

Essay vs Report: Similarities, Differences, and Proper Use

When it comes to academic writing, two terms that often get confused are essays and reports. While they may seem similar on the surface, there are some key differences between the two. In this article, we will explore the differences between essays and reports and help you understand which one is the proper word to use in different situations.
Let’s define what each term means. An essay is a piece of writing that presents an argument or point of view on a specific topic. It typically includes an introduction, body paragraphs, and a conclusion. A report, on the other hand, is a document that presents information in an organized manner, often with headings and subheadings. Reports can be analytical, descriptive, or persuasive.
So, which one is the proper word to use? The answer is that it depends on the type of writing you are doing. If you are presenting an argument or point of view, you should use the term “essay.” If you are presenting information in an organized manner, you should use the term “report.”
In the rest of this article, we will explore the differences between essays and reports in more detail. We will look at the structure, purpose, and language used in each type of writing. By the end of this article, you will have a clear understanding of the differences between essays and reports and when to use each one.
Define Essay
An essay is a piece of writing that presents an argument or a viewpoint on a specific topic. It is a form of expression that allows the writer to convey their thoughts, opinions, and ideas to the reader. Essays can be written on a variety of subjects, including literature, history, philosophy, and science. They are typically shorter in length than reports and are often used to demonstrate a student’s understanding of a particular topic.
Define Report
A report is a document that provides information about a particular topic or issue. It is a structured and formal piece of writing that is used to communicate the results of research, investigations, or experiments. Reports can be written on a wide range of subjects, including business, science, and engineering. They are typically longer in length than essays and often include tables, graphs, and other visual aids to help convey information.
How To Properly Use The Words In A Sentence
When it comes to academic writing, it is important to understand the difference between an essay and a report. While both require research and analysis, they have distinct differences in structure and purpose. One of the key factors in using these words correctly is knowing how to properly use them in a sentence.
How To Use “Essay” In A Sentence
An essay is a piece of writing that presents an argument and supports it with evidence. When using the word “essay” in a sentence, it is important to make sure that it is being used in the correct context. Here are some examples:
- She wrote a compelling essay on the importance of education.
- His essay on climate change was well-researched and persuasive.
- The professor assigned a five-page essay on the history of the Roman Empire.
As you can see, the word “essay” is typically used to describe a specific type of writing assignment that requires research and analysis. It is important to use the word in a way that accurately reflects its meaning and purpose.
How To Use “Report” In A Sentence
A report is a formal document that presents information in a structured format. Reports are often used to communicate the results of research or investigations. When using the word “report” in a sentence, it is important to make sure that it is being used in the correct context. Here are some examples:
- The company issued a report on its quarterly earnings.
- The student submitted a report on the effects of pollution on local wildlife.
- The committee presented a report on its findings to the board of directors.
As you can see, the word “report” is typically used to describe a formal document that presents information in a structured format. It is important to use the word in a way that accurately reflects its meaning and purpose.
More Examples Of Essay & Report Used In Sentences
As we continue to explore the differences between an essay and a report, it’s helpful to see how these terms are used in real-world contexts. Here are some examples of using “essay” and “report” in sentences:
Examples Of Using “Essay” In A Sentence
- She spent all night working on her essay for the scholarship application.
- The professor assigned a five-page essay on the effects of climate change.
- My favorite author just released a new essay collection.
- After reading her essay, I was impressed by her writing skills.
- The student’s essay was full of insightful analysis.
- He won first prize in the essay contest with his powerful and persuasive argument.
- She wrote a personal essay about her experience with mental illness.
- The essay question asked us to compare and contrast two different theories.
- I need to finish my essay before I can go out with my friends.
- He wrote a humorous essay about his disastrous first date.
Examples Of Using “Report” In A Sentence
- The investigative journalist filed a report on the corruption scandal.
- We need to compile a report on the progress of the project.
- The doctor’s report showed that the patient’s condition had improved.
- She presented a detailed report on the state of the local economy.
- The police officer filed a report on the car accident.
- The committee will review the report before making a decision.
- The environmental group released a report on the impact of plastic pollution.
- The annual report highlighted the company’s achievements and challenges.
- He wrote a report summarizing the key findings of his research.
Common Mistakes To Avoid
When it comes to academic writing, using the terms essay and report interchangeably is a common mistake that many students make. However, it is important to understand that these two types of writing are distinct and require different approaches. In this section, we will highlight some of the most common mistakes people make when using essay and report interchangeably and provide tips on how to avoid them in the future.
Mistake #1: Failing To Understand The Purpose Of Each Type Of Writing
One of the biggest mistakes people make when using essay and report interchangeably is failing to understand the purpose of each type of writing. While both types of writing require research and analysis, the purpose of an essay is to present an argument or point of view, while the purpose of a report is to present information.
For example, if you were asked to write about the causes of climate change, an essay would require you to take a position and argue your point of view, while a report would require you to present factual information about the causes of climate change without taking a position.
To avoid this mistake, it is important to carefully read the instructions for each assignment and identify the purpose of the writing. If you are unsure, ask your instructor for clarification.
Mistake #2: Using The Wrong Structure
Another common mistake people make when using essay and report interchangeably is using the wrong structure. Essays typically follow a five-paragraph structure, with an introduction, three body paragraphs, and a conclusion. Reports, on the other hand, can have various structures depending on the purpose and audience.
For example, a business report may have a cover page, table of contents, executive summary, introduction, methodology, results, conclusion, and recommendations. Using the wrong structure can result in a poorly organized and confusing piece of writing.
To avoid this mistake, it is important to carefully read the instructions for each assignment and identify the required structure. If you are unsure, ask your instructor for clarification.
Mistake #3: Ignoring Formatting Requirements
Formatting is another area where people often make mistakes when using essay and report interchangeably. Essays and reports have different formatting requirements, including font size, line spacing, and citation style.
For example, essays typically use MLA or APA citation style, while reports may use APA or Chicago citation style. Ignoring formatting requirements can result in a lower grade or even plagiarism accusations.
To avoid this mistake, it is important to carefully read the instructions for each assignment and identify the required formatting requirements. If you are unsure, ask your instructor for clarification.
By understanding the purpose of each type of writing, using the correct structure, and following formatting requirements, you can avoid common mistakes when using essay and report interchangeably. Always remember to carefully read the instructions for each assignment and ask your instructor for clarification if you are unsure about any aspect of the writing.
Context Matters
When it comes to writing, the choice between an essay and a report can depend heavily on the context in which they are used. While both forms of writing share similarities, such as being used to convey information and make an argument, they have distinct differences that make them better suited for certain situations.
Examples Of Different Contexts
One example of a context in which an essay might be preferred is in a literature or humanities class. Essays are often used to analyze and interpret literary works or other cultural artifacts. In this context, the writer is expected to provide a critical analysis of the subject matter and offer their own interpretation of its meaning.
On the other hand, a report might be more appropriate in a business or scientific setting. Reports are often used to present research findings or to provide information to a specific audience. In this context, the writer is expected to provide clear and concise information that is easy to understand and that can be used to make informed decisions.
Another example of a context in which the choice between an essay and a report might change is in an academic setting. In some cases, professors might specify which form of writing they prefer for a particular assignment. For example, a professor might ask for a report on a specific topic in a science class, while in a history class, the same professor might ask for an essay that analyzes a particular event or period in history.
Ultimately, the choice between an essay and a report depends on the context in which they are used. While both forms of writing share similarities, they have distinct differences that make them better suited for certain situations. By understanding these differences and considering the context in which they are used, writers can choose the appropriate form of writing to effectively convey their message and achieve their goals.
Exceptions To The Rules
While the rules for using essays and reports may seem clear-cut, there are exceptions where these rules may not apply. Here are some examples:
1. Scientific Writing
In scientific writing, the term “report” is often used to describe a specific type of document that is distinct from an essay. Scientific reports typically follow a structured format and include sections such as an abstract, introduction, methods, results, and conclusion. In this case, using the term “essay” to describe this type of document would be incorrect.
2. Creative Writing
When it comes to creative writing, the rules for using essays and reports may not be as clear-cut. While essays are typically used for non-fiction writing, such as personal essays or literary criticism, some writers may use the term “essay” to describe a work of fiction that is structured in a similar way. Similarly, a writer may use the term “report” to describe a work of non-fiction that is more narrative in style.
3. Academic Disciplines
The rules for using essays and reports may also vary depending on the academic discipline. For example, in some fields, such as history or political science, the term “report” may be used to describe a research paper that includes a detailed analysis of primary sources. In other fields, such as psychology or sociology, the term “essay” may be used to describe a more reflective or personal piece of writing.
4. Context And Audience
Finally, the rules for using essays and reports may also depend on the context and audience for the document. For example, in a business setting, the term “report” may be used to describe a formal document that includes data and analysis, while the term “essay” may be used to describe a more informal piece of writing that is meant to persuade or inform.
Practice Exercises
One of the best ways to improve your understanding and use of essay and report is through practice exercises. Here are some examples:
Exercise 1: Fill In The Blank
Choose the correct word (essay or report) to fill in the blank:
- She wrote a/an ___________ on the causes of climate change.
- He handed in a/an ___________ on the history of the Roman Empire.
- The student submitted a/an ___________ on the effects of social media on mental health.
- The journalist wrote a/an ___________ on the latest political scandal.
Answer Key:
Exercise 2: Identify The Purpose
Read the following sentences and identify whether the purpose is to inform or to persuade:
- The purpose of this ___________ is to argue that the death penalty should be abolished.
- This ___________ provides an overview of the causes and effects of air pollution.
- The ___________ analyzes the financial performance of the company over the past year.
- In this ___________, the author explores the theme of love in Shakespeare’s sonnets.
- essay (persuade)
- report (inform)
- essay (inform)
By practicing with exercises like these, you can improve your ability to distinguish between essays and reports and use them effectively in your own writing.
After exploring the differences between essays and reports, it is clear that these two forms of writing serve different purposes and require different approaches. Essays are typically more subjective and allow for more creativity, while reports are more objective and require a focus on facts and data.
It is important for writers to understand the differences between these two forms of writing in order to effectively communicate their message to their intended audience. Whether it be for academic or professional purposes, knowing when to write an essay or a report can make a significant impact on the success of the writing.
Key Takeaways
- Essays and reports serve different purposes and require different approaches.
- Essays are subjective and allow for creativity, while reports are objective and focus on facts and data.
- Understanding the differences between these two forms of writing is important for effective communication.
By utilizing proper grammar and language use, writers can elevate their writing and effectively communicate their message to their intended audience. Continual learning and improvement in these areas can lead to greater success in both academic and professional settings.
Shawn Manaher is the founder and CEO of The Content Authority. He’s one part content manager, one part writing ninja organizer, and two parts leader of top content creators. You don’t even want to know what he calls pancakes.
- +44 (0) 207 391 9032
Recent Posts
- The Complete Guide to Copy Editing: Roles, Rates, Skills, and Process
How to Write a Paragraph: Successful Essay Writing Strategies
- Everything You Should Know About Academic Writing: Types, Importance, and Structure
- Concise Writing: Tips, Importance, and Exercises for a Clear Writing Style
- How to Write a PhD Thesis: A Step-by-Step Guide for Success
- How to Use AI in Essay Writing: Tips, Tools, and FAQs
- Copy Editing Vs Proofreading: What’s The Difference?
- How Much Does It Cost To Write A Thesis? Get Complete Process & Tips
- How Much Do Proofreading Services Cost in 2024? Per Word and Hourly Rates With Charts
- Academic Editing: What It Is and Why It Matters
- Academic News
- Custom Essays
- Dissertation Writing
- Essay Marking
- Essay Writing
- Essay Writing Companies
- Model Essays
- Model Exam Answers
- Oxbridge Essays Updates
- PhD Writing
- Significant Academics
- Student News
- Study Skills
- University Applications
- University Essays
- University Life
- Writing Tips

Essay vs Report: What Are the Key Differences?
(Last updated: 5 April 2024)
Since 2006, Oxbridge Essays has been the UK’s leading paid essay-writing and dissertation service
We have helped 10,000s of undergraduate, Masters and PhD students to maximise their grades in essays, dissertations, model-exam answers, applications and other materials. If you would like a free chat about your project with one of our UK staff, then please just reach out on one of the methods below.
Reports and essays serve as fundamental forms of scholarly communication, each with its distinct purpose, structure, and style. While both convey information and analysis, they vary in their objectives, audience, and presentation. In this comprehensive guide, we'll explore the different nuances between reports and essays, unpacking their key characteristics and offering insights into when and how to utilise each form effectively.
Reports: Capturing Data and Analysis
Reports are structured documents designed to convey factual information, findings, and analysis on a specific topic or issue. They are commonly used in academic, professional, and scientific contexts to present research outcomes, project evaluations, or business insights. Key features of reports include:
- Objective Presentation : Reports aim to provide an objective overview of data, observations, and analysis without personal interpretation or opinion.
- Structured Format : Reports typically follow a structured format, including sections such as introduction, methods, results, discussion, and conclusions.
- Visual Aids : Reports often incorporate tables, charts, graphs, and other visual aids to enhance the presentation of data and facilitate understanding.
- Audience Focus : Reports are usually intended for a specific audience, such as academic peers, business stakeholders, or policymakers, who require concise and actionable information.
Essays: Exploring Ideas and Arguments
Essays, on the other hand, are scholarly compositions that explore and analyse ideas, arguments, and theories within a particular subject area. They provide opportunities for critical thinking, reflection, and interpretation of course material or research findings. Key features of essays include:
- Thesis-driven Structure : Essays typically present a central thesis or argument, supported by evidence, analysis, and interpretation.
- Logical Progression : Essays follow a logical progression of ideas, with clear transitions between paragraphs and sections to guide the reader through the argument.
- Engagement with Sources : Essays engage with a range of scholarly sources, including academic articles, books, and primary documents, to support the argument and provide context.
- Critical Analysis : Essays encourage critical analysis and evaluation of ideas, theories, and evidence, often requiring students to synthesise information and draw their conclusions.
Key Differences: Report vs Essay
While both reports and essays involve research, analysis, and communication of ideas, there are key differences in their purpose, structure, and approach:
Purpose : Reports aim to present factual information and analysis to inform decision-making, while essays explore ideas, theories, and arguments to provoke thought and discussion.
Structure : Reports follow a structured format with clear sections, while essays offer more flexibility in organisation and presentation.
Language and Style : Reports use formal, concise language and avoid personal opinions, while essays may incorporate personal voice, reflections, and interpretations.
Audience : Reports are often written for a specific audience, such as stakeholders or decision-makers, while essays are typically written for academic audiences or peers.
Choosing the Right Format
The choice between a report and an essay depends on the nature of the assignment, the requirements of the task, and the expectations of the audience. Consider the following factors when determining which format to use:
Purpose : Clarify the purpose of the document—is it to present factual information (report) or to explore and analyse ideas (essay)?
Audience : Consider the intended audience and their expectations regarding format, style, and depth of analysis.
Scope and Depth : Assess the scope and depth of the topic—are you presenting data and findings (report) or engaging in critical analysis and interpretation (essay)?
Instructions : Review the assignment instructions carefully to determine whether a specific format is required and to understand the evaluation criteria.
Leveraging the Power of Structure and Style
Reports and essays are valuable tools for scholarly communication, each offering unique opportunities for knowledge dissemination and intellectual exploration. By understanding the differences between reports and essays and knowing when to employ each format, students and researchers can effectively convey information, analyse ideas, and engage with academic discourse. Whether crafting a data-driven report or crafting a compelling essay, mastering the nuances of structure and style is essential for academic success.

Essay exams: how to answer ‘To what extent…’

How to write a master’s essay

Writing Services
- Essay Plans
- Critical Reviews
- Literature Reviews
- Presentations
- Dissertation Title Creation
- Dissertation Proposals
- Dissertation Chapters
- PhD Proposals
- CV Writing Service
- Business Proofreading Services
Editing Services
- Proofreading Service
- Editing Service
- Academic Editing Service
Additional Services
- Marking Services
- Consultation Calls
- Personal Statements
- Tutoring Services
Our Company
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Become a Writer
Terms & Policies
- Fair Use Policy
- Policy for Students in England
- Privacy Policy
- Terms & Conditions
- [email protected]
- Contact Form
Payment Methods
Cryptocurrency payments.

