

Writing Rubrics [Examples, Best Practices, & Free Templates]
Writing rubrics are essential tools for teachers.
Rubrics can improve both teaching and learning. This guide will explain writing rubrics, their benefits, and how to create and use them effectively.
What Is a Writing Rubric?

Table of Contents
A writing rubric is a scoring guide used to evaluate written work.
It lists criteria and describes levels of quality from excellent to poor. Rubrics provide a standardized way to assess writing.
They make expectations clear and grading consistent.
Key Components of a Writing Rubric
- Criteria : Specific aspects of writing being evaluated (e.g., grammar, organization).
- Descriptors : Detailed descriptions of what each level of performance looks like.
- Scoring Levels : Typically, a range (e.g., 1-4 or 1-6) showing levels of mastery.
Example Breakdown
| Criteria | 4 (Excellent) | 3 (Good) | 2 (Fair) | 1 (Poor) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grammar | No errors | Few minor errors | Several errors | Many errors |
| Organization | Clear and logical | Mostly clear | Somewhat clear | Not clear |
| Content | Thorough and insightful | Good, but not thorough | Basic, lacks insight | Incomplete or off-topic |
Benefits of Using Writing Rubrics
Writing rubrics offer many advantages:
- Clarity : Rubrics clarify expectations for students. They know what is required for each level of performance.
- Consistency : Rubrics standardize grading. This ensures fairness and consistency across different students and assignments.
- Feedback : Rubrics provide detailed feedback. Students understand their strengths and areas for improvement.
- Efficiency : Rubrics streamline the grading process. Teachers can evaluate work more quickly and systematically.
- Self-Assessment : Students can use rubrics to self-assess. This promotes reflection and responsibility for their learning.
Examples of Writing Rubrics
Here are some examples of writing rubrics.
Narrative Writing Rubric
| Criteria | 4 (Excellent) | 3 (Good) | 2 (Fair) | 1 (Poor) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Story Elements | Well-developed | Developed, some details | Basic, missing details | Underdeveloped |
| Creativity | Highly creative | Creative | Some creativity | Lacks creativity |
| Grammar | No errors | Few minor errors | Several errors | Many errors |
| Organization | Clear and logical | Mostly clear | Somewhat clear | Not clear |
| Language Use | Rich and varied | Varied | Limited | Basic or inappropriate |
Persuasive Writing Rubric
| Criteria | 4 (Excellent) | 3 (Good) | 2 (Fair) | 1 (Poor) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Argument | Strong and convincing | Convincing, some gaps | Basic, lacks support | Weak or unsupported |
| Evidence | Strong and relevant | Relevant, but not strong | Some relevant, weak | Irrelevant or missing |
| Grammar | No errors | Few minor errors | Several errors | Many errors |
| Organization | Clear and logical | Mostly clear | Somewhat clear | Not clear |
| Language Use | Persuasive and engaging | Engaging | Somewhat engaging | Not engaging |
Best Practices for Creating Writing Rubrics
Let’s look at some best practices for creating useful writing rubrics.
1. Define Clear Criteria
Identify specific aspects of writing to evaluate. Be clear and precise.
The criteria should reflect the key components of the writing task. For example, for a narrative essay, criteria might include plot development, character depth, and use of descriptive language.
Clear criteria help students understand what is expected and allow teachers to provide targeted feedback.
Insider Tip : Collaborate with colleagues to establish consistent criteria across grade levels. This ensures uniformity in expectations and assessments.
2. Use Detailed Descriptors
Describe what each level of performance looks like.
This ensures transparency and clarity. Avoid vague language. Instead of saying “good,” describe what “good” entails. For example, “Few minor grammatical errors that do not impede readability.”
Detailed descriptors help students gauge their performance accurately.
Insider Tip : Use student work samples to illustrate each performance level. This provides concrete examples and helps students visualize expectations.
3. Involve Students
Involve students in the rubric creation process. This increases their understanding and buy-in.
Ask for their input on what they think is important in their writing.
This collaborative approach not only demystifies the grading process but also fosters a sense of ownership and responsibility in students.
Insider Tip : Conduct a workshop where students help create a rubric for an upcoming assignment. This interactive session can clarify doubts and make students more invested in their work.
4. Align with Objectives
Ensure the rubric aligns with learning objectives. This ensures relevance and focus.
If the objective is to enhance persuasive writing skills, the rubric should emphasize argument strength, evidence quality, and persuasive techniques.
Alignment ensures that the assessment directly supports instructional goals.
Insider Tip : Regularly revisit and update rubrics to reflect changes in curriculum and instructional priorities. This keeps the rubrics relevant and effective.
5. Review and Revise
Regularly review and revise rubrics. Ensure they remain accurate and effective.
Solicit feedback from students and colleagues. Continuous improvement of rubrics ensures they remain a valuable tool for both assessment and instruction.
Insider Tip : After using a rubric, take notes on its effectiveness. Were students confused by any criteria? Did the rubric cover all necessary aspects of the assignment? Use these observations to make adjustments.
6. Be Consistent
Use the rubric consistently across all assignments.
This ensures fairness and reliability. Consistency in applying the rubric helps build trust with students and maintains the integrity of the assessment process.
Insider Tip : Develop a grading checklist to accompany the rubric. This can help ensure that all criteria are consistently applied and none are overlooked during the grading process.
7. Provide Examples
Provide examples of each performance level.
This helps students understand expectations. Use annotated examples to show why a particular piece of writing meets a specific level.
This visual and practical demonstration can be more effective than descriptions alone.
Insider Tip : Create a portfolio of exemplar works for different assignments. This can be a valuable resource for both new and experienced teachers to standardize grading.
How to Use Writing Rubrics Effectively
Here is how to use writing rubrics like the pros.
1. Introduce Rubrics Early
Introduce rubrics at the beginning of the assignment.
Explain each criterion and performance level. This upfront clarity helps students understand what is expected and guides their work from the start.
Insider Tip : Conduct a rubric walkthrough session where you discuss each part of the rubric in detail. Allow students to ask questions and provide examples to illustrate each criterion.
2. Use Rubrics as a Teaching Tool
Use rubrics to teach writing skills. Discuss what constitutes good writing and why.
This can be an opportunity to reinforce lessons on grammar, organization, and other writing components.
Insider Tip : Pair the rubric with writing workshops. Use the rubric to critique sample essays and show students how to apply the rubric to improve their own writing.
3. Provide Feedback
Use the rubric to give detailed feedback. Highlight strengths and areas for improvement.
This targeted feedback helps students understand their performance and learn how to improve.
Insider Tip : Instead of just marking scores, add comments next to each criterion on the rubric. This personalized feedback can be more impactful and instructive for students.
4. Encourage Self-Assessment
Encourage students to use rubrics to self-assess.
This promotes reflection and growth. Before submitting their work, ask students to evaluate their own writing against the rubric.
This practice fosters self-awareness and critical thinking.
Insider Tip : Incorporate self-assessment as a mandatory step in the assignment process. Provide a simplified version of the rubric for students to use during self-assessment.
5. Use Rubrics for Peer Assessment
Use rubrics for peer assessment. This allows students to learn from each other.
Peer assessments can provide new perspectives and reinforce learning.
Insider Tip : Conduct a peer assessment workshop. Train students on how to use the rubric to evaluate each other’s work constructively. This can improve the quality of peer feedback.
6. Reflect and Improve
Reflect on the effectiveness of the rubric. Make adjustments as needed for future assignments.
Continuous reflection ensures that rubrics remain relevant and effective tools for assessment and learning.
Insider Tip : After an assignment, hold a debrief session with students to gather their feedback on the rubric. Use their insights to make improvements.
Check out this video about using writing rubrics:
Common Mistakes with Writing Rubrics
Creating and using writing rubrics can be incredibly effective, but there are common mistakes that can undermine their effectiveness.
Here are some pitfalls to avoid:
1. Vague Criteria
Vague criteria can confuse students and lead to inconsistent grading.
Ensure that each criterion is specific and clearly defined. Ambiguous terms like “good” or “satisfactory” should be replaced with concrete descriptions of what those levels of performance look like.
2. Overly Complex Rubrics
While detail is important, overly complex rubrics can be overwhelming for both students and teachers.
Too many criteria and performance levels can complicate the grading process and make it difficult for students to understand what is expected.
Keep rubrics concise and focused on the most important aspects of the assignment.
3. Inconsistent Application
Applying the rubric inconsistently can lead to unfair grading.
Ensure that you apply the rubric in the same way for all students and all assignments. Consistency builds trust and ensures that grades accurately reflect student performance.
4. Ignoring Student Input
Ignoring student input when creating rubrics can result in criteria that do not align with student understanding or priorities.
Involving students in the creation process can enhance their understanding and engagement with the rubric.
5. Failing to Update Rubrics
Rubrics should evolve to reflect changes in instructional goals and student needs.
Failing to update rubrics can result in outdated criteria that no longer align with current teaching objectives.
Regularly review and revise rubrics to keep them relevant and effective.
6. Lack of Examples
Without examples, students may struggle to understand the expectations for each performance level.
Providing annotated examples of work that meets each criterion can help students visualize what is required and guide their efforts more effectively.
7. Not Providing Feedback
Rubrics should be used as a tool for feedback, not just scoring.
Simply assigning a score without providing detailed feedback can leave students unclear about their strengths and areas for improvement.
Use the rubric to give comprehensive feedback that guides students’ growth.
8. Overlooking Self-Assessment and Peer Assessment
Self-assessment and peer assessment are valuable components of the learning process.
Overlooking these opportunities can limit students’ ability to reflect on their own work and learn from their peers.
Encourage students to use the rubric for self and peer assessment to deepen their understanding and enhance their skills.
What Is a Holistic Scoring Rubric for Writing?
A holistic scoring rubric for writing is a type of rubric that evaluates a piece of writing as a whole rather than breaking it down into separate criteria
This approach provides a single overall score based on the general impression of the writing’s quality and effectiveness.
Here’s a closer look at holistic scoring rubrics.
Key Features of Holistic Scoring Rubrics
- Single Overall Score : Assigns one score based on the overall quality of the writing.
- General Criteria : Focuses on the overall effectiveness, coherence, and impact of the writing.
- Descriptors : Uses broad descriptors for each score level to capture the general characteristics of the writing.
Example Holistic Scoring Rubric
| Score | Description |
|---|---|
| 5 | : Exceptionally clear, engaging, and well-organized writing. Demonstrates excellent control of language, grammar, and style. |
| 4 | : Clear and well-organized writing. Minor errors do not detract from the overall quality. Demonstrates good control of language and style. |
| 3 | : Satisfactory writing with some organizational issues. Contains a few errors that may distract but do not impede understanding. |
| 2 | : Basic writing that lacks organization and contains several errors. Demonstrates limited control of language and style. |
| 1 | : Unclear and poorly organized writing. Contains numerous errors that impede understanding. Demonstrates poor control of language and style. |
Advantages of Holistic Scoring Rubrics
- Efficiency : Faster to use because it involves a single overall judgment rather than multiple criteria.
- Flexibility : Allows for a more intuitive assessment of the writing’s overall impact and effectiveness.
- Comprehensiveness : Captures the overall quality of writing, considering all elements together.
Disadvantages of Holistic Scoring Rubrics
- Less Detailed Feedback : Provides a general score without specific feedback on individual aspects of writing.
- Subjectivity : Can be more subjective, as it relies on the assessor’s overall impression rather than specific criteria.
- Limited Diagnostic Use : Less useful for identifying specific areas of strength and weakness for instructional purposes.
When to Use Holistic Scoring Rubrics
- Quick Assessments : When a quick, overall evaluation is needed.
- Standardized Testing : Often used in standardized testing scenarios where consistency and efficiency are priorities.
- Initial Impressions : Useful for providing an initial overall impression before more detailed analysis.
Free Writing Rubric Templates
Feel free to use the following writing rubric templates.
You can easily copy and paste them into a Word Document. Please do credit this website on any written, printed, or published use.
Otherwise, go wild.
| Criteria | 4 (Excellent) | 3 (Good) | 2 (Fair) | 1 (Poor) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Well-developed, engaging, and clear plot, characters, and setting. | Developed plot, characters, and setting with some details missing. | Basic plot, characters, and setting; lacks details. | Underdeveloped plot, characters, and setting. | |
| Highly creative and original. | Creative with some originality. | Some creativity but lacks originality. | Lacks creativity and originality. | |
| No grammatical errors. | Few minor grammatical errors. | Several grammatical errors. | Numerous grammatical errors. | |
| Clear and logical structure. | Mostly clear structure. | Somewhat clear structure. | Lacks clear structure. | |
| Rich, varied, and appropriate language. | Varied and appropriate language. | Limited language variety. | Basic or inappropriate language. |
| Criteria | 4 (Excellent) | 3 (Good) | 2 (Fair) | 1 (Poor) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strong, clear, and convincing argument. | Convincing argument with minor gaps. | Basic argument; lacks strong support. | Weak or unsupported argument. | |
| Strong, relevant, and well-integrated evidence. | Relevant evidence but not strong. | Some relevant evidence, but weak. | Irrelevant or missing evidence. | |
| No grammatical errors. | Few minor grammatical errors. | Several grammatical errors. | Numerous grammatical errors. | |
| Clear and logical structure. | Mostly clear structure. | Somewhat clear structure. | Lacks clear structure. | |
| Persuasive and engaging language. | Engaging language. | Somewhat engaging language. | Not engaging language. |
Expository Writing Rubric
| Criteria | 4 (Excellent) | 3 (Good) | 2 (Fair) | 1 (Poor) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thorough, accurate, and insightful content. | Accurate content with some details missing. | Basic content; lacks depth. | Incomplete or inaccurate content. | |
| Clear and concise explanations. | Mostly clear explanations. | Somewhat clear explanations. | Unclear explanations. | |
| No grammatical errors. | Few minor grammatical errors. | Several grammatical errors. | Numerous grammatical errors. | |
| Clear and logical structure. | Mostly clear structure. | Somewhat clear structure. | Lacks clear structure. | |
| Precise and appropriate language. | Appropriate language. | Limited language variety. | Basic or inappropriate language. |
Descriptive Writing Rubric
| Criteria | 4 (Excellent) | 3 (Good) | 2 (Fair) | 1 (Poor) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vivid and detailed imagery that engages the senses. | Detailed imagery with minor gaps. | Basic imagery; lacks vivid details. | Little to no imagery. | |
| Highly creative and original descriptions. | Creative with some originality. | Some creativity but lacks originality. | Lacks creativity and originality. | |
| No grammatical errors. | Few minor grammatical errors. | Several grammatical errors. | Numerous grammatical errors. | |
| Clear and logical structure. | Mostly clear structure. | Somewhat clear structure. | Lacks clear structure. | |
| Rich, varied, and appropriate language. | Varied and appropriate language. | Limited language variety. | Basic or inappropriate language. |
Analytical Writing Rubric
