Principles of Management Class 12 Important Questions and Answers Business Studies Chapter 2
We have given these Business Studies Class 12 Important Questions Chapter 2 Principles of Management to solve different types of questions in the exam. Go through these Principles of Management Class 12 Important Questions and Answers & Previous Year Questions to score good marks in the board examination.

Important Questions of Principles of Management Class 12 Business Studies Chapter 2
Question 1. Appliances India Ltd. is engaged in a manufacturing and distribution of home appliances since 1987. It has a good name in the market as the company is producing good quality appliances. It has separate departments for manufacturing, finance, sales, maintenance services and technical services to achieve specialisation. Since, the areas of operations of the company have increased and customers have become more demanding, the company decided to modify the existing principle of management to meet the changing requirements of the environment. State the general principle of management which the company wants to modify to meet the changing requirements. (Delhi 2019) Answer: The company wants to modify the principle of ‘Division of Work’.
Question 2. State the role of ‘speed boss’ in functional foremanship. (Foreign 2016; Delhi 2016) Answer: Speed boss is responsible for maintaining speed of production, investigating causes of delay and removing it.
Question 3. State the role of ‘gang boss’ in functional foremanship. (All India 2016; Delhi 2016; Foreign 2016) Answer: Gang boss is responsible for keeping machines and tools ready for work.
Question 4. State the role of ‘inspector’ in ‘functional foremanship’. (All India 2016: Delhi 2016; Foreign 2016) Answer: The inspector is responsible for maintaining quality of work.
Question 5. State the role of ‘route clerk’ in functional foremanship. (All India 2016) Answer: Route-clerk is responsible for specifying the route of production.
Question 6. What is determined by fatigue study? (Foreign 2014) Or State the objective of fatigue study. (All India 2010; Foreign 2010) Answer: The objective of fatigue study is to maintain the efficiency level of workers by determining the amount and frequency of rest intervals in completing a task.
Question 7. What is the objective of ‘method study’ as a technique of scientific management? (Delhi 2014) Answer: The main objective of method study is to find out the best way of doing the job.
Question 8. State the objective of time study. (All India 2014,2010; Delhi 2010) Or What is determined by time study? (All India 2014; Foreign 2010) Answer: The main objective of time study is to determine the standard time required to perform a job.
Question 9. ‘Accurate cause and effect relationship cannot be established by principles of management.’ Why? (Compartment 2013) Answer: Since management principles are applicable on human resource of a concern, and human behaviour is unpredictable, accurate cause and effect cannot be established by them.
Question 10. Why do principles of management try to establish the relationship between cause and effect? State. (Comportment 2013) Answer: Establishing cause and effect relationship through management principles helps manager, to solve day-to-day problems easily and effectively.
Question 11. What is meant by ‘principles of management’? (All India 2013 2009, Delhi 2011) Answer: Principles of management are general guidelines, which can be used for conduct in work places under certain situations. It also helps manager to take and implement thoughtful decisions.
Question 12. Ayesha, a manager, decided that there will be separate departments for finance, marketing, production and sales in her company. By doing so she is following a principle of management. Name the principle. (Compartment 2013) Answer: Division of work
Question 13. Shreya, a manager feels that employees should get enough time to adapt to a new environment to show results. By doing so she is following a principle of management. Name the principle. (Comportment 2013) Answer: Stability of personnel
Question 14. Name the following principles of management: (a) that prevents dual subordination and (b) that prevents overlapping of working of two divisions. (Compartment 2012) Answer: (a) Unity of command (b) Unity of direction
Question 15. Distinguish between the principles of ‘unity of command’ and ‘unity of direction’ on the basis of implications. (Comportment 2012) Answer: Difference between unity of command and unity of direction on the basis of implications is stated below: Unity of command It affects individual employee. Unity of direction It affects the entire organisation.
Question 16. Define ‘scientific management’. (Comportment 2012) Or What is meant by scientific management? (Foreign 2011) Answer: Scientific management In words of Taylor, scientific management means knowing exactly what you want men to do and seeing that they do in the best and the cheapest way.
Question 17. State why ‘principles of management’ are called contingent. (All India (C) 2012) Or What is meant by the statement ‘principles of management are contingent’? (All India 2011,2010; Foreign 2011) Or Give any one reason why principles of management are called “contingent”. (Delhi 2010; Foreign 2010) Or Why is it said that ‘principles of management are contingent’? (Foreign 2011) Answer: The application of principles of management is contingent as it depends upon the prevailing situation at a particular point of time.
Question 18. What is meant by ‘universal applicability of principles of management’? (Delhi 2011) Answer: ‘Universal applicability of principles of management’ means that the principles of management are intended to apply to all types of organisations at all places.
Question 19. State any one reason why principles of management are important? (All India 2011) Answer: Principles of management are important as they help managers in taking thoughtful and scientific decisions.
Question 20. What is meant by the statement ‘principles of management are flexible’? (Delhi 2011) Or Give any one reason why principles of management are not rigid prescriptions? (All India 2010; Delhi 2010) Answer: Principles of management are flexible, which means that they are not rigid, and can be modified by the manager as per the situation.
Question 21. What is meant by Fayol’s principle of ‘esprit de corps’? (Delhi 2011) Answer: Fayol’s principle of ‘esprit de corps’ suggests that management should promote team spirit of unity and harmony among the employees.
Question 22. State any one principle of scientific management. (Delhi 2011) Answer: Science, not rule of thumb It advocates that there is only one best method to maximise efficiency and this method should substitute rule of thumb throughout the organisation.
Question 23. Name the principle of scientific management which emphasises on study and analysis of methods rather than estimation. Or Name the principle of scientific management which suggests the introduction of scientific investigation and analysis. (Delhi (C) 2011) Answer: Science, not rule of thumb.
Question 24. Give any one reason why principles of management do not provide readymade solution to all managerial problems. (All India 2010; Delhi 2010; Foreign 2010) Answer: Principles of management do not provide readymade solution to all managerial problems because principles provide general guidelines to managers whereas real business situations are extremely complex and not based on theoretical knowledge.
Question 25. Which principle of management implies that there should be ‘one head and one plan for a group of activities having the same objective? (All India 2010) Answer: Principle of unity of direction implies that there should be ‘one head and one plan’ for a group of activities having the same objective.
Question 26. Which principle of management states that an employee should receive orders from one superior only? (Delhi (C) 2010) Answer: Unity of command states that an employee should receive orders from one superior only.
Question 27. State the objective of motion study. (All India 2010; Delhi 2010; Foreign 2010) Answer: The objective of motion study is to eliminate unnecessary and wasteful motions so that it takes less time to complete the job efficiently.
Question 28. Which technique of Taylor differentiates between an efficient worker and an inefficient worker? (All India 2010) Answer: Differential piece wage system differentiates between an efficient worker and an inefficient worker.
Question 29. Which revolution involves a change in the attitude of workers and management towards one another, from competition to cooperation? (Delhi (C) 2010) Answer: Mental revolution involves a change in the attitude of workers and management towards one another, from competition to cooperation.
Question 30. Explain briefly ‘unity of direction’ and ‘order’ as principles of general management. (All India 2017) Answer: ‘Unity of direction’ and ‘order’ as principles of general management are discussed below: (i) Unity of direction ‘One unit and one plan for the group of activities having the same objective is the essence of this principle. It implies that there should be one head and one plan for a group of activities having the same objective. It means that the efforts of members of the organisation should be directed towards the achievement of a common goal. It was forwarded by Fayol.
(ii) Order According to Fayol, ‘People and material must be in suitable place at appropriate time for maximum efficiency’. This principle states that there should be a place for everything and everyone in an organisation and that thing or person should be found at its alloted place. This will lead to increased productivity and efficiency.
Question 31. Explain briefly ‘initiative’ and ‘esprit de corps’ as principles of general management. (All India 2017) Answer: ‘Initiative’ and ‘esprit de corps’ as principles of general management are discussed below: (i) Initiative It means freedom to think of new ideas and execute them. The principle of initiative implies that the managers of an organisation should encourage their subordinates to take initiative and think of new ideas or policies that are beneficial for the organisation and execute them. By ‘encouraging initiative, the management can motivate employees to work better and harder.
(ii) Esprit de corps This principle states that union is strength. It refers to team spirit, i.e. harmony in the work group and mutual understanding among the workers. A group of workers working collectively in harmony and with mutual cooperation leads to the achievement of goals efficiently. Unity among the personnel can be accomplished through proper communication and coordination.
Question 32. Explain briefly ‘remuneration of employees’ and ‘scalar chain’ as principles of general management. (All India 2017) Answer: Remuneration of employees According to Fayol, the quantum and methods of remuneration payable to employees should be fair and reasonable. It should be satisfactory to both employers and employees, which gives them a reasonable standard of living and should be within the paying capacity of the company.

