility of additive manufacturing.
29. Importing health supplements

Tap into the growing wellness industry by importing a wide range of health supplements. Target health-conscious consumers, fitness enthusiasts, and wellness stores seeking natural and effective supplements. Offer a variety of vitamins, minerals, herbal extracts, and dietary supplements that promote well-being.
30. Exporting virtual reality devices
Capitalize on the immersive world of virtual reality by exporting a range of advanced VR devices. Target gaming enthusiasts, tech-savvy consumers, and businesses in the entertainment and training sectors seeking cutting-edge virtual reality experiences. Offer state-of-the-art VR headsets and accessories that transport users to virtual realms.
31. Importing fresh fruits
Bring the vibrant flavors of fresh fruits from around the world to local markets by importing a diverse range of seasonal and exotic fruits. Target health-conscious consumers, grocery stores, and restaurants looking for high-quality and flavorful fruit options.
32. Exporting dairy products
Share the goodness of dairy products with international markets by exporting a variety of high-quality dairy goods. Target food distributors, grocery chains, and culinary establishments seeking premium dairy products. Offer a selection of cheeses, butter, yogurts, and other dairy delicacies.
33. Importing luxury watches
Import luxury watches from prestigious brands. Target watch enthusiasts, collectors, and luxury retailers who appreciate craftsmanship and exclusivity. Offer a curated selection of high-end timepieces that exemplify precision engineering, timeless design, and exceptional quality.
34. Exporting educational materials
Empower students and educators globally by exporting a wide range of educational materials. Target schools, educational institutions, and e-learning platforms seeking comprehensive and engaging learning resources. Offer a variety of textbooks, digital learning materials, educational software, and teaching aids that support curriculum requirements.
35. Importing traditional crafts
Preserve and promote cultural heritage by importing traditional crafts from artisans around the world. Target cultural enthusiasts, art collectors, and fair trade organizations seeking authentic and handmade crafts. Offer a diverse range of traditional artifacts, handwoven textiles, pottery, jewelry, and decorative items that showcase the rich cultural traditions and skilled craftsmanship of different regions.
36. Exporting DIY kits

Encourage creativity and hands-on learning by exporting do-it-yourself (DIY) kits. Target hobbyists, crafters, and parents seeking engaging and educational activities. Offer a range of DIY kits that provide all the necessary materials and instructions for various projects, such as woodworking, knitting, jewelry making, or model building.
37. Importing plant-based products
Embrace the rising demand for plant-based alternatives by importing a wide range of plant-based products. Target health-conscious consumers, vegans, and environmentally conscious individuals seeking sustainable and cruelty-free options. Offer plant-based foods, beverages, snacks, and personal care products that provide a healthy and ethical choice.
38. Exporting travel gear
Equip globetrotters with essential travel gear by exporting a variety of travel accessories. Target frequent travelers, adventure enthusiasts, and travel retailers seeking durable and functional products. Offer a range of travel gear, including luggage, backpacks, travel organizers, travel adapters, and other travel essentials.
39. Importing designer clothes
Bring the world of fashion to your market by importing a selection of designer clothes from renowned fashion houses. Target fashion-forward individuals, luxury boutiques, and high-end retailers who seek exclusive and stylish garments. Offer a curated collection of designer clothing, including haute couture, ready-to-wear, and accessories.
40. Exporting photography equipment
Capture the attention of photography enthusiasts worldwide by exporting a range of high-quality photography equipment. Target professional photographers, hobbyists, and photography retailers seeking reliable and innovative gear. Offer a variety of cameras, lenses, lighting equipment, tripods, and accessories.
41. Importing high-end cosmetics

Unleash the allure of luxury beauty by importing high-end cosmetics from prestigious brands. Target beauty enthusiasts, upscale department stores, and luxury beauty retailers seeking premium beauty products. Offer a selection of high-quality makeup, skincare, and fragrance items that exemplify luxury, innovation, and exceptional performance.
42. Exporting pet supplies
Cater to the needs of pet owners worldwide by exporting a comprehensive range of pet supplies. Target pet stores, online retailers, and animal lovers seeking high-quality and innovative pet products. Offer a diverse selection of pet food, toys, accessories, grooming products, and healthcare items, ensuring the well-being, comfort, and happiness of beloved pets.
43. Importing quality footwear
Step up the fashion game by importing a range of high-quality footwear options. Target fashion-conscious individuals, shoe retailers, and boutique stores seeking stylish and durable shoes. Offer a variety of footwear styles, including casual shoes, athletic sneakers, formal dress shoes, and more.
44. Exporting kitchen gadgets
Streamline culinary experiences by exporting a wide range of innovative kitchen gadgets. Target cooking enthusiasts, home chefs, and kitchenware retailers seeking functional and time-saving tools. Offer a variety of kitchen gadgets, including cutting-edge appliances, cooking utensils, food prep accessories, and smart kitchen devices.
45. Importing eco-friendly fabrics
Embrace sustainability in the textile industry by importing a range of eco-friendly fabrics. Target eco-conscious fashion brands, designers, and conscious consumers seeking sustainable and ethically produced textiles. Offer a selection of organic cotton, bamboo, hemp, or recycled fabrics that meet stringent environmental standards.
46. Exporting homemade candles

Illuminate the global market with the charm of homemade candles by exporting a variety of handcrafted creations. Target candle enthusiasts, home decor stores, and gift shops looking for unique and artisanal candles. Offer a range of homemade candles in various scents, shapes, and designs.
47. Importing quality bed linens
Elevate the comfort and style of bedrooms by importing a selection of high-quality bed linens. Target luxury hotels, boutique accommodations, and bedding retailers seeking luxurious and durable linens. Offer a range of bed sheets, duvet covers, pillowcases, and bedding accessories crafted from premium fabrics.
48. Exporting organic seeds
Nurture a greener world by exporting a diverse range of organic seeds. Target organic farmers, gardeners, and eco-conscious consumers seeking sustainable gardening solutions. Offer a variety of organic vegetables, fruit, and herb seeds, providing customers with reliable and GMO-free options for growing their own organic produce.
49. Importing gourmet popcorn
Delight popcorn enthusiasts with a touch of gourmet by importing a variety of delectable popcorn flavors. Target gourmet food stores, movie theaters, and snack enthusiasts seeking unique and high-quality popcorn options. Offer a range of gourmet popcorn flavors, including savory, sweet, and unique combinations.
50. Exporting craft spirits
In the vast landscape of import-export business ideas, exporting artisanal craft spirits stands out as a promising one. Quench the thirst of spirits aficionados in international markets by providing a selection of these craft spirits. Target connoisseurs, bars, and liquor retailers seeking unique and high-quality alcoholic beverages. This export business can offer a range of craft spirits, such as small-batch whiskies, specialty gins, and unique-flavored vodkas.
51. Importing innovative lighting
Light up the path to success in your import-export business by importing a range of cutting-edge lighting solutions. Cater to architects, interior designers, and lighting retailers seeking unique and technologically advanced lighting options. This import business can offer a variety of innovative lighting fixtures, smart lighting systems, and energy-efficient solutions that enhance ambiance, improve functionality, and promote sustainability.
52. Exporting board games
Get into the import-export business by promoting entertainment and connection, specifically through exporting a diverse range of engaging board games. Appeal to families, board game enthusiasts, and specialty toy stores seeking interactive and entertaining gaming experiences. An export business like this can offer a variety of board games that cater to various age groups and interests.
53. Importing smart home devices
Embrace the future of connected living by venturing into the import-export business of smart home devices. Appeal to tech-savvy homeowners, smart home integrators, and technology retailers seeking innovative and intelligent home automation solutions. An import business like this can offer a variety of smart devices, including voice-controlled assistants, smart thermostats, security systems, lighting controls, and home entertainment systems.
54. Exporting handmade soap
Enrich daily self-care routines with an export business that exports a collection of handmade soaps crafted with care. Cater to natural beauty enthusiasts, boutique bath and body stores, and eco-conscious consumers seeking gentle and luxurious cleansing options. This export business could offer a range of handmade soaps made from natural ingredients, featuring unique scents and nourishing properties.
55. Importing specialty rice

