
- Customer Reviews
- Net 30 Account
- Wise Services
- Steps & Timeline
- Work at a Glance
- Market Research at a Glance
- Business Plan Writing Services
- Bank Business Plan
- Investor Business Plan
- Franchise Business Plan
- Cannabis Business Plan
- Strategic Business Plan
- Corporate Business Plan
- Merge and Acquisition Business Plan (M&A)
- Private Placement Memorandums (PPM)
- Sample Business Plans
- Professional Feasibility Study
- PowerPoint Presentations
- Pitch Deck Presentation Services
- Business Plan Printing
- Market Research
- L-1 Business Plan
- E-2 Business Plan
- EB-5 Business Plan
- EB-5 Regional Centers
- Immigration Attorneys
- Nonprofit Business Plan
- Exit Business Planning
- Business Planning
- Business Formation
- Business License
- Business Website
- Business Branding
- Business Bank Account
- Digital Marketing
- Business Funding Resources
- Small Business Loans
- Venture Capital
- Net 30 Apply


What is a business plan? Definition, Purpose, and Types
Table of Contents
What is a business plan?
Looking for someone to write a business plan, purposes of a business plan, what are the essential components of a business plan, executive summary, business description or overview, product and price, competitive analysis, target market, marketing plan, financial plan, funding requirements, types of business plan, lean startup business plans, traditional business plans, need guidance with your business plan, how often should a business plan be reviewed and revised, what are the key elements of a lean startup business plan, what are some of the reasons why business plans don't succeed.
In the world of business, a well-thought-out plan is often the key to success. This plan, known as a business plan, is a comprehensive document that outlines a company’s goals, strategies , and financial projections. Whether you’re starting a new business or looking to expand an existing one, a business plan is an essential tool.
As a business plan writer and consultant , I’ve crafted over 15,000 plans for a diverse range of businesses. In this article, I’ll be sharing my wealth of experience about what a business plan is, its purpose, and the step-by-step process of creating one. By the end, you’ll have a thorough understanding of how to develop a robust business plan that can drive your business to success.
A business plan is a roadmap for your business. It outlines your goals, strategies, and how you plan to achieve them. It’s a living document that you can update as your business grows and changes.
Find professional business plan writers for your business success.
These are the following purpose of business plan:
- Attract investors and lenders: If you’re seeking funding for your business , a business plan is a must-have. Investors and lenders want to see that you have a clear plan for how you’ll use their money to grow your business and generate revenue.
- Get organized and stay on track: Writing a business plan forces you to think through all aspects of your business, from your target market to your marketing strategy. This can help you identify any potential challenges and opportunities early on, so you can develop a plan to address them.
- Make better decisions: A business plan can help you make better decisions about your business by providing you with a framework to evaluate different options. For example, if you’re considering launching a new product, your business plan can help you assess the potential market demand, costs, and profitability.

The executive summary is the most important part of your business plan, even though it’s the last one you’ll write. It’s the first section that potential investors or lenders will read, and it may be the only one they read. The executive summary sets the stage for the rest of the document by introducing your company’s mission or vision statement, value proposition, and long-term goals.
The business description section of your business plan should introduce your business to the reader in a compelling and concise way. It should include your business name, years in operation, key offerings, positioning statement, and core values (if applicable). You may also want to include a short history of your company.
In this section, the company should describe its products or services , including pricing, product lifespan, and unique benefits to the consumer. Other relevant information could include production and manufacturing processes, patents, and proprietary technology.
Every industry has competitors, even if your business is the first of its kind or has the majority of the market share. In the competitive analysis section of your business plan, you’ll objectively assess the industry landscape to understand your business’s competitive position. A SWOT analysis is a structured way to organize this section.
Your target market section explains the core customers of your business and why they are your ideal customers. It should include demographic, psychographic, behavioral, and geographic information about your target market.
Marketing plan describes how the company will attract and retain customers, including any planned advertising and marketing campaigns . It also describes how the company will distribute its products or services to consumers.
After outlining your goals, validating your business opportunity, and assessing the industry landscape, the team section of your business plan identifies who will be responsible for achieving your goals. Even if you don’t have your full team in place yet, investors will be impressed by your clear understanding of the roles that need to be filled.
In the financial plan section,established businesses should provide financial statements , balance sheets , and other financial data. New businesses should provide financial targets and estimates for the first few years, and may also request funding.
Since one goal of a business plan is to secure funding from investors , you should include the amount of funding you need, why you need it, and how long you need it for.
- Tip: Use bullet points and numbered lists to make your plan easy to read and scannable.
Access specialized business plan writing service now!
Business plans can come in many different formats, but they are often divided into two main types: traditional and lean startup. The U.S. Small Business Administration (SBA) says that the traditional business plan is the more common of the two.
Lean startup business plans are short (as short as one page) and focus on the most important elements. They are easy to create, but companies may need to provide more information if requested by investors or lenders.
Traditional business plans are longer and more detailed than lean startup business plans, which makes them more time-consuming to create but more persuasive to potential investors. Lean startup business plans are shorter and less detailed, but companies should be prepared to provide more information if requested.
Access 14 free business plan samples!
A business plan should be reviewed and revised at least annually, or more often if the business is experiencing significant changes. This is because the business landscape is constantly changing, and your business plan needs to reflect those changes in order to remain relevant and effective.
Here are some specific situations in which you should review and revise your business plan:
- You have launched a new product or service line.
- You have entered a new market.
- You have experienced significant changes in your customer base or competitive landscape.
- You have made changes to your management team or organizational structure.
- You have raised new funding.
A lean startup business plan is a short and simple way for a company to explain its business, especially if it is new and does not have a lot of information yet. It can include sections on the company’s value proposition, major activities and advantages, resources, partnerships, customer segments, and revenue sources.

