
How to Write a Master's Thesis: A Guide to Planning Your Thesis, Pursuing It, and Avoiding Pitfalls
#scribendiinc
Part 1: Initial Considerations
Who needs to write a master’s thesis.
Thesis writing is one of the more daunting challenges of higher education. That being said, not all master's students have to write a thesis. For example, fields that place a stronger emphasis on applied knowledge, such as nursing, business, and education, tend to have projects and exams to test students on the skills and abilities associated with those fields. Conversely, in disciplines that require in-depth research or highly polished creative abilities, students are usually expected to prove their understanding and independence with a thesis.
What's Your Goal?
Do you want to write a thesis? The process is a long one, often spanning years. It's best to know exactly what you want before you begin. Many people are motivated by career goals. For example, hiring managers may see a master's degree as proof that the candidate is an expert within their field and can lead, motivate, and demonstrate initiative for themselves and others. Others dream of earning their doctorate, and they see a master's degree as a stepping stone toward their Ph.D .

No matter what your desired goal is, you should have one before you start your thesis. With your goal in mind, your work will have a purpose, which will allow you to measure your progress more easily.
Major Types of Theses
Once you've carefully researched or even enrolled in a master's program—a feat that involves its own planning and resources —you should know if you are expected to produce a quantitative (which occurs in many math and science programs), qualitative (which occurs in many humanities programs), or creative (which occurs in many creative writing, music, or fine arts programs) thesis.
Time and Energy Considerations
Advanced degrees are notoriously time and energy consuming. If you have a job, thesis writing will become your second job. If you have a family, they will need to know that your thesis will take a great deal of your attention, energy, and focus.

Your studies should not consume you, but they also should not take a back seat to everything else. You will be expected to attend classes, conduct research, source relevant literature, and schedule meetings with various people as you pursue your master's, so it's important to let those you care about know what's going on.
As a general note, most master's programs expect students to finish within a two-year period but are willing to grant extra time if requested, especially if that time is needed to deal with unexpected life events (more on those later).
Part 2: Form an Initial Thesis Question, and Find a Supervisor
When to begin forming your initial thesis question.
Some fields, such as history, may require you to have already formed your thesis question and to have used it to create a statement of intent (outlining the nature of your research) prior to applying to a master’s program. Others may require this information only after you've been accepted. Most of the time, you will be expected to come up with your topic yourself. However, in some disciplines, your supervisor may assign a general research topic to you.
Overall, requirements vary immensely from program to program, so it's best to confirm the exact requirements of your specific program.
What to Say to Your Supervisor
You will have a supervisor during your master's studies. Have you identified who that person will be? If yes, have you introduced yourself via email or phone and obtained information on the processes and procedures that are in place for your master's program? Once you've established contact, request an in-person meeting with him or her, and take a page of questions along with you. Your questions might include:
- Is there a research subject you can recommend in my field?
- I would like to pursue [target research subject] for my thesis. Can you help me narrow my focus?
- Can you give me an example of a properly formatted thesis proposal for my program?
Don't Be Afraid to Ask for Help (to a Degree)
Procedures and expectations vary from program to program, and your supervisor is there to help remove doubt and provide encouragement so you can follow the right path when you embark on writing your thesis. Since your supervisor has almost certainly worked with other graduate students (and was one at some point), take advantage of their experience, and ask questions to put your mind at ease about how to write a master’s thesis.
That being said, do not rely too heavily on your supervisor. As a graduate student, you are also expected to be able to work independently. Proving your independent initiative and capacity is part of what will earn you your master's degree.
Part 3: Revise Your Thesis
Read everything you can get your hands on.
Whether you have a question or need to create one, your next step is simple and applies to all kinds of theses: read.

Seek Out Knowledge or Research Gaps
Read everything you can that relates to the question or the field you are studying. The only way you will be able to determine where you can go is to see where everyone else has been. After you have read some published material, you will start to spot gaps in current research or notice things that could be developed further with an alternative approach. Things that are known but not understood or understood but not explained clearly or consistently are great potential thesis subjects. Addressing something already known from a new perspective or with a different style could also be a potentially valuable project. Whichever way you choose to do it, keep in mind that your project should make a valuable contribution to your field.

Talk with Experts in Your Field (and Don't Be Afraid to Revise Your Thesis)
To help narrow down your thesis topic, talk to your supervisor. Your supervisor will have an idea of what is current in your field and what can be left alone because others are already working on it. Additionally, the school you are attending will have programs and faculty with particular areas of interest within your chosen field.
On a similar note, don't be surprised if your thesis question changes as you study. Other students and researchers are out there, and as they publish, what you are working on can change. You might also discover that your question is too vague, not substantial enough, or even no longer relevant. Do not lose heart! Take what you know and adjust the question to address these concerns as they arise. The freedom to adapt is part of the power you hold as a graduate student.
Part 4: Select a Proposal Committee
What proposal committees are and why they're useful.
When you have a solid question or set of questions, draft a proposal.

You'll need an original stance and a clear justification for asking, and answering, your thesis question. To ensure this, a committee will review your thesis proposal. Thankfully, that committee will consist of people assigned by your supervisor or department head or handpicked by you. These people will be experts who understand your field of study and will do everything in their power to ensure that you are pursuing something worthwhile. And yes, it is okay to put your supervisor on your committee. Some programs even require that your supervisor be on your committee.
Just remember that the committee will expect you to schedule meetings with them, present your proposal, respond to any questions they might have for you, and ultimately present your findings and thesis when all the work is done. Choose those who are willing to support you, give constructive feedback, and help address issues with your proposal. And don't forget to give your proposal a good, thorough edit and proofread before you present it.
How to Prepare for Committee Meetings
Be ready for committee meetings with synopses of your material for committee members, answers for expected questions, and a calm attitude. To prepare for those meetings, sit in on proposal and thesis defenses so you can watch how other graduate students handle them and see what your committee might ask of you. You can even hold rehearsals with friends and fellow students acting as your committee to help you build confidence for your presentation.