The above figure illustrates the scalar chain. If D and O wants to communicate, the message should usually move up through C, B, A, M, N and then O. Communication through this process takes time.
Question 33. Explain ‘unity of command’ and ‘equity’ as principles of general management. (Delhi 2017) Answer: Unity of command According to this principle, one subordinate should receive orders from one superior only at a given point of time. The principle is necessary to avoid confusion and conflict. Equity The principle of equity implies a sense of fairness and justice to all workers working in an organisation. Observance of equity alone would make workers loyal and devoted to the organisation. Equity does not mean equal salary to a peon and supervisor.
But equity means application of same disciplinary rules, leave rules, etc irrespective of their grade, position and gender, language, religion or nationality, etc.
Question 34. Explain briefly ‘discipline’ and ‘scalar chain’ as principles of general management. (Delhi 2017) Answer: Discipline According to Fayol, discipline is obedience, application and outward mark of respect. It is the obedience to organisational rules and employment agreement which are necessary for the working of the organisation. According to Fayol, discipline requires good superiors at all levels, clear and fair agreements and judicious application of penalties.
Scalar chain It is the chain of superiors ranking from the top to the lowest ranks. The principle of scalar chain suggests that there should be a clear line of authority from top to bottom linking managers at all levels. The scalar chain serves as the chain of command and also as the chain of communication. Under the chain of command, orders and instructions, issued at higher levels, flow through intermediate managers before reaching the lower levels.
Question 35. Explain ‘order’ and ‘initiative’ as principles of general management. (Delhi 2017) Answer: Order: According to Fayol, ‘People and material must be in suitable place at appropriate time for maximum efficiency’. This principle states that there should be a place for everything and everyone in an organisation and that thing or person should be found at its alloted place. This will lead to increased productivity and efficiency.
Initiative: According to Fayol, ‘Initiative means taking the first step with self motivation, it is thinking out and executing the plan’. It is one of the traits of an intelligent person. Initiative should be encouraged because employees get satisfaction when they are allowed to take initiative. But it does not mean going against the established practices of the company for the sake of being different.
Question 36. Name and explain the principle of management according to which a manager should replace T with ‘We’ in all his’conversation with workers? (Delhi 2013) Answer: Esprit de corps: It is the principle of management, according to which a manager should replace ‘I’ with ‘We’ in all his conversation with workers. Literally speaking, the phrase ‘esprit de corps’ means the spirit of loyalty and devotion which unites the members of the group.
According to Fayol, management should promote a team spirit of unity and harmony among employees. A manager should replace T with ‘We’ in all his conversations with workers to foster team spirit. This will give rise to a spirit of mutual trust and belongingness among team members.
Question 37. Explain ‘harmony, not discord’ as a principle of scientific management? (Delhi 2013) Answer: According to this principle, there should be complete harmony between the management and the workers working in an organisation. To support this, Taylor advocated a complete ‘mental revolution’, i.e. change in the attitude of both workers and management towards one another, from competition to cooperation. Both should realise the importance of each other.
Question 38. Explain ‘cooperation, not individualism’ as a principle of scientific management? (Delhi 2013) Answer: ‘Cooperation, not individualism’ is a principle of scientific management which states that there should be complete cooperation between the workers and management in an oganisation instead of individualism and competition. In the absence of constant and willing cooperation between the two sides, maximum prosperity for both the parties cannot be achieved.
Question 39. Explain how principles of management: (i) provide useful insight into reality and (ii) help in thoughtful decision-making (Delhi 2012) Answer: (i) Provide useful insight into reality The principles of management provide useful insight into real world situations. Managers may apply these principles to fulfil their tasks and responsibilities. These principles guide the managers in taking and implementing thoughtful decisions.
(ii) Thoughtful decision-making These principles help in enhancing knowledge, ability and understanding of managerial situations and circumstances. They must be timely, realistic and subject to measurement and evaluation. They emphasise logic rather than blind faith and are free from bias and prejudice.
Question 40. Explain how principles of management: (i) help in optimum utilisation of resources and effective administration, and (ii) help the managers in meeting changing environment requirements. (All India 2012) Answer: (i) Principles of management help in optimum utilisation of resources by equipping managers to foresee the cause and effect relationship of their decisions and actions, as such the wastage associated with a trial and error approach can be overcome. Principles of management help in effective administration by limiting the boundaries of management discretion so that their decisions may be free from personal prejudice and bias.
(ii) Principles of management help the managers in meeting changing environment requirements because they can be modified according to the changes taking place in the environment, e.g. the principle of division of work has now been extended to the entire business. Therefore, companies are focusing on their competency and outsourcing non-core business.
Question 41. Explain how principles of management: (i) help the managers in taking scientific decisions, and (ii) provide the managers with useful insights into real world situations. (All India 2012) Answer: (i) Scientific decisions The knowledge of management principles enables managers to learn the cause and effect relationship between variables operating in the organisation. They are able to develop a scientific and objective approach towards problem solving and decision-making.
(ii) Provide the manager with useful insight into reality Management principles act as guidelines for the managers. These principles improve knowledge, ability and understanding of managers under various managerial situations. The effects of these principles help the managers to learn from their mistakes.
Question 42. Name and explain the technique of scientific management which helps in establishing interchangeability of manufactured parts and products. (All India 2010: Delhi 2010) Answer: Standardisation is the process of setting standards for every business activity process, raw materials, time, product and machinery. Taylor advocated the standardisation of tools, and equipment, cost system and several other items. The objectives of standardisation are:
- To reduce a given line or product to fixed types.
- To establish interchangeability of manufactured parts and products.
- To establish quality standards.
- To establish performance standards of men and machines.
Question 43. Name and explain the principle of management which requires judicious application of penalties by the management. (All India 2010; Delhi 2010) Answer: Discipline According to Fayol, discipline is obedience, application and outward mark of respect. It is the obedience to organisational rules and employment agreement which are necessary for the working of the organisation. According to Fayol, discipline requires good superiors at all levels, clear and fair agreements and judicious application of penalties.
Question 44. Name and explain the principle of management in which workers should be encouraged to develop and carry out their plans for improvement in the organisation. (Delhi (C) 2010) Answer: Initiative According to Fayol, ‘Initiative means taking the first step with self motivation, it is thinking out and executing the plan’. It is one of the traits of an intelligent person. Initiative should be encouraged because employees get satisfaction when they are allowed to take initiative. But it does not mean going against the established practices of the company for the sake of being different.
Question 45. State any four or five features of principles of management. (All India 2019,2015; Delhi 2019,2015: Compartment 2012) Or Explain any five characteristics which reflect the nature of principles of management. (Delhi (C) 2010) Answer: Management principles are broad and general guidelines for decision-making and behaviour. Following features highlight the characteristics of management principles: (i) Universal application Management principles are applied in every situation where the objectives are attained through group efforts. All social, economic, political or ‘ religious organisations apply management principles for their successful operations. Every organisation must make the best possible use of its available resources by the application of management principles alongwith managerial functions such as planning, organising, staffing, directing and controlling.
(ii) Flexibility: The principles of management are not rigid prescriptions, which have to be followed absolutely. They are flexible and can be modified by the manager when the situation so demands. They give the manager enough discretion to do so.
(iii) General statements: Management principles are concerned with human behaviour which cannot be tested under laboratory conditions. Human behaviour cannot be predicted accurately. Therefore, management principles are not as exact as the principles of physical science.
(iv) Influencing human behaviour Human element is an essential factor of production. It activates and extracts work from other factors also. Each person is different from other as regards to his ability, knowledge, skills, social status, attitudes and ideologies. Management is concerned with the integration of individual efforts.
(v) Cause and effect relationship Management principles also form a cause and effect relationship. It indicates the consequences of certain actions or inactions in the business, e.g. if wages are paid on piece rate system, the quantity of work will increase but the quality will suffer. The principle of unity of command will avoid confusion, duplication and overlapping of work.
Question 46. State any four points which highlight the importance of principles of management. (All India 2019, 2015) Or What is meant by principles of management? State any three points of their importance. (Delhi 2015) Or Explain how principles of management: (i) help in optimum utilisation of resources and effective administration and (ii) help in the thoughtful decision-making. (Foreign 2012) Answer: Management principles are essential for the successful running of business organisation. These principles are guidelines to management. They highlight the areas where the management should pay immediate attention. These principles simplify the process of management, increase the overall efficiency of management and help in the achievement of objectives.
The significance of management principles can be summarised as follows: (i) Provide the manager with useful insight into reality Management principles act as guidelines for the managers. These principles improve knowledge, ability and understanding of managers under various managerial situations. The effects of these principles help the managers to learn from their mistakes.
(ii) Optimum utilisation of resources Several principles of management aim at optimum utilisation of all types of resources for the attainment of organisational goals, e.g. principles of division of work, discipline, unity of direction, order, etc facilitate better utilisation of human efforts and physical resources.
(iii) Scientific decisions The knowledge of management principles enables managers to learn the cause and effect relationship between variables operating in the organisation. They are able to develop a scientific and objective approach towards problem solving and decision-making.
(iv) Meeting changing environment requirements Every businessman has to cope up with the changes that are taking place in the business environment. Management principles train the managers to implement the changes in right direction and at right level in the organisation.
(v) Fulfilling social responsibility A manager is able to achieve efficiency and economy in the activities of his enterprise by applying management principles. These principles are aimed at maximising profits without loss of social value. In other words, management principles seek to ensure that the resources of the society are utilised fully and good quality products at fair prices are made available to society.
Question 47. Explain the following techniques of scientific management. (a) Fatigue study (b) Differential piece wage system (Delhi 2019) Answer: (a) Fatigue study Fatigue in work is natural. When the worker is given continuous work, he will get tired and lose speed and efficiency. He needs rest after working for a few hours. Scientific management studies the nature of work to determine the standard time for finishing the job and to find out when the workers need rest. The nature, time and period of rest are pre-determined. Necessary changes should also be made in the working methods and conditions to reduce fatigue.
(b) Taylor wanted to differentiate between efficient and inefficient workers. Under this system of wage payment, wages are paid on the basis of work done. According to him, higher rates were given to the workers who are producing standard products or more and lower rates were given to those who are producing less. e.g. Standard output = 100 units/day Wage rate 1 = ₹ 10/unit for standard output (100 units) or more Wage rate 2 = ₹ 7/unit for below standard output Worker 1 = Output 99 units Wages = 99 × 7 = ₹ 693 Worker 2 = Output 101 units Wages = 101 × 10 = ₹ 1010 Thus, a difference of ₹ 317 (1,010 – 693), for different of 2 units is enough to motivate the inefficient work for more output.
Question 48. Explain the following principles of scientific management: (a) Harmony, not discord (b) Development of each and every person to his or her greatest efficiency and prosperity. (Delhi 2019) Answer: (a) Taylor believed ‘management should share the gains with workers’. This has been emphasised by the principle of ‘harmony, not discord’, which also emphasised on mental revolution.
Harmony, not discord The interests of the employers and employees should be fully harmonised so as to create a good relationship. Taylor emphasised that there should be complete harmony between the management and workers. This requires a transformation in the thinking of both, which can be achieved through mental revolution.
Management should share the gains of the company with the workers. At the same time, workers should work and embrace changes. Taylor beleived in, that prosperity for the employer cannot exist for a long time unless it is accompanied by prosperity for the employees and vice-versa.
In the same way, Fayol’s principle of ‘remuneration of employees’ suggested that the employees compensation should depend on the earning capacity of the company and should give them a reasonable standard of living. Remuneration of employees According to Fayol, the quantum and methods of remuneration payable to employees should be fair and reasonable. It should be satisfactory to both employers and employees. Thus, we can say that Taylor’s and Fayol’s principles are mutually complementary.
(b) Development of each and every person to his/her greatest efficiency and prosperity Industrial efficiency depends upon the efficiency of workers and worker’s efficiency depends upon proper training and their proper selection. Taylor suggested that due care should be taken while selecting the employees and after selection, they must be given job according to their physical, mental and intellectual capabilities. Employees must be sent for training from time to time to update their knowledge. This will ensure greatest efficiency and prosperity for both workers and management.
Question 49. Deewan Ltd. is a multinational consulting company with its headquarters at Washington D.C. It hires young people from different countries of the world. It is a company in which people dream to work because of its work environment, pay and growth prospectus. The company has a culture of open communication and people of various nationalities work together in a discrimination free environment. The behaviour of managers of Deewan Ltd. emphasises kindliness and justice which ensures loyality and devotion of workers. It also promotes mutual trust and belongingness among team members. In this way, management of Deewan Ltd. is able to achieve its objectives by promoting teamwork. By doing so managers of Deewan Ltd. are following some principles of management. Identify and explain any two such principles. (Comportment 2018) Answer: The principles followed are:
- Esprit de corps
Question 50. Sanket, after completing his entrepreneurship course from U.S.A. returned to India and started a coffee shop ‘Fioma Coffee’ in a famous mall in Mumbai. The speciality of the coffee shop was the special aroma of coffee and a wide variety of flavours to choose from. Somehow, the business was neither profitable nor pupular. Sanket was keen to find out the reason. He appointed Riya, an MBA from a reputed management institute as a manager to find out the causes of the business not doing well. Riya, took a feedback from the clients and found out that though they loved the special unique aroma of coffee but were not happy with the long waiting time being taken to process the order. She analysed and found out that there were many unnecessary obstructions which could be eliminated. She fixed a standard time for processing order. She also realised that there were many flavours whose demand was not enough. So, she also decided to discontinue the sale of such flavours. As a result, within a short period Riya was able to attract the customers. Identify and explain any two techniques of scientific management used by Riya to solve the problem. (All India 2017; Delhi 2017) Answer: The two techniques of scientific management used by Riya are: (i) Time study It refers to determine the standard time required to complete a particular activity. The standard time is determined on the basis of average time taken to complete the work. This study is conducted with the help of a stop watch. The main objective of this study is to get the estimated figure of labour cost to determine the number of required workers and to decide the suitable incentive plan.
(ii) Simplification It helps in eliminating unnecessary diversity of products and thus, results in saving cost. It aims at eliminating superfluous varieties, sizes and dimensions. It leads to reduction in wastage of inventories, fuller utilisation of equipment and increased turnover.
Question 51. Principles of Taylor and Fayol are mutually complementary. One believed that management should not close its ears to constructive suggestions made by the employees while the other suggested that a good company should have an employee suggestion system, whereby suggestions which result in substantial time or cost reduction should be rewarded. Identify and explain the principles of Taylor and Fayol referred in the above para. (Delhi 2014) Answer: Cooperation and individualism Management should not close its ears to constructive suggestions made by the employees, is related with the principle of Taylor, i.e. ‘cooperation not individualism’. This principle is an extension of principle of harmony. Competition should be replaced by cooperation. Management and workers both should realise that they need each other. For this, management should entertain the constructive suggestions of employees and at the same time, workers should also cooperate with management.
Initiative Another principle is related with Fayol, i.e. ‘initiative’ in which he suggested that employees at all levels should take initiatives or actions without any force or boundations. This will help to motivate them and they will work hard for the betterment of the organisation. He stressed that a good company should have an employee suggestion system where by initiatives/ suggestions which result in substantial cost/time reduction should be awarded.
Question 52. Principles of Taylor and Fayol are mutually complementary. One believed that the management should share the gains with the workers, while the other suggested that employees compensation should depend on the earning capacity of the company and should give them a reasonable standard of living. Identify and explain the principles of Fayol and Taylor referred to in the above para. (All India 2014) Answer: Taylor believed ‘management should share the gains with workers’. This has been emphasised by the principle of ‘harmony, not discord’, which also emphasised on mental revolution.
Question 53. Principles of Taylor and Fayol are mutually complementary. One believed that the management should scientifically select the person and the work assigned should suit his/her physical and intellectual capabilities, while the other suggested that the work can be performed more efficiently if divided into specialised tasks. Identify and explain the principles of Fayol and Taylor referred to in the above para. (Foreign 2014) Answer: The principle of Fayol referred to in the above para is division of work. Division of work Every employee should be assigned only one type of work. It means that total work is divided into small tasks/jobs and a trained specialist performs each job. The objective of division of labour derive the benefits from the principle of specialisation which can be applied to all work.
For example, publishing of a book involves several operations like computer typing of text material, proof reading, printing, binding, etc. All the operations are performed by different people who are experts in their respective field.
The principle of Taylor referred to in the above para is development of each and every person to his/her greatest efficiency and prosperity. Development of each and every person to his/her greatest efficiency and prosperity Industrial efficiency depends upon the efficiency of workers and worker’s efficiency depends upon proper training and their proper selection. Taylor suggested that due care should he taken while selecting the employees and after selecti on, they must be given job according to their physical, mental and intellectual capabilities. Employees must be sent for training from time to time to update their knowledge. This will ensure greatest efficiency and prosperity for both workers and management.
Question 54. Explain ‘harmony not discord’ as a principle and ‘fatigue study’ as a technique of scientific management. (Comportment 2013) Answer: Taylor believed ‘management should share the gains with workers’. This has been emphasised by the principle of ‘harmony, not discord’, which also emphasised on mental revolution.
Fatigue study: Fatigue in work is natural. When the worker is given continuous work, he will get tired and lose speed and efficiency. He needs rest after working for a few hours. Scientific management studies the nature of work to determine the standard time for finishing the job and to find out when the workers need rest. The nature, time and period of rest are pre-determined. Necessary changes should also be made in the working methods and conditions to reduce fatigue.
Question 55. Explain ‘science, not rule of thumb’ as a principle and ‘time-study’ as a technique of scientific management. (compartment 2013) Answer: Science, not rule of thumb: Taylor has emphasised that in scientific management, organised knowledge should be applied, which will replace the rule of thumb. Scientific investigations should be used for taking managerial decisions instead of making the decisions on opinions, intuitions, estimates, prejudices, likes and dislikes, etc. Under scientific management, decisions are made on the basis of facts developed by the application of scientific methods.
Time study: Time study It refers to determine the standard time required to complete a particular activity. The standard time is determined on the basis of average time taken to complete the work. This study is conducted with the help of a stop watch. The main objective of this study is to get the estimated figure of labour cost, to determine the number of required workers and to decide the suitable incentive plan.
Question 56. Explain the technique of scientific management, i.e. the extension of principle of division of work and specialisation. (Delhi 2012) Or Explain the technique of scientific management which separates the planning and execution work. (Foreign 2012) Answer: Functional foremanship It is an extension of the principles of division of work and specialisation. The term, functional foremanship means separation of planning from execution. Each worker is supervised by various specialists. For this, Taylor suggested that under the factory manager, there is a planning incharge and a production incharge. The main function of the planning incharge is to plan all aspects of a job to be performed.
Under planning incharge, following four personnel are appointed:
- Route clerk
- Instmction card clerk
- Time and cost clerk
- Disciplinarian
Under production incharge, following four personnel are appointed who are concerned with the execution of the plans:
- Repair boss
Question 57. Explain that technique of scientific management which is the strongest motivator for a worker to reach standard performance. (All India 2012) Answer: Differential piece wage system is the strongest motivator for a worker to reach standard performance. It is a method of wage payment in which efficient and inefficient workers are paid at different rates. In this method, increase in efficiency is co-related with an increase in the wage rate. That is why, an efficient worker gets more wages, whereas, an inefficient worker gets less.
Workers are paid on the basis of number of units produced. If a worker produces more than a certain number of units (standard output), he gets higher wage per piece/units, on his total output. If he produces below the standard number, he gets lower rate per piece. Because of different rates of wage for different sets of workers, this is known as differential piece rate plan.
Question 58. Explain the technique of ‘simplification and standardisation of work’ given by Taylor. (Compartment 2012) Answer: Simplification means eliminating superfluous sizes, varieties and dimensions. Its aim is to:
- eliminate unnecessary diversity of products and thereby reduce costs.
- help in achieving economy in the use of required machines and tools.
Standardisation of work is the technique of scientific management, which helps in establishing interchangeability of manufactured parts and products. It is the process of setting standards for every business activity, process, raw materials, time, machinery and methods to achieve efficiency. Standardisation of product implies that the size, design, quality, shape, etc of the product should meet the requirements and tastes of consumers.
The objectives of standardisation are:
- To maintain quality standards.
- To set up performance standards for men.
- To provide interchangeability of manufacture and products.
- To achieve target production.
Question 59. Explain with the help of an example ‘differential piece wage system’ given by Taylor. (Compartment 2012) Answer: Taylor wanted to differentiate between efficient and inefficient workers. Under this system of wage payment, wages are paid on the basis of work done. According to him, higher rates were given to the workers who are producing standard products or more and lower rates were given to those who are producing less. e.g. Standard output = 100 units/day Wage rate 1 = ₹ 10/unit for standard output (100 units) or more Wage rate 2 = ₹ 7/unit for below standard output Worker 1 = Output 99 units Wages = 99 × 7 = ₹ 693 Worker 2 = Output 101 units Wages = 101 × 10 = ₹ 1010 Thus, a difference of ₹ 317 (1,010 – 693), for different of 2 units is enough to motivate the inefficient work for more output.
Question 60. Explain the following techniques of scientific management: (Compartment 2012) (i) Time study (ii) Motion study Or Explain the techniques of ‘method study’ and ‘motion study’ given by Taylor. (Comportment 2012) Answer: The ultimate aim of scientific management is to maximise production at the minimum cost.
Scientific management is introduced through the techniques of work study, standardisation, simplification, functional foremanship etc. Following are the five techniques of scientific management: (i) Time study: It refers to determine the standard time required to complete a particular activity. The standard time is determined on the basis of average time taken to complete the work. This study is conducted with the help of a stop watch. The main objective of this study is to get the estimated figure of labour cost, to determine the number of required workers and to decide the suitable incentive plan.
(ii) Motion study: This is the analysis of physical movements in doing a work. Every work involves various forms of human movements such as lifting, holding, turning, etc. Under motion study, each movement is analysed to find out easier ways of doing the work and eliminate useless motions. Following steps are involved in motion study:
- Selection of efficient workers.
- Analysis of the motions involved in a work.
- Finding the minimum time involved in doing a work.
- Keeping record of the best moves and unnecessary/unproductive actions.
(iii) Method study: It refers to identifying the most suitable way to do a particular activity. To conduct this study, process chart and operation research techniques are used. The main objective of this study is to minimise the cost of production and maximise the quality and level of consumer satisfaction.
(iv) Fatigue study: Fatigue in work is natural. When the worker is given continuous work, he will get tired and lose speed and efficiency. He needs rest after working for a few hours. Scientific management studies the nature of work to determine the standard time for finishing the job and to find out when the workers need rest. The nature, time and period of rest are pre-determined. Necessary changes should also be made in the working methods and conditions to reduce fatigue.
(v) Functional foremanship: Taylor suggested functional foremanship for better supervision of workers. Under functional foremanship, there are specialist foremen for each job. He classified specialist foremen into two departments, namely planning and production departments. Both the departments have eight foremen in all. The names and functions of these foremen are as follows: (a) Planning Department: Route clerk Determining the process of production and the route through which the raw materials will pass. Instruction card clerk Laying down instructions according to which the workers are required to, perform work. Time and cost clerk Setting the time table for doing a job as per the pre-determined route and time schedule. He specifies the material and labour cost with respect to each operation. Disciplinarian Maintaining proper discipline in the factory.
(b) Production Department Gang boss Arranging machines, materials, tools, workers, etc for the job. Speed boss Maintaining the planned speed of . production, investigating the causes for delay and remove them. Repair boss Maintenance of the machines and equipments, proper arrangements for their oiling, greasing, cleaning and repair, preventing misuse of machines, etc. Inspectors Seeing that the work confirms to the standard of quality laid down by the planning department.
Question 61. Explain any two techniques of Taylor’s scientific management. (All India 2011; Delhi 2011) Answer: Two techniques of Taylor’s scientific management are as follows: (i) Functional foremanship: It is an extension of the principles of division of work and specialisation. The term, functional foremanship means separation of planning from execution. Each worker is supervised by various specialists. For this, Taylor suggested that under the factory manager, there is a planning incharge and a production incharge. The main function of the planning incharge is to plan all aspects of a job to be performed.
(ii) Standardisation and simplification: Standardisation refers to the process of setting standards for every business activity. It can be standardisation of process, raw material, time, product, machinery, methods or working conditions. These standards are the benchmarks which must be adhered during production. Simplification aims at eliminating unnecessary varieties, sizes and dimensions of products. It results in saving of cost of labour, machines and tools.
Question 62. Explain the concept of ‘functional foremanship’ and ‘mental revolution’ in scientific management as enunciated hy ‘Taylor’. (Delhi (C) 2011) Answer: Fuiictional foremanship: Two techniques of Taylor’s scientific management are as follows: (i) Functional foremanship: It is an extension of the principles of division of work and specialisation. The term, functional foremanship means separation of planning from execution. Each worker is supervised by various specialists. For this, Taylor suggested that under the factory manager, there is a planning incharge and a production incharge. The main function of the planning incharge is to plan all aspects of a job to be performed.
Mental revolution Mental refers to mind and revolution refers to radical change. Therefore, mental revolution refers to a change of mind. According to Taylor, scientific management, in its essence, involves a complete mental revolution on the part of both sides of industry, viz workers and management.
No scheme of scientific management could be a success, unless and until both these groups fully cooperate with each other through developing and maintaining best friendly relations. This requires a mental revolution on the part of management and workers by giving up an attitude of hostility and enmity towards each other.
Question 63. Explain any two principles of Taylor’s scientific management. (Foreign 2011; Delhi 2011) Or Explain any three principles of scientific management. (All India 2019) Answer: Principles of scientific management are as follows (any two): (i) Science, not rule of thumb Taylor has emphasised that in scientific management, organised knowledge should be applied, which will replace the rule of thumb. Scientific investigations should be used for taking managerial decisions instead of making the decisions on opinions, intuitions, estimates, prejudices, likes and dislikes, etc. Under scientific management, decisions are made on the basis of facts developed by the application of scientific methods.
(ii) Harmony, not discord (Conflict) There should be harmony between the management and the workers. This requires change of mental attitudes of the workers and the management towards each other. Taylor called it mental revolution.
Management should share gains of the company with workers. They should create suitable working conditions and resolve all problems scientifically. Menial revolution on the part of workers require that they should be disciplined, loyal and sincere in fulfilling the tasks assigned to them. Instead of fighting for dividing surplus or profit, the management and workers should cooperate to increase it.
(iii) Cooperation, not individualism There should be cooperation between workers and management. It is only through cooperation with workmen, the managers can ensure that work is carried out according to plans. Cooperation is based on mutual faith so managers should develop understanding with workers to secure the cooperation.
(iv) Development of each and every person to his/her greatest efficiency and prosperity Industrial efficiency depends upon the efficiency of workers and worker’s efficiency depends upon proper training and their proper selection. Taylor suggested that due care should be taken while selecting the employees and after selection, they must be given job according to their physical, mental and intellectual capabilities. Employees must be sent for training from time to time to update their knowledge. This will ensure greatest efficiency and prosperity for both workers and management.
(v) Maximum output in place of restricted output The aim of both management and the workers should be to maximise output. This should be done by both parties in their own self interest. For management, increased production means more profits and lower cost of production. For workers, increased output may offer attractive wages. In this way, self interest implies both management and the workers to achieve maximum output. Maximum output will also be in the interest of the society.
Question 64. Explain Fayol’s principles of ‘equity’ and ‘order’ with examples. (All India 2011; Foreign 2011) Answer: (i) Equity The principle of equity implies a sense of fairness and justice to all workers working in an organisation. Observance of equity alone would make workers loyal and devoted to the organisation. Equity does not mean equal salary to a peon and supervisor.
But equity means application of same disciplinary rules, leave rules, etc irrespective of their grade, position and gender, language, religion or nationality, etc. For example, the rules for granting medical leave to an employee should be same irrespective of their position, grade or gender.
(ii) Order According to Fayol, ‘People and material must be in suitable place at appropriate time for maximum efficiency’. This principle states that there should be a place for everything and everyone in an organisation and that thing or person should be found at its alloted place. This will lead to increased productivity and efficiency. For example, raw material should be available at the place prescribed for it.
Question 65. Explain the following principles of Fayol with the help of one example for each (i) Discipline (ii) Unity of command (Delhi (C) 2011) Answer: (i) Discipline Discipline is obedience, application and outward mark of respect. It means obedience to the rules of the organisation on the part of both superiors and subordinates. Discipline is necessary for the smooth running of the organisation. According to Fayol, ‘Discipline requires good superiors at all levels, clear and fair agreement and judicious application of penalties’. Discipline does not mean only rules and regulations but it also means development of commitment on the part of employees towards organisation as well as towards each other.
For example, in XYZ Ltd, management and labour union have entered into an agreement whereby workers have agreed to revive the business out of loss. In return, management would raise the wages of workers. Here ‘discipline’ means the workers and management both will honour their commitments.