| Criteria | 4 (Excellent) | 3 (Good) | 2 (Fair) | 1 (Poor) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Insightful, thorough, and well-supported analysis. | Good analysis with some depth. | Basic analysis; lacks depth. | Weak or unsupported analysis. | |
| Strong, relevant, and well-integrated evidence. | Relevant evidence but not strong. | Some relevant evidence, but weak. | Irrelevant or missing evidence. | |
| No grammatical errors. | Few minor grammatical errors. | Several grammatical errors. | Numerous grammatical errors. | |
| Clear and logical structure. | Mostly clear structure. | Somewhat clear structure. | Lacks clear structure. | |
| Precise and appropriate language. | Appropriate language. | Limited language variety. | Basic or inappropriate language. |
Final Thoughts: Writing Rubrics
I have a lot more resources for teaching on this site.
Check out some of the blog posts I’ve listed below. I think you might enjoy them.
Read This Next:
- Narrative Writing Graphic Organizer [Guide + Free Templates]
- 100 Best A Words for Kids (+ How to Use Them)
- 100 Best B Words For Kids (+How to Teach Them)
- 100 Dictation Word Ideas for Students and Kids
- 50 Tricky Words to Pronounce and Spell (How to Teach Them)
Rubric Best Practices, Examples, and Templates
A rubric is a scoring tool that identifies the different criteria relevant to an assignment, assessment, or learning outcome and states the possible levels of achievement in a specific, clear, and objective way. Use rubrics to assess project-based student work including essays, group projects, creative endeavors, and oral presentations.
Rubrics can help instructors communicate expectations to students and assess student work fairly, consistently and efficiently. Rubrics can provide students with informative feedback on their strengths and weaknesses so that they can reflect on their performance and work on areas that need improvement.
How to Get Started
Best practices, moodle how-to guides.
- Workshop Recording (Spring 2024)
- Workshop Registration
Step 1: Analyze the assignment
The first step in the rubric creation process is to analyze the assignment or assessment for which you are creating a rubric. To do this, consider the following questions:
- What is the purpose of the assignment and your feedback? What do you want students to demonstrate through the completion of this assignment (i.e. what are the learning objectives measured by it)? Is it a summative assessment, or will students use the feedback to create an improved product?
- Does the assignment break down into different or smaller tasks? Are these tasks equally important as the main assignment?
- What would an “excellent” assignment look like? An “acceptable” assignment? One that still needs major work?
- How detailed do you want the feedback you give students to be? Do you want/need to give them a grade?
Step 2: Decide what kind of rubric you will use
Types of rubrics: holistic, analytic/descriptive, single-point
Holistic Rubric. A holistic rubric includes all the criteria (such as clarity, organization, mechanics, etc.) to be considered together and included in a single evaluation. With a holistic rubric, the rater or grader assigns a single score based on an overall judgment of the student’s work, using descriptions of each performance level to assign the score.
Advantages of holistic rubrics:
- Can p lace an emphasis on what learners can demonstrate rather than what they cannot
- Save grader time by minimizing the number of evaluations to be made for each student
- Can be used consistently across raters, provided they have all been trained
Disadvantages of holistic rubrics:
- Provide less specific feedback than analytic/descriptive rubrics
- Can be difficult to choose a score when a student’s work is at varying levels across the criteria
- Any weighting of c riteria cannot be indicated in the rubric
Analytic/Descriptive Rubric . An analytic or descriptive rubric often takes the form of a table with the criteria listed in the left column and with levels of performance listed across the top row. Each cell contains a description of what the specified criterion looks like at a given level of performance. Each of the criteria is scored individually.
Advantages of analytic rubrics:
- Provide detailed feedback on areas of strength or weakness
- Each criterion can be weighted to reflect its relative importance
Disadvantages of analytic rubrics:
- More time-consuming to create and use than a holistic rubric
- May not be used consistently across raters unless the cells are well defined
- May result in giving less personalized feedback
Single-Point Rubric . A single-point rubric is breaks down the components of an assignment into different criteria, but instead of describing different levels of performance, only the “proficient” level is described. Feedback space is provided for instructors to give individualized comments to help students improve and/or show where they excelled beyond the proficiency descriptors.
Advantages of single-point rubrics:
- Easier to create than an analytic/descriptive rubric
- Perhaps more likely that students will read the descriptors
- Areas of concern and excellence are open-ended
- May removes a focus on the grade/points
- May increase student creativity in project-based assignments
Disadvantage of analytic rubrics: Requires more work for instructors writing feedback
Step 3 (Optional): Look for templates and examples.
You might Google, “Rubric for persuasive essay at the college level” and see if there are any publicly available examples to start from. Ask your colleagues if they have used a rubric for a similar assignment. Some examples are also available at the end of this article. These rubrics can be a great starting point for you, but consider steps 3, 4, and 5 below to ensure that the rubric matches your assignment description, learning objectives and expectations.
Step 4: Define the assignment criteria
Make a list of the knowledge and skills are you measuring with the assignment/assessment Refer to your stated learning objectives, the assignment instructions, past examples of student work, etc. for help.
Helpful strategies for defining grading criteria:
- Collaborate with co-instructors, teaching assistants, and other colleagues
- Brainstorm and discuss with students
- Can they be observed and measured?
- Are they important and essential?
- Are they distinct from other criteria?
- Are they phrased in precise, unambiguous language?
- Revise the criteria as needed
- Consider whether some are more important than others, and how you will weight them.
Step 5: Design the rating scale
Most ratings scales include between 3 and 5 levels. Consider the following questions when designing your rating scale:
- Given what students are able to demonstrate in this assignment/assessment, what are the possible levels of achievement?
- How many levels would you like to include (more levels means more detailed descriptions)
- Will you use numbers and/or descriptive labels for each level of performance? (for example 5, 4, 3, 2, 1 and/or Exceeds expectations, Accomplished, Proficient, Developing, Beginning, etc.)
- Don’t use too many columns, and recognize that some criteria can have more columns that others . The rubric needs to be comprehensible and organized. Pick the right amount of columns so that the criteria flow logically and naturally across levels.
Step 6: Write descriptions for each level of the rating scale
Artificial Intelligence tools like Chat GPT have proven to be useful tools for creating a rubric. You will want to engineer your prompt that you provide the AI assistant to ensure you get what you want. For example, you might provide the assignment description, the criteria you feel are important, and the number of levels of performance you want in your prompt. Use the results as a starting point, and adjust the descriptions as needed.
Building a rubric from scratch
For a single-point rubric , describe what would be considered “proficient,” i.e. B-level work, and provide that description. You might also include suggestions for students outside of the actual rubric about how they might surpass proficient-level work.
For analytic and holistic rubrics , c reate statements of expected performance at each level of the rubric.
- Consider what descriptor is appropriate for each criteria, e.g., presence vs absence, complete vs incomplete, many vs none, major vs minor, consistent vs inconsistent, always vs never. If you have an indicator described in one level, it will need to be described in each level.
- You might start with the top/exemplary level. What does it look like when a student has achieved excellence for each/every criterion? Then, look at the “bottom” level. What does it look like when a student has not achieved the learning goals in any way? Then, complete the in-between levels.
- For an analytic rubric , do this for each particular criterion of the rubric so that every cell in the table is filled. These descriptions help students understand your expectations and their performance in regard to those expectations.
Well-written descriptions:
- Describe observable and measurable behavior
- Use parallel language across the scale
- Indicate the degree to which the standards are met
Step 7: Create your rubric
Create your rubric in a table or spreadsheet in Word, Google Docs, Sheets, etc., and then transfer it by typing it into Moodle. You can also use online tools to create the rubric, but you will still have to type the criteria, indicators, levels, etc., into Moodle. Rubric creators: Rubistar , iRubric
Step 8: Pilot-test your rubric
Prior to implementing your rubric on a live course, obtain feedback from:
- Teacher assistants
Try out your new rubric on a sample of student work. After you pilot-test your rubric, analyze the results to consider its effectiveness and revise accordingly.
- Limit the rubric to a single page for reading and grading ease
- Use parallel language . Use similar language and syntax/wording from column to column. Make sure that the rubric can be easily read from left to right or vice versa.
- Use student-friendly language . Make sure the language is learning-level appropriate. If you use academic language or concepts, you will need to teach those concepts.
- Share and discuss the rubric with your students . Students should understand that the rubric is there to help them learn, reflect, and self-assess. If students use a rubric, they will understand the expectations and their relevance to learning.
- Consider scalability and reusability of rubrics. Create rubric templates that you can alter as needed for multiple assignments.
- Maximize the descriptiveness of your language. Avoid words like “good” and “excellent.” For example, instead of saying, “uses excellent sources,” you might describe what makes a resource excellent so that students will know. You might also consider reducing the reliance on quantity, such as a number of allowable misspelled words. Focus instead, for example, on how distracting any spelling errors are.
Example of an analytic rubric for a final paper
| Above Average (4) | Sufficient (3) | Developing (2) | Needs improvement (1) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Thesis supported by relevant information and ideas | The central purpose of the student work is clear and supporting ideas always are always well-focused. Details are relevant, enrich the work. | The central purpose of the student work is clear and ideas are almost always focused in a way that supports the thesis. Relevant details illustrate the author’s ideas. | The central purpose of the student work is identified. Ideas are mostly focused in a way that supports the thesis. | The purpose of the student work is not well-defined. A number of central ideas do not support the thesis. Thoughts appear disconnected. |
| (Sequencing of elements/ ideas) | Information and ideas are presented in a logical sequence which flows naturally and is engaging to the audience. | Information and ideas are presented in a logical sequence which is followed by the reader with little or no difficulty. | Information and ideas are presented in an order that the audience can mostly follow. | Information and ideas are poorly sequenced. The audience has difficulty following the thread of thought. |
| (Correctness of grammar and spelling) | Minimal to no distracting errors in grammar and spelling. | The readability of the work is only slightly interrupted by spelling and/or grammatical errors. | Grammatical and/or spelling errors distract from the work. | The readability of the work is seriously hampered by spelling and/or grammatical errors. |
Example of a holistic rubric for a final paper
| The audience is able to easily identify the central message of the work and is engaged by the paper’s clear focus and relevant details. Information is presented logically and naturally. There are minimal to no distracting errors in grammar and spelling. : The audience is easily able to identify the focus of the student work which is supported by relevant ideas and supporting details. Information is presented in a logical manner that is easily followed. The readability of the work is only slightly interrupted by errors. : The audience can identify the central purpose of the student work without little difficulty and supporting ideas are present and clear. The information is presented in an orderly fashion that can be followed with little difficulty. Grammatical and spelling errors distract from the work. : The audience cannot clearly or easily identify the central ideas or purpose of the student work. Information is presented in a disorganized fashion causing the audience to have difficulty following the author’s ideas. The readability of the work is seriously hampered by errors. |
Single-Point Rubric
| Advanced (evidence of exceeding standards) | Criteria described a proficient level | Concerns (things that need work) |
|---|---|---|
| Criteria #1: Description reflecting achievement of proficient level of performance | ||
| Criteria #2: Description reflecting achievement of proficient level of performance | ||
| Criteria #3: Description reflecting achievement of proficient level of performance | ||
| Criteria #4: Description reflecting achievement of proficient level of performance | ||
| 90-100 points | 80-90 points | <80 points |
More examples:
- Single Point Rubric Template ( variation )
- Analytic Rubric Template make a copy to edit
- A Rubric for Rubrics
- Bank of Online Discussion Rubrics in different formats
- Mathematical Presentations Descriptive Rubric
- Math Proof Assessment Rubric
- Kansas State Sample Rubrics
- Design Single Point Rubric
Technology Tools: Rubrics in Moodle
- Moodle Docs: Rubrics
- Moodle Docs: Grading Guide (use for single-point rubrics)
Tools with rubrics (other than Moodle)
- Google Assignments
- Turnitin Assignments: Rubric or Grading Form
Other resources
- DePaul University (n.d.). Rubrics .
- Gonzalez, J. (2014). Know your terms: Holistic, Analytic, and Single-Point Rubrics . Cult of Pedagogy.
- Goodrich, H. (1996). Understanding rubrics . Teaching for Authentic Student Performance, 54 (4), 14-17. Retrieved from
- Miller, A. (2012). Tame the beast: tips for designing and using rubrics.
- Ragupathi, K., Lee, A. (2020). Beyond Fairness and Consistency in Grading: The Role of Rubrics in Higher Education. In: Sanger, C., Gleason, N. (eds) Diversity and Inclusion in Global Higher Education. Palgrave Macmillan, Singapore.
- Home div.mega__menu -->
- Guiding Principles
- Assessment Cycle
- Equity in Assessment
- FAQs About Assessment
- Learning Outcomes & Evidence
- Undergraduate Learning Goals & Outcomes
- University Assessment Reports
- Program Assessment Reports
- University Survey Reports
- Assessment in Action
- Internal Assessment Grant
- Celebrating Assessment at LMU
- Assessment Advisory Committee
- Workshops & Events
- Assessment Resources
- Recommended Websites
- Recommended Books
- Contact div.mega__menu -->
Creative Writing Example Rubric
|
| 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 |
| Students will write well organized, cohesive papers.
| Work functions well as a whole. Piece has a clear flow and a sense of purpose. | Response has either a strong lead, developed body, or satisfying conclusion, but not all three. | Uneven. Awkward or missing transitions. Weakly unified. | Wanders. Repetitive. Inconclusive. | Incoherent and fragmentary. Student didn't write enough to judge. |
| Students will use appropriate voice and tone in writing.
| Voice is confident and appropriate. Consistently engaging. Active, not passive voice. Natural. A strong sense of both authorship and audience. | The speaker sounds as if he or she cares too little or too much about the topic. Or the voice fades in and out. Occasionally passive. | Tone is okay. But the paper could have been written by anyone. Apathetic or artificial. Overly formal or informal. | "I just want to get this over with." | Mechanical and cognitive problems so basic that tone doesn't even figure in. Student didn't write enough to judge. |
| Students will demonstrate original, creative writing.
| Excellent use of imagery; similes; vivid, detailed descriptions; figurative language; puns; wordplay; metaphor; irony. Surprises the reader with unusual associations, breaks conventions, thwarts expectations. | Some startling images, a few stunning associative leaps with a weak conclusion or lesser, more ordinary images and comparisons. Inconsistent. | Sentimental, predictable, or cliché. | Borrows ideas or images from popular culture in an unreflective way. | Cursory response. Obvious lack of motivation and/or poor understanding of the assignment. |
Rubric is a modification of one presented by: University Community Links (n.d.). Hot writing rubric. Retrieved August 19, 2008 from http://www.uclinks.org/reference/evaluation/HOT.html