Reports and essays: key differences

Know what to expect
Explore the main differences between reports and essays and how to write for your assignments
You'll complete assignments with different requirements throughout your degree, so it's important to understand what you need to do for each of them. Here we explore the key differences between reports and essays.
This page describes general features of academic reports and essays. Depending on your subject you may use all of these features, a selection of them, or you may have additional requirements.
There is no single right way to write a report or essay, but they are different assignments. At a glance:
- Reports depend heavily on your subject and the type of report.
- Essays usually have specific content and a planned structure with a focus on sense and flow. You subject might need different types of information in your introduction – some disciplines include a short background and context here, while others begin their discussion, discuss their resources or briefly signpost the topic.
Differences between reports and essays
This table compares reports and essays and provides an outline of the standard structure for each. Your assignment will also depend on your discipline, the purpose of your work, and your audience – so you should check what you need to do in your course and module handbooks, instructions from your lecturer, and your subject conventions.
| Reports | Essays |
|---|---|
| Reports have a table of contents. | Essays don't have a table of contents. |
| Reports are divided into headed and numbered sections and sometimes sub-sections, using the IMRaD format(see below). | Essays are not divided into sections but you may have separate headed appendices. |
| Reports often originate from outside academic subjects and are typically used in the world of work. | Essays originate in academic settings, including practice-based subjects. |
| Reports often present data and findings that you have collected yourself, for example through a survey, experiment or case study. Some reports focus on applying theory to your field of work. | Essays usually focus on analysing or evaluating theories, past research by other people, and ideas. They may include applying theory to practice if you are in a practice-based field. |
| A report usually contains tables, charts and diagrams. | Essays don't usually include tables, charts, or diagrams. |
| Reports usually include descriptions of the methods used. | Essays don't usually refer to the methods you used to arrive at your conclusions. |
| The discussion in a report often comments on how the report research could be improved and extended, and may evaluate the methods and processes used. | Essays don't usually reflect on the process of researching and writing the essay itself. |
| Reports sometimes include recommendations. | Essays don't include recommendations. |
Table adapted from Cottrell, 2003, p. 209.
The structure of reports
Most reports use an IMRaD structure: Introduction, Methods, Results and Discussion.
Below are some common sections that also appear in reports. Some sections include alternative headings.
1. Table of contents
Your contents shows the number of each report section, its title, page number and any sub-sections. Sub-section numbers and details start under the section title, not the margin or the number.
2. Abstract or Executive summary
This brief summary of the report is usually the last thing you write.
3. Introduction
Your introduction describes the purpose of the report, explains why it necessary or useful, and sets out its precise aims and objectives.
4. Literature review
This describes current research and thinking about the problem or research question, and is often incorporated into the introduction.
5. Methods or Methodology
This describes and justifies the methods or processes used to collect your data.
6. Results or Findings
This section presents the results (or processed data) from the research and may consist of mainly tables, charts and or diagrams.
7. Discussion, or Analysis, or Interpretation
This section analyses the results and evaluates the research carried out.
8. Conclusion
The conclusion summarises the report and usually revisits the aims and objectives.
9. Recommendations
In this section the writer uses the results and conclusions from the report to make practical suggestions about a problem or issue. This may not be required.
10. Appendices
You can include raw data or materials that your report refers to in the appendix, if you need to. The data is often presented as charts, diagrams and tables. Each item should be numbered : for example, write Table 1 and its title; Table 2 and its title, and so on as needed.
Structure of essays
Introduction.
Your essay introduction contextualises and gives background information about the topic or questions being discussed, and sets out what the essay is going to cover.
Your essay body is divided into paragraphs. These paragraphs help make a continuous, flowing text.
The conclusion summarises the main points made in the essay. Avoid introducing new information in your conclusion.
Bibliography or Reference list
This is a list of the resources you've used in your essay. This is usually presented alphabetically by authors’ surname.
Reference for the Table of Distinctions above:
Cottrell, S. (2003). The Study Skills Handbook (2nd ed.). Basingstoke: Palgrave.
Download our report and essay differences revision sheet
Download this page as a PDF for your report and essay revision notes.

Key features of academic reports

Basic essay structure

Writing clear sentences
Find an undergraduate or postgraduate degree course that suits you at Portsmouth.

Guidance and support
Find out about the guidance and support you'll get if you need a helping hand with academic life – or life in general – when you study with us at Portsmouth.

- Key Differences
Know the Differences & Comparisons
Difference Between Essay and Report

On the other hand, an essay can be understood as a piece of writing, on a specific topic or subject, which expresses the author’s own ideas and knowledge about the subject.
The basic difference between essay and report is that while an essay is argumentative and idea-based, reports are informative and fact-based. Now, let us move further to understand some more points of differences.
Content: Essay Vs Report
Comparison chart.
| Basis for Comparison | Essay | Report |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | An essay refers to a literary device, in which almost everything is discussed or stated about a subject. | Reports are the documentation and analysis of the findings and recommendations from the practical research. |
| Based on | Subjective analysis of theories and past research by experts and one's own ideas. | Past research, as well as present data and findings. |
| Presents | Facts and writer's personal ideas and views | Information |
| Division | It is divided into cohesive paragraphs | It is divided into sections which contains headings and subheadings. |
| Graphical Representation | It does not contain charts, graphs, tables and diagrams. | It contains charts, graphs, tables and diagrams. |
| Conclusion and recommendation | Conclusion depends on writers person's experience and views, and it does not include recommendations. | There is independent conclusion and recommendations are included. |
Definition of Essay
An essay can be understood as a comprehensive literary composition, written in a narrative style and presents a particular topic, supports an argument and highlights the writer’s view or ideology. An essay is used to check a person’s outlook and understanding on specific matters and also his/her ability to describe and argue in a way which convinces the reader or informs him/her about a specific topic.
One can make use of learned materials, along with his/her own research, to write an essay effectively. It includes both narrative and subjective thoughts. Further, an essay supports a single idea at a time, for which several components need to be covered in it so as to appear logical and chronological.
It can be a learned argument, observation of day to day life, literary criticism, political manifestos, recollections, and reflections of the writer. It starts with a question and attempts to answer or give suggestions to the problem, on the basis of the existing theories or the writer’s personal opinion and assessment.
While writing an essay, it must be kept in mind that the approach used by the writer should be positive, even if the topic of argument is negative.
Definition of Report
The report implies a well structured factual document which is created and presented after conducting an independent enquiry, research or investigation on a specific subject. It serves as a basis for problem-solving and decision making.
Reports are prepared for a definite purpose and contain relevant information in a proper format, for a particular audience. It is used to identify, observe and analyse the issues, events, findings, that occurred practically, i.e. in real life.
A report is designed with the aim of informing the reader about the event, situation or issue, in a very simple and objective manner, while enabling them to get the desired information quickly and easily. It provides recommendations for future actions. Information collected from research, or from carrying out a project work is presented in a clear and concise manner, under a set of headings and subheadings, that helps the reader to get the desired information quickly and easily.
Characteristics of an Ideal Report
- It must be clear and concise.
- It is written in easy language which the readers can understand easily.
- It has to be appropriate and accurate.
- It should be well drafted and organised, with specific sections, headings and sub-headings.
A report summary can be provided orally, however detailed reports are usually in the form of written documents. It contains – Title Page, Acknowledgement, Authorization Letter, Table of Contents, Executive Summary, Introduction, Discussion, Results, Conclusion, Recommendations and References.
Moreover, Cover letter, Copyright notice, Bibliography, Glossary and Appendices may also form part of a report.
Key Differences Between Essay and Report
The difference Between report and essay is discussed here in detail:
- An essay is a brief literary composition, which is used to describe, present, argue, and analyse the idea or topic. Conversely, a report is a formal and concise document consisting of findings from the practical research. It aims at investigating and exploring the problem under study.
- An essay is written on the basis of subjective analysis of theories and past research, by other people and own ideas, on the concerned subject. As against, a report is objective and factual, which is based on past research, as well as present data and findings.
- An essay talks about general facts and events along with the writer’s personal ideas and views, on the topic in a non-fictional manner. On the contrary, a report contains information which the reader can use to identify the facts or support in decision making or solving issues if any.
- When it comes to sections, a report usually contains different sections, with catchy headings which may attract the attention of the audience. As against, an essay does not have any section, its flow is continuous. However, it is divided into cohesive paragraphs.
- A report uses tables, charts, graphs, diagrams, statistics and many more for a clear and better presentation of the information. But, in the case of essays, they are not used.
- The conclusion in an essay is based on the writer’s personal opinion and views on the topic itself which must be optimistic, and it does not provide any recommendations for future actions. On the other hand, a report gives an independent conclusion, but it may contain the opinion of the experts or previous researchers and recommendations are included, about how the research can be improved and extended.
In a nutshell, Essays are descriptive, subjective and evaluative, whereas, a report is descriptive, objective and analytical. Essays are mainly used in an academic context, whereas reports are preferred in the field of research.
The report is used to present the researched information in a written format, to the audience. Conversely, essays are used to identify what the writer knows about the topic and how well the writer understand the question.
You Might Also Like:

Anna H. Smith says
November 26, 2020 at 3:22 pm
Thank you for explaining this so eloquently. Excellent post, I will keep this handy and refer to it often from now on, the information is so clear and so insightful, thanks for giving a clear difference. It’s a very educative article.!
Presley Dube says
November 20, 2021 at 3:43 pm
very useful to me thank you.
Leonard says
August 8, 2022 at 2:52 pm
Thanks for sharing such nice information about this topic.
Ignatius Phiri says
March 20, 2023 at 10:39 pm
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- RMIT Australia
- RMIT Europe
- RMIT Vietnam
- RMIT Global
- RMIT Online
- Alumni & Giving

- What will I do?
- What will I need?
- Who will help me?
- About the institution
- New to university?
- Studying efficiently
- Time management
- Mind mapping
- Note-taking
- Reading skills
- Argument analysis
- Preparing for assessment
- Critical thinking and argument analysis
- Online learning skills
- Starting my first assignment
- Researching your assignment
- What is referencing?
- Understanding citations
- When referencing isn't needed
- Paraphrasing
- Summarising
- Synthesising
- Integrating ideas with reporting words
- Referencing with Easy Cite
- Getting help with referencing
- Acting with academic integrity
- Artificial intelligence tools
- Understanding your audience
- Writing for coursework
- Literature review
- Academic style
- Writing for the workplace
- Spelling tips
- Writing paragraphs
- Writing sentences
- Academic word lists
- Annotated bibliographies
- Artist statement
- Case studies
- Creating effective poster presentations
- Essays, Reports, Reflective Writing
- Law assessments
- Oral presentations
- Reflective writing
- Art and design
- Critical thinking
- Maths and statistics
- Sustainability
- Educators' guide
- Learning Lab content in context
- Latest updates
- Students Alumni & Giving Staff Library
Learning Lab
Getting started at uni, study skills, referencing.
- When referencing isn't needed
- Integrating ideas
Writing and assessments
- Critical reading
- Poster presentations
- Postgraduate report writing
Subject areas
For educators.
- Educators' guide
- Reports vs essays
Students are sometimes unclear about different genres of assessment tasks.
Students often ask the question "What is the difference between a report and an essay?" This short video explains what a report is in academic writing, how it is used in different situations, and the structure of a report including executive summary, introduction, findings and conclusion.
What is a report?
A report is a piece of writing that tells you about some experience, event, or situation. This could include just doing research on some topic, a practical experiment, some issue that has arisen in a company/organisation, or a system, or even a piece of equipment, maybe.
Reports are often problem-based, but not always. It describes what you have found out, and it goes deeper - it explains and analyses what you have found out. Reports are very structured and there is an expected format. They always have sections and headings.
Have a look at this report outline:
“The aim of this report was to investigate Unilab staff attitudes to the use of mobile phones in staff and team meetings. A staff survey and policies on mobile phone use from a number of similar companies were analysed. There was significant support for a clear company policy on mobile phone use, including their banning in certain situations. The results of this research reflected the findings from similar studies. The report concluded that personal mobile phones should not be turned on during all staff meeting times.”
Most reports have executive summaries. In some disciplines, we call it an “abstract”. They are not the same as the introduction. An executive summary summarises the whole report. That means that there will be a sentence or two representing each section of the report. You always write it after you have completed the full report. Have a look at how the writer summarises each main section in one sentence (refer to executive summary above). As you can see, it’s got a very definite structure drawn from the larger report. It is very different to the introduction which just talks about the broad context, the purpose of the report, and what is going to be covered in the following sections. It gives the reader an idea of what is ahead – it does not give the overview like the executive summary.
The other important sections are the Findings and Discussion. This is where you would describe and then analyse your findings. Your findings will be reporting what you have discovered during your research, or your experiment, or an observation you have made. In the discussion section, you must delve deeper: you have to analyse and make sense of these findings and not just state what they are.
Finally, in the conclusion, you summarise your findings or use your findings or to come out with a more unified understanding or outcome. In some disciplines like business, you might be asked to give solutions or recommendations to overcome a problem that you have noticed. Recommendations might have their own section or be included in the conclusion, too.
For more information about reports, try the tutorials. Thanks for watching!
The table below shows the main differences between reports and essays.
- Provides objective information: Can be constructed collaboratively.
- Highly structured into sections identified using headings.
- Sections can be read in isolation of the most of the text: the reader can dip in and out.
- Objective report and analysis of facts.
- Grounded in practice but often links to theory.
- For a specific audience.
- Includes tables, graphs and diagrams.
- Dot points used for conciseness.
- Presents a particular writer's claim or argument.
- Structured by paragraphing with key points identified in topic sentences.
- Paragraphs are read in the context of the whole: the reader starts at the beginning and reads the entire text.
- Subjective argument or interpretation.
- Grounded in theory but sometimes linked to practice.
- For a generalised audience.
- Meaning is conveyed through text.
- Meaning constructed through sentences.
- Purpose of reports and sources to use
- Overall structure of a report
- Sample report structures
Still can't find what you need?
The RMIT University Library provides study support , one-on-one consultations and peer mentoring to RMIT students.
- Facebook (opens in a new window)
- Twitter (opens in a new window)
- Instagram (opens in a new window)
- Linkedin (opens in a new window)
- YouTube (opens in a new window)
- Weibo (opens in a new window)
- Copyright © 2024 RMIT University |
- Accessibility |
- Learning Lab feedback |
- Complaints |
- ABN 49 781 030 034 |
- CRICOS provider number: 00122A |
- RTO Code: 3046 |
- Open Universities Australia
No products in the basket.
Report vs Essay: A Clear and Complete Comparison of Them
Publish Date: 10 November 2023
Reports and essays are both forms of academic writing. They each serve different purposes and cater to specific audiences. Thus, understanding the differences between them is crucial. This blog post will delve into the differences between reports and essays. Also, we will explore their purposes and structures. Furthermore, we will look at their content and writing styles. And finally, we will look at the situations where each format is usable.

Table of contents
Report vs essay: purpose and audience.
- Report vs Essay: Structural Differences
Report vs Essay: Content and Focus
Report vs essay: writing style and tone, when to use report vs essay.
Before we get into the specifics, look at the purposes and target audiences of reports and essays. Thus, helping us understand the core difference between a report and an essay.
- Purpose of Reports: Reports are documents designed to give out information. Namely, they are usually an analysis or research findings on a particular topic . They aim to inform and persuade. Or, they may provide recommendations to a specific audience. Moreover, reports are often used in a professional or organisational context.
- Purpose of Essays: Essays, on the other hand, are more broad in nature. They usually present various arguments or ideas. Thus, they analyse concepts or interpret information. Essays encourage critical thinking and often involve personal opinions. Therefore, making them a platform for expressing ideas and engaging readers.
- Target Audience for Report vs Essay: Reports usually target decision-makers, stakeholders, or experts in a specific field. Namely, those who need accurate and correct information. However, Essays target a broader audience. Such as, educators, peers, or the general public. Hence, they usually aim to provoke thoughtful discussion and debate.
Structural Differences
To start the comparison, let’s look at how essays are written and how reports are written. Therefore, we can compare how they differ in style and structure.