- Unrealistic assumptions: Business plans are often based on assumptions about the market, the competition, and the company’s own capabilities. If these assumptions are unrealistic, the plan is doomed to fail.
- Lack of focus: A good business plan should be focused on a specific goal and how the company will achieve it. If the plan is too broad or tries to do too much, it is unlikely to be successful.
- Poor execution: Even the best business plan is useless if it is not executed properly. This means having the right team in place, the necessary resources, and the ability to adapt to changing circumstances.
- Unforeseen challenges: Every business faces challenges that could not be predicted or planned for. These challenges can be anything from a natural disaster to a new competitor to a change in government regulations.
What are the benefits of having a business plan?
- It helps you to clarify your business goals and strategies.
- It can help you to attract investors and lenders.
- It can serve as a roadmap for your business as it grows and changes.
- It can help you to make better business decisions.
How to write a business plan?
There are many different ways to write a business plan, but most follow the same basic structure. Here is a step-by-step guide:
- Executive summary.
- Company description.
- Management and organization description.
- Financial projections.
How to write a business plan step by step?
Start with an executive summary, then describe your business, analyze the market, outline your products or services, detail your marketing and sales strategies, introduce your team, and provide financial projections.
Why do I need a business plan for my startup?
A business plan helps define your startup’s direction, attract investors, secure funding, and make informed decisions crucial for success.
What are the key components of a business plan?
Key components include an executive summary, business description, market analysis, products or services, marketing and sales strategy, management and team, financial projections, and funding requirements.
Can a business plan help secure funding for my business?
Yes, a well-crafted business plan demonstrates your business’s viability, the use of investment, and potential returns, making it a valuable tool for attracting investors and lenders.
Related Posts

Why Experienced Legal Consultation is Crucial for New Businesses

Creating a ‘Second Brain’ to Manage Information Overload and Enhance Focus

What Are Mobile App Development Services? Guide for Businesses and Startups
Quick links.

- Investor Business Plans
- M&A Business Plan
- Private Placement
- Feasibility Study
- Hire a Business Plan Writer
- Business Valuation Calculator
- Business Plan Examples
- Real Estate Business Plan
- Business Plan Template
- Business Plan Pricing Guide
- Business Plan Makeover
- Business Credit Cards
- SBA Loans, Bank Funding & Business Credit
- Finding & Qualifying for Business Grants
- Leadership for the New Manager
- Content Marketing for Beginners
- All About Crowdfunding
- A Comprehensive Guide to Venture Capitalists
- EB-5 Regional Centers, A Step-By-Step Guide
- Logo Designer
- Landing Page
- PPC Advertising

- Business Entity
- Business Licensing
- Virtual Assistant
- Business Phone
- Business Address
- E-1 Visa Business Plan
- EB1-A Visa Business Plan
- EB1-C Visa Business Plan
- EB2-NIW Business Plan
- H1B Visa Business Plan
- O1 Visa Business Plan
- Business Brokers
- Merger & Acquisition Advisors
- Franchisors
Proud Sponsor of
- 1-800-496-1056

- (613) 800-0227

- +44 (1549) 409190

- +61 (2) 72510077

🎧 Real entrepreneurs. Real stories.
Subscribe to The Hurdle podcast today!
What is a Business Plan? Definition and Resources

9 min. read
Updated July 29, 2024

If you’ve ever jotted down a business idea on a napkin with a few tasks you need to accomplish, you’ve written a business plan — or at least the very basic components of one.
The origin of formal business plans is murky. But they certainly go back centuries. And when you consider that 20% of new businesses fail in year 1 , and half fail within 5 years, the importance of thorough planning and research should be clear.
But just what is a business plan? And what’s required to move from a series of ideas to a formal plan? Here we’ll answer that question and explain why you need one to be a successful business owner.
- What is a business plan?