Crafting Effective Rubrics for Creative Assignments
Developing effective rubrics for creative assignments isn't just about ticking boxes or applying standard criteria. It's about diving into the vibrant world of creativity and understanding how to objectively assess artistic expression and innovation. Whether you're a teacher in music, art, or writing, this guide will walk you through constructing rubrics that respect and measure creativity, ensuring your students not only meet but also exceed expectations with clarity and inspiration.
Understanding the Importance of Creative Rubrics
Rubrics are essential tools in education, often used to assess student work across a range of subjects, including the creative arts. They provide a structured framework that clearly outlines the expectations for assignments, making the grading process transparent and consistent. This is particularly vital in creative disciplines, where subjective judgment can often cloud the assessment process.
Why Creative Assignments Need Specialized Rubrics
Creative tasks differ significantly from traditional academic assignments because they involve personal expression, innovation, and originality. Standard rubrics might fail to capture these unique aspects as they tend to focus more on conventional metrics like correctness and completeness. Creative rubrics, on the other hand, are designed to value the originality and expressive qualities of the work, recognizing that creativity can manifest in varied and unexpected ways.
For instance, a creative rubric for an art project might prioritize elements such as innovation, aesthetic appeal, and emotional impact, alongside more traditional criteria like technique and composition.
Unique Challenges in Evaluating Creativity
Evaluating creativity poses unique challenges because it requires assessors to recognize and reward originality and inventive thinking. This can be subjective, as what seems creative to one person might not seem so to another. Effective creative rubrics help mitigate these challenges by setting clear, specific criteria that focus on the creative process and its outcomes, rather than just the final product.
Benefits of Using Rubrics in Creative Disciplines
Rubrics bring numerous advantages to the educational process, particularly in creative fields:
- Increased Transparency and Consistency: Rubrics lay out explicit criteria and performance levels, which helps students understand what is expected of them and how they can meet or exceed these expectations.
- Support for Critical Thinking: By detailing specific criteria for creativity, rubrics encourage students to think critically about how they approach their creative work. This can spur deeper engagement with the material and promote higher levels of creative expression ( ASCD ).
- Enhanced Feedback: Rubrics provide a framework for detailed, constructive feedback. Students receive insights not just into what they did well, but also how they can improve, which is crucial for artistic development ( Cornell Teaching ).
In summary, rubrics tailored for creative disciplines play a crucial role in educational settings. They provide a balanced framework that respects and nurtures creativity while maintaining academic rigor and fairness in assessment. This enables educators to effectively guide and evaluate student progress in creative fields.
Designing Your Creative Rubric
Creating a rubric for creative assignments involves several strategic steps to ensure it not only assesses student work effectively but also encourages creativity and growth. Here’s how you can design a rubric that respects and enhances the creative process while maintaining clarity and objectivity in evaluation.
Steps to Construct a Rubric for Creative Disciplines
- Define Clear Learning Objectives : Start by outlining what you expect students to learn or demonstrate through their creative work. These objectives should be specific, measurable, and aligned with the overall goals of the assignment ( MIT Teaching + Learning Lab ).
- Identify Relevant Criteria : Decide on the criteria or components of the assignment that you will assess. These should directly reflect the learning objectives and could include aspects like originality, technical skills, aesthetic quality, and emotional impact. It’s essential to choose criteria that capture the essence of creativity in the discipline.
- Determine Performance Levels : Establish distinct levels of achievement for each criterion. Commonly, rubrics feature three to five levels—such as beginning, developing, proficient, and exemplary—to describe varying degrees of mastery or accomplishment.
- Develop Descriptors for Each Level : Write detailed descriptions for what each level of performance looks like for every criterion. These descriptors should be specific, observable, and measurable, avoiding vague language to ensure that expectations are clear and understandable ( MIT Teaching + Learning Lab ).
- Review and Refine the Rubric : Before finalizing the rubric, it’s helpful to review it with colleagues or test it on sample assignments. This can help you refine the language, ensure alignment with learning objectives, and confirm that the rubric is clear and functional for both assessment and student feedback.
Importance of Choosing the Right Criteria and Performance Levels
Selecting appropriate criteria and defining precise performance levels are crucial because they directly influence how students approach and execute their creative projects. Well-chosen criteria ensure that students are not just being creative but are also meeting the educational goals of the assignment. Performance levels that are clearly delineated help students understand exactly where they stand and what they need to improve, which is particularly important in subjective fields like creative arts ( MIT Teaching + Learning Lab ).
Tips on Using Language That Encourages Creative Freedom
- Encourage Exploration : Use language that prompts students to explore and experiment beyond basic requirements. Phrases like "explore diverse perspectives" or "experiment with different techniques" can open up creative possibilities.
- Focus on Growth : Frame feedback in a way that emphasizes progress and potential for further development. For instance, instead of saying a student "failed to meet criteria," you might say "approaching criteria, with room to expand on creative execution."
- Be Specific and Constructive : Provide clear, constructive feedback that students can use to improve their work. Instead of vague compliments or criticisms, offer specific suggestions that guide students on how to enhance their creative output.
By carefully constructing a rubric with these elements, educators can create a valuable tool that not only assesses creativity fairly and effectively but also inspires students to push their creative boundaries.
Examples of Rubrics Across Creative Disciplines
Rubrics play a crucial role in educational settings, particularly in creative disciplines where the assessment of subjective elements like artistry and originality is essential. This section explores examples of rubrics used in music, art, and writing, and discusses how these rubrics are tailored to meet the specific needs of each discipline while balancing structure with creative freedom.
Art Rubrics
In the world of art education, rubrics serve as a roadmap for assessing students' creative outputs, considering not only the final product but also the creative process and technical skills. Art rubrics often include criteria such as creativity, craftsmanship, and effort, which help in evaluating the students' ability to use various materials and techniques effectively. For example, teachers might assess the neatness of artwork, the originality of the design, and the students' engagement with the creative process throughout the project's duration. This approach encourages students to exceed mere replication of techniques and embrace their unique artistic expressions.

