Search Modern Language Association
Log in to Modern Language Association
- Annual Report
- MLA News Digest Archive
- Mission and Strategic Priorities
- Advertising
- Join the MLA Mailing List
- The MLA Staff
- Delegate Assembly
- Executive Council
- Related Organizations
- Donate to the MLA
- Leading Contributors to the MLA
- MLA Webinars Site
- ADE-ALD Summer Seminar and MAPS Leadership Institute
- MLA Convention Seminars
- Presidential Theme for the 2025 Convention
- 2025 Convention Program Forms
- A Letter from MLA Executive Director Paula M. Krebs Urging Support of Convention Attendance
- MLA Exhibit Hall
- Access Guidelines for MLA Convention Session Organizers and Presenters
- Calls for Papers
- Policies for Forums and Allied Organizations
- Procedures for Organizing Convention Meetings
- Exhibiting at the 2025 MLA Convention
- Sponsorship and Marketing
- Convention History
- Appropriate Conduct at the MLA Annual Convention
- Membership Benefits
- Join the MLA
- MLA Academic Program Services
- MLA Newsletter
- MLA Strategic Partnership Network
- Member Resources
- Member Search
- Renew Your Membership

MLA Handbook Plus
- Buy the MLA Handbook
- MLA Style Support
Publications
- Backlist Titles
- Forthcoming Titles
- Library Subscriptions
- What We Publish
- What We Value
- How to Propose a Volume
- Contribute to a Book in Development
- Request Your Complimentary MLA Handbook
- About the MLA International Bibliography
- Free Online Course
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Submitting Work to the MLA International Bibliography
- Tutorial Videos
- Using the MLA International Bibliography
- A Video from Paula Krebs about Humanities Successes
- Executive Council Actions
- MLA Pathways
- Resources on Academic Freedom, Free Speech, and the Right to Protest
- Resources on Collective Action
- 2024 MLA Institutes on Reading and Writing Pedagogy
- Career Resources
- Conferences, Fellowships, and Announcements
- MLA Grants and Awards
- MLA Professional Development Webinars
- MLA Sit and Write Sessions
- MLA Webinars on the Public Humanities
- Reimagining Humanities Coursework for Career Readiness: A Workshop
- MLA Language Map
- Reports and Professional Guidelines