Indulge the market with exceptional rice varieties by starting an import business that brings in a curated selection of specialty grains. Cater to discerning food enthusiasts, fine dining establishments, and rice connoisseurs in search of distinct and high-quality rice options. This import business could offer premium varieties like fragrant basmati, aromatic jasmine, or unique wild and black rice.
56. Exporting Craft Distilled Spirits
Capitalize on the rising popularity of craft spirits by exporting locally distilled beverages such as bourbon, whiskey, or gin. These products can appeal to international consumers seeking high-quality, artisanal spirits with a unique American twist.
57. Importing Exotic Fruit Preserves
Introduce exotic fruit preserves and jams from countries known for their diverse fruits, like tropical regions. These can cater to consumers looking for unique, flavorful additions to their breakfasts and snacks.
58. Exporting Locally Sourced Honey
Export honey sourced locally, each offering distinct flavors based on local flora. American honey varieties can be marketed to international customers as a natural and high-quality product.
59. Importing Traditional Pottery and Ceramics
Import traditional pottery and ceramics from countries with a rich history in pottery-making, such as Mexico or Japan. These unique and handcrafted items can appeal to consumers who value cultural authenticity and craftsmanship.
60. Exporting High-Quality Nuts and Seeds
Focus on exporting a variety of nuts and seeds grown in your area, such as almonds, pecans, or chia seeds. These nutritious products can appeal to health-conscious consumers in international markets.
61. Importing Specialty Tea Blends
Bring in specialty tea blends from countries like China, India, or Japan, offering a range of flavors and health benefits. This caters to tea enthusiasts and those seeking wellness-focused beverages.
62. Exporting Artisanal Baked Goods
Develop a niche in exporting artisanal baked goods like gourmet cookies, specialty bread, or unique pastries. Emphasize the quality, uniqueness, and American culinary style to appeal to international tastes.
63. Importing Handwoven Baskets and Textiles
Import handwoven baskets and textiles from Africa or South America, showcasing traditional weaving techniques and patterns. These items can attract customers interested in unique home decor and sustainable, artisanal crafts.
64. Exporting Award-Winning Cheeses
Export a selection of award-winning cheeses from various U.S. regions, known for their quality and flavor. These can appeal to international food connoisseurs and upscale markets.
65. Importing Exotic Spices and Herbs
Venture into the import of exotic spices and herbs from globally renowned regions. Consider sourcing unique spices like vanilla from Madagascar, turmeric from India, or cardamom from Guatemala.
What is the most profitable import-export business?