Report Structure:
Reports follow a structured format. This includes a title page, abstract, introduction, method, findings, conclusion, recommendations, and references. Thus, it ensures a logical flow of information. Therefore, allowing readers to easily understand the research process and outcomes.
Essay Structure:
Essays have a more flexible and varied structure. However, they generally consist of an introduction, body paragraphs, and a conclusion. There is no fixed rule for the paragraphs in the body. However, essays often present arguments in a structured manner. Additionally, supporting them with evidence and analysis. Furthermore, citations and references are used to show the sources used. Therefore, improving the credibility of the arguments discussed in the essay.
Now, let’s look at the content and focus differences between reports and essays. Hence, understanding the approaches writers take within these two forms of writing.
- Content in Reports: Reports focus on presenting data, analysis, and research findings. They rely on facts, charts, graphs, and tables to support their conclusions. The content in reports is objective. Therefore, it aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the topic under investigation.
- Content in Essays: Essays prioritise arguments, discussions, and understandings. They explore various ideas. Also, they may look at theories or concepts. Additionally, essay writers often give personal opinions on matters. Essays may delve into historical context or case studies to support their claims. Thus, encouraging readers to properly assess the presented information.
- Focus in Reports: Reports maintain a neutral stance. Therefore, focusing on the presentation of information without personal bias. The focus lies on providing accurate data and analysis. In turn, let readers draw their own conclusions based on the evidence.
- Focus in Essays: Essays adopt a biased approach. Hence, encouraging writers to express their opinions and ideas. The focus is on exploring various viewpoints. Namely, engaging with existing writing, and challenging common ideas. Essays invite readers to consider the writer’s perspective and think about the ideas presented.
Moving forward, we will look at the writing styles that are different in reports and essays. Also, we will be diving into the details of language and expression within each.
- Writing Style in Reports: Reports use a formal and clear writing style. Hence, the language used is technical and straightforward. Thus, making sure of clarity and precision in giving out information. Furthermore, passive voice is often preferred in reports to maintain an impersonal tone.
- Writing Style in Essays: Essays exhibit a formal to semi-formal writing style. This is characterised by analytical and persuasive language. Moreover, writers craft their sentences carefully by employing language devices. Thus, improving the persuasiveness of their arguments. Active voice is common in essays. Thus, allowing writers to convey their ideas in a more personal and direct way.
- Tone Differences in Report vs Essay: The tone in reports remains neutral and free of personal opinions or emotions. The focus is on providing information without influencing the reader’s judgment.
Here, we will discuss the situations where reports and essays should be used in place of each other. Thus, guiding writers on when to opt for one over the other.
- Situations Where Reports are Preferred: Reports are preferred in analytics and academic research. They are ideal for research findings, market analyses, or financial data. Furthermore, they are usually meant for those who need detailed and factual information. Namely, people like stakeholders, managers, or field experts.
- Situations Where Essays are Preferred: Essays find their place in personal writing. Writings such as literary analyses and philosophical ideas. Additionally, they are useful when looking at abstract concepts and literary works. Also, they are useful for debating social issues or sharing personal opinions. Essays invite readers to engage in thinking. Thus, making them suitable for educational purposes.
- Choosing the Appropriate Format: Choosing between a report and an essay depends on the purpose of the communication. Is the goal to inform professionals, decision-makers, or experts? If so, a report would be the appropriate choice due to its structured and factual nature. However, if the aim is to provoke thought, stimulate discussion, or present personal viewpoints, an essay would be the preferred format. Thus, allowing for a more exploratory and engaging approach.
In short, reports are like detailed and organised summaries. Thus, making them great for serious topics and professional settings. Meanwhile, essays are more like personal conversations. Thus, making them perfect for expressing ideas and opinions in a friendly way. Knowing when to use each one helps you share your thoughts better. So, keep this in mind for the next time. Happy Writing!
Are you looking for report writing help? If so, consider checking out our Report Writing Course for the best learning experience!

Course Description :
- Certificate: Free
- Accreditation Status: CPD Accredited
- Credits: 12
Related Blog Posts

Indian Head Massage: The Ultimate Way to Soothe and Relax
In the modern world, stress and tension are everywhere. So, the search for relaxation and soothing methods is ever-present. Among …

Benefits of using a Language Translator
Are you someone who is working in a diverse cultural environment where you need to talk to people in different …

Complete Guide to Close Protection: Boost Your Security Skills
Security concerns are on the rise every day. Therefore, the demand for those skilled in close protection is higher than …
Payment Varify

- Copyright ©
2024 Unified Course All rights reserved.
Save up to 85%
New year sale, on 556+ of awesome course.
LibAnswers: Library and Learning Services
What is the difference between an essay and a report.
Reports are typically used to present the findings from a particular project, experiment, or investigation in a systematic way. Essays are used to develop a discussion of a topic or build an argument.
Reports present information in a different way from an essay. Whilst essays are generally quite fluid in terms of structure, enabling the author to explore a topic through a series of paragraphs, a report will be highly structured with section headings and subheadings that have a clear function. Reports often use tables, bullet points and graphics to present information.
Links & Files
- Learn more about different types of assignment
- Learn more about academic writing
- Academic Writing
- Last Updated Aug 21, 2023
- Answered By Anna Nunn
FAQ Actions
- Share on Facebook
Comments (0)
➔ About the Library
➔ Meet the Team
➔ Customer Service Charter
➔ Library Policies & Regulations
➔ Privacy & Data Protection
Essential Links
➔ Database A-Z
➔ Frequently Asked Questions
➔Discover the Library
➔Referencing Help
➔ Print & Copy Services
➔ Service Updates
Library & Learning Services, University of Suffolk, Library Building, Long Street, Ipswich, IP4 1QJ
✉ Email Us: [email protected]
✆ Call Us: +44 (0)1473 3 38700

Home » Language » Difference Between Essay and Report
Difference Between Essay and Report
Main difference – essay vs report.
Essay and report writing is an area that confuses many people . Despite having some similarities, they both are written in different styles. Both Essays and Reports must be written in a formal academic style while carefully checking grammar, spelling, and presentations. There are some common features in essay and report writing as both start with an introduction, body with discussions and analysis, and finally conclusions that demonstrate writer’s analytical thinking ability. However, there are some significant differences between Essays and Reports, and writers should be well aware of these differences before starting to write. The main difference between these two types of writings is their purpose ; an essay presents writer’s personal ideas and opinions about a certain topic while a report provides unbiased information about a certain issue.
What is an Essay
Essay is a piece of writing that describes, analyzes and evaluates a certain topic or an issue . An essay generally contains a combination of facts, statistics and writer’s personal view and opinions. An essay can be categorized into various types, depending on the nature of the title and the style of the author. Descriptive, Narrative, Argumentative, Persuasive, and Expository are some of these types of Essays. Though there is no strict format for essay writing, an essay generally includes an introduction, body, and conclusion. Essays are mostly used in the field of Education and are usually about academic subjects.
What are the Different Types of Essays
How to write an essay, what is a report.
A report is a systematic, well-organised document that defines and analyses a certain issue or a problem . The primary aim of a report is to provide information. A report is divided into several sections, headings, and sub-headings. A report is divided into sections in this manner so that anyone can scan the document and find quickly, the specific information he/she needs. Reports are used in different fields, and various types of reports written for different purposes can be found in our day to day life. Reports are generally written for practical purposes. Academic reports, Business reports, Laboratory reports are examples of such reports. Another significant feature that can be observed in a report is that the writer indicates recommendations, solutions to the issue at the end of the report. Graphs, tables, sentences in bullet points can also be used in report writing.
Let us now look at the difference between essay and report separately. One of the main difference between essay and report is the purpose. An essay is written to present writer’s personal ideas and opinions while a report is written to provide information about a certain issue. Another significant difference between essay and report is the format. A report is divided into sections, headings, and sub-headings, but an essay is never divided into sections and headings; it has interconnecting paragraphs. The conclusion of a report is unbiased and recommendations are provided at the end while the conclusion of an essay depends heavily on the opinion of the author. A report contains graphs and tables while an essay rarely contains graphs and tables. An appendix can be attached to the report for further reference. One of the most efficient features of a report, is that the information can be found quickly by scanning the headings and sections but, in an essay, it is difficult to find a specific information without reading the whole essay.

About the Author: Hasa
Hasanthi is a seasoned content writer and editor with over 8 years of experience. Armed with a BA degree in English and a knack for digital marketing, she explores her passions for literature, history, culture, and food through her engaging and informative writing.

You May Also Like These
Library Guides

Academic Support
- Code of Practice
- Get Academic Support
The purpose of an essay
When we write an essay we are often looking at topics in depth. The essay may voice an opinion, or explain something in detail. The essay may include arguments or counter arguments or offer solutions to problems.Tthere are many different ways to approach writing an essay. The purpose of an essay is to provide a detailed insight in to an aspect of a topic.
The purpose of a report
A report often discusses the results of a practical investigation. For example a report could discuss an experiment and its results or discuss research that has been undertaken. The purpose of a report is to help people to find the information they need quickly . For example they may need to see the results of an experiment but not want to know how it was carried out.
The common structure of an essay
An essay has the following structure: introduction, main body of the essay and conclusion. Each part of the essay is written in paragraphs. It is not common practice to use headings within an essay. The paragraphs within the essay should link together clearly as the reader is going to be reading every section. This can be done by trying to link each paragraph to the other.
The common structure of a report
Reports often include the following features:
A list of contents - this shows your reader where they can find the exact information they are looking for.
An abstract - an abstract is a brief summary of the report journal article or research. It usually outlines its purpose, methodology and findings ( results)
An introduction - h ere you say what you are going to be discussing in the report and why the report is important .
A literature review - this shows what you have read before completing your report.
Methodology - this explains what you did and how you did it
The results - here you present your findings
Discussion - i n this section you discuss your results.
Conclusions - here you say what the report has shown and what you think could be learnt from the report.
Recommendations - often a report will include your recommendations - what you think should be done next having considered the results.
The main differences between a report and an essay
Reports are divided into many sections whereas essays have three main sections divided into paragraphs.
Reports include an abstract, essays do not.
Reports can use bullet points, essays do not.
Reports can use subheadings for each of the sections, it is rare for essays to have subheadings.
Reports often include graphs and tables , essays do not.
Similarities between report writing and essay writing
Both use a formal style- this means that we don't use shortened words, we remember we are writing for an academic audience, we don't use slang, and we write in sentences, using a formal style.
Both avoid sounding personal - in academic writing it is important to sound objective . This means that you don't try to sway your reader with your own opinions and viewpoints but you put your points across using proof and evidence. With this in mind, in reports and essay writing personal pronouns (Example: I) should be avoided.
Both need to be clear- whatever you are writing it is important that you make your writing clear. In both reports and essays an introduction will be included to show the purpose of the piece of work, and a conclusion to sum up the key points. The main body of both texts should be written in a logical well ordered way.
- Last Updated: Apr 25, 2024 1:19 PM
- URL: https://libguides.gre.ac.uk/academicskills
Library policies | Library Code of Conduct | IT Service Status | Portal © University of Greenwich | FOI | Privacy and cookies | Legal | Terms & conditions

Choose Your Test
Sat / act prep online guides and tips, the 3 popular essay formats: which should you use.
General Education

Not sure which path your essay should follow? Formatting an essay may not be as interesting as choosing a topic to write about or carefully crafting elegant sentences, but it’s an extremely important part of creating a high-quality paper. In this article, we’ll explain essay formatting rules for three of the most popular essay styles: MLA, APA, and Chicago.
For each, we’ll do a high-level overview of what your essay’s structure and references should look like, then we include a comparison chart with nitty-gritty details for each style, such as which font you should use for each and whether they’re a proponent of the Oxford comma. We also include information on why essay formatting is important and what you should do if you’re not sure which style to use.
Why Is Your Essay Format Important?
Does it really matter which font size you use or exactly how you cite a source in your paper? It can! Style formats were developed as a way to standardize how pieces of writing and their works cited lists should look.
Why is this necessary? Imagine you’re a teacher, researcher, or publisher who reviews dozens of papers a week. If the papers didn’t follow the same formatting rules, you could waste a lot of time trying to figure out which sources were used, if certain information is a direct quote or paraphrased, even who the paper’s author is. Having essay formatting rules to follow makes things easier for everyone involved. Writers can follow a set of guidelines without trying to decide for themselves which formatting choices are best, and readers don’t need to go hunting for the information they’re trying to find.
Next, we’ll discuss the three most common style formats for essays.
MLA Essay Format
MLA style was designed by the Modern Language Association, and it has become the most popular college essay format for students writing papers for class. It was originally developed for students and researchers in the literature and language fields to have a standardized way of formatting their papers, but it is now used by people in all disciplines, particularly humanities. MLA is often the style teachers prefer their students to use because it has simple, clear rules to follow without extraneous inclusions often not needed for school papers. For example, unlike APA or Chicago styles, MLA doesn’t require a title page for a paper, only a header in the upper left-hand corner of the page.
MLA style doesn’t have any specific requirements for how to write your essay, but an MLA format essay will typically follow the standard essay format of an introduction (ending with a thesis statement), several body paragraphs, and a conclusion.
One of the nice things about creating your works cited for MLA is that all references are structured the same way, regardless of whether they’re a book, newspaper, etc. It’s the only essay format style that makes citing references this easy! Here is a guide on how to cite any source in MLA format. When typing up your works cited, here are a few MLA format essay rules to keep in mind:
- The works cited page should be the last paper of your paper.
- This page should still be double-spaced and include the running header of your last name and page number.
- It should begin with “Works Cited” at the top of the page, centered.
- Your works cited should be organized in alphabetical order, based on the first word of the citation.
APA Essay Format
APA stands for the American Psychological Association. This format type is most often used for research papers, specifically those in behavioral sciences (such as psychology and neuroscience) and social sciences (ranging from archeology to economics). Because APA is often used for more research-focused papers, they have a more specific format to follow compared to, say, MLA style.
All APA style papers begin with a title page, which contains the title of the paper (in capital letters), your name, and your institutional affiliation (if you’re a student, then this is simply the name of the school you attend). The APA recommends the title of your paper not be longer than 12 words.
After your title page, your paper begins with an abstract. The abstract is a single paragraph, typically between 150 to 250 words, that sums up your research. It should include the topic you’re researching, research questions, methods, results, analysis, and a conclusion that touches on the significance of the research. Many people find it easier to write the abstract last, after completing the paper.
After the abstract comes the paper itself. APA essay format recommends papers be short, direct, and make their point clearly and concisely. This isn’t the time to use flowery language or extraneous descriptions. Your paper should include all the sections mentioned in the abstract, each expanded upon.
Following the paper is the list of references used. Unlike MLA style, in APA essay format, every source type is referenced differently. So the rules for referencing a book are different from those for referencing a journal article are different from those referencing an interview. Here’s a guide for how to reference different source types in APA format . Your references should begin on a new page that says “REFERENCES” at the top, centered. The references should be listed in alphabetical order.

Chicago Essay Format
Chicago style (sometimes referred to as “Turabian style”) was developed by the University of Chicago Press and is typically the least-used by students of the three major essay style formats. The Chicago Manual of Style (currently on its 17th edition) contains within its 1000+ pages every rule you need to know for this style. This is a very comprehensive style, with a rule for everything. It’s most often used in history-related fields, although many people refer to The Chicago Manual of Style for help with a tricky citation or essay format question. Many book authors use this style as well.
Like APA, Chicago style begins with a title page, and it has very specific format rules for doing this which are laid out in the chart below. After the title page may come an abstract, depending on whether you’re writing a research paper or not. Then comes the essay itself. The essay can either follow the introduction → body → conclusion format of MLA or the different sections included in the APA section. Again, this depends on whether you’re writing a paper on research you conducted or not.
Unlike MLA or APA, Chicago style typically uses footnotes or endnotes instead of in-text or parenthetical citations. You’ll place the superscript number at the end of the sentence (for a footnote) or end of the page (for an endnote), then have an abbreviated source reference at the bottom of the page. The sources will then be fully referenced at the end of the paper, in the order of their footnote/endnote numbers. The reference page should be titled “Bibliography” if you used footnotes/endnotes or “References” if you used parenthetical author/date in-text citations.
Comparison Chart
Below is a chart comparing different formatting rules for APA, Chicago, and MLA styles.
| or ). | |||
| including the title page. | |||
How Should You Format Your Essay If Your Teacher Hasn’t Specified a Format?
What if your teacher hasn’t specified which essay format they want you to use? The easiest way to solve this problem is simply to ask your teacher which essay format they prefer. However, if you can’t get ahold of them or they don’t have a preference, we recommend following MLA format. It’s the most commonly-used essay style for students writing papers that aren’t based on their own research, and its formatting rules are general enough that a teacher of any subject shouldn’t have a problem with an MLA format essay. The fact that this style has one of the simplest sets of rules for citing sources is an added bonus!