Request Your Free Member Copy

Buy the MLA Handbook

The MLA Style Center
What is mla style.
Building confidence in the information and ideas we share with one another is perhaps more important today than ever before, and for nearly a century it has been the driving principle behind MLA style, a set of standards for writing and documentation used by writers to find and evaluate information, alert their audience to the trustworthiness of their findings through citation, and shape the expression of their ideas in conversation with others.
Resources for MLA Style
Our new, subscription-based digital platform, MLA Handbook Plus is
- Trusted: The only authorized subscription-based digital resource featuring the latest edition of the MLA Handbook is available for unlimited simultaneous users.
- Evolving: Get the same content as the print edition, plus seamless annual updates and forthcoming additional resources such as videos and companion titles.
- Dynamic: Features an easy-to-search interface, cross-linking of related material, and a split view that lets students see illustrations while reading corresponding content.
- Flexible: Whether on campus, at home, or in a coffee shop, students can access the platform from anywhere—perfect for remote or hybrid learning environments.
- Affordable: Tiered pricing model based on full-time undergraduate enrollments in US higher education institutions (with custom pricing options for secondary schools, consortia, international schools, campus systems, and other organizations).
- Accessible: Meets current accessibility standards—ensuring that learning MLA style is available to all.
Contact [email protected] for more info.
MLA Handbook , 9th Edition
The ninth edition of the MLA Handbook , published in spring 2021, builds on the MLA's unique approach to documenting sources using a template of core elements—facts common to most sources, like author, title, and publication date—that allows writers to cite any type of work, from books, e-books, and journal articles in databases to song lyrics, online images, social media posts, dissertations, and more. With this focus on source evaluation as the cornerstone of citation, MLA style promotes the skills of information and digital literacy so crucial today. The new edition offers
- New chapters on grammar, punctuation, capitalization, spelling, numbers, italics, abbreviations, and principles of inclusive language
- Guidelines on setting up research papers in MLA format with updated advice on headings, lists, and title pages for group projects
- Revised, comprehensive, step-by-step instructions for creating a list of works cited in MLA format that are easier to learn and use than ever before
- A new appendix with hundreds of example works-cited-list entries by publication format, including websites, YouTube videos, interviews, and more
- Detailed examples of how to find publication information for a variety of sources
- Newly revised explanations of in-text citations, including comprehensive advice on how to cite multiple authors of a single work
- Detailed guidance on using notes in MLA style
- Instructions on quoting, paraphrasing, summarizing, and avoiding plagiarism
- Annotated bibliography examples
- Numbered sections throughout for quick navigation
- Advanced tips for professional writers and scholars
The MLA Style Center offers free online resources on MLA style, including an interactive MLA format template, answers to common questions on Ask the MLA, advice from the MLA editors, and more. Get updates by signing up for The Source newsletter, and follow us on Twitter @MLAstyle .
Explore our new content updates to the MLA Handbook Plus platform!
What’s New on MLA Handbook Plus ?
What is mla handbook plus .
MLA Handbook Plus is a new, subscription-based digital product providing online access to the ninth edition of the MLA Handbook. To learn more about MLA Handbook… Read More
What’s New in the Ninth Edition of the MLA Handbook (Spring 2021)
Published in April 2021, the ninth edition of the MLA Handbook works as both a textbook and a reference guide. You can order a copy… Read More
MLA Guide to Digital Literacy , 2nd Edition: An Interview with the Author
by Ellen C. Carillo
Ellen C. Carillo talks to the MLA about the MLA Guide to Digital Literacy , second edition. Read More
How do I alphabetize Irish surnames in the works-cited list?
This post explains how to alphabetize Irish surnames Read More
Teaching Resources
A Century of Queer Korean Fiction : An Interview with Samuel Perry
Toward Educational Justice: An Interview with the Editors of Teaching Literature and Writing in Prisons
Henrique Maximiano Coelho Neto’s Sphinx: A Neo-Gothic Novel from Brazil : An Interview with M. Elizabeth Ginway
A Reflection on Disability Studies: Enabling the Humanities on Its Twentieth Anniversary
Teaching Claire de Duras’s Ourika
Teaching Nineteenth-Century Activist Rhetorics Today: An Interview
How and Why to Teach Late-Twentieth-Century Mexicana and Chicana Writers: An Interview
Advice from the Editors
Similar but Different: Using Compare with and Compare to
Forego versus Forgo
Was and Were with the Subjunctive
Their , There , and They’re : Learn the Difference
Attributive Nouns; or, Why There Is Sometimes No Apostrophe in Terms Such As Teachers Union
Terms for Key Concepts
Laying versus Lying
Getting to the Bottom of Principle and Principal
Ask the MLA
How do i alphabetize a works-cited-list entry that begins with a hashtag or another symbol.
The MLA recommends that writers should “ignore symbols when alphabetizing” (“How”). This includes hashtags. Thus, if an entry begins with a hashtag or another symbol,… Read More
How do I cite a work accessed through Wayback Machine ?
Wayback Machine is an archive of websites that lives on the Internet Archive ’s site, so you would treat the Internet Archive as the container of… Read More
- Plagiarism and grammar
- Citation guides
MLA Citation Generator
Keep all of your citations in one safe place
Create an account to save all of your citations
Don't let plagiarism errors spoil your paper
The complete guide to mla & citations, what you’ll find in this guide.
This page provides an in-depth overview of MLA format. It includes information related to MLA citations, plagiarism, proper formatting for in-text and regular citations, and examples of citations for many different types of sources.
Looking for APA? Check out the Citation Machine’s guide on APA format . We also have resources for Chicago citation style as well.
How to be a responsible researcher or scholar
Putting together a research project involves searching for information, disseminating and analyzing information, collecting information, and repurposing information. Being a responsible researcher requires keeping track of the sources that were used to help develop your research project, sharing the information you borrowed in an ethical way, and giving credit to the authors of the sources you used. Doing all of these things prevents plagiarism.
What is Plagiarism?
Plagiarism is the act of using others’ information without giving credit or acknowledging them. There are many examples of plagiarism. Completely copying another individual’s work without providing credit to the original author is a very blatant example of plagiarism. Plagiarism also occurs when another individual’s idea or concept is passed off as your own. Changing or modifying quotes, text, or any work of another individual is also plagiarism. Believe it or not, you can even plagiarize yourself! Reusing a project or paper from another class or time and saying that it’s new is plagiarism. One way to prevent plagiarism is to add citations in your project where appropriate.
What is a Citation?
A citation shows the reader of your project where you found your information. Citations are included in the body of a project when you add a quote to your project. Citations are also included in the body when you’re paraphrasing another individual’s information. These citations in the body of a research paper are called in-text citations. They are found directly next to the information that was borrowed and are very brief to avoid causing distraction while reading a project. These brief citations include the last name of the author and a page number. Scroll down for an in-depth explanation and examples of MLA in-text citations.
In-text citations provide us with a brief idea as to where you found your information, though they usually don't include the title and other components. Look on the last page of a research project to find complete citations.
Complete citations are found on what MLA calls a works-cited list, which is sometimes called an MLA bibliography. All sources that were used to develop a research project are found on the works-cited list. Complete citations are also created for any quotes or paraphrased information used in the text. Complete citations include the author’s name, the title, publisher, year published, page numbers, URLs, and a few other pieces of information.
Looking to create your citations in just a few clicks? Need an MLA format website or book citation? Visit Citation Machine.net! Our Citation Machine MLA generator, which is an MLA citation website, will create all of your citations in just a few clicks. Click here to see more styles .
Why Does it Matter?
Citing your sources is an extremely important component of your research project. It shows that you’re a responsible researcher and that you located appropriate and reputable sources that support your thesis or claim. In addition, if your work ends up being posted online or in print, there is a chance that others will use your research project in their own work!
Scroll down to find directions on how to create citations.
How the Modern Language Association Helps You Become a Responsible Researcher
What is mla format.
The Modern Language Association is an organization that was created to develop guidelines on everything language and literature related. They have guidelines on proper grammar usage and research paper layouts. In addition, they have English and foreign language committees, numerous books and journal publications, and an annual conference. They are not connected with this guide, but the information here reflects the association’s rules for formatting papers and citations.
What are citations?
The Modern Language Association is responsible for creating standards and guidelines on how to properly cite sources to prevent plagiarism. Their style is most often used when writing papers and citing sources in the liberal arts and humanities fields. “Liberal arts” is a broad term used to describe a range of subjects including the humanities, formal sciences such as mathematics and statistics, natural sciences such as biology and astronomy, and social sciences such as geography, economics, history, and others. The humanities focuses specifically on subjects related to languages, art, philosophy, religion, music, theater, literature, and ethics.
Believe it or not, there are thousands of other types of citation styles. While this citation style is most often used for the liberal arts and humanities fields, many other subjects, professors, and schools prefer citations and papers to be styled in MLA format.
What’s the difference between a bibliography and a works-cited list?
Great question. The two terms cause a lot of confusion and are consistently misused not only by students but educators as well! Let’s start with what the two words mean.
A bibliography displays the sources the writer used to gain background knowledge on the topic and also research it in-depth. Before starting a research project, you might read up on the topic in websites, books, and other sources. You might even dive a bit deeper to find more information elsewhere. All of these sources you used to help you learn about the topic would go in an MLA format bibliography. You might even include other sources that relate to the topic.
A works-cited list displays all of the sources that were mentioned in the writing of the actual paper or project. If a quote was taken from a source and placed into a research paper, then the full citation goes on the works-cited list.
Both the works-cited list and bibliography go at the end of a paper. Most teachers do not expect students to hand in both a bibliography AND a works-cited list. Teachers generally expect to see a works-cited list, but sometimes erroneously call it a bibliography. If you’re not sure what your teacher expects, a page in MLA bibliography format, a works-cited list, or both, ask for guidance.
Why do we use this MLA style?
These specific guidelines and standards for creating citations were developed for numerous reasons. When scholars and researchers in literature, language, and numerous other fields all cite their sources in the same manner, it makes it easier for readers to look at a citation and understand the different components of a source. By looking at an MLA citation, we can see who the author is, the title of the source, when it was published, and other identifiable pieces of information.
Imagine how difficult it would be to understand the various components of a source if we didn’t all follow the same guidelines! Not only would it make it difficult to understand the source that was used, but it would also make it difficult for readers to locate it themselves. This streamlined process aides us in understanding a researcher’s sources.
How is the new version different than previous versions?
This citation style has changed dramatically over the past couple of years. The MLA Handbook is currently in its 9th edition.
The new version expands upon standards previously set in the 8th edition of the MLA Handbook, including the core elements. The structure of citations remains the same, but some formatting guidance and terminology have changed.
- DOI numbers are now formatted as https://doi.org/xx.xxxx/xxx.xxxx.xxxx
- Seasons in publishing daters are lowercased: spring 2020
- The term “optional elements” is now “supplemental elements”
- “Narrative in-text citations” are called “citations in prose”
In addition, new information was added on the following:
- Hundreds of works-cited-list entries
- MLA formatting for papers
- Punctuation, spelling, and other mechanics of prose
- Chapter on inclusive language
- Notes (bibliographic and content)
For more information on MLA 9, click here .
A Deeper Look at Citations
What do they look like.
There are two types of citations. The first is a full, or complete, citation. These are found at the end of research projects. These citations are usually listed in alphabetical order by the author’s last names and include all of the information necessary for readers to be able to locate the source themselves.
Full citations are generally placed in this MLA citation format:
%%Last name of the author, First name of the author. “Source’s Title.” Container’s Title, roles and names of any other individuals who helped contribute to the source, the version of the source, any numbers associated with the source, the name of the publisher, the date the source was published, the location where individuals can find the source themselves (usually a DOI, URL, or page range).
There are times when additional information is added into the full citation.
Not sure how to transfer the information from your source into your citation? Confused about the term, “containers”? See below for information and complete explanations of each citation component.
The second type of citation, called an “in-text citation,” is included in the main part, or body, of a project when a researcher uses a quote or paraphrases information from another source. See the next section to find out how to create in-text citations.
What are in-text citations?
As stated above, in-text citations are included in the main part of a project when using a quote or paraphrasing a piece of information from another source. We include these types of citations in the body of a project for readers to quickly gain an idea as to where we found the information.
These in-text citations are found directly next to the quote or paraphrased information. They contain a small tidbit of the information found in the regular MLA citation. The regular, or complete, citation is located at the end of a project, on the works-cited list.
Here’s what a typical in-text citation looks like:
In the book The Joy Luck Club, the mother uses a vast amount of Chinese wisdom to explain the world and people’s temperaments. She states, “Each person is made of five elements…. Too much fire and you have a bad temper...too little wood and you bent too quickly...too much water and you flowed in too many directions” (Tan 31).
This specific in text citation, (Tan 31), is called an MLA parenthetical citation because the author’s name is in parentheses. It’s included so the reader sees that we are quoting something from page 31 in Tan’s book. The complete, regular citation isn’t included in the main part of the project because it would be too distracting for the reader. We want the reader to focus on our work and research, not get caught up on our sources.
Here’s another way to cite in the text:
In Tan’s novel The Joy Luck Club, the mother uses a vast amount of Chinese wisdom to explain the world and people’s temperaments. She states, “Each person is made of five elements... Too much fire and you have a bad temper... too little wood and you bent too quickly... too much water and you flowed in too many directions" (31).
If the reader would like to see the source’s full information, and possibly locate the source themselves, they can refer to the last part of the project to find the regular citation.
The regular citation, at the end of the project looks like this:
%%Tan, Amy. The Joy Luck Club. Penguin, 1989, p. 31.
Notice that the first word in the full citation (Tan) matches the “Tan” used in the body of the project. It’s important to have the first word of the full citation match the term used in the text. Why? It allows readers to easily find the full citation on the works-cited list.
If your direct quote or paraphrase comes from a source that does not have page numbers, it is acceptable to place a line number (use line or lines), paragraph number (use the abbreviation par. or pars.), sections (sec. or secs.), or chapters (ch. or chs.). Only use these other terms if they are actually labeled on the source. If it specifically says on the source, “Section 1,” for example, then it is acceptable to use “sec. 1” in the in-text citation.
If there are no numbers to help readers locate the exact point in the source, only include the author’s last name.
To determine how to create in-text citations for more than one author, no authors, or corporate authors, refer to the “Authors” section below.
More about quotations and how to cite a quote:
- Use quotes from outside sources to help illustrate and expand on your own points. The majority of your paper should be your own writing and ideas.
- Include the quote exactly as you found it. It is okay to use only certain words or phrases from the quote, but keep the words (spelling and capitalization) and punctuation the same.
- It is acceptable to break up a direct quote with your own writing.
Example from a movie:
Dorothy stated, "Toto," then looked up and took in her surroundings, "I’ve a feeling we’re not in Kansas anymore" ( Wizard of Oz ).
- The entire paper should be double-spaced, including quotes.
- If the quote is longer than four lines, it is necessary to make a block quote. Block quotes show the reader that they are about to read a lengthy amount of text from another source.
- Start the quote on the next line, half an inch from the left margin.
- Do not use any indents at the beginning of the block quote.
- Only use quotation marks if there are quotation marks present in the source.
- If there is more than one paragraph in the block quote, indent the beginning of the paragraphs after the first one an additional half an inch from the left margin.
- Add your in-text citation after the final period of the block quote. Do not add an additional period after the parenthetical citation.
While his parents sat there in surprise, Colton went onto say:
“Cause I could see you,” Colon said matter-of-factly. “I went up and out of my body and I was looking down and I could see the doctor working on my body. And I saw you and Mommy. You were in a little room by yourself, praying; and Mommy was in a different room, and she was praying and talking on the phone.” (Burpo xxi)
How to create a paraphrase:
As stated above, the majority of your paper should be your own writing and ideas. It’s acceptable to include quotes, but they shouldn’t crowd your paper. If you’re finding that you’re using too many quotes in your paper, consider adding paraphrases. When you reiterate a piece of information from an outside source in your own words, you create a paraphrase.
Here’s an example:
Readers discover in the very first sentence of Peter Pan that he doesn’t grow up (Barrie 1).
What paraphrases are:
- Recycled information in the paper writer’s own words and writing style.
- They’re still references! Include an in-text citation next to the paraphrased information.
What paraphrases are not:
- A copy and pasted sentence with a few words substituted for synonyms.
Confused about whether footnotes and endnotes should be used?
Footnotes and endnotes are completely acceptable to use in this style. Use a footnote or endnote if:
- Adding additional information will help the reader understand the content. This is called a content note .
- You need to cite numerous sources in one small section of your writing. Instead of clogging up a small paragraph with in-text citations (which could cause confusion for the reader), include a footnote or endnote. This is called a bibliographic note .
Keep in mind that whether you choose to include in-text citations or footnotes/endnotes, you need to also include a full reference on the MLA format works-cited list.
Content note example:
Even Maurice Sendak’s work (the mastermind behind Where the Wild Things Are and numerous other popular children’s picture books) can be found on the banned books list. It seems as though nobody is granted immunity. 1
- In the Night Kitchen ’s main character is nude on numerous pages. Problematic for most is not the nudity of the behind, but the frontal nudity.
Work Cited:
%%Sendak, Maurice. In The Night Kitchen. Harper Collins, 1996.
Bibliographic note example:
Dahl had a difficult childhood. Both his father and sister passed away when he was a toddler. He was then sent away by his mother to boarding school (de Castella). 1
- Numerous books, such as Matilda, James and the Giant Peach, and The BFG, all feature characters with absent or difficult parents.
MLA Works Cited:
Include 4 full citations for: de Castella’s article, Matilda, James and the Giant Peach, and The BFG .
Don’t forget to create full, or regular citations, and place them at the end of your project.
If you need help with in-text and parenthetical citations, CitationMachine.net can help. Our MLA citation generator is simple and easy to use!
Common Knowledge: What Is It and How Will It Affect My Writing?
Footnotes, endnotes, references, proper structuring. We know it’s a lot. Thankfully, you don’t have to include a reference for EVERY piece of information you add to your paper. You can forget about including a reference when you share a piece of common knowledge.
Common knowledge is information that most people know. For example, these are a few facts that are considered common knowledge:
- The Statue of Liberty is located in New York City
- Tokyo is the capital of Japan
- Romeo and Juliet is a play written by William Shakespeare
- English is the language most people speak in England
- An elephant is an animal
We could go on and on. When you include common knowledge in your paper, omit a reference. One less thing to worry about, right?
Before you start adding tons of common knowledge occurrences to your paper to ease the burden of creating references, we need to stop you right there. Remember, the goal of a research paper is to develop new information or knowledge. You’re expected to seek out information from outside sources and analyze and distribute the information from those sources to form new ideas. Using only common knowledge facts in your writing involves absolutely zero research. It’s okay to include some common knowledge facts here and there, but do not make it the core of your paper.
If you’re unsure if the fact you’re including is common knowledge or not, it doesn’t hurt to include a reference. There is no such thing as being overly responsible when it comes to writing and citing.
Wikipedia - Yay or Nay?
If you’re wondering whether it’s okay to use Wikipedia in your project, the answer is, it depends.
If Wikipedia is your go-to source for quick information on a topic, you’re not alone. Chances are, it’s one of the first websites to appear on your results page. It’s used by tons of people, it’s easily accessible, and it contains millions of concise articles. So, you’re probably wondering, “What’s the problem?”
The issue with Wikipedia is that it’s a user-generated site, meaning information is constantly added and modified by registered users. Who these users are and their expertise is somewhat of a mystery. The truth is anyone can register on the site and make changes to articles.
Knowing this makes some cringe, especially educators and librarians, since the validity of the information is questionable. However, some people argue that because Wikipedia is a user-generated site, the community of registered users serve as “watchdogs,” ensuring that information is valid. In addition, references are included at the bottom of each article and serve as proof of credibility. Furthermore, Wikipedia lets readers know when there’s a problem with an article. Warnings such as “this article needs clarification,” or “this article needs references to prove its validity” are shared with the reader, thus promoting transparency.
If you choose to reference a Wikipedia article in your research project, and your teacher or professor says it’s okay, then you must reference it in your project. You would treat it just as you would with any other web source.
However, you may want to instead consider locating the original source of the information. This should be fairly easy to do thanks to the references at the bottom of each article.
Specific Components of a Citation
This section explains each individual component of the citation, with examples for each section for full citations and in-text citations.
Name of the author
The author’s name is usually the first item listed in the MLA citation. Author names start with the last name, then a comma is added, and then the author’s first name (and middle name if applicable) is at the end. A period closes this information.
Here are two examples of how an author’s name can be listed in a full citation:
Twain, Mark.
Poe, Edgar Allan.
For in-text:
(Author’s Last name page number) or Author’s Last name... (page).
Wondering how to format the author’s name when there are two authors working jointly on a source? When there are two authors that work together on a source, the author names are placed in the order in which they appear on the source. Place their names in this format:
Author 1’s Last Name, First name, and Author 2’s First Name Last Name.
Here are two examples of how to cite two authors:
Clifton, Mark, and Frank Riley.
Paxton, Roberta J., and Michael Jacob Fox.
(Author 1’s Last name and Author 2’s Last name page number) or Author 1’s Last name and Author 2’s Last name... (page).
There are many times when three or more authors work together on a source. This often happens with journal articles, edited books, and textbooks.
To cite a source with three or more authors, place the information in this format:
Author 1’s Last name, First name, et al.
As you can see, only include the first author’s name. The other authors are accounted for by using “et al.” In Latin, et al. is translated to “and others.” If using the Citation Machine citation generator, this abbreviation is automatically added for you.
Here’s an example of a citation for three or more authors:
%%Warner, Ralph, et al. How to Buy a House in California. Edited by Alayna Schroeder, 12th ed., Nolo, 2009.
(Author 1’s Last name et al. page number)
Is there no author listed on your source? If so, exclude the author’s information from the citation and begin the citation with the title of the source.
For in-text: Use the title of the source in parentheses. Place the title in italics if the source stands alone. Books and films stand alone. If it’s part of a larger whole, such as a chapter in an edited book or an article on a website, place the title in quotation marks without italics.
( Back to the Future )
(“Citing And Writing”)
Other in-text structures:
Authors with the same last name in your paper? MLA essay format requires the use of first initials in-text in this scenario.
Ex: (J. Silver 45)
Are you citing more than one source by the same author? For example, two books by Ernest Hemingway? Include the title in-text.
Example: (Hemingway, For Whom The Bell Tolls 12).
Are you citing a film or song? Include a timestamp in the format of hours:minutes:seconds. ( Back to the Future 00:23:86)
Was the source found on social media, such as a tweet, Reddit, or Instagram post? If this is the case, in an MLA format paper, you are allowed to start the citation with the author’s handle, username, or screen name.
Here is an example of how to cite a tweet:
%%@CarlaHayden. “I’m so honored to talk about digital access at @UMBCHumanities. We want to share the @libraryofcongress collection.” Twitter , 13 Apr. 2017, 6:04 p.m., twitter.com/LibnOfCongress/status/852643691802091521.
While most citations begin with the name of the author, they do not necessarily have to. Quite often, sources are compiled by editors. Or, your source may be done by a performer or composer. If your project focuses on someone other than the author, it is acceptable to place that person’s name first in the citation. If you’re using the MLA works cited generator at Citation Machine.net, you can choose the individual’s role from a drop-down box.
For example, let’s say that in your research project, you focus on Leonardo DiCaprio’s performances as an actor. You’re quoting a line from the movie Titanic in your project, and you’re creating a complete citation for it in the works-cited list.
It is acceptable to show the reader that you’re focusing on Leonardo DiCaprio’s work by citing it like this in the MLA works-cited list:
%%DiCaprio, Leonardo, performer. Titanic . Directed by James Cameron. Paramount, 1997.
Notice that when citing an individual other than the author, place the individual’s role after their name. In this case, Leonardo DiCaprio is the performer.
This is often done with edited books, too. Place the editor’s name first (in reverse order), add a comma, and then add the word editor.
If you’re still confused about how to place the authors together in a citation, the tools at CitationMachine.net can help! Our website is easy to use and will create your citations in just a few clicks!
Titles and containers
The titles are written as they are found on the source and in title form, meaning the important words start with a capital.
Here’s an example of a properly written title:
Practical Digital Libraries: Books, Bytes, and Bucks.
Wondering whether to place your title in italics or quotation marks? It depends on whether the source sits by itself or not. If the source stands alone, meaning that it is an independent source, place the title in italics. If the title is part of a larger whole, place the title of the source in quotation marks and the source it is from in italics.
When citing full books, movies, websites, or albums in their entirety, these titles are written in italics.
However, when citing part of a source, such as an article on a website, a chapter in a book, a song on an album, or an article in a scholarly journal, the part is written with quotation marks and then the titles of the sources that they are found in are written in italics.
Here are some examples to help you understand how to format titles and their containers.
To cite Pink Floyd’s entire album, The Wall , cite it as:
%%Pink Floyd. The Wall. Columbia, 1979.
To cite one of the songs on Pink Floyd’s album in MLA formatting, cite it as:
%%Pink Floyd. “Another Brick in the Wall (Part I).” The Wall, Columbia, 1979, track 3.
To cite a fairy tale book in its entirety, cite it as:
%%Colfer, Chris. The Land of Stories. Little Brown, 2016.
To cite a specific story or chapter in the book, cite it as:
%%Colfer, Chris. “Little Red Riding Hood.” The Land of Stories, Little Brown, 2016, pp. 58-65.
More about containers
From the section above, you can see that titles can stand alone, or they can sit in a container. Many times, sources can sit in more than one container. Wondering how? When citing an article in a scholarly journal, the first container is the journal. The second container? It’s the database that the scholarly journal is found in. It is important to account for all containers, so readers are able to locate the exact source themselves.
When citing a television episode, the first container is the name of the show and the second container is the name of the service that it could be streaming on, such as Netflix .
If your source sits in more than one container, the information about the second container is found at the end of the citation.
Use the following format to cite your source with multiple containers :
%%Last name of the author, First name of the author. “Source’s Title.” Container’s Title, roles and names of any other individuals who helped contribute to the source, the version of the source, any numbers associated with the source, the name of the publisher, the date the source was published, the location where individuals can find the source themselves (usually a URL or page range). Title of Second Container, roles and names of any other contributors, the version of the second container, any numbers associated with the second container, the name of the second container’s publisher, the date the second container was published, location.
If the source has more than two containers, add on another full section at the end for each container.
Not all of the fields in the citation format above need to be included in your citation. In fact, many of these fields will most likely be omitted from your citations. Only include the elements that will help your readers locate the source themselves.
Here is an example of a citation for a scholarly journal article found in a database. This source has two containers: the journal itself is one container, and the site it sits on is the other.
%%Zanetti, Francois. “Curing with Machine: Medical Electricity in Eighteenth-Century Paris.” Technology and Culture, vol. 54, no. 3, July 2013, pp. 503-530. Project Muse, muse.jhu.edu/article/520280.
If you’re still confused about containers, the Citation Machine MLA cite generator can help! MLA citing is easier when using the tools at CitationMachine.net.
Other contributors
Many sources have people besides the author who contribute to the source. If your research project focuses on an additional individual besides the author, or you feel as though including other contributors will help the reader locate the source themselves, include their names in the citation.
To include another individual in the citation, after the title, place the role of the individual, the word “by,” and then their name in standard order.
If the name of the contributor comes after a period, capitalize the first letter in the role of the individual. If it comes after a comma, the first letter in the role of the individual is lowercased.
Here’s an example of a citation for a children’s book with the name of the illustrator included:
%%Rubin, Adam. Dragons Love Tacos. Illustrated by Daniel Salmieri, Penguin, 2012.
The names of editors, directors, performers, translators, illustrators, and narrators can often be found in this part of the citation.
If the source that you’re citing states that it is a specific version or edition, this information is placed in the “versions” section of the citation.
When including a numbered edition, do not type out the number, use the numeral. Also, abbreviate the word “edition” to “ed.”
Here is an example of a citation with a specific edition:
%%Koger, Gregory. “Filibustering and Parties in the Modern State.” Congress Reconsidered, edited by Lawrence C. Dodd and Bruce I. Oppenheimer, 10th ed., CQ Press, 2013, pp. 221-236. Google Books, books.google.com/books?id=b7gkLlSEeqwC&lpg=PP1&dq=10th%20edition&pg=PR6#v=onepage&q=10th%20edition&f=false.
Many sources have numbers associated with them. If you see a number different than the date, page numbers, or editions, include this information in the “numbers” section of the citation. For MLA citing, this includes volume and/or issue numbers (use the abbreviations vol. and no.), episode numbers, track numbers, or any other numbers that will help readers identify the specific source that you used. Do not include ISBN (International Standard Book Numbers) in the citation.
It is important to include the name of the publisher (the organization that created or published the source), so that readers can locate the exact source themselves.
Include publishers for all sources except periodicals. Also, for websites, exclude this information when the name of the publisher matches the name of the website. Furthermore, the name of the publisher is often excluded from the citation for second containers, since the publisher of the second container is not necessarily responsible for the creation or production of the source’s content.
Publication dates
Publication dates are extremely important to include in citations. They allow the reader to understand when sources were published. They are also used when readers are attempting to locate the source themselves.
Dates can be written in MLA in one of two ways. Researchers can write dates as:
Day Mo. Year
Mo. Day, Year
Whichever format you decide to use, use the same format for all of your citations. If using the Citation Machine citation generator, the date will be formatted in the same way for each citation.
While it isn’t necessary to include the full date for all source citations, use the amount of information that makes the most sense to help your readers understand and locate the source themselves.
Wondering what to do when your source has more than one date? Use the date that is most applicable to your research.
The location generally refers to the place where the readers can find the source. This includes page ranges, URLs, DOI numbers, track numbers, disc numbers, or even cities and towns.
You can usually leave out http:// or https:// from URLs unless you want to hyperlink them. For DOIs, use http:// or https:// before the DOI: https://doi.org/xx.xxxx/xxx.xxxx.xxxx .
For page numbers, when citing a source found on only one page, use p.
Example: p. 6.
When citing a source that has a page range, use pp. and then add the page numbers.
Example: pp. 24-38.
Since the location is the final piece of the citation, place a period at the end. When it comes to URLs, many students wonder if the links in citations should be live or not. If the paper is being shared electronically with a teacher and other readers, it may be helpful to include live links. If you’re not sure whether to include live links or not, ask your teacher or professor for guidance.
Looking for an online tool to do the work for you? Citation Machine citing tools could help! Our site is simple (and fun!) to use.
Need some more help? There is further good information here .
Common Citation Examples
ALL sources use this format:
%%Last name of the author, First name of the author. “Source’s Title.” Container’s Title, roles and names of any other individuals who helped contribute to the source, the version of the source, any numbers associated with the source, the name of the publisher, the date the source was published, the location where individuals can find the source themselves (usually a URL or page range). *Title of Second Container, roles and names of any other contributors, the version of the second container, any numbers associated with the second container, the name of the second container’s publisher, the date the second container was published, location.
*If the source does not have a second container, omit this last part of the citation.
Remember, the Citation Machine MLA formatter can help you save time and energy when creating your citations. Check out our MLA Citation Machine pages to learn more.
- Journal Articles
How to Format a Paper
When it comes to formatting your paper or essay for academic purposes, there are specific MLA paper format guidelines to follow.
- Use paper that is 8½-by-11 inch in size. This is the standard size for copier and printer paper.
- Use high quality paper.
- Your research paper or essay should have a one-inch margin on the top, bottom, left, and right sides of the paper.
- While most word processors automatically format your paper to have one-inch margins, you can check or modify the margins of your paper by going to the “Page setup” section of your word processor.
Which font is acceptable to use?
- Use an easily readable font, specifically one that allows readers to see the difference between regular and italicized letters.
- Times New Roman, Arial, and Helvetica are recommended options.
- Use 12-point size font.
Should I double-space the paper, including citations?
- Double-space the entire paper.
- There should be a double space between each piece of information in the heading.
- Place a double space between the heading and the title.
- Place a double space between the title and the beginning of the essay.
- The works-cited list should be double-spaced as well. All citations are double-spaced.
Justification & Punctuation
- Text should be left-justified, meaning that the text is aligned, or flush, against the left margin.
- Indents signal to the reader that a new concept or idea is about to begin.
- Use the “tab” button on your keyboard to create an indent.
- Add one space after all punctuation marks.
Heading & Title
- Include a proper heading and title
- The heading should include the following, on separate lines, starting one inch from the top and left margins:
- Your full name
- Your teacher or professor’s name
- The course number
- Dates in the heading and the body of your essay should be consistent. Use the same format, either Day Month Year or Month Day, Year throughout the entire paper
- Examples: 27 July 2017 or July 27, 2017
- The title should be underneath the heading, centered in the middle of the page, without bold, underlined, italicized, or all capital letters.
Page numbers
- Number all pages, including the very first page and the works-cited list.
- Place page numbers in the top right corner, half an inch from the top margin and one inch from the right margin.
- Include your last name to the left of the page number. Example: Jacobson 4
Here’s an example to provide you with a visual:

If you need help with sentence structure or grammar, check out our paper checker. The paper checker will help to check every noun , verb , and adjective . If there are words that are misspelled or out of place, the paper checker will suggest edits and provide recommendations.
- If a citation flows onto the second line, indent it in half an inch from the left margin (called a “hanging indent”).
- For more information on the works-cited list, refer to “How to Make a Works Cited Page,” which is found below.
How to Create a Title Page
According to the Modern Language Association’s official guidelines for formatting a research paper, it is unnecessary to create or include an individual title page, or MLA cover page, at the beginning of a research project. Instead, follow the directions above, under “Heading & Title,” to create a proper heading. This heading is featured at the top of the first page of the research paper or research assignment.
If your instructor or professor does in fact require or ask for an MLA title page, follow the directions that you are given. They should provide you with the information needed to create a separate, individual title page. If they do not provide you with instructions, and you are left to create it at your own discretion, use the header information above to help you develop your research paper title page. You may want to include other information, such as the name of your school or university.
How to Make a Works Cited Page
The MLA Works Cited page is generally found at the end of a research paper or project. It contains a list of all the citations of sources used for the research project. Follow these directions to format the works-cited list to match the Modern Language Association’s guidelines.
- The “Works Cited” page has its own page at the end of a research project.
- Include the same running head as the rest of the project (Your last name and then the page number). The “Works Cited” page has the final page number for the project.
- Name the page “Works Cited,” unless your list only includes one citation. In that case, title it in MLA “Work Cited.”
- The title of the page (either “Works Cited” or “Work Cited”) is placed one inch from the top of the page, centered in the middle of the document.
- Double space the entire document, even between the title of the page and the first citation.
- Citations are listed in alphabetical order by the first word in the citation (usually the last name of the author or the first word in the title if the citation does not include the author’s name. Ignore “A,” “An,” and “The” if the title begins with these words.)
- If there are multiple citations by the same author, place them in chronological order by the date published.
- Also, instead of writing the author’s name twice in both citations, use three hyphens.
%%Angelou, Maya. I Know Why the Caged Bird Sings. Random House, 2009.
%%---. Gather Together in My Name. Random House, 1974.
- All citations begin flush against the left margin. If the citation is long and rolls onto a second or third line, indent the lines below the first line half an inch from the left margin. This is called a “hanging indent.” The purpose of a hanging indent is to make the citations easier to read. If you’re using our MLA citation machine, we’ll format each of your references with a hanging indent for you.
%%Wai-Chung, Ho. “Political Influences on Curriculum Content and Musical Meaning: Hong Kong Secondary Music Education, 1949-1997.” Journal of Historical Research in Music Education, vol. 22, no. 1, 1 Oct. 2000, pp. 5-25. Periodicals Index Online, search-proquest-com.i.ezproxy.nypl.org/pio/docview/1297849364/citation/6B70D633F50C4EA0PQ/78?accountid=35635.
- MLA “Works Cited” pages can be longer than one page. Use as many pages as necessary. If you have only one source to cite, do not place the one citation below the text of your paper. In MLA, a “Work Cited” page is still created for that individual citation.
Here’s a sample paper to give you an idea of what an MLA paper could look like. Included at the end is an MLA “Works Cited” page example.

Looking to add a relevant image, figure, table, or musical score to your paper? Here’s the easy way to do it, while following guidelines set forth by the Modern Language Association:
- Place the image, figure, table, or music close to where it’s mentioned in the text.
- Provide source information and any additional notes directly below the image, figure, table, or music.
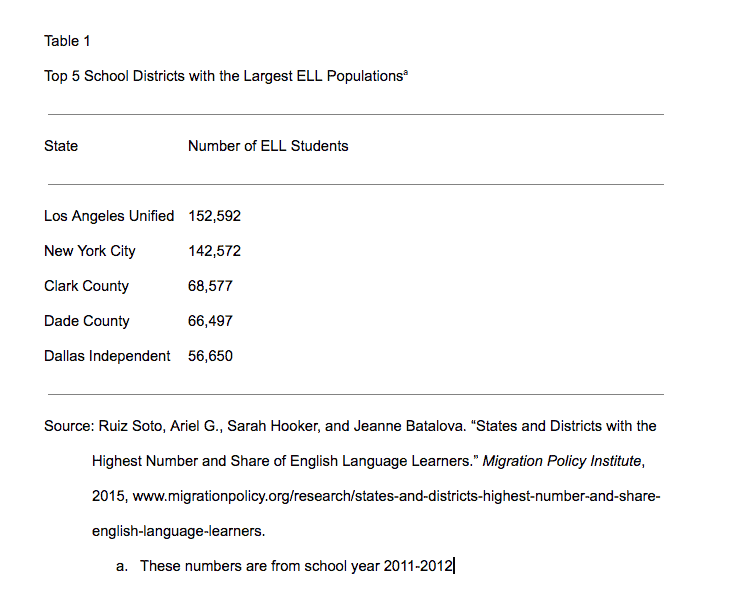
For tables:
- Label the table as “Table” followed by an arabic numeral such as “1.” Table 1 is the table closest to the beginning of the paper. The next table mentioned in the text would be Table 2, and so on.
- Create a title for the table and place it below the label. Capitalize all important words.
- The label (Table 1) and the title should be flush against the left margin.
- Double-space everything.
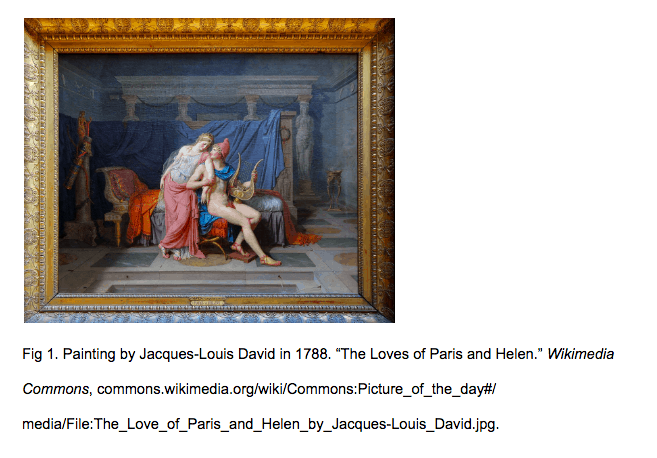
- A figure can be a map, photograph, painting, pie chart, or any other type of image.
- Create a label and place it below the figure. The figure first mentioned in the text of the project is either “Figure 1” or “Fig 1.” Though figures are usually abbreviated to “Fig.” Choose one style and use it consistently. The next mentioned figure is “Figure 2” or “Fig. 2.”, and so on.
- Place a caption next to the label. If all of the source information is included in the caption, there isn’t a need to replicate that information in the works-cited list.
MLA Final Checklist
Think you’re through? We know this guide covered a LOT of information, so before you hand in that assignment, here’s a checklist to help you determine if you have everything you need:
_ Are both in-text and full citations included in the project? Remember, for every piece of outside information included in the text, there should be a corresponding in-text citation next to it. Include the full citation at the end, on the “Works Cited” page.
_ Are all citations, both in-text and full, properly formatted in MLA style? If you’re unsure, try out our citation generator!
_ Is your paper double-spaced in its entirety with one inch margins?
_ Do you have a running header on each page? (Your last name followed by the page number)
_ Did you use a font that is easy to read?
_ Are all citations on the MLA format works-cited list in alphabetical order?
Our plagiarism checker scans for any accidental instances of plagiarism. It scans for grammar and spelling errors, too. If you have an adverb , preposition , or conjunction that needs a slight adjustment, we may be able to suggest an edit.
Common Ways Students Accidentally Plagiarize
We spoke a bit about plagiarism at the beginning of this guide. Since you’re a responsible researcher, we’re sure you didn’t purposely plagiarize any portions of your paper. Did you know students and scholars sometimes accidentally plagiarize? Unfortunately, it happens more often than you probably realize. Luckily, there are ways to prevent accidental plagiarism and even some online tools to help!
Here are some common ways students accidentally plagiarize in their research papers and assignments:
1. Poor Paraphrasing
In the “How to create a paraphrase” section towards the top of this page, we share that paraphrases are “recycled information, in the paper writer’s own words and writing style.” If you attempt to paraphrase a few lines of text and it ends up looking and sounding too close to the original author’s words, it’s a poor paraphrase and considered plagiarism.
2. Incorrect Citations
If you cite something incorrectly, even if it’s done accidentally, it’s plagiarism. Any incorrect information in a reference, such as the wrong author name or the incorrect title, results in plagiarism.
3. Forgetting to include quotation marks
When you include a quote in your paper, you must place quotation marks around it. Failing to do so results in plagiarism.
If you’re worried about accidental plagiarism, try our Citation Machine Plus essay tool. It scans for grammar, but it also checks for any instances of accidental plagiarism. It’s simple and user-friendly, making it a great choice for stress-free paper editing and publishing.
Updated June 15, 2021
Written and edited by Michele Kirschenbaum and Wendy Ikemoto. Michele Kirschenbaum has been an awesome school librarian since 2006 and is an expert in citing sources. Wendy Ikemoto has a master’s degree in library and information science and has been working for Citation Machine since 2012.
- Citation Machine® Plus
- Citation Guides
- Chicago Style
- Harvard Referencing
- Terms of Use
- Global Privacy Policy
- Cookie Notice
- DO NOT SELL MY INFO
- Free Tools for Students
- MLA Citation Generator
Free MLA Citation Generator
Generate accurate citations in MLA format automatically, with MyBib!

😕 What is an MLA Citation Generator?
An MLA citation generator is a software tool designed to automatically create academic citations in the Modern Language Association (MLA) citation format. The generator will take information such as document titles, author, and URLs as in input, and output fully formatted citations that can be inserted into the Works Cited page of an MLA-compliant academic paper.
The citations on a Works Cited page show the external sources that were used to write the main body of the academic paper, either directly as references and quotes, or indirectly as ideas.
👩🎓 Who uses an MLA Citation Generator?
MLA style is most often used by middle school and high school students in preparation for transition to college and further education. Ironically, MLA style is not actually used all that often beyond middle and high school, with APA (American Psychological Association) style being the favored style at colleges across the country.
It is also important at this level to learn why it's critical to cite sources, not just how to cite them.
🙌 Why should I use a Citation Generator?
Writing citations manually is time consuming and error prone. Automating this process with a citation generator is easy, straightforward, and gives accurate results. It's also easier to keep citations organized and in the correct order.
The Works Cited page contributes to the overall grade of a paper, so it is important to produce accurately formatted citations that follow the guidelines in the official MLA Handbook .
⚙️ How do I use MyBib's MLA Citation Generator?
It's super easy to create MLA style citations with our MLA Citation Generator. Scroll back up to the generator at the top of the page and select the type of source you're citing. Books, journal articles, and webpages are all examples of the types of sources our generator can cite automatically. Then either search for the source, or enter the details manually in the citation form.
The generator will produce a formatted MLA citation that can be copied and pasted directly into your document, or saved to MyBib as part of your overall Works Cited page (which can be downloaded fully later!).
MyBib supports the following for MLA style:

Daniel is a qualified librarian, former teacher, and citation expert. He has been contributing to MyBib since 2018.