Writing Rubrics
For writing, rubrics are designed to evaluate components such as clarity of argument, use of evidence, organization, and grammatical accuracy. They can range from holistic rubrics, which provide a single cumulative score based on an overall impression of the work, to more detailed analytic rubrics that assess specific elements of the writing process. For instance, a writing rubric might describe levels of achievement for criteria like thesis strength, coherence of arguments, and depth of analysis, thus guiding students on how to enhance their writing skills ( CITL ).
Music Rubrics
Music educators use rubrics to assess performances and compositions. These rubrics may evaluate rhythm accuracy, pitch precision, expression, and interpretation of pieces. In music education, it is vital to balance technical assessment with creative expression, allowing students to understand both the mechanics of music and the artistic expression involved. The rubric might include criteria for technical skills, such as scale accuracy, as well as for more subjective measures like emotional conveyance and dynamic variation.
Customization and Balancing Creativity
One of the key aspects of creating effective rubrics in creative disciplines is the ability to customize them according to the specific needs of the discipline and the particular objectives of the assignment. Educators often modify rubrics to highlight the creative process over the final product, encouraging students to explore different methods and ideas. This customization supports critical thinking and innovation, essential skills in any creative field.
Moreover, while rubrics provide a structured assessment framework, they also need to leave room for personal expression and originality. It's about finding that sweet spot where students are guided by clear expectations but not restricted in their creative endeavors. This balance ensures that rubrics enhance the learning experience rather than confining it, fostering an environment where creativity can thrive.
In summary, well-designed rubrics in creative disciplines are indispensable tools that not only streamline the assessment process but also enhance educational outcomes by clearly defining expectations and encouraging creative growth.
Implementing and Adjusting Your Rubric
Introducing and integrating rubrics effectively into creative assignments can significantly enhance both teaching and learning experiences. Adjusting them based on feedback ensures that they remain relevant and useful over time. Here's how you can go about this vital process.
Guidelines for Introducing Rubrics to Students
Start by clearly defining the purpose and goals of the rubric. Explain how it aligns with the learning outcomes of the course and how it will be used to evaluate their work. It's beneficial to go through the rubric criteria with your students, discussing each criterion and what different levels of performance look like. This helps demystify the grading process and aligns student efforts with the expected outcomes.
Integrating Rubrics into Assignments
When introducing rubrics, provide them at the start of the assignment. This practice helps students use the rubric as a guide throughout their creative process. Encourage students to refer back to the rubric during their project development to self-assess their progress and make adjustments before final submission. This approach not only fosters a deeper understanding of the criteria but also empowers students to take charge of their learning ( Berkeley Teaching ).
Refining Rubrics Based on Feedback
Feedback is crucial for refining rubrics. After an assignment, gather feedback from students on the clarity and utility of the rubric. Did it help them understand what was expected? Were there any areas of confusion that could be clarified? Similarly, peer feedback among educators who use the rubric can provide insights into its effectiveness and areas for improvement. Adjust the rubric based on this feedback to better meet students' needs and enhance its educational impact( Center for Teaching and Learning ).
The Dynamic Nature of Rubrics
Rubrics should not be static; they need to evolve based on student performance and changing educational goals. Regularly review and adjust your rubric to reflect new learning objectives, changes in course content, or shifts in pedagogical priorities. This might involve adding new criteria, adjusting performance levels, or refining descriptors to be more precise and actionable ( Berkeley Teaching ).
Effective rubrics are tools for both assessment and teaching. They clarify expectations, guide student learning, streamline grading processes, and enhance feedback quality. By thoughtfully integrating and continuously refining rubrics, educators can significantly improve the learning journey for their students in creative disciplines.

Arthur Wang
Mastering scaffolding techniques for diverse age groups and skill levels, embracing practicality: how hands-on learning enhances creative education.

Mastering the Art: Navigating the Creative Writing Rubric
My name is Debbie, and I am passionate about developing a love for the written word and planting a seed that will grow into a powerful voice that can inspire many.

Understanding the Creative Writing Rubric: A Step-by-Step Guide
Decoding the criteria: unraveling the secrets of the rubric, skills and techniques: honing your craft for rubric success, skills and techniques to achieve rubric success, crafting a captivating narrative: engaging your reader from start to finish, embracing authenticity: channeling your unique voice in writing, polishing your prose: mastering grammar, spelling, and punctuation, mastering grammar, spelling, and punctuation, breaking boundaries: experimenting with structure and style in creative writing, taking feedback to improve: using the rubric as a tool for growth, frequently asked questions, the way forward.
When it comes to creative writing, it can sometimes feel like navigating a vast, uncharted territory. How can you be sure if your piece is hitting all the right marks? Enter the creative writing rubric, a powerful tool that can help you understand and evaluate your work objectively. In this step-by-step guide, we will demystify the world of rubrics and unravel their importance in assessing your creative writing.
Step 1: Familiarize Yourself with the Rubric Components
- Structure: The rubric will assess how well your writing flows , including elements such as introduction, body paragraphs, and conclusion.
- Language and Vocabulary: This component evaluates your mastery of language, including grammar, spelling, and the use of diverse vocabulary.
- Imagery and Descriptions: Here, the rubric considers your ability to paint vivid pictures with words and create a sensory experience for the reader.
- Pacing and Tension: This aspect appraises the way you build suspense, create momentum, and maintain the reader’s interest.
Step 2: Break Down Each Component
Now that you’re familiar with the rubric’s elements, take the time to analyze each component individually, understanding what its criteria entails. For example, under Structure, you might consider whether your piece has a strong and engaging opening, clear progression of ideas, and a satisfying resolution.
By breaking down each component, you will gain a deeper understanding of what is expected in your creative writing and be better equipped to assign yourself an accurate score. Remember, the rubric is not meant to stifle your creativity, but rather to provide guidance and ensure your work meets certain standards.
Understanding the criteria of a rubric is like deciphering a secret code. It may seem complex at first glance, but with a little guidance, you can unravel its mysteries and excel in your assignments. Here, we will demystify the secrets of the rubric, ensuring you have a clear roadmap to success.
To begin with, pay close attention to the key terms in the rubric. These are the secret clues that will help you understand what is expected of you. Look for words like “analyze,” “synthesize,” “evaluate,” or “compare and contrast.” Understanding these action words will guide you in tailoring your work to meet the requirements. Next, examine the weightage assigned to each criterion. Some criteria may carry more points than others, indicating their relative importance.
- Break down the rubric into smaller tasks to make it less overwhelming.
- Understand the scoring system, whether it’s numerical or descriptive.
- Use examples from rubric criteria to guide your research and writing.
Keep in mind that rubrics are designed to provide clarity and fairness in grading. Use the rubric as a checklist while working on your assignment. Regularly refer back to it to ensure you are meeting all the requirements. Remember, each criterion is like a piece of the puzzle that fits together to create a comprehensive project.

When it comes to ensuring success in the world of rubrics, honing your craft is essential. Here are some valuable skills and techniques that can help you excel and achieve that coveted top score:
- Clear Communication: One of the most important skills to develop is the ability to clearly communicate your ideas. Effective communication not only helps you express your thoughts but also ensures that your work is easily understood and meets the rubric criteria.
- Research and Analysis: Conducting thorough research and analyzing your findings is key to producing high-quality work. Dive deep into your subject matter, explore various perspectives, and back your arguments with credible sources. This will demonstrate your dedication to the topic and enable you to make informed decisions throughout your project.
Additionally, practicing the following techniques can further enhance your chances of achieving rubric success:
- Time Management: Effectively managing your time ensures that you stay organized and complete all required tasks within the given timeframe. Prioritize your work, create a schedule, and allocate specific periods for research, drafting, proofreading, and revision. This will help you avoid last-minute stress and submit a polished final product.
- Creative Problem-Solving: Facing challenges is inevitable, but skillful problem-solving can set you apart. Embrace creativity and think outside the box when confronted with obstacles. This ability to find innovative solutions will impress evaluators and make your project stand out among the rest.
By developing these skills and mastering these techniques, you will be well on your way to achieving rubric success. Remember, practice makes perfect! As you continue to refine these abilities, your projects will consistently meet and exceed the expectations outlined in any rubric.
When it comes to writing a captivating narrative, the goal is to draw your readers in and keep them hooked until the very end. A captivating narrative has the power to transport readers to different worlds, make them feel deeply connected to the characters, and leave a lasting impression. Here are some key tips and techniques to help you engage your readers from start to finish:
- Create relatable characters: Characters are at the heart of any narrative. Develop complex and relatable characters that your readers can connect with emotionally. Give them unique personalities, desires, and flaws that make them feel real.
- Set the stage: Transport your readers to the world of your story by vividly describing the setting. Engage their senses with rich descriptions of sights, sounds, smells, and textures. Whether it’s a bustling city, a mysterious island, or a quaint countryside, make sure your readers can visualize it in their minds.
- Build suspense: Keep your readers on the edge of their seats by introducing tension and conflict. Create obstacles and challenges for your characters to overcome, and gradually escalate the stakes. This will keep your readers invested and eager to find out what happens next.
Remember, captivating narratives are crafted through careful attention to detail, evocative descriptions, and well-developed characters. By implementing these tips, you’ll be able to engage your readers from the very first sentence and hold their attention throughout your entire narrative. Happy writing!