What's Next?
Thinking about taking an AP English class? Read our guide on AP English classes to learn whether you should take AP English Language or AP English Literature (or both!)
Compound sentences are an importance sentence type to know. Read our guide on compound sentences for everything you need to know about compound, complex, and compound-complex sentences.
Need ideas for a research paper topic? Our guide to research paper topics has over 100 topics in ten categories so you can be sure to find the perfect topic for you.

Christine graduated from Michigan State University with degrees in Environmental Biology and Geography and received her Master's from Duke University. In high school she scored in the 99th percentile on the SAT and was named a National Merit Finalist. She has taught English and biology in several countries.
Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!
Improve With Our Famous Guides
- For All Students
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 160+ SAT Points
How to Get a Perfect 1600, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 800 on Each SAT Section:
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading
Score 800 on SAT Writing
Series: How to Get to 600 on Each SAT Section:
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading
Score 600 on SAT Writing
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
What SAT Target Score Should You Be Aiming For?
15 Strategies to Improve Your SAT Essay
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 4+ ACT Points
How to Get a Perfect 36 ACT, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 36 on Each ACT Section:
36 on ACT English
36 on ACT Math
36 on ACT Reading
36 on ACT Science
Series: How to Get to 24 on Each ACT Section:
24 on ACT English
24 on ACT Math
24 on ACT Reading
24 on ACT Science
What ACT target score should you be aiming for?
ACT Vocabulary You Must Know
ACT Writing: 15 Tips to Raise Your Essay Score
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
Is the ACT easier than the SAT? A Comprehensive Guide
Should you retake your SAT or ACT?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!
Looking for Graduate School Test Prep?
Check out our top-rated graduate blogs here:
GRE Online Prep Blog
GMAT Online Prep Blog
TOEFL Online Prep Blog
Holly R. "I am absolutely overjoyed and cannot thank you enough for helping me!”
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Research paper
- Research Paper Format | APA, MLA, & Chicago Templates
Research Paper Format | APA, MLA, & Chicago Templates
Published on November 19, 2022 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on January 20, 2023.
The formatting of a research paper is different depending on which style guide you’re following. In addition to citations , APA, MLA, and Chicago provide format guidelines for things like font choices, page layout, format of headings and the format of the reference page.
Scribbr offers free Microsoft Word templates for the most common formats. Simply download and get started on your paper.
APA | MLA | Chicago author-date | Chicago notes & bibliography
- Generate an automatic table of contents
- Generate a list of tables and figures
- Ensure consistent paragraph formatting
- Insert page numbering
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Formatting an apa paper, formatting an mla paper, formatting a chicago paper, frequently asked questions about research paper formatting.
The main guidelines for formatting a paper in APA Style are as follows:
- Use a standard font like 12 pt Times New Roman or 11 pt Arial.
- Set 1 inch page margins.
- Apply double line spacing.
- If submitting for publication, insert a APA running head on every page.
- Indent every new paragraph ½ inch.
Watch the video below for a quick guide to setting up the format in Google Docs.
The image below shows how to format an APA Style title page for a student paper.
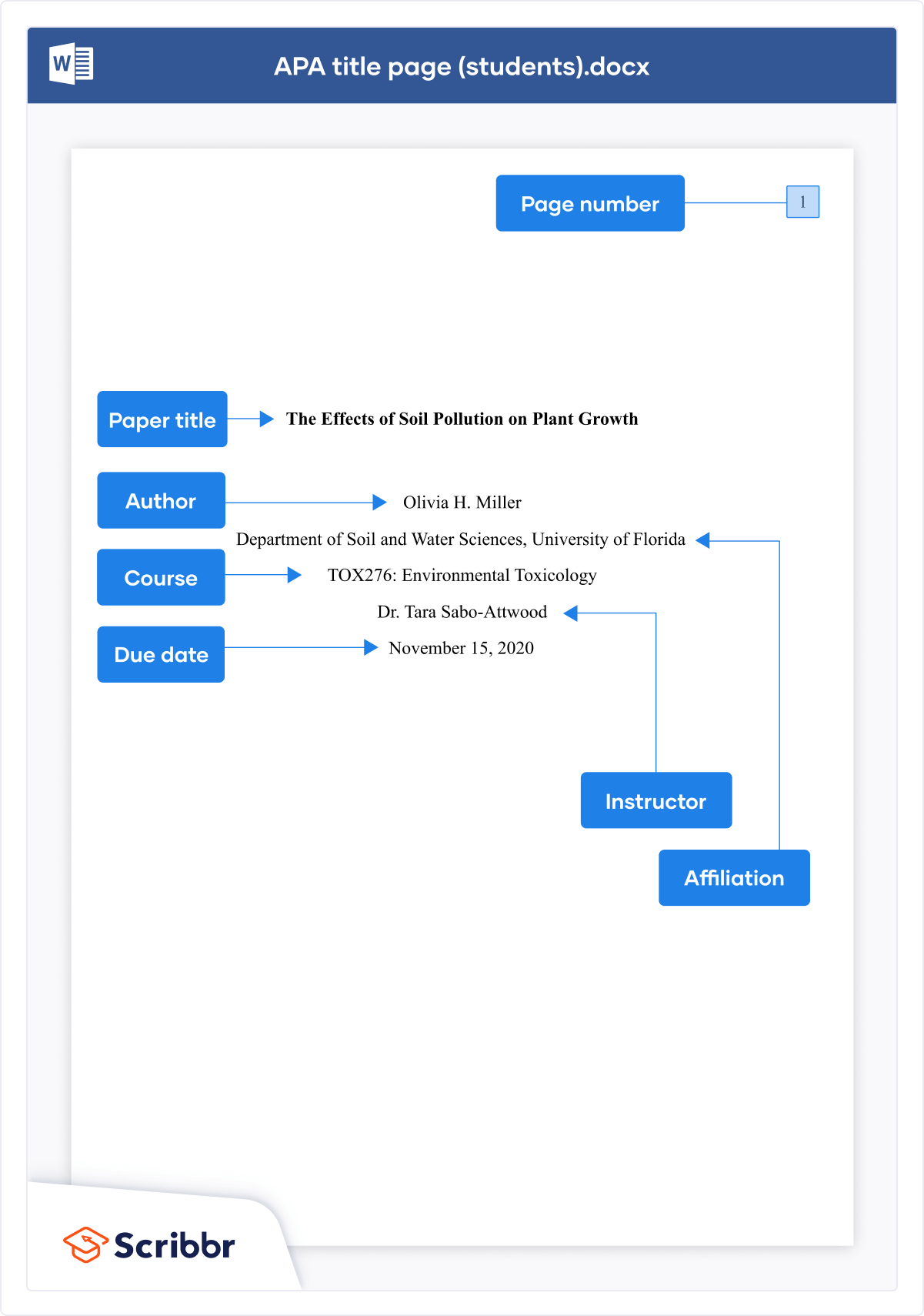
Running head
If you are submitting a paper for publication, APA requires you to include a running head on each page. The image below shows you how this should be formatted.
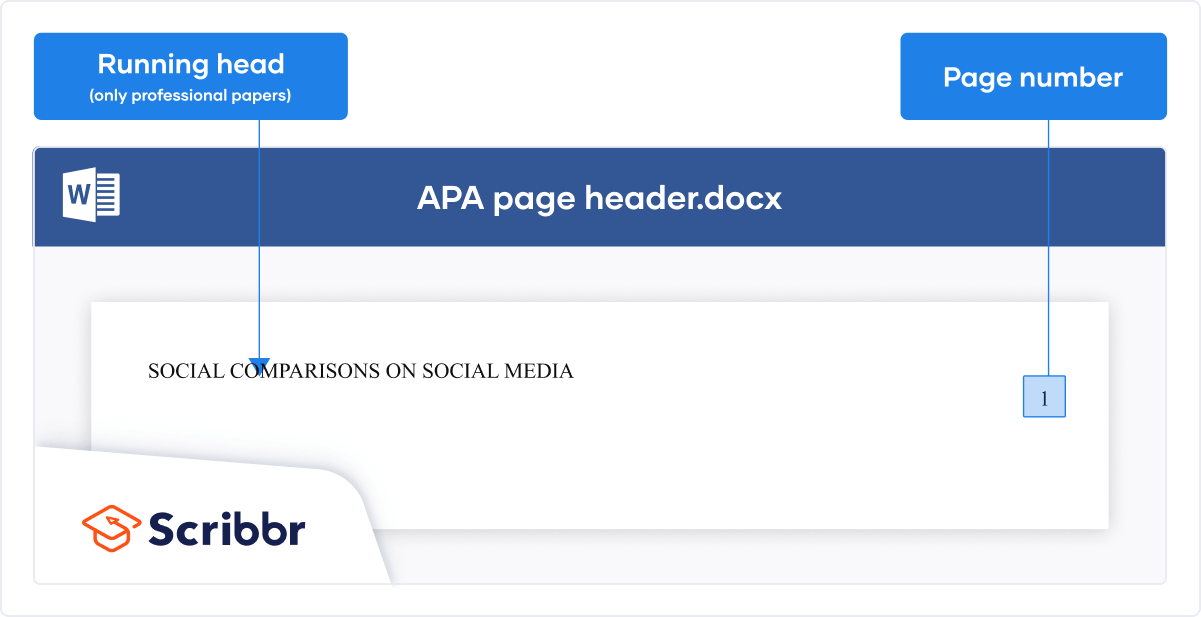
For student papers, no running head is required unless you have been instructed to include one.
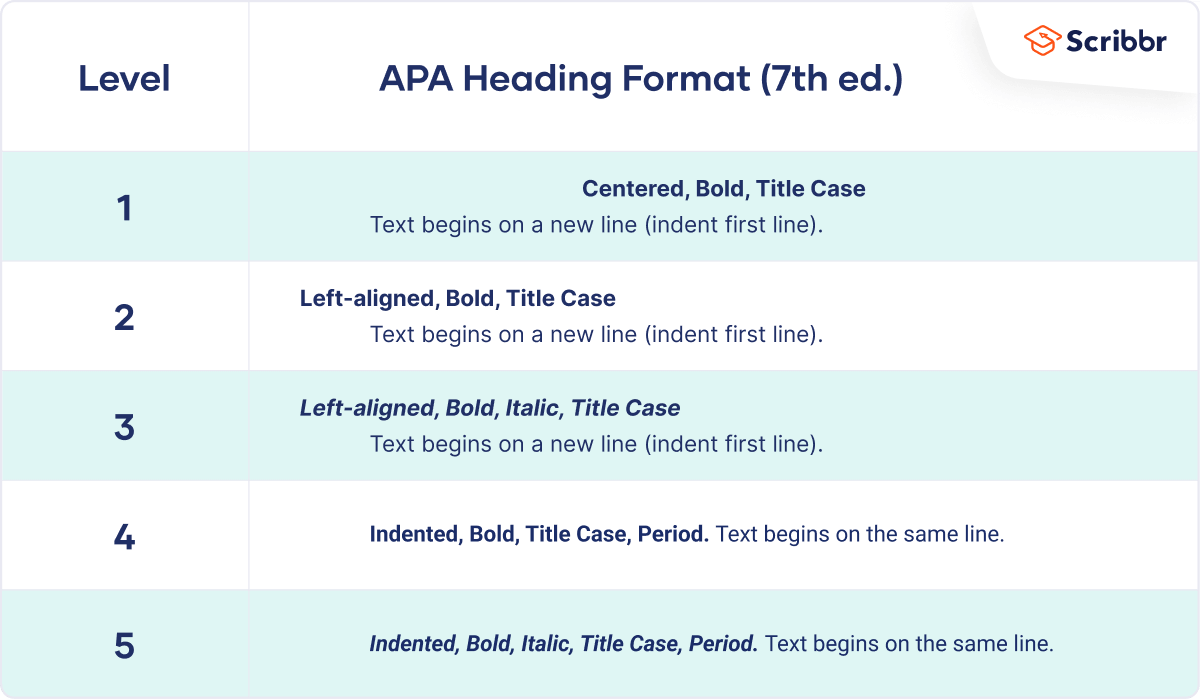
APA provides guidelines for formatting up to five levels of heading within your paper. Level 1 headings are the most general, level 5 the most specific.
Reference page
APA Style citation requires (author-date) APA in-text citations throughout the text and an APA Style reference page at the end. The image below shows how the reference page should be formatted.
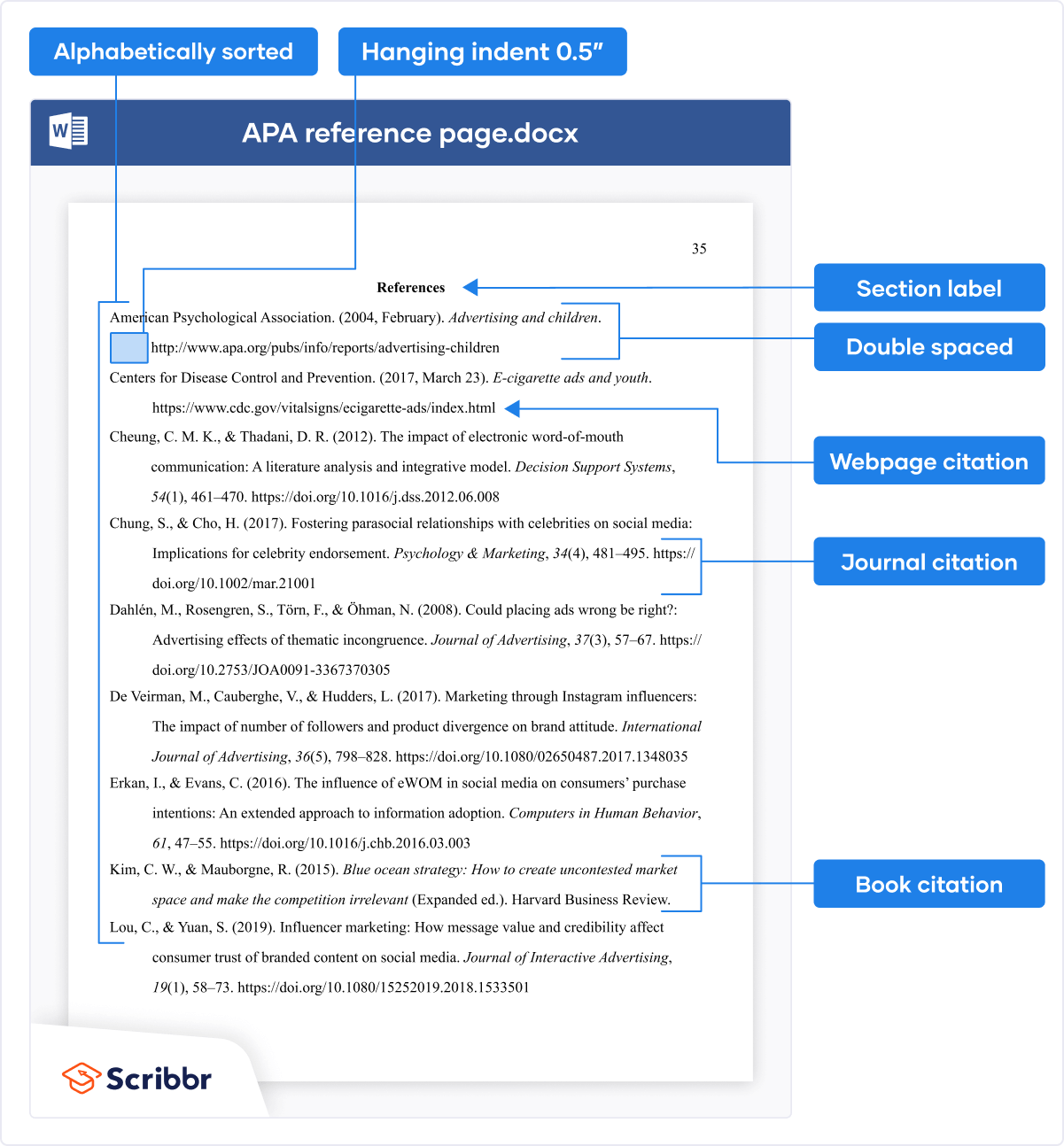
Note that the format of reference entries is different depending on the source type. You can easily create your citations and reference list using the free APA Citation Generator.
Generate APA citations for free
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