Part 5: Write Your Thesis
What to do once your proposal is approved.
After you have written your thesis proposal and received feedback from your committee, the fun part starts: doing the work. This is where you will take your proposal and carry it out. If you drafted a qualitative or quantitative proposal, your experimentation or will begin here. If you wrote a creative proposal, you will now start working on your material. Your proposal should be strong enough to give you direction when you perform your experiments, conduct interviews, or craft your work. Take note that you will have to check in with your supervisor from time to time to give progress updates.

Thesis Writing: It's Important to Pace Yourself and Take Breaks
Do not expect the work to go quickly. You will need to pace yourself and make sure you record your progress meticulously. You can always discard information you don't need, but you cannot go back and grab a crucial fact that you can't quite remember. When in doubt, write it down. When drawing from a source, always create a citation for the information to save your future self time and stress. In the same sense, you may also find journaling to be a helpful process.
Additionally, take breaks and allow yourself to step away from your thesis, even if you're having fun (and especially if you're not). Ideally, your proposal should have milestones in it— points where you can stop and assess what you've already completed and what's left to do. When you reach a milestone, celebrate. Take a day off and relax. Better yet, give yourself a week's vacation! The rest will help you regain your focus and ensure that you function at your best.
How to Become More Comfortable with Presenting Your Work
Once you start reaching your milestones, you should be able to start sharing what you have. Just about everyone in a graduate program has experience giving a presentation at the front of the class, attending a seminar, or watching an interview. If you haven't (or even if you have), look for conferences and clubs that will give you the opportunity to learn about presenting your work and become comfortable with the idea of public speaking. The more you practice talking about what you are studying, the more comfortable you'll be with the information, which will make your committee defenses and other official meetings easier.
Published authors can be called upon to present at conferences, and if your thesis is strong, you may receive an email or a phone call asking if you would share your findings onstage.
Presenting at conferences is also a great way to boost your CV and network within your field. Make presenting part of your education, and it will become something you look forward to instead of fear.
What to Do If Your Relationship with Your Supervisor Sours
A small aside: If it isn't already obvious, you will be communicating extensively with others as you pursue your thesis. That also means that others will need to communicate with you, and if you've been noticing things getting quiet, you will need to be the one to speak up. Your supervisor should speak to you at least once a term and preferably once a week in the more active parts of your research and writing. If you give written work to your supervisor, you should have feedback within three weeks.
If your supervisor does not provide feedback, frequently misses appointments, or is consistently discouraging of your work, contact your graduate program advisor and ask for a new supervisor. The relationship with your supervisor is crucial to your success, especially if she or he is on your committee, and while your supervisor does not have to be friendly, there should at least be professional respect between you.
What to Do If a Crisis Strikes
If something happens in your life that disrupts everything (e.g., emotional strain, the birth of a child, or the death of a family member), ask for help. You are a human being, and personal lives can and do change without warning. Do not wait until you are falling apart before asking for help, either. Learn what resources exist for crises before you have one, so you can head off trauma before it hits. That being said, if you get blindsided, don't refuse help. Seek it out, and take the time you need to recover. Your degree is supposed to help you become a stronger and smarter person, not break you.
Part 6: Polish and Defend Your Master's Thesis
How to write a master’s thesis: the final stages.
After your work is done and everything is written down, you will have to give your thesis a good, thorough polishing. This is where you will have to organize the information, draft it into a paper format with an abstract, and abbreviate things to help meet your word-count limit. This is also where your final editing and proofreading passes will occur, after which you will face your final hurdle: presenting your thesis defense to your committee. If they approve your thesis, then congratulations! You are now a master of your chosen field.
Conclusion and Parting Thoughts
Remember that you do not (and should not) have to learn how to write a master’s thesis on your own. Thesis writing is collaborative, as is practically any kind of research.

While you will be expected to develop your thesis using your own initiative, pursue it with your own ambition, and complete it with your own abilities, you will also be expected to use all available resources to do so. The purpose of a master's thesis is to help you develop your own independent abilities, ensuring that you can drive your own career forward without constantly looking to others to provide direction. Leaders get master's degrees. That's why many business professionals in leadership roles have graduate degree initials after their last names. If you already have the skills necessary to motivate yourself, lead others, and drive change, you may only need your master's as an acknowledgement of your abilities. If you do not, but you apply yourself carefully and thoroughly to the pursuit of your thesis, you should come away from your studies with those skills in place.
A final thought regarding collaboration: all theses have a section for acknowledgements. Be sure to say thank you to those who helped you become a master. One day, someone might be doing the same for you.
Image source: Falkenpost/Pixabay.com
We’re Masters at Master’s Theses! Make Yours Shine.
Let our expert academic editors perfect your writing, or get a free sample, about the author.