AI Generator

MLA format is a widely accepted style for writing and documenting scholarly papers, particularly in the humanities. It provides guidelines for formatting manuscripts , citing sources, and structuring works cited pages, ensuring consistency and clarity. Adhering to MLA format helps writers present their research in a professional and organized manner, facilitating readability and academic integrity.
What is MLA Format?
MLA format, established by the Modern Language Association, is a widely-used style for writing and documenting scholarly papers in the humanities. It features in-text citation , a “Works Cited” page, double-spacing, one-inch margins, and specific guidelines for formatting headings, titles, and quotations to ensure clarity and consistency in academic writing.
MLA Format Examples
- Author’s Last Name, First Name. Title of Book . Publisher, Year of Publication.
- Example: Smith, John. The Art of Writing . Penguin, 2020.
- Author’s Last Name, First Name. “Title of Article.” Title of Journal , vol. number, no. number, Year, pages.
- Example: Doe, Jane. “Exploring Literature.” Literary Journal , vol. 5, no. 3, 2019, pp. 45-67.
- Author’s Last Name, First Name. “Title of Web Page.” Title of Website , Publisher, Date of Publication, URL.
- Example: Brown, Lisa. “Understanding MLA Format.” Writing Resources , Purdue OWL, 15 Mar. 2021, www.owl.purdue.edu/mlaformat .
- Author’s Last Name, First Name. “Title of Chapter.” Title of Book , edited by Editor’s First Name Last Name, Publisher, Year, pages.
- Example: Taylor, Robert. “Modern Poetry.” Anthology of Modern Literature , edited by Sarah Green, Norton, 2018, pp. 120-135.
- Editor’s Last Name, First Name, editor. Title of Book . Publisher, Year.
- Example : Anderson, Mary, editor. Cultural Studies . Routledge, 2017.
- Author’s Last Name, First Name. “Title of Article.” Title of Magazine , Date of Publication, pages.
- Example: Clark, Emily. “The Future of Education.” Education Today , 12 June 2021, pp. 22-25.
- Author’s Last Name, First Name. “Title of Article.” Title of Newspaper , Date of Publication, pages.
- Example: Adams, Michael. “Tech Innovations in 2022.” The New York Times , 5 Jan. 2022, p. B1.
- Title of Film . Directed by Director’s First Name Last Name, performance by Lead Actor’s First Name Last Name, Production Company, Year.
- Example: Inception . Directed by Christopher Nolan, performance by Leonardo DiCaprio, Warner Bros., 2010.
- Author’s Last Name, First Name. “Title of Video.” Website , uploaded by Uploader’s Name, Date of Upload, URL.
- Example : Johnson, Mark. “ How to Write in MLA Format.” YouTube , uploaded by Academic Tips, 10 Feb. 2021, www.youtube.com/academic-tips-mla .
- Author’s Last Name, First Name. “Title of Paper.” Title of Conference , Date, Location.
- Example: Lee, Anna. “The Impact of Social Media on Education.” International Conference on Education , 23 Apr. 2021, Boston, MA.
When to use MLA Format
MLA format is commonly used in the humanities, especially for writing papers and citing sources in subjects like:
- Essay , research papers, and articles analyzing novels, poems, plays, and other literary works.
- Papers exploring cultural phenomena, media studies, and societal impacts on culture.
- Research involving comparative literature, translations, and linguistic studies.
- Essays and papers discussing philosophical theories, arguments, and historical texts.
- Research papers analyzing art movements, specific artworks, and artist biographies.
- Analyses of plays, playwrights, theatrical performances, and historical context of theater.
- Humanities-focused historical research papers, particularly those involving textual analysis.
- Research involving film, television, digital media, and their cultural implications.
MLA format is preferred in these fields for its emphasis on detailed citation and textual analysis, ensuring clarity, consistency, and academic integrity in scholarly writing.
How to set up your paper in MLA Format
Setting up your paper in MLA format is crucial for academic writing, ensuring that your work meets the standards for scholarly communication. Follow these steps to format your paper correctly:
1. General Guidelines
- Font : Use a readable font like Times New Roman, size 12.
- Margins : Set all margins to 1 inch on all sides.
- Line Spacing : Double-space the entire paper, including any notes and the works cited page.
- Indentation : Indent the first line of each paragraph one-half inch from the left margin. Use the Tab key instead of the space bar.
2. Header and Title
- Header : Create a header in the upper right-hand corner that includes your last name, followed by a space and the page number. Number all pages consecutively with Arabic numerals (1, 2, 3, etc.).
- In the upper left-hand corner, list your name, your instructor’s name, the course, and the date. Double-space this information.
- Center the title. Do not underline, italicize, or place your title in quotation marks. Write the title in Title Case (standard capitalization), not in all capital letters.
3. In-Text Citations
- When quoting or paraphrasing, include an in-text citation with the author’s last name and the page number from which the quote or paraphrase is taken, like this: (Smith 123).
4. Works Cited Page
- Title : Center the title “Works Cited” at the top of the page. Do not italicize or underline it.
- Entries : Begin each entry at the left margin; if an entry runs more than one line, indent the subsequent lines one-half inch from the left margin (hanging indent).
- Alphabetical Order : List the entries alphabetically by the author’s last name. If no author is given, alphabetize by the title.
Example of the First Page
Jane Doe Professor Smith English 101 20 May 2023 Centered Title in Title Case The first paragraph of your paper begins here, with the first line indented one-half inch. Subsequent paragraphs should also be indented one-half inch from the left margin.
Example of a Works Cited Entry
Works Cited Smith, John. The Great Gatsby . Scribner, 2004.
Formatting Header and Title in MLA
Formatting the header and title correctly is an important step in ensuring your paper adheres to MLA standards. Here’s a detailed guide on how to set up the header and title for your MLA paper:
The header in MLA format is placed in the upper right-hand corner of each page, including the first page. Here are the steps to set it up:
- Open your document in a word processing program like Microsoft Word or Google Docs.
- In Microsoft Word: Go to the “Insert” tab and select “Header.” Choose the “Blank” option.
- In Google Docs: Click on “Insert” and then “Headers & footers,” followed by “Header.”
- Type your last name followed by a space.
- In Microsoft Word: While the cursor is still in the header, go to the “Design” tab, click on “Page Number,” and choose “Top of Page” then “Plain Number 3.”
- In Google Docs: While the cursor is in the header, click on “Insert,” then “Page numbers,” and select the option to have the page numbers in the upper right corner.
- Set the font and size : Ensure the font is Times New Roman, size 12, matching the rest of your document.
2. Title Page Setup
MLA format does not require a separate title page unless specifically requested by your instructor. Instead, the title is placed on the first page of your paper. Here’s how to format it:
Information Block
- Position the cursor at the top of the first page.
- Your full name
- Your instructor’s name
- The course name or number
- The date in the format: Day Month Year (e.g., 20 May 2023)
- Double-space after the date.
- Center the title of your paper. The title should be in Title Case, which means you capitalize the major words.
- Do not use bold, italics, underline, or quotation marks for the title. Write it in plain text.
Example of the First Page Setup
Jane Doe Professor Smith English 101 20 May The Impact of Climate Change on Migration The first paragraph of your paper begins here, with the first line indented one-half inch. Subsequent paragraphs should also be indented one-half inch from the left margin.
Headings and Subheadings in MLA Format
MLA (Modern Language Association) format provides a flexible guideline for structuring your academic paper. While the MLA Handbook (9th edition) does not provide specific rules for headings and subheadings, it encourages consistency and clarity. Here’s a guide on how to create and format headings and subheadings in your MLA-style paper.
General Guidelines
- Font and Size: Use a readable font like Times New Roman, size 12.
- Consistency: Ensure that the format and style of headings and subheadings are consistent throughout the paper.
- No Bold or Italics: Headings should not be bolded or italicized. They should be in plain text, maintaining the same font and size as the rest of the paper.
- Title Case: Capitalize the first and last words and all principal words in headings and subheadings.
Levels of Headings
MLA does not have specific rules for the number of heading levels. However, using up to five levels of headings is common. Below is a suggested format for organizing your paper with headings and subheadings.
First-Level Heading (H2)
Centered, Title Case
Causes of Climate Change
Second-Level Heading (H3)
Left-aligned, Title Case
Human Activities
Third-Level Heading (H4)
Indented, Title Case, Ends with a Period.
Burning of Fossil Fuels.
Fourth-Level Heading (H5)
Indented, Sentence case, Ends with a period.
Deforestation and land use changes.
Fifth-Level Heading (H6)
Indented, italicized, Sentence case, Ends with a period.
Use of agricultural practices.
Examples of Headings in a Paper
Here’s an example of how to structure a paper using these headings:
Causes of Climate Change Human activities significantly contribute to climate change through various means. Human Activities Human activities that impact climate change include the burning of fossil fuels, deforestation, and certain agricultural practices. Burning of Fossil Fuels. The combustion of coal, oil, and natural gas releases large amounts of CO2 into the atmosphere. Deforestation and land use changes. The removal of trees decreases the planet’s capacity to absorb CO2. Use of agricultural practices. Certain farming practices, like livestock production, increase methane emissions. Natural Factors Natural factors also play a role in climate change, albeit to a lesser extent than human activities. Volcanic Eruptions. Eruptions release particles that can cool the Earth by blocking sunlight. Solar Variations Changes in solar energy affect the Earth’s climate cycles.
Quotations in MLA Format
Quotations are an essential part of academic writing, providing evidence and supporting arguments. MLA (Modern Language Association) format has specific guidelines for incorporating quotations into your text. Here’s a detailed guide on how to format both short and long quotations in MLA style.
1. Short Quotations
Short quotations are defined as fewer than four lines of prose or three lines of verse. These quotations should be incorporated into the text and enclosed in double quotation marks.
- Introduce the quotation with a signal phrase that includes the author’s last name followed by the page number in parentheses.
- Place the period after the parenthetical citation.
According to Smith, “climate change is the greatest challenge facing humanity today” (123).
2. Long Quotations
Long quotations, also known as block quotations, are used for prose that is more than four lines or verse that is more than three lines. These should be formatted as a freestanding block of text and indented one inch from the left margin. Quotation marks are not used.
- Introduce the block quotation with a signal phrase that ends with a colon.
- Start the quotation on a new line and indent the entire block one inch from the left margin.
- Double-space the quotation.
- Place the parenthetical citation after the period at the end of the quotation.
Smith discusses the impacts of climate change in detail:
Climate change affects all regions around the world. Polar ice caps are melting, sea levels are rising, and weather patterns are becoming more extreme. These changes threaten the habitats of countless species, and the economic and social systems of human communities are also at risk. Immediate action is required to mitigate these effects and adapt to the changes that are already underway. (123)
3. Adding or Omitting Words
Adding Words: When adding words for clarity, enclose the added text in square brackets.
Smith notes that “immediate action [by global leaders] is required to mitigate these effects” (123).
Omitting Words: To omit words from a quotation, use an ellipsis (…). Ensure that the omission does not change the meaning of the original text.
Smith argues that “climate change affects all regions…and weather patterns are becoming more extreme” (123).
4. Quoting Poetry
For quoting poetry, maintain the original formatting as much as possible. Use a slash (/) to indicate line breaks within the text.
Short Poetry Quotations:
- Enclose the quotation in double quotation marks.
- Use a slash (/) to indicate line breaks.
In Frost’s “The Road Not Taken,” the speaker reflects, “Two roads diverged in a yellow wood, / And sorry I could not travel both” (1-2).
Long Poetry Quotations:
- Introduce the quotation with a signal phrase ending with a colon.
- Maintain the original line breaks.
In his poem “The Road Not Taken,” Frost writes:
Two roads diverged in a yellow wood, And sorry I could not travel both And be one traveler, long I stood And looked down one as far as I could To where it bent in the undergrowth; (1-5)
5. Quoting Dialogue
When quoting dialogue from a play or script, each character’s speech begins on a new line, and the character’s name is written in all capital letters followed by a period.
- Introduce the quotation with a signal phrase.
- Start the quotation on a new line and indent each line of the characters’ speech one inch from the left margin.
- Double-space the dialogue.
In Shakespeare’s Macbeth , the witches proclaim:
FIRST WITCH. When shall we three meet again In thunder, lightning, or in rain? SECOND WITCH. When the hurlyburly’s done, When the battle’s lost and won. (1.1.1-4)
Paraphrases in MLA Format
Paraphrasing involves restating someone else’s ideas in your own words. In MLA (Modern Language Association) format, it’s essential to credit the original source even when you paraphrase. Here’s a detailed guide on how to properly format paraphrases in MLA style.
1. General Guidelines for Paraphrasing
- Restate the original text: Ensure that the paraphrase is in your own words and that it accurately reflects the meaning of the original text.
- Provide an in-text citation: Include the author’s last name and the page number where the original idea can be found.
- No quotation marks: Do not use quotation marks around a paraphrase since you are not using the exact words from the source.
2. In-Text Citations for Paraphrases
The in-text citation for a paraphrase is similar to that for a direct quotation. It includes the author’s last name and the page number in parentheses.
Basic Format: (Author’s Last Name Page Number)
Example: According to Smith, climate change poses a significant challenge to humanity, requiring immediate and concerted action from global leaders (123).
3. Incorporating Paraphrases into Your Text
You can introduce a paraphrase in several ways to smoothly integrate it into your writing. Here are some examples:
Using a Signal Phrase
Signal phrases introduce the source of the paraphrase and are typically followed by the paraphrased material and a parenthetical citation.
Example: Smith argues that immediate action is necessary to address the widespread impacts of climate change, which threaten both natural ecosystems and human societies (123).
Integrating the Paraphrase
Integrate the paraphrase directly into your sentence, ensuring it flows naturally with your own writing.
Example: The widespread impacts of climate change, including rising sea levels and more extreme weather patterns, require urgent action to mitigate damage to both ecosystems and human communities (Smith 123).
4. Multiple Authors
When paraphrasing a source with multiple authors, include all authors’ last names or use “et al.” for three or more authors.
Two Authors:
Example: According to Johnson and Smith, sustainable practices are essential for mitigating the effects of climate change (45).
Three or More Authors:
Example: Research indicates that sustainable practices are crucial for mitigating climate change impacts (Johnson et al. 45).
5. No Author
If the source has no author, use a shortened title of the work instead. Place the title in quotation marks if it’s an article or in italics if it’s a book or other standalone work.
Example: Measures to address climate change must be implemented urgently to prevent further environmental degradation (“Climate Action” 12).
6. Multiple Works by the Same Author
If you cite multiple works by the same author, include a shortened version of the title in the citation to differentiate between them.
Example: Smith argues that sustainable practices are necessary for environmental conservation (“Environmental Policies” 56) and that global cooperation is key to effective climate action (“Global Strategies” 78).
7. Citing Indirect Sources
If you need to paraphrase information from a source cited within another source, use “qtd. in” to indicate the original source.
Example: According to Brown, environmental education plays a crucial role in raising awareness about climate change (qtd. in Smith 89).
Example of a Paragraph with Paraphrases
Original Text: “Climate change affects all regions around the world. Polar ice caps are melting, sea levels are rising, and weather patterns are becoming more extreme. These changes threaten the habitats of countless species, and the economic and social systems of human communities are also at risk. Immediate action is required to mitigate these effects and adapt to the changes that are already underway” (Smith 123). Paraphrased Paragraph: Smith notes that climate change has a global impact, causing the melting of polar ice caps, rising sea levels, and more extreme weather events. These environmental changes endanger numerous species’ habitats and pose risks to human economic and social structures. Therefore, Smith emphasizes the need for swift measures to mitigate and adapt to these evolving challenges (123).
Using Abbreviations in MLA Format
Abbreviations can help make your writing more concise and clear. However, it is important to use them correctly and consistently. Here is a guide on how to use abbreviations in MLA (Modern Language Association) format.
- Introduce Abbreviations: When you first introduce an abbreviation, spell out the full term followed by the abbreviation in parentheses. After this initial introduction, you can use the abbreviation alone.
- Consistency: Use the abbreviation consistently throughout your paper after introducing it.
- Periods: Use periods with certain abbreviations (e.g., a.m., p.m., U.S.), but do not use them for acronyms (e.g., NASA, MLA).
Types of Abbreviations
Acronyms and initialisms.
Acronyms are formed from the initial letters of words and pronounced as words (e.g., NASA). Initialisms are formed from the initial letters but pronounced as individual letters (e.g., FBI).
Example: The Modern Language Association (MLA) provides guidelines for formatting academic papers. According to MLA guidelines, authors should use consistent formatting throughout their work.
When citing sources, abbreviate the names of months (except May, June, and July) in the Works Cited page.
Example: Jan., Feb., Mar., Apr., Aug., Sept., Oct., Nov., Dec.
Works Cited Entry Example: Smith, John. “The Effects of Climate Change.” Environmental Studies Journal , vol. 12, no. 4, Aug. 2020, pp. 123-45.
Common Latin Abbreviations
Certain Latin abbreviations are commonly used in academic writing. Here are a few examples:
- e.g. (exempli gratia): means “for example”
- i.e. (id est): means “that is”
- etc. (et cetera): means “and so on”
- et al. (et alii): means “and others”
Example: There are many theories on climate change (e.g., greenhouse effect, solar variability).
Abbreviating Titles and Terms
Use standard abbreviations for titles and terms when they appear in citations.
- ed. (edition)
- rev. ed. (revised edition)
- vol. (volume)
- no. (number)
Examples: Doe, Jane, ed. Anthology of Modern Poetry . 3rd ed., Penguin Books, 2019. Brown, Sarah. History of Medieval Europe . Rev. ed., vol. 2, Academic Press, 2018.
Abbreviating Locations in Works Cited
Abbreviate the names of U.S. states and countries in publisher locations.
- Cambridge, MA
Works Cited Entry Example: Smith, John. The Great Migration . Cambridge UP, 2015.
In-Text Citations with Abbreviations
Use abbreviations in in-text citations as necessary to keep them concise. For example, abbreviate the titles of works that are long or frequently cited within the text.
Example: (Tolkien, LOTR 23)
Abbreviating Corporate Authors
When a corporate author is commonly known by an abbreviation, you can use the abbreviation after introducing it.
Example: The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) has made significant advancements in space exploration. According to NASA, the Mars rover has sent back valuable data (NASA).
Common MLA Abbreviations
- ch. (chapter)
- sec. (section)
- trans. (translator)
- UP (University Press)

Example of Proper Abbreviation Usage in a Paragraph
When citing sources, the Modern Language Association (MLA) recommends abbreviating the names of months except for May, June, and July. For instance, an article published in March would be cited as “Mar.” (MLA Handbook 123). Additionally, when referring to organizations like the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA), the abbreviation can be used after the first mention. NASA has reported new findings from the Mars rover mission (NASA).
Formatting Numbers in MLA Format
When writing papers in MLA (Modern Language Association) format, it’s important to know the guidelines for formatting numbers. Here’s a concise guide to help you understand when to use numerals and when to spell out numbers.
General Rules
- Spell out numbers that can be written in one or two words.
- Examples: one, thirty-six, ninety-nine, one hundred, fifteen hundred
- Use numerals for numbers that require more than two words.
- Examples: 101, 1,250, 7,891
Specific Cases
- Spell out numbers when they begin a sentence.
- Example: One hundred students attended the lecture.
- Note: If rewriting the sentence to avoid starting with a number, it is acceptable. Example: There were 100 students who attended the lecture.
- Use numerals for dates.
- Example: June 5, 2024
- Use numerals with a.m. and p.m.
- Examples: 10:30 a.m., 5:00 p.m.
- For round numbers, you may spell out the time if clarity is preserved.
- Example: He arrived at six o’clock in the evening.
- Use numerals and the percent symbol (%).
- Example: The survey showed that 75% of participants agreed.
- Always use numerals.
- Example: Please refer to page 45 for more information.
- Use a combination of numerals and words for very large round numbers.
- Example: 2.5 million, 3 billion
- Spell out simple fractions and use numerals for more complex fractions.
- Examples: Two-thirds of the class, 3/8 of an inch
- Use numerals for decades and spell out centuries.
- Examples: the 1990s, the twenty-first century
Examples in Context
- There are fifty-two weeks in a year.
- The population of the city is approximately 1.2 million.
- She bought three dozen eggs.
- On April 15, 2022, the event will take place.
- The meeting starts at 9:00 a.m.
- About 40% of the respondents disagreed with the statement.
- The results are discussed on page 23.
- He has lived here since the 1980s.
- The twentieth century saw many technological advances.
- There are 52 weeks in a year. (Should be spelled out)
- The population of the city is approximately one million two hundred thousand. (Use numerals)
- She bought 3 dozen eggs. (Spell out)
Using Lists in MLA Format
Lists can be a useful way to present information clearly and concisely. In MLA (Modern Language Association) format, there are specific guidelines for incorporating lists into your writing. Here’s a guide on how to format both bulleted and numbered lists according to MLA style.
- Introduce the list with a complete sentence followed by a colon.
Example: There are several reasons to visit the museum:
- Ensure that each item in the list follows the same grammatical structure.
- Free admission
- Guided tours
- Educational workshops
Bulleted Lists
Bulleted lists are used to present items that do not need to be in a specific order.
- Introduce the list with a complete sentence.
- Use a colon at the end of the introductory sentence.
- Begin each item with a capital letter.
- Use a period after each item if the items are complete sentences; otherwise, do not use periods.
Example: The museum offers the following activities:
- Art exhibitions
- Interactive workshops
Numbered Lists
Numbered lists are used to present items that need to be in a specific order, such as steps in a process.
- Use periods after each item if the items are complete sentences.
Example: Follow these steps to register for the workshop:
- Visit the museum’s website.
- Click on the “Events” tab.
- Select the desired workshop.
- Complete the registration form.
In-Text Lists
In-text lists are used within a sentence and are typically introduced with a colon or parentheses.
Comma-Separated Lists:
- Use commas to separate items in a simple list within a sentence.
- Example: The museum offers guided tours, art exhibitions, and interactive workshops.
Semicolon-Separated Lists:
- Use semicolons to separate items in a complex list within a sentence.
- Example: The museum offers several activities: guided tours for all ages; art exhibitions featuring local artists; and interactive workshops on weekends.
Lists with Complete Sentences
When each item in the list is a complete sentence, use periods at the end of each item.
- The museum offers free admission every first Sunday of the month.
- It has a wide range of art exhibitions from contemporary to classical art.
- Interactive workshops are available for children and adults alike.
Example in Context
Here is an example of how to integrate a list into an MLA-formatted paper:
Text Example:
Visiting the museum can be a rewarding experience for several reasons:
- Free Admission: The museum offers free admission every first Sunday of the month.
- Diverse Exhibitions: It features a wide range of art exhibitions, from contemporary to classical art.
- Interactive Workshops: There are interactive workshops available for both children and adults.
In addition to these activities, the museum also provides guided tours and educational programs, making it an excellent destination for visitors of all ages.
MLA Format vs. APA Format
What is mla format.
MLA format is a style guide for writing and documenting research in the humanities, particularly in English studies, provided by the Modern Language Association.
How do you cite a book in MLA format?
Author’s Last Name, First Name. Title of Book . Publisher, Year of Publication. Example: Smith, John. The Great Gatsby . Scribner, 2004.
How do you format the first page of an MLA paper?
Include your name, instructor’s name, course, and date in the upper left corner. Center the title, and start the text on a new line, double-spaced.
What should be included in an MLA Works Cited page?
List all sources cited in the text, alphabetized by the author’s last name. Include full publication details for each source.
How do you format in-text citations in MLA?
nclude the author’s last name and page number in parentheses after the quote or paraphrase. Example: (Smith 123).
Do I need a title page in MLA format?
No, MLA format typically does not require a separate title page unless specified by the instructor.
How do you cite a website in MLA format?
Author’s Last Name, First Name. “Title of Web Page.” Title of Website , Publisher, Publication Date, URL.
How do you handle multiple authors in an MLA citation?
For two authors, use both last names (Smith and Jones). For three or more, use the first author’s last name followed by “et al.” (Smith et al.).
How are block quotes formatted in MLA?
Indent the entire quote one inch from the left margin, double-space, and omit quotation marks. Place the parenthetical citation after the period.
What font and size should be used in MLA format?
Use a readable font like Times New Roman, size 12, and double-space the entire document.
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting

Ask A Librarian Help

The links in the MLA Style Center reflect MLA Style 9th Edition.