The main guidelines for writing an MLA style paper are as follows:
- Use an easily readable font like 12 pt Times New Roman.
- Use title case capitalization for headings .
Check out the video below to see how to set up the format in Google Docs.
On the first page of an MLA paper, a heading appears above your title, featuring some key information:
- Your full name
- Your instructor’s or supervisor’s name
- The course name or number
- The due date of the assignment
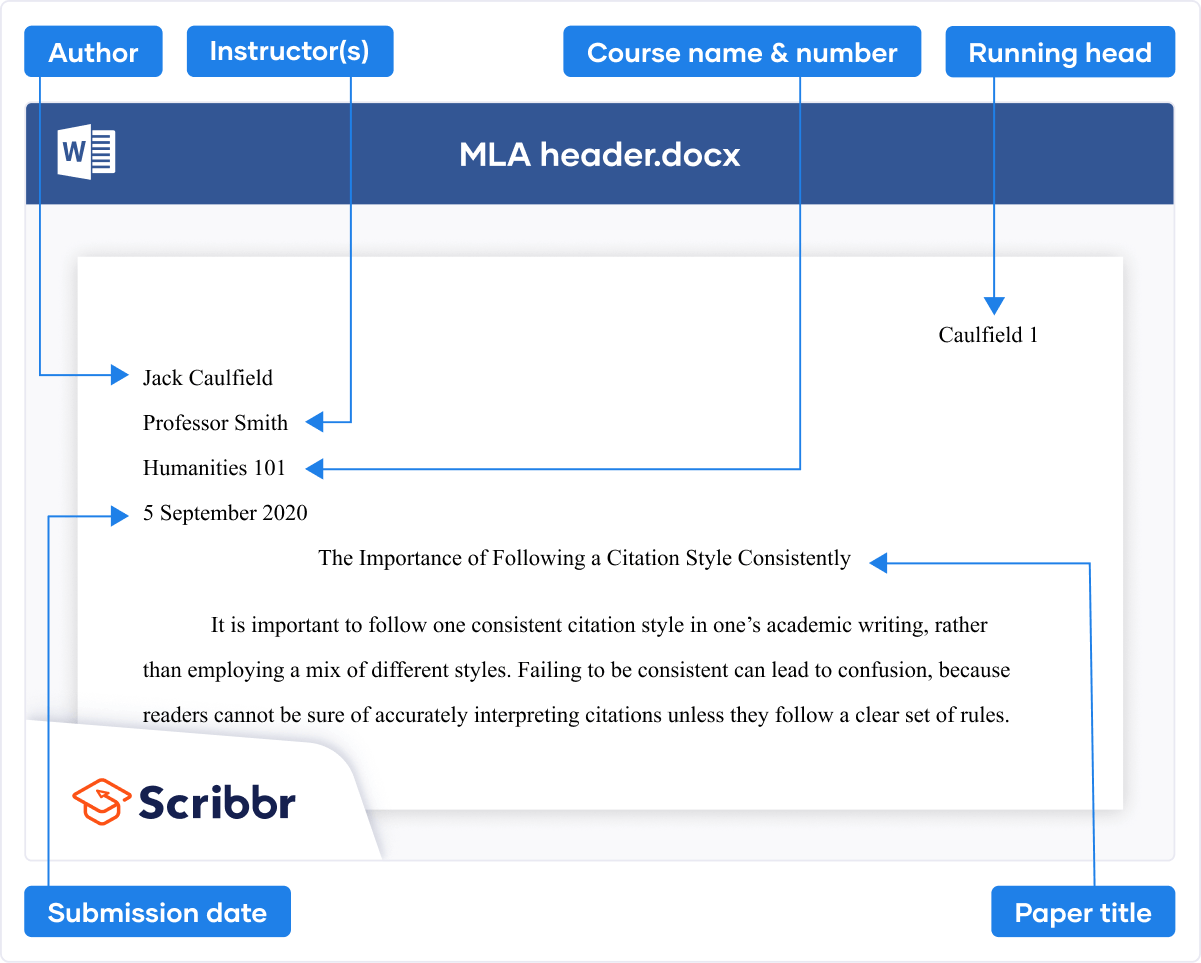
Page header
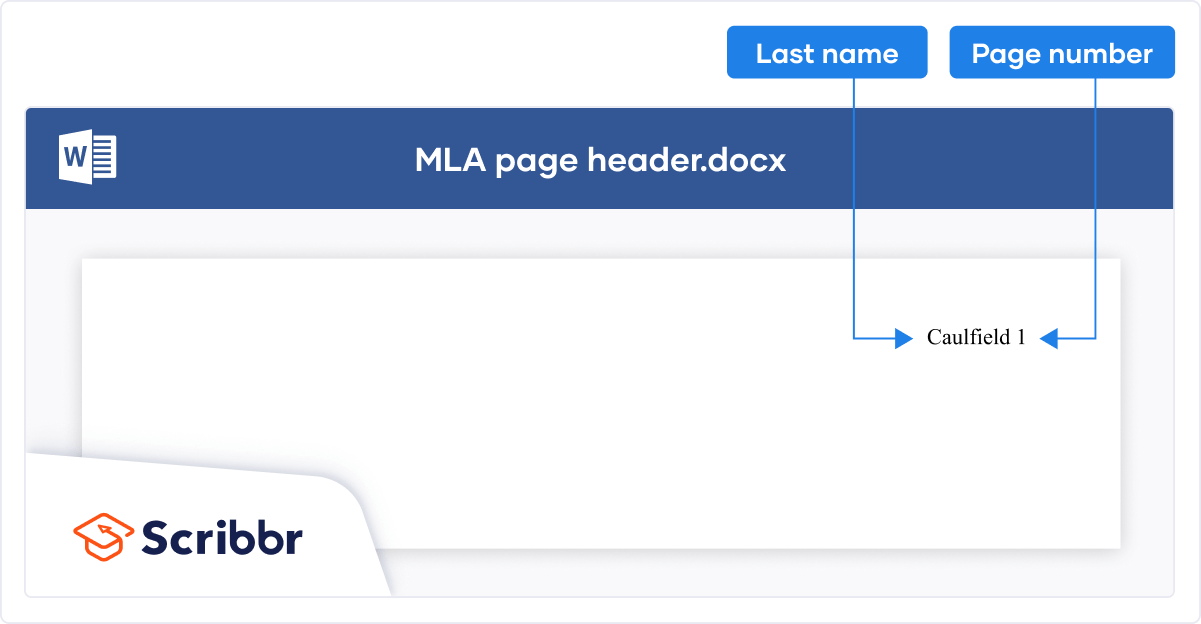
A header appears at the top of each page in your paper, including your surname and the page number.
Works Cited page
MLA in-text citations appear wherever you refer to a source in your text. The MLA Works Cited page appears at the end of your text, listing all the sources used. It is formatted as shown below.
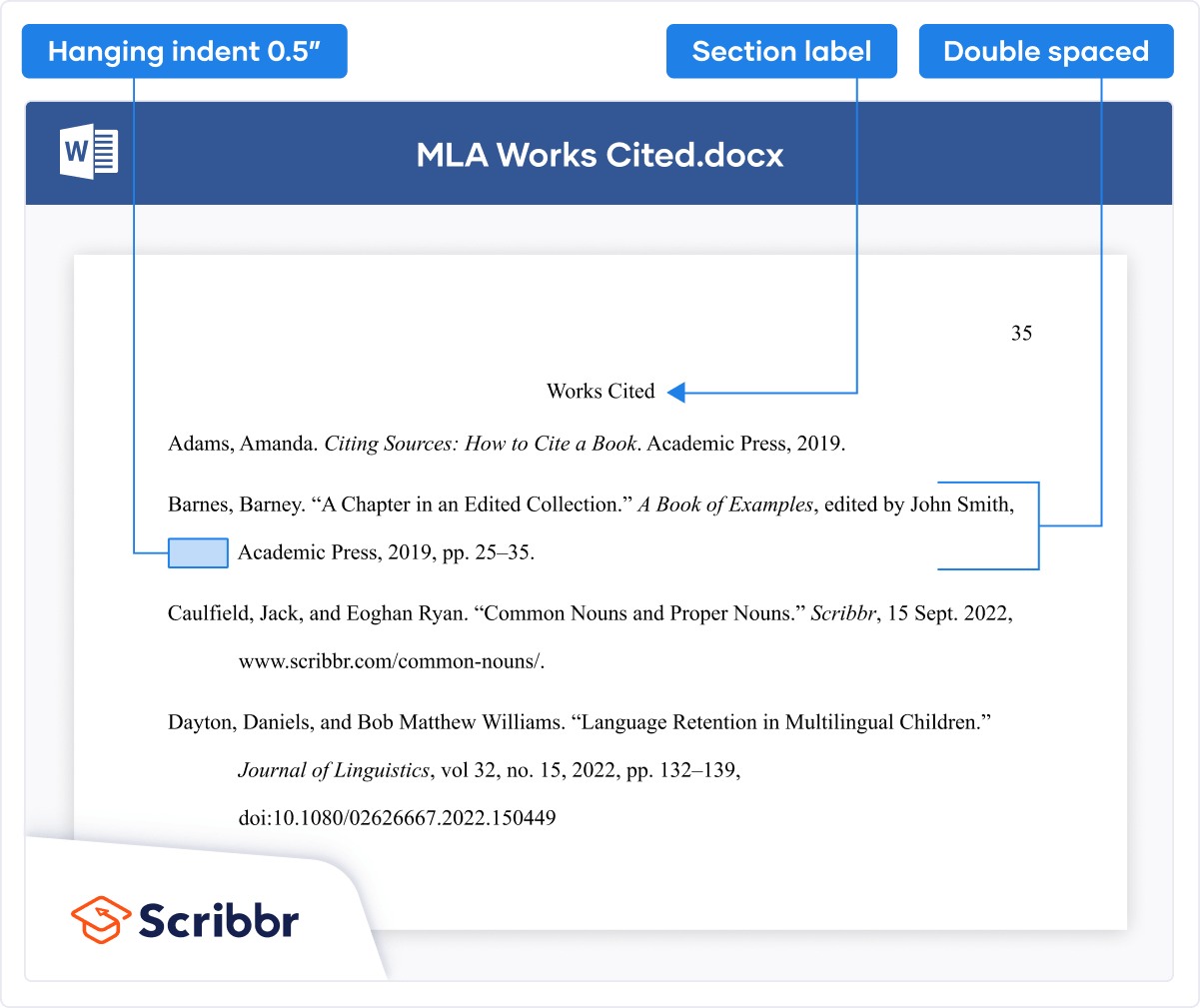
You can easily create your MLA citations and save your Works Cited list with the free MLA Citation Generator.
Generate MLA citations for free
The main guidelines for writing a paper in Chicago style (also known as Turabian style) are:
- Use a standard font like 12 pt Times New Roman.
- Use 1 inch margins or larger.
- Place page numbers in the top right or bottom center.
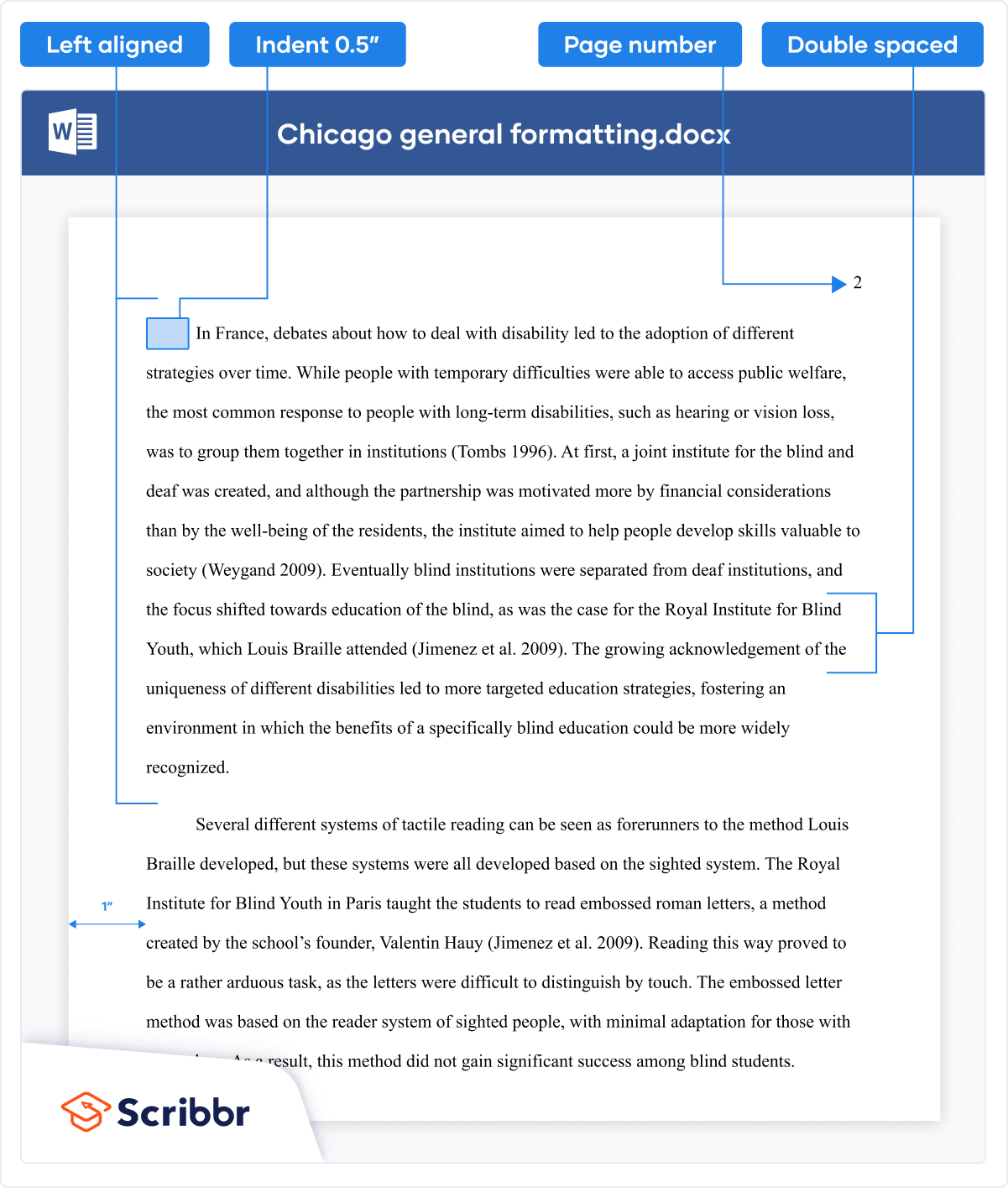
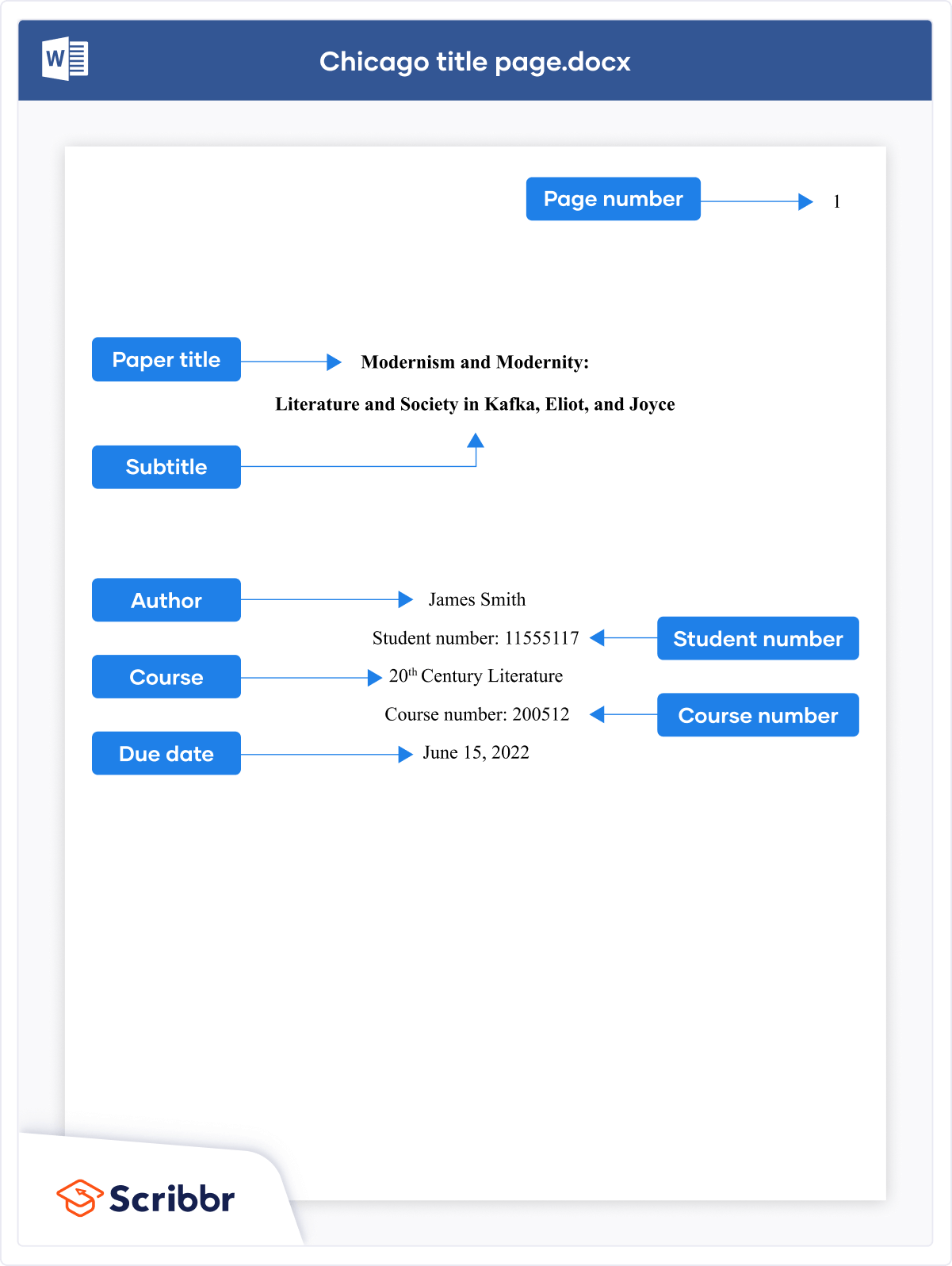
Chicago doesn’t require a title page , but if you want to include one, Turabian (based on Chicago) presents some guidelines. Lay out the title page as shown below.
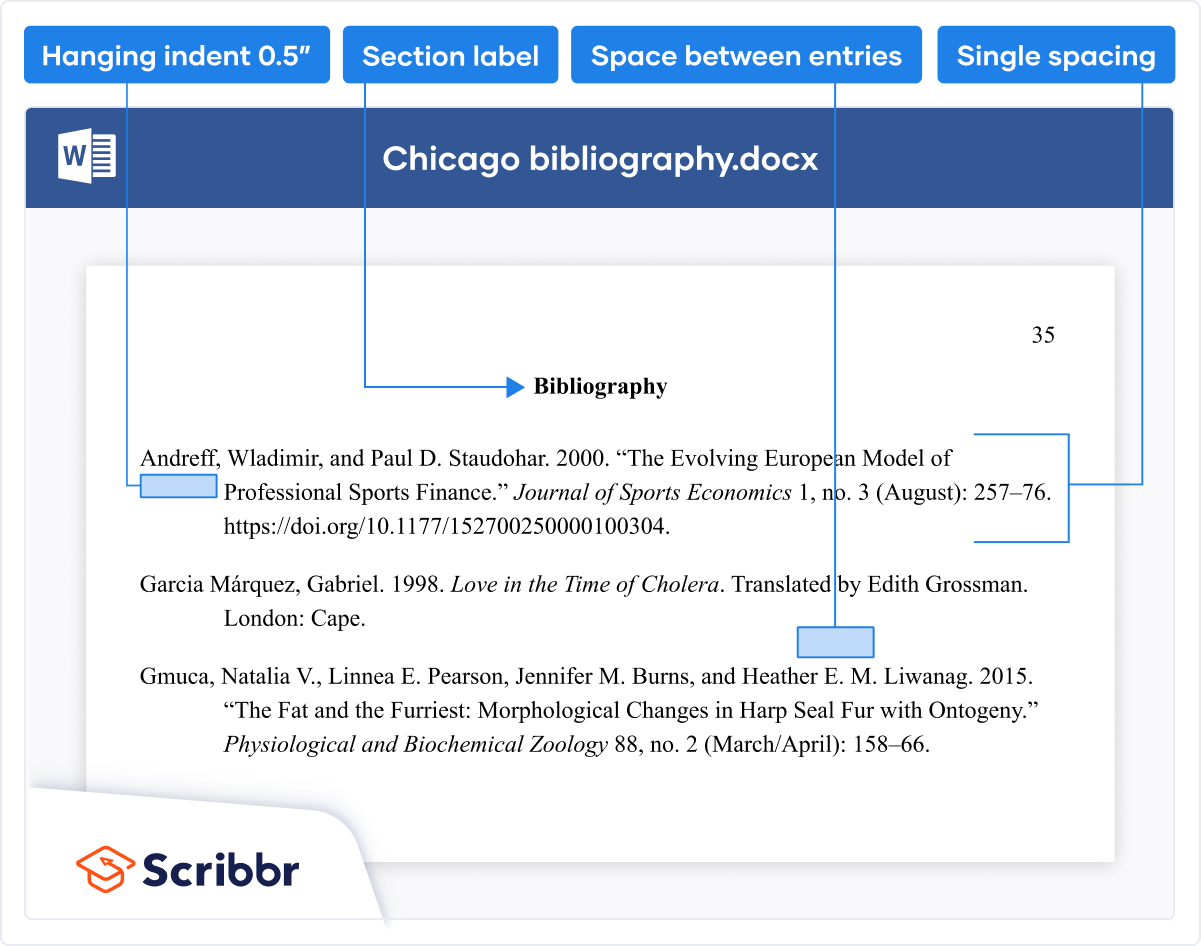
Bibliography or reference list
Chicago offers two citation styles : author-date citations plus a reference list, or footnote citations plus a bibliography. Choose one style or the other and use it consistently.
The reference list or bibliography appears at the end of the paper. Both styles present this page similarly in terms of formatting, as shown below.
To format a paper in APA Style , follow these guidelines:
- Use a standard font like 12 pt Times New Roman or 11 pt Arial
- Set 1 inch page margins
- Apply double line spacing
- Include a title page
- If submitting for publication, insert a running head on every page
- Indent every new paragraph ½ inch
- Apply APA heading styles
- Cite your sources with APA in-text citations
- List all sources cited on a reference page at the end
The main guidelines for formatting a paper in MLA style are as follows:
- Use an easily readable font like 12 pt Times New Roman
- Include a four-line MLA heading on the first page
- Center the paper’s title
- Use title case capitalization for headings
- Cite your sources with MLA in-text citations
- List all sources cited on a Works Cited page at the end
The main guidelines for formatting a paper in Chicago style are to:
- Use a standard font like 12 pt Times New Roman
- Use 1 inch margins or larger
- Place page numbers in the top right or bottom center
- Cite your sources with author-date citations or Chicago footnotes
- Include a bibliography or reference list
To automatically generate accurate Chicago references, you can use Scribbr’s free Chicago reference generator .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2023, January 20). Research Paper Format | APA, MLA, & Chicago Templates. Scribbr. Retrieved June 11, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/research-paper/research-paper-format/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, apa format for academic papers and essays, mla format for academic papers and essays, chicago style format for papers | requirements & examples, what is your plagiarism score.
Trying to devise a structure for your essay can be one of the most difficult parts of the writing process. Making a detailed outline before you begin writing is a good way to make sure your ideas come across in a clear and logical order. A good outline will also save you time in the revision process, reducing the possibility that your ideas will need to be rearranged once you've written them.
The First Steps
Before you can begin outlining, you need to have a sense of what you will argue in the essay. From your analysis and close readings of primary and/or secondary sources you should have notes, ideas, and possible quotes to cite as evidence. Let's say you are writing about the 1999 Republican Primary and you want to prove that each candidate's financial resources were the most important element in the race. At this point, your notes probably lack much coherent order. Most likely, your ideas are still in the order in which they occurred to you; your notes and possible quotes probably still adhere to the chronology of the sources you've examined. Your goal is to rearrange your ideas, notes, and quotes—the raw material of your essay—into an order that best supports your argument, not the arguments you've read in other people's works. To do this, you have to group your notes into categories and then arrange these categories in a logical order.
Generalizing
The first step is to look over each individual piece of information that you've written and assign it to a general category. Ask yourself, "If I were to file this in a database, what would I file it under?" If, using the example of the Republican Primary, you wrote down an observation about John McCain's views on health care, you might list it under the general category of "Health care policy." As you go through your notes, try to reuse categories whenever possible. Your goal is to reduce your notes to no more than a page of category listings.
Now examine your category headings. Do any seem repetitive? Do any go together? "McCain's expenditure on ads" and "Bush's expenditure on ads," while not exactly repetitive, could easily combine into a more general category like "Candidates' expenditures on ads." Also, keep an eye out for categories that no longer seem to relate to your argument. Individual pieces of information that at first seemed important can begin to appear irrelevant when grouped into a general category.
Now it's time to generalize again. Examine all your categories and look for common themes. Go through each category and ask yourself, "If I were to place this piece of information in a file cabinet, what would I label that cabinet?" Again, try to reuse labels as often as possible: "Health Care," "Foreign Policy," and "Immigration" can all be contained under "Policy Initiatives." Make these larger categories as general as possible so that there are no more than three or four for a 7-10 page paper.
With your notes grouped into generalized categories, the process of ordering them should be easier. To begin, look at your most general categories. With your thesis in mind, try to find a way that the labels might be arranged in a sentence or two that supports your argument. Let's say your thesis is that financial resources played the most important role in the 1999 Republican Primary. Your four most general categories are "Policy Initiatives," "Financial Resources," "Voters' Concerns," and "Voters' Loyalty." You might come up with the following sentence: ÒAlthough McCain's policy initiatives were closest to the voters' concerns, Bush's financial resources won the voters' loyalty.Ó This sentence should reveal the order of your most general categories. You will begin with an examination of McCain's and Bush's views on important issues and compare them to the voters' top concerns. Then you'll look at both candidates' financial resources and show how Bush could win voters' loyalty through effective use of his resources, despite his less popular policy ideas.
With your most general categories in order, you now must order the smaller categories. To do so, arrange each smaller category into a sentence or two that will support the more general sentence you've just devised. Under the category of "Financial Resources," for instance, you might have the smaller categories of "Ad Expenditure," "Campaign Contributions" and "Fundraising." A sentence that supports your general argument might read: "Bush's early emphasis on fundraising led to greater campaign contributions, allowing him to have a greater ad expenditure than McCain."
The final step of the outlining process is to repeat this procedure on the smallest level, with the original notes that you took for your essay. To order what probably was an unwieldy and disorganized set of information at the beginning of this process, you need now only think of a sentence or two to support your general argument. Under the category "Fundraising," for example, you might have quotes about each candidate's estimation of its importance, statistics about the amount of time each candidate spent fundraising, and an idea about how the importance of fundraising never can be overestimated. Sentences to support your general argument might read: "No candidate has ever raised too much money [your idea]. While both McCain and Bush acknowledged the importance of fundraising [your quotes], the numbers clearly point to Bush as the superior fundraiser [your statistics]." The arrangement of your ideas, quotes, and statistics now should come naturally.
Putting It All Together
With these sentences, you have essentially constructed an outline for your essay. The most general ideas, which you organized in your first sentence, constitute the essay's sections. They follow the order in which you placed them in your sentence. The order of the smaller categories within each larger category (determined by your secondary sentences) indicates the order of the paragraphs within each section. Finally, your last set of sentences about your specific notes should show the order of the sentences within each paragraph. An outline for the essay about the 1999 Republican Primary (showing only the sections worked out here) would look something like this:
I. POLICY INITIATIVES
II. VOTERS' CONCERNS
III. FINANCIAL RESOURCES
A. Fundraising
a. Original Idea
b. McCain Quote/Bush Quote
c. McCain Statistics/Bush Statistics
B. Campaign Contributions
C. Ad Expenditure
IV. VOTERS' LOYALTY
Copyright 2000, David Kornhaber, for the Writing Center at Harvard University