A Scribendi in-house editor, Anthony is happily putting his BA in English from Western University to good use with thoughtful feedback and incisive editing. An avid reader and gamer, he can be found during his off hours enjoying narrative-driven games and obscure and amusing texts, as well as cooking for his family.
Have You Read?
"The Complete Beginner's Guide to Academic Writing"
Related Posts

How to Write a Thesis or Dissertation

Selecting a Thesis Committee

Thesis/Dissertation Writing Series: How to Write a Literature Review
Upload your file(s) so we can calculate your word count, or enter your word count manually.
We will also recommend a service based on the file(s) you upload.
| File | Word Count | Include in Price? |
|---|
English is not my first language. I need English editing and proofreading so that I sound like a native speaker.
I need to have my journal article, dissertation, or term paper edited and proofread, or I need help with an admissions essay or proposal.
I have a novel, manuscript, play, or ebook. I need editing, copy editing, proofreading, a critique of my work, or a query package.
I need editing and proofreading for my white papers, reports, manuals, press releases, marketing materials, and other business documents.
I need to have my essay, project, assignment, or term paper edited and proofread.
I want to sound professional and to get hired. I have a resume, letter, email, or personal document that I need to have edited and proofread.
Prices include your personal % discount.
Prices include % sales tax ( ).

/images/cornell/logo35pt_cornell_white.svg" alt="masteral thesis"> Cornell University --> Graduate School
Guide to writing your thesis/dissertation, definition of dissertation and thesis.
The dissertation or thesis is a scholarly treatise that substantiates a specific point of view as a result of original research that is conducted by students during their graduate study. At Cornell, the thesis is a requirement for the receipt of the M.A. and M.S. degrees and some professional master’s degrees. The dissertation is a requirement of the Ph.D. degree.
Formatting Requirement and Standards
The Graduate School sets the minimum format for your thesis or dissertation, while you, your special committee, and your advisor/chair decide upon the content and length. Grammar, punctuation, spelling, and other mechanical issues are your sole responsibility. Generally, the thesis and dissertation should conform to the standards of leading academic journals in your field. The Graduate School does not monitor the thesis or dissertation for mechanics, content, or style.
“Papers Option” Dissertation or Thesis
A “papers option” is available only to students in certain fields, which are listed on the Fields Permitting the Use of Papers Option page , or by approved petition. If you choose the papers option, your dissertation or thesis is organized as a series of relatively independent chapters or papers that you have submitted or will be submitting to journals in the field. You must be the only author or the first author of the papers to be used in the dissertation. The papers-option dissertation or thesis must meet all format and submission requirements, and a singular referencing convention must be used throughout.
ProQuest Electronic Submissions
The dissertation and thesis become permanent records of your original research, and in the case of doctoral research, the Graduate School requires publication of the dissertation and abstract in its original form. All Cornell master’s theses and doctoral dissertations require an electronic submission through ProQuest, which fills orders for paper or digital copies of the thesis and dissertation and makes a digital version available online via their subscription database, ProQuest Dissertations & Theses . For master’s theses, only the abstract is available. ProQuest provides worldwide distribution of your work from the master copy. You retain control over your dissertation and are free to grant publishing rights as you see fit. The formatting requirements contained in this guide meet all ProQuest specifications.
Copies of Dissertation and Thesis
Copies of Ph.D. dissertations and master’s theses are also uploaded in PDF format to the Cornell Library Repository, eCommons . A print copy of each master’s thesis and doctoral dissertation is submitted to Cornell University Library by ProQuest.
- Linguistics
- Composition Studies
HOW TO WRITE YOUR MASTER THESIS: THE EASY HANDBOOK

- Beirut Arab University
Discover the world's research
- 25+ million members
- 160+ million publication pages
- 2.3+ billion citations

- A Lengálová
- Recruit researchers
- Join for free
- Login Email Tip: Most researchers use their institutional email address as their ResearchGate login Password Forgot password? Keep me logged in Log in or Continue with Google Welcome back! Please log in. Email · Hint Tip: Most researchers use their institutional email address as their ResearchGate login Password Forgot password? Keep me logged in Log in or Continue with Google No account? Sign up
- Thesis Action Plan New
- Academic Project Planner
Literature Navigator
Thesis dialogue blueprint, writing wizard's template, research proposal compass.
- See Success Stories
- Access Free Resources
- Why we are different
- All Products
- Coming Soon
Structure of a Master Thesis: Essential Components