When considering import-export business ideas, several stand out due to their potentially high profitability. However, keep in mind that a variety of factors, such as location, expertise, market conditions, and individual business strategies, can significantly influence profitability.
- Electronics Import-Export: The electronics industry is continually evolving and growing, with product demand skyrocketing. According to Predence Research , the global consumer electronics market size is expected to hit US$ 1.13 trillion by 2030. As consumers seek the latest gadgets and devices, an import-export business in this sector will enjoy high-profit margins.
- Pharmaceutical Import-Export: The global pharmaceutical industry is another significant sector with high profitability potential. According to Grand View Research, the global pharmaceutical manufacturing market was valued at USD 405.52 billion in 2020 and is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 11.34% from 2021 to 2028. With the continuous development of new treatments and increasing global healthcare needs, this import-export business presents a promising opportunity for import-export businesses. Keep in mind, though, that this industry requires a comprehensive understanding of regulations and standards across different countries.
- Import-Export of Luxury Goods: Luxury goods like high-end fashion, watches, and jewelry often carry high-profit margins. In 2022, the luxury market generated positive growth for 95% of brands, showing that the demand for these products is rising. However, it’s crucial to understand consumer preferences, brand positioning, and customs regulations in the target markets for a successful venture in this import-export business.
- Food and Beverage Import-Export: Globalization and changing consumer preferences have boosted the food and beverage sector’s potential profitability. With an increase in demand for exotic and international food items, a small business has the opportunity to specialize in importing or exporting unique food and beverages, such as specialty coffee, teas, or artisanal foods.
- Renewable Energy Equipment Import-Export: Bloomberg notes that nearly half of the world’s power will come from wind and solar by 2050. As more countries shift toward sustainable energy solutions, the demand for renewable energy equipment has increased. Businesses dealing with importing and exporting items like solar panels, wind turbines, or electric vehicle parts are finding increasing market opportunities.
Remember, while these sectors have shown high profitability, conducting thorough market research, understanding industry regulations, and developing robust relationships with suppliers and customers for success in the import-export business is crucial.
How can I start my own import business?
We’re here to guide you if you’re contemplating launching your own import business. Below are key steps, paired with helpful tips and resources, for establishing your import business.
- Research and Plan: Embarking on your import business begins with in-depth market research. Identify markets that appeal to you and where you see a demand-supply gap. Craft a detailed business plan encapsulating your business concept, target market, operational blueprint, marketing strategy, and financial forecasts. Tip: Use resources like the U.S. Small Business Administration to gather information and effectively shape your business plan.
- Understand legal requirements: Understanding the import business laws and regulations of your home country and your trading partner countries is crucial. You must comprehensively know duties, taxes, necessary licenses, and customs procedures. Tip: Governmental trade agencies’ websites, such as those of U.S. Customs and Border Protection , offer valuable information on import regulations and compliance.
- Establish your business: With your plan ready, it’s time to establish your import business ideas formally. This involves registering your business, obtaining the necessary licenses, and setting up business bank accounts. Tip: Your local Chamber of Commerce or Small Business Development Centers (SBDCs) can guide this process.
- Build Relationships: Robust relationships with manufacturers, suppliers, and buyers are the lifeblood of a successful import business. Ensure you’re actively networking and nurturing these relationships. Tip: Joining industry trade shows and industry-specific online forums can be effective ways to connect with potential business partners.
- Organize Logistics: Decide on the logistics of how your goods will be transported, stored, and distributed. Collaborating with freight forwarders or shipping companies might be necessary. Tip: Platforms like Freightos allow you to compare and book freight companies, simplifying this step for you.
- Market your business: Finally, make your business visible. Leverage diverse marketing channels to reach your target audience, such as websites, social media, and local business events. Tip: Online marketing tools like Google My Business , Canva for designing social media posts, or Campaign Monitor for email marketing can prove valuable in this step.
Launching an import business is challenging, but with the correct approach, resources, and dedication, it can become a profitable venture.
Table: Starting an Import Business: Steps, Tips, and Resources
Navigating International Trade as an Export Company
As an export company, global trade presents a unique blend of complexities and opportunities. Tapping into the international market isn’t just about having the best import-export business ideas; it requires a thorough understanding of trade agreements, customs regulations, international logistics, and currency exchange. Here’s a deeper dive into these aspects and how to navigate them:
- Trade Agreements and Customs Regulations: A critical element of international trade is understanding the trade agreements and customs regulations of the countries you’re exporting to. These agreements can dictate the tariffs, quotas, and necessary documentation for your exports. Adhering to these regulations is essential for smooth customs clearance and avoiding potential legal issues.
- International Logistics: Managing the logistics of transporting goods internationally can be complex, with factors like shipping methods, packaging, labeling, insurance, and documentation playing a crucial role. A strategic approach to logistics can lead to cost savings, timely delivery, and customer satisfaction.
- Building Relationships with Foreign Partners: The best import-export business ideas heavily depend on fostering robust relationships with foreign partners, be they buyers, suppliers, or local agents. These relationships can offer valuable insights into local markets, consumer behaviors, and business customs, helping you tailor your strategies accordingly.
- Currency Exchange Rates: Currency exchange rates can significantly impact your bottom line in international trade. Understanding currency markets and hedging strategies can help mitigate the risks associated with fluctuating exchange rates.
Despite these complexities, operating in the global market comes with numerous benefits. It offers the potential to increase your customer base and revenue significantly. It can also help diversify your business, reducing dependency on a single market and increasing resilience to local economic fluctuations.
FAQs: Import-Export Business Ideas
What is a good export business idea.
A good export business idea leverages a product’s or service’s competitive advantage in your home country and addresses a demand gap in an overseas market. It could be an item that’s unique to your region, a product you can produce at a lower cost, or a trending product in global markets. Always ensure the idea aligns with your resources, capabilities, and business vision.
What do I need to know about the exporting business?
There are several key elements to know about the exporting business:
- Market Research: For a profitable import-export business, it’s critical to understand your target market. This includes comprehending customer needs, local regulations, and potential competitors.
- Product Selection: The product or service you decide to export in your export business should possess a distinct competitive advantage and satisfy an existing demand in your target market.
- Legal Aspects: It’s crucial to get acquainted with the export regulations in your home country and the import rules in your target market when operating an import-export business. This includes understanding duties, taxes, licenses, and customs procedures.
- Logistics: A firm grasp of the process of transporting your product to your customer is vital for your export business. It involves everything from packaging, shipping, and insurance to documentation.
- Financing: It’s crucial to be aware of the costs involved in exporting when planning your import-export business. Additionally, explore financing options and payment terms that provide protection for your business.