Question 66. Explain Fayol’s principles of ‘Scalar chain’ and ‘Discipline’ with the help of examples. (Foreign 2011) Answer: (i) Scalar chain It is the chain of superiors ranking from the top to the lowest ranks. The principle of scalar chain suggests that there should be a clear line of authority from top to bottom linking managers at all levels. The scalar chain serves as the chain of command and also as the chain of communication. Under the chain of command, orders and instructions, issued at higher levels, flow through intermediate managers before reaching the lower levels. The chain should not be violated in normal course of formal comipunication. However, in emergency, communication can take place between two people working at the same level but in different departments, through gang plank.
(ii) Discipline Discipline is obedience, application and outward mark of respect. It means obedience to the rules of the organisation on the part of both superiors and subordinates. Discipline is necessary for the smooth running of the organisation. According to Fayol, ‘Discipline requires good superiors at all levels, clear and fair agreement and judicious application of penalties’. Discipline does not mean only rules and regulations but it also means development of commitment on the part of employees towards organisation as well as towards each other.
Question 67. Explain the following principles of Fayol with the help of one example of each. (i) Division of work (ii) Unity of direction (All India 2011; Delhi (C) 2011) Answer: (i) Division of work Every employee should be assigned only one type of work. It means that total work is divided into small tasks/jobs and a trained specialist performs each job. The objective of division of labour derive the benefits from the principle of specialisation which can be applied to all work. For example, publishing of a book involves several operations like computer typing of text material, proof reading, printing, binding, etc. All the operations are performed by different people who are experts in their respective field.
(ii) Unity of direction ‘One unit and one plan’ for the group of activities having the same objective. This principle implies that there should be one head and one plan for a group of activities having the same objective. It means that the efforts of members of the organisation should be directed towards the achievement of a common goal. For example, the mission of a company is to provide quality products at an affordable prices to the customers. This should serve as a direction for all the departments, namely, purchasing, financing, quality control and marketing.

However, in emergency, communication can take place between two people working at the same level but in different departments, through gang plank. For example, if in XYZ Ltd, E wants to communicate with R. He will have to follow the path in chain like first he delivers information to D, then D to C, B, A, M, N, O and at last E transfers the message to R. But in case of emergency, E can directly contact with R according to the concept of gang plank.
(ii) Stability of tenure of personnel According to this principle, there should be a reasonable security of jobs. Labour turnover should be minimised to maintain organisational efficiency. Personnel should be selected and appointed after due and rigorous procedure.
But once selected, they should be kept at their post/position for a minimum fixed tenure. They should be given reasonable time to show results. Any adhodsm in this regard will create unstability/insecurity among employees. They would tend to leave the organisation. Under this situation, recruitment, selection and training cost will be high.
eg. If Amav is hired for the post of executive in a company, then, according to this principle, he should be kept on the same position for a fixed tenure say for 1 year, so that he can show results.
Question 69. (i) Name and explain the principle of management in which workers should be encouraged to develop and carry out their plans for improvements in the organisation. (ii) Name and explain the technique of scientific management which is an extension of the principle of division of work and specialisation. (Foreign 2010) Answer: (i) Principle of initiative According to Fayol, ‘Initiative means taking the first step with self motivation, it is thinking out and executing the plan’. It is one of the traits of an intelligent person. Initiative should be encouraged because employees get satisfaction when they are allowed to take initiative. But it does not mean going against the established practices of the company for the sake of being different.
(ii) Functional foremanship Taylor suggested functional foremanship for better supervision of workers. Under functional foremanship, there are specialist foremen for each job. He classified specialist foremen into two departments, namely planning and production departments. Both the departments have eight foremen in all The names and functions of these foremen are as follows: (a) Planning Department: Route clerk Determining the process of production and the route through which the raw materials will pass. Instruction card clerk Laying down instructions according to which the workers are required to perform work. Time and cost clerk Setting the time table for doing a job as per the pre-determined route and time schedule. He specifies the material and labour cost with respect to each operation. Disciplinarian Maintaining proper discipline in the factory.
(b) Production Department: Gang boss Arranging machines, materials, tools, workers, etc for the job. Speed boss Maintaining the planned speed of production, investigating the causes for delay and remove them. Repair boss Maintenance of the machines and equipments, proper arrangements for their oiling, greasing, cleaning and repair, preventing misuse of machines, etc. Inspectors Seeing that the work confirms to the standard of quality laid down by the planning department.
Question 70. Explain following techniques of scientific management. (a) Time study (b) Motion study (c) Function foremanship (All India 2019; Delhi 2019) Answer: (a) Time study: It refers to determine the standard time required to complete a particular activity. The standard time is determined on the basis of average time taken to complete the work. This study is conducted with the help of a stop watch. The main objective of this study is to get the estimated figure of labour cost, to determine the number of required workers and to decide the suitable incentive plan.
(b) Motion study: This is the analysis of physical movements in doing a work. Every work involves various forms of human movements such as lifting, holding, turning, etc. Under motion study, each movement is analysed to find out easier ways of doing the work and eliminate useless motions. Following steps are involved in motion study:
(c) Functional foremanship Taylor suggested functional foremanship for better supervision of workers. Under functional foremanship, there are specialist foremen for each job. He classified specialist foremen into two departments, namely planning and production departments. Both the departments have eight foremen in all The names and functions of these foremen are as follows: (a) Planning Department: Route clerk Determining the process of production and the route through which the raw materials will pass. Instruction card clerk Laying down instructions according to which the workers are required to perform work. Time and cost clerk Setting the time table for doing a job as per the pre-determined route and time schedule. He specifies the material and labour cost with respect to each operation. Disciplinarian Maintaining proper discipline in the factory.
Question 71. Explain following principles of general management. (a) Division of work (b) Authority and responsibility (c) Discipline (All India 2019) Answer: (a) Division of work Every employee should be assigned only one type of work. It means that total work is divided into small tasks/jobs and a trained specialist performs each job. The objective of division of labour derive the benefits from the principle of specialisation which can be applied to all work. For example, publishing of a book involves several operations like computer typing of text material, proof reading, printing, binding, etc. All the operations are performed by different people who are experts in their respective field.
(b) Authority and responsibility Authority means the right to give orders and obtain obedience. On the other hand, responsibility means obligation to complete the assigned task on time. According to Fayol, there must be a balance between authority and responsibility. Excess of authority without matching responsibility may result in misuse of authority, whereas excess responsibility without adequate authority may lead to failure of organisational goals.
(c) Discipline: Discipline is obedience, application and outward mark of respect. It means obedience to the rules of the organisation on the part of both superiors and subordinates. Discipline is necessary for the smooth running of the organisation. According to Fayol, ‘Discipline requires good superiors at all levels, clear and fair agreement and judicious application of penalties’. Discipline does not mean only rules and regulations but it also means development of commitment on the part of employees towards organisation as well as towards each other.

(b) Subordination of individual interest to general interest The interest of an organisation is to achieve its goals. These goals are achieved after integrating the efforts of different individuals who are working in the organisation to satisfy their own personal needs. Sometimes, an individual starts giving priority to his own interest. Thus, the interests of various stakeholders, i.e. owners, shareholders, creditors, financers and the society cannot be sacrificed for one individual.
(c) Stability of tenure of personnel According to this principle, there should be a reasonable security of jobs. Labour turnover should be minimised to maintain organisational efficiency. Personnel should be selected and appointed after due and rigorous procedure.
Question 73. Explain the following techniques of scientific management. (a) Method study (b) Fatigue study (c) Differential piece wage system (All India 2019) Answer: (a) Method study It refers to identifying the most suitable way to do a particular activity. To conduct this study, process chart and operation research techniques are used. The main objective of this study is to minimise the cost of production and maximise the quality and level of consumer satisfaction.
(b) Fatigue study Fatigue in work is natural. When the worker is given continuous work, he will get tired and lose speed and efficiency. He needs rest after working for a few hours. Scientific management studies the nature of work to determine the standard time for finishing the job and to find out when the workers need rest. The nature, time and period of rest are pre-determined. Necessary changes should also be made in the working methods and conditions to reduce fatigue.
(c) Taylor wanted to differentiate between efficient and inefficient workers. Under this system of wage payment, wages are paid on the basis of work done. According to him, higher rates were given to the workers who are producing standard products or more and lower rates were given to those who are producing less. e.g. Standard output = 100 units/day Wage rate 1 = ₹ 10/unit for standard output (100 units) or more Wage rate 2 = ₹ 7/unit for below standard output Worker 1 = Output 99 units Wages = 99 × 7 = ₹ 693 Worker 2 = Output 101 units Wages = 101 × 10 = ₹ 1010 Thus, a difference of ₹ 317 (1,010 – 693), for different of 2 units is enough to motivate the inefficient work for more output.

(b) Equity: The principle of equity implies a sense of fairness and justice to all workers working in an organisation. Observance of equity alone would make workers loyal and devoted to the organisation. Equity does not mean equal salary to a peon and supervisor. But equity means application of same disciplinary rules, leave rules, etc irrespective of their grade, position and gender, language, religion or nationality, etc. For example, the rules for granting medical leave to an employee should be same irrespective of their position, grade or gender.
(c) Initiative According to Fayol, ‘Initiative means taking the first step with self motivation, it is thinking out and executing the plan’. It is one of the traits of an intelligent person. Initiative should be encouraged because employees get satisfaction when they are allowed to take initiative. But it does not mean going against the established practices of the company for the sake of being different.
Question 75. Karan Nath took over ‘D’ North Motor Company’ from his ailing father three months ago. In the past, the company was not performing well. Karan was determined to improve the company’s performance. He observed that the methods of production as well as selection of employees in the company were not scientific. He believed that there was only one best method to maximise efficiency. He also felt that once the method is developed, the workers of the company should be trained to learn that ‘best method’. He asked the Production Manager to develop the best method and carry out the necessary training. The Production Manager developed this method using several parameters right from deciding the sequence of operations, place for men, machines and raw materials till the delivery of the product to the customers. This method was implemented throughout the organisation. It helped in increasing the output, improving the quality and reducing the cost and wastage. Identify and explain the principles and the technique of scientific management followed hy the Production Manager in the above case.CBSE 2018 Answer: The principles of scientific management followed in the above case are : (i) Science, not rule of thumb According to Taylor, each job should be performed in an organisation as per the scientific approach, as there is always one best method to maximise efficiency. This method can be developed through study and analysis. Selecting ‘one best method’ for activities can result in saving time, effort, money and resources.
(ii) Development of each and every person to his/her greatest efficiency According to this principle, ‘Each person should be scientifically selected and then assigned work as per their specialisation and in any case, if training is required, then impart training to them as efficient employees would produce more and earn more’. Worker training is essential to learn the ‘best method’ developed as per the scientific approach. This would ensure greatest efficiency for both, workers and the organisation.
The techniques of scientific management followed in this case are: (i) Standardisation It is the process of setting standards for every business activity, process, raw materials, time, machinery and methods, to achieve efficiency. Standardisation of product implies that the size, design, quality, shape etc of the product should meet the requirements and tastes of consumers. Simplification means eliminating superfluous sizes, varieties and dimensions. Its aim is to:
- Eliminate unnecessary diversity of products and thereby reduce costs.
- Help in achieving economy in the use of required machines and tools.
(ii) Method study This technique of scientific management is conducted to find out the ‘one best method or way’ of performing a particular task. The objective of this study is to minimise the cost of production and maximise the quality and satisfaction of the customer.
Question 76. Explain any four characteristics of ‘principles of management.’ (Delhi 2016) Or Explain any four points that highlight the nature of principles of management. (Delhi 2016; Foreign 2016) Or Describe the nature of principles of management with the help of any four points. (All India 2016) Answer: Following points characterise the nature of management principles: (i) Universal applicability These principles are universal and can be applied in all types of organisations whether it is profit making or non-profit making, small or large, private or government and manufacturing or service sector. They are equally applicable in a school, government office, military organisation, etc. They are also applicable to a limited company with separate departments like production, finance, marketing, etc.
(ii) General guidelines Management principles are general guidelines, as they cannot be applied blindly in all the situations. They do not provide readymade strait jacket solutions to all managerial problems, but only give the solution of a given problem.
(iii) Formed by practice and experimentation: The principles of management are developed after deep and thorough research work. Proper observations and experiments are conducted under different conditions by leaders and scholars of management thoughts to develop them. Thus, they contribute to development of management both as a science and an art. These are also evaluated on the basis of experience of managers.
(iv) Flexible The management principles are dynamic and not static or rigid prescriptions, which are to be followed absolutely. They are flexible in nature and can be modified by the manager as per the given situation.
Question 77. Explain any four points which highlight . the importance of principles of management. (All India 2016; Foreign 2016) Answer: Four points which highlight the importance of principles of management are: (i) To provide managers with useful insights into reality Principles help managers to improve their knowledge and understanding of managerial situations. These principles enable managers to learn from past mistakes and conserve time by solving recurring problems quickly. Hence, we can say, these principles provide managers an insight of real world situations.
(ii) Optimum utilisation of resources and effective administration We are aware of the fact that resources are limited in nature. Optimum utilisation of resources emphasise that resources should be utilised in such a manner that it should give maximum benefit with minimum cost. It also increases the efficiency of management, as through these principles managers adopt a systematic and logical approach to overcome the problems and discard hit and trial approaches.
(iii) Scientific decision Management principles help in thoughtful decision- making because they are based on logic rather than blind faith. Such decisions are free from bias and prejudice. These principles develop scientific approach as they give a realistic and subjective measurement for evaluation.
(iv) Meeting changing environment requirements Modem business environment is complex and ever-changing. In order to be successful, organisations have to adapt to these changes. Principles are dynamic in nature. They are flexible and frequently adapt to changes, which are favourable and profitable for the business.
Question 78. With the help of a diagram explain ‘Functional Foremanship’ as a technique of scientific management. (Delhi 2015) Answer: Functional foremanship Taylor suggested functional foremanship for better supervision of workers. Under functional foremanship, there are specialist foremen for each job. He classified specialist foremen into two departments, namely planning and production departments. Both the departments have four foremen in all.
The names and functions of these foremen are as follows: (i) Planning Department: Route clerk Determining the process of production and the route through which the raw materials will pass.
Instruction card clerk Laying down instructions according to which the workers are required to perform work. Time and cost clerk Setting the time table for doing a job as per the pre-determined route and time schedule. He specifies the material and labour cost with respect to each operation. Disciplinarian Maintaining proper discipline in the factory.