Writing a master thesis is a crucial milestone in a student's academic journey. It serves as a testament to their research capabilities, analytical skills, and subject matter expertise. Understanding the structure of a master thesis is essential for crafting a well-organized and coherent document. This article delves into the essential components of a master thesis, providing a comprehensive guide to help students navigate this complex process with confidence.
Key Takeaways
- A well-crafted title page and abstract are essential for making a strong first impression and summarizing the thesis effectively.
- The introduction and research questions section sets the stage by establishing the context, defining the research problem, and formulating key questions.
- A thorough literature review identifies existing research, highlights gaps, and establishes the theoretical framework for the study.
- The methodology section details the research design, data collection methods, and data analysis techniques, ensuring the study's reliability and validity.
- The findings and discussion section presents the results, interprets the findings, and explores their implications for future research.
Title Page and Abstract
Your title and abstract will be used by search engines to help potential audiences locate your work, so clarity will help to draw the attention of your targeted readers. The title page is the first impression of your thesis. It should include the title, your name, and the institution's name. Ensure that the title is concise yet descriptive enough to convey the essence of your research. Formatting your thesis correctly is crucial, as it sets the tone for the rest of your work.
The abstract is a brief summary of your thesis, usually around 150-300 words. It should provide a snapshot of your research, including the problem statement, methodology, results, and conclusions. Include the heading “ABSTRACT” in all capital letters, and center it 2″ below the top of the page. One double-spaced line below “ABSTRACT”, center your name, followed by a colon and the title of the thesis or dissertation. Use as many lines as necessary. Be sure that your name and the title exactly match the name and title used on the Title page. This section is often the most read part of your thesis, so make it compelling and informative.
Keywords are essential for indexing and searchability. They should be specific to your research and reflect the core topics of your thesis. Place them immediately after the abstract. These keywords will help other researchers find your work more easily. Including relevant keywords can significantly reduce thesis anxiety by making your research more accessible and easier to locate in academic databases.
Introduction and Research Questions
An introduction sets up the topic, purpose, and relevance of your thesis, as well as expectations for your reader. This should:
- Ground your research topic, sharing any background information your reader may need
- Define the scope of your work
- Introduce any existing research on your topic, situating your work within a broader problem or debate
- State your research question(s)
- Outline (briefly) how the remainder of your work will proceed
Establishing the Context
The introduction should provide a comprehensive background to the topic. This includes a brief review of current knowledge and an indication of the gap in knowledge that your research aims to fill. Grounding your research topic is essential for helping your reader understand the broader context of your work.
Defining the Research Problem
Clearly define the research problem you are addressing. This involves stating the aim of your research and how it fits into the identified gap. The research problem should be specific and manageable within the scope of your thesis.
Formulating Research Questions
The introduction should also provide at least one research question that you try to answer. Knowing how to find research question is crucial for guiding your research process. These questions should be clear, focused, and researchable, setting the stage for your methodology and analysis.
Literature Review
A literature review is a critical component of your master thesis, providing an overview of existing research on your topic. It allows you to identify gaps in the literature and position your research within the broader academic context. A well-structured literature review not only summarizes existing studies but also critically evaluates them to highlight the relevance and originality of your work.
Methodology
Your methodology chapter shows your reader how you conducted your research. It should be written clearly and methodically, easily allowing your reader to critically assess the credibility of your argument. Furthermore, your methods section should convince your reader that your method was the best way to answer your research question.
Findings and Discussion
Presenting the results.
In this section, you will present the core findings of your research. Ensure that the data is organized logically, often using tables or figures for clarity. The purpose of the discussion section is to interpret and describe the significance of your findings in relation to what was already known about the research problem. This is where you highlight the key results and provide a detailed account of the data collected.
Interpreting the Findings
Here, you will delve into the meaning of your results. Did they meet your expectations? How well do they fit within the framework that you built? You can refer back to any relevant source material to situate your results within your field, but leave most of that analysis in your literature review. For any unexpected results, offer explanations or alternative interpretations of your data. This section should also relate your specific results to previous research or theory , pointing out what the limitations were of your study, and noting any questions that remain unanswered.
Implications for Future Research
Discuss the broader implications of your findings. What do they mean for the field? How can they inform future research? This is where you can suggest areas for further investigation and propose how future studies can build on your work. Emphasize that your research aims/objectives have been achieved and outline any potential applications of your findings. This section can also include conclusions and suggestions for future research directions, ensuring that your study contributes to the ongoing academic dialogue.
Conclusion and Recommendations
In the conclusion of your master thesis, you must emphasize that your research objectives have been achieved . This section should succinctly review the results in relation to the original problem statement, assessing the success of the study based on the criteria of success outlined in the introduction. Additionally, it is crucial to point out the limitations of your study, provide explanations for unexpected results, and note any questions that remain unanswered.
References and Appendices
Citing sources.
In your thesis, it is crucial to properly cite all sources to maintain academic integrity and avoid plagiarism. Ensure that you follow the specific citation style required by your institution, whether it be APA, MLA, Chicago, or another format. Each citation style has its own set of rules for formatting references, so be meticulous in adhering to these guidelines. Proper citation not only gives credit to the original authors but also allows readers to trace the origins of your research.
Formatting the Reference List
Your reference list should be formatted consistently and appear at the end of your thesis. This section should include all the sources you have cited throughout your work. Pay attention to the alphabetical order and the specific formatting rules of your chosen citation style. A well-organized reference list enhances the credibility of your research and provides a clear roadmap for readers to follow your scholarly trail.
Including Supplementary Material
Appendices should go after your references/works cited list , and they should be formatted as heading 1. Appendices are used to provide additional information that is not essential to the main text but may be useful for the interested reader. This can include extensive tables, mathematical proofs, or series of graphics. Each appendix should have a title, a letter (Appendix A, B, C), and an introductory paragraph. Remember, your thesis should be understandable without reading any appendices, but these supplementary materials can offer valuable insights and data for those who wish to delve deeper.
For more detailed information and additional resources, please visit our website . Our comprehensive guides and innovative tools are designed to help you overcome any academic challenge with ease. Don't miss out on our special offers and free previews!
In conclusion, the structure of a master thesis is a critical component that ensures the clarity, coherence, and academic rigor of the research presented. Each section, from the introduction to the conclusion, plays a vital role in guiding the reader through the research journey, providing context, methodology, findings, and interpretations. Adhering to a well-defined structure not only facilitates the writing process but also enhances the overall quality and impact of the thesis. By meticulously organizing their work, students can effectively communicate their research contributions and demonstrate their scholarly competence. As such, understanding and implementing the essential components of a master thesis is indispensable for academic success.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the purpose of the title page in a master thesis.
The title page provides essential information about the thesis, including the title, author, institution, department, and date of submission. It serves as the formal introduction to the document.
How should I structure the abstract of my thesis?
An abstract should be a concise summary of the main points of your research, including the research problem, methods, results, and conclusions. It typically ranges from 150 to 300 words.
Why are keywords important in a thesis?
Keywords help to categorize your research and make it easier for others to find your work in databases and search engines. They should represent the main topics and concepts of your thesis.
What should be included in the literature review section?
The literature review should survey existing research related to your topic, identify gaps in the literature, and establish the theoretical framework for your study.
What are the common methodologies used in thesis research?
Common methodologies include qualitative methods (such as interviews and case studies), quantitative methods (such as surveys and experiments), and mixed methods, which combine both qualitative and quantitative approaches.
How do I properly cite sources in my thesis?
Proper citation involves following a specific citation style (such as APA, MLA, or Chicago) to give credit to the original authors of the works you referenced. This includes in-text citations and a comprehensive reference list at the end of your thesis.