The links in Purdue OWL reflect MLA Style 9th Edition.
- Citation Style Chart via Purdue OWL:
- MLA Works Cited: Electronic Sources (Web Publications) Websites, pages on websites, eBooks, images, eArticles, social media...
- MLA Works Cited: Other Common Sources Interviews; speeches, lectures, or presentations; panel discussions; painting, sculpture, or photograph; conference proceedings, song or album; film or movie; podcasts; digital files
- MLA Works Cited Page: Books in Print
- MLA Works Cited Page: Periodicals in Print (Journals, Magazines & Newspapers)
- MLA In-Text Citations: The Basics
- MLA Style Sample Paper
- MLA Style Sample Works Cited
- MLA 9th PowerPoint Presentation

- << Previous: Finding and Accessing eBooks Tutorial
- Next: Library Instruction Recap >>
- Last Updated: May 20, 2024 1:54 PM
- URL: https://libguides.ggc.edu/ENGL_4412_Weiss

What Is A Bibliography?

Bibliography Definition: Overview
A bibliography is a list of sources used in researching and writing a work, such as a book, article, or academic paper. It includes detailed information about each source, like the author's name, title, and publication date. Bibliographies serve to credit authors, avoid plagiarism, provide references for readers, and demonstrate the research scope. They can be annotated, which includes summaries or evaluations, or simply list the sources. Proper formatting depends on the required citation style, such as APA, MLA, or Chicago.
Simply put, a bibliography lists all the sources you’ve used while working on a paper. It’s a window where your readers can check and verify the validity of your claims, and to know the origins of your research. Academic papers aren’t the only works that have bibliographies. Websites, interviews, and articles can also have them.
The definition of bibliography encompasses many of these resource lists. Adding an extensive and authentic bibliography to your work credits the original authors and enhances credibility and trustworthiness.
Purpose of A Bibliography
The purpose of a bibliography is to help you keep track of your research, assist readers in finding more information on the topic, prove that your information comes from trustworthy sources, and give credit to the original sources and authors.
A bibliography has many purposes. That’s why your academic paper must have one. It serves to help in many different things:
- Improves your work’s credibility : It backs up your information and makes it credible and trustworthy.
- Counters plagiarism : It helps give credit to your sources and their authors which helps uphold integrity and counters plagiarism.
- Serves as guidance : By demonstrating your sources, your bibliography helps your readers the ability to explore your topic further and gain a deeper understanding of it.
Struggling with your Annotated Bibliography?
Our experts are here to help! Get professional assistance in creating an annotated bibliography for any academic assignment and save your precious time.
Types of Bibliographies
Now we’ve gone over the basics of what’s a bibliography, let’s explore the different types. There are several types of them, each having a different purpose:
- Descriptive bibliographies : These provide very detailed information about the sources. They provide information on physical attributes, printing history, format, and edition.
- Enumerative bibliographies : These are not as detailed. They are organized either chronologically, alphabetically, or chronologically.
- Analytical bibliographies : These types examine the sources’ history, context, and production. They offer a deeper analytical view of the sources.
Annotated Bibliographies
A hard entry is the annotated bibliography. Here’s a more extensive guide on how to write an annotated bibliography for your convenience. These go beyond just listing sources. You typically include summaries and evaluations of your source entries with this type.
By doing so, you help your readers grasp the importance of each source and how it contributes to your work. When you properly create an annotated bibliography, you showcase your critical thinking capabilities. This, in turn, can enhance your paper’s overall credibility, and it also helps your readers in their further research.
We’ve explored the many aspects of what is a bibliography and answered the main questions. So, in the spirit of better understanding, let’s also learn about footnotes.
Footnotes give additional information or citations at the bottom of a page. Footnotes are used to give credit or to highlight your sources without disrupting the flow of your main work. They can also be used to provide additional details that support your writing.
Footnotes can provide context and explanations and can highlight references. This, in turn, guides your readers and helps them fully understand your message.
Common Mistakes When Creating Your Bibliography
There are many avoidable pitfalls you can counter just by reading our guides, but if you’re tired and need an extra hand, you can always send in a request for help with your bibliography or even a request to ‘ Write my book report .’ We’ll be on that task ASAP. If you’re feeling fit to learn more, here are some crucial pointers to remember:
- Incomplete citations : Be sure to finish your citations by providing all the necessary information like author, title, publication date, and publisher.
- Bad formatting : Be consistent and stick to one citation style for your bibliography.
- Missing sources : Make sure all the sources you reference in your work are in your bibliography.
- Wrong order : Make sure you’ve organized your entries accordingly.
Formatting and Style
We’ve tackled all the definitions and the bibliography meaning. Now, let’s take a look at the crucial elements of formatting and style. Here’s what to remember:
- APA (American Psychological Association) : This style is commonly used in the social sciences. It highlights the author and publication year in in-text citations.
- MLA (Modern Language Association) : Very widely used in literature and language studies. It highlights the author and page number for in-text citations.
- Chicago/Turabian : This style is used in many different disciplines since it’s considered versatile. This style has two systems. One is the notes and bibliography style, used widely in the humanities. The other one is the author-date system, which is used in the sciences. Turabian is a simplified version of Chicago and is used by students.
- Harvard : This one uses author-date in-text citations and uses a reference list. It’s used in many different fields and is quite popular in Australia and the UK.
Key Takeaways
“What is a bibliography?” Now we know. Let’s remember some of the key points we’ve encountered in this guide for future reference:
- Different types : descriptive, enumerative, analytical.
- Avoiding common pitfalls : complete citations, be consistent, organize and include all sources.
- Choose one style : Choose MLA, APA, Chicago/Turabian or Harvard and stick to one style for your whole bibliography.
We hope you’ll retain all the information we’ve given you. You can always come back to our article if you need more time to memorize. We wish you luck in all your academic ventures.
Did you like our Bibliography Guide?
Need more help? Tap into our pool of professional writers and get expert writing services!
What is a bibliography page?
It’s a section at the end of your paper or your book. Here, you list all the sources that you used. You include details about the books, articles, websites, and every other material you used when researching.
What is bibliographic information?
This refers to the details about a source in your bibliography. This refers to the author’s name, the work’s title, the publication date, the publisher, and so on. This information helps your readers verify and find your sources.
What is a bibliography in an essay?
It’s the list of your sources that can be found at the end of your essay. It gives credit to your sources and backs up your claims.
What is the purpose of a bibliography?
Its purpose is to provide you and your readers with a clear, authentic, and organized list of sources. Sources you’ve used to back up your research and writing. It improves your work’s credibility, trustworthiness, and professionalism.
A good annotated bibliography is essentially a brief description of works cited. An important difference between your own ideas and scientific writing is how credible the sources are. The works cited in your annotated bibliography offer a brief description of your research process.
What is an annotated bibliography?
It’s like a standard bibliography but has an additional summary and evaluation of each source. It can be difficult to make, that's why an annotated bibliography writing service can be helpful when you’re having trouble.
A high-quality bibliography writing service knows every detail of the citation process - from the author date style and page numbers to multi source volumes and style guides. Give it a try and feel the difference!
What is a bibliographic reference?
This simply refers to a source you’ve used in your research. They serve to acknowledge the authors and works you’ve sourced to avoid plagiarism, give credit, and guide your readers.
When working on an annotated bibliography, the works cited from doing your own research, have to be on the references page. A good annotated bibliography entry has a references list in a style guide proposed by the university in APA format, MLA works cited format or any format for bibliographic information.
- Essay Editor
Create a Perfect Essay Structure

Hello Aithors! We're back again with another feature highlight. Today, we want to talk about a tool that can be a game-changer for your essay writing process - our Table of Contents tool.
Writing an essay isn't just about getting your ideas down on paper. It's about presenting them in a clear, structured way that makes sense to your reader. However, figuring out the best structure for your essay can sometimes be a tough nut to crack. That's why we developed the Table of Contents feature.
The best part about this tool is how easy it is to use. When you're about to start an Aithor essay, the Table of Contents tool is the sixth step. You can set up a structure for your essay before the AI starts writing the text. This helps you map out your essay before you dive into the writing part.
But what if you want to make changes to the structure? No problem! The Table of Contents feature is flexible and allows you to adjust the structure to fit your needs. You can add a new point, remove a section, or switch around the order. And all of this can be done with just a few clicks.
So, if the thought of structuring your essay feels overwhelming, let our Table of Contents feature help. We believe it can make your essay-writing process simpler and more enjoyable. Give it a try and see how it works for you. Happy writing, Aithors!
Related articles
How to write an essay in apa format.
There are a few styles of organizing and formatting material in an academic essay. To get high grades it is necessary to learn specific characteristics of each one. After reading this article students are certain to figure out how to write in APA format. What is APA format for an essay? It was the American Psychological Association who offered to use the APA style when formatting articles and academic papers. The specialists described all its aspects in a special Publication Manual, printed i ...
How To Write Reflection Essays
How often do you contemplate how the tapestry of your experiences shapes your thoughts? A reflection paper lets you explore that. It's like deep diving into your life’s precious moments, examining how stories, books, events, or even lectures have influenced your views. This type of academic essay integrates a personal perspective, allowing you to openly express your opinions. In this guide, we will delve into the specifics of reflective writing, share some tips, and show some self-reflection es ...
What Is Chat GPT?
AI GPT chats have been getting a lot of attention over the last year. Not surprising since this new technology promises to change our future completely. The first and most well-known AI GPT chat software is ChatGPT officially released on November 30, 2022. In this article, we will answer the question “What is Chat GPT?”, explore how it works, and find out where to use the Chat GPT model. Chat GPT: definition As the name implies, ChatGPT is a chatbot that uses generative AI to process input p ...
How to Write Informative Essays
Informative essays are one of the main types of academic writing students must complete as part of the educational process. While this is a typical assignment in any curriculum, it can be hard to distinguish between different types of essays and how to write them. In this article, we’ll delve into the genre of this essay type, learn the definition of an informative essay, and how to write an informational essay. What is an informative essay? An informative essay is a piece of academic writin ...
Ace Your Graduation Speech with Aithor
Hello, Aithors! Can you feel it? That's the buzz of graduation season in the air:) And while we're all about the caps flying and the proud smiles, we also know that being asked to write a graduation speech can feel a bit like being handed a mountain to climb. Crafting a graduation speech is all about capturing the spirit of the journey you've been on, from the triumphs to the trials, and everything in between. It's a reflection of where you've been, and a beacon of light pointing towards where ...
APA or MLA: Choosing the Right Citation Style for Your Paper
When it comes to academic writing, properly citing your sources is crucial. It not only helps you avoid plagiarism but also adds credibility to your work by showing that you've done your research. However, with various citation styles out there, it can be tricky to know which one to use. Two of the most common styles are APA (American Psychological Association) and MLA (Modern Language Association). In this article, we'll take a closer look at the APA vs MLA format to help you decide which is ri ...
MLA Format Essays: A Comprehensive Guide
Finishing an essay is one thing, but formatting it is a completely different affair. There are many style guides out there, so it can be hard to understand the differences between them. Today, you will learn about MLA format writing, what it is, when it’s used, and how to write MLA format essays. What is an MLA Style Essay? An MLA format essay is a piece of writing created in accordance with the MLA Style Handbook. This guide was developed by the Modern Language Association, the leading profe ...
Synthesis Essay Examples
A synthesis essay is another piece of academic discourse that students often find difficult to write. This assignment indeed requires a more nuanced approach to writing and performing research. It’s particularly relevant to students taking an AP English Language and Composition exam, so learning how to write a synthesis essay is crucial to getting a high score. This article will explore the definition of a synthesis essay, its functions, and objectives, and provide a tutorial on how to write a ...
- How it works
- Pay for essays
- Do my homework
- Term Paper Writing Service
- Do my assignment
- Coursework help
- Our Writers