Question 79. Explain the following techniques of scientific management (Delhi 2015) (i) Differential piece wage system (ii) Motion study Answer: (i) Differential piece wage system Differential piece wage system is the strongest motivator for a worker to reach standard performance. It is a method of wage payment in which efficient and inefficient workers are paid at different rates. In this method, increase in efficiency is co-related with an increase in the wage rate.
That is why, an efficient worker gets more wages, whereas, an inefficient worker gets less. Workers are paid on the basis of number of units produced. If a worker produces more than a certain number of units (standard output), he gets higher wage per piece/ units, on his total output. If he produces below the standard number, he gets lower rate per piece. Because of different rates of wage for different sets of workers, this is known as differential piece rate plan.
(ii) Motion study This is the analysis of physical movements in doing a work. Every work involves various forms of human movements such as lifting, holding, turning, etc. Under motion study, each movement is analysed to find out easier ways of doing the work and eliminate useless motions. Following steps are involved in motion study: (a) Selection of efficient workers. (b) Analysis of the motions involved in a work. (c) Finding the minimum time involved in doing a work. (d) Keeping record of the best moves and unnecessary/unproductive actions.
Question 80. Explain the following techniques of scientific management: (Delhi 2015) (ii) Time study (ii) Simplification of work Answer: (i) Time study It determines the standard time taken to perform a well-defined job. Time measuring devices were used to conduct this study. This type of study is helpful in deciding the time required to perform a job. It also helps in determining a fair day’s work for the workman and it also facilitates in determining incentive schemes and labour costs.
(ii) Simplification of work It means ehminating superfluous sizes, varieties and dimensions in a product. Its aim is to:
- Helps in achieving economy in the use of required machines and tools.
Question 81. Explain the following principles of management. (i) Subordination of individual interest to general interest (ii) Development of each and every person to his or her greatest efficiency (All India 2015) Answer: (i) Subordination of individual interest to general interest The interest of an organisation is to achieve its goals. These goals are achieved after integrating the efforts of different individuals who are working in the organisation to satisfy their own personal needs. Sometimes, an individual starts giving priority to his own interest. Thus, the interests of various stakeholders, i.e. owners, shareholders, creditors, financers and the society cannot be sacrificed for one individual.
(ii) Development of each and every individual to his or her greatest efficiency According to this principle, ‘Each person should be scientifically selected and then assigned work as per their specialisation and in any case, if training is required, then impart training to them as efficient employees would produce more and earn more’.
If training is required, then impart training to thym as efficient employees would produce more and earn more’. Worker training is essential to learn the ‘best method’ developed as per the scientific approach. This would ensure greatest efficiency for both, workers and the organisation.
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1. Principles of management are not (a) absolute (b) flexible (c) universal (d) behavioural Answer: (a) absolute
Question 2. Which of the following is not the principle of management given by Taylor? (a) Cooperation, not individualism (b) Science, not rule of thumb (c) Harmony, not discord (d) Functional foremanship Answer: (d) Functional foremanship
Question 3. WTiat is the objective of functional foremanship? (a) Improve quality of supervision of workers (b) Improve quality of work (c) Improve quality of production (d) None of the above Answer: (a) Improve quality of supervision of workers
Hint: The primary objective of functional foremanship is to improve the quality of supervision of workers. According to Taylor, a single worker or supervisor cannot be expected to be an expert in all aspects.
Question 4. How are principles of management formed? (a) By experience of customers (b) By propagation of social scientists (c) By experience of managers (d) By scientists, in a laboratory Answer: (c) By experience of managers
Question 5. Which of the following statements best describe the principle of division of work? (a) Resources should be divided among jobs (b) Labour should be divided (c) Work should be divided into small tasks (d) It leads to specialisation Answer: (c) Work should be divided into small tasks
Hint: According to Fayol, if work is divided into small tasks and assigned to trained specialists, then it will help in taking the advantage of specialisation.
Question 6. According to which principle, powers and duties should go hand in hand? (a) Coordination (b) Unity of direction (c) Authority and responsibility (d) Discipline Answer: (c) Authority and responsibility
Hint: According to Fayol, there must be a balance between authority and responsibility. Excess of authority without matching responsibility may result in misuse of authority, whereas excess responsibility without adequate authority may lead to failure of organisational goals. Therefore, authority and responsibility should go hand in hand.
Question 7. Under work study technique of scientific management, involves change in the attitude of workers and management. Both should realise the importance of the other and should cooperate with each other. (a) functional foremanship (b) standardisation and simplification of work (c) mental revolution (d) None of the above Answer: (c) mental revolution
Hint: Mental revolution involves change in the attitude of workers and management. Both should aim to increase the size of surplus. Managers should share their gains with workers, while workers should contribute to increase profits. This attitude will bring prosperity to both, the company as well as the workers.
Question 8. What is the main objective of simplification in scientific management? (a) To determine the productive moments (b) To determine the unproductive moments (c) To determine the best possible way or method to perform a task (d) To eliminate unnecessary diversity of products Answer: (d) To eliminate unnecessary diversity of products
Hint: The main objective of simplification in scientific management is to eliminate unnecessary diversity of products. It results in saving cost of labour, machines and tools. It helps in achieving economy in the use of required machines and tools.
Question 9. FW Taylor focuses on (a) increasing productivity (b) increasing profit (c) minimising productivity (d) minimising growth Answer: (a) increasing productivity
Question 10. Gang plank is introduced in which principle? (a) Authority and responsibility (b) Initiative (c) Scalar chain (d) Coordination Answer: (c) Scalar chain
Question 11. “He/she keeps machines, materials, tools etc ready for operations by concerned workers”. Whose work is described by this sentence under functional foremanship? (a) Instruction and clerk (b) Repair boss (c) Gang boss (d) Route clerk Answer: (c) Gang boss
Hint: Gang boss keeps machines, materials, tools etc ready for operations by concerned workers, i.e. he is responsible for keeping machines and tools Hint ready for work.
Question 12. The principles of management is significant because of (a) initiative (b) adaptation to changing technology (c) optimum utilisation of resources (d) increase in efficiency Answer: (d) increase in efficiency
Hint: The principles of management helps in increasing efficiency in production as the principles lay down the general guidelines so that a manager can take valuable decisions or appropriate steps to accomplish desired goals.
Question 13. This technique of scientific management has an objective to find out how long person can perform the standard task without any adverse effects. Which technique is discussed here? (a) Work study technique (b) Motion study technique (c) Fatigue study technique (d) Differential piece wage system Answer: (c) Fatigue study technique
Question 14. Which of the following statement is incorrect? (a) The aim of both Taylor and Fayol is to maximise the efficiency and achieve the aims (b) Taylor and Fayol both advocated on division of work and responsibility (c) Both Taylor and Fayol have contributed immensely to the knowledge of management (d) None of the above Answer: (d) None of the above
Hint: None of the above statements are incorrect as Taylor and Fayol, both focused on maintaining good industrial relations. They give solutions to managerial problems. They presented a systematic study on management. Both of them develop their ideas, thoughts and principles after a thorough analysis and experimentation.
CBSE NCERT Solutions
NCERT and CBSE Solutions for free
Principles of Management Class 12 Business Studies Notes and Questions
Please refer to Principles of Management Class 12 Business Studies notes and questions with solutions below. These revision notes and important examination questions have been prepared based on the latest Business Studies books for Class 12 . You can go through the questions and solutions below which will help you to get better marks in your examinations.
Class 12 Business Studies Principles of Management Notes and Questions
Q. 1. In your school, you observe that books are kept in office, chalks in the library and office records in the staff room. 1. Which principle of management is violated here and why? 2. How will that affect the achievement of school objectives? 3. As a manager, what steps will you take to rectify the shortcomings? Ans. 1. The principle of ‘Order’ 2. In the absence of orderliness, school objectives will not be achieved efficiently and effectively. 3. Things should be placed at appropriate places to achieve maximum efficiency with given time framework. Q. 2. The production manager of an automobile company asked the foreman to achieve a target production of 200 scooters per day. But he did not give him the authority of requisition tools and materials from the stores department. Can the production manger blame the foreman if he is not able to achieve the desired target? Explain briefly the principle relating to the situation. Ans. No, the production manager cannot blame the foreman because he did not give him the authority to requisition tools and materials form the stores department. Since he has no authority, he could not fulfill his responsibility. In this case the principle of ‘Authority and Responsibility’ is violated. Fayol suggested tht there must be a balance between authority and responsibility. Authority and responsibility must go hand in hand. Responsibility without adequate authority will make the subordinate ineffective, I.e., he will not be able to perform his duties properly. At the same time giving authority without fixing responsibility may lead to misuse of of authority. Q. 3. Soniya Ltd. was engaged in the business of manufacturing auto components. Lately, its business was expanding due to increased demand for cars. The competition was also increasing. In order to keep its market share intact, the company directed its workforce to work overtime. But this resulted in many problems. Due to increased pressure of work the efficiency of workers declined. Sometimes, the subordinates had to work for more than one superiors. The workers were becoming indisciplined. The spirit of teamwork, which had haracterized the company previously, had begun to wane. Identify any three principles of management (as given by Henry Fayol) which were begin violated, quoting the lines from the above case. Ans. 1. Unity of command “Sometimes, the subordinates had to work for more than one superiors.’ 1. Discipline ‘ The workers were becoming indisciplined.’ 1. Spirit de corps ‘The spirit of teamwork, which had characterized the company previously, had begun to wane.’ Q. 4. The production manager of Harsh Ltd. instructs a salesman to go slow in selling the product, where the marketing manager is insisting on fast selling to achieve the target. Which principle of management is being violated in this case? Ans. Unity of command Q. 5. Kanika and Priyanka are typists in a company having same educational qualifications. Kanika is getting Rs. 16000 per month and Priyanka Rs. 10000 per month as salary for the same working hours. Which principle of management is violated in this case. Ans. Principle of equity Q. 6. Rishabh, a manager, very often speaks to people at all levels, passing on instructions regarding his department and also the other departments. Which principle of management is being overlooked? Ans. Principle of Scalar Chain. Q. 7. The management and workers have entered into an agreement that workers will do overtime to cover up looses of the company. In return, the manager will increase the wages. But management later refused to increase the wages. Name the principle violated in this situation. Ans. Principle of discipline Q. 8. In Simran Ltd., an employee has the objective of maximizing his salary, but the organizational objective is to maximize output at competitive cost. There was some dispute on this for a while. Eventually, the organization’s interest was given priority over employees’ interest. Name the principle related to this situation. Ans. Principle of subordination of individual interest to general interest. Q. 9. Radhika opens a jewelry showroom in Jaipur after completing a course in jewelry designing. She has employed eleven persons in her showroom. For greater productivity, she divides the work into small tasks and each employee is trained to perform his/her specialized job. The sales persons are allowed to close a deal with a buyer by giving a maximum of 10% discount, whereas the decision to given any further discount rests with Radhika as the final authority. In the earlier days of starting of the business, five of her employees were asked to put in extra hours of work. In return she had promised to give them a special incentive within a year. Therefore, after six months when the business was doing well, she awarded a cash bonus to each of these employees to honour her commitment. However, when it comes to setting the conflicts among her employees, she tends to b e more biased towards her female employees. In context of the above case: 1. Identify and explain the various principles of management that are being applied by Radhika by quoting lines from the paragraph. 2. Identify and explain the principle of management which is being violated by Radhika by quoting lines from the paragraph. 3. State any one effect of the violation of the principle of management by Radhika as identified in part (b) of the question. Ans. 1. The various principles of management that are being applied by Radhika are listed below: Principle of Division of work: “For greater productivity, she divides the work into small tasks and each employee is trained to perform his/her specialized job.” Principle of Centralization and Decentralization: “The sales persons are allowed to close a deal with a buyer by giving a maximum of 10% discount, whereas the decision to give any further discount rests with Radhika as the final authority.” Principle of Discipline: “Therefore, after six months when the business was doing well, she awarded a each bonus to each of these employees to honour her commitment.” 1. The principle of management which is being violated by Radhika is Equity. “However, when it comes to setting the conflicts among her employees, she tends to be more biased towards her female employees.” 1. One effect of the violation of the Principle of Equity is that it may lead to job dissatisfaction among the male workers. Q. 10. Neeraj is selected for the post of software developer in an IT Company. On the first day of his joining Mehul, his project manager tells Neeraj that during the course of his work he will come across many such opportunities which may temp him to misuse his powers for individual or family’s benefit at the cost of larger general interest of the company. In such situations, he should rather exhibit exemplary behavior as it will raise his stature in the eyes of the company. Also, for interacting with anyone in the company on official matters, he should adopt the formal chain of authority and communication. In context of the above case: 1. Identify and explain the various principles of management that Mehul is advising Neeraj to follow while doing his job. 2. List any two values that Mehul wants to communicate to Neraj. Ans. The various principles of management that Mehul is advising Neeraj to follow while doing his job are as follows: 1. Subordination of Individual Interest to General Interest: 2. Scalar Chain: The two values that Mehul wants to communicate to Neeraj are: 1. Honesty 2. Self restraint Q. 11. Davinder is a class twelfth commerce student in a reputed school in Punjab. Satinder is his elder brother who is doing his Masters in Hospital administration from Delhi after completing his B. Sc course. During vacations when Satinder comes home, Davinder shows him the business studies project that he is preparing on the topic ‘Principles of Management’. Satinder tells him that these principles are also a part of MBA course curriculum at the beginner’s level as they form the core of management in practice. But he finds these principle different from those of pure science. In context of the above case: 1. Outline the concept of principles of management. 2. Why does Satinder find the principle of management different from those of pure science? 3. Why do the principles of management form the core of management in practice? Explain by giving any two points highlighting the importance of principles of management. Ans. 1. The principles of management serve as a broad and general guideline for the managerial decision making and action. 2. Satinder finds the principles of management different from those of pure science because the management inciples are not as rigit as principles of pure science. This is due to the fact that they deal with the human behavior and thus, need to be applied creatively in the light of given situation. 3. The importance of principles of management is described below: 1. Providing managers with useful insights into reality: 2. Optimum utilization of resources and effective administration: Q. 12. Nutan Tiffin Box service was started in Mumbai by Mumbai dabbawalas. The Dabbawalas who are the soul of entire Mumbai aim to provide prompt and efficient services by providing tasty homemade tiffin to all office goers at right time and place. The service is uninterrupted even on the days of bad weather, political unrest and social disturbances. Recently they have started online booking system through their website’ mydabbawals.com’. owing to their tremendous popularity amongst the happy and satisfied customers and members, the dabbawalas were invited as guest lecturers by top business schools. The Dabbawals operate in a group of 25-30 people along with a group pleader. Each group teams up with other groups in order to deliver the tiffin on time. They are not transferred on frequent basis as they have to remember the addresses of their customers. They follow certain rules while doing trade-No alcohol during working hours; No leave without permission; Wearing of white cap & carrying ID cards during business hours. Recently on the suggestion of a few self motivated fellow men, the dabbawalas thought out and executed a plan of providing food left in tiffins by customers to slum children. They have instructed their customers to place red sticker if food is left in the tiffin, to be fed to poor children later. 1. State any one principle of management given by Fayol & one characteristic of management mentioned in the above case. 2. Given any two values which the Dabbawalas want to communicate to the society. Ans. 1. Principles of management (any one) 1. Stability of Personnel 2. Initiative 3. Discipline 4. Esprit de corps Characteristic of management (any one) 1. Goal oriented 2. Group activity Values that have been communicated by the Dabbawalas: (any two) 1. Fulfilling social responsibility; 2. Empathy towards disadvantaged children; 3. Team work (or any other suitable value) Q. 13. ‘Aapka vidyalaya’ believes in holistic development of students and encourages team building through a mix of curricular, co-curricular and sports activities. On its founders day a stage performance had to be put up. A committee of ten prefects was constituted to plan different aspect of the function. They all decided to use recycled paper for decoration. There was a spirit of unit and harmony and all members supported each other. With mutual trust and belongingness the programme was systematically planned and executed. Kartik, one of the prefects realized that unknowingly the group had applied one of the principles of management while planning and executing the programme. He was so inspired by the success of the function that he asked his father to apply to same principle in his business. His father replied that he was already using this principle. 1. Identify the principle of management applied for the success of the programme. 2. State any two features of management highlighted in the above para. 3. Identify any two values which ‘Aapka Vidyalaya’ communicated to the society. Ans. 1. Espirit de corps 2. 1. Management is pervasive–‘ …he asked his father to apply the same principle in his business.’ Management is pervasive as it can be applied to all types/levels of organizations. 2. Management is a group activity –‘ There was a spirit of unity and harmony and all members supported each other.’ Management is a group activity because it requires team work and/or coordination of individual efforts. 3. Values being communicated to the society: (Any two) 1. Concern for the environment. 2. Holistic development of children. 3. Teamwok Q. 14. Nikita and Salman completed the MBA and started working in a multinational company at the same level. Both are working hard and are happy with their employer. Salman had the habit of backbiting and wrong reporting about his colleagues to impress his boss. All the employees in the organization knew about it. At the time of performance appraisal the performance of Nikita was judged better than Salman. Even then their boss, Mohammed Sharif decided to promote Salman stating that being a female Nikita will not be able to handle the complications of a higher post. 1. Identify and explain the principle of management which was not followed by this multinational company. 2. Identify the values which are being ignored quoting the liens the above para. Ans. 1. The principle violated is EQUITY. It advocates that there should be no discrimination against anyone on account of sex, religion, language, caste, belief, nationality etc. It emphasizes kindliness and justice in the behavior of managers towards the workers to ensure loyalty and devotion. The valuation which are being ignored are: 1. Good human behavior because ‘Salman had the habit of backing and wrong reporting about his colleagues to impress his boss.’ 2. Gender Equality because ‘Their boss decided to promote Salman stating that being a female Nikita will not be able to handle the complications of a higher post.’ Q. 15. Sigma Ltd. is a large company manufacturing electric motors. The company has several departments – Production, Marketing, Finance and HR. Mr. Shashank, CEO of the company set the target sale of 10 crore in a month. To increase the sales, the marketing manager, Mr. Ishaan insists on offering 10% discount to customers. But the finance manager, Mr. Mohak does not approve such discount as it would mean loss of revenue. Because of dual subordination, the sales manager, Mr. Anshik could not achieve the sales target. 1. Which concept of management Sigman Ltd. is lacking? State it 2. Which principle of management has been overlooked by this company? State it. 3. Which principle of management has been overlooked by this company? State it. Ans. 1. The company is lacking ‘Coordination’. It is the process by which the activities of different departments are synchronized to ensure unity of action. 1. Unity of command There should be one and only one boss for every individual employee.If an employee gets orders from two superiors at the same time, the principle of unity of command is violated.Consequences of violation:Authority is undermined, discipline is in jeopardy, order is disturbed and stability is threatened. 1. Spirit de Corps Management should promote a team spirit of unity and harmony6 among employees.It is necessary for coordination. Q. 16. ABC Ltd. is engaged in producing electricity from domestic garbage. There is almost equal division of work and responsibility between workers and management. The management even takes workers into confidence before taking important decisions. All the workers are satisfied as the behavior of the management is very good. 1. State the principle of management described in the above para. 2. Identify any two values which the company wants to communicate to the society. Ans. 1. The principle of Taylor described in the above para is Cooperation, Not Individualism. It states that there should be complete cooperation between the labour and the management.Competition should be replaced by cooperation. Values which the company wants to communicate to the society are: 1. Good behavior in human interaction. 2. Concern for the environment.