A business plan lays out a strategic roadmap for any new or growing business.
Any entrepreneur with a great idea for a business needs to conduct market research , analyze their competitors , validate their idea by talking to potential customers, and define their unique value proposition .
The business plan captures that opportunity you see for your company: it describes your product or service and business model , and the target market you’ll serve.
It also includes details on how you’ll execute your plan: how you’ll price and market your solution and your financial projections .
Reasons for writing a business plan
If you’re asking yourself, ‘Do I really need to write a business plan?’ consider this fact:
Companies that commit to planning grow 30% faster than those that don’t.
Creating a business plan is crucial for businesses of any size or stage. It helps you develop a working business and avoid consequences that could stop you before you ever start.
If you plan to raise funds for your business through a traditional bank loan or SBA loan , none of them will want to move forward without seeing your business plan. Venture capital firms may or may not ask for one, but you’ll still need to do thorough planning to create a pitch that makes them want to invest.
But it’s more than just a means of getting your business funded . The plan is also your roadmap to identify and address potential risks.
It’s not a one-time document. Your business plan is a living guide to ensure your business stays on course.
Related: 14 of the top reasons why you need a business plan
Brought to you by
Create a professional business plan
Using ai and step-by-step instructions.
Secure funding
Validate ideas
Build a strategy
What research shows about business plans
Numerous studies have established that planning improves business performance:
- 71% of fast-growing companies have business plans that include budgets, sales goals, and marketing and sales strategies.
- Companies that clearly define their value proposition are more successful than those that can’t.
- Companies or startups with a business plan are more likely to get funding than those without one.
- Starting the business planning process before investing in marketing reduces the likelihood of business failure.
The planning process significantly impacts business growth for existing companies and startups alike.
Read More: Research-backed reasons why writing a business plan matters
When should you write a business plan?
No two business plans are alike.
Yet there are similar questions for anyone considering writing a plan to answer. One basic but important question is when to start writing it.
A Harvard Business Review study found that the ideal time to write a business plan is between 6 and 12 months after deciding to start a business.
But the reality can be more nuanced – it depends on the stage a business is in, or the type of business plan being written.
Ideal times to write a business plan include:
- When you have an idea for a business
- When you’re starting a business
- When you’re preparing to buy (or sell)
- When you’re trying to get funding
- When business conditions change
- When you’re growing or scaling your business
Read More: The best times to write or update your business plan
How often should you update your business plan?
As is often the case, how often a business plan should be updated depends on your circumstances.
A business plan isn’t a homework assignment to complete and forget about. At the same time, no one wants to get so bogged down in the details that they lose sight of day-to-day goals.
But it should cover new opportunities and threats that a business owner surfaces, and incorporate feedback they get from customers. So it can’t be a static document.
Related Reading: 5 fundamental principles of business planning
For an entrepreneur at the ideation stage, writing and checking back on their business plan will help them determine if they can turn that idea into a profitable business .
And for owners of up-and-running businesses, updating the plan (or rewriting it) will help them respond to market shifts they wouldn’t be prepared for otherwise.
It also lets them compare their forecasts and budgets to actual financial results. This invaluable process surfaces where a business might be out-performing expectations and where weak performance may require a prompt strategy change.
The planning process is what uncovers those insights.
Related Reading: 10 prompts to help you write a business plan with AI
- How long should your business plan be?
Thinking about a business plan strictly in terms of page length can risk overlooking more important factors, like the level of detail or clarity in the plan.
Not all of the plan consists of writing – there are also financial tables, graphs, and product illustrations to include.
But there are a few general rules to consider about a plan’s length:
- Your business plan shouldn’t take more than 15 minutes to skim.
- Business plans for internal use (not for a bank loan or outside investment) can be as short as 5 to 10 pages.
A good practice is to write your business plan to match the expectations of your audience.
If you’re walking into a bank looking for a loan, your plan should match the formal, professional style that a loan officer would expect . But if you’re writing it for stakeholders on your own team—shorter and less formal (even just a few pages) could be the better way to go.
The length of your plan may also depend on the stage your business is in.
For instance, a startup plan won’t have nearly as much financial information to include as a plan written for an established company will.
Read More: How long should your business plan be?
What information is included in a business plan?
The contents of a plan business plan will vary depending on the industry the business is in.
After all, someone opening a new restaurant will have different customers, inventory needs, and marketing tactics to consider than someone bringing a new medical device to the market.
But there are some common elements that most business plans include:
- Executive summary: An overview of the business operation, strategy, and goals. The executive summary should be written last, despite being the first thing anyone will read.
- Products and services: A description of the solution that a business is bringing to the market, emphasizing how it solves the problem customers are facing.
- Market analysis: An examination of the demographic and psychographic attributes of likely customers, resulting in the profile of an ideal customer for the business.
- Competitive analysis: Documenting the competitors a business will face in the market, and their strengths and weaknesses relative to those competitors.
- Marketing and sales plan: Summarizing a business’s tactics to position their product or service favorably in the market, attract customers, and generate revenue.
- Operational plan: Detailing the requirements to run the business day-to-day, including staffing, equipment, inventory, and facility needs.
- Organization and management structure: A listing of the departments and position breakdown of the business, as well as descriptions of the backgrounds and qualifications of the leadership team.
- Key milestones: Laying out the key dates that a business is projected to reach certain milestones , such as revenue, break-even, or customer acquisition goals.
- Financial plan: Balance sheets, cash flow forecast , and sales and expense forecasts with forward-looking financial projections, listing assumptions and potential risks that could affect the accuracy of the plan.
- Appendix: All of the supporting information that doesn’t fit into specific sections of the business plan, such as data and charts.
Read More: Use this business plan outline to organize your plan
- Different types of business plans
A business plan isn’t a one-size-fits-all document. There are numerous ways to create an effective business plan that fits entrepreneurs’ or established business owners’ needs.
Here are a few of the most common types of business plans for small businesses:
- One-page plan : Outlining all of the most important information about a business into an adaptable one-page plan.
- Growth plan : An ongoing business management plan that ensures business tactics and strategies are aligned as a business scales up.
- Internal plan : A shorter version of a full business plan to be shared with internal stakeholders – ideal for established companies considering strategic shifts.
Business plan vs. operational plan vs. strategic plan
- What questions are you trying to answer?
- Are you trying to lay out a plan for the actual running of your business?
- Is your focus on how you will meet short or long-term goals?
Since your objective will ultimately inform your plan, you need to know what you’re trying to accomplish before you start writing.
While a business plan provides the foundation for a business, other types of plans support this guiding document.
An operational plan sets short-term goals for the business by laying out where it plans to focus energy and investments and when it plans to hit key milestones.
Then there is the strategic plan , which examines longer-range opportunities for the business, and how to meet those larger goals over time.
Read More: How to use a business plan for strategic development and operations
- Business plan vs. business model
If a business plan describes the tactics an entrepreneur will use to succeed in the market, then the business model represents how they will make money.
The difference may seem subtle, but it’s important.
Think of a business plan as the roadmap for how to exploit market opportunities and reach a state of sustainable growth. By contrast, the business model lays out how a business will operate and what it will look like once it has reached that growth phase.
Learn More: The differences between a business model and business plan
- Moving from idea to business plan
Now that you understand what a business plan is, the next step is to start writing your business plan .
The best way to start is by reviewing examples and downloading a business plan template . These resources will provide you with guidance and inspiration to help you write a plan.
We recommend starting with a simple one-page plan ; it streamlines the planning process and helps you organize your ideas. However, if one page doesn’t fit your needs, there are plenty of other great templates available that will put you well on your way to writing a useful business plan.
Tim Berry is the founder and chairman of Palo Alto Software , a co-founder of Borland International, and a recognized expert in business planning. He has an MBA from Stanford and degrees with honors from the University of Oregon and the University of Notre Dame. Today, Tim dedicates most of his time to blogging, teaching and evangelizing for business planning.

Table of Contents
- Reasons to write a business plan
- Business planning research
- When to write a business plan
- When to update a business plan
- Information to include
- Business vs. operational vs. strategic plans
Related Articles

6 Min. Read
Free Agriculture Sample Business Plan PDF + How to Write

5 Min. Read
Should You Stick to the Business Plan or Change It?

10 Min. Read
When Should You Write a Business Plan?

How to Write a Yoga Studio Business Plan + Free Sample Plan PDF
The LivePlan Newsletter
Become a smarter, more strategic entrepreneur.
Your first monthly newsetter will be delivered soon..
Unsubscribe anytime. Privacy policy .