Paper Format
Consistency in the order, structure, and format of a paper allows readers to focus on a paper’s content rather than its presentation.
To format a paper in APA Style, writers can typically use the default settings and automatic formatting tools of their word-processing program or make only minor adjustments.
The guidelines for paper format apply to both student assignments and manuscripts being submitted for publication to a journal. If you are using APA Style to create another kind of work (e.g., a website, conference poster, or PowerPoint presentation), you may need to format your work differently in order to optimize its presentation, for example, by using different line spacing and font sizes. Follow the guidelines of your institution or publisher to adapt APA Style formatting guidelines as needed.

Academic Writer ®
Master academic writing with APA’s essential teaching and learning resource

Course Adoption
Teaching APA Style? Become a course adopter of the 7th edition Publication Manual

Instructional Aids
Guides, checklists, webinars, tutorials, and sample papers for anyone looking to improve their knowledge of APA Style

Learn the Standard Essay Format: MLA, APA, Chicago Styles

Being able to write an essay is a vital part of any student's education. However, it's not just about linearly listing ideas. A lot of institutions will require a certain format that your paper must follow; prime examples would be one of a basic essay format like MLA, the APA, and the Chicago formats. This article will explain the differences between the MLA format, the APA format, and the Chicago format. The application of these could range from high school to college essays, and they stand as the standard of college essay formatting. EssayPro — dissertation services , that will help to make a difference!
What is an Essay Format: Structure
Be it an academic, informative or a specific extended essay - structure is essential. For example, the IB extended essay has very strict requirements that are followed by an assigned academic style of writing (primarily MLA, APA, or Chicago):
| Title Page | Paragraph 1 must include a research question, thesis, and outline of the essay’s importance. |
|---|---|
| Abstract | Comprised of 3 paragraphs, totaling about 300 words, with 100 words in each. Paragraph 2 covers key resources, scope and limits of research, etc. Paragraph 3 concludes what you’ve already reached in your essay. |
| Table of Contents (with page numbers) | Includes sections like Research question, Thesis, Introduction, Arguments, Sub-headings, Conclusion, Appendix, Works cited (bibliography). |
| Introduction | The research question is required. |
| Body | |
| Conclusion | |
| Bibliography/Works Cited |
This outline format for an extended essay is a great example to follow when writing a research essay, and sustaining a proper research essay format - especially if it is based on the MLA guidelines. It is vital to remember that the student must keep track of their resources to apply them to each step outlined above easily. And check out some tips on how to write an essay introduction .
Lost in the Labyrinth of Essay Formatting?
Navigate the complexities of essay structures with ease. Let our experts guide your paper to the format it deserves!
How to Format an Essay (MLA)

To write an essay in MLA format, one must follow a basic set of guidelines and instructions. This is a step by step from our business essay writing service.
| Font | 12pt Times New Roman |
|---|---|
| Spacing | Double spaced everywhere No extra spaces, especially between paragraphs |
| Heading | Example of the heading on the first page of the essay (upper left corner): |
| Margins | One-inch margin on the top, bottom, left and right |
| Page Numbers | Last name and page number must be put on every page of the essay as a “header”. Otherwise, it would go in place of the text. |
| Title | There needs to be a proper essay title format, centered and above the first line of the essay of the same font and size as the essay itself |
| Indentation | Just press tab (1/2 inch, just in case) |
| Align | Align to the left-hand side, and make sure it is aligned evenly |
Essay in MLA Format Example
Mla vs. apa.
Before we move on to the APA essay format, it is important to distinguish the two types of formatting. Let’s go through the similarities first:
- The formatting styles are similar: spacing, citation, indentation.
- All of the information that is used within the essay must be present within the works cited page (in APA, that’s called a reference page)
- Both use the parenthetical citations within the body of the paper, usually to show a certain quote or calculation.
- Citations are listed alphabetically on the works cited / reference page.
What you need to know about the differences is not extensive, thankfully:
- MLA style is mostly used in humanities, while APA style is focused more on social sciences. The list of sources has a different name (works cited - MLA / references - APA)
- Works cited differ on the way they display the name of the original content (MLA -> Yorke, Thom / APA -> Yorke T.)
- When using an in-text citation, and the author’s name is listed within the sentence, place the page number found at the end: “Yorke believes that Creep was Radiohead’s worst song. (4).” APA, on the other hand, requires that a year is to be inserted: “According to Yorke (2013), Creep was a mess.”
Alright, let’s carry over to the APA style specifics.
Order an Essay Now & and We Will Cite and Format It For Free :
How to format an essay (apa).
The APA scheme is one of the most common college essay formats, so being familiar with its requirements is crucial. In a basic APA format structure, we can apply a similar list of guidelines as we did in the MLA section:
| Font | 12pt Times New Roman |
|---|---|
| Spacing | Double-space |
| Page Numbers | Add a concise title header to the top left of each page, keeping it under 50 characters. Also, include a page number in the top right corner. |
| Title Page | |
| Headings | Format all headings in bold and title case. Apply specific additional criteria for different heading levels as needed. |
If you ask yourself how to format an essay, you can always turn to us and request to write or rewrite essay in APA format if you find it difficult or don't have time.
Note that some teachers and professors may request deviations from some of the characteristics that the APA format originally requires, such as those listed above.