When it comes to writing, there is a magical power in embracing your authenticity and channeling your unique voice. Writing in your own voice not only allows you to create a deep connection with your readers but also sets you apart from other writers. Embracing authenticity means being true to yourself, expressing your thoughts, and conveying your emotions in a way that reflects who you are.
So, how can you harness this power and infuse your writing with your unique voice? The key lies in the following steps:
- Know yourself: Take the time to explore your strengths, weaknesses, and passions. Understanding who you are as a person will allow you to reflect your authentic self in your writing.
- Be honest and vulnerable: Authenticity requires honesty and vulnerability. Don’t shy away from sharing personal experiences, opinions, or emotions. Your readers will appreciate your openness and relate to your genuine voice.
- Find your writing style: Experiment with different writing styles and techniques until you discover the one that truly resonates with you. Whether it’s casual and conversational or formal and eloquent, incorporating your unique writing style will make your voice shine.

Writing is a craft, and just like any other skill, it requires practice and attention to detail. In this section, we’ll explore some essential tips and techniques to sharpen your writing by improving your grasp of grammar, spelling, and punctuation.
To begin with, let’s not forget the fundamental importance of grammar. Proper grammar ensures that ideas are conveyed accurately and clearly, providing a solid foundation for effective communication. Remember to:
- Use subject-verb agreement: Agreement between subjects and verbs is vital to maintain grammatical structure. Be mindful of singular and plural forms and ensure consistency throughout your writing.
- Avoid run-on sentences: Run-on sentences can make your writing confusing and challenging to read. Split long sentences into shorter ones using appropriate punctuation such as commas, semicolons, or periods.
- Eliminate wordiness: Cut out unnecessary words and phrases that don’t add value to your writing. Be concise and focus on expressing your ideas clearly without excessive verbiage.
Next, let’s tackle the often perplexing realm of spelling. Proper spelling not only makes your writing appear polished but also ensures that your message is conveyed accurately. Consider these useful spelling tips:
- Proofread carefully: Always proofread your work to catch any spelling mistakes that might have slipped through the cracks. Use spell-check tools, but keep in mind that they aren’t foolproof and may miss certain errors.
- Create a personal spelling list: Keep track of words you commonly misspell and review them regularly. By familiarizing yourself with these words, you’ll be more likely to spell them correctly in your writing.
- Consult reliable resources: When in doubt, consult trusted dictionaries or grammar guides to confirm the correct spelling of a word. These references will provide the guidance you need to enhance your spelling accuracy.
When it comes to creative writing, there are no limits to the ways you can tell a story. Breaking boundaries in terms of structure and style allows writers to push the boundaries of traditional storytelling and explore new realms of creativity. By experimenting with different techniques, writers can create unique and captivating pieces that stand out from the crowd.
One of the ways writers can break free from the conventional structure is by playing with the chronology of their story. By using flashbacks, flash-forwards, or even non-linear narratives, writers can create a sense of suspense and surprise for their readers. This unconventional approach enables them to engage readers’ curiosity and make them question what will happen next. Additionally, experimenting with structure can involve using unconventional paragraph breaks or employing poetic techniques, such as enjambment or caesura, to add a rhythmic and musical quality to the prose.
Feedback is a valuable asset for growth and learning. Whether you’re a student, a professional, or an artist, feedback helps us understand our strengths and weaknesses, allowing us to enhance our skills and improve our work. One effective tool for utilizing feedback is the rubric. A rubric is like a roadmap that provides clear guidelines and expectations, making it easier to assess performance objectively.
How can you make the most out of a rubric to enhance your growth? Firstly, carefully read and familiarize yourself with the rubric criteria. Take note of the different aspects being assessed, such as content, structure, creativity, or technical skills, depending on your field. Use this as an opportunity to evaluate your past work honestly and identify areas for improvement. Additionally, pay close attention to the descriptors for each level of performance. It’s crucial to understand what constitutes excellence, proficiency, and basic competence according to the rubric. Determine where you currently stand and set well-defined goals that align with your desired level of achievement.
Q: Why is it important to understand the creative writing rubric? A: Understanding the creative writing rubric is important because it allows you to grasp what is expected of you in terms of writing quality and content. It provides a clear framework for assessing your work and helps you meet the desired criteria.
Q: What are the key components of a creative writing rubric? A: A typical creative writing rubric usually includes criteria such as language use, organization, creativity, cohesion, and content knowledge. These elements are evaluated to determine the overall quality of your writing piece.
Q: How can I improve my language use in the context of creative writing? A: To enhance your language use, focus on using varied vocabulary, incorporating descriptive details, and fine-tuning your grammar and punctuation. Make sure your language evokes emotion and creates vivid imagery for the reader.
Q: How important is organization in creative writing? A: Organization is essential in creative writing to ensure that your ideas flow logically and coherently. Pay attention to your introduction, body paragraphs, and conclusion, ensuring they are well-structured and transition seamlessly.
Q: How can I demonstrate creativity in my writing? A: To showcase your creativity, think outside the box and experiment with different writing techniques. Use imaginative language, employ unique metaphors or similes, and develop original plotlines and characters that captivate the reader’s attention.
Q: What does cohesion mean in the context of creative writing? A: Cohesion refers to the seamless flow of ideas throughout your writing. Achieve cohesion by using transitional phrases, maintaining consistency in tone and style, and ensuring that each sentence and paragraph supports the main theme or message.
Q: What role does content knowledge play in the creative writing rubric? A: Content knowledge indicates your understanding of the subject matter and the ability to communicate it effectively. Conduct thorough research if necessary and demonstrate your expertise through well-developed ideas, accurate information, and engaging storytelling.
Q: How can I use the creative writing rubric to evaluate my own work? A: First, familiarize yourself with the rubric and its criteria. Then, objectively assess your piece considering each component individually. Identify areas that need improvement and revise accordingly. By doing so, you can align your work with the rubric’s expectations and enhance the overall quality of your writing.
Q: Are there any resources available to help me understand and use the creative writing rubric effectively? A: Yes, several writing resources offer explanations and examples of creative writing rubrics. Additionally, your teacher or instructor may provide guidance or sample essays that align with the rubric criteria. Don’t hesitate to reach out for assistance or clarification.

Painted Panoramas: How to Describe Leaves in Creative Writing
Unleash Your Inner Artist with Brainstorm Art Techniques
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Reach out to us for sponsorship opportunities.
Welcome to Creative Writing Prompts
At Creative Writing Prompts, we believe in the power of words to shape worlds. Our platform is a sanctuary for aspiring writers, seasoned wordsmiths, and everyone. Here, storytelling finds its home, and your creative journey begins its captivating voyage.
© 2024 Creativewriting-prompts.com

- Gradebook App
- Student Reports
- Training & Consulting
- Literacy Booster Offer
- Subscription Pricing
- Professional Development
- Our Mission
- Case Studies
- Privacy Policy & Terms of Service
- Review Mode

A Teacher’s Guide to a Short Story Writing Rubric
A short story writing rubric can your students become fantastic short story writers! Today, we’re going to dive into the world of short story writing rubrics—a tool that can make your teaching journey smoother and your students’ writing skills shine.
What’s a Short Story Writing Rubric, Anyway?
Before we dive in, let’s clear the air about what a short story writing rubric is. Think of it as your trusty roadmap for assessing and guiding your students through the process of crafting awesome short stories. It’s like a checklist, a set of guidelines, or even a secret recipe for creating engaging tales.
Why Do You Need a Short Story Writing Rubric?
You might be wondering, “Why should I bother with a rubric when grading short stories?” Well, here’s the scoop:
- Clarity : A rubric lays out your expectations for students in a clear and understandable way. No surprises!
- Consistency : It helps ensure that all your students are judged fairly and consistently, no matter who’s doing the grading.
- Feedback : Rubrics provide a structured way to give feedback. Instead of writing a novel on each paper, you can pinpoint areas for improvement efficiently.
- Growth : By using a rubric, you give students a roadmap for success, helping them see where they excel and where they need to improve.
Creating Your Short Story Writing Rubric

Step 1: Determine Your Criteria
Decide what aspects of short story writing are most important to you and your curriculum. Here are some common criteria to consider:
- Plot : Is the story engaging? Does it have a clear beginning, middle, and end?
- Characters : Are the characters well-developed and relatable?
- Setting : Does the story transport the reader to a specific time and place?
- Dialogue : Is the dialogue natural and does it advance the plot?
- Grammar and Style : Is the writing clear, and are there few grammatical errors?
- Creativity : Does the story stand out, offering fresh ideas or unique twists?
Step 2: Define Levels of Proficiency
For each of your criteria, create different levels of proficiency . Let’s use a four-level rubric as an example:
- Beginning : This level represents a starting point where students are just beginning to grasp the concept.
- Developing : At this level, students are making progress and showing improvement.
- Achieving : Achieving level indicates that students have reached a satisfactory level of proficiency.
- Mastering : This is the highest level, reserved for students who have demonstrated exceptional mastery of the criterion.
With these four levels, you can provide a more nuanced assessment of your students’ short stories and better guide their development.
Step 3: Describe Each Level
Now, describe what each level means for each criterion. Be specific! For example:
- Plot (Level 3) : The story’s plot is engaging, with a clear beginning, middle, and end. It includes unexpected twists that captivate the reader.
- Plot (Level 2) : The story has a good plot with a clear structure. While it’s engaging, there’s room for a bit more creativity.
- Plot (Level 1) : The story lacks a clear structure, making it difficult to follow.
Repeat these descriptions for all your criteria.
Using Your Short Story Writing Rubric
Alright, you’ve got your rubric ready , but how do you use it effectively?
- Share It : Start by giving your students the rubric before they start writing. This way, they know what you’ll be looking for.
- Self-Assessment : Encourage students to assess their own work using the rubric before turning it in. It’s a great way for them to identify areas they can improve.
- Peer Review : Have students exchange their stories and use the rubric to assess their classmates’ work. It promotes collaboration and helps students see different writing styles.
- Provide Feedback : When grading, use the rubric as a guide. Be sure to provide specific feedback on each criterion to help students understand where they excelled and where they can improve.
- Goal Setting : After grading, discuss the rubric with your students. Help them set goals for their next short story based on your feedback.
Final Thoughts
In the world of teaching short story writing, a rubric is like your secret sauce. It helps you create consistency, provide meaningful feedback, and guide your students toward becoming top-notch storytellers.
So, go ahead, create your short story writing rubric , and watch your students’ writing skills soar to new heights. Happy teaching, and may your classrooms be filled with captivating short stories!
That’s a wrap on our guide to short story writing rubrics for grade 7 teachers. We hope you found this information helpful and can’t wait to see the amazing stories your students will produce.
Try our Rubric Builder for Teachers!
Recent Posts
How a literacy rubric will maximize student success, report card writing made simple.
- Executive Functioning Rubrics are a Game Changer
The Teacher’s Guide to Mastering Orthographic Mapping
- Can Rubrics Help with Executive Functioning Skills?
Recent Comments
- 5 Reasons Teachers Love Analytical Rubrics - SUPERRUBRIC - SUPERRUBRIC.COM on 3 Rubrics for Elementary Reading & Writing
- A WordPress Commenter on Discussion Forum Rubric – Free Rubric Maker
Trending Now
- Discussion Forum Rubric – Free Rubric Maker March 18, 2021
- Book Report Rubric – Free Rubric Maker September 19, 2022
- A Teacher’s Guide to a Short Story Writing Rubric October 29, 2023
Recently Posted
- How A Literacy Rubric Will Maximize Student Success May 20, 2024