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
What Is a Business Plan?
Understanding business plans, how to write a business plan, common elements of a business plan, the bottom line, business plan: what it is, what's included, and how to write one.
Adam Hayes, Ph.D., CFA, is a financial writer with 15+ years Wall Street experience as a derivatives trader. Besides his extensive derivative trading expertise, Adam is an expert in economics and behavioral finance. Adam received his master's in economics from The New School for Social Research and his Ph.D. from the University of Wisconsin-Madison in sociology. He is a CFA charterholder as well as holding FINRA Series 7, 55 & 63 licenses. He currently researches and teaches economic sociology and the social studies of finance at the Hebrew University in Jerusalem.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/adam_hayes-5bfc262a46e0fb005118b414.jpg)
- How to Start a Business: A Comprehensive Guide and Essential Steps
- How to Do Market Research, Types, and Example
- Marketing Strategy: What It Is, How It Works, How To Create One
- Marketing in Business: Strategies and Types Explained
- What Is a Marketing Plan? Types and How to Write One
- Business Development: Definition, Strategies, Steps & Skills
- Business Plan: What It Is, What's Included, and How to Write One CURRENT ARTICLE
- Small Business Development Center (SBDC): Meaning, Types, Impact
- How to Write a Business Plan for a Loan
- Business Startup Costs: It’s in the Details
- Startup Capital Definition, Types, and Risks
- Bootstrapping Definition, Strategies, and Pros/Cons
- Crowdfunding: What It Is, How It Works, and Popular Websites
- Starting a Business with No Money: How to Begin
- A Comprehensive Guide to Establishing Business Credit
- Equity Financing: What It Is, How It Works, Pros and Cons
- Best Startup Business Loans
- Sole Proprietorship: What It Is, Pros & Cons, and Differences From an LLC
- Partnership: Definition, How It Works, Taxation, and Types
- What is an LLC? Limited Liability Company Structure and Benefits Defined
- Corporation: What It Is and How to Form One
- Starting a Small Business: Your Complete How-to Guide
- Starting an Online Business: A Step-by-Step Guide
- How to Start Your Own Bookkeeping Business: Essential Tips
- How to Start a Successful Dropshipping Business: A Comprehensive Guide
A business plan is a document that outlines a company's goals and the strategies to achieve them. It's valuable for both startups and established companies. For startups, a well-crafted business plan is crucial for attracting potential lenders and investors. Established businesses use business plans to stay on track and aligned with their growth objectives. This article will explain the key components of an effective business plan and guidance on how to write one.
Key Takeaways
- A business plan is a document detailing a company's business activities and strategies for achieving its goals.
- Startup companies use business plans to launch their venture and to attract outside investors.
- For established companies, a business plan helps keep the executive team focused on short- and long-term objectives.
- There's no single required format for a business plan, but certain key elements are essential for most companies.
Investopedia / Ryan Oakley
Any new business should have a business plan in place before beginning operations. Banks and venture capital firms often want to see a business plan before considering making a loan or providing capital to new businesses.
Even if a company doesn't need additional funding, having a business plan helps it stay focused on its goals. Research from the University of Oregon shows that businesses with a plan are significantly more likely to secure funding than those without one. Moreover, companies with a business plan grow 30% faster than those that don't plan. According to a Harvard Business Review article, entrepreneurs who write formal plans are 16% more likely to achieve viability than those who don't.
A business plan should ideally be reviewed and updated periodically to reflect achieved goals or changes in direction. An established business moving in a new direction might even create an entirely new plan.
There are numerous benefits to creating (and sticking to) a well-conceived business plan. It allows for careful consideration of ideas before significant investment, highlights potential obstacles to success, and provides a tool for seeking objective feedback from trusted outsiders. A business plan may also help ensure that a company’s executive team remains aligned on strategic action items and priorities.
While business plans vary widely, even among competitors in the same industry, they often share basic elements detailed below.
A well-crafted business plan is essential for attracting investors and guiding a company's strategic growth. It should address market needs and investor requirements and provide clear financial projections.
While there are any number of templates that you can use to write a business plan, it's best to try to avoid producing a generic-looking one. Let your plan reflect the unique personality of your business.
Many business plans use some combination of the sections below, with varying levels of detail, depending on the company.
The length of a business plan can vary greatly from business to business. Regardless, gathering the basic information into a 15- to 25-page document is best. Any additional crucial elements, such as patent applications, can be referenced in the main document and included as appendices.
Common elements in many business plans include:
- Executive summary : This section introduces the company and includes its mission statement along with relevant information about the company's leadership, employees, operations, and locations.
- Products and services : Describe the products and services the company offers or plans to introduce. Include details on pricing, product lifespan, and unique consumer benefits. Mention production and manufacturing processes, relevant patents , proprietary technology , and research and development (R&D) information.
- Market analysis : Explain the current state of the industry and the competition. Detail where the company fits in, the types of customers it plans to target, and how it plans to capture market share from competitors.
- Marketing strategy : Outline the company's plans to attract and retain customers, including anticipated advertising and marketing campaigns. Describe the distribution channels that will be used to deliver products or services to consumers.
- Financial plans and projections : Established businesses should include financial statements, balance sheets, and other relevant financial information. New businesses should provide financial targets and estimates for the first few years. This section may also include any funding requests.
Investors want to see a clear exit strategy, expected returns, and a timeline for cashing out. It's likely a good idea to provide five-year profitability forecasts and realistic financial estimates.
2 Types of Business Plans
Business plans can vary in format, often categorized into traditional and lean startup plans. According to the U.S. Small Business Administration (SBA) , the traditional business plan is the more common of the two.
- Traditional business plans : These are detailed and lengthy, requiring more effort to create but offering comprehensive information that can be persuasive to potential investors.
- Lean startup business plans : These are concise, sometimes just one page, and focus on key elements. While they save time, companies should be ready to provide additional details if requested by investors or lenders.
Why Do Business Plans Fail?
A business plan isn't a surefire recipe for success. The plan may have been unrealistic in its assumptions and projections. Markets and the economy might change in ways that couldn't have been foreseen. A competitor might introduce a revolutionary new product or service. All this calls for building flexibility into your plan, so you can pivot to a new course if needed.
How Often Should a Business Plan Be Updated?