Research Paper Structure: The Complete Guide

A professional writer with ten years of experience and a Ph.D. in Modern History, Catharine Tawil writes engaging and insightful papers for academic exchange. With deep insight into the impact of historical events on the present, she provides a unique perspective in giving students a feel for the past. Her writing educates and stimulates critical thinking, making her a treasure to those wading through the complexities of history.
A research paper is an academic work depicting the design and results of a study. It can be an academic assignment in undergraduate and postgraduate programs. Moreover, it is an integral requirement in doctoral programs, where postgrads’ research papers are published in reputable journals to add credibility to their research findings.
Ordering different parts of a research paper is critical for fulfilling academic standards, streamlining your writing, and avoiding distractions and sidetracks. Although outlining may seem like a waste of time, it is the most efficient use of your time at the pre-writing stage, as it will help you order your thoughts and ideas and develop a plan of action to follow throughout the study.
In this post, we’ll cover the basics of the research paper formatting, provide a basic template of a research paper structure, and provide a detailed description of each section, including the title page and abstract, introduction and literature review, methodology, results, discussion, and conclusion. You can skip to a specific section if you have questions or concerns about it or check out the full article for an in-depth understanding of the full structure.
Essential Components of a Research Paper
Unlike other types of academic assignments, research papers have a structure more complex than a simple trio of introduction, body, and conclusion. You are expected to follow the established academic norms and include specific information for your paper to have any scientific value. The basic research paper structure example comprises the following parts:
Introduction
- Literature review
Methodology
- Acknowledgments
Please note that some sections of a research paper outlined above are optional. For example, you only need to include appendices if you wish to share a large volume of data that would make the paper unwieldy. You can also adjust this research paper setup to fit your study and word count requirements better. For instance, you can combine the results and discussion sections or the introduction and literature review.
Formatting Requirements
Although the research paper structure is basically the same for all fields of study and topics, the papers can look drastically different when following research paper formatting guidelines of various formatting styles, be it Chicago, MLA, or APA. You must learn the appropriate style at the onset of the writing process, so remember to ask your academic advisor about it if there’s no mention of the formatting style within general requirements.
Once you know which research paper formatting style to use, get your hands on the relevant formatting guidebook. You can find most of the requirements online or sign out a book from a college library. Considering most formatting guidebooks are huge, focus on the main aspects that can make or break your paper, such as:
- Margins, font, and spacing. Most research paper format guidelines require 1-inch margins on all sides, a legible font of at least 12 pt, and double-spaced lines.
- Page numbering. Requirements vary, but typically, you’ll need to include page numbers in the upper right-hand corner, half an inch from the corner.
- Headings and subheadings. Refer to MLA or APA handbooks to learn specific research paper headings requirements or ask your professor, as the guidelines differ greatly.
- In-text citations and reference list. In most cases, research paper in-text citations require the name of the main author along with the page number or the publication year. Reference list formatting varies across different styles, but you can use automatic citation generators to speed up the formatting process.
With formatting requirements out of the way, let’s now focus on individual components of a research paper to help you understand what each section should contain to be well received.
Title Page and Abstract
The research paper title page format depends on the required formatting style:
- MLA does not require a separate title page (unless specifically requested). Instead, in the upper left-hand corner of the first page, type your name, your instructor’s name, course name, and date (each on a new line, double-spaced). After that, center the title of the page and include its text.
- APA requires a separate title page, which should include the title of the paper, your name and affiliation, as well as the course name and number, your instructor’s name, and the assignment’s due date.
A research paper abstract is brief summary of the main points of the research paper. Depending on the formatting style, it can be from 100 to 250 words long, highlighting the research objective, key methodology, and results highlights. An abstract should help readers decide if your work is worth reading at a glance.
An APA research paper organization requires an abstract on a separate page, with the “Abstract” heading and the paper’s summary (without indent). Below the abstract, type “Keywords:” (in italics) and list the keywords researchers would use to find your paper in the library or online.
The opening section of the research paper outline gives students pause because they never know what the introduction should entail. If you’re stuck with writer’s block and don’t know how to start the paper, answer these four questions, and you’ll have all the major pieces necessary for the introduction:
- What’s the context of the problem? Open with a general view of the issue and its current state without going into too much detail (that’s what the literature review is for). The background information should fit within one or two paragraphs and lead directly to the next point.
- What is the issue? The problem statement or question is the core of this part of the research paper structure. Think of it as a thesis statement for an essay. Everything you write in other sections of a research paper should always tie to your problem statement.
- How do you plan to solve the problem? You can formulate research objectives or hypotheses that your study will try to achieve or prove. Short papers typically have one hypothesis, while longer works usually have two or more related objectives.
- How will your study improve the issue? The answer can circle back to the background you laid out at the beginning of the research paper introduction and highlight the benefits (and potential drawbacks and limitations) of your research. It’s the major “selling point” of the study, which should explain why anyone should care about it.
You can always leave the introduction for last and tackle it once the rest of the paper is done. That’s especially helpful if you use writer’s block as an excuse to procrastinate and put off writing other parts of a research paper.
Literature Review
The primary objective of a research paper literature review is to provide context and prove the relevance of your topic, as specified in the introduction. To that end, you need to find credible, objective, and relevant sources and synthesize any data pertaining to your research. It’s important to avoid simple paraphrasing or summarization of reference data and instead provide its analysis and synthesize your own hypothesis.
Aside from the similarities found in references, this part of the research paper structure should also focus on discrepancies, contradictions, and knowledge gaps. These will prove your study has merit and can resolve the existing issues. Moreover, the knowledge gaps will help lead up to your main research question, which you may repeat near the end of the literature review.
Depending on the topic of your study, you can organize the literature review:
- Chronologically. You can go from the oldest sources published to the latest or from the latest events to situations long past. This approach is often the easiest, but it doesn’t fit all topics and fields of study.
- Thematically. If you wish to cover two or more aspects of the issue, you can dedicate a subsection to each and analyze them together in the final subsection of the literature review. This is the most popular approach, as it can work for most topics.
- Methodologically. If you want to focus on the differences and similarities in research methodology, you can split the literature review into several subsections, devoting each one to a single methodology. This approach works for select subjects and can make the most of systemic studies.
If you’re working on an empirical study, you can stop there, but if your work is mostly theoretical, this stage of the research paper writing process could also involve developing a theoretical framework. It will help put your findings and results into perspective.
Although it may seem simple at first glance, a literature review takes a long time, most of which you’ll spend looking for reliable sources. Luckily, you can easily outsource this task. All you need to do is say, “Write my paper for me”, and our experts will take over ASAP.
The research paper methodology section is an integral part of the piece, as it helps ensure the reproducibility of your results and increases your credibility. This part should answer two main questions:
- What? What did your study involve? What resources, software, materials, or samples did you use? What were the ethical considerations of your research?
- How? How much time did your study take? How did you choose participants? How did you collect data and analyze it?
Keep these questions in mind when working out a research design, picking data collection procedures and analysis techniques. If you rely on standard methods, a quick description with a citation would be enough for the methodology part of the research paper structure. But if you employ a unique approach, make sure to describe it in minute detail to ensure anyone can repeat the process and achieve the same results.
For obvious reasons, the methodology section will differ greatly depending on your field of study and topic. For example, qualitative and quantitative research methods are vastly different. At the same time, quantitative analysis of sociology or linguistics research will be nothing like analyzing blood tests for nursing students or analyzing the success of a marketing campaign for a business and management class. While the tools (i.e., programming language or table processing software) may be similar, the application will be different, and you should highlight these distinctions in your methodology section.
Although you can put off working on this section of the structure of a research paper, it can be helpful to put your methodology on paper before embarking on the study. A clear idea of the protocols you plan to employ should keep your study on track and minimize methodological errors.
The research paper results present the study findings as the ultimate product of your research. Instead of the raw data, you can present analysis results and visual aids in the form of tables, figures, and graphs, provide statistical analysis results, and refer interested readers to appendices containing raw data.
Remember to follow the formatting style requirements for tables and figures, which differ for APA and MLA. The same applies to lists and other visual aids. You should also ensure these materials do not destroy your paper’s readability. For example, a three-page table is much more difficult to grasp than a couple of charts highlighting the same data. Moreover, if you plan to present your findings on a poster or a PowerPoint presentation, it pays to work out the best way to present your insights that will fit all formats, including print and projection.
It’s important to draw the line between the results and discussion parts of the research paper structure. The first presents analysis, while the latter relies on interpretations (or implications) of that analysis. Understanding the distinction can be quite challenging, especially if you’re working out the structure of a research paper for the first time.
Discussion and Conclusion
The research paper discussion connects the introduction and research question with the study results. Instead of merely analyzing data, this section should explain whether your initial hypothesis was correct or not. Moreover, the final section, along with the research paper conclusion, should cover the implications of the findings and their potential practical and theoretical applications. This part can also include the limitations of the study and the need for further research if you feel that it could be useful.
It may seem counterproductive, but you shouldn’t shy away from shortcomings, mistakes, and negative results achieved in your study. Instead of waiting for uncomfortable questions from your instructor, present the bad along with the good and hypothesize potential ways of correcting errors or minimizing the negative influences. In some cases, negative results can be just as valuable (if not more so) than positive findings.
Remember to include the research paper references and appendices after the conclusion to wrap up your work and make it better with careful editing, proofreading, and formatting.
What is the purpose of a research paper?
The main objective is to present and share research insights and discoveries, which you should account for when structuring a research paper. Adding literature review and methodology sections is critical for highlighting the study’s relevance and ensuring its reproducibility.
How do I structure the different sections of a research paper?
Structuring a research paper means adding an introduction, literature review, methodology, results, discussion, and conclusion. You can organize each of these sections thematically or chronologically or use a funnel structure, going from the broad context strokes to a narrow view of the problem.
What are the key formatting guidelines for a research paper?
Specific requirements for the structure of a research paper outline and its contents depend on the preferred formatting style. However, at its core, each formatting style focuses on readability. That’s where 12 pt to 14 pt font size and double line spacing come from. Refer to the relevant formatting style handbook for specific recommendations.
How do I effectively write the introduction and literature review?
The introduction is a critical part of the research paper structure that should include your primary research objective (or question), hypotheses, and the study’s relevance. A literature review is designed to support the claims you make within the introduction by generously using reference data.
What is the difference between the results and discussion sections?
Related posts