If you think: 'I want someone write a research paper for me ', you can do it at Essaypro.
Essay in APA Format Example
Apa format chronobiology, chicago style.
The usage of Chicago style is prevalent in academic writing that focuses on the source of origin. This means that precise citations and footnotes are key to a successful paper.
Chicago Style Essay Format
The same bullet point structure can be applied to the Chicago essay format.
| Title Page | Below the page, put the title in regular text. If it's longer than one line, double-space it. Center your full name in the middle. Double-space each line for the course number, instructor's name, and the date separately. |
|---|---|
| Margins | Use one-inch margins apart from the right side. |
| Spacing | Double spaced everywhere. No extra spaces, especially between paragraphs. |
| Font | Times New Roman (12pt) |
| Page Numbers | On each page, add your last name and page number in the top right corner. Don't number the title page. Begin numbering the text from the second page. |
| Footnotes | The Chicago format requires footnotes on paraphrased or quoted passages. |
| Bibliography | The bibliography is very similar to that of MLA. Gather the proper information and input it into a specialized citation site. |

Tips for Writing an Academic Paper
There isn’t one proper way of writing a paper, but there are solid guidelines to sustain a consistent workflow. Be it a college application essay, a research paper, informative essay, etc. There is a standard essay format that you should follow. For easier access, the following outline will be divided into steps:
Choose a Good Topic
A lot of students struggle with picking a good topic for their essays. The topic you choose should be specific enough so you can explore it in its entirety and hit your word limit if that’s a variable you worry about. With a good topic that should not be a problem. On the other hand, it should not be so broad that some resources would outweigh the information you could squeeze into one paper. Don’t be too specific, or you will find that there is a shortage of information, but don’t be too broad or you will feel overwhelmed. Don’t hesitate to ask your instructor for help with your essay writing.
Start Research as Soon as Possible
Before you even begin writing, make sure that you are acquainted with the information that you are working with. Find compelling arguments and counterpoints, trivia, facts, etc. The sky is the limit when it comes to gathering information.
Pick out Specific, Compelling Resources
When you feel acquainted with the subject, you should be able to have a basic conversation on the matter. Pick out resources that have been bookmarked, saved or are very informative and start extracting information. You will need all you can get to put into the citations at the end of your paper. Stash books, websites, articles and have them ready to cite. See if you can subtract or expand your scope of research.
Create an Outline
Always have a plan. This might be the most important phase of the process. If you have a strong essay outline and you have a particular goal in mind, it’ll be easy to refer to it when you might get stuck somewhere in the middle of the paper. And since you have direct links from the research you’ve done beforehand, the progress is guaranteed to be swift. Having a list of keywords, if applicable, will surely boost the informational scope. With keywords specific to the subject matter of each section, it should be much easier to identify its direction and possible informational criteria.
Write a Draft
Before you jot anything down into the body of your essay, make sure that the outline has enough information to back up whatever statement you choose to explore. Do not be afraid of letting creativity into your paper (within reason, of course) and explore the possibilities. Start with a standard 5 paragraph structure, and the content will come with time.
Ask for a Peer Review of Your Academic Paper
Before you know it, the draft is done, and it’s ready to be sent out for peer review. Ask a classmate, a relative or even a specialist if they are willing to contribute. Get as much feedback as you possibly can and work on it.
Final Draft
Before handing in the final draft, go over it at least one more time, focusing on smaller mistakes like grammar and punctuation. Make sure that what you wrote follows proper essay structure. Learn more about argumentative essay structure on our blog. If you need a second pair of eyes, get help from our service.
Want Your Essay to Stand Out in Structure and Style?
Don't let poor formatting overshadow your ideas. Find your essay on sale and ensure your paper gets the professional polish it deserves!
What Is Essay Format?
How to format a college essay, how to write an essay in mla format.

is an expert in nursing and healthcare, with a strong background in history, law, and literature. Holding advanced degrees in nursing and public health, his analytical approach and comprehensive knowledge help students navigate complex topics. On EssayPro blog, Adam provides insightful articles on everything from historical analysis to the intricacies of healthcare policies. In his downtime, he enjoys historical documentaries and volunteering at local clinics.

Related Articles
.webp)
Skip to Content
Massey University
- Search OWLL
- Handouts (Printable)
- Pre-reading Service
- StudyUp Recordings
- StudyUp Postgraduate
- Academic writing
- Intro to academic writing
- What is academic writing?
- Writing objectively
- Writing concisely
- 1st vs. 3rd person
- Inclusive language
- Te Reo Māori
- Assignment planning
- Assignment planning calculator
- Interpreting the assignment question
- Command words
- Organising points
- Researching
- Identifying academic sources
- Evaluating source quality
- Editing & proofreading
- Apostrophes
- Other punctuation
- Active voice
- American vs. British spelling
- Conditionals
- Prepositions
- Pronoun Reference
- Sentence fragments
- Sentence Structure
- Subject-verb agreement
Formatting and layout
- Word limits and assignment length
- Commonly confused words
- How assignments are marked
- Marking guides
- Getting an A
- Levels of assessment
- Using feedback
- Professional emails
- Forum posts
- Forum netiquette guidelines
- Sharing personal information
- Writing about personal experiences
- Assignment types
- What is an essay?
- Essay planning and structure
- Introduction
- Thesis statement
- Body paragraphs
- Essay revision
- Essay writing resources
- What is a report?
- Report structure
- Analysing issues for a report
- Business report
- What is a business report?
- Business report structure
- Inductive vs. deductive reports
- Other kinds of business communication
- Business report format and layout
- What is a lab report?
- Lab report structure
- Science lab report writing resources
- Psychology lab report writing resources
- Lab report body paragraphs
- Literature review
- What is a literature review?
- Writing a literature review
- Literature review structure
- Literature review writing resources
- Research proposal
- Writing a research proposal
- Research proposal structure
- Other types
- Article critique
- Book review
- Annotated bibliography
- Reflective writing
- Oral presentation
- Thesis / dissertation
- Article / conference paper
- Shorter responses
- PhD confirmation report
- Computer skills
- Microsoft Word
- Basic formatting
- Images, tables, & figures
- Long documents
- Microsoft Excel
- Basic spreadsheets
- Navigating & printing spreadsheets
- Charts / graphs & formulas
- Microsoft PowerPoint
- Basic skills
- Advanced skills
- Distance study
- Getting started
- How to study
- Online study techniques
- Distance support
- Reading & writing
- Reading strategies
- Writing strategies
- Grammar resources
- Listening & speaking
- Listening strategies
- Speaking strategies
- Maths & statistics
- Trigonometry
- Finance formulas
- Postgraduate study
- Intro to postgrad study
- Planning postgrad study
- Postgrad resources
- Postgrad assignment types
- Referencing
- Intro to referencing
- What is referencing?
- Why reference?
- Common knowledge
- Referencing styles
- What type of source is this?
- Reference list vs. bibliography
- Referencing software
- Quoting & paraphrasing
- Paraphrasing & summarising
- Paraphrasing techniques
- APA Interactive
- In-text citation
- Reference list
- Online material
- Other material
- Headings in APA
- Tables and Figures
- Referencing elements
- 5th vs. 6th edition
- 6th vs. 7th edition
- Chicago style
- Chicago Interactive
- About notes system
- Notes referencing elements
- Quoting and paraphrasing
- Author-date system
- MLA Interactive
- Abbreviations
- List of works cited
- Captions for images
- 8th vs 9th edition
- Oxford style
- Other styles
- Harvard style
- Vancouver style
- Legal citations
- Visual material
- Sample assignments
- Sample essay 1
- Sample essay 2
- Sample annotated bibliography
- Sample book review
- Study skills
- Time management
- Intro to time management
- Procrastination & perfectionism
- Goals & motivation
- Time management for internal students
- Time management for distance students
- Memory skills
- Principles of good memory
- Memory strategies
- Note-taking
- Note-taking methods
- Note-taking in lectures
- Note-taking while reading
- Digital note-taking
- Reading styles
- In-depth reading
- Reading comprehension
- Reading academic material
- Reading a journal article
- Reading an academic book
- Critical thinking
- What is critical thinking?
- Constructing an argument
- Critical reading
- Logical fallacies
- Tests & exams
- Exam & test study
- Planning exam study
- Gathering & sorting information
- Reviewing past exams
- Phases of revision
- Last-minute study strategies
- Question types
- Short answer
- Multi-choice
- Problem / computational
- Case-study / scenario
- Open book exam
- Open web exam or test
- Take home test
- In the exam
- Online exam
- Physical exam
Assignments vary in their requirements for formatting and layout. Check for formatting requirements in your course materials or with your course coordinator. Aim for consistency in your formatting. Most assignments are now submitted electronically and formatted as follows:
- Use a clearly legible font and font size (Times New Roman is the most common font and 12 point is the most common size).
- Set page margins to around 1 inch/2.5cm.
- Use 1.5 or double line spacing.
- Keep the space between paragraphs consistent. Two styles are:
- Do not indent paragraphs and leave a blank line between paragraphs. (This is the most common style.)
- Indent the first line of each paragraph, but leave no spaces between paragraphs.
- Ensure text alignment is consistent throughout the document. Assignment guidelines and style guides vary when it comes to text alignment . If you are following APA style , then align text left (also see the annotated sample APA student assignment ).
- For help with formatting in Microsoft Word see Basic formatting .
Always double-check for the formatting requirements of your individual course.
Cover sheet
Assignments that are submitted electronically via Stream will not usually require a cover sheet. If you have been asked to include a cover sheet, then refer to your assignment guidelines, which should detail what is to be included. If in doubt, contact your lecturer or course coordinator directly for clarification.
Most assignments do not require a title page. Usually, it is sufficient to include the assignment title or question at the top of the first page and to place other details (name, student ID number, and course number) in a header . If a cover sheet is included, all the necessary information is already included on the cover sheet. However, title pages are sometimes needed for longer assignments, postgraduate assignments, or certain types of report.
The format of these title pages varies according to the specific requirements of the assignment, but typically contain:
- The title, centred, in the upper half of the page (e.g., about 3 or 4 lines down from the top margin of the page). Your title should be concise and, ideally, no more than a single line. If you have a subtitle, it can be separated from the main title with a blank, double-spaced line. The title should be in bold font and in title case (i.e., the first word of major words over three letters is capitalised). The title font is the same style and size and the rest of the cover page details (e.g., Times New Roman or Calibri, 12pt). Note: According to the 7th edition of the APA style guide, the title (in bold, centred, and title case) should appear on the first line of the first page of text. This may not be necessary, however, and you should ask your lecturer or course coordinator for clarification.
- The author's name and ID number. Use one blank double-spaced line between the assignment title and your centred name and ID. Write your name in full rather than using initials. Your name should be non-bold and the same size and font as the rest of the cover page. Omit all titles, degrees or licenses (e.g., Dr, Ms, Mr, PhD, RN). Multiple authors should be given alphabetically. The lecturer’s name and title (e.g., Dr.). The lecturer’s name should follow a blank, double-spaced line after the class code and name, and be non-bold and the same size and font as the rest of the cover page.
- The due date of the assignment. The due date should follow a blank, double-spaced line after the lecturer’s name, and be non-bold and the same size and font as the rest of the cover page.
If you've been asked to format your title page using APA style, see here for formatting guidelines. See here for an example of a title page formatted according to APA 7th edition guidelines.
Some assignment types require headings and sub-headings, whereas others do not use any.
Essays , for example, do not usually use sub-headings unless you have specific instructions that they can be included. The only sub-heading common in essays is References, for the reference list. Instead of headings, the first sentence of each paragraph should signal the topic to the reader (see essay body paragraphs for more on this).
Reports , on the other hand, often require specific headings, such as Introduction, Discussion, and so forth.
If you are unsure whether to use headings or not, ask your course coordinator for clarification. If you do use headings and sub-headings, keep the style consistent throughout the assignment. If you are using APA style , see here for advice about formatting headings.
Tables and figures
Most assignments do not use appendices, but sometimes you need to include additional information, transcripts, questionnaire details, or raw data. These should go in an appendix.
If there is only one appendix, it is given the title “Appendix”. If there are several appendices, each is given a letter (follow the same order that they are mentioned in the body of the assignment): “Appendix A”, “Appendix B”, “Appendix C”, etc.
The title is used to refer to the appendix in the body of the assignment:
The analysis shows that the mean was well above expected (see Appendix B for details).
Style guides differ on whether the appendices should come before or after the reference list / bibliography.
APA style (the style most commonly used at Massey University) and Massey University's Thesis Presentation Guide put the appendices after the reference list / bibliography.
Page authorised by Director - Centre for Learner Success Last updated on 28 April, 2021
Quick links
- Academic Q+A
Have a study or assignment writing question? Ask an expert at Academic Q+A
Live online workshops
- StudyUp (undergraduate)
- Campus workshops
- Albany (undergraduate)
- Albany (postgraduate)
- Albany (distance)
- Manawatu (undergraduate)
- Manawatu (postgraduate)
Upcoming events
- All upcoming events
- Academic writing and learning support
- 0800 MASSEY | (+64 6 350 5701)
- [email protected]
- Online form
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
MLA Formatting and Style Guide