How frequently a business plan needs to be revised will depend on its nature. Updating your business plan is crucial due to changes in external factors (market trends, competition, and regulations) and internal developments (like employee growth and new products). While a well-established business might want to review its plan once a year and make changes if necessary, a new or fast-growing business in a fiercely competitive market might want to revise it more often, such as quarterly.
What Does a Lean Startup Business Plan Include?
The lean startup business plan is ideal for quickly explaining a business, especially for new companies that don't have much information yet. Key sections may include a value proposition , major activities and advantages, resources (staff, intellectual property, and capital), partnerships, customer segments, and revenue sources.
A well-crafted business plan is crucial for any company, whether it's a startup looking for investment or an established business wanting to stay on course. It outlines goals and strategies, boosting a company's chances of securing funding and achieving growth.
As your business and the market change, update your business plan regularly. This keeps it relevant and aligned with your current goals and conditions. Think of your business plan as a living document that evolves with your company, not something carved in stone.
University of Oregon Department of Economics. " Evaluation of the Effectiveness of Business Planning Using Palo Alto's Business Plan Pro ." Eason Ding & Tim Hursey.
Bplans. " Do You Need a Business Plan? Scientific Research Says Yes ."
Harvard Business Review. " Research: Writing a Business Plan Makes Your Startup More Likely to Succeed ."
Harvard Business Review. " How to Write a Winning Business Plan ."
U.S. Small Business Administration. " Write Your Business Plan ."
SCORE. " When and Why Should You Review Your Business Plan? "
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/GettyImages-904536858-c089bc26f4fd4025b23f536345ba73ae.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices
Do you REALLY need a business plan?
The top three questions that I get asked most frequently as a professional business plan writer will probably not surprise you:
- What is the purpose of a business plan – why is it really required?
- How is it going to benefit my business if I write a business plan?
- Is a business plan really that important – how can I actually use it?
Keep reading to get my take on what the most essential advantages of preparing a business plan are—and why you may (not) need to prepare one.
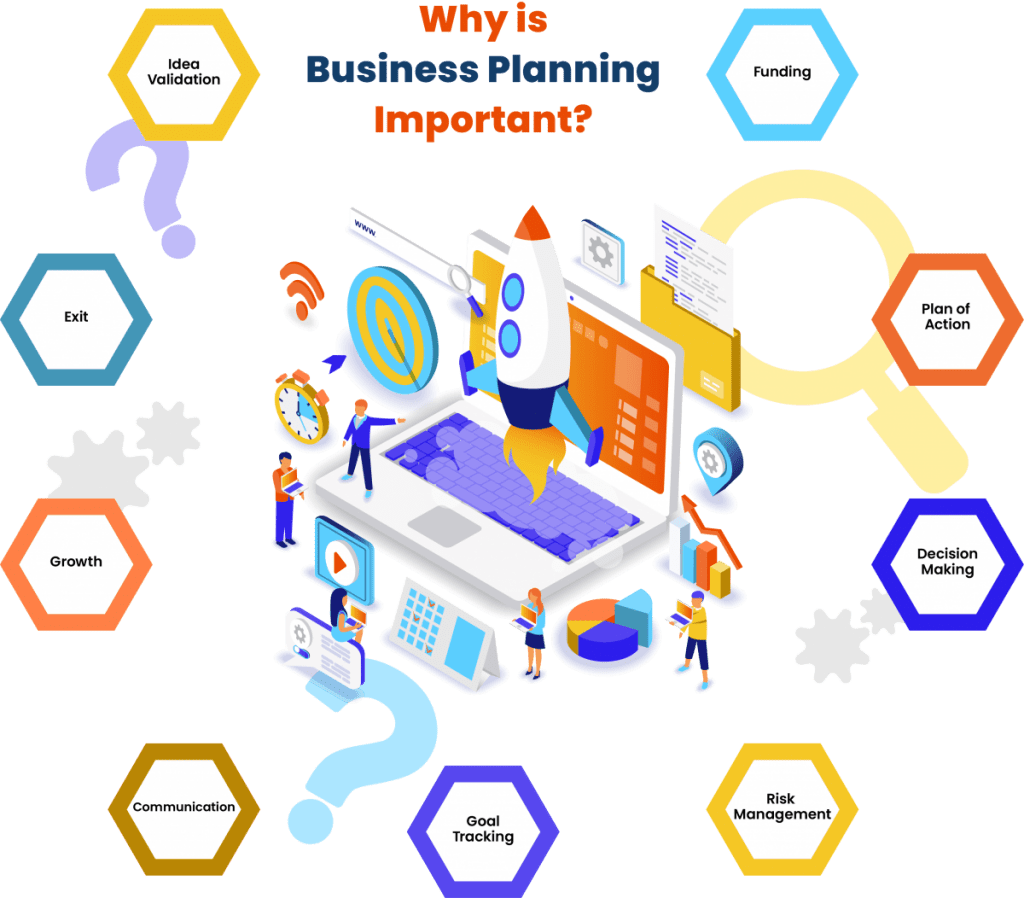
The importance, purpose and benefit of a business plan is in that it enables you to validate a business idea, secure funding, set strategic goals – and then take organized action on those goals by making decisions, managing resources, risk and change, while effectively communicating with stakeholders.
Let’s take a closer look at how each of the important business planning benefits can catapult your business forward:
1. Validate Your Business Idea
The process of writing your business plan will force you to ask the difficult questions about the major components of your business, including:
- External: industry, target market of prospective customers, competitive landscape
- Internal: business model, unique selling proposition, operations, marketing, finance
Business planning connects the dots to draw a big picture of the entire business.
And imagine how much time and money you would save if working through a business plan revealed that your business idea is untenable. You would be surprised how often that happens – an idea that once sounded so very promising may easily fall apart after you actually write down all the facts, details and numbers.
While you may be tempted to jump directly into start-up mode, writing a business plan is an essential first step to check the feasibility of a business before investing too much time and money into it. Business plans help to confirm that the idea you are so passionate and convinced about is solid from business point of view.
Take the time to do the necessary research and work through a proper business plan. The more you know, the higher the likelihood that your business will succeed.
2. Set and Track Goals
Successful businesses are dynamic and continuously evolve. And so are good business plans that allow you to:
- Priorities: Regularly set goals, targets (e.g., sales revenues reached), milestones (e.g. number of employees hired), performance indicators and metrics for short, mid and long term
- Accountability: Track your progress toward goals and benchmarks
- Course-correction: make changes to your business as you learn more about your market and what works and what does not
- Mission: Refer to a clear set of values to help steer your business through any times of trouble
Essentially, business plan is a blueprint and an important strategic tool that keeps you focused, motivated and accountable to keep your business on track. When used properly and consulted regularly, it can help you measure and manage what you are working so hard to create – your long-term vision.
As humans, we work better when we have clear goals we can work towards. The everyday business hustle makes it challenging to keep an eye on the strategic priorities. The business planning process serves as a useful reminder.
3. Take Action
A business plan is also a plan of action . At its core, your plan identifies where you are now, where you want your business to go, and how you will get there.
Planning out exactly how you are going to turn your vision into a successful business is perhaps the most important step between an idea and reality. Success comes not only from having a vision but working towards that vision in a systematic and organized way.
A good business plan clearly outlines specific steps necessary to turn the business objectives into reality. Think of it as a roadmap to success. The strategy and tactics need to be in alignment to make sure that your day-to-day activities lead to the achievement of your business goals.
4. Manage Resources
A business plan also provides insight on how resources required for achieving your business goals will be structured and allocated according to their strategic priority. For example:
Large Spending Decisions
- Assets: When and in what amount will the business commit resources to buy/lease new assets, such as computers or vehicles.
- Human Resources: Objectives for hiring new employees, including not only their pay but how they will help the business grow and flourish.
- Business Space: Information on costs of renting/buying space for offices, retail, manufacturing or other operations, for example when expanding to a new location.
Cash Flow It is essential that a business carefully plans and manages cash flows to ensure that there are optimal levels of cash in the bank at all times and avoid situations where the business could run out of cash and could not afford to pay its bills.
Revenues v. Expenses In addition, your business plan will compare your revenue forecasts to the budgeted costs to make sure that your financials are healthy and the business is set up for success.
5. Make Decisions
Whether you are starting a small business or expanding an existing one, a business plan is an important tool to help guide your decisions:
Sound decisions Gathering information for the business plan boosts your knowledge across many important areas of the business:
- Industry, market, customers and competitors
- Financial projections (e.g., revenue, expenses, assets, cash flow)
- Operations, technology and logistics
- Human resources (management and staff)
- Creating value for your customer through products and services
Decision-making skills The business planning process involves thorough research and critical thinking about many intertwined and complex business issues. As a result, it solidifies the decision-making skills of the business owner and builds a solid foundation for strategic planning , prioritization and sound decision making in your business. The more you understand, the better your decisions will be.
Planning Thorough planning allows you to determine the answer to some of the most critical business decisions ahead of time , prepare for anticipate problems before they arise, and ensure that any tactical solutions are in line with the overall strategy and goals.
If you do not take time to plan, you risk becoming overwhelmed by countless options and conflicting directions because you are not unclear about the mission , vision and strategy for your business.