Vibrant Teaching
Teaching Resources Creator and Blogger
3 Types of Writing Rubrics for Effective Assessments
There are so many different writing rubrics out there and it may be difficult to find the right one. Below you will find a guide with 3 types of effective writing rubrics. Choosing the right one depends on the writing genre and your needs for the assessment.
Student-Friendly Rubrics
There are two ways to think about student-friendly rubrics. The first way is to use a rubric that students can complete as a self-assessment. The second way is to use a rubric that is completed by the teacher but is easy for students to understand. These rubrics are often based on the standards but shown in a different way. Instead of writing the actual standard on the rubric, include a one or two-word category.
See the example below of a third grade informative writing rubric. The first rubric uses the words introduction, content, linking words, closing, and mechanics for the categories. The second rubric lists each standard that goes with those categories. As you can see, the first option covers the same information but uses fewer words and is much easier for students to use and understand.
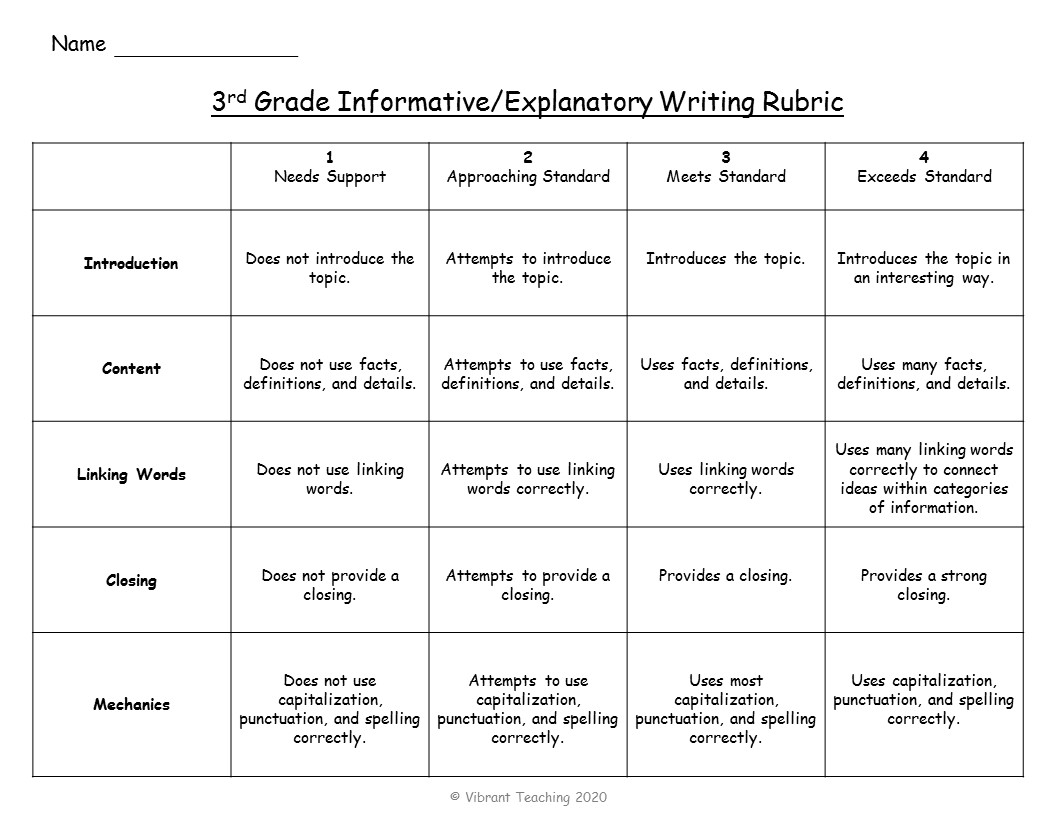
When do you use student-friendly rubrics? These are great for students to assess themselves. The student and teacher can fill out the rubric separately and then meet for a conference to discuss any differences. This same strategy can also be done with two students, but instead of a conference, they will meet to edit and revise their work. Another option is for teachers to fill out the writing rubric and hand it back to students with feedback. The student-friendly rubrics are easy for kids to understand and are still aligned with the standards.

Teacher-Friendly Rubrics
Teacher-friendly rubrics list each standard and use more details in the descriptions. This helps teachers know what to look for when assessing a writing piece. It will be very clear from the rubric whether or not the student is meeting or exceeding the standard. These writing rubrics are also quick and easy for teachers to use but may be more difficult for students to understand.
The examples below are standards based teacher-friendly rubrics. On the left side, you will see each Common Core Standard. The descriptions on the right side match each standard accordingly. These rubrics are used for assessing narrative writing in 1st grade, 2nd grade, 3rd grade, 4th grade, and 5th grade.
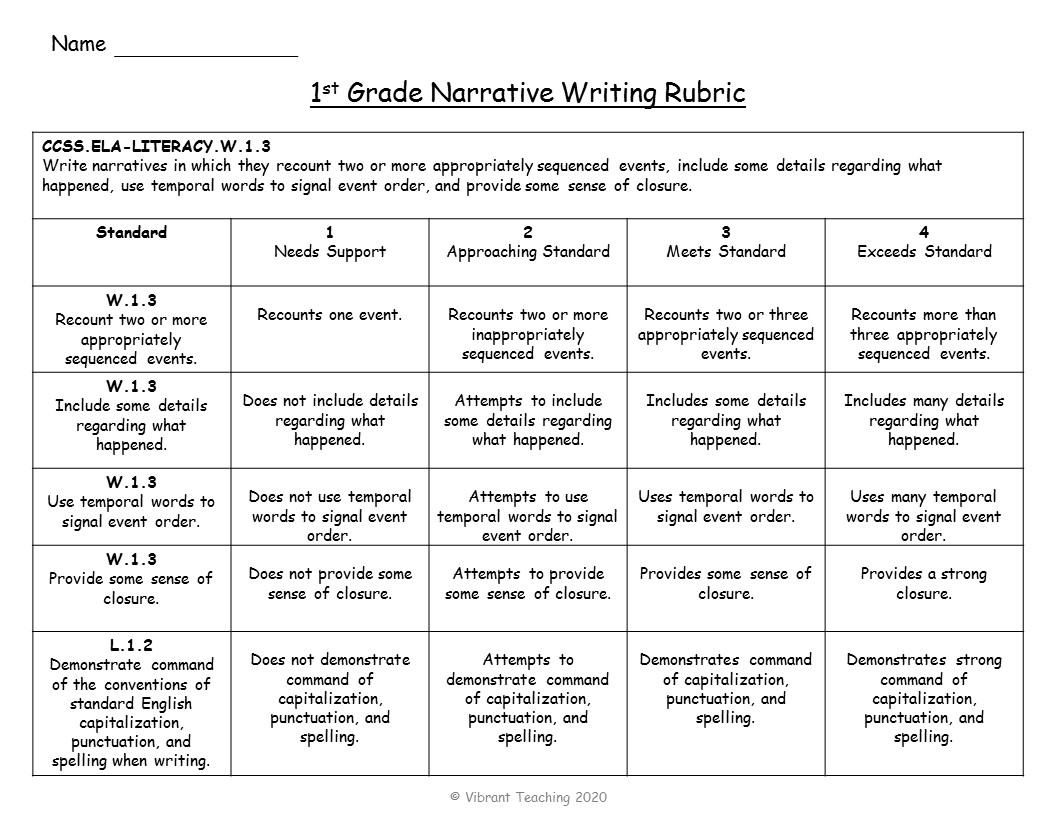
When do you use teacher-friendly rubrics? These are ideal when a teacher needs to get an accurate assessment for recording grades or writing report cards. They can choose whether or not to hand these rubrics back to students or use them for their records. Teacher-friendly rubrics are also helpful to show parents, especially at conferences.
Time-Saving Rubrics
Time-saving rubrics are a combination of student-friendly and teacher-friendly rubrics. These are standards based and list each standard on the left side. The difference is that instead of a description there is a number in each box such as 1, 2, 3, or 4. These numbers tell whether or not the student is meeting the standard.
1= needs support
2 = approaching standard, 3 = meets standard, 4 = exceeds standard.
The benefits of these rubrics are that they save time and energy by easily circling the number for each standard. It is quick for teachers to use but also easy for students to understand. Some teachers may also choose to include a section for the total score and comments depending on their needs. Check out some of the examples below for opinion writing.
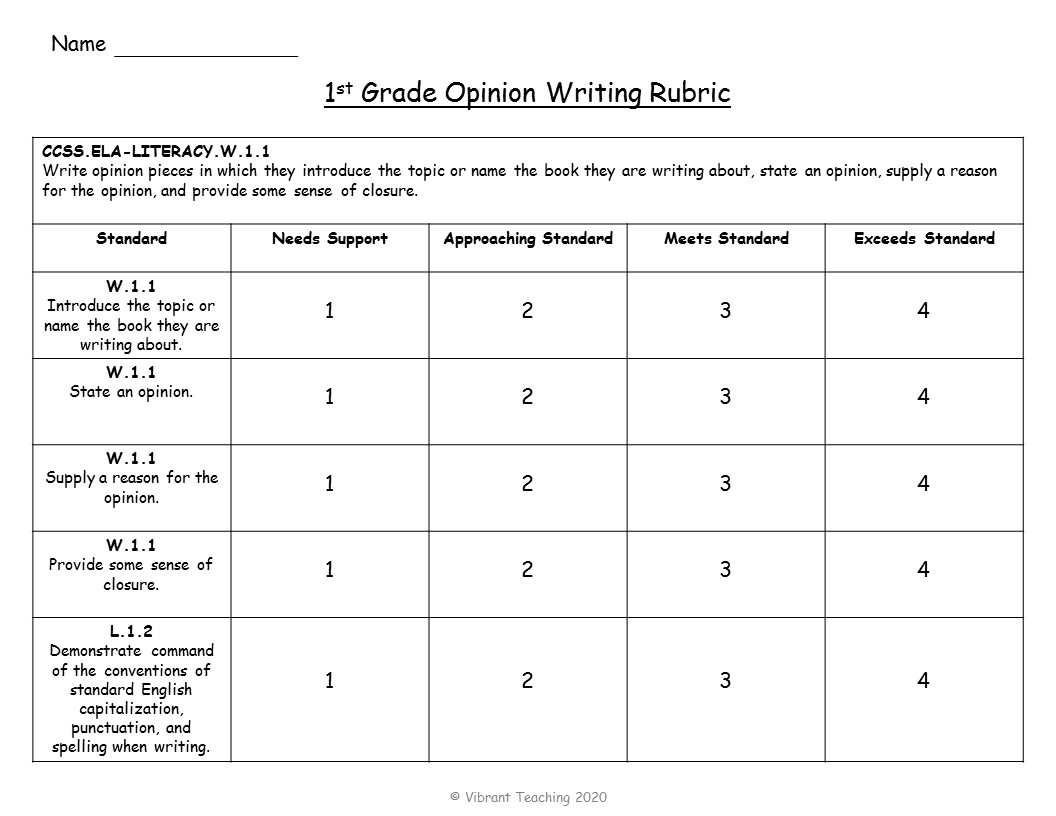
When do you use time-saving rubrics? Well of course these are helpful when teachers want to save time. The best part is the rubrics are still standards based but also very easy for students and parents to understand. Use these anytime!
Writing Rubrics Conclusion
I hope you have found these 3 types of writing rubrics helpful and will utilize them with your class. Think about what your goal is with the assessment and choose the best rubric for both you and your students. You may find that a mix of all three is beneficial throughout the school year.
Writing Rubrics by Grade Level
Grab these standards based writing rubrics. Each grade level includes 9 rubrics in 3 different options . Choose from student-friendly, teacher-friendly, and time-saving rubrics. These are ideal for assessing narrative, opinion, and informative pieces. Click each grade level below to learn more. Also, check out this Monthly Writing Prompts blog post for more resources and ideas.