Discovering Statistics Using IBM SPSS Statistics: A Fun and Informative Guide

Unlocking the Power of Data: A Review of 'Essentials of Modern Business Statistics with Microsoft Excel'

Discovering Statistics Using SAS: A Comprehensive Review

The Thesis Survival Kit: Essential Tools and Resources for a Successful Journey

Looking for a Thesis Proposal Example? Here’s the Best Format to Follow

How to Research for Your Thesis Paper Without Feeling Overwhelmed

Thesis Action Plan

- Rebels Blog
- Blog Articles
- Affiliate Program
- Terms and Conditions
- Payment and Shipping Terms
- Privacy Policy
- Return Policy
© 2024 Research Rebels, All rights reserved.
Your cart is currently empty.
- Home »
find your perfect postgrad program Search our Database of 30,000 Courses
How to write a masters dissertation or thesis: top tips.
It is completely normal to find the idea of writing a masters thesis or dissertation slightly daunting, even for students who have written one before at undergraduate level. Though, don’t feel put off by the idea. You’ll have plenty of time to complete it, and plenty of support from your supervisor and peers.
One of the main challenges that students face is putting their ideas and findings into words. Writing is a skill in itself, but with the right advice, you’ll find it much easier to get into the flow of writing your masters thesis or dissertation.
We’ve put together a step-by-step guide on how to write a dissertation or thesis for your masters degree, with top tips to consider at each stage in the process.
1. Understand your dissertation or thesis topic
There are slight differences between theses and dissertations , although both require a high standard of writing skill and knowledge in your topic. They are also formatted very similarly.
At first, writing a masters thesis can feel like running a 100m race – the course feels very quick and like there is not as much time for thinking! However, you’ll usually have a summer semester dedicated to completing your dissertation – giving plenty of time and space to write a strong academic piece.
By comparison, writing a PhD thesis can feel like running a marathon, working on the same topic for 3-4 years can be laborious. But in many ways, the approach to both of these tasks is quite similar.
Before writing your masters dissertation, get to know your research topic inside out. Not only will understanding your topic help you conduct better research, it will also help you write better dissertation content.
Also consider the main purpose of your dissertation. You are writing to put forward a theory or unique research angle – so make your purpose clear in your writing.
Top writing tip: when researching your topic, look out for specific terms and writing patterns used by other academics. It is likely that there will be a lot of jargon and important themes across research papers in your chosen dissertation topic.
2. Structure your dissertation or thesis
Writing a thesis is a unique experience and there is no general consensus on what the best way to structure it is.
As a postgraduate student , you’ll probably decide what kind of structure suits your research project best after consultation with your supervisor. You’ll also have a chance to look at previous masters students’ theses in your university library.
To some extent, all postgraduate dissertations are unique. Though they almost always consist of chapters. The number of chapters you cover will vary depending on the research.
A masters dissertation or thesis organised into chapters would typically look like this:
| Section | Description |
| Title page | The opening page includes all relevant information about the project. |
| Abstract | A brief project summary including background, methodology and findings. |
| Contents | A list of chapters and figures from your project. |
| Chapter 1 – Background | A description of the rationale behind your project. |
| Chapter 2 – Literature Review | A summary and evaluation of the literature supporting your project. |
| Chapter 3 – Methodology | A description of the specific methodology used in your project. |
| Chapter 4-6 – Data analysis and Findings | An overview of the key findings and data from your research. |
| Chapter 7 - Discussion and Evaluation | A description of what the data means and what you can draw from the findings. |
| Chapter 8 - Conclusion | Main summary of your overall project and key findings. |
| Bibliography | A list of the references cited in your dissertation or thesis. |
| Appendices | Additional materials used in your research. |
Write down your structure and use these as headings that you’ll write for later on.
Top writing tip : ease each chapter together with a paragraph that links the end of a chapter to the start of a new chapter. For example, you could say something along the lines of “in the next section, these findings are evaluated in more detail”. This makes it easier for the reader to understand each chapter and helps your writing flow better.
3. Write up your literature review
One of the best places to start when writing your masters dissertation is with the literature review. This involves researching and evaluating existing academic literature in order to identify any gaps for your own research.
Many students prefer to write the literature review chapter first, as this is where several of the underpinning theories and concepts exist. This section helps set the stage for the rest of your dissertation, and will help inform the writing of your other dissertation chapters.
What to include in your literature review
The literature review chapter is more than just a summary of existing research, it is an evaluation of how this research has informed your own unique research.
Demonstrate how the different pieces of research fit together. Are there overlapping theories? Are there disagreements between researchers?
Highlight the gap in the research. This is key, as a dissertation is mostly about developing your own unique research. Is there an unexplored avenue of research? Has existing research failed to disprove a particular theory?
Back up your methodology. Demonstrate why your methodology is appropriate by discussing where it has been used successfully in other research.