6. Manage Risk
Some level of uncertainty is inherent in every business, but there is a lot you can do to reduce and manage the risk, starting with a business plan to uncover your weak spots.
You will need to take a realistic and pragmatic look at the hard facts and identify:
- Major risks , challenges and obstacles that you can expect on the way – so you can prepare to deal with them.
- Weaknesses in your business idea, business model and strategy – so you can fix them.
- Critical mistakes before they arise – so you can avoid them.
Essentially, the business plan is your safety net . Naturally, business plan cannot entirely eliminate risk, but it can significantly reduce it and prepare you for any challenges you may encounter.
7. Communicate Internally
Attract talent For a business to succeed, attracting talented workers and partners is of vital importance.
A business plan can be used as a communication tool to attract the right talent at all levels, from skilled staff to executive management, to work for your business by explaining the direction and growth potential of the business in a presentable format.
Align performance Sharing your business plan with all team members helps to ensure that everyone is on the same page when it comes to the long-term vision and strategy.
You need their buy-in from the beginning, because aligning your team with your priorities will increase the efficiency of your business as everyone is working towards a common goal .
If everyone on your team understands that their piece of work matters and how it fits into the big picture, they are more invested in achieving the objectives of the business.
It also makes it easier to track and communicate on your progress.
Share and explain business objectives with your management team, employees and new hires. Make selected portions of your business plan part of your new employee training.
8. Communicate Externally
Alliances If you are interested in partnerships or joint ventures, you may share selected sections of your plan with the potential business partners in order to develop new alliances.
Suppliers A business plan can play a part in attracting reliable suppliers and getting approved for business credit from suppliers. Suppliers who feel confident that your business will succeed (e.g., sales projections) will be much more likely to extend credit.
In addition, suppliers may want to ensure their products are being represented in the right way .
Professional Services Having a business plan in place allows you to easily share relevant sections with those you rely on to support the organization, including attorneys, accountants, and other professional consultants as needed, to make sure that everyone is on the same page.
Advisors Share the plan with experts and professionals who are in a position to give you valuable advice.
Landlord Some landlords and property managers require businesses to submit a business plan to be considered for a lease to prove that your business will have sufficient cash flows to pay the rent.
Customers The business plan may also function as a prospectus for potential customers, especially when it comes to large corporate accounts and exclusive customer relationships.
9. Secure Funding
If you intend to seek outside financing for your business, you are likely going to need a business plan.
Whether you are seeking debt financing (e.g. loan or credit line) from a lender (e.g., bank or financial institution) or equity capital financing from investors (e.g., venture or angel capital), a business plan can make the difference between whether or not – and how much – someone decides to invest.
Investors and financiers are always looking at the risk of default and the earning potential based on facts and figures. Understandably, anyone who is interested in supporting your business will want to check that you know what you are doing, that their money is in good hands, and that the venture is viable in the long run.
Business plans tend to be the most effective ways of proving that. A presentation may pique their interest , but they will most probably request a well-written document they can study in detail before they will be prepared to make any financial commitment.
That is why a business plan can often be the single most important document you can present to potential investors/financiers that will provide the structure and confidence that they need to make decisions about funding and supporting your company.
Be prepared to have your business plan scrutinized . Investors and financiers will conduct extensive checks and analyses to be certain that what is written in your business plan faithful representation of the truth.
10. Grow and Change
It is a very common misconception that a business plan is a static document that a new business prepares once in the start-up phase and then happily forgets about.
But businesses are not static. And neither are business plans. The business plan for any business will change over time as the company evolves and expands .
In the growth phase, an updated business plan is particularly useful for:
Raising additional capital for expansion
- Seeking financing for new assets , such as equipment or property
- Securing financing to support steady cash flows (e.g., seasonality, market downturns, timing of sale/purchase invoices)
- Forecasting to allocate resources according to strategic priority and operational needs
- Valuation (e.g., mergers & acquisitions, tax issues, transactions related to divorce, inheritance, estate planning)
Keeping the business plan updated gives established businesses better chance of getting the money they need to grow or even keep operating.
Business plan is also an excellent tool for planning an exit as it would include the strategy and timelines for a transfer to new ownership or dissolution of the company.
Also, if you ever make the decision to sell your business or position yourself for a merger or an acquisition , a strong business plan in hand is going to help you to maximize the business valuation.
Valuation is the process of establishing the worth of a business by a valuation expert who will draw on professional experience as well as a business plan that will outline what you have, what it’s worth now and how much will it likely produce in the future.
Your business is likely to be worth more to a buyer if they clearly understand your business model, your market, your assets and your overall potential to grow and scale .
Related Questions
Business plan purpose: what is the purpose of a business plan.
The purpose of a business plan is to articulate a strategy for starting a new business or growing an existing one by identifying where the business is going and how it will get there to test the viability of a business idea and maximize the chances of securing funding and achieving business goals and success.
Business Plan Benefits: What are the benefits of a business plan?
A business plan benefits businesses by serving as a strategic tool outlining the steps and resources required to achieve goals and make business ideas succeed, as well as a communication tool allowing businesses to articulate their strategy to stakeholders that support the business.
Business Plan Importance: Why is business plan important?
The importance of a business plan lies in it being a roadmap that guides the decisions of a business on the road to success, providing clarity on all aspects of its operations. This blueprint outlines the goals of the business and what exactly is needed to achieve them through effective management.
Sign up for our Newsletter
Get more articles just like this straight into your mailbox.
Related Posts
Recent Posts
This website uses cookies to enhance the user experience.
What stage is your business at?
Tell us and we'll match you with a special liveplan discount:, new business idea, startup phase, established business, new business discount, great, we have special savings for organizing your business ideas., get full access to liveplan for 50% off, save big with any monthly package, startup discount, great, we have special savings for businesses just starting up., save big on liveplan premium, save big with any liveplan premium package, established business discount, great, we have special savings for businesses that are up and running., get annual access to liveplan for 40% off, save big with any annual package.
Enter your email address to unlock it.
We care about your privacy. See our Privacy Policy .
🎧 Real entrepreneurs. Real stories.
Subscribe to The Hurdle podcast
You can do this! Tour LivePlan to see how simple business planning can be.
Have an expert write your plan, build your forecast, and so much more.