- Marketing Strategy: To build the best import-export business, developing a strategy to promote your product or service in your target market is necessary. This includes taking into account cultural nuances and local business practices.
- Building Relationships: As far as the import-export business is concerned, it’s essential to establish robust relationships with partners. These can include buyers, local agents, and freight forwarders.
Remember, continuous learning and adapting are keys to success in the dynamic world of international trade.
How can I make my import business more profitable?
Increasing the profitability of your import business ideas involves both strategic planning and execution. Firstly, streamline operations for improved efficiency, which could include better negotiation with suppliers, process automation, and optimizing logistics. Cultivate strong customer relationships to encourage repeat business, and diversify your product line to cater to wider customer interests and boost sales.
Consider expanding into new markets for a broader customer base and enhanced revenue, and employ effective marketing strategies to attract more customers. Since the import industry is highly dynamic, continually updating your knowledge of global market trends and regulatory changes is crucial to staying competitive and capitalizing on new opportunities.
What are some unique export business ideas?
Navigating the world of exports offers a broad spectrum of unique business opportunities. Here are a few that stand out due to their novelty and potential profitability:
Cultural Artifacts Export
Every culture has unique artifacts, crafts, and local products that are in demand globally. Exporting these authentic cultural artifacts can promote your local culture globally and cater to a niche market of collectors, decorators, and culture enthusiasts.
Eco-friendly products export
With the rising awareness of environmental issues and sustainability, eco-friendly products have seen a surge in demand. Export business ideas focusing on items like organic textiles, bamboo products, or recycled materials meet global demand and align with the trend towards sustainability.
Health and Wellness Products Export
The health and wellness sector is booming. Exporting products in this space, such as natural health supplements, functional foods, or fitness equipment, can be lucrative as consumers worldwide are becoming more health-conscious.
Innovative Technology Export
Technological innovations, particularly in clean energy, artificial intelligence, or healthcare sectors, can be promising export products. With the rapid pace of technological advancement, there’s always a global demand for cutting-edge solutions.
Which import and export business is most profitable?
The profitability of import-export business ideas can greatly depend on factors like the chosen product or service, market demand, competition, business model, and the entrepreneur’s expertise. Generally, businesses dealing with high-demand products, such as technology, consumer electronics, machinery, pharmaceuticals, and certain food products, can yield high profits.
However, unique and niche products with less competition can also prove highly profitable if there’s specific market demand. Conducting thorough market research, understanding global trends, and ensuring a clear competitive advantage for achieving high profitability is crucial.
What is the best product for import and export?
The “best” product for import-export business significantly depends on various factors, including your business model, target market, local and international trends, and available resources. Typically, products with high demand and low supply in a specific market are excellent choices.
These might include technological goods, consumer electronics, machinery, pharmaceuticals, and certain fashion or food products. However, niche products with less competition can also prove lucrative. Remember to do thorough market research before settling on a specific product.
Is the import business profitable?
An import business can be profitable, but it depends on various factors. These include the demand and supply of your chosen product in the target market, your ability to source the product at competitive prices, the efficiency of your supply chain, and the effectiveness of your marketing strategies.
It’s essential to conduct thorough market research, manage costs effectively, and continuously adapt to market trends and consumer preferences changes to ensure profitability.
Is the export business profitable?
Absolutely, export business ideas can be highly profitable. However, profitability depends on several factors, such as the product’s competitiveness in the global market, demand and supply conditions, your ability to manage export logistics effectively, and your marketing strategies.
Proper research, understanding international trade regulations, building strong relationships with buyers, and keeping up-to-date with market trends are crucial for running a profitable export company.
What factors determine the best import-export business?
A combination of factors often determines the “best” import-export business:
- Market Demand: In the import-export business sector, a product or service with high demand in the target market can pave the way for successful business opportunities.
- Competitive Advantage: A unique selling proposition for a product or service or a more competitive price point can greatly contribute to the success of an export business.
- Regulatory Compliance: In managing an import-export business, it’s crucial to understand and comply with the import-export regulations in both the home and target markets.
- Logistical Efficiency: A well-managed supply chain within your export business, which includes efficient transportation, storage, and delivery of goods, can substantially influence profitability.
- Marketing Strategy: Deploying effective marketing strategies within your import-export business that resonate with the target audience can significantly boost your business’s success.
- Customer Satisfaction: Ensuring the provision of quality products and excellent customer service in your import-export business can stimulate repeat business and establish a strong reputation in the market.
Considering these factors can help determine the best import-export business ideas.
What are the risks associated with the import-export business?
Engaging in the import-export business comes with its set of challenges and risks. Here are some of the primary risks to consider:
- Currency Exchange Risk : Fluctuations in currency exchange rates can significantly impact the profitability of transactions. If your home currency devalues against the currency of your trading partner, you might end up receiving less money than expected.
- Regulatory and Compliance Risks : Each country has its own set of regulations regarding imports and exports. Not adhering to these regulations can result in hefty fines, penalties, or even bans on doing business in that country.
- Shipping and Logistics Risks : Transportation can pose various risks like damage, theft, or loss of goods. Delays due to customs, weather conditions, or political unrest can also impact timely delivery and, consequently, customer satisfaction.
- Payment Risks : There’s always a risk of not receiving payment, especially when dealing with new clients or unstable regions. Different payment terms, such as open accounts, letters of credit, or advance payments, come with their own set of risks.
- Political and Economic Risks : Political instability, economic downturns, or drastic regulatory changes in a country can disrupt your business operations and affect profitability.
- Cultural and Language Barriers : Misunderstandings arising from cultural differences or language barriers can lead to miscommunication, affecting negotiations, partnerships, or customer relations.
- Product Quality and Standards Risk : The product you import or export may not meet the standards or expectations of the target market. This can lead to returns, rejections, or loss of reputation.
To mitigate these risks, it’s essential to conduct thorough research, build strong relationships, employ risk management strategies, and stay updated on global trends and changes.
Can you make money from importing?
Yes, you can certainly make money by running an international business. You can create a profitable business model by sourcing products from countries where they are cheaper or better made and selling them in markets where they are in demand.
However, it’s important to factor in shipping, taxes, duties, and storage costs. Also, understanding import regulations, establishing reliable supply chains, and implementing effective marketing strategies are crucial to ensuring import business profitability.
Image: Envato Elements

Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
© Copyright 2003 - 2024, Small Business Trends LLC. All rights reserved. "Small Business Trends" is a registered trademark.

Where to Trade I What to Trade | How to Trade I When to Trade
Export business plan and exporter’s road map.
Export business plan and Exporter’s Roadmap are two critical tools that exporters use to ensure that their international trade ventures are successful. An export business plan is a comprehensive document that outlines an exporter’s objectives, strategies, and tactics for exporting goods or services to foreign markets. An Exporter’s Roadmap, on the other hand, is a step-by-step guide that outlines the key stages of the export process and provides exporters with a clear roadmap for success. In this blog, we’ll take a closer look at these two tools and how they can help exporters to achieve their international trade goals.
The first step in developing an export business plan is to define your objectives. What do you hope to achieve through exporting? Are you looking to expand your customer base, increase sales, or enter new markets? Once you have defined your objectives, you can start to develop a strategy for achieving them. This may involve researching potential markets, identifying potential customers, and developing a marketing plan to promote your products or services in those markets.
The next step in developing an export business plan is to identify your target market. Who are your ideal customers? What are their needs and preferences? What are the cultural, economic, and political factors that may affect your ability to do business in those markets? Once you have identified your target market, you can start to develop a plan for reaching them. This may involve developing relationships with local distributors or agents, attending trade shows and exhibitions, or leveraging digital marketing channels to reach potential customers.
Once you have developed a strategy for reaching your target market, you can start to develop a plan for financing your export activities. This may involve securing financing from banks or other financial institutions, seeking government grants or subsidies, or leveraging trade finance tools such as letters of credit or export credit insurance. It is important to have a clear understanding of your financing options and to develop a plan for managing your cash flow and mitigating financial risks.
An Exporter’s Roadmap provides exporters with a clear, step-by-step guide to the export process. The roadmap typically includes a series of milestones or checkpoints that exporters need to achieve in order to successfully export their products or services. Some of the key stages in an Exporter’s Roadmap may include:
- Market research: This involves researching potential markets, identifying potential customers, and developing a plan for reaching them.
- Product development: This involves adapting your products or services to meet the needs and preferences of your target market.
- Regulatory compliance: This involves ensuring that your products or services meet the regulatory requirements of your target market.
- Export documentation: This involves preparing the necessary documentation for exporting your products or services, such as export licenses, shipping documents, and customs declarations.
- Logistics: This involves managing the physical movement of your products or services from your warehouse to your customer’s location, including transportation, shipping, and storage.
- Payment and financing: This involves managing the financial aspects of your export activities, including payment terms, financing options, and managing currency risk.
An Exporter’s Roadmap can be a valuable tool for exporters, as it provides a clear and structured approach to the export process. By following the roadmap, exporters can ensure that they have considered all the key aspects of the export process and have developed a plan for managing the risks and challenges that may arise.
In conclusion, developing an export business plan and an Exporter’s Roadmap are two critical steps for exporters looking to succeed in international trade. By developing a clear strategy, identifying your target market, securing financing, and following a structured roadmap, exporters can increase their chances of success and achieve their international trade objectives. Whether you are a seasoned exporter or just starting out, these tools can help you to navigate the complex and ever-changing world of international trade.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published.
You may use these <abbr title="HyperText Markup Language">HTML</abbr> tags and attributes: <a href="" title=""> <abbr title=""> <acronym title=""> <b> <blockquote cite=""> <cite> <code> <del datetime=""> <em> <i> <q cite=""> <s> <strike> <strong>
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Please input characters displayed above.
Go to homepage business.govt.nz business.govt.nz
Business.govt.nz, create a good export plan.
Exporting can be a great way to tap into bigger markets. It can be exciting and rewarding, but also frustrating and financially risky. You can reduce the risk and uncertainty through market research, planning and getting financial support if needed.
Do as much research as possible before you plan. Think of research as an investment that helps you make more informed decisions, plan better, manage risks better and avoid mistakes.
Create your own export plan
Use our template that we created with NZTE to find detailed resources, guide your thinking, and record your plan.
Choose an overseas market
You may have a country in mind already. Perhaps you have a personal preference, or you know which markets are most promising for your business. Either way, you still need to do your research.
If you aren’t sure which market to choose, take these steps:
- Identify what matters most to your business. For example, distance may be important if your products are highly perishable. Being able to employ highly skilled staff may be critical if your company prides itself on excellent after sales service.
- Exclude markets that are politically unstable or where it may be hard to get profits out. Limit yourself to low-risk countries.
- Sort the remaining markets against the factors you identified in step 1.
Explore countries that New Zealand has free trade agreements with. Free trade agreements are arrangements between countries that remove barriers to trade, create opportunities and give businesses more certainty. For example, countries might not impose tariffs, or might streamline processes.
Learn about trade agreements and get help
Free trade agreements in force (external link) — Ministry of Foreign Affairs and Trade
Most successful exporters focus on one market before trying to dominate the world.
Australia is the logical first choice for many New Zealand exporters. It’s a good test market before exporting further away. Australia is close, English-speaking, politically stable, easy to reach and culturally similar. You can export New Zealand-made goods duty-free too, under New Zealand–Australia Closer Economic Relations.
Plan your research
Research takes time. How long depends on what you already know and how much time you have, but don’t be surprised if it takes many months.
Save yourself valuable time and money by prioritising the most important areas and being well prepared. Ask yourself these questions:
- What information do I need?
- Where can I find this information?
- Why do I need this information? What will I do with it?
- When do I need this information?
- What is this information worth in dollar terms?
- What is the likely cost of not getting this information?
Organise your information
Because research is so valuable and time consuming, make sure you save information safely and back it up.
Organising information by country is particularly useful. Use one notebook or folder for each country where you do business. Keep information updated, otherwise it will quickly stop being useful. Consider including things like product, advertising and labelling changes.
Comprehensive information will make your notebook or folder a rich first source of information when you make decisions. It can also be a good way for new staff to learn about the market.
Keep your research somewhere that more than one person can access. That way, you won’t lose it when someone leaves, and others can update it.
Do the research
Do online research, and talk to experts and other exporters. Ask for tips about doing business overseas. Find out how to adapt to local customs and protocols. Learn from others’ mistakes and successes.
Below are the most common types of information you’ll need about your potential market.
About your market
Find out the opportunities and challenges, eg:
- the market size, both in geographical size and dollar value
- market trends
- consumer spending patterns
- income per person (per capita income).
Such figures are important indicators of the market potential for your goods or services.
Don’t just look at country-level figures. Regions can vary significantly, and you may find urban–rural differences too.
What your customers want and how they think
Learn how to grow your business overseas with myNZTE's free tools and guides (external link) — myNZTE
Market insights for exporters (external link) — New Zealand Story
When you’ve decided on a market, sign up for market intelligence reports to keep on top of what’s happening.
Market Intelligence Reports (external link) — Ministry of Foreign Affairs and Trade
About your competition
Knowing your competition well is vital. Visit their sites. Find out what goods and services they offer. How do they market and price those goods and services? Will you need to adapt what you do?
Looking outwards at your market
How to research your market and competitors
About possible partners
If you’re thinking of partnering with another company to manufacture or distribute, research that company carefully first.
Do due diligence
Teaming up with other businesses
About trade and production statistics
Is the market for your type of goods and services growing or shrinking? Examine the trade and manufacturing statistics for your market over time to find out.
What’s made locally in that market? What’s imported, and from where?
Imports and exports (external link) — StatsNZ
About legal and regulatory requirements
- what taxes and duties you’ll need to pay
- what laws and regulations you’ll have to follow.
Laws and regulations in your potential market can be barriers because they make exporting costly, hard, or both. Barriers created by government policies and regulations often mean you have to:
- carry out administrative procedures
- restrict how much you can export
- license or label products a certain way
- store and protect data a certain way
- appoint certain types of people to your board
- procure materials a certain way
- limit the price of your goods or services.
The New Zealand Customs Service and freight forwarders can tell you what different countries require. Your local Chamber of Commerce may also be able to help with export documentation.
Exporting laws
Compliance and logistics 101 (external link) — myNZTE
Contact chambers of commerce (external link) — New Zealand Chamber Network
Export resources (external link) — New Zealand Customs Service
About intellectual property
Find out how to protect your intellectual property, copyright and trademarks. Protection is especially important in countries that tend not to respect intellectual property.
Protecting your intellectual property overseas
Copyright and trade marks (external link) — New Zealand Customs Service
About culture
Don’t forget culture. Being sensitive to local customs can make the difference between winning a contract or not. For example, in some cultures, taking a business card without studying it is considered disrespectful.
Find out the cultural and business dos and don’ts in your market, and think about how you’ll overcome cultural or language barriers.
Find other information if you need to
You can also get information from the following sources:
- foreign government websites
- business websites set up for specific countries
- your local Chamber of Commerce — they might have information and seminars for members at little or no cost. They might also have networks with Chambers of Commerce all around the world.
- the Export Library and Information Service — they offer free, up-to-date and reliable information. Find details like country profiles, foreign exchange rates and time zone information.
New Zealand Chamber Network (external link)
Export Library & Information Service (external link) — New Zealand School of Export
Think about intellectual property if you export a service
Stopping someone from copying your ideas is always important. Be extra careful when you sell a service, a process or a unique way of working.
Check the intellectual property law in the other country when you’re choosing an export market. Also do one of these things:
- register your patent in your overseas target market
- apply for a patent under the Patent Co-operation Treaty.
Applying for patents in different markets is worthwhile. The process includes searches for existing patents, so you’ll find out if you might infringe on any.
Filing international patent applications (external link) — New Zealand Intellectual Property Office
Learn more about finance and modelling
If you’d like to make better financial decisions, use our free resources to improve your understanding of finance and financial modelling.
Advanced finance: 7 key concepts
Financial models: Step-by-step guide
Get financial help
If you’re ready to export but aren’t sure you can afford it, you might be able to raise money. For example, you could:
- get funding from angel investors
- get investment from friends and family
- sell a share in your company
Use the Funding Explorer to find out your options (external link)
Or you could apply for grants, vouchers (subsidies) for training, or other forms of help.
Government grants and help for your established business
New Zealand Export Credit gives trade credit insurance and financial guarantees to exporters.
Who New Zealand Export credit is and how to apply (external link) — New Zealand Export Credit
Solutions for exporters (external link) — New Zealand Export Credit
We appreciate your feedback
"Rate this" is required
You must enable JavaScript to submit this form
2024 federal budget's key takeaways: Housing and carbon rebates, students and sin taxes
Budget sees nearly $53b in new spending over the next 5 years.