Q. 17. Voltech India Ltd. is manufacturing LED bulbs to save electricity and running under heavy losses. To revive from the losses, the management thought of shifting the unit to a backward area where labour is available at a low cost. The management also asked the workers to work overtime without any additional payment and promised to increased to wages of the workers after achieving its mission. Within a short period the company started earning profits because both the management and the workers honoured their commitments. 1. State the principle of management described in the above para. 2. Identify any two values that the company wants to communicate to the society. Ans. 1. The principle of management described in the above para is Discipline. Discipline is the obedience to organizational rules and employment agreement which are necessary for the working of the organization. Values that the company wants to communicate to the society are: 1. Concern for the environment 2. Development of backward regions Q. 18. Kushal Ltd. is a leading automobile company in which the various departments are setting up their own objectives without paying any interest to the organizational objectives. 1. Which aspect of management the company is lacking? What will be its impact on the organization? 2. Identify the principle of management which has been overlooked by this organization. 3. State any two values neglected by the people of this organization. Ans. 1. The company is lacking ‘Coordination’. Its different departments like production, marketing, etc. do not coordinate their work.In the absence of coordination, there will be overlapping and chaos instead of harmony and integration of activities.The company will fail to achieve its objectives. 1. Subordination of individual interest to general interest. 2. Values: 1. Mutual cooperation 2. Unity of action 3. Optimum utilization of resources Q. 19. Telco Ltd. is manufacturing files and folders from old clothes to discourage use of plastic fields and folders. For this, they employ people from nearby villages where very less job opportunities are available. An employee, Harish, designed a plan for cost reduction but it was not welcomed by the production manager. Another employee gave some suggestion for improvement in design, but it was also not appreciated by the production manager. 1. State the principle of management described in the above para. 2. Identify any two values that the company wants to communicate to the society. Ans. 1. Initiative. It means eagerness to initiate action without being asked to do so. 2. Values which the company wants to communicate to the society are: 1. Sensitivity towards the environment 2. Creation of job opportunities 3. Development of backward regions. Q. 20. Khandelwal Ltd., a tyre manufacturing concern has been established for more than ten years. Having made good profits in the past, company wanted to expand further and hence did not declare bonus for the previous year. The workers got agitated and trade union declared strike and demanded bonus and other facilities. The management decided not to give into their demands. 1. Which principle of scientific management is overlooked in the given case? 2. State any two values overlooked/ignored by the management in the above case. Ans. 1. Harmony, not Discord 2. Values overlooked are: 1. Mutual understanding 2. Empathy 3. Peace and stability 4. Law and Order 5. Sense of belongingness (any two) Q. 21. Hritik is desirous of setting up a small factory to manufacture different kinds of eco-friendly packaging materials. He proposes to adopt to logical approach to his business rather than hit and trial method as he knows that this can result in tremendous saving of human energy as well as wastage of time and materials. He plans to adopt paternalistic style of management in practice in order to avoid any kind of class-conflict that may emerge between him and the workers. Moreover, he plans to seek the opinion of his workers before taking any important decisions and also offers incentives to them for providing valuable suggestions for the business. In context of the above case: 1. Identify and explain the various principle of scientific management that Hritik plans to apply in his business. 2. List any two values that he wants to communicate to the society by offering eco-friendly packaging material. Ans. The various principle of scientific management that Hritik plans to apply in his business are described below: 1. Science, not Rule of Thumb: 2. Harmony, Not Discord: 3. Cooperation, Not Individualism: The two values that Harit wants to communicate to the society by offering eco-friendly packaging material are: 1. Concern for environment 2. Sense of responsibility Q. 22. Gaurika has been appointed as the chief organizer of a weeklong cultural event. Being a staunch follower of scientific management, she decides to execute her work by putting into practice the various techniques of scientific management. On the basis of several observations, she is able to determine that the standard time taken by the security officer at the gat to check the credentials of each visitor is 30 seconds. So she decides to employ two persons on this job for every function along with the other necessary support staff. She considers the fact that every day, the functions will take place in three shifts of four hours each, therefore it is important to give breaks to the support staff even in a single shift to take her/his lunch etc. moreover, on introspection, she determines that the best way to distribute refreshment boxes to the visitors will be to hand it over to them at the exit gate as it would help to save time and eliminate any kind of confusion. In the context of the above case: 1. Identify and explain the various techniques of work study which have been put into practice by Gaurika. 2. List any two values that Gaurika wants to communicate to the society. Ans. 1. The various techniques of work study which have been put into practice by GaurikaBare outlined below: 1. Time Study: 2. Fatigue Study: 3. Method Study: The two values that Gaurika wants to communicate to the society are: 1. Optimum utilization of resources 2. Concern for employees Q. 23. ‘Study Buddy Pvt.’ Is company dealing in stationery items. In order to establish standards of excellence and quality in materials and in the performance of men and machines, the company adheres to benchmarks during production. Moreover, its products are available in limited varieties, sizes and dimensions thereby eliminating superfluous diversity of products. Identify the technique of scientific management which has been adopted by ‘Study Buddy Pvt. Ltd.’ Ans. Standardization and Simplification of Work is the technique of scientific management which has been adopted by ‘Study Buddy Pvt. Ltd.’ Q. 24. Tina and Anshu completed their MBA and started working in a multinational company at the same level. Both are working hard. Anshu has the habit of backbiting and wrong reporting about his colleagues to impress the boss. All the employees in the organization know about it. At the time of performance appraisal also Tina’s performance was rated better than Anshu. Even then their boss decided to promote Anshu stating that being a female, Tina will not be able to handle the complications of higher post. 1.Identify and explain the principle of management that was not followed by this company. 2.Identify the values being ignore. Ans. 1.Company is violating the “Principle of Equity.” 2.The values ignored are 1.Gender equality 2.eward for performance 3.Good human behavior.
Q. 25. In one of his principles, Taylor suggested that job performance should be based on scientific enquiry and not on will/wish or personal intuition of manager? 1.Name that principle. 2.What values can be followed by using this principle? Ans. 1.Principle of “Science not rule of thumb.” 2.If manager is using this technique he can follow the value of objectivity it as when decisions are taken scientifically he cannot be biased.
Q. 26. The production department of Alpha Ltd. was not performing well on detailed analysis, it was observed that the workers of that department were overburdened. They were forced to work for longer hours without any break. So the management planned to replace the production manager. They appointed Mr. Hari as the new Production Manager. He observed the average worker and note down their times. He noted down the time they worked and the time they required to be fresh to join back the work. Based on this observation, he set the break intervals for workers. He gave small breaks to workers to recharge their energy. 1. Name and explain the technique of scientific management used by Mr. Hari. 2. State the value which Mr. Hari wants to communicate to the society by allowing rest intervals to workers. Ans. 1. Fatigue study. 2. Value of humanity/sympathy/respect towards employees. Q. 27. In the staff meeting the principal of the school raised objection that teachers start the teacher after 5 to 10 minutes in third floor classes. He warned them as students are complaining about this. The teachers explained the principal that when we climb steps from ground to third floor. We get some tiredness and need 5 to 10 minutes rest before starting the lecture. The principal planned to install a lift in school so that teachers do not waste their energy on wasteful activity of climbing steps. 1. State the techniques of scientific management used by principal. 2. State any other technique of scientific management. Ans. 1. “Technique of motion study.” 2. Other two techniques: 1. Functional foremanship 2. Time study. Q. 28. In a factory the toolbox was kept under the table of every worker, whenever worker needs tools he had to bend tape out tool from tool box and keep it back after use. The newly appointed supervisor observed it and suggested to keep a stool near every worker’s chain where toolbox can he placed so that workers do not waste their energy in bending again and again. 1. Which technique of scientific management is used by New Supervisor. 2. State the objective of motion study. Ans. 1. Motion study. 2. The objective of motion study is to eliminate unproductive movements of workers. Q. 29. Mr. Mukesh used to manufacture shoes by employing labour who were easily available. When his son after completing his MBA joined the business, he analysed that if we use capital intensive method by using a machine it will reduce the cost and the quality of shoes will also improve.
1. Which technique of Scientific management is used by his son. 2. What is the objective of that technique. Ans. 1. Method Study 2. Finding the best way of doing thing. Q. 30. Mr. Kapoor, Finance manager of ABC Ltd. applied for leave to attend a family function in Amritsar. The director of the company requested him to cancel his leave as there is an important meeting schedule on that date. Mr. Kapoor immediately agreed and cancelled his trip as he thought attending meeting is more important for company’s benefit. 1. Which principle of Fayol is applied by Mr. Kapoor? 2. Explain that principle. Ans. 1. Principle of subordination of individual interest to general interest. 2. According to this principle, the interest of organization must supersede the interest of individuals or employees. In the organization all the employees are working with some objective and there is always an objective of organization. Q. 31. The manager of ABC Ltd. asked his workers to work overtime to increase the production and earn more but he did not paid extra wages to workers for extra time worked. The workers started feeling dissatisfied and stop contributing maximum. 1. Which principle of Fayol is violated in the above case. 2. Explain that principles. Ans. 1. Principle of Remuneration. 2. According to this principle, the interest of organization must supersede the interest of individuals or employees. Q. 32. Mr. Rajiv is the owner of ‘Laxmi Dairy.’ He is producing various milk products. He always tests various ways of producing different products and chooses the best and most economical way of production. He is also very particular about fixing a place for everything and he makes sure that all the employees are given a fixed place so that there is no wastage of time and delay in production. 1. Which technique of scientific management is applied by Mr. Rajiv? 2. Which principle of Henry Fayol is followed by him? Ans. 1. Method Study 2. Principle of order Q. 33. Mr. Rajiv the senior manager of Unique enterprise considered himself very wise and used to take all the decisions himself without consulting the employees, he never used to help any one nor he used to take help of anyone. The employees of unique enterprise were not working efficiently and company’s profit margin started declining to tackle the problem, the company appointed a new manager from IIM Bangalore. The new manager after joining made a policy that all the decisions will be taken after consulting employees in the meeting. All employees must give some suggestions and best suggestions will be rewarded with financial and nonfinancial incentives. This policy had a very positive effects on company. 1. State the principle of Hencry Fayol used by new manager. 2. State the technique of scientific management related to above case. Ans. 1. Principle of initiative. 2. “Cooperation not individualism.” Q. 34. In a school principal makes sure that every instruction, order or information given by him must be passed to vice-principal then Head of the department and then to teachers and students must be informed by respective teachers only. He never allows teachers to directly communicate with him. 1. Stat the Principle of Henry Fayol followed by the school principal. 2. In case of emergency which concept of Scalar Chain can be used by teacher to pass urgent message directly to principal. Ans. 1. Scalar Chain. 2. Gang-plank. Q. 35. Pawan is working as a Production Manager in CFL Ltd. which manufactures CFL bulbs. There is no class-conflict between the management and workers. The working conditions are very good. The company is earning huge profits. As a policy, the management shares the profits earned with the workers because they believe in the prosperity of the employees. 1. State the principle of management described in the above paragraph. 2. Identify any two values which the company wants to communicate to society. Ans. 1. The principle of management described in the above paragraph is ‘Harmony, not discord’. 2. The two values that the company wants to communicate to the society are: 1. Prosperity 2. Sharing Q. 36. The principles of Taylor and Fayol are mutually complementary. On believed that management should share the gains with the workers while the other suggested that employees’ compensation should depend on the earning capacity of the company and should give them a reasonable standard of living. Identify and explain the principles of Fayol and Taylor referred to in the above paragraph. Ans. The principles of Fayol and Taylor referred to in the above paragraph are ‘Remuneration of employees’ and ‘Harmony, Not Discord’. 1. Remuneration of Employees: 2. Harmony, not Discord: Q. 37. The principles of Taylor and Fayol are mutually complementary. One believed that management should not close its ears to constructive suggestions made by the employees while the other suggested that a good company should have an employee suggestion system whereby suggestions which result in substantial time or cost reduction should be rewarded. Identify and explain the principles of Taylor and Fayol referred to in the above paragraph. Ans. The principles of Fayol and Taylor referred to in the above paragraph respectively are ‘Initiative’ and ‘Cooperation and Not Individualism’. 1. Initiative: 2. Cooperation and Not Individualism: Q. 38. Hina and Harish are typists in a company having the same educational qualifications. Hina gets Rs. 3,000 per month and Harish gets Rs. 4,000 per month as salaries for the same working hours. Which principle of management is being violated in this case? Name and explain the principle. Ans. The principle of Equity has been violated in this case. It emphasizes kindliness and justice in the behavior of managers towards workers. No discrimination should be made by them on the basis of caste, creed, gender or otherwise. Q. 39. Rajveer works as a plant superintendent in a carpet making factory. In order to complete the export orders on time, the production manager asks him to make the workers work over time whereas the finance manager is strictly against this practice because it will increase the cost of production. Moreover, Rajveer feels that since the company is manufacturing handmade carpets as well as machine made carpets there is a lot of overlapping of activities. Therefore, there should be two separate divisions for both of them wherein each division should have its own in charge, plans and execution resources. In context of the above case: 1. Identify and explain the principle of management which is being violated. 2. Also identify the principle of management that Rajveer feels should be implemented in the factory. 3. Give any two differences between the principle of management as identified in part (a) and part (b) respectively. Ans. The principle of management which is being violated in stated below: 1. Unity of command: 2. Unity of direction: 3. The difference between the principle of Unity of Command and Unity of Direction is given below:
Q. 40. Gurpreet is running a retail mart in Varansi to provide various types of products of daily use under one roof to the buyers. The employee turnover in his business is very high and he is perpetually on a look out for new staff. The fact of the matter is that he lacks managerial skills and assigns work to his employees on adhoc basis without letting them settle down in a specific work. This approach of his creates a sense of insecurity among the employees and they tend to leave the job very quickly. However, he is a very god fearing person and offers fair wages to his employees so they can afford a reasonable standard of living. In context of the above case: 1. Identify and explain the principle of management which Gurpreet is unable to apply and is perpetually ona look out for new staff. 2. “He is a very god fearing person and offers fair wages to his employees so they can afford a reasonable standard of living.” Name and explain the relevant principle of management will have been brought into effect by Gurpreet. Ans. 1. Stability of Personnel; 2. Remuneration of Employees: Q. 41. After finishing her BBA degree course, Tanya gets a job of Assistant Manager in a retail company through the reference of her cousin Taruna who works in the same company as a Senior Manager. Taruna decides to guide Tanya through her experience by making her aware of the important facts about management in practice. She tells her that neither the principles of management provide any readymade, straitjacket solutions to all managerial problems nor they are not rigid prescriptions, which have to be followed absolutely. In context of the above case: 1. Identify the two features of principles of management mentioned in the above paragraph by quoting lines from the paragraph. 2. Why do the principles of management not provide readymade, straitjacket solutions to all managerial problems? The two features of principles of management mentioned in the above paragraph are as follows: 1. General guidelines: 2. Flexibile: 1. As the real business situations are very complex and dynamic and are a result of many factors, the principles of management not provide readymade, straitjacket solutions to all managerial problems. Q. 42. Raj and Simran are both qualified eye surgeons and good friends. After obtaining a certificate of practice, they decide to persue a career of their own choice. Raj starts an eye care centre in the city whereas Simran joins a government hospital in a small village. They meet after a long time in a party. Raj invites Simran to visit his eye care centre and she accepts his invitation. She observes at his clinic that there is a fixed place for everything and everyone and it is present there so that there is no hinderance in the activities of the clinic. Also, Raj always tends to replace ‘I’ will ‘We’ in all his conversations with the staff members. Later on Raj shares with her that he always deals with lazy staff sternly to send the message that everyone is equal in his eyes. In context of the above case: 1. Identify and explain the various principles of management that Raj is applying for the successful management of his eye care centre. 2. List any two values that Simran wants to communicate to the society by taking up a job in a village. Ans. 1. The various principles of management that Raj is applying for the successful management of his eye care centre are described below: 1. Order: 2. Spirit de Corps: 3. Equity: The two values that Simran wants communicate to the society by taking up a job in a village are: 1. Humanity 2. Concern for poor Q. 43. Anshul owns a small scale factory where utility items are prepared from waste material like paper mache items, paper and cloth bags, decorative material etc. over the past few weeks, he was observing that the productivity of one of his very efficient worker, Ramdas, is going down. So he decides to probe into the matter and confronts Ramdas one day. On being asked, Ramdas shares with Anshul that he has deliberately slowed down in his work as many of the less efficient workers often pull his leg saying that there is no need for him to be more efficient when everybody is being paid at the same rate. Taking a lesson from this insight, Anshul decides to implement an incentive bonus plan so as differentiate between efficient and inefficient workers. In context of the above case: 1. Name and explain the incentive bonus plan that Anshul may implement so as differentiate between efficient and inefficient workers. 2. State any two values that Anshul wants to communicate to the society by setting up a special type of business. Ans. Differential Piece wage System is the incentive bonus plan that Ashul may implement so as differentiate between efficient and inefficient workers. Q. 44. Swaraj is running an office furniture showroom. Most of his clients are businessmen and they prefer to buy goods on credit. Keeping this in mind, he has given the power to the sales manager, Mr. Bhardwaj, to offer a credit period of only 20 days, while negotiating a deal with a buyer. On a specific day, Mr. Bhardwaj finds that if he can offer a credit period of 30 days as an exception to a prospective buyer, he is likely to finalize a highly profitable deal for the business. So Mr. Bhardwaj requests Swaraj to grant him additional authority for offering a credit period of 30 days in the interest of the business. But swaraj refuses to extend his authority and as a result, the deal is not finalized. In context of the above case: 1. Can Mr. Bhardwaj be held responsible for loss of the deal? Why or why not? Give a suitable reason in support of your answer. 2. Also, explain the related principle. Ans. 1. No, Mr. Bhardwaj cannot be held responsible for loss of the deal in the above case as he was not given the necessary authority to carry out his responsibility. There is an imbalance in authority and responsibility. 2. The name of the related principle is Authority and Responsibility.
Important Notes for NCERT Class 12 Business Studies Chapter Principles of Management
Taylor s Scientific Management: F.W. Taylor (1856-1915) was an American mechanical engineer who believed in analysing the work scientifically and finds one best way to do any work. His book Principles of Scientific Management was published in 1911. Principles of Scientific Management: Taylor gave the following principles of scientific management: (1) Science and not the rule of thumb: which implies developing one standard method through work study unifying the best practices globally which would result in optimum resource utilization. (2) Harmony, Not discord: which implies that there should be mental revolution on part of managers, workers and owners to respect each other’s role and eliminate any class conflict to realize organizational objectives. (3) Cooperation not individualism: It is an extension of the Principle of Harmony, Not discord whereby constructive suggestions of workers should be adopted and they should not go on strike as both management and workers share responsibility and perform together. In fact there should be complete cooperation between the labour and the management instead of individualism. (4) Development of Each and Every Person to His or Her greatest Efficiency and Prosperity: Which implies development of competencies of all persons of an organization after their scientific selection and assigning work suited to their temperament and abilities. Techniques of Scientific Management (1) Functional Foremanship: Functional foremanship is a technique in which planning and execution are separated. There are 8 types of specialized professionals 4 each under planning and execution who keep a watch on all workers to extract optimum performance.
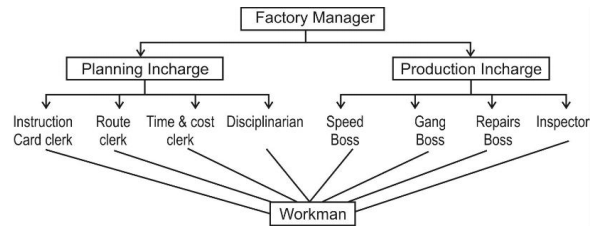
(2) Standardisation and Simplification of work: Standardization refers to developing standards for every business activity whereas Simplification refers to eliminating superfluous varieties of product or service. It results in savings of cost of labour, machines and tools. It leads to fuller utilization of equipment and increase in turnover. (3) Method Study: The objective of method study is to final out one best way of doing the job to maximise efficiency in the use of materials, machinery, manpower and capital. (4) Motion Study: Motion study seeks to eliminate unnecessary motions in the execution of a job to enable it to be completed in less time efficiently. (5) Time study: It determines the standard time taken to perform a well-defined job. The objective of time study is to determine the number of workers to be employed, frame suitable incentive schemes & determine labour costs. (6) Fatigue study: Fatigue study seeks to determine amount and frequency or rest intervals in completing a task. (7) Differential Piece Wage system: Differential Piece Wage system seeks to reward a more efficient worker by giving him/her more wages for more quantity of standard production achieved. (8) Mental Revolution: It involves a change in the attitude of workers and management towards one another from competition to cooperation. Foyol s Principles of Management: Henri Fayol (1841-1925) was a French Mechanical engineer who gave 14 general principles of Management which are as under: (1) Division of Work: Work is divided into small tasks / jobs and each one is done by a trained specialist which leads to greater efficiency. (2) Authority and Responsibility: Managers are empowered with authority to give orders and obtain obedience and responsible for the accomplishment of task for which they are granted authority. (3) Discipline: it is the obedience to organizational rules and employment agreement which are necessary for working of the organization. (4) Unity of Command: There should be only one boss for every employee. If an employee gets orders from two superiors at the save time the principle of unity of command is violated. (5) Unity of Direction: Each group of activities having the same objective must have one head and one plan. This ensures unity of action and coordination. (6) Subordination of Individual Interest to General Interest: The Interest of an organization should take priority over the interests of any one individual employee. (7) Remuneration of Employees: The overall pay and compensation should be fair to both employees and the organization. (8) Centralization and Decentralization: The concentration of decision-making authority is called centralization whereas its dispersal among more than one person is known as decentralization. Both should be balanced. (9) Scalar Chain: The formal lines of authority between superiors and subordinates from the highest to the lowest ranks is known as scalar chain. This chain should not be violated but in emergency employees at same level can contact through Gang Plank.
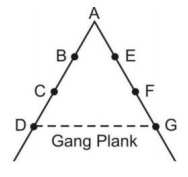
(10) Order: A place for everything (everyone) and everything (everyone) in its place. People & materials must be in suitable places at appropriate time for maximum efficiency. (11) Equity: The working environment of any organization should be free from all form of discrimination and the principles of Justice and fair play should be followed. (12) Stability of Personnel: After being selected and appointed after due and rigorous procedure the selected person should be kept at the post for a minimum period decided to show result. (13) Initiative: Workers should be encouraged to develop and carry out their plans for improvements. Initiative means taking the first step with self-motivation It is thinking out and executing the plan. (14) Esprit De Corps: Management should promote team spirit, unity and harmony among employees. Management should promote a team work.