Integrations
For Small Businesses
For Advisors & Mentors
Planning a Business
What Is a Business Plan? Definition and Planning Essentials Explained

11 min. read
Updated September 23, 2024
What is a business plan? It’s the roadmap for your business. The outline of your goals, objectives, and the steps you’ll take to get there. It describes the structure of your organization, how it operates, as well as the financial expectations and actual performance.
A business plan can help you explore ideas, successfully start a business, manage operations, and pursue growth. In short, a business plan is a lot of different things. It’s more than just a stack of paper and can be one of your most effective tools as a business owner.
Let’s explore the basics of business planning, the structure of a traditional plan, your planning options, and how you can use your plan to succeed.
What is a business plan?
A business plan is a document that explains how your business operates. It summarizes your business structure, objectives, milestones, and financial performance. Again, it’s a guide that helps you, and anyone else, better understand how your business will succeed.

Why do you need a business plan?
The primary purpose of a business plan is to help you understand the direction of your business and the steps it will take to get there. Having a solid business plan can help you grow up to 30% faster , and according to our own 2021 Small Business research working on a business plan increases confidence regarding business health—even in the midst of a crisis.
These benefits are directly connected to how writing a business plan makes you more informed and better prepares you for entrepreneurship. It helps you reduce risk and avoid pursuing potentially poor ideas. You’ll also be able to more easily uncover your business’s potential.
The biggest mistake you can make is not writing a business plan, and the second is never updating it. By regularly reviewing your plan, you can understand what parts of your strategy are working and those that are not.
That just scratches the surface of why having a plan is valuable. Check out our full write-up for fifteen more reasons why you need a business plan .
What can you do with your plan?
So what can you do with a business plan once you’ve created it? It can be all too easy to write a plan and just let it be. Here are just a few ways you can leverage your plan to benefit your business.
Test an idea
Writing a plan isn’t just for those who are ready to start a business. It’s just as valuable for those who have an idea and want to determine whether it’s actually possible. By writing a plan to explore the validity of an idea, you are working through the process of understanding what it would take to be successful.
Market and competitive research alone can tell you a lot about your idea.
- • Is the marketplace too crowded?
- • Is the solution you have in mind not really needed?
Add in the exploration of milestones, potential expenses, and the sales needed to attain profitability, and you can paint a pretty clear picture of your business’s potential.