What's in the new federal budget?
Social sharing.
Finance Minister Chrystia Freeland today tabled a 400-page-plus budget her government is pitching as a balm for anxious millennials and Generation Z.
The budget proposes $52.9 billion in new spending over five years, including $8.5 billion in new spending for housing. To offset some of that new spending, Ottawa is pitching policy changes to bring in new revenue.
Here are some of the notable funding initiatives and legislative commitments in budget 2024.
Ottawa unloading unused offices to meet housing targets
One of the biggest pillars of the budget is its housing commitments. Before releasing the budget, the government laid out what it's calling Canada's Housing Plan — a pledge to "unlock" nearly 3.9 million homes by 2031.

The government says two million of those would be net new homes and it believes it can contribute to more than half of them.
It plans to do that by:
- Converting underused federal offices into homes. The budget promises $1.1 billion over ten years to transform 50 per cent of the federal office portfolio into housing.
- Building homes on Canada Post properties. The government says the 1,700-plus Canada Post offices across the country can be used to build new homes while maintaining postal services. The federal government says it's assessing six Canada Post properties in Quebec, Alberta and British Columbia for development potential "as a start."
- Rethinking National Defence properties. The government is promising to look at redeveloping properties and buildings on National Defence lands for military and civilian use.
- Building apartments. Ottawa is pledging a $15 billion top-up to the Apartment Construction Loan Program, which says it will build 30,000 new homes across Canada.
Taxing vacant land?
As part of its push on housing, the federal government also says it's looking at vacant land that could be used to build homes.
It's not yet committing to new measures but the budget says the government will consider introducing a new tax on residentially zoned vacant land.
- Freeland's new federal budget hikes taxes on the rich to cover billions in new spending
- Are you renting with no plans to buy? Here's what the federal budget has for you
The government said it plans to launch consultations on the measure later this year.
Help for students
There's also something in the budget for students hunting for housing.

The government says it will update the formula used by the Canada Student Financial Assistance Program to calculate housing costs when determining financial need, to better reflect the cost of housing in the current climate.
The government estimates this could deliver more aid for rent to approximately 79,000 students each year, at an estimated cost of $154.6 million over five years.
- Updated Federal budget's funding boost for defence spread out over multiple years
- Liberals pledge $9B in new money for Indigenous communities in 2024 budget
The government is also promising to extend increased student grants and interest-free loans, at an estimated total cost of $1.1 billion this year.
Increase in taxes on capital gains
To help cover some of its multi-billion dollar commitments, the government is proposing a tax hike on capital gains — the profit individuals make when assets like stocks and second properties are sold.
The government is proposing an increase in the taxable portion of capital gains, up from the current 50 per cent to two thirds for annual capital gains over $250,000.
New investment to lead 'housing revolution in Canada,' Freeland says
Freeland said the change would impact the wealthiest 0.1 per cent.
There's still some protection for small businesses. There's been a lifetime capital gains exemption which allows Canadians to exempt up to $1,016,836 in capital gains tax-free on the sale of small business shares and farming and fishing property. This June the tax-free limit will be increased to $1.25 million and will continue to be indexed to inflation thereafter, according to the budget.
The federal government estimates this could bring in more than $19 billion over five years, although some analysts are not convinced.
Disability benefit amounts to $200 per month
Parliament last year passed the Canada Disability Benefit Act, which promised to send a direct benefit to low-income, working-age people with disabilities.
Budget 2024 proposes funding of $6.1 billion over six years, beginning this fiscal year, and $1.4 billion per year ongoing, for a new Canada Disability Benefit.
Advocates had been hoping for something along the lines of $1,000 per month per person . They'll be disappointed.
According to the budget document, the maximum benefit will amount to $2,400 per year for low income individuals with disabilities between the ages of 18 and 64 — about $200 a month.
- Federal government plans to lease public lands for construction through new housing strategy
- Alberta premier says she's prepared to take Ottawa to court over housing deals
The government said it plans for the Canada Disability Benefit Act to come into force in June 2024 and for payments to start in July 2025.
Carbon rebate for small businesses coming
The federal government has heard an earful from small business advocates who accuse it of reneging on a promise to return a portion of carbon pricing revenues to small businesses to mitigate the tax's economic costs.
- What's behind the carbon tax, and does it work?
- Federal government scales back carbon tax rebates for small businesses
The budget proposes to return fuel charge proceeds from 2019-20 through 2023-24 to an estimated 600,000 businesses with 499 or fewer employees through a new refundable tax credit.
The government said this would deliver $2.5 billion directly to Canada's small- and medium-sized businesses.
Darts and vape pods will cost more
Pitching it as a measure to cut the number of people smoking and vaping, the Liberals are promising to raise revenues on tobacco and smoking products.
Starting Wednesday, the total tobacco excise duty will be $5.49 per carton. The government estimates this could increase federal revenue by $1.36 billion over five years starting in 2024-25.

The budget also proposes to increase the vaping excise duty rates by 12 per cent effective July 1. That means an increase of 12 to 24 cents per pod, depending on where you live.
- 'Stay the hell away from our kids': Health minister vows to restrict nicotine pouches — but how?
Ottawa hopes this increase in sin taxes will bring in $310 million over five years, starting in 2024-25.
More money for CBC
Heritage Minister Pascale St-Onge has mused about redefining the role of the public broadcaster before the next federal election . But before that happens, CBC/Radio-Canada is getting a top-up this year.

The budget promises $42 million more in 2024-25 for CBC/Radio-Canada for "news and entertainment programming." CBC/Radio-Canada received about $1.3 billion in total federal funding last year.
The government says it's doing this to ensure that Canadians across the country, including rural, remote, Indigenous and minority language communities, have access to independent journalism and entertainment.
Last year, the CBC announced a financial shortfall, cut 141 employees and eliminated 205 vacant positions. In a statement issued Tuesday, CBC spokesperson Leon Mar said the new funding means the corporation can balance its budget "without significant additional reductions this year."
Boost for Canada's spy agency

As the government takes heat over how it has handled the threat of foreign election interference, it's promising more money to bolster its spy service.
The Canadian Security Intelligence Service is in line to receive $655.7 million over eight years, starting this fiscal year, to enhance its intelligence capabilities and its presence in Toronto.
- CSIS chief defends his spies' work after PM casts doubt on reliability of agency's reports
- Trudeau says it's his job to question CSIS intelligence, call out 'contradictions'
The budget also promises to guarantee up to $5 billion in loans for Indigenous communities to participate in natural resource development and energy projects in their territories.
These loans would be provided by financial institutions or other lenders and guaranteed by the federal government, meaning Indigenous borrowers who opt in could benefit from lower interest rates, the budget says.
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

Catharine Tunney is a reporter with CBC's Parliament Hill bureau, where she covers national security and the RCMP. She worked previously for CBC in Nova Scotia. You can reach her at [email protected]
- Follow Cat on Twitter
Add some “good” to your morning and evening.
Your weekly guide to what you need to know about federal politics and the minority Liberal government. Get the latest news and sharp analysis delivered to your inbox every Sunday morning.