Top-3 Hiding Places for Your Cheat Notes

How to Restate a Thesis | Your Student-Friendly Guide With Examples

How to write a hook in an essay: top tips from pro writers
What are you waiting for?
You are a couple of clicks away from tranquility at an affordable price!
Free All-in-One Office Suite with PDF Editor
Edit Word, Excel, and PPT for FREE.
Read, edit, and convert PDFs with the powerful PDF toolkit.
Microsoft-like interface, easy to use.
Windows • MacOS • Linux • iOS • Android
Select areas that need to improve
- Didn't match my interface
- Too technical or incomprehensible
- Incorrect operation instructions
- Incomplete instructions on this function
Fields marked * are required please
Please leave your suggestions below
- Quick Tutorials
- Practical Skills
How to Add Page Numbers in Word for Your Papers? [For Students]
As a student, adding page numbers while writing your research papers, dissertations, and theses etc., can be tricky; especially if your document uses a specific formatting style. But, it's not impossible. How can you add page numbers in Word without any complications? After using Word for multiple papers of my own, I have identified the quickest and easiest way of adding page numbers in Word. In this article, I will show you exactly how.
Typical Issues with Adding Page Numbers in Word
It is common for students to encounter a number of different problems while inserting page numbers in Word. Let’s walk through each of these problems and solve them. Here are a few typical issues you might have come across while adding page numbers in your document:
1.Locating the “Insert Page Number” Option
You can normally find the “Page Number” option in the Insert tab on your Toolbar to add page numbers like below:
2.Errors While Adding Page Numbers
Some students have also encountered an error while adding page numbers by clicking the button “More page numbers from Office.com”. This further gives the resulting error, “no online content available”. To prevent this error you should follow the below steps to diagnose the problem:
Update your Office to ensure that everything is up to date or;
Disable add-ins;
Check for permissions.
In case the above options don’t work, you can try troubleshooting via the system, and proceed with using the built-in templates of page numbers without accessing online content.
3.Formatting Page Numbers
As per the format you will be using for your paper or thesis, you will need to format your page numbers accordingly. There are a variety of ways you can display your page numbers and edit them.
For this, we will explore all the ways you can do this in the guide below:
How to Add Page Numbers to Your Paper in Word [Basic]
In my experience, it was quite simple to add page numbers in my documents, and only got a little tricky when I wanted to format them. I can understand that for some students with a nearer deadline, this can be a frustrating experience. This is why I’ve compiled all the different ways you can add a page number to your paper in Word. To demonstrate, I’ll be using WPS Office, which is easy to follow along and compatible with all Word document versions and devices (Mobile, Windows, or Mac).
Step 1 : First, open the document where you want to add in your page numbers.
If you haven’t started on your document yet, that is okay. You can add in your page numbers and continue your writing later.
Step 2 : Head over to your Toolbar and go to your Insert tab to add in your page numbers
Step 3 : In your Insert tab, you will see the option of “Page Number” and click on it.
Step 4 : After clicking on “Page Number”, you will see a number of different ways you can display your page numbers.
These are built-in templates. Choose the one that best fits your needs.
Note : It might be helpful for you to note that certain academic writing styles require you to use only specific number formats.
For instance, if you are writing your thesis or research paper in APA, MLA, or Chicago format, your page number should be on the top right corner.
How to Add Page Numbers Starting from a Specific Page in Word
For certain academic documents you don’t need page numbers on specific pages, and sometimes you do. It can get a little annoying when you delete a page number from the first page but the next page is still numbered at 2.
It can be helpful to note that if your document is in APA or MLA format, your title page should be page numbered at 1. However, if you’re following the Chicago format, your title page should not have page number at all.
Here’s a simple number of steps you can follow to add page numbers starting from a specific page in Word:
Step 1 : Go to the specific page you want your page numbers to begin.
Step 2 : Insert a section break - “Next Page” in your previous page.
If you have already written your paper, there are pretty good chances you have already inserted your section breaks. Well done on that!
Step 3 : Double click on either the Header or Footer of the page (where you want to add the page number)
Step 4 : Uncheck the box that says “Link to Previous”
Step 5 : Go to the Insert Tab
Step 6 : Click on “Page Numbers” and choose the format you want
If you want your page number to start from 1, follow these steps after the above:
Step 7 : Click on “Page Numbers” once more and scroll down the menu to “Insert Page Number…”. This will open a pop-up box.
Step 8. In the pop-up menu, go to the option “Start at” and enter 1.
Your page numbers will be in line after this. While this process may seem a little lengthy, it is always helpful in my experience to make sure that you insert your section breaks while you are writing your paper. This helps in giving your paper a finished look, makes creating your table of contents easier, and will make many formatting tasks simpler in the long-run.
Using this, you can even use different number formatting styles for different sections of your page, as per your writing format (APA, MLA or Chicago). For instance if you want to use Roman numbers in the initial sections:
Repeat Steps 1-7.
In the pop-up menu, go to the option “Number Format” and select the formatting you want.
Advanced Format of Page Numbers in Word
If you’ve been tasked with formatting page numbers as “Page X of Y'' in Word, there is no need to worry. This method adds clarity, enhances professionalism, and makes your paper easier to navigate for your reader.
You don’t need to manually add this in, as I’ve noticed some students attempt to do so.
While adding these page numbers manually is possible, I would not recommend it. Why? Here are a few downsides to it. If your document is long and consists of 200+ pages, you might be up all night adding these page numbers.
Secondly, even if your document is short, as soon as you add in an extra page in your paper, all your previous total page numbers will automatically be incorrect and you will have to go back in to edit them out.
Word, especially WPS, makes this a lot easier and makes this process a lot more dynamic. Let’s dive into this process:
Step 1 : When inserting page numbers, go to the Insert tab and the “Page Numbers” Option
Step 2 : When the menu opens up, go to Format Page Numbers
Step 3 : In the Format Option, select “Page 1 of X” and click Ok.
Now it will be easier for you and others to navigate through your paper. I have also noticed that it is also easier to refer to or bookmark pages in this particular case.
Use WPS AI to Refine Your Papers
With AI monopolizing the industry, I have found WPS Office readily equipped with everything I need for my writing. When writing research papers, theses, dissertations, WPS AI offers me invaluable assistance in refining my papers and adds finesse to them.
Using WPS has set aside any difficulty that I normally encountered in my writing. With all my writing easily proofread, I can also use simple word replacements and grammar checks to present my arguments in the best way possible.
Here is how students can make use of WPS AI during academic writing, whether it's a thesis or a class assignment:
Step 1 : One of the uses of WPS AI would be to utilize the WPS AI spell check feature to ensure your work is error-free. To do this, visit the Review tab in WPS Writer.
Step 2 : Next, click on the "AI Spell Check" button to open WPS AI Spell Check.
Step 3 : With WPS AI spell check open on the right side of the screen, where all the grammatical errors will be displayed, click on "Accept All" to avoid going through all the corrections.
Step 4 : Furthermore, WPS AI spell check can be tailored according to the academic style being followed. To do this, click on the "Set Goals" button.
Step 5 : Now, set the Domain as "Academic", and then click on the Academic Format of your choice.
WPS AI can also be used to improve writing, or we can also use it to shorten or elongate the content that we have.
Step 1 : Open your academic document on WPS Writer and use your cursor to select the text that you want to improve.
Step 2 : Now, right-click to open the context menu, and then click on the "WPS AI" button.
Step 3 : This will enable the WPS AI assistant, which provides a couple of options for students such as "Improve Writing", "Change Layout", "Make Longer", and others.
Step 4 : Once you have chosen any option, WPS AI will process your request, and the results will be displayed. If you're not content with the results, click on the "Rewrite" option.
Step 5 : Students can also decide to "Replace" or "Discard" the results accordingly.
WPS AI is not just a simple addition to office suites anymore. With the introduction of AI, it acts as an assistant for students, capable of helping them at every step, from brainstorming ideas to refining their work. So why wait? Download WPS Office now and see how it is making life easier for thousands of students!
Use Word, Excel, and PPT for FREE, No Ads.
Edit PDF files with the powerful PDF toolkit.
Microsoft-like interface. Easy to learn. 100% Compatibility.
Boost your productivity with WPS's abundant free Word, Excel, PPT, and CV templates.
Converting Your Papers to PDF While Preserving the Format
As a student, most of your submissions require your papers and documents to be in a PDF format. There are a number of ways you can convert your papers to PDF, however there is no guarantee that your format will remain the same.
Sometimes, converting from Word to PDF will either change your font, or add something on a different page or mess up your alignment.
WPS makes your life easier by having a built-in option to convert your Word documents to PDF while preserving your format.
To make it simpler for you, follow the below steps to do the same.
Step 1 : Go to the Menu.
Step 2 : Click “Export to PDF”.
Step 3 : Select “Common PDF” and then “Export to PDF”.
You can go through your document as well and you will find all your formatting intact.
FAQs about Adding Page Numbers in Word
Q1. how do i stop page numbering from a specific page in word.
There are different ways you can remove page numbers from a specific page or stop page numbering in Word. You can follow the below steps and you will successfully remove your page number.
Click on the page number that you want to remove
Press Delete
If, however, you only want to remove the page number from the first page of the document, then you can simply go to the Header/Footer tab, and select “Different First Page”.
Q2. How do I exclude a page from page numbering?
If you want to exclude certain pages from page numbering, you can follow the below steps to make it simple:
Step 1 : Go to the specific page you want your page number to be excluded
Step 3 : Double click on either the Header or Footer of the page (where you want to delete the page number)
Step 6 : Click on “Page Numbers” and click “Remove Page Number”.
Q3. How to create different headers or footers for odd and even pages
Here is a straightforward guide on how to create custom headers and footers in Microsoft Word:
Step 1 : Open the Word document you wish to customize. Double-click on the header section of the document.
Step 2 : In the Header and Footer ribbon, locate and select the option for "Different Odd & Even Pages."
Step 3 : On an odd page, click on the header or footer area you want to edit. Enter your document title, then press Tab twice.
Step 4 : Go to "Page Number", select "Current Position", and pick a style.
Step 5 : Move to an even page. Repeat the process for page numbering on the even page.
Step 6 : Press Tab twice and type in your document title.
Step 7 : Finally, click on "Close Header and Footer" or press Esc to conclude.
Q4. Can we customize the appearance of page numbers in Word?
Word provides robust customization options for page numbers. You can adjust the font, size, color, style, and positioning of page numbers to align perfectly with your document's layout and design requirements.
Simplify Your Thesis with WPS Writer: Effortless Page Numbering
At the end of your thesis, adding page numbers will be one less problem for you now. With all the tricks up your sleeve on how to add page numbers in Word as per your need, you can format your file exactly the way you want to. WPS, a student-friendly Office-Suite, makes your life easier in more than one way. Download WPS Writer now, to get the full experience.
- 1. How to Add Page Numbers In Word Starting on Page 2 (Step by Step)
- 2. How to add page numbers in word document excluding cover page
- 3. How to add page numbers on certain pages in word
- 4. How to do page numbers in word on page 3 (Step-by Step)
- 5. How to start page numbers on page 2 in WPS Writer
- 6. How to Delete a Page in Word for Your Thesis/Dissertation? [For Students]
15 years of office industry experience, tech lover and copywriter. Follow me for product reviews, comparisons, and recommendations for new apps and software.
Main Navigation
- Contact NeurIPS
- Code of Ethics
- Code of Conduct
- Create Profile
- Journal To Conference Track
- Diversity & Inclusion
- Proceedings
- Future Meetings
- Exhibitor Information
- Privacy Policy
NeurIPS 2024
Conference Dates: (In person) 9 December - 15 December, 2024
Homepage: https://neurips.cc/Conferences/2024/
Call For Papers
Abstract submission deadline: May 15, 2024
Full paper submission deadline, including technical appendices and supplemental material (all authors must have an OpenReview profile when submitting): May 22, 2024
Author notification: Sep 25, 2024
Camera-ready, poster, and video submission: Oct 30, 2024 AOE
Submit at: https://openreview.net/group?id=NeurIPS.cc/2024/Conference
The site will start accepting submissions on Apr 22, 2024
Subscribe to these and other dates on the 2024 dates page .
The Thirty-Eighth Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS 2024) is an interdisciplinary conference that brings together researchers in machine learning, neuroscience, statistics, optimization, computer vision, natural language processing, life sciences, natural sciences, social sciences, and other adjacent fields. We invite submissions presenting new and original research on topics including but not limited to the following:
- Applications (e.g., vision, language, speech and audio, Creative AI)
- Deep learning (e.g., architectures, generative models, optimization for deep networks, foundation models, LLMs)
- Evaluation (e.g., methodology, meta studies, replicability and validity, human-in-the-loop)
- General machine learning (supervised, unsupervised, online, active, etc.)
- Infrastructure (e.g., libraries, improved implementation and scalability, distributed solutions)
- Machine learning for sciences (e.g. climate, health, life sciences, physics, social sciences)
- Neuroscience and cognitive science (e.g., neural coding, brain-computer interfaces)
- Optimization (e.g., convex and non-convex, stochastic, robust)
- Probabilistic methods (e.g., variational inference, causal inference, Gaussian processes)
- Reinforcement learning (e.g., decision and control, planning, hierarchical RL, robotics)
- Social and economic aspects of machine learning (e.g., fairness, interpretability, human-AI interaction, privacy, safety, strategic behavior)
- Theory (e.g., control theory, learning theory, algorithmic game theory)
Machine learning is a rapidly evolving field, and so we welcome interdisciplinary submissions that do not fit neatly into existing categories.
Authors are asked to confirm that their submissions accord with the NeurIPS code of conduct .
Formatting instructions: All submissions must be in PDF format, and in a single PDF file include, in this order:
- The submitted paper
- Technical appendices that support the paper with additional proofs, derivations, or results
- The NeurIPS paper checklist
Other supplementary materials such as data and code can be uploaded as a ZIP file
The main text of a submitted paper is limited to nine content pages , including all figures and tables. Additional pages containing references don’t count as content pages. If your submission is accepted, you will be allowed an additional content page for the camera-ready version.
The main text and references may be followed by technical appendices, for which there is no page limit.
The maximum file size for a full submission, which includes technical appendices, is 50MB.
Authors are encouraged to submit a separate ZIP file that contains further supplementary material like data or source code, when applicable.
You must format your submission using the NeurIPS 2024 LaTeX style file which includes a “preprint” option for non-anonymous preprints posted online. Submissions that violate the NeurIPS style (e.g., by decreasing margins or font sizes) or page limits may be rejected without further review. Papers may be rejected without consideration of their merits if they fail to meet the submission requirements, as described in this document.
Paper checklist: In order to improve the rigor and transparency of research submitted to and published at NeurIPS, authors are required to complete a paper checklist . The paper checklist is intended to help authors reflect on a wide variety of issues relating to responsible machine learning research, including reproducibility, transparency, research ethics, and societal impact. The checklist forms part of the paper submission, but does not count towards the page limit.
Please join the NeurIPS 2024 Checklist Assistant Study that will provide you with free verification of your checklist performed by an LLM here . Please see details in our blog
Supplementary material: While all technical appendices should be included as part of the main paper submission PDF, authors may submit up to 100MB of supplementary material, such as data, or source code in a ZIP format. Supplementary material should be material created by the authors that directly supports the submission content. Like submissions, supplementary material must be anonymized. Looking at supplementary material is at the discretion of the reviewers.
We encourage authors to upload their code and data as part of their supplementary material in order to help reviewers assess the quality of the work. Check the policy as well as code submission guidelines and templates for further details.
Use of Large Language Models (LLMs): We welcome authors to use any tool that is suitable for preparing high-quality papers and research. However, we ask authors to keep in mind two important criteria. First, we expect papers to fully describe their methodology, and any tool that is important to that methodology, including the use of LLMs, should be described also. For example, authors should mention tools (including LLMs) that were used for data processing or filtering, visualization, facilitating or running experiments, and proving theorems. It may also be advisable to describe the use of LLMs in implementing the method (if this corresponds to an important, original, or non-standard component of the approach). Second, authors are responsible for the entire content of the paper, including all text and figures, so while authors are welcome to use any tool they wish for writing the paper, they must ensure that all text is correct and original.
Double-blind reviewing: All submissions must be anonymized and may not contain any identifying information that may violate the double-blind reviewing policy. This policy applies to any supplementary or linked material as well, including code. If you are including links to any external material, it is your responsibility to guarantee anonymous browsing. Please do not include acknowledgements at submission time. If you need to cite one of your own papers, you should do so with adequate anonymization to preserve double-blind reviewing. For instance, write “In the previous work of Smith et al. [1]…” rather than “In our previous work [1]...”). If you need to cite one of your own papers that is in submission to NeurIPS and not available as a non-anonymous preprint, then include a copy of the cited anonymized submission in the supplementary material and write “Anonymous et al. [1] concurrently show...”). Any papers found to be violating this policy will be rejected.
OpenReview: We are using OpenReview to manage submissions. The reviews and author responses will not be public initially (but may be made public later, see below). As in previous years, submissions under review will be visible only to their assigned program committee. We will not be soliciting comments from the general public during the reviewing process. Anyone who plans to submit a paper as an author or a co-author will need to create (or update) their OpenReview profile by the full paper submission deadline. Your OpenReview profile can be edited by logging in and clicking on your name in https://openreview.net/ . This takes you to a URL "https://openreview.net/profile?id=~[Firstname]_[Lastname][n]" where the last part is your profile name, e.g., ~Wei_Zhang1. The OpenReview profiles must be up to date, with all publications by the authors, and their current affiliations. The easiest way to import publications is through DBLP but it is not required, see FAQ . Submissions without updated OpenReview profiles will be desk rejected. The information entered in the profile is critical for ensuring that conflicts of interest and reviewer matching are handled properly. Because of the rapid growth of NeurIPS, we request that all authors help with reviewing papers, if asked to do so. We need everyone’s help in maintaining the high scientific quality of NeurIPS.
Please be aware that OpenReview has a moderation policy for newly created profiles: New profiles created without an institutional email will go through a moderation process that can take up to two weeks. New profiles created with an institutional email will be activated automatically.
Venue home page: https://openreview.net/group?id=NeurIPS.cc/2024/Conference
If you have any questions, please refer to the FAQ: https://openreview.net/faq
Abstract Submission: There is a mandatory abstract submission deadline on May 15, 2024, six days before full paper submissions are due. While it will be possible to edit the title and abstract until the full paper submission deadline, submissions with “placeholder” abstracts that are rewritten for the full submission risk being removed without consideration. This includes titles and abstracts that either provide little or no semantic information (e.g., "We provide a new semi-supervised learning method.") or describe a substantively different claimed contribution. The author list cannot be changed after the abstract deadline. After that, authors may be reordered, but any additions or removals must be justified in writing and approved on a case-by-case basis by the program chairs only in exceptional circumstances.
Ethics review: Reviewers and ACs may flag submissions for ethics review . Flagged submissions will be sent to an ethics review committee for comments. Comments from ethics reviewers will be considered by the primary reviewers and AC as part of their deliberation. They will also be visible to authors, who will have an opportunity to respond. Ethics reviewers do not have the authority to reject papers, but in extreme cases papers may be rejected by the program chairs on ethical grounds, regardless of scientific quality or contribution.
Preprints: The existence of non-anonymous preprints (on arXiv or other online repositories, personal websites, social media) will not result in rejection. If you choose to use the NeurIPS style for the preprint version, you must use the “preprint” option rather than the “final” option. Reviewers will be instructed not to actively look for such preprints, but encountering them will not constitute a conflict of interest. Authors may submit anonymized work to NeurIPS that is already available as a preprint (e.g., on arXiv) without citing it. Note that public versions of the submission should not say "Under review at NeurIPS" or similar.
Dual submissions: Submissions that are substantially similar to papers that the authors have previously published or submitted in parallel to other peer-reviewed venues with proceedings or journals may not be submitted to NeurIPS. Papers previously presented at workshops are permitted, so long as they did not appear in a conference proceedings (e.g., CVPRW proceedings), a journal or a book. NeurIPS coordinates with other conferences to identify dual submissions. The NeurIPS policy on dual submissions applies for the entire duration of the reviewing process. Slicing contributions too thinly is discouraged. The reviewing process will treat any other submission by an overlapping set of authors as prior work. If publishing one would render the other too incremental, both may be rejected.
Anti-collusion: NeurIPS does not tolerate any collusion whereby authors secretly cooperate with reviewers, ACs or SACs to obtain favorable reviews.
Author responses: Authors will have one week to view and respond to initial reviews. Author responses may not contain any identifying information that may violate the double-blind reviewing policy. Authors may not submit revisions of their paper or supplemental material, but may post their responses as a discussion in OpenReview. This is to reduce the burden on authors to have to revise their paper in a rush during the short rebuttal period.
After the initial response period, authors will be able to respond to any further reviewer/AC questions and comments by posting on the submission’s forum page. The program chairs reserve the right to solicit additional reviews after the initial author response period. These reviews will become visible to the authors as they are added to OpenReview, and authors will have a chance to respond to them.
After the notification deadline, accepted and opted-in rejected papers will be made public and open for non-anonymous public commenting. Their anonymous reviews, meta-reviews, author responses and reviewer responses will also be made public. Authors of rejected papers will have two weeks after the notification deadline to opt in to make their deanonymized rejected papers public in OpenReview. These papers are not counted as NeurIPS publications and will be shown as rejected in OpenReview.
Publication of accepted submissions: Reviews, meta-reviews, and any discussion with the authors will be made public for accepted papers (but reviewer, area chair, and senior area chair identities will remain anonymous). Camera-ready papers will be due in advance of the conference. All camera-ready papers must include a funding disclosure . We strongly encourage accompanying code and data to be submitted with accepted papers when appropriate, as per the code submission policy . Authors will be allowed to make minor changes for a short period of time after the conference.
Contemporaneous Work: For the purpose of the reviewing process, papers that appeared online within two months of a submission will generally be considered "contemporaneous" in the sense that the submission will not be rejected on the basis of the comparison to contemporaneous work. Authors are still expected to cite and discuss contemporaneous work and perform empirical comparisons to the degree feasible. Any paper that influenced the submission is considered prior work and must be cited and discussed as such. Submissions that are very similar to contemporaneous work will undergo additional scrutiny to prevent cases of plagiarism and missing credit to prior work.
Plagiarism is prohibited by the NeurIPS Code of Conduct .
Other Tracks: Similarly to earlier years, we will host multiple tracks, such as datasets, competitions, tutorials as well as workshops, in addition to the main track for which this call for papers is intended. See the conference homepage for updates and calls for participation in these tracks.
Experiments: As in past years, the program chairs will be measuring the quality and effectiveness of the review process via randomized controlled experiments. All experiments are independently reviewed and approved by an Institutional Review Board (IRB).
Financial Aid: Each paper may designate up to one (1) NeurIPS.cc account email address of a corresponding student author who confirms that they would need the support to attend the conference, and agrees to volunteer if they get selected. To be considered for Financial the student will also need to fill out the Financial Aid application when it becomes available.
Home / Guides / Citation Guides / Citation Basics
Citation Basics
Learn what a citation is, how to cite the best evidence, and why you should cite.
- Citation Examples
- Citing Evidence
- Why Do I Cite? When Do I Cite?
- Differences Between Footnotes, Endnotes, and Parenthetical Citations
- Annotated Bibliographies
- Capitalization Rules
- Citing Website with No Author
- Italicizing Titles
- How to Tell if a Website is Credible
- Paraphrasing vs Summarizing
- Citing a Source in a Foreign Language
- Primary vs Secondary Sources
- What is Considered Common Knowledge?
- What is Considered a Scholarly Source?
Harvard Referencing
Plagiarism Basics
Plagiarism Checker
Upload a paper to check for plagiarism against billions of sources and get advanced writing suggestions for clarity and style.
Get Started
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
MLA Works Cited Page: Books