4. Write up your research
For instance, a more theoretical-based research topic might encompass more writing from a philosophical perspective. Qualitative data might require a lot more evaluation and discussion than quantitative research.
Methodology chapter
The methodology chapter is all about how you carried out your research and which specific techniques you used to gather data. You should write about broader methodological approaches (e.g. qualitative, quantitative and mixed methods), and then go into more detail about your chosen data collection strategy.
Data collection strategies include things like interviews, questionnaires, surveys, content analyses, discourse analyses and many more.
Data analysis and findings chapters
The data analysis or findings chapter should cover what you actually discovered during your research project. It should be detailed, specific and objective (don’t worry, you’ll have time for evaluation later on in your dissertation)
Write up your findings in a way that is easy to understand. For example, if you have a lot of numerical data, this could be easier to digest in tables.
This will make it easier for you to dive into some deeper analysis in later chapters. Remember, the reader will refer back to your data analysis section to cross-reference your later evaluations against your actual findings – so presenting your data in a simple manner is beneficial.
Think about how you can segment your data into categories. For instance, it can be useful to segment interview transcripts by interviewee.
Top writing tip : write up notes on how you might phrase a certain part of the research. This will help bring the best out of your writing. There is nothing worse than when you think of the perfect way to phrase something and then you completely forget it.
5. Discuss and evaluate
Once you’ve presented your findings, it’s time to evaluate and discuss them.
It might feel difficult to differentiate between your findings and discussion sections, because you are essentially talking about the same data. The easiest way to remember the difference is that your findings simply present the data, whereas your discussion tells the story of this data.
Your evaluation breaks the story down, explaining the key findings, what went well and what didn’t go so well.
In your discussion chapter, you’ll have chance to expand on the results from your findings section. For example, explain what certain numbers mean and draw relationships between different pieces of data.
Top writing tip: don’t be afraid to point out the shortcomings of your research. You will receive higher marks for writing objectively. For example, if you didn’t receive as many interview responses as expected, evaluate how this has impacted your research and findings. Don’t let your ego get in the way!
6. Write your introduction
Your introduction sets the scene for the rest of your masters dissertation. You might be wondering why writing an introduction isn't at the start of our step-by-step list, and that’s because many students write this chapter last.
Here’s what your introduction chapter should cover:
Problem statement
Research question
Significance of your research
This tells the reader what you’ll be researching as well as its importance. You’ll have a good idea of what to include here from your original dissertation proposal , though it’s fairly common for research to change once it gets started.
Writing or at least revisiting this section last can be really helpful, since you’ll have a more well-rounded view of what your research actually covers once it has been completed and written up.
Masters dissertation writing tips
When to start writing your thesis or dissertation.
When you should start writing your masters thesis or dissertation depends on the scope of the research project and the duration of your course. In some cases, your research project may be relatively short and you may not be able to write much of your thesis before completing the project.
But regardless of the nature of your research project and of the scope of your course, you should start writing your thesis or at least some of its sections as early as possible, and there are a number of good reasons for this:
Academic writing is about practice, not talent. The first steps of writing your dissertation will help you get into the swing of your project. Write early to help you prepare in good time.
Write things as you do them. This is a good way to keep your dissertation full of fresh ideas and ensure that you don’t forget valuable information.
The first draft is never perfect. Give yourself time to edit and improve your dissertation. It’s likely that you’ll need to make at least one or two more drafts before your final submission.
Writing early on will help you stay motivated when writing all subsequent drafts.
Thinking and writing are very connected. As you write, new ideas and concepts will come to mind. So writing early on is a great way to generate new ideas.
How to improve your writing skills
The best way of improving your dissertation or thesis writing skills is to:
Finish the first draft of your masters thesis as early as possible and send it to your supervisor for revision. Your supervisor will correct your draft and point out any writing errors. This process will be repeated a few times which will help you recognise and correct writing mistakes yourself as time progresses.
If you are not a native English speaker, it may be useful to ask your English friends to read a part of your thesis and warn you about any recurring writing mistakes. Read our section on English language support for more advice.
Most universities have writing centres that offer writing courses and other kinds of support for postgraduate students. Attending these courses may help you improve your writing and meet other postgraduate students with whom you will be able to discuss what constitutes a well-written thesis.
Read academic articles and search for writing resources on the internet. This will help you adopt an academic writing style, which will eventually become effortless with practice.
Keep track of your bibliography