Middle School Writing Rubrics

Angela Sutton
Related posts.

What are Writing Prompts? A Helpful Guide for Teachers

3 Distance Learning Tips

3 Reasons to Use Student Awards
No comments, leave a reply cancel reply.
I accept the Privacy Policy

I specialize in helping elementary teachers with writing resources, tips, and ideas. My goal is to save teachers time and energy so they can be vibrant inside and outside of the classroom! Read More
SEARCH THE BLOG
Subscribe to our mailing list.
Get the news right in your inbox!
Health and Wellness
Writing Rubrics
Samples of Basic, Expository, and Narrative Rubrics
- Grading Students for Assessment
- Lesson Plans
- Becoming A Teacher
- Assessments & Tests
- Elementary Education
- Special Education
- Homeschooling
Rubric Basics
How to score a rubric, basic writing rubric, narrative writing rubric, expository writing rubric.
- M.S., Education, Buffalo State College
- B.S., Education, Buffalo State College
An easy way to evaluate student writing is to create a rubric . A rubric is a scoring guide that helps teachers evaluate student performance as well as a student product or project. A writing rubric allows you, as a teacher, to help students improve their writing skills by determining what areas they need help in.
To get started in creating a rubric, you must:
- Read through the students' writing assignment completely.
- Read each criterion on the rubric and then reread the assignment, this time focusing on each feature of the rubric .
- Circle the appropriate section for each criterion listed. This will help you score the assignment at the end.
- Give the writing assignment a final score.
To learn how to turn a four-point rubric into a letter grade, use the basic writing rubric below as an example. The four-point rubric uses four potential points the student can earn for each area, such as 1) strong, 2) developing, 3) emerging, and 4) beginning. To turn your rubric score into a letter grade, divide the points earned by the points possible.
Example: The student earns 18 out of 20 points. 18/20 = 90 percent; 90 percent = A
Suggested Point Scale :
88-100 = A 75-87 = B 62-74 = C 50-61 = D 0-50 = F
|
|
|
| Score | |
Establishes a clear focus Uses descriptive language Provides relevant information Communicates creative ideas | Develops a focus Uses some descriptive language Details support idea Communicates original ideas | Attempts focus Ideas not fully developed | Lacks focus and development | ||
Establishes a strong beginning, middle, and end Demonstrates an orderly flow of ideas | Attempts an adequate introduction and ending Evidence of logical sequencing | Some evidence of a beginning, middle, and end Sequencing is attempted | Little or no organization Relies on single idea | ||
Uses effective language Uses high-level vocabulary Use of sentence variety | Diverse word choice Uses descriptive words Sentence variety | Limited word choice Basic sentence structure | No sense of sentence structure | ||
Few or no errors in: grammar, spelling, capitalization, punctuation | Some errors in: grammar, spelling, capitalization, punctuation | Has some difficulty in: grammar, spelling, capitalization, punctuation | Little or no evidence of correct grammar, spelling, capitalization or punctuation | ||
Easy to read Properly spaced Proper letter formation | Readable with some spacing/forming errors | Difficult to read due to spacing/forming letter | No evidence of spacing/forming letters |
|
|
|
| |
Skillfully combines story elements around main idea Focus on topic is profoundly clear | Combines story elements around main idea Focus on topic is clear | Story elements do not reveal a main idea Focus on topic is somewhat clear | There is no clear main idea Focus on topic is not clear | |
| Characters, plot, and setting are developed strongly Sensory details and narratives are skillfully evident | Characters, plot, and setting are developed Sensory details and narratives are evident | Characters, plot, and setting are minimally developed Attempts to use narratives and sensory details | Lacks development on characters, plot, and setting Fails to use sensory details and narratives |
Strong and engaging description Sequencing of details are effective and logical | Engaging description Adequate sequencing of details | Description needs some work Sequencing is limited | Description and sequencing needs major revision | |
Voice is expressive and confident | Voice is authentic | Voice is undefined | Writer's voice is not evident | |
Sentence structure enhances meaning | Purposeful use of sentence structure | Sentence structure is limited | No sense of sentence structure | |
A strong sense of writing conventions is apparent | Standard writing conventions is apparent | Grade level appropriate conventions | Limited use of appropriate conventions |
|
|
|
| |
Informative with clear focus and supporting details | Informative with clear focus | Focus needs to be expanded and supporting details are needed | Topic needs to be developed | |
Very well organized; easy to read | Has a beginning, middle, and end | Little organization; needs transitions | Organization is needed | |
Voice is confident throughout | Voice is confident | Voice is somewhat confident | Little to no voice; needs confidence | |
Nouns and verbs make essay informative | Use of nouns and verbs | Needs specific nouns and verbs; too general | Little to no use of specific nouns and verbs | |
Sentences flow throughout piece | Sentences mostly flow | Sentences need to flow | Sentences are difficult to read and do not flow | |
Zero errors | Few errors | Several errors | Many errors make it hard to read |
- Scoring Rubric for Students
- Sample Essay Rubric for Elementary Teachers
- Rubric Template Samples for Teachers
- 5 Types of Report Card Comments for Elementary Teachers
- 200 Report Card Comments
- Report Card Comments for Math
- Sample Report Card Comments for Social Studies
- Science Report Card Comments
- Report Card Comments for English Classes at School
- 5 Steps to Building a Student Portfolio
- Writing Prompts for Elementary School Students
- Writing a Lesson Plan: Closure and Context
- Grading for Proficiency in the World of 4.0 GPAs
- Writing Prompts for 7th Grade
- How to Write a Lesson Plan
- T.E.S.T. Season for Grades 7-12
- Home
- Writing Rubrics
- Creative Writing Rubrics
Creative Writing Rubric
All of our essay rubrics on one convenient page.
Print the FREE download of any of these creative writing rubrics. See the bottom of the page for helps on using and developing rubrics. And if you don't see exactly what you are looking for, look for the help page at the bottom of this page to find how you develop a rubric for your students' exact needs.
Elementary Writing Rubrics
These essay rubrics will help you identify the writing skills expected for elementary students as their writing slowly progresses.
Kindergarten Writing Rubric
1st Grade Writing Rubric
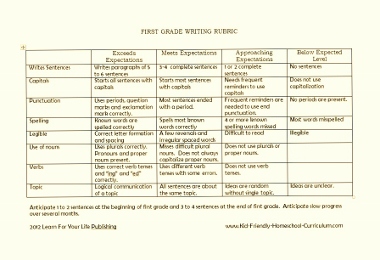
2nd Grade Writing Rubric
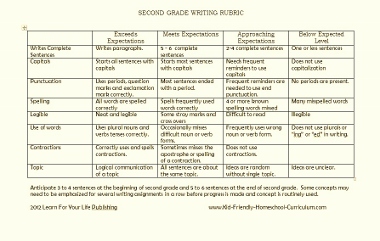
Read More: Writing Rubric for 2nd Grade
3rd Grade Writing Rubric
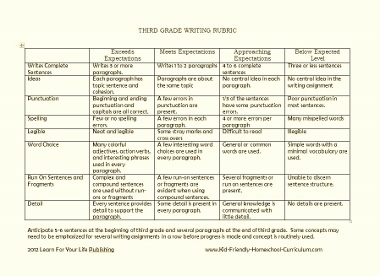
Read More: 3rd Grade Writing Rubric .
4th Grade Writing Rubric
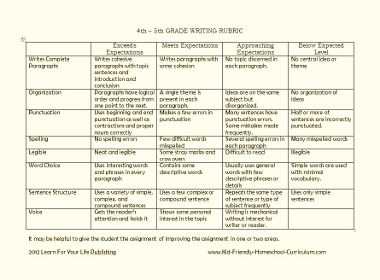
Read More: 4th Grade Writing Rubric .
5th Grade Writing Rubric
Read More: 5th Grade Writing Rubric .
Six Traits (+1) Writing
6 +1 traits writing rubric.
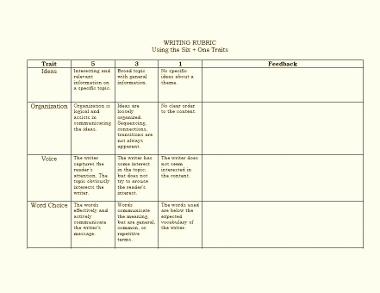
Read More: Six Traits Writing Rubric
Middle School and High School Writing Rubrics
100 point rubric for essays.
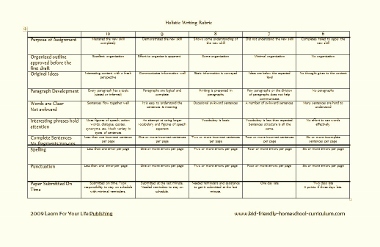
Research Paper Rubrics

Read More: Research Paper Rubric .
Blank Paper Rubrics

Read More: Developing your own research rubric .

Ready To Use Resources

Top of This Page
About Our Site
Hands-on learning.

Our Site At A Glance
- Ordering Information
- Privacy Statement
By Karen Newell Copyright© 2009 - 2023 Learn For Your Life All Rights Reserved
New Pages Site Map Contact About Us
| Advertisement |
Creative hobbies may greatly benefit mental health

Painting, woodworking, writing: Whatever you turn to creatively, it could equal or exceed work in terms of maintaining mental health, new research shows.
"Crafting and other artistic activities showed a meaningful effect in predicting people's sense that their life is worthwhile," said study lead author Dr. Helen Keyes , of Anglia Ruskin University in Britain. Advertisement
"Indeed, the impact of crafting was bigger than the impact of being in employment," she added. "Not only does crafting give us a sense of achievement, it is also a meaningful route to self-expression. This is not always the case with employment."
- Work stress may increase risk of heart rhythm disorder
- Study: Your body experiences 'massive' biomolecular changes in your 40s and 60s
- United States remains last for life expectancy among English-speaking countries
Folks were asked about their level of participation in cultural, digital and sporting activities.
People were also queried about their levels of loneliness and "sensations of happiness, anxiety and life satisfaction, and to give their impression of whether life is worthwhile," according to a journal news release.
More than a third (37.4%) of respondents said they'd been involved in some kind of arts or crafts activity over the past month. Advertisement
People who engaged in a creative pursuit scored higher in terms of happiness, life satisfaction and the sense that life is worthwhile, compared to folks who weren't involved in arts or crafts, the researchers found.
"The well-being effects were present even after we accounted for things like employment status and level of deprivation," Keyes said in a journal news release. "It seems that crafting can contribute positively to your well-being above and beyond these other aspects of your life."
Perhaps because many arts and crafts are done while alone, engagement didn't seem to affect people's levels of loneliness.
The study was only designed to show associations, so it could not prove cause and effect.
In her own life, Keyes said she's an avid devotee of DIY projects such as painting and decorating.
"There is certainly something immensely satisfying about seeing the results of your work appear before your eyes," she said. "It feels great to focus on one task and engage your mind creatively."
Policymakers might want to take guidance from the new findings, Keyes said.
"Governments and national health services might consider funding and promoting crafting, or even socially prescribing these activities for at-risk populations, as part of a promotion and prevention approach to well-being and mental health," she said. Advertisement
More information
Find out more about the benefits of being creative at the American Psychiatric Association .
Copyright © 2024 HealthDay. All rights reserved.