- Get Connected
- globalEDGE Blog
2024 Olympics: The Plan for a Healthier Production
Published: 4/10/2024 10:10:37 AM

Image Source
The Olympics need no introduction.
It is the largest sporting event in the world, hosting over 200 countries’ greatest athletes and all of their supporters. This significant event usually takes some ample preparation. For the city lucky enough to host, they have to make sure that they can handle the large number of events and viewers that will flock to the city for the games. One concern over the years has been the logistics behind the games. Many extravagant stadiums and venues were created in the past, but after the games, these large stadiums go to waste and find themselves with no function or practicality. As the concern for global warming rises, the Olympics also have seen a lot of backlash regarding their practices. The 2024 Summer Games, hosted in Paris, France, hope to be the first giant step in the opposite direction. The organizers of the games plan for this to be the most sustainable and environmentally conscious Olympics ever.
To understand why a new path for the Olympics is needed, we must look into the past to see the cause of raised concerns. Looking back on the 2008 games, China spent around 43 billion dollars on their stadiums. This is above the average since 2000, which is 21.2 billion . With these funds, China built some of the world’s most outstanding venues, including the “Bird’s Nest,” a state-of-the-art, 91,000-capacity stadium. The stadium hosted the opening and closing events, soccer games, and track and field events. While this event space has continued to boast thousands of visitors daily, it is the only one to remain in use since its creation.
Many other venues have lost their purpose and have gone unused since the games . This is known as an “Olympic hangover.” Single cities trying to accommodate a large influx of tourists and then trying to repurpose the venues after the fact has caused struggles that are hard to overcome. Beijing isn’t the only city that has dealt with this. The greatest economic example can be found in Montreal, Canada. After the 1976 Winter Games, Montreal was left with a bill of 1.4 billion dollars , much higher than the expected costs of 250 million. It took the city 30 years to pay off all of the debt. Like Beijing, it was also left with a large stadium needing new functions. These trends happen at every Olympics. Paris 2024 looks to change the status quo.
The Paris Olympics plans to use fewer resources and be more environmentally friendly than any Olympics before. The goal is to keep the emissions lower than half of what was recorded at the London games in 2012. One way to reach this goal is to work on the energy supply. Diesel fuel is the most typical fuel supply for sporting events. Working with companies like EDF, Paris plans to offer 100% renewable electric energy to power the games. Another way to combat the emissions has been to repurpose older structures rather than build new stand-alone structures. The pool from the 1924 Olympics is being repurposed and will be used for the games. 95% of the buildings used are either already built or temporary structures. The city has planted many trees for the past few years to offset more environmental impact. They also plan to buy carbon credits to offset all the emissions that they produce. Check out my other blog for more information on how carbon credit works.
Another big thing that Paris is looking to change is transportation during the Olympics. Another global edge blog, Paris’s Parking Price Surge by Paris Carter, details how they are trying to push the public closer to sustainable transportation. In partnership with Toyota and TMH France, they have also promoted using electric vehicles when it comes to working vehicles. Toyota supplies forklifts, and TMH sponsors the use of battery-powered pallet trucks.
Overall, this could be a massive step in legitimizing the process of significant sporting events. These international or domestic events are some of the most critical times of the year for marketing, revenue, and brand awareness. If the Paris Olympics can show an excellent example of sustainable practices, it would be a significant first step towards a new norm.
- Business (General)
Share this article
- Top Stories
- Stock Market
- BUYING RATES
- FOREIGN INTEREST RATES
- Philippine Mutual Funds
- Leaders and Laggards
- Stock Quotes
- Stock Markets Summary
- Non-BSP Convertible Currencies
- BSP Convertible Currencies
- US Commodity futures
- Infographics
- B-Side Podcasts
- Agribusiness
- Arts & Leisure
- Special Features
- Special Reports
- BW Launchpad

Singapore manufacturer plans air filter plant in Philippines

THE Department of Trade and Industry (DTI) said that a subsidiary of outsourcing fi rm Wagmi Solutions plans to establish a manufacturing facility in the Philippines to diversify operations away from Mexico and China.
In a statement on Monday, the DTI said it met with representatives of Wagmi on the sidelines of the US-Japan-Philippines Trilateral Meeting to discuss the project of unit NanoForge Technologies.
“The proposed facility will specialize in the production of high ef fi ciency particulate air (HEPA) fi lters, designed to remove a significant percentage of airborne particles, including dust, pollen, mold, bacteria, and viruses,” the DTI said.
“Nanoforge will manufacture and export these HEPA fi lters to its main customer, Medify Air — a major air purifier brand in the US,” it added.
The project is also expected to directly bene fi t coconut farmers, as the plant will use activated carbon sourced from coconut shells.
“We welcome NanoForge’s investment, which aligns perfectly with our goals to strengthen the coconut industry and create more jobs,” Trade Secretary Alfredo E. Pascual said.
“Through the Philippine Economic Zone Authority (PEZA), we are committed to ensuring that this venture is successful and bene fi cial for all parties involved,” he added.
According to the DTI, NanoForge’s air fi lters have residential, commercial, and industrial applications.
“In 2024, Wagmi registered NanoForge Technologies in the Philippines to produce HEPA fi lters for Medify Air, aiming to diversify manufacturing operations currently based in China and Mexico,” it added.
Following the meeting with the DTI, Wagmi will meet with PEZA officials to discuss the incentives under the Corporate Recovery and Tax Incentives for Enterprises Act.
These incentives include an income tax holiday, reduced corporate income tax, and tax- and duty-free imports of capital equipment, raw materials, and spare parts.
“Additionally, they provide value-added tax exemptions, a substantial domestic sales allowance, and exemption from local government taxes and fees,” the DTI said. — Justine Irish D. Tabile
RELATED ARTICLES MORE FROM AUTHOR
RCEF needs to be extended, given set percentage of tariffs, DA says
PSA hikes 1st quarter palay output estimate
Energy regulator ‘confident’ in resumption of normal reserve market operations soon

Shares down on PLDT’s budget overrun, Wall Street
Philippines ranks second on global cyberattack list, xtreme appliances maps store expansion.
A Software Billionaire Is Betting Big on an ‘Insane’ Climate Fix
By Brian Kahn
Moore’s Law says that the number of transistors crammed onto microchips will double every two years, magnifying computing power with a minimum cost increase. It’s been a key benchmark for technological progress since Intel Corporation co-founder Gordon Moore coined the rule in 1965.
The concept is instructive for Mike Cannon-Brookes, the billionaire co-founder of software giant Atlassian Corp. But that’s not the sector where it’s most applicable. In his estimation, technology’s most important law applies to the radical transformation of the energy system in the coming decades.
“Moore’s Law is not a law of physics, it’s a law of belief,” ...
Learn more about Bloomberg Law or Log In to keep reading:
Learn about bloomberg law.
AI-powered legal analytics, workflow tools and premium legal & business news.
Already a subscriber?
Log in to keep reading or access research tools.