The easiest way to keep the track of all the articles you have read for your research is to create a database where you can summarise each article/chapter into a few most important bullet points to help you remember their content.
Another useful tool for doing this effectively is to learn how to use specific reference management software (RMS) such as EndNote. RMS is relatively simple to use and saves a lot of time when it comes to organising your bibliography. This may come in very handy, especially if your reference section is suspiciously missing two hours before you need to submit your dissertation!
Avoid accidental plagiarism
Plagiarism may cost you your postgraduate degree and it is important that you consciously avoid it when writing your thesis or dissertation.
Occasionally, postgraduate students commit plagiarism unintentionally. This can happen when sections are copy and pasted from journal articles they are citing instead of simply rephrasing them. Whenever you are presenting information from another academic source, make sure you reference the source and avoid writing the statement exactly as it is written in the original paper.
What kind of format should your thesis have?
Read your university’s guidelines before you actually start writing your thesis so you don’t have to waste time changing the format further down the line. However in general, most universities will require you to use 1.5-2 line spacing, font size 12 for text, and to print your thesis on A4 paper. These formatting guidelines may not necessarily result in the most aesthetically appealing thesis, however beauty is not always practical, and a nice looking thesis can be a more tiring reading experience for your postgrad examiner .
When should I submit my thesis?
The length of time it takes to complete your MSc or MA thesis will vary from student to student. This is because people work at different speeds, projects vary in difficulty, and some projects encounter more problems than others.
Obviously, you should submit your MSc thesis or MA thesis when it is finished! Every university will say in its regulations that it is the student who must decide when it is ready to submit.
However, your supervisor will advise you whether your work is ready and you should take their advice on this. If your supervisor says that your work is not ready, then it is probably unwise to submit it. Usually your supervisor will read your final thesis or dissertation draft and will let you know what’s required before submitting your final draft.
Set yourself a target for completion. This will help you stay on track and avoid falling behind. You may also only have funding for the year, so it is important to ensure you submit your dissertation before the deadline – and also ensure you don’t miss out on your graduation ceremony !
To set your target date, work backwards from the final completion and submission date, and aim to have your final draft completed at least three months before that final date.
Don’t leave your submission until the last minute – submit your work in good time before the final deadline. Consider what else you’ll have going on around that time. Are you moving back home? Do you have a holiday? Do you have other plans?
If you need to have finished by the end of June to be able to go to a graduation ceremony in July, then you should leave a suitable amount of time for this. You can build this into your dissertation project planning at the start of your research.
It is important to remember that handing in your thesis or dissertation is not the end of your masters program . There will be a period of time of one to three months between the time you submit and your final day. Some courses may even require a viva to discuss your research project, though this is more common at PhD level .
If you have passed, you will need to make arrangements for the thesis to be properly bound and resubmitted, which will take a week or two. You may also have minor corrections to make to the work, which could take up to a month or so. This means that you need to allow a period of at least three months between submitting your thesis and the time when your program will be completely finished. Of course, it is also possible you may be asked after the viva to do more work on your thesis and resubmit it before the examiners will agree to award the degree – so there may be an even longer time period before you have finished.
How do I submit the MA or MSc dissertation?
Most universities will have a clear procedure for submitting a masters dissertation. Some universities require your ‘intention to submit’. This notifies them that you are ready to submit and allows the university to appoint an external examiner.
This normally has to be completed at least three months before the date on which you think you will be ready to submit.
When your MA or MSc dissertation is ready, you will have to print several copies and have them bound. The number of copies varies between universities, but the university usually requires three – one for each of the examiners and one for your supervisor.
However, you will need one more copy – for yourself! These copies must be softbound, not hardbound. The theses you see on the library shelves will be bound in an impressive hardback cover, but you can only get your work bound like this once you have passed.
You should submit your dissertation or thesis for examination in soft paper or card covers, and your university will give you detailed guidance on how it should be bound. They will also recommend places where you can get the work done.
The next stage is to hand in your work, in the way and to the place that is indicated in your university’s regulations. All you can do then is sit and wait for the examination – but submitting your thesis is often a time of great relief and celebration!
Some universities only require a digital submission, where you upload your dissertation as a file through their online submission system.
Related articles
What Is The Difference Between A Dissertation & A Thesis
How To Get The Most Out Of Your Writing At Postgraduate Level
Dos & Don'ts Of Academic Writing
Dispelling Dissertation Drama
Writing A Dissertation Proposal
Postgrad Solutions Study Bursaries