We hope the above Principles of Management Class 12 Business Studies are useful for you. If you have any questions then post them in the comments section below. Our teachers will provide you an answer. Also refer to MCQ Questions for Class 12 Business Studies
Related Posts

Outcomes of Democracy Class 10 Social Science Notes and Questions

CBSE Class 12 English Should Wizard hit Mommy? Summary and Questions

CBSE Class 10 English Amanda Summary
- NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Class 12
- NCERT Class 12 Business Studies
- Chapter 2: Principles Of Management
NCERT Solution for Class 12 Business Studies Chapter 2 - Principles of Management
NCERT Solutions are considered an extraordinarily helpful book while preparing for the CBSE Class 12 Business Studies examinations. The solutions of NCERT have been prepared by the subject matter experts at BYJU’S.
Download PDF of NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Business Studies Chapter 2 – Principles of Management

Access NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Business Studies Chapter 2
Very short answer questions ncert business studies solutions class 12 chapter 2.
1. What makes principles of management flexible?
Management principles are varied, and one rule cannot be applied to all cases. Thus, a manager has to assess the situation and then determine the best solution to the issue at hand. For this reason, management principles are flexible.
2. State the main objective of time study.
Time study was undertaken to determine a standard time that is required to complete a designated job. This time would then be set as the standard time for the job completion. The benefit of this process is that it will help employers to determine the number of resources required to complete a particular job and also determine their wages.
3. Name the principle that is an extension of the ‘harmony, not discord’.
It is cooperation, not individualism which is the extension of the ‘principle harmony, not discord’
4. State any two causes of fatigue that may create hindrance in the employee’s performance.
Causes of fatigue that creates hindrances in the performance of employees are:
1. Not having a cordial relationship with the people in superior positions
2. Long working hours at the organisation
5. Sanaklal and Gagan started their career in Wales Limited (a printing press) after going through a rigorous recruitment process. Since they had no prior work experience, the firm decided to give them one year to prove themselves. Name the principle of management followed by Wales Limited.
Wales Limited followed the principle of ‘Stability of Personnel’. 6. Which technique is used by Taylor for distinguishing efficient and inefficient workers?
Taylor used the system of Differential Piece Wage System under which wages for workers were determined using a set standard. The workers who performed better were given higher wages than workers who performed below the standard.
Short Answer Questions NCERT Business Studies Solutions Class 12 Chapter 2
1. How is the principle of ‘Unity of Command’ useful to management? Explain briefly.
Unity of command is a principle of management that a person should be answerable to only one of his superiors. It states that if a person receives commands from two or more people, then this principle is violated. If such a principle is violated, it creates confusion for the employee, which can lead to instability and disturbance in the workflow. Therefore, to maintain a steady workflow and uninterrupted operations in the organisation, unity of command is essential for management.
2. Define Scientific Management. State any three of its principles.
Scientific management is a theory of management that was developed by Frederick Taylor in 1911. It is a classical theory of management which focuses on ways of getting work done in the best way possible to increase efficiency and effectiveness in work. Scientific management is the use of tools and techniques and personnel specialised to carry out the task for achieving quality and cost reduction.
Here are three principles of scientific management
1. Science, not rule of thumb: In this principle, Taylor laid emphasis on focusing on following management practices that are scientific in nature, and not deciding by the rule of thumb. As per the rule of thumb practice, managers will assess a situation and use trial and error to find a solution. Taylor suggested that instead of using such old methods, the approach to a situation should be scientific. Following such practice will result in a balanced result and improves efficiency and cost.
2. Harmony, not Discord: This principle states that there should be a harmonious work environment between managers and workers. The more they are on good terms with each other, the more will be the performance of the organisation. The workers should feel that they are a part of the organisation and their contributions are very much essential for the organisation to grow. Management shall respond to the needs of the workers, and in a similar way, the workers should respond back by giving their best for the organisation. Taylor termed this as a mental revolution and suggested that it would improve harmony and propel the resources to work towards the common goals of the organisation.
3. Cooperation, not individualism: As per this principle, the managers and workers should cooperate with each other in completing the activities. The work standards should be jointly determined by them, it will increase the level of involvement, and more productive results can be achieved.
3. If an organisation does not provide the right place for physical and human resources in an organisation, which principle is violated? What are the consequences of it?
In such a situation, the principle that is violated is the principle of order. It states that there should be a right arrangement of resources. In other words, the right people at the right place and at the right time. Following this approach helps in carrying out the tasks effortlessly. Whenever that principle is violated, it results in unnecessary delay at work and ensures chaos. Delays in completing work will result in a loss for the company.
4. Explain any four points regarding significance of Principles of Management.
Principles of management have the following significance
1. Management principles are based on years of observation and implementation into real-life issues. Hence, these principles guide managers in tackling real-world problems easily.
2. Management principles are based on logic rather than on beliefs. These principles are derived from real-life situations and therefore are based on logic and reasoning. It helps managers in making decisions which are devoid of personal bias.
3. Principles are the foundation of management education. They helped it to grow as a discipline, and such principles also offer a basis on which further research programs can be carried out to develop new methods and techniques.
4. Management principles help organisations to perform at the best of their capacity or, in other words, ensure optimum utilisation of the available resources.
5. Explain the principle of ‘Scalar Chain’ and gangplank.
Scalar chains can be defined as the formal chain of authority that follows a straight line from highest to lowest rank. It specifies the route through which information needs to be communicated to the designated authority.
Gangplank is an alternative route which is used in case of emergencies. Its main aim is to shorten the communication route. It facilitates communication with higher authorities directly, surpassing the defined chains of hierarchy.
Diagrammatically it can be represented as:

6. A production manager at top level in a resulted corporate, Mr. Rathore holds the responsibility for ordering raw material for the firm. While deciding on the supplier for the financial year 2017-18, he gave the order to his cousin at a higher price per unit instead of the firm’s usual supplier who was willing to lower the rates for the order. Which principle of management was violated by Mr. Rathore? What are the positive impacts of following the above identified principle?
In this case, Mr. Rathore has violated the principle of Subordination of individual interest to the general interest. As per this principle, an individual should put organisational goals on priority over any personal interest.
The positive impacts of this principle are:
1. Harmony in the working environment and a good office culture
2. Increase in employee productivity
3. Employees feel they are a part of the organisation
4. Helps in achieving organisations goals
Long Answer Questions NCERT Business Studies Solutions Class 12 Chapter 2
1. Explain the Principles of Scientific management given by Taylor.
1. Science, not rule of thumb: In this principle, Taylor laid emphasis on focusing on following management practices that are scientific in nature and not deciding by the rule of thumb. As per the rule of thumb practice, managers will assess a situation and use trial and error to find a solution. Taylor suggested that instead of using such old methods, the approach to a situation should be scientific. Following such practice will give a balanced result and improves efficiency and cost.
4. Personnel Development: An organisation has to focus on developing its workers as well as the organisation itself. Developed or skilled workers will be in a better position to help an organisation grow. To increase competitiveness, an organisation can announce incentives in order to build competitiveness among workers. Employees should be hired in a scientific manner which will put the best employee suited for a role as per their capability. Efficiency can be achieved with proper training for workers. In other words, a properly trained resource will develop himself as well as the organisation.
2. Explain the following Principles of management given by Fayol with examples:
(a) Unity of direction
(c) Espirit de corps
(e) Centralisation and decentralisation
(f) Initiative
a. Unity of Direction: This principle states that each unit of the organisation should be working towards attaining a common business objective. It helps in avoiding work overlapping and also increases profitability. For example, a company producing two different products should have separate management for each.
b. Equity: This principle focuses on treating all employees equally. Equality should be based on religion, caste, creed etc. It will promote harmony among the workers. For e.g., workers from different religions should be treated equally in a company.
c. Espirit de corps: This principle states that employees in an organisation should work with each other and maintain unity. The team spirit is improved when all resources are working unitedly, and this feeling should be promoted by the manager.
d. Order: There should be order in work being done. The management should hire the right people at right place and right time. Doing such things helps in carrying out the activities in a smooth manner. For e.g., if the user manual pages are arranged in a sequence, shuffling them will result in delay in production.
e. Centralisation and Decentralisation: Centralisation is the concentration of power or authority in the hands of selected people in an organisation. Whereas decentralisation is shifting the authority to middle and lower levels of management. For e.g., if CEO has all decision-making powers, it is centralisation, whereas if the decision-making power is distributed to managers of middle and lower levels, then it is decentralisation.
f. Initiative: As per this principle, workers should be motivated and provided incentives. They should be encouraged to suggest points for improvement, it will make them take more initiative for the development of the organisation.
3. Explain the technique of ‘Functional Foremanship’ and the concept of ‘Mental Revolution’ as enunciated by Taylor.
Functional foremanship is an extension of the principle of division of labour. It was suggested by Taylor. According to his observation, it is not possible for a single worker to be an expert in every aspect of production. Therefore, he suggested that eight persons should be performing the duties of a foreman, and therefore this came to be known as functional foremanship. Under this, the following roles were present.
1. Instruction Card Clerk: Whose role is to give instructions to workers
2. Route Clerk: His role was to specify the route of production
3. Time and Cost Clerk: His role was to prepare the time and costs sheet
4. Disciplinarian: His role was to maintain discipline in the production facility
The above four roles were working under the planning supervisor.
Now the other four persons who work under the production supervisor are:
1. Speed Boss: Responsible for the timely completion of the designated job
2. Gang Boss: Responsible for keeping machines in a ready state for work
3. Repair boss: Was responsible for keeping machines and tools in proper working condition.
4. Inspector: This person was responsible for maintaining the quality of the work.
Mental revolution: Mental revolution is the concept which revolves around bringing a change in the attitude of the workers and managers. It aims to improve the thinking of both in order to create a working environment that is conducive to both manager and worker. The basic premise of this concept is that both the worker and the manager should understand their importance in an organisation, and both of them should work towards achieving a common goal for the organisation. Management should be taking care of the needs of its workers and periodically share the benefits in the form of incentives or bonuses to keep them motivated. Workers, in return, should do their best in order to develop the organisation. Thus, we can say the mental revolution is based on mutual trust and cooperation among managers and workers, which can bring about great changes in an organisation.
4. Discuss the following techniques of Scientific Work Study:
(a) Time Study
(b) Motion Study
(c) Fatigue Study
(d) Method Study
(e) Simplification and standardisation of work.
(a) Time Study: This study determines the standard time which is required in order to perform a job. Multiple readings are taken to arrive at a standard time for a particular task. Based on that it following things can be determined
1. Number of workers required to perform the task
2. Determine the costs associated with hiring such workers (i.e. wages)
(b) Motion Study: This study was based on movements that needed to be taken while performing a task. The purpose of this study is to eliminate unwanted movements in order to complete a task in a shorter time. For this study Taylor along with his assistant Frank Gilbreth studied the movements of a worker and then categorised the same into three classes productive, incidental and unproductive. The purpose was to eliminate unproductive employees and reduce instances of incidental workers.
(c) Fatigue Study: Fatigue study was for determining the amount and frequency of rest taken during the completion of a designated task. A worker without rest will be unable to perform to his full capacity. Fatigue is detrimental to productivity hence this study is conducted to understand the standard intervals of break that help a worker regain the energy to carry on working with the same efficiency.
(d) Method Study: The objective of this study is to find the best method of completing a particular work. It takes into consideration all the activities involved in the completion of a task. By determining the best method, lower costs can be incurred along with more productivity.
(e) Standardisation and Simplification of Work: Standardisation is based on scientific management techniques. It is the setting of standards or benchmarks for any activity. The purpose of standardisation is to improve the quality of work and attain excellence. It also determines standards of performance for both man and machines.
Simplification is all about eliminating the diversity in the products that are unnecessary and utilizing the best of the resources, reducing the inventories and increasing the turnover of the organisation. In addition to reducing labour and machine cost. Simplification helps in the optimum uses of the resources and removes unnecessary costs for the organisation.
5. Discuss the differences between the contributions of Taylor and Fayol.
6. Discuss the relevance of Taylor and Fayol’s contribution in the contemporary business environment.
The principles of both Fayol and Taylor play a significant role in the contemporary business environment. These principles provide a guideline to managers for making decisions and taking appropriate actions. Business situations can be best understood with the application of these principles. Such principles are not used as it is described, but managers can take guidance from these and determine how to confront a situation. It can be used in various scenarios, and the decisions which are taken by managers will be backed by facts and logic, which makes it more applicable. By providing insight into real word business cases, they help managers in decision-making. As these principles have industry-wide applicability and are based on human behaviour, they provide insight into human and material resources. It helps in the development of an organisation by improving effectiveness and efficiency with minimum use of resources and cost.
7. ‘Bhasin’ limited was engaged in the business of food processing and selling its products under a popular brand. Lately the business was expanding due to good quality and reasonable prices. Also with more people working the market for processed food was increasing. New players were also coming to cash in on the new trend. In order to keep its market share in the short run the company directed its existing workforce to work overtime. But this resulted in many problems. Due to increased pressure of work the efficiency of the workers declined.
Sometimes the subordinates had to work for more than one superior resulting in declining efficiency. The divisions that were previously working on one product were also made to work on two or more products. This resulted in a lot of overlapping and wastage. The workers were becoming undisciplined. The spirit of teamwork, which had characterised the company previously, was beginning to wane. Workers were feeling cheated, and initiative was declining. The quality of the products was beginning to decline, and market share was on the verge of decreasing. Actually, the company had implemented changes without creating the required infrastructure.
a. Identify the Principles of Management (out of 14 given by Henry Fayol) that were being violated by the company. b. Explain these principles in brief. c. What steps should the company management take in relation to the above principles to restore the company to its past glory?
1. Following principles of management were violated:
i. Unity of Command (employees working under more than one superior)
ii. Division of Work (employees made to work on more than one product)
iii. Discipline (workers not following discipline)
iv. Espirit de corps (workers lacked spirit of team work)
v. Initiative (workers were not feeling like taking initiative)
2. The principles are described below
a. Unity of command: The workers should be reporting to only one superior. Employees receiving orders from more than one superior will result in confusion and affect work.
b. Division of work: Employees should be given specialised tasks so that they will be completed effectively and efficiently.
c. Discipline: Organisations should be following rules and regulations, and they should be followed by both workers and management.
d. Espirit de corps: The teamwork motive should be developed among employees. It will improve productivity.
e. Initiative: Motivation and incentives should be provided to workers, and they should be encouraged to provide suggestions for improvement.
3. Steps which can be taken by the company are:
i. Scientific management should be applied.
ii. Only one superior should be there to provide instruction to subordinates in order for smooth functioning.
iii. Individuals must be assigned tasks as per their specialisation. It increases productivity.
iv. Motivation and proper incentives should be provided to workers
v. Teamwork and coordination among workers should be promoted for organisational development.
8. (Further information related to the above question 7) The management of company ‘Bhasin Limited now realised its folly. In order to rectify the situation, it appointed a management consultant ‘Mukti Consultants- to recommend a restructure plan to bring the company back on the rails. ‘Mukti Consultants undertook a study of the production process at the plant of the company Bhasin Limited and recommended the following changes —
• The company should introduce scientific management with regard to production. • Production Planning including routing, scheduling, dispatching and feedback should be implemented. • In order to separate planning from operational management ‘Functional foremanship’ should be introduced. • ‘Work study’ should be undertaken to optimise the use of resources. • ‘Standardisation’ of all activities should be implemented to increase efficiency and accountability. • To motivate the workers ‘Differential Piece Rate System’ should be implemented.
(The above changes should be introduced apart from the steps recommended as an answer to Part C – Case problem 7 above.).
It was expected that the changes will bring about a radical transformation in the working of the company and it will regain its pristine glory.
a. Do you think that introduction of scientific management as recommended by Mukti consultants will result in intended outcome? b. What precautions should the company undertake to implement the changes? c. Give your answer with regard to each technique separately as enunciated in points 1 through 6 in the case problem.
1. Yes, as suggested by the new management consultant, i.e. Mukti Consultants, scientific management techniques will be helpful for the organisation. It will improve the quality and quantity of the product with a reduction in costs.
2. The following precautions need to be taken:
a. Specialised staff having training should be recruited, and existing staff can be further trained.
b. Production planning should be undertaken in a systematic way
c. Functional foremanship should be introduced with proper incentives and motivation for the employees.
d. Different other methods should be introduced apart from work study. It can be a motion study, method study, time and fatigue study.
e. Standardisation techniques can be used in case of different aspects of production
f. Employees can be offered monetary incentives so that they work more efficiently.
NCERT Solution for Class 12 Business Studies Chapter 2 – Principles of Management provides us with a brief introduction to the concepts. It provides a clear picture of the forms of principles of management.
- What is Principle? – It reflects a statement that reflects the fundamental verity about some factor based on cause and effect kinship.
- Management principles – It is a statement of truth; they act as a guide to thought and actions to the managerial decision actions and their execution.
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Business Studies Chapter 2 provides a broad range of illustrative examples, which helps the students to comprehend and learn quickly. The above-mentioned are the illustrations for the Class 12 CBSE syllabus. For more solutions and study materials of NCERT solutions for Class 12 Business Studies, visit BYJU’S or download the app for more information and the best learning experience.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.
Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Business Chapter 2 - Principles Of Management
- NCERT Solutions
- Business Studies
- Chapter 2 Principles Of Management

Class 12 NCERT Solutions Business Studies - Principles of Management - Free PDF Download
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Business studies Chapter 2 Principles of Management are provided here in easy-to-understand language. These solutions for Principles of Management are extremely beneficial for Class 12 Commerce students. Principles of Management Solutions is helpful for quickly completing your homework, projects, and preparing for exams. All questions and answers from the NCERT Book of Class 12 Business Studies Chapter 2 are provided here for you for free. These NCERT Solutions are prepared by subject experts at Vedantu and are 100% accurate.