Document your strategy and goals
Understanding where you’re going and how you’re going to get there is vital for those starting or managing a business. Writing your plan helps you do that. It ensures that you consider all aspects of your business, know what milestones you need to hit, and can effectively make adjustments if that doesn’t happen.
With a plan in place, you’ll know where you want your business to go and how you’ve performed in the past. This alone prepares you to take on challenges, review what you’ve done before, and make the right adjustments.
Pursue funding
Even if you do not intend to pursue funding right away, having a business plan will prepare you for it. It will ensure that you have all of the information necessary to submit a loan application and pitch to investors.
So, rather than scrambling to gather documentation and write a cohesive plan once it’s relevant, you can keep it up-to-date and attempt to attain funding. Just add a use of funds report to your financial plan and you’ll be ready to go.
The benefits of having a plan don’t stop there. You can then use your business plan to help you manage the funding you receive. You’ll not only be able to easily track and forecast how you’ll use your funds but also easily report on how it’s been used.
Better manage your business
A solid business plan isn’t meant to be something you do once and forget about. Instead, it should be a useful tool that you can regularly use to analyze performance, make strategic decisions, and anticipate future scenarios. It’s a document that you should regularly update and adjust as you go to better fit the actual state of your business.
Doing so makes it easier to understand what’s working and what’s not. It helps you understand if you’re truly reaching your goals or if you need to make further adjustments. Having your plan in place makes that process quicker, more informative, and leaves you with far more time to actually spend running your business.
What should your business plan include?
The content and structure of your business plan should include anything that will help you use it effectively. That being said, there are some key elements that you should cover and that investors will expect to see.
Executive summary
The executive summary is a simple overview of your business and your overall plan. It should serve as a standalone document that provides enough detail for anyone—including yourself, team members, or investors—to fully understand your business strategy. Make sure to cover:
- • The problem you’re solving
- • A description of your product or service
- • Your target market
- • Organizational structure
- • A financial summary
- • Necessary funding requirements.
This will be the first part of your plan, but it’s easiest to write it after you’ve created your full plan.
Products & Services
When describing your products or services, you need to start by outlining the problem you’re solving and why what you offer is valuable. This is where you’ll also address current competition in the market and any competitive advantages your products or services bring to the table.
Lastly, outline the steps or milestones you’ll need to hit to launch your business successfully. If you’ve already achieved some initial milestones, like taking pre-orders or early funding, be sure to include them here to further prove your business’s validity.
Market analysis
A market analysis is a qualitative and quantitative assessment of the current market you’re entering or competing in. It helps you understand the industry’s overall state and potential, who your ideal customers are, the positioning of your competition, and how you intend to position your own business.
This helps you better explore the market’s long-term trends, what challenges to expect, and how you will need to introduce and even price your products or services.
Check out our full guide for how to conduct a market analysis in just four easy steps.
Marketing & sales
Here you detail how you intend to reach your target market. This includes your sales activities, general pricing plan, and the beginnings of your marketing strategy. If you have any branding elements, sample marketing campaigns, or messaging available—this is the place to add them.
Additionally, it may be wise to include a SWOT analysis that demonstrates your business or specific product/service position. This will showcase how you intend to leverage sales and marketing channels to deal with competitive threats and take advantage of any opportunities.
Check out our full write-up to learn how to create a cohesive marketing strategy for your business.
Organization & management
This section addresses the legal structure of your business, your current team, and any gaps that need to be filled. Depending on your business type and longevity, you’ll also need to include your location, ownership information, and business history.
Basically, add any information that helps explain your organizational structure and how you operate. This section is particularly important for pitching to investors but should be included even if attempted funding is not in your immediate future.
Financial projections
Possibly the most important piece of your plan, your financials section is vital for showcasing your business’s viability. It also helps you establish a baseline to measure against and makes it easier to make ongoing strategic decisions as your business grows. This may seem complex, but it can be far easier than you think.
Focus on building solid forecasts, keep your categories simple, and lean on assumptions. You can always return to this section to add more details and refine your financial statements as you operate.
Here are the statements you should include in your financial plan:
- • Sales and revenue projections
- • Profit and loss statement
- • Cash flow statement
- • Balance sheet
The appendix is where you add additional detail, documentation, or extended notes that support the other sections of your plan. Don’t worry about adding this section at first; only add documentation that you think will benefit anyone reading your plan.
Types of business plans explained
While all business plans cover similar categories, the style and function depend on how you intend to use your business plan . So, to get the most out of your plan, it’s best to find a format that suits your needs. Here are a few common business plan types worth considering.
Traditional business plan
The tried-and-true traditional business plan (sometimes called a detailed business plan ) is a formal document meant for external purposes. It is typically required when applying for a business loan or pitching to investors.
It can also be used when training or hiring employees, working with vendors, or any other situation where the full details of your business must be understood by another individual.
A traditional business plan follows the outline above and can be anywhere from 10-50 pages depending on the amount of detail included, the complexity of your business, and what you include in your appendix. We recommend only starting with this business plan format if you plan to immediately pursue funding and already have a solid handle on your business information.
Business model canvas
The business model canvas is a one-page template designed to demystify the business planning process. It removes the need for a traditional, copy-heavy business plan, in favor of a single-page outline that can help you and outside parties better explore your business idea.
The structure ditches a linear structure in favor of a cell-based template. It encourages you to build connections between every element of your business. It’s faster to write out and update and much easier for you, your team, and anyone else to visualize your business operations.
The business model canvas is really best for those exploring their business idea for the first time, but keep in mind that it can be difficult to actually validate your idea this way as well as adapt it into a full plan.
One-page business plan
The true middle ground between the business model canvas and a traditional business plan is the one-page business plan . Sometimes referred to as a lean plan, this format is a simplified version of the traditional plan that focuses on the core aspects of your business. It basically serves as a beefed-up pitch document and can be finished as quickly as the business model canvas.
By starting with a one-page plan, you give yourself a minimal document to build from. You’ll typically stick with bullet points and single sentences making it much easier to elaborate or expand sections into a longer-form business plan.
A one-page business plan is useful for those exploring ideas, needing to validate their business model, or who need an internal plan to help them run and manage their business.
Growth plan
Now, the option that we here at LivePlan recommend is a growth plan . However, growth planning is less of a specific document type and more of a methodology. It takes the simplicity and styling of the one-page business plan and turns it into a process for you to continuously plan, test, review, refine, and take action based on performance.
It holds all of the benefits of the single-page plan, including the potential to complete it in as little as 27-minutes .
However, it’s even easier to convert into a more detailed business plan thanks to how heavily it’s tied to your financials. The overall goal of growth planning isn’t to just produce documents that you use once and shelve. Instead, the growth planning process helps you build a healthier company that thrives in times of growth and stable through times of crisis.
It’s faster, concise, more focused on financial performance, and ensures that your plan is always up-to-date.
How can you write your own business plan?
Now that you know the definition of a business plan, it’s time to write your own.
Get started by downloading our free business plan template or try a business plan builder like LivePlan for a fully guided experience and an AI-powered Assistant to help you write, generate ideas, and analyze your business performance.
No matter which option you choose, writing a business plan will set you up for success. You can use it to test an idea, figure out how you’ll start, and pursue funding. And if you review and revise your plan regularly, it can turn into your best business management tool.
Like this post? Share with a friend!
Kody currently works as the Inbound and Content Marketing Specialist at Palo Alto Software and runs editorial for both LivePlan and Bplans, working with various freelance specialists and in-house writers. A graduate of the University of Oregon, he specializes in SEO research, content writing, and branding.

Table of Contents
Related articles.

Elon Glucklich
October 10, 2024
Budget Vs Forecast: Differences Explained + What to Prioritize

Noah Parsons
October 15, 2024
How to Do a Sales Forecast for Your Business the Right Way

October 1, 2024
Cash Flow Statement: Definition + How to Create and Read it

July 31, 2024
What is Cash Runway + How to Calculate it

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Business plan writers are responsible for crafting the face of a business organization they hope to build. It cannot be easy because a business plan should be a versatile document that covers vario…
A business plan is a comprehensive document that outlines a company's goals, strategies, and financial projections. It provides a detailed description of the …
This plan, known as a business plan, is a comprehensive document that outlines a company’s goals, strategies, and financial projections. Whether you’re starting a new business or looking to expand an …
A business plan lays out a strategic roadmap for any new or growing business. Any entrepreneur with a great idea for a business needs to conduct market research, analyze their competitors, validate their idea by …
What Is a Business Plan? A business plan is a document that outlines a company's goals and the strategies to achieve them. It's valuable for both startups and...
A business plan is an operating document that describes the dream of an entrepreneur with the objectives and plans to achieve them. A business plan shows the …
The importance, purpose and benefit of a business plan is in that it enables you to validate a business idea, secure funding, set strategic goals – and then take organized action on those goals by making decisions, managing …
A business plan is a document that explains how your business operates. It summarizes your business structure, objectives, milestones, and financial performance. Again, it’s a guide that helps you, and …