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
The following overview should help you better understand how to cite sources using MLA 9 th edition, including how to format the Works Cited page and in-text citations.
Please use the example at the bottom of this page to cite the Purdue OWL in MLA. See also our MLA vidcast series on the Purdue OWL YouTube Channel .
Creating a Works Cited list using the ninth edition
MLA is a style of documentation that may be applied to many different types of writing. Since texts have become increasingly digital, and the same document may often be found in several different sources, following a set of rigid rules no longer suffices.
Thus, the current system is based on a few guiding principles, rather than an extensive list of specific rules. While the handbook still describes how to cite sources, it is organized according to the process of documentation, rather than by the sources themselves. This gives writers a flexible method that is near-universally applicable.
Once you are familiar with the method, you can use it to document any type of source, for any type of paper, in any field.
Here is an overview of the process:
When deciding how to cite your source, start by consulting the list of core elements. These are the general pieces of information that MLA suggests including in each Works Cited entry. In your citation, the elements should be listed in the following order:
- Title of source.
- Title of container,
- Other contributors,
- Publication date,
Each element should be followed by the corresponding punctuation mark shown above. Earlier editions of the handbook included the place of publication and required different punctuation (such as journal editions in parentheses and colons after issue numbers) depending on the type of source. In the current version, punctuation is simpler (only commas and periods separate the elements), and information about the source is kept to the basics.
Begin the entry with the author’s last name, followed by a comma and the rest of the name, as presented in the work. End this element with a period.
Bhabha, Homi K. The Location of Culture. Routledge, 1994.
Title of source
The title of the source should follow the author’s name. Depending upon the type of source, it should be listed in italics or quotation marks.
A book should be in italics:
Henley, Patricia. The Hummingbird House . MacMurray, 1999.
An individual webpage should be in quotation marks. The name of the parent website, which MLA treats as a "container," should follow in italics:
Lundman, Susan. "How to Make Vegetarian Chili." eHow, www.ehow.com/how_10727_make-vegetarian-chili.html.*
A periodical (journal, magazine, newspaper) article should be in quotation marks:
Bagchi, Alaknanda. "Conflicting Nationalisms: The Voice of the Subaltern in Mahasweta Devi's Bashai Tudu." Tulsa Studies in Women's Literature , vol. 15, no. 1, 1996, pp. 41-50.
A song or piece of music on an album should be in quotation marks. The name of the album should then follow in italics:
Beyoncé. "Pray You Catch Me." Lemonade, Parkwood Entertainment, 2016, www.beyonce.com/album/lemonade-visual-album/.
*The MLA handbook recommends including URLs when citing online sources. For more information, see the “Optional Elements” section below.
Title of container
The eighth edition of the MLA handbook introduced what are referred to as "containers," which are the larger wholes in which the source is located. For example, if you want to cite a poem that is listed in a collection of poems, the individual poem is the source, while the larger collection is the container. The title of the container is usually italicized and followed by a comma, since the information that follows next describes the container.
Kincaid, Jamaica. "Girl." The Vintage Book of Contemporary American Short Stories, edited by Tobias Wolff, Vintage, 1994, pp. 306-07.
The container may also be a television series, which is made up of episodes.
“94 Meetings.” Parks and Recreation, created by Greg Daniels and Michael Schur, performance by Amy Poehler, season 2, episode 21, Deedle-Dee Productions and Universal Media Studios, 2010.
The container may also be a website, which contains articles, postings, and other works.
Wise, DeWanda. “Why TV Shows Make Me Feel Less Alone.” NAMI, 31 May 2019, www.nami.org/Blogs/NAMI-Blog/May-2019/How-TV-Shows-Make-Me-Feel-Less-Alone . Accessed 3 June 2019.
In some cases, a container might be within a larger container. You might have read a book of short stories on Google Books , or watched a television series on Netflix . You might have found the electronic version of a journal on JSTOR. It is important to cite these containers within containers so that your readers can find the exact source that you used.
“94 Meetings.” Parks and Recreation , season 2, episode 21, NBC , 29 Apr. 2010. Netflix, www.netflix.com/watch/70152031?trackId=200256157&tctx=0%2C20%2C0974d361-27cd-44de-9c2a-2d9d868b9f64-12120962.
Langhamer, Claire. “Love and Courtship in Mid-Twentieth-Century England.” Historical Journal , vol. 50, no. 1, 2007, pp. 173-96. ProQuest, doi:10.1017/S0018246X06005966. Accessed 27 May 2009.
Other contributors
In addition to the author, there may be other contributors to the source who should be credited, such as editors, illustrators, translators, etc. If their contributions are relevant to your research, or necessary to identify the source, include their names in your documentation.
Foucault, Michel. Madness and Civilization: A History of Insanity in the Age of Reason. Translated by Richard Howard , Vintage-Random House, 1988.
Woolf, Virginia. Jacob’s Room . Annotated and with an introduction by Vara Neverow, Harcourt, Inc., 2008.
If a source is listed as an edition or version of a work, include it in your citation.
The Bible . Authorized King James Version, Oxford UP, 1998.
Crowley, Sharon, and Debra Hawhee. Ancient Rhetorics for Contemporary Students. 3rd ed., Pearson, 2004.
If a source is part of a numbered sequence, such as a multi-volume book or journal with both volume and issue numbers, those numbers must be listed in your citation.
Dolby, Nadine. “Research in Youth Culture and Policy: Current Conditions and Future Directions.” Social Work and Society: The International Online-Only Journal, vol. 6, no. 2, 2008, www.socwork.net/sws/article/view/60/362. Accessed 20 May 2009.
Quintilian. Institutio Oratoria. Translated by H. E. Butler, vol. 2, Loeb-Harvard UP, 1980.
The publisher produces or distributes the source to the public. If there is more than one publisher, and they are all are relevant to your research, list them in your citation, separated by a forward slash (/).
Klee, Paul. Twittering Machine. 1922. Museum of Modern Art, New York. The Artchive, www.artchive.com/artchive/K/klee/twittering_machine.jpg.html. Accessed May 2006.
Women's Health: Problems of the Digestive System . American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, 2006.
Daniels, Greg and Michael Schur, creators. Parks and Recreation . Deedle-Dee Productions and Universal Media Studios, 2015.
Note : The publisher’s name need not be included in the following sources: periodicals, works published by their author or editor, websites whose titles are the same name as their publisher, websites that make works available but do not actually publish them (such as YouTube , WordPress , or JSTOR ).
Publication date
The same source may have been published on more than one date, such as an online version of an original source. For example, a television series might have aired on a broadcast network on one date, but released on Netflix on a different date. When the source has more than one date, it is sufficient to use the date that is most relevant to your writing. If you’re unsure about which date to use, go with the date of the source’s original publication.
In the following example, Mutant Enemy is the primary production company, and “Hush” was released in 1999. Below is a general citation for this television episode:
“Hush.” Buffy the Vampire Slayer , created by Joss Whedon, performance by Sarah Michelle Gellar, season 4, Mutant Enemy, 1999 .
However, if you are discussing, for example, the historical context in which the episode originally aired, you should cite the full date. Because you are specifying the date of airing, you would then use WB Television Network (rather than Mutant Enemy), because it was the network (rather than the production company) that aired the episode on the date you’re citing.
“Hush.” Buffy the Vampire Slayer, created by Joss Whedon, performance by Sarah Michelle Gellar, season 4, episode 10, WB Television Network, 14 Dec. 1999 .
You should be as specific as possible in identifying a work’s location.
An essay in a book or an article in a journal should include page numbers.
Adiche, Chimamanda Ngozi. “On Monday of Last Week.” The Thing around Your Neck, Alfred A. Knopf, 2009, pp. 74-94 .
The location of an online work should include a URL. Remove any "http://" or "https://" tag from the beginning of the URL.
Wheelis, Mark. "Investigating Disease Outbreaks Under a Protocol to the Biological and Toxin Weapons Convention." Emerging Infectious Diseases , vol. 6, no. 6, 2000, pp. 595-600, wwwnc.cdc.gov/eid/article/6/6/00-0607_article. Accessed 8 Feb. 2009.
When citing a physical object that you experienced firsthand, identify the place of location.
Matisse, Henri. The Swimming Pool. 1952, Museum of Modern Art, New York .
Optional elements
The ninth edition is designed to be as streamlined as possible. The author should include any information that helps readers easily identify the source, without including unnecessary information that may be distracting. The following is a list of optional elements that can be included in a documented source at the writer’s discretion.
Date of original publication:
If a source has been published on more than one date, the writer may want to include both dates if it will provide the reader with necessary or helpful information.
Erdrich, Louise. Love Medicine. 1984. Perennial-Harper, 1993.
City of publication:
The seventh edition handbook required the city in which a publisher is located, but the eighth edition states that this is only necessary in particular instances, such as in a work published before 1900. Since pre-1900 works were usually associated with the city in which they were published, your documentation may substitute the city name for the publisher’s name.
Thoreau, Henry David. Excursions . Boston, 1863.
Date of access:
When you cite an online source, the MLA Handbook recommends including a date of access on which you accessed the material, since an online work may change or move at any time.
Bernstein, Mark. "10 Tips on Writing the Living Web." A List Apart: For People Who Make Websites, 16 Aug. 2002, alistapart.com/article/writeliving. Accessed 4 May 2009.
As mentioned above, while the MLA handbook recommends including URLs when you cite online sources, you should always check with your instructor or editor and include URLs at their discretion.
A DOI, or digital object identifier, is a series of digits and letters that leads to the location of an online source. Articles in journals are often assigned DOIs to ensure that the source is locatable, even if the URL changes. If your source is listed with a DOI, use that instead of a URL.
Alonso, Alvaro, and Julio A. Camargo. "Toxicity of Nitrite to Three Species of Freshwater Invertebrates." Environmental Toxicology , vol. 21, no. 1, 3 Feb. 2006, pp. 90-94. Wiley Online Library, doi: 10.1002/tox.20155.
Creating in-text citations using the previous (eighth) edition
Although the MLA handbook is currently in its ninth edition, some information about citing in the text using the older (eighth) edition is being retained. The in-text citation is a brief reference within your text that indicates the source you consulted. It should properly attribute any ideas, paraphrases, or direct quotations to your source, and should direct readers to the entry in the Works Cited list. For the most part, an in-text citation is the author’s name and the page number (or just the page number, if the author is named in the sentence) in parentheses :
When creating in-text citations for media that has a runtime, such as a movie or podcast, include the range of hours, minutes and seconds you plan to reference. For example: (00:02:15-00:02:35).
Again, your goal is to attribute your source and provide a reference without interrupting your text. Your readers should be able to follow the flow of your argument without becoming distracted by extra information.
How to Cite the Purdue OWL in MLA
Entire Website
The Purdue OWL . Purdue U Writing Lab, 2019.
Individual Resources
Contributors' names. "Title of Resource." The Purdue OWL , Purdue U Writing Lab, Last edited date.
The new OWL no longer lists most pages' authors or publication dates. Thus, in most cases, citations will begin with the title of the resource, rather than the developer's name.
"MLA Formatting and Style Guide." The Purdue OWL, Purdue U Writing Lab. Accessed 18 Jun. 2018.
AP Central for Educators
Supporting Students from Day One to Exam Day
Access free AP resources from anywhere.
Deadline: Free Score-Send Selections
Have students follow these steps to choose a free score-send recipient before the June 20 deadline.
AP Annual Conference 2024
Join us in Las Vegas on July 24–26 for the AP Annual Conference.

The Latest in AP
AP Summer Institutes
Explore upcoming summer workshops to expand your teaching skills.
AP Alumni Network
Encourage seniors to join this network to advocate for future AP students.
AP Courses and Exams
Find course and exam information, classroom resources, and instructions for completing the Course Audit.
Explore teaching resources and useful information for every AP subject.
AP Course Audit
Learn how to complete the Course Audit and get your course authorized.
Important Dates
POSTMARK JUNE 15
Deadline: Return AP Exam Invoices and Payments
Deadline: students use free score sends.
This is the deadline for students to access My AP and indicate or change the recipient of their free score report.
AP Scores Released
AP score reports are available to designated colleges, students, high schools, and districts.
Start and Expand Your AP Program
Bring ap to your school.
Learn how to get approved to administer AP Exams and offer AP courses at your school.
Build Your AP Program
Learn how to expand your AP program to offer more subjects and reach more students.

Professional Learning for Teachers
Deepen your instruction and elevate your students’ learning potential by participating in professional learning programs, both in person and online. Benefit from the experience of your colleagues through AP Mentoring and the AP Community.

Find Resources for Your Role
Find resources to enhance your instruction and support your students.
AP Coordinators
Find key dates, resources, and everything you need to administer exams.
Find key dates, teacher resources, and professional learning opportunities.
District Leaders
Find user guides, key dates, and resources to support teachers, parents, and students.
More to Explore
Ap community.
Connect online with colleagues, participate in discussions with experts, and share classroom-ready materials.
AP Coordinator Resources
Download the AP Coordinator’s Manual, guides for creating sections in AP Classroom, and additional resources.
Have Questions?
Ap faq center.
Find answers to frequently asked questions about the AP Program.
AP Contacts
Contact the AP Program with questions.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Scientific reports typically follow a structured format and include sections such as an abstract, introduction, methods, results, and conclusion. In this case, using the term "essay" to describe this type of document would be incorrect. ... Choose the correct word (essay or report) to fill in the blank: She wrote a/an _____ on the causes of ...
Key Differences: Report vs Essay . While both reports and essays involve research, analysis, and communication of ideas, there are key differences in their purpose, structure, and approach: ... Structure: Reports follow a structured format with clear sections, while essays offer more flexibility in organisation and presentation. Language and ...
Essays usually focus on analysing or evaluating theories, past research by other people, and ideas. They may include applying theory to practice if you are in a practice-based field. A report usually contains tables, charts and diagrams. Essays don't usually include tables, charts, or diagrams.
In a nutshell, Essays are descriptive, subjective and evaluative, whereas, a report is descriptive, objective and analytical. Essays are mainly used in an academic context, whereas reports are preferred in the field of research. The report is used to present the researched information in a written format, to the audience.
For a generalised audience. Meaning is conveyed through text. Meaning constructed through sentences. Students often ask the question, What is the difference between a report and an essay? Here we have a helpful summary of the main differences between essays and reports presented in a table and a video.
Target Audience for Report vs Essay: Reports usually target decision-makers, stakeholders, or experts in a specific field. Namely, those who need accurate and correct information. ... However, if the aim is to provoke thought, stimulate discussion, or present personal viewpoints, an essay would be the preferred format. Thus, allowing for a more ...
Essays are used to develop a discussion of a topic or build an argument. Reports present information in a different way from an essay. Whilst essays are generally quite fluid in terms of structure, enabling the author to explore a topic through a series of paragraphs, a report will be highly structured with section headings and subheadings that ...
An essay is written to present writer's personal ideas and opinions while a report is written to provide information about a certain issue. Another significant difference between essay and report is the format. A report is divided into sections, headings, and sub-headings, but an essay is never divided into sections and headings; it has ...
The main differences between a report and an essay. Reports are divided into many sections whereas essays have three main sections divided into paragraphs. Reports include an abstract, essays do not. Reports can use bullet points, essays do not. Reports can use subheadings for each of the sections, it is rare for essays to have subheadings.
In this article, we'll explain essay formatting rules for three of the most popular essay styles: MLA, APA, and Chicago. For each, we'll do a high-level overview of what your essay's structure and references should look like, then we include a comparison chart with nitty-gritty details for each style, such as which font you should use for ...
Argumentative essays. An argumentative essay presents an extended, evidence-based argument. It requires a strong thesis statement—a clearly defined stance on your topic. Your aim is to convince the reader of your thesis using evidence (such as quotations) and analysis.. Argumentative essays test your ability to research and present your own position on a topic.
These sample papers demonstrate APA Style formatting standards for different student paper types. Students may write the same types of papers as professional authors (e.g., quantitative studies, literature reviews) or other types of papers for course assignments (e.g., reaction or response papers, discussion posts), dissertations, and theses.
Indent the first line of every paragraph of text 0.5 in. using the tab key or the paragraph-formatting function of your word-processing program. Page numbers: Put a page number in the top right corner of every page, including the title page or cover page, which is page 1. Student papers do not require a running head on any page.
Title: You need a comprehensive but concise title to set the right tone and make a good impression. It should be reflective of the general themes in the report. Table of Contents: Your title page must be followed by a table of contents. We suggest writing an entire report first and creating a table of content later.
Formatting an APA paper. The main guidelines for formatting a paper in APA Style are as follows: Use a standard font like 12 pt Times New Roman or 11 pt Arial. Set 1 inch page margins. Apply double line spacing. If submitting for publication, insert a APA running head on every page. Indent every new paragraph ½ inch.
The final step of the outlining process is to repeat this procedure on the smallest level, with the original notes that you took for your essay. To order what probably was an unwieldy and disorganized set of information at the beginning of this process, you need now only think of a sentence or two to support your general argument.
General Format Guidelines on writing an APA style paper In-Text Citations ... General guidelines for referring to the works of others in your essay Author/Authors How to refer to authors in-text, including single and multiple authors, unknown authors, organizations, etc. Reference List. Resources on writing an APA style reference list ...
To format a paper in APA Style, writers can typically use the default settings and automatic formatting tools of their word-processing program or make only minor adjustments. Consistency in the order, structure, and format of a paper allows readers to focus on a paper's content rather than its presentation. To format a paper in APA Style ...
Otherwise, it would go in place of the text. Title. There needs to be a proper essay title format, centered and above the first line of the essay of the same font and size as the essay itself. Indentation. Just press tab (1/2 inch, just in case) Align. Align to the left-hand side, and make sure it is aligned evenly.
Most assignments are now submitted electronically and formatted as follows: Use a clearly legible font and font size (Times New Roman is the most common font and 12 point is the most common size). Set page margins to around 1 inch/2.5cm. Use 1.5 or double line spacing. Keep the space between paragraphs consistent.
The Online Writing Lab (the Purdue OWL) at Purdue University houses writing resources and instructional material, and we provide these as a free service at Purdue. Students, members of the community, and users worldwide will find information to assist with many writing projects. Teachers and trainers may use this material for in-class and out ...
MLA (Modern Language Association) style is most commonly used to write papers and cite sources within the liberal arts and humanities. This resource, updated to reflect the MLA Handbook (9th ed.), offers examples for the general format of MLA research papers, in-text citations, endnotes/footnotes, and the Works Cited page.
1. Be authentic. One of the most essential parts of how to format a college application essay is to be authentic. The college wants to know who you are, and they will be reading dozens of essays a day. The best way to make yours stand out is to just be yourself instead of focusing on what you think they want to hear.
Professional Learning for Teachers. Deepen your instruction and elevate your students' learning potential by participating in professional learning programs, both in person and online. Benefit from the experience of your colleagues through AP Mentoring and the AP Community. View Learning Opportunities.