Topics Covered in Class 12 Business Studies Chapter 2 Principles of Management
Principle of Management: The Concept
Nature of Principle of Management
Significance of Principle of Management
Taylor’s Scientific Management
Principles of Scientific Management
Techniques of Scientific Management
Functional Foremanship
Standardisation and Simplification of Work (Method Study, Motion Study, Time Study, and Fatigue Study)
Differential Piece Wage System
Fayol Principle of Management
Fayol V/S Taylor
Access NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Business Studies Chapter 2 – Principles of Management
1. What makes principles of management flexible?
Ans : The principles of management can be modified according to the demand of the situation, hence they are not rigid, and enjoy flexibility.
2. State the main objective of time study.
Ans: To determine the standard time taken to perform a well: defined job.
3. Name the principle that is an extension of the 'harmony, not discord'.
Ans: Cooperation, not individualism.
4. State any two causes of fatigue that may create hindrance in the employee's performance .
Ans: The two causes of fatigue are:
Long working hours without breaks,
Dissatisfactory working conditions.
5. Sanaklal and Gagan started their career in Wales Limited after going through a rigorous recruitment process. Since they had no prior work experience, the firm decided to give them one year to prove themselves. Name the principle of management followed by Wales Limited.
Ans: Wales Limited followed the principle of 'Stability of Personnel'.
6. Which technique is used by Taylor for distinguishing efficient and inefficient workers?
Ans : Differential Piece Wage System was used by Taylor under which workers are paid according to their efficiency. An efficient worker will get higher wages as compared to an inefficient worker.
7. How is the principle of 'Unity of Command' useful to management? Explain briefly.
Ans: Unity of command states that a person should get orders from, and be answerable to only one superior. If a person gets orders from two or more superiors at the same time, unity of command is violated and it leads to confusion for the employee regarding what tasks to be done and whom to report.
Therefore, to maintain a smooth workflow and stability in the organization, unity of command is essential for management. If there is no unity of command, all the employees will be confused regarding what is to be done, and who to listen, which will consequently disrupt the flow of work, causing delays and efficiency.
8. Define Scientific Management. State any three of its principles.
Ans : Scientific management means the use of tools and techniques and specialized personnel to carry out the task for achieving better quality and cost reduction. It is a theory of management developed by Frederick Taylor in 1911 which focuses on the ways of getting the work done in the best and most cost-effective way.
Three principles of scientific management
Science, not rule of thumb: In this principle Taylor states that the management should follow scientific methods and not the 'Rule of Thumb’ approach. Rule of thumb insists on finding solutions through trial and error approach. Taylor says that following scientific methods will result in tremendous savings of time and materials.
Cooperation not individualism: A spirit of cooperation should exist between the workers and management, and not the spirit of individualism. Both management and the workers should cooperate with each other. Management should consider all the good suggestions made by the employees and workers should never think of doing unreasonable things to get their demands fulfilled.
Development of each and every person to his /her greatest efficiency and prosperity: In this principle, Taylor said that adequate opportunities and training must be available for employees, so that with increased skills, and better knowledge about how to do a task, they can work for the improvement of their performance, and enhancement of efficiency and achieve greater heights in their careers.
9 . If an organization does not provide the right place for physical and human resources in an organization, which principle is violated? What are the consequences for it?
Ans: The principle of 'order' is violated if an organization does not provide the right place for physical and human resources in an organization.
According to this principle there should be a place for everything and everyone and every person or thing should be found in its/his allocated place. If this principle is violated then the objectives will not be achieved efficiently and effectively. Since a lot of time will be wasted in finding out the resources, a lot of wastage of energy and delay in taking decisions or performing the work will take place.
10. Explain any four points regarding the significance of Principles of management.
Ans: Significance of principles of management are as follows:
Optimum utilisation of resources and effective administration: Principles of management are designed in a way that they guide the managers whenever need arises, hence they can take decisions on time without wasting their time attempting trial and error methods. This results in enhancement of productivity, time and cost saving as well as optimum utilisation of resources.
Scientific decisions: Principles of management help in scientific decision making because the decisions based on principles are free from bias and prejudice. Here emphasis is on logic rather than blind faith.
Meeting changing environment requirements: Principles of management help the managers in meeting the changing environmental needs because they are flexible in nature and can be modified according to the changes taking place in the environment.
Provide managers with useful insights into real world situations: Principles of management provide useful insights into reality, as they are made after considering the past mistakes. This helps in saving time by solving recurring problems quickly. Principles also increase managers knowledge, skills, ability and understanding of managerial situations and circumstances.
11. Explain the principle of 'Scalar Chain' and gang plank.
Ans: Scalar chain requires the managers to follow a well defined chain of communication that flows from top to bottom. That is in a scalar chain, the information passes in a certain and defined manner from the top to bottom so as to avoid any ambiguity in communication.
Gang plank is an exception of scalar chain that states that in the situation of emergency where quick decisions and communications are needed, two managers who are working at the same managerial position can have a quick communication with one another.
For example:
A is heading 2 teams where B and F are at the same level, C and G are at the same level and D and H are at the same level.
Line of communication is B - C - D and F - G - H. In this D and H cannot directly contact each other, as per the principle of scalar chain.
But if an emergency arises, then using the prescribed flow may take a lot of time to communicate with each other.
Hence, to avoid this problem a system known as 'Gang plank' which is an exception of the scalar chain was introduced where employees working at the same level such as D or H could contact each other whenever urgent need arises.
(Image Will Be Updated Soon)
12. A production manager at top level in a reputed corporate, Mr. Rathore holds the responsibility for ordering new material for the firm. While deciding on the supplier for the financial year 2017-18, he gave the order to his cousin at a higher price per unit instead of the firm's usual supplier who was willing to lower the rates for the order. Which principle of management was violated by Mr. Rathore? What are the positive impacts of following the above identified principle?
Ans: The principle of subordination of individual interest to general interest is violated. According to this principle, an individual should give priority to its organizational goals over any personal interest.
The positive impacts of following this principle are:
Better coordination between personal and organizational goals.
Maintenance of peace and harmony within the organization.
Increase in employee productivity as their efforts are directed towards the fulfilment of organizational goals, which will further help them in achieving their personal goals.
Employees do not feel separated from the organization.
Helps in achieving organizational goals.
13. Explain the principles of scientific management given by Taylor.
Ans: The principles of scientific management given by Taylor are as follows:
Science, not Rule of Thumb : This principle states that the management should follow scientific methods and not the rule of thumb method, which insists on finding solutions through trial and error approach. According to Taylor, following scientific methods will result in tremendous savings of time and materials, as well imparts more simplicity and ease of performing work.
Cooperation, Not Individualism: A spirit of cooperation should exist between the workers and management, and not the spirit of individualism. Both management and workers should cooperate with each other, and work collectively and cooperatively for the achievement of organizational goals. Management should consider all the good suggestions made by the employees and workers should never think of doing unreasonable things to the management to get their demands fulfilled.
Harmony, Not Discord: There must exist proper peace and harmony between the management and the workers for the smooth flow of the operations of the organization. As managers are the link between workers and the owners, the management should share profits with workers to keep them motivated and workers should also be willing to accept the changes for the good of the company.
During times of conflict between management and workers, both should change their thinking and mentality towards each other, this concept is called mental revolution.
Development of each and every person to his/ her greatest efficiency and prosperity: According to this principle, adequate opportunities and training must be made available to employees, so that they strive to improve their performance and efficiency through enhanced skills, and are able to achieve new heights in their careers.
14 . Explain the following principles of management given by Fayol with examples.
(a) Unity of Direction:
Ans: According to this principle, the efforts of each unit of the organization having a similar head and plan should move towards the achievement of the same objectives. Each division should have its own incharge and resources, so as to prevent overlapping of activities.
For Example: A company manufacturing two different products should have separate incharge for both the products. Hence two different departments and divisions needs to be created. In case there is a single incharge, then there might be chances of duplication and poor utilisation of resources.
(b) Equity:
Ans: According to this principle, All the employees should be treated equally and as fairly as possible. No one should be discriminated against on the basis of their caste, religion, complexion, gender, nationality etc.
Example: Men and women should be treated equally in a company.
(c) Esprit de Corps:
Ans: It means unity is strength. According to this principle management should promote a spirit of mutual trust and belongingness among team members. It focuses on the word ‘We’ Instead of ‘I’
For example: In the military all the soldiers work together with trust and confidence for the other members so as to collectively achieve their goal.
(d) Order :
Ans: According to this principle, there should be a place for everyone and everything and each person or the thing should be found in its/ his place. It helps in carrying out the activities on time, and in a smooth manner.
For Example: In a plant layout, production is supposed to be taken on Machine 1 and Machine 2 in a sequence, then both the machines should be arranged near to each other. If both the machines are far away from each other, then there can be delay in the production process, thus causing reduced productivity, and high costs.
(e) Centralisation and Decentralisation:
Ans: Centralisation is the concentration of power in the hands of selected persons in an organization. Decentralisation means sharing the authority with middle and lower levels in the organization. A balance should exist between complete centralisation and decentralisation in the organization.
For Example: When all the decisions making powers are in the hands of top level management, it is centralisation, it is suitable in cases like military etc., and if the power to take decisions is shared to middle and lower levels then it is decentralisation, it is suitable when the other level of management have suitable knowledge and skills to take a decision.
(f) Initiative:
Ans: According to this principle, workers should be provided with incentives to keep them motivated to work for the achievement of organizational goals. They should be encouraged to carry out their plans for improvement, it will make them comfortable to take more initiatives for the development of the organization.
For example, considering the suggestions and feedback from the workers while making decisions will make them feel motivated and a part and parcel of the organization.
15. Explain the technique of 'Functional Foremanship' and the concept of 'Mental Revolution' as enunciated by Taylor.
Ans: Functional Foremanship is an extension to the principle of division of labor. In this technique each worker will work under eight foreman in the related process or function of production.
Taylor divides the eight foreman under two incharges:
Planning incharge
Production incharge.
Planning incharge includes:
Instruction card clerk: His role is to give instructions to workers.
Route clerk: He is responsible for the specification of the production route.
Time and cost clerk: His role is to prepare time and costs sheets.
Disciplinarian: His role is to ensure discipline.
Production incharge includes:
Speed boss: His role is to ensure that the work completes in a timely and accurate manner.
Gang boss: He is responsible to keep machines and tools in a ready state of work.
Repairs boss: His role involves keeping the machines and tools in proper working conditions, and arranging for their repairs as and when needed.
Inspector: He is responsible for checking the quality of work.
Mental revolution:
Mental revolution focuses on the transformation of the mindset and attitude of workers and management towards each other. Management should try their best to satisfy the needs of the employees and workers should also do their best in order to develop the organization. Both should realise the importance of each other and cooperate with one another.
16. Discuss the following techniques of Scientific work Study.
(a) Time Study:
Ans: Time study helps in finding out the standard time required to perform a well- defined job. Time study also assists in the determination of wages, drafting incentive schemes, manpower requirements etc.
(b) Motion Study:
Ans: It refers to the study of movements like changing positions, lifting objects, putting objects etc., which are undertaken while doing a job. The objective of motion study is to eliminate the unnecessary movements in order to complete a task in a shorter time.
(c) Fatigue Study:
Ans: It seeks to determine the amount and frequency of rest intervals in completing a task to increase productivity. Rest is essential to perform the work with full capacity. This study helps to find out the standard intervals of break that help a worker to regain its energy.
(d) Method Study:
Ans: The objective of method study is to find out the best way of doing the job. By determining the best method one can minimise the cost of production and maximise the quality and satisfaction of the customer.
(e) Simplification and standardization of work:
Ans: Standardization refers to setting of standards or benchmarks for every business activity, such as standardization of work, process, etc. Standardization thrives to achieve quality work, and quality products by establishing standards of performance for men and machines. For example there are standards for gold (hallmark), agricultural products (Agmark), industrial products(ISI) that assure that the product is a quality product.
Simplification of work aims at eliminating the unnecessary diversity in the products. It helps in savings of cost of labor, machine and tools and increased turnover. There are shoe sizes, cloth sizes such as M, L, XL etc., this is done to reduce unnecessary variations, and expenses.
17. Discuss the differences between the contributions of Taylor and Fayol.
Ans: The differences between the contributions of Taylor and Fayol are:
18. Discuss the relevance of Taylor and Fayol’s contribution in the contemporary business environment.
Ans: Principles of both Taylor and Fayol play a significant role in the contemporary business environment.
Act as guidelines: These principles act as a guideline to managers for making decisions and taking appropriate actions.
Flexible: Such principles can be modified according to the demand of the situation which helps the managers to solve the problem accordingly.
Can be used in a number of situations: It can be used in various situations and the decisions based on this will be backed by facts and logic which makes it more applicable.
Provides lessons: These principles help the managers to learn from their past mistakes by providing insight into real word business.
Universally Applicable: These principles have universal applicability which makes them more reliable.
Higher efficiency: It helps in development of an organization by improving efficiency and effectiveness with minimum use of resources and cost.
19. ‘Bhasin’ limited was engaged in the business of food processing and selling its products under a popular brand. Lately the business was expanding due to good quality and reasonable prices. Also with more people working the market for processed food was increasing. New players were also coming to cash in the new trend. In order to keep its market share in the short run the company directed its existing workforce to work overtime. But this resulted in many problems. Due to increased pressure of work the efficiency of the workers declined. Sometimes the subordinates had to work for more than one superior resulting in declining efficiency. The divisions that were previously working on one product were also made to work on two or more products. This resulted in a lot of overlapping and wastage. The workers were becoming indisciplined. The spirit of teamwork, which had characterised the company, previously was beginning to wane. Workers were feeling cheated and initiative was declining. The quality of the products was beginning to decline and market share was on the verge of decrease. Actually the company had implemented changes without creating the required infrastructure.
a. Identify the Principles of Management (out of 14) that were being violated by the company.
Ans: Following principles of management were violated:
Unity of Command: As employees were working under more than one superior.
Unity of Direction: As the divisions were made to work on more than one product.
Esprit de Corps: As the workers lacked the spirit of teamwork.
Discipline: The workers were getting discipled due to increased pressure.
Initiative: As workers were feeling cheated, and were lacking any initiative.
Order: The implementation of changes were made without arranging for proper infrastructure.
Division of work: They were made to work overtime, without any proper division of work.
b. Explain these principles in brief.
Ans: The principles are explained below:
Unity of Command: There should be one and only one superior for every individual employee as if the employees receives orders from more than one superior, then it may lead to confusion in the minds of employers regarding what to do and who to follow.
Unity of Direction: According to this principle, the efforts of each unit of the organization having a similar head and plan should move towards the achievement of the same objectives. Each division should have its own incharge and resources, so as to prevent overlapping of activities.
Esprit de Corps: According to this principle, efforts should be made on the part of management to promote a sense of mutual trust and belongingness among the team members. Also use of the word ‘We’ should be prioritized over the word ‘I’ to inculcate the sense of unity among the members.
Discipline: Everyone should follow the rules and regulations which are necessary for the working of the organization.
Initiative: According to Fayol, subordinates should be encouraged to make and execute plans within the prescribed limits of authority.
Order: According to this principle, there should be a place for everyone and everything and each person or the thing should be found in its/ his place. It helps in carrying out the activities on time, and in a smooth manner.
Division of work: Each task is performed by a specialist or trained employee so that it will be completed effectively and efficiently.
c. What steps should the company management take in relation to the above principles to restore the company to its past glory?
Ans: Steps which can be taken by the company are:
Motivation and proper incentive should be provided to workers.
Scientific management should be adopted.
Teamwork and coordination should be promoted for development of the organization.
One subordinate should receive instruction from one superior only for smooth functioning of the organization.
There must be separate divisions for different products.
Efforts should be made regarding the arrangement of proper infrastructure.
The work should be divided optimally, and overtime should be avoided.
20. (Further information related to the above question) The management of company Bhasin limited now realised its folly. In order to rectify the situation it appointed a management consultant: Mukti Consultants to recommend a restructure plan to bring the company back on the rails. Mukti Consultants undertook a study of the production process at the plant of the company Bhasin limited and recommend the following changes:
The company should introduce scientific management with regard to production.
Production Planning including routing, scheduling, dispatching and feedback should be implemented.
In order to separate planning from operational management ' Functional Foremanship' should be introduced.
'Work study' should be undertaken to optimise the use of resources.
'Standardisation' of all activities should be implemented to increase efficiency and accountability.
To motivate the workers ' Differential Piece Rate System' should be implemented.
(The above changes should be introduced apart from the steps recommended as an answer to part c case problem above.)
It was expected that the changes will bring about a radical transformation in the working of the company and it will regain its pristine glory.
(a) Do you think that introduction of scientific management as recommended by M consultants will result in intended outcome?
Ans: Yes, the scientific management techniques recommended by Mukti Consultants will prove beneficial for the organization. It will improve the quantity and quality of product with reduction in costs, more simplicity and ease of work.
(b) What precautions should the company undertake to implement the changes?
Ans: Following precautions need to be taken:
Production planning should be implemented in a systematic way.
Differential piece rate system should not promote unhealthy and ugly competition between the workers.
Functional foremanship should be introduced with proper motivation for the employees.
Standardization techniques should be implemented in different aspects of production, and proper methods should be developed for their training so that quality products are produced.
Employees can be offered monetary incentives to motivate them to work more efficiently.
Not only work study, other methods should be introduced like motion study, time study, and fatigue study.
(c) Give your answer with regard to each technique separately as enunciated in points 1 through 6 in the case problem.
Ans: Each technique as specified in the case problem is:
Scientific management
It means the use of tools and techniques and specialized personnel to carry out the task for achieving better quality and cost reduction. It is a theory of management developed by Frederick Taylor in 1911 which focuses on the ways of getting the work done in the best and most cost-effective way. The firm should adopt scientific management so as to take benefits of better division of labor, cost reduction and increased efficiency.
Production Plan:
It refers to the planning of production operations so that a smooth and coordinated flow of production is made possible. It involves elements like
Routing: It determines the route through which the raw materials will be transformed into finished goods.
Scheduling: It provides a proper timeline and schedule in respect to time, day, date, regarding the beginning and completion of a particular operation.
Dispatching: It involves the issuance of instructions and orders for the commencement of the production work.
Feedback: It refers to the identification of deviations and errors in the production plan, based on the set standards and current performance.
Functional Foremanship
It is an extension to the principle of division of labor. In this technique each worker will work under eight foreman in the related process or function of production. Taylor divides the eight foreman under two incharges so that there is no confusion in the minds of workers regarding their incharges:
Hence, the company should employ functional foremanship so as to keep the planning and operational functional separate.
Work Study:
To enhance the efficiency, productivity and performance of the workers, various techniques of work study could be used by the company, such as.
Time Study: Time study helps in finding out the standard time required to perform a well- defined job. Time study also assists in the determination of wages, drafting incentive schemes, manpower requirement etc.
Motion Study: It refers to the study of movements like changing positions, lifting objects, putting objects etc., which are undertaken while doing a job. The objective of motion study is to eliminate the unnecessary movements in order to complete a task in a shorter time.
Fatigue Study: It seeks to determine the amount and frequency of rest intervals in completing a task to increase productivity. This study helps to find out the standard intervals of break that help a worker to regain its energy.
Method Study: The objective of method study is to find out the best way of doing the job. By determining the best method one can minimise the cost of production and maximise the quality and satisfaction of the customer.
Standardization
To ensure proper product quality and accountability, the firm should go for standardization.
It refers to setting of standards or benchmarks for every business activity, such as standardization of work, process, etc so as to achieve quality work, and quality products by establishing standards of performance for both men and machines.
Differential Piece Wage System
To keep the workers motivated, and raise their efficiency levels the company should employ a differential piece wage system. It is a system which was used by Taylor under which workers are paid according to their efficiency. An efficient worker will get higher wages as compared to an inefficient worker.
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Business Studies Chapter - 2
Ncert business studies class 12 chapter 2 free pdf download.
Learning has never been easier as now NCERT Solutions are also available in the form of free PDF downloads. The free PDF downloads are also available for studies Class 12 chapter 2. Much like the NCERT Solutions, the free PDF download also consists of chapter summaries in terms of definitions, key concepts, tables, figures and diagrams and questions and answers. Students highly prefer using the free PDF download as it is easily accessible to students across the country.
NCERT Solutions Business Studies Class 12 Chapter 2 Principles of Management
The second chapter for Class 12 students studying Business Studies is about the principles of management. This is an important chapter of the subject and carries much more marks weightage in board examination. The various topics and subtopics covered in the chapter 2 Principles of Management are Fayol’s principles of management, Taylor’s scientific management. Furthermore, concepts and fundamentals on principles of management are also taught in this subject. The students who are having difficulty understanding the chapter on principles of management can now refer to NCERT Solutions or the free PDF download by NCERT either through their website or the mobile application. With help of this study material, students can understand the key concepts in a much easier way and thereby improve their overall performance in the exams.
Mark-Wise Weightage for Business Studies Class 12 chapter 2
CBSE board has divided marks for various sections of the final exam paper or boards paper. Business studies is also a subject for Class 12 students that has its unique marking scheme provided by the CBSE board. The distribution of marks is also specified for each chapter. Below is a table provided with the details specified for Business Studies Class 12 chapter 2.
Why is Referring to NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Business Studies Chapter 2 Beneficial For Students?
The NCERT Solutions are a set of study material that can be used for easy and quick last-minute preparations for board examinations. With the help of various questions and answers, definitions, tables and figures, it becomes very simple for students to revise and score well in their exams
Moreover, NCERT Solutions as well as the free PDF download has been created by subject experts that provide 100% accurate information. Therefore, NCERT Solutions are highly credible and recommended by many students and teachers.
Easy access of study material for different chapters and subjects across the internet as well the mobile application makes the NCERT Solutions more popular amongst the students of Class 12 preparing for chapter 2 of the Business Studies subject.
We hope that these NCERT solutions of CBSE Class 12 Business Studies NCERT Solutions for Chapter 2 Principle of Management have been useful to you. For any other related study material, visit Vedantu’s official website
Important Study Materials for Business Studies Class 12 Chapter 2: Principles of Management
Ncert solutions links for class 12 business studies, important study materials for class 12 business studies.
Along with this, students can also download additional study materials provided by Vedantu for CBSE Class 12 Business Studies–
FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Business Chapter 2 - Principles Of Management
1. How are the principles of management developed?
Chapter 2 for Class 12 Business Studies subjects covers the topic principles of management. One of the key concepts covered is about the development of principles of management. The development of these principles has taken many years that are very observed and analyzed by managers across different organisations. Since every manager faces various situations in different business organisations, the knowledge they put together for analysis is also diverse. This furthermore helps in developing principles of management that can apply decision-making skills and actions across various situations. Therefore, principles of management are developed by managers through their many years of experience.
2. Who is Henry Fayol?
Henry Fayol is a popular personality in the world of business and management. He was born in 1841 and from the young age of 19, he started working in the French mining industry. He used this experience of working as an engineer in the mining industry to develop the theory of business administration. Fayol’s principles of management are popularly used in business settings. He is also known for developing the concept of “Administrative Principles”. This principle is taught to students pursuing Business Studies as it can help them understand various administrative principles of different businesses and organisations. These are some of the key characteristics for which Henry Fayol is popular.