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
When you are gathering book sources, be sure to make note of the following bibliographic items: the author name(s), other contributors such as translators or editors, the book’s title, editions of the book, the publication date, the publisher, and the pagination.
The 8 th edition of the MLA handbook highlights principles over prescriptive practices. Essentially, a writer will need to take note of primary elements in every source, such as author, title, etc. and then assort them in a general format. Thus, by using this methodology, a writer will be able to cite any source regardless of whether it’s included in this list.
Please note these changes in the new edition:
- Commas are used instead of periods between Publisher, Publication Date, and Pagination.
- Medium is no longer necessary.
- Containers are now a part of the MLA process. Commas should be used after container titles.
- DOIs should be used instead of URLS when available.
- Use the term “Accessed” instead of listing the date or the abbreviation, “n.d."
Below is the general format for any citation:
Author. Title. Title of container (do not list container for standalone books, e.g. novels), Other contributors (translators or editors), Version (edition), Number (vol. and/or no.), Publisher, Publication Date, Location (pages, paragraphs URL or DOI). 2 nd container’s title, Other contributors, Version, Number, Publisher, Publication date, Location, Date of Access (if applicable).
Basic Book Format
The author’s name or a book with a single author's name appears in last name, first name format. The basic form for a book citation is:
Last Name, First Name. Title of Book . City of Publication, Publisher, Publication Date.
* Note: the City of Publication should only be used if the book was published before 1900, if the publisher has offices in more than one country, or if the publisher is unknown in North America.
Book with One Author
Gleick, James. Chaos: Making a New Science . Penguin, 1987.
Henley, Patricia. The Hummingbird House . MacMurray, 1999.
Book with More Than One Author
When a book has two authors, order the authors in the same way they are presented in the book. Start by listing the first name that appears on the book in last name, first name format; subsequent author names appear in normal order (first name last name format).
Gillespie, Paula, and Neal Lerner. The Allyn and Bacon Guide to Peer Tutoring . Allyn and Bacon, 2000.
If there are three or more authors, list only the first author followed by the phrase et al. (Latin for "and others") in place of the subsequent authors' names. (Note that there is a period after “al” in “et al.” Also note that there is never a period after the “et” in “et al.”).
Wysocki, Anne Frances, et al. Writing New Media: Theory and Applications for Expanding the Teaching of Composition . Utah State UP, 2004.
Two or More Books by the Same Author
List works alphabetically by title. (Remember to ignore articles like A, An, and The.) Provide the author’s name in last name, first name format for the first entry only. For each subsequent entry by the same author, use three hyphens and a period.
Palmer, William J. Dickens and New Historicism . St. Martin's, 1997.
---. The Films of the Eighties: A Social History . Southern Illinois UP, 1993.
Book by a Corporate Author or Organization
A corporate author may include a commission, a committee, a government agency, or a group that does not identify individual members on the title page.
List the names of corporate authors in the place where an author’s name typically appears at the beginning of the entry.
American Allergy Association. Allergies in Children . Random House, 1998.
When the author and publisher are the same, skip the author, and list the title first. Then, list the corporate author only as the publisher.
Fair Housing—Fair Lending. Aspen Law & Business, 1985.
Book with No Author
List by title of the book. Incorporate these entries alphabetically just as you would with works that include an author name. For example, the following entry might appear between entries of works written by Dean, Shaun and Forsythe, Jonathan.
Encyclopedia of Indiana . Somerset, 1993.
Remember that for an in-text (parenthetical) citation of a book with no author, you should provide the name of the work in the signal phrase and the page number in parentheses. You may also use a shortened version of the title of the book accompanied by the page number. For more information see the In-text Citations for Print Sources with No Known Author section of In-text Citations: The Basics .
A Translated Book
If you want to emphasize the work rather than the translator, cite as you would any other book. Add “translated by” and follow with the name(s) of the translator(s).
Foucault, Michel. Madness and Civilization: A History of Insanity in the Age of Reason . Translated by Richard Howard, Vintage-Random House, 1988.
If you want to focus on the translation, list the translator as the author. In place of the author’s name, the translator’s name appears. His or her name is followed by the label, “translator.” If the author of the book does not appear in the title of the book, include the name, with a “By” after the title of the book and before the publisher. Note that this type of citation is less common and should only be used for papers or writing in which translation plays a central role.
Howard, Richard, translator. Madness and Civilization: A History of Insanity in the Age of Reason . By Michel Foucault, Vintage-Random House, 1988.
Republished Book
Books may be republished due to popularity without becoming a new edition. New editions are typically revisions of the original work. For books that originally appeared at an earlier date and that have been republished at a later one, insert the original publication date before the publication information.
For books that are new editions (i.e. different from the first or other editions of the book), see An Edition of a Book below.
Butler, Judith. Gender Trouble . 1990. Routledge, 1999.
Erdrich, Louise. Love Medicine . 1984. Perennial-Harper, 1993.
An Edition of a Book
There are two types of editions in book publishing: a book that has been published more than once in different editions and a book that is prepared by someone other than the author (typically an editor).
A Subsequent Edition
Cite the book as you normally would, but add the number of the edition after the title.
Crowley, Sharon, and Debra Hawhee. Ancient Rhetorics for Contemporary Students . 3rd ed., Pearson, 2004.
A Work Prepared by an Editor
Cite the book as you normally would, but add the editor after the title with the label "edited by."
Bronte, Charlotte. Jane Eyre, edited by Margaret Smith, Oxford UP, 1998.
Note that the format for citing sources with important contributors with editor-like roles follows the same basic template:
...adapted by John Doe...
Finally, in the event that the source features a contributor that cannot be described with a past-tense verb and the word "by" (e.g., "edited by"), you may instead use a noun followed by a comma, like so:
...guest editor, Jane Smith...
Anthology or Collection (e.g. Collection of Essays)
To cite the entire anthology or collection, list by editor(s) followed by a comma and "editor" or, for multiple editors, "editors." This sort of entry is somewhat rare. If you are citing a particular piece within an anthology or collection (more common), see A Work in an Anthology, Reference, or Collection below.
Hill, Charles A., and Marguerite Helmers, editors. Defining Visual Rhetorics . Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, 2004.
Peterson, Nancy J., editor. Toni Morrison: Critical and Theoretical Approaches . Johns Hopkins UP, 1997.
A Work in an Anthology, Reference, or Collection
Works may include an essay in an edited collection or anthology, or a chapter of a book. The basic form is for this sort of citation is as follows:
Last name, First name. "Title of Essay." Title of Collection , edited by Editor's Name(s), Publisher, Year, Page range of entry.
Some examples:
Harris, Muriel. "Talk to Me: Engaging Reluctant Writers." A Tutor's Guide: Helping Writers One to One , edited by Ben Rafoth, Heinemann, 2000, pp. 24-34.
Swanson, Gunnar. "Graphic Design Education as a Liberal Art: Design and Knowledge in the University and The 'Real World.'" The Education of a Graphic Designer , edited by Steven Heller, Allworth Press, 1998, pp. 13-24.
Note on Cross-referencing Several Items from One Anthology: If you cite more than one essay from the same edited collection, MLA indicates you may cross-reference within your works cited list in order to avoid writing out the publishing information for each separate essay. You should consider this option if you have several references from a single text. To do so, include a separate entry for the entire collection listed by the editor's name as below:
Rose, Shirley K, and Irwin Weiser, editors. The Writing Program Administrator as Researcher . Heinemann, 1999.
Then, for each individual essay from the collection, list the author's name in last name, first name format, the title of the essay, the editor's last name, and the page range:
L'Eplattenier, Barbara. "Finding Ourselves in the Past: An Argument for Historical Work on WPAs." Rose and Weiser, pp. 131-40.
Peeples, Tim. "'Seeing' the WPA With/Through Postmodern Mapping." Rose and Weiser, pp. 153-67.
Please note: When cross-referencing items in the works cited list, alphabetical order should be maintained for the entire list.
Poem or Short Story Examples :
Burns, Robert. "Red, Red Rose." 100 Best-Loved Poems, edited by Philip Smith, Dover, 1995, p. 26.
Kincaid, Jamaica. "Girl." The Vintage Book of Contemporary American Short Stories , edited by Tobias Wolff, Vintage, 1994, pp. 306-07.
If the specific literary work is part of the author's own collection (all of the works have the same author), then there will be no editor to reference:
Whitman, Walt. "I Sing the Body Electric." Selected Poems, Dover, 1991, pp. 12-19.
Carter, Angela. "The Tiger's Bride." Burning Your Boats: The Collected Stories, Penguin, 1995, pp. 154-69.
Article in a Reference Book (e.g. Encyclopedias, Dictionaries)
For entries in encyclopedias, dictionaries, and other reference works, cite the entry name as you would any other work in a collection but do not include the publisher information. Also, if the reference book is organized alphabetically, as most are, do not list the volume or the page number of the article or item.
"Ideology." The American Heritage Dictionary. 3rd ed. 1997.
A Multivolume Work
When citing only one volume of a multivolume work, include the volume number after the work's title, or after the work's editor or translator.
Quintilian. Institutio Oratoria . Translated by H. E. Butler, vol. 2, Loeb-Harvard UP, 1980.
When citing more than one volume of a multivolume work, cite the total number of volumes in the work. Also, be sure in your in-text citation to provide both the volume number and page number(s) ( see "Citing Multivolume Works" on our in-text citations resource .)
Quintilian. Institutio Oratoria . Translated by H. E. Butler, Loeb-Harvard UP, 1980. 4 vols.
If the volume you are using has its own title, cite the book without referring to the other volumes as if it were an independent publication.
Churchill, Winston S. The Age of Revolution . Dodd, 1957.
An Introduction, Preface, Foreword, or Afterword
When citing an introduction, a preface, a foreword, or an afterword, write the name of the author(s) of the piece you are citing. Then give the name of the part being cited, which should not be italicized or enclosed in quotation marks; in italics, provide the name of the work and the name of the author of the introduction/preface/foreword/afterword. Finish the citation with the details of publication and page range.
Farrell, Thomas B. Introduction. Norms of Rhetorical Culture , by Farrell, Yale UP, 1993, pp. 1-13.
If the writer of the piece is different from the author of the complete work , then write the full name of the principal work's author after the word "By." For example, if you were to cite Hugh Dalziel Duncan’s introduction of Kenneth Burke’s book Permanence and Change, you would write the entry as follows:
Duncan, Hugh Dalziel. Introduction. Permanence and Change: An Anatomy of Purpose, by Kenneth Burke, 1935, 3rd ed., U of California P, 1984, pp. xiii-xliv.
Book Published Before 1900
Original copies of books published before 1900 are usually defined by their place of publication rather than the publisher. Unless you are using a newer edition, cite the city of publication where you would normally cite the publisher.
Thoreau, Henry David. Excursions . Boston, 1863.
Italicize “The Bible” and follow it with the version you are using. Remember that your in-text (parenthetical citation) should include the name of the specific edition of the Bible, followed by an abbreviation of the book, the chapter and verse(s). (See Citing the Bible at In-Text Citations: The Basics .)
The Bible. Authorized King James Version , Oxford UP, 1998.
The Bible. The New Oxford Annotated Version , 3rd ed., Oxford UP, 2001.
The New Jerusalem Bible. Edited by Susan Jones, Doubleday, 1985.
A Government Publication
Cite the author of the publication if the author is identified. Otherwise, start with the name of the national government, followed by the agency (including any subdivisions or agencies) that serves as the organizational author. For congressional documents, be sure to include the number of the Congress and the session when the hearing was held or resolution passed as well as the report number. US government documents are typically published by the Government Printing Office.
United States, Congress, Senate, Committee on Energy and Natural Resources. Hearing on the Geopolitics of Oil . Government Printing Office, 2007. 110th Congress, 1st session, Senate Report 111-8.
United States, Government Accountability Office. Climate Change: EPA and DOE Should Do More to Encourage Progress Under Two Voluntary Programs . Government Printing Office, 2006.
Cite the title and publication information for the pamphlet just as you would a book without an author. Pamphlets and promotional materials commonly feature corporate authors (commissions, committees, or other groups that does not provide individual group member names). If the pamphlet you are citing has no author, cite as directed below. If your pamphlet has an author or a corporate author, put the name of the author (last name, first name format) or corporate author in the place where the author name typically appears at the beginning of the entry. (See also Books by a Corporate Author or Organization above.)
Women's Health: Problems of the Digestive System . American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, 2006.
Your Rights Under California Welfare Programs . California Department of Social Services, 2007.
Dissertations and Master's Theses
Dissertations and master's theses may be used as sources whether published or not. Unlike previous editions, MLA 8 specifies no difference in style for published/unpublished works.
The main elements of a dissertation citation are the same as those for a book: author name(s), title (italicized) , and publication date. Conclude with an indication of the document type (e.g., "PhD dissertation"). The degree-granting institution may be included before the document type (though this is not required). If the dissertation was accessed through an online repository, include it as the second container after all the other elements.
Bishop, Karen Lynn. Documenting Institutional Identity: Strategic Writing in the IUPUI Comprehensive Campaign . 2002. Purdue University, PhD dissertation.
Bile, Jeffrey. Ecology, Feminism, and a Revised Critical Rhetoric: Toward a Dialectical Partnership . 2005. Ohio University, PhD dissertation.
Mitchell, Mark. The Impact of Product Quality Reducing Events on the Value of Brand-Name Capital: Evidence from Airline Crashes and the 1982 Tylenol Poisonings. 1987. PhD dissertation. ProQuest Dissertations and Theses.
List the names of corporate authors in the place where an author’s name typically appears at the beginning of the entry if the author and publisher are not the same.
Fair Housing—Fair Lending. Aspen Law & Business, 1985.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
MLA (Modern Language Association) style is most commonly used to write papers and cite sources within the liberal arts and humanities. This resource, updated to reflect the MLA Handbook (9th ed.), offers examples for the general format of MLA research papers, in-text citations, endnotes/footnotes, and the Works Cited page.
MLA format is a widely used citation style for academic papers. Learn how to format your title page, header, and Works Cited page with our free template and examples. Watch our 3-minute video to see how easy it is to apply MLA rules to your document.
Use 12-point size. Double space the entire research paper, even the Works Cited page. Leave one space after periods and other punctuation marks, unless your instructor tells you to leave two spaces. These guidelines come from the MLA Style Center's web page "Formatting a Research Paper.".
Create manual citation. The guidelines for citing an essay in MLA format are similar to those for citing a chapter in a book. Include the author of the essay, the title of the essay, the name of the collection if the essay belongs to one, the editor of the collection or other contributors, the publication information, and the page number (s).
This guide follows the 9th edition (the most recent) of the MLA Handbook, published by the Modern Language Association in 2021. To cite sources in MLA style, you need. In-text citations that give the author's last name and a page number. A list of Works Cited that gives full details of every source. Make sure your paper also adheres to MLA ...
Get started with MLA style. Learn how to document sources, set up your paper, and improve your teaching and writing. Document Sources Works Cited Quick Guide Learn how to use the MLA format template. Digital Citation Tool Build citations with our interactive template. In-Text Citations Get help with in-text citations. Endnotes and Footnotes Read our …
With this focus on source evaluation as the cornerstone of citation, MLA style promotes the skills of information and digital literacy so crucial today. The new edition offers. New chapters on grammar, punctuation, capitalization, spelling, numbers, italics, abbreviations, and principles of inclusive language.
In order to properly cite a source in MLA style, you must have both citation types in your paper. Every in-text citation has a works cited list entry. Every works cited list entry has at least one (maybe more) corresponding in-text citation. In-text citations. The basic element needed for an in-text citation is the author's surname. The ...
Congratulations to the students whose essays were selected for the 2023 edition of Writing with MLA Style! Essays were selected as examples of excellent student writing that use MLA style for citing sources. Essays have been lightly edited. If your institution subscribes to MLA Handbook Plus, you can access annotated versions of the essays selected …
MLA Guide to Digital Literacy, 2nd Edition: An Interview with the Author. by Ellen C. Carillo Ellen C. Carillo talks to the MLA about the MLA Guide to Digital Literacy, second edition.Read More
Revised on March 5, 2024. An MLA in-text citation provides the author's last name and a page number in parentheses. If a source has two authors, name both. If a source has more than two authors, name only the first author, followed by " et al. ". If the part you're citing spans multiple pages, include the full page range.
As you find each source you want to use, create a citation. Note: don't wait to cite; do so early! Those citations you've created will then be placed at the end of the paper, on a page entitled "Works Cited". Formatting: List entries alphabetically by the first word (often an author's last name). Double-space
When it comes to formatting your paper or essay for academic purposes, there are specific MLA paper format guidelines to follow. Use paper that is 8½-by-11 inch in size. This is the standard size for copier and printer paper. Use high quality paper.
Generate MLA format citations and create your works cited page accurately with our free MLA citation generator. Now fully compatible with MLA 8th and 9th Edition. ... The citations on a Works Cited page show the external sources that were used to write the main body of the academic paper, either directly as references and quotes, or indirectly ...
MLA format is a widely accepted style for writing and documenting scholarly papers, particularly in the humanities. It provides guidelines for formatting manuscripts, citing sources, and structuring works cited pages, ensuring consistency and clarity.Adhering to MLA format helps writers present their research in a professional and organized manner, facilitating readability and academic integrity.
MLA Handbook 9th Edition 1.0: Introduction to Formatting Your Research Project The following guidelines have been widely adopted by instructors and educational institutions to standardize manuscript formatting, making it easier for instructors to evaluate papers and theses and for writers to focus on making decisions about their research, ideas ...
How to cite in MLA format. MLA is one of the most common citation styles used by students and academics. This quick guide explains how to cite sources according to the 9th edition (the most recent) of the MLA Handbook.You can also use Scribbr's free citation generator to automatically generate references and in-text citations.. An MLA citation has two components:
A bibliography is a list of sources used in researching and writing a work, such as a book, article, or academic paper. It includes detailed information about each source, like the author's name, title, and publication date. Bibliographies serve to credit authors, avoid plagiarism, provide references for readers, and demonstrate the research scope.
MLA Format Essays: A Comprehensive Guide. Finishing an essay is one thing, but formatting it is a completely different affair. There are many style guides out there, so it can be hard to understand the differences between them. Today, you will learn about MLA format writing, what it is, when it's used, and how to write MLA format essays.
EasyBib® has tools to help you create citations for over 50 source types in this style, as well as a guide to show you how an MLA paper should be formatted. Review the guide to learn how to format a paper's title page, paragraphs, margins, quotations, abbreviations, numbers, tables, and more! There are even tips on editing, as well as on the ...
The research paper title page format depends on the required formatting style: MLA does not require a separate title page (unless specifically requested). Instead, in the upper left-hand corner of the first page, type your name, your instructor's name, course name, and date (each on a new line, double-spaced).
Revised on March 5, 2024. An MLA website citation includes the author's name, the title of the page (in quotation marks), the name of the website (in italics), the publication date, and the URL (without "https://"). If the author is unknown, start with the title of the page instead. If the publication date is unknown, or if the content is ...
Well done on that! Step 3: Double click on either the Header or Footer of the page (where you want to add the page number) Step 4: Uncheck the box that says "Link to Previous". Link to Previous option in Header/Footer tab. Step 5: Go to the Insert Tab. Step 6: Click on "Page Numbers" and choose the format you want.
Formatting instructions: All submissions must be in PDF format, and in a single PDF file include, ... Please do not include acknowledgements at submission time. If you need to cite one of your own papers, you should do so with adequate anonymization to preserve double-blind reviewing. For instance, write "In the previous work of Smith et al ...
Annotated Bibliographies. APA vs MLA. Capitalization Rules. Citing Website with No Author. Italicizing Titles. How to Tell if a Website is Credible. Paraphrasing vs Summarizing. Citing a Source in a Foreign Language. Primary vs Secondary Sources.
Cite a book automatically in MLA. The 8 th edition of the MLA handbook highlights principles over prescriptive practices. Essentially, a writer will need to take note of primary elements in every source, such as author, title, etc. and then assort them in a general format. Thus, by using this methodology, a writer will be able to cite any ...