Latest Headlines

Trending Stories


Creative Writing doctoral student Abhijit Sarmah named for the second consecutive year as finalist for major poetry fellowship

For the second year in a row, UGA doctoral student Abhijit Sarmah is among 12 finalists for the 2024 Ruth Lilly and Dorothy Sargent Rosenberg Poetry Fellowships . The five Fellowship recipients, who were announced today , will each receive $27,000 and an invitation to publish in Poetry magazine . All 12 finalists will receive a stipend to attend a professional development opportunity of their choice.
The Poetry Foundation awards five Ruth Lilly and Dorothy Sargent Rosenberg Poetry Fellowships annually. Among the largest awards offered to young poets in the US, the prize is intended to support exceptional US poets between 21 and 31 years of age. The fellowships were established in 1989 by the Indianapolis philanthropist Ruth Lilly and expanded in 2013 with a gift from the Dorothy Sargent Rosenberg Memorial Fund.
“Being named a finalist for the prestigious Ruth Lilly and Dorothy Sargent Rosenberg Poetry Fellowship is really an honor. I am deeply grateful to Professor LeAnne Howe, Professor Barbara McCaskill, Professor Andrew Zawacki and Professor Aruni Kashyap for their support and guidance throughout the application process for this fellowship and beyond. Their faith in my work inspires me to keep achieving bigger milestones. Also heartfelt thanks to the wonderful folks at Willson Center— especially Professor Nicholas Allen, Winnie Smith and Dave Marr— who provide opportunities to interact with prominent poets like A.E. Stallings and Stephen Sexton. Those interactions have taught me a lot, including how to navigate the literary world and edit my own work.” -Abhijit Sarmah
A UGA Arts Lab Graduate Fellow and Ruth Pack Scholar, Sarmah is working on a hybrid memoir and a poetry collection, tentatively titled Potential Insurgent . Apart from his scholarly and creative work, he volunteers for various events and organizations at UGA, and was a selection committee member for Backlight Student Film Festival, a planning committee member for the International Street Festival and social chair for the English Graduate Organisation. He was awarded a 2024 Michael G. Moran Graduate Student Award by the Department of English at UGA. Currently, he is serving as the guest editor of poetry for The Headlight Review (Kennesaw State University).
"I have worked with Abhijit Sarmah for two years at the University of Georgia. A son of Assam, India, Sarmah's poetry is a kaleidoscope of emotions and images provoked by the Indian army’s indiscriminate violence in Assam. Sarmah writes from the experiences of a young man whose friends must flee to survive, violence against his loved ones at the hands of Indian soldiers and numerous events that made many around him take arms against their own country. Yet, Abhijit's poetry is not just an exploration of Indian army's cruelty against the Assamese, it's also a vehicle for memories of a brother's laughter, his sister's experiments in cooking, adventures with boyhood friends, and the community of townspeople he grew up with. His work blisters the heart." -LeAnne Howe Eidson Distinguished Professor of American Literature & Director of the Institute of Native American Studies
“This honor speaks to the strength of Abhijit’s work. We are very proud to have him as a student in our PhD program!” -Magdalena Zurawski Associate Professor of English and Creative Writing & Director of Creative Writing
Abhijit Sarmah
Abhijit Sarmah is a poet and researcher specializing in Indigenous literatures. He holds a Master of Philosophy (MPhil.) degree from Dibrugarh University, India and is currently pursuing a PhD at the University of Georgia in Athens GA, USA. He is also a UGA Arts Lab Graduate Fellow (2022-25) and has received such honors as the Ruth Pack Scholarship from the Institute of Native American Studies and Michael G. Moran Graduate Student Award from the Department of English at UGA. His work has been published in a range of print and online journals, including Poetry , The Margins , Lunch Ticket , Glassworks Magazine , Porter House Review , and The Lincoln Review . Sarmah was a finalist for the prestigious Ruth Lilly and Dorothy Sargent Rosenberg Poetry Fellowships for two consecutive years (2023 and 2024) and has received nominations for the Best of the Net and The Pushcart Prize.
Support English at UGA
We greatly appreciate your generosity. Your gift enables us to offer our students and faculty opportunities for research, travel, and any number of educational events that augment the classroom experience. Support the efforts of the Department of English by visiting our giving section. Give Now
EVERY DOLLAR CONTRIBUTED TO THE DEPARTMENT HAS A DIRECT IMPACT ON OUR STUDENTS AND FACULTY.

IMAGES
COMMENTS
1. Define Clear Criteria. Identify specific aspects of writing to evaluate. Be clear and precise. The criteria should reflect the key components of the writing task. For example, for a narrative essay, criteria might include plot development, character depth, and use of descriptive language.
A: A rubric for creative writing is a scoring tool used to assess and evaluate written works based on specific criteria. It outlines the expectations and benchmarks for various aspects of the writing, such as plot development, characterization, language use, and overall impact.
For creative writing, rubrics will emphasize the importance of originality, voice, and audience appeal. Levels of proficiency in a writing rubric. Point-based rubrics will show the total number of points you can score based on proficiency in each criterion. By ensuring your work matches the criteria in the highest categories, you should earn a ...
Use rubrics to assess project-based student work including essays, group projects, creative endeavors, and oral presentations. ... Disadvantage of analytic rubrics: Requires more work for instructors writing feedback. Step 3 (Optional): Look for templates and examples.
Conventions—10 points. -Spelling is correct throughout piece -Punctuation is used correctly -Punctuation is deliberately manipulated in a sophisticated manner to affect style -Format and presentation is correct/professional (Times New Roman, size 12, double spaced)
CREATIVE WRITING RUBRIC 40pts Be sure to follow the rubric thoroughly. You will have the first 5 minutes to review it and then the rest of the hour to write the assessed piece. If you print to the wrong printer it is an automatic 10 points off. If you aren't sure, ask! Effective- 5 pts Adequate- 4 pts Approaching- 2pts Below Standard- 0pt
Creative Writing Example Rubric. Students will write well organized, cohesive papers. Work functions well as a whole. Piece has a clear flow and a sense of purpose. Response has either a strong lead, developed body, or satisfying conclusion, but not all three. Uneven. Awkward or missing transitions. Weakly unified.
In summary, rubrics tailored for creative disciplines play a crucial role in educational settings. They provide a balanced framework that respects and nurtures creativity while maintaining academic rigor and fairness in assessment. This enables educators to effectively guide and evaluate student progress in creative fields.
Enter the creative writing rubric, a powerful tool that can help you understand and evaluate your work objectively. In this step-by-step guide, we will demystify the world of rubrics and unravel their importance in assessing your creative writing. Step 1: Familiarize Yourself with the Rubric Components.
Rubric: Creative Writing Section 1: Prepared Sample Ideas and Content - Concept, organization, detail 1 2 3 4 5 Not admissible Average Excellent
Step 3: Describe Each Level. Now, describe what each level means for each criterion. Be specific! For example: Plot (Level 3): The story's plot is engaging, with a clear beginning, middle, and end. It includes unexpected twists that captivate the reader. Plot (Level 2): The story has a good plot with a clear structure.
%PDF-1.6 %âãÏÓ 125 0 obj > endobj 143 0 obj >/Filter/FlateDecode/ID[74E671D6E0BF304FBCE6AB1490DB26F3>8959C3AA2112404C955ACB77BA906764>]/Index[125 26]/Info 124 0 R ...
Rubrics without carefully determined and relative grade weights can often produce a final score that does not align with the instructor's expectations for the score. Here is a sample of a rubric with a range of points within each performance level. Step 4: Create a format for the rubric.
Create a named range by selecting cells and entering the desired name into the text box. To enable screen reader support, press Ctrl+Alt+Z To learn about keyboard shortcuts, press Ctrl+slash. Anyone on the Internet can find and access. No sign-in required. Accessed by screen readers for people who might have trouble seeing your content.
Holistic scoring is a quick method of evaluating a composition based on the reader's general impression of the overall quality of the writing—you can generally read a student's composition and assign a score to it in two or three minutes. Holistic scoring is usually based on a scale of 0-4, 0-5, or 0-6.
Writing rubrics contribute meaningfully to the teaching of writing. Think of them as a coaching aide. In class and in conferences, you can use the language of the rubric to help you move past generic statements about what makes good writing good to statements about what constitutes success on the assignment and in the genre or discourse ...
See the example below of a third grade informative writing rubric. The first rubric uses the words introduction, content, linking words, closing, and mechanics for the categories. The second rubric lists each standard that goes with those categories. As you can see, the first option covers the same information but uses fewer words and is much ...
To learn how to turn a four-point rubric into a letter grade, use the basic writing rubric below as an example. The four-point rubric uses four potential points the student can earn for each area, such as 1) strong, 2) developing, 3) emerging, and 4) beginning. To turn your rubric score into a letter grade, divide the points earned by the ...
Abstract—Assessment is a crucial component of teaching creative writing. However, the discipline lags far behind its composition and literary counterparts to develop a plausible method for evaluating creativity. Therefore, after reviewing the past and current literature on the topic, this study describes the design and implementation of an ...
Writing Rubrics. Creative Writing Rubrics. We provide a menu of FREE creative writing rubrics and essay rubrics for elementary, middle school and high school. Tips on how to use rubrics to guide and improve writing are provided, as well as instructions on creating your own writing rubrics for your specific needs.
The Creative Thinking VALUE Rubric is intended to help faculty assess creative thinking in a broad range of transdisciplinary or interdisciplinary work samples or collections of work. The rubric is made up of a set of attributes that are common to creative thinking across disciplines. Examples of work samples or collections of work that could ...
Try these rubrics with genre-based writing prompts for narrative, personal narrative, informational, and opinion writing. 3 Student Friendly Rubrics: 1 Narrative, 1 Opinion, and 1 Informative Helpful for students to self-. 5 th. Creative Writing, English Language Arts, Writing. CCSS.
The W's MFA in Creative Writing expects around 28 students for the fall semester, as it kicks off its 10 th year. The program is a hybrid between online and in-person classes. Much of the course load is achieved through synchronous online classes during the regular semester. There are also four shorter residency classes held on location, such ...
Painting, woodworking, writing: Whatever you turn to creatively, it could equal or exceed work in terms of maintaining mental health, new research shows. "Crafting and other artistic activities ...
Director of Creative Writing. Abhijit Sarmah. Abhijit Sarmah is a poet and researcher specializing in Indigenous literatures. He holds a Master of Philosophy (MPhil.) degree from Dibrugarh University, India and is currently pursuing a PhD at the University of Georgia in Athens GA, USA. He is also a UGA Arts Lab Graduate Fellow (2022-25) and has ...