NCERT Solutions Class 12 Business Studies
Cbse study materials, jee study materials, neet study materials.
myCBSEguide
- Business Studies
- Important Questions of Class...
Important Questions of Class 12 Business Studies Principles of Management
Table of Contents
myCBSEguide App
Download the app to get CBSE Sample Papers 2024-25, NCERT Solutions (Revised), Most Important Questions, Previous Year Question Bank, Mock Tests, and Detailed Notes.
Important Questions of Class 12 Business Studies Principles of Management. myCBSEguide has just released Chapter Wise Question Answers for class 12 Business Studies. There chapter wise Practice Questions with complete solutions are available for download in myCBSEguide website and mobile app. These test papers with solution are prepared by our team of expert teachers who are teaching grade in CBSE schools for years. There are around 4-5 set of solved Business Studies Test Papers from each and every chapter. The students will not miss any concept in these Chapter wise question that are specially designed to tackle Exam. We have taken care of every single concept given in CBSE Class 12 Business Studies syllabus and questions are framed as per the latest marking scheme and blue print issued by CBSE for class 12.
CBSE Class 12 Business Studies Ch – 2
Download as PDF
Practice Test for Class 12 Business Studies
Chapter – 2 Principles of Management
- Workers should be paid more wages.
- The management and workers should not play the game of one-upmanship.
- Both management and workers require each other.
- It implies change of attitude of management only
- 1856 to 1915
- 1856 to 1935
- 1856 to 1925
- 1856 to 1905
- Scalar Chain
- Part of business
- Tested in Laboratories
- Applied Everywhere
- What is the aim of Method study? (1)
- “Workers should be encouraged to develop and carry out their plans for development.” Identify the particular principle of management by Fayol. (1)
- ‘Accurate cause and effect relationship cannot be established by principles of management.’ Why? (1)
- The Production Manager of Bharat Ltd. instructs a salesman to go slow in selling the product, whereas the Marketing Manager is insisting on fast selling to achieve the target. Which principle of management is being violated in this case? State any one of the consequences of violation of this principle. (1)
- Explain briefly ‘discipline’ and ‘scalar chain’ as principles of general management. (3)
Explain how principles of management:
- help the managers in taking scientific decisions, and
- provide the managers with useful insights into real-world situations. (3)
For the last three years, Elpis Technology Solutions p(Ltd.) is not functioning smoothly and systematically. The relations between management and employees are becoming bitter day by day. After a complete analysis, it was observed that employees are not working effectively and efficiently and management is not fulfìlling its commitment of increments and promotions,
- Which management principle is being ignored in the given case?
- Can the problem be solved if only management becomes serious in fulfilling its promises? What should be the appropriate course of action to achieve smooth and systematic functioning of Mahagun Industries? (4)
What are the adverse effects of the violation of the following principles? Give one adverse effect for each.
- Division of work
- Unity of Command
- Remuneration
- Stability of tenure (4)
- Explain Fayol’s principles of ‘equity’ and ‘order’ with examples. (5)
Explain the following principles of Fayol with the help of one example of each.
- Unity of direction (5)
- Explain any four points which highlight the importance of principles of management. (6)
- Mental revolution involves a change in the attitude of workers and management towards one another from competition to cooperation.
- Management should share a part of surplus with workers.
- Workers should also contribute their might so that the company makes profits.
- Fredrick Winslow Taylor (March 20,1856 – March 21, 1915) was an American mechanical engineer.
- He died in 1915 due to pneumonia.
- Esprit de corps is a French phrase that translates into ‘group spirit’.
- It is one of the principles of Henri Fayol.
- Management should promote a team spirit of unity and harmony among employees, according to Fayol.
- Principles of mangement cannot be tested in laboratories as these principles are applied on human behaviour.
- Principles of management are formed by experience and collective wisdom of managers as well as experimentation.
- These can be applied and tested in real life situation rather than in laboratories.
- Method study is basically conducted to simplify the work or working methods and must go towards higher productivity and reduced cost.
- Principle of initiative, According to this principle top management provides opportunities to its employees to suggest new ideas, experiences and more convenient methods of work.
- They apply to human behaviour and it is unpredictable.
- In reality, prevailing conditions may vary in different organisations at different points of time.
- The principle of management which is being violated in this case is Unity of Command. Consequence will be that salesman will be confused regarding whose instructions should he follow. Therefore, it may be difficult to carry out the order of two persons when they are contradictory.
- Discipline According to Fayol, discipline is obedience, application and the outward mark of respect. It is the obedience to organizational rules and employment agreement which are necessary for the working of the organization. According to Fayol, discipline requires- good superiors at all levels, dear and fair agreements and judicious application of penalties. Discipline can be of two types – imposed and self. It is really difficult to inculcate self-discipline among the employees as human beings are prone to get influenced and lured by various distractions. Therefore, it is nothing but the imposed discipline which needs to be applied in an organization. Scalar chain It is the chain of superiors ranging from the top to the lowest ranks. The principle of the scalar chain suggests that there should be a clear line of authority from top to bottom linking managers at all levels. The scalar chain serves a the chain of command and also as the chain of communication. Under the chain of command, order sand instructions, issued at higher levels, flow through intermediate managers before reaching the lower levels. However, Scalar chain prolongs the chain of communication as there has to be a formal chain of command to be followed. As a measure to speed up communication, Fayol introduced Gang plank which means that two subordinates working at the same level of different departments can communicate with each other directly without following official chain of communication.
- Scientific decisions: The knowledge of management principles enables managers to learn the cause and effect relationship between variable, operating in the organization. They are able to develop a scientific and objective approach toward- problem solving and decision-making. The managers are no longer dependent upon their experience, intuitions, and instincts rather they adapt invariably as per the prevailing situation which makes the decisions more scientific in nature.
- Provide the manager with useful insight into reality: Management principles act as guidelines for the managers. These principles improve knowledge, ability, and understanding of managers under various managerial situations. The effects of these principles help the managers to learn from their mistakes. They deeply introspect the pros and cons of their decisions.
- The principle of ‘Discipline’ is being violated.
- No, the problem cannot be solved through management efforts only. For smooth and systematic functioning of Elpis Technology Solutions p(Ltd.), both employees and management should be disciplined. Employees must be disciplined to work effectively and efficiently and management should meet their commitment of increments and promotions.
- Division of work: The violation of this principle leads to the dearth of specialization among the employees.
- Unity of Command: The violation of this principle leads to confusion in the mind of the subordinate in following the orders.
- Remuneration: The violation of this principle leads to a situation of unrest among the employees and makes them demotivated.
- Order: Improper placement of men and material may lead to wastage of resources.
- Stability of tenure: Instability and insecurity among employees and they would tend to leave the organization.
- Equity The principle of equity implies a sense of fairness and justice for all workers working in an organization. Observance of equity alone would make workers loyal and devoted to the organization. Equity does not mean equal salary to a peon and supervisor But equity means the application of the same disciplinary rules, leave rules, etc irrespective of their grade, position, and gender, language, religion or nationality, etc.for instance, a male and female working at the same level in an organization are getting different salary, then this is the violation of the principle of equity.
- Order According to Fayol, ‘People and material must be in a suitable place at an appropriate time for maximum efficiency’ This principle states that there should be a place for everything and everyone in an organization and that thing or person should be found at its allotted place This will lead to increased productivity and efficiency as it saves the time and specifically the wastage of time. For example, raw material should be available at the place prescribed for it so that the workers must not waste their time and remain focused on the production activities. This makes the organization productive as a whole.
- Division of work: Every employee should be assigned only one type of work. It means that total work is divided into small tasks/jobs and a trained specialist performs each Job. The objective of the division of labor derive the benefits from the principle of specialization which can be applied to all work. Division of work minimizes the efforts and the burden of the tasks to be performed. It enables an individual to not to become ‘jack of all trades and master of none’. for example, publishing of a book involves several operations like computer typing of text material. proofreading, printing, binding, etc. All the operations are performed by different people who are experts in their respective field.
- Unity of direction: One unit and one plan for the group of activities having the same objective This principle implies that there should be one head and one plan for a group of activities having the same objective. It means that the efforts of members of the organization should be directed towards the achievement of a common goal, For example, the mission of a company is to provide quality products at an affordable price to the customers. This should serve as a direction for all the departments, namely, purchasing. financing, quality control, and marketing. This develops a sense of oneness among the employees and all of them realize they ‘sail in the same boat’, therefore, the onus of any success or failure is on all of them and not on any specific individual.
- To Provide Managers with Useful Insights into Reality: Principles of management are derived on the basis of continuous observation and analysis of events which managers face in real world situations. They help managers to improve their knowledge, ability and understanding of managerial situations These principles enable managers to learn from past mistakes and conserve time by solving recurring problems quickly. Thus, management principles increase the efficiency of managers.
- Optimum Utilisation of Resources and Effective Administration: Optimum utilisation of resources emphasise that resources(physical, financial and human) should be utilised in such a manner that they should give maximum benefit with minimum cost. Principles of management help in organising various activities in such a way that results in elimination of unwanted activities there by reducing inefficiency and wastage of resources. It also increases the efficiency of management, as through these principles managers adopt a systematic and logical approach to overcome the problems and discard hit and trial approaches.
- Scientific Decision: Management principles help in thoughtful decision making because they are based on logical reasoning after making detailed research and investigation rather than blind faith or guess work. Such decisions are free from bias and prejudice. These principles develop a scientific approach as they give a realistic and subjective measurement for evaluation. Management principles are based on the objective assessment of the situation.
- Meeting Changing Environment Requirements: Modern business environment is complex and ever-changing. In order to be survive and grow, organisations have to adapt to these changes. Although, principles are general guidelines but they are flexible and can be frequently modified as per business environment, which are favourable and profitable for the business.
Chapter Wise Extra Question of Class 12 Business Studies
Part -i and part – ii.
- Nature and Significance of Management
- Principles of Management
- Business Environment
- Controlling
- Financial Management
- Financial Markets
- Marketing Management
- Consumer Protection
Test Generator
Create question paper PDF and online tests with your own name & logo in minutes.
Question Bank, Mock Tests, Exam Papers, NCERT Solutions, Sample Papers, Notes
Related Posts
- Important Questions for Class 12 Business Studies Consumer Protection
- Important Questions for Class 12 Financial Management Business Studies
- Extra Questions of Class 12 Business Studies Controlling
- Important Questions for Class 12 Directing Business Studies
- Class 12 Business Studies Staffing Extra Questions
- Practice Questions for Class 12 Organising Business Studies
- Practice Questions for Class 12 Business Studies Business Environment
- Class 12 Business Studies Nature and Significance of Management Extra Questions
Leave a Comment
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Read and download free pdf of CBSE Class 12 Business Studies Principles of Management Assignment. Get printable school Assignments for Class 12 Business Studies.
Important Questions with Answers for CBSE Class 12 Business Studies Chapter 2 – Principles of Management which is outlined by expert Business Studies teachers from the latest version of CBSE (NCERT) books. Question 1. What is meant by ‘Management Principles’?
The Class 12 Business Studies Chapter 2 Principles of Management Notes cover key principles such as Division of Work, Authority, and Responsibility, and Unity of Command, which are essential for effective management practices.
Go through these Principles of Management Class 12 Important Questions and Answers & Previous Year Questions to score good marks in the board examination. Question 1. Appliances India Ltd. is engaged in a manufacturing and distribution of home appliances since 1987.
Please refer to Principles of Management Class 12 Business Studies notes and questions with solutions below. These revision notes and important examination questions have been prepared based on the latest Business Studies books for Class 12.
NCERT Solution for Class 12 Business Studies Chapter 2 – Principles of Management provides us with a brief introduction to the concepts. It provides a clear picture of the forms of principles of management.
Principles of management are broad and general guidelines for managerial decision making and behavior (i.e. they guide the practice of management). Nature of Principles of Management. The nature of principles of management can be described in the following points: 1.
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Business studies Chapter 2 Principles of Management are provided here in easy-to-understand language. These solutions for Principles of Management are extremely beneficial for Class 12 Commerce students.
Important Questions of Class 12 Business Studies Principles of Management. myCBSEguide has just released Chapter Wise Question Answers for class 12 Business Studies. There chapter wise Practice Questions with complete solutions are available for download in myCBSEguide website and mobile app.
ed into 6 distinctive . hases: 1. Early Perspectives; 2. Classical Management Theory; 3. Neo Classical Theory . Human Relations Approach; 4. Behavioural Science Approac. — Organisational Humanism; 5. Management. Science/Operationa.