COMMENTS
According to the United States International Trade Commission (USITC), the total value of US goods and services exports in 2022 was approximately $2.09 trillion, and the value of imports was approximately $3.0 trillion. This resulted in a trade deficit of roughly $948.1 billion for the year.
The financial plan is a critical section of the export business plan, detailing the expected costs, revenue projections, and financial forecasts related to your international expansion. It should include budgets, cash flow statements, break-even analysis, and return on investment calculations. This information helps stakeholders, including ...
4. Write an Import-export business plan. An Import-export business plan lets you understand the facts, limits, and goals of selling internationally. You can use it to set clear targets, plan when to do things, and track your progress. It can also help your team stay focused on reaching these goals.
Here are 6 steps to writing the perfect business plan for your import-export company: 1. Start with an Executive Summary. Think of this as the ultimate introduction to your business. It should concisely delineate exactly what you want as a business owner. Remember, you need to know where your business is going.
Starting an export business doesn't have to be difficult. With the help of Cargo Export USA, your business will be operational and earning money at a rapid pace. Let us help you unlock the door to international success. Connect with us through the site or call our team at (866) 301-0635 .
Import-export merchant (or free agent) - this type of business buys merchandise from a manufacturer, and resells that merchandise around the world. In addition to explaining the type of import-export business you will operate, the Company Analysis section of your business plan needs to provide background on the business.
With this template, you can create a comprehensive business plan that covers all aspects of your import-export operations, including: Outlining your strategies and goals for entering and expanding in international markets. Identifying target markets and customers to effectively position your products or services.
Executive Summary: Start your business plan with a concise executive summary that provides an overview of your import/export venture. Clearly define your business goals, target market, competitive advantage, and a brief description of the products or services you intend to import or export. Market Analysis: Conduct a thorough market analysis to ...
Explore the Globe. A strong export business plan requires market research to identify which global markets hold the most potential for your company's product or service. Trade statistics can ...
Vending Services Business Plan. Chef Vending is a start-up vending machine and commercial food and beverage dispensing equipment company. Give your import/export business a leg up on the competition by writing a winning business plan. Get a head start by checking out these sample business plans for fitness equipment importers, artificial ...
Here is a free business plan sample for an import/export company. January 29, 2024. If you're considering entering the dynamic world of international trade but are unsure how to start, you've landed on the right page. In the content that follows, we will present to you a comprehensive sample business plan tailored for an import/export company.
The key is developing an exporting business plan, as outlined below. Export Plan Basics. Once you've decided to sell abroad or pursue new export markets, a well-thought out export plan increases your chances that the best options will be chosen, resources will be used wisely, and execution will lead to a successful result. ...
Export.gov, the U.S. federal government's export portal, also links to many resources, including the following: If your business is just getting started, contact your nearest Small Business Development Center (SBDC) or Score representative for help in developing an overall business plan. If you are an established firm with a record of ...
2. Pick a product to import or export. The next step in starting an import/export business is to find a product or industry you are passionate about and that you think could sell in international ...
June 28 , 2016 Office of Small Business. The U.S. Small Business Administration (SBA) has created a hands-on exporting preparation guide and innovative tool called the Export Business Planner. It is designed to serve as a roadmap for creating an export business plan, exploring foreign markets and financing, developing a marketing plan, and more.
The Export Business Plan analysis leads to an identification of the economic, policies and social trends etc, which may affect the international evolution of the sector where the company plans to develop its activity. Once the principal strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats are identified you must extract some conclusions and at the ...
An estimated 66% of small business owners believe technology can help subdue the top three barriers to exporting, according to a report by Google and the U.S. Chamber of Commerce. Digital tools assist with: Communications challenges. Finance and payment collection. Tariffs and customs issues.
Learn How To Export. Small, medium, and large businesses all have the amazing opportunity to expand internationally, however there are several steps that must be taken to ensure that your company is ready to export. Find out the first steps to take by watching the informative series on export planning called "Get Ready to Export." Export ...
Your business plan evolves alongside the experience. Regular review and optimization ensure congruence with operational realities. Business Plan Template for an Import/Export Business. I. Executive Summary: Overview: Briefly describe your Import/Export business, mission, and vision. Objectives: Key business goals and milestones to achieve.
The steps of the export business plan are as follows; -Approval of Top Management Must Be Obtained. Before the research is done and the plan is written, the person or department responsible for the target market entry strategy should inform the senior management about this and get approval. By doing this, it can be understood whether the key ...
OPENING GLOBAL DOORS FOR BUSINESS IN WISCONSIN. For hands-on exporting assistance, tools and resources—plus in-market representatives covering 96 countries and territories around the world—look to WEDC. WEDC can help you with research and planning to successfully launch or expand an exporting strategy. And with more than 600 global ...
10. Exporting Local Artworks. Promote your region's artistic talent by exporting local artworks, such as paintings, sculptures, or handmade crafts. This export business idea targets art collectors, interior designers, and galleries, showcasing the cultural and artistic expressions of your home country. 11.
An export business plan is a comprehensive document that outlines an exporter's objectives, strategies, and tactics for exporting goods or services to foreign markets. An Exporter's Roadmap, on the other hand, is a step-by-step guide that outlines the key stages of the export process and provides exporters with a clear roadmap for success. ...
Create a good export plan. Exporting can be a great way to tap into bigger markets. It can be exciting and rewarding, but also frustrating and financially risky. You can reduce the risk and uncertainty through market research, planning and getting financial support if needed. Do as much research as possible before you plan.
CONCOLESE officials are divided about setting export restrictions as technologies for cobalt-free electric vehicle batteries rapidly advance. The Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) has sought input from several international industry organizations and foreign research bodies on potentially implementing cobalt export quotas to drive up prices.
The government estimates this could increase federal revenue by $1.36 billion over five years starting in 2024-25. A man exhales vapor while using a vape pen in Vancouver on Nov. 24, 2020. (Ben ...
As the concern for global warming rises, the Olympics also have seen a lot of backlash regarding their practices. The 2024 Summer Games, hosted in Paris, France, hope to be the first giant step in the opposite direction. The organizers of the games plan for this to be the most sustainable and environmentally conscious Olympics ever.
THE Department of Trade and Industry (DTI) said that a subsidiary of outsourcing fi rm Wagmi Solutions plans to establish a manufacturing facility in the Philippines to diversify operations away from Mexico and China.. In a statement on Monday, the DTI said it met with representatives of Wagmi on the sidelines of the US-Japan-Philippines Trilateral Meeting to discuss the project of unit ...
Atlassian is an enterprise software giant with a global footprint, but while Cannon-Brookes' efforts to address climate change have made him a household name in Australia, he still has a relatively low profile elsewhere. If his plans to make Australia a renewable energy-exporting powerhouse come true, though, it would make him one of the leading figures in the energy transition.