Exclusive bursaries Open day alerts Funding advice Application tips Latest PG news
Complete Our Destination Survey

Take 2 minutes to complete our Destination Survey for the chance to win a Postgrad Study Bursary worth £2,000.
All we need to know is:
- Your university
- Your PG course
- Affiliate Program

- UNITED STATES
- 台灣 (TAIWAN)
- TÜRKIYE (TURKEY)
- Academic Editing Services
- - Research Paper
- - Journal Manuscript
- - Dissertation
- - College & University Assignments
- Admissions Editing Services
- - Application Essay
- - Personal Statement
- - Recommendation Letter
- - Cover Letter
- - CV/Resume
- Business Editing Services
- - Business Documents
- - Report & Brochure
- - Website & Blog
- Writer Editing Services
- - Script & Screenplay
- Our Editors
- Client Reviews
- Editing & Proofreading Prices
- Wordvice Points
- Partner Discount
- Plagiarism Checker
- APA Citation Generator
- MLA Citation Generator
- Chicago Citation Generator
- Vancouver Citation Generator
- - APA Style
- - MLA Style
- - Chicago Style
- - Vancouver Style
- Writing & Editing Guide
- Academic Resources
- Admissions Resources
Masters Thesis vs. PhD Dissertation: Key Differences
Whether you are a graduate student just starting out in academia or a professor advising a student, making the distinction between a dissertation and a thesis is critically important to writing a strong dissertation and becoming a stronger writer. Unfortunately, the difference remains unclear since the terms are used interchangeably by graduate students, doctoral researchers, academic publishers & universities.
If you’re not sure whether you’re writing a thesis or a dissertation, this article will help you understand the differences between the two whether you’re a PhD or master’s degree student.
Main Differences Between a Dissertation and a Thesis
While theses and dissertations share many similarities (they are both advanced graduate research papers), they actually refer to two different types of academic writing, and their differences include important concepts such as scope, purpose, length, and research requirements.
Most importantly, the difference between a thesis and a dissertation depends on the level of education. Far beyond being a simple essay, a thesis is for graduate students pursuing a master’s degree while a dissertation is written by doctoral students, also referred to as PhD candidates.
There are a few key differences between a thesis versus a dissertation.
The biggest difference between a thesis and a dissertation is that a thesis makes arguments based on existing research. Meanwhile, a dissertation often requires the PhD candidate to conduct research and then perform an analysis.
More specifically, a thesis often takes the form of a literature review , which is a compilation of research knowledge in a particular field of study that proves one is competent in that subject. On the other hand, a dissertation is a more specific type of research paper written by those working toward a specific doctorate degree that contributes knowledge, theory, or methods to a field of study.
What is a master’s thesis?
A master’s thesis is an academic research paper that requires a greater degree of research than an undergraduate thesis or term paper. It is marked by a higher standard of writing, and students are expected to demonstrate competence, literacy, and mastery of a subject. It usually takes two or three years to complete. Finally, a master’s degree thesis is usually written in order to obtain a research degree and is not intended to be published separately.
What is a PhD dissertation?
A PhD dissertation is a substantial piece of independent research that is required of all students who are pursuing a doctorate degree. It is a piece of original work that has not been published elsewhere and, most importantly, makes a new contribution to the field. This contribution may be a new way of thinking about an existing topic or even a novel theory. The research performed for a dissertation is usually conducted over a period of several years to half a decade.
Features of a Master’s Thesis vs PhD Dissertation
| -Original and novel testing of ideas and a hypothesis -An independent work or experimentation -Demonstrated competence and understanding of industry techniques as well as their limitations -Thorough knowledge of the literature -Ability to use synthesize and criticize the literature for the research topic -Ability to present the work in an academic capacity (conference, seminar, recitation, defense, etc.) | |
| -All of the above characteristics -A novel contribution to the scientific literature not published previously -Original research produced directly by the author (graduate student) -A clear research question/hypothesis clearly answered (or falsified) -Advances in methods, observations, interpretation, etc. |
Content and Structural Differences
So how is dissertation writing different from thesis writing?
Now that you know the definitions of a dissertation and thesis, let’s dive into some clear ways in which they differ in structure and other main characteristics.
How long is a thesis vs dissertation?
Length is the most obvious factor in differentiating between writing a thesis or dissertation.
Generally, a doctoral dissertation has greater breadth, depth, and intention than a master’s thesis since it is based on original research. While the standard length of a master’s thesis is around 100 pages , a doctoral dissertation can be upwards of 400-500 pages.
While most students can finish their PhD dissertation or thesis in as little as 1-2 years, it can take as long as 7 years depending on the school, program, and dissertation topic. As doctoral programs have their own formatting requirements, check with your school or university to find out what you need for your own dissertation or thesis. Most dissertations are organized into chapters, but the number of chapters varies as well.

Differences in research methods
A thesis and dissertation are both graduate-level research reports. This means they require students to investigate and report on a specific topic. But what is the difference in the scale of research between a master’s versus doctoral degree? The answer comes down to how much and what type of data you collect .
Data sources for a thesis vs dissertation
A master’s thesis is limited to secondary or reported knowledge . This knowledge has already been published, analyzed, and scrutinized in the literature. A thesis does not typically offer anything new in that regard. Your purpose is usually to write a comprehensive literature review on a novel or underreported topic using already-reported data.
| -Academic journal articles -Scholarly books and publications -Academic periodicals and magazines -Survey reportsIndustry and corporate reports -Government data (census, environmental, etc.) -Published statistics -Prior studies |
On the other hand, a doctoral dissertation reports on novel data and is published so it can be scrutinized by others. It culminates in your dissertation defense.
| -All of the above sources -Laboratory experiments and investigations (e.g. basic sciences) -First-hand surveys, interviews, and focus groups (e.g. psychology, social sciences) -Unpublished data (i.e. verified data from experiments but too narrow to publish) -Abstracts, reviews, and conference presentations by other researchers |
The above lists clearly show that a PhD researcher and dissertation writer must have specific hands-on experience about not only the result of others’ research but also how the researchers obtained the data. A dissertation must venture into criticism of how other studies performed their experiments, whereas a master’s student will only report on and evaluate the results.
Differences in research scope
As mentioned above, a thesis is more of a literature review written to demonstrate competence and mastery of a field of study. In short, you are a reliable “reporter” of information related to that subject. A thesis shows that you know the technical jargon, understand the subject, are familiar with industry tools, and can translate that information to a general audience. This is why a master’s degree is sufficient and often preferred for industry jobs.
In contrast, a doctoral dissertation goes beyond simply using the building blocks of your subject and actually creates new tools, knowledge, and theories to advance the subject as a whole. If a master’s degree holder is like a seasoned Rolling Stone journalist, then a doctorate is the band/musician who actually makes the music.

So should you pursue a thesis or a dissertation?
The benefits of earning a graduate degree are huge. According to the US Census Bureau , those with an advanced degree earn 3.7 times as much as a high school dropout, and 13.1% hold a master’s, professional, or doctorate degree. If you’re a curious undergraduate student thinking of applying to graduate school, which is the right choice?
In short, a dissertation is more focused and in-depth than a thesis. While a doctoral dissertation is based on original research, a thesis is often an extension or review of others’ research in order to demonstrate literacy. Further, a dissertation can be used as the basis or subject of a thesis, but not vice versa.
Editing a Dissertation vs Thesis
So far, we’ve focused a lot on differences such as research and purpose, but in the end, a thesis or dissertation is a written document that requires skill, focus, discipline, subject knowledge, organization, and scheduling.
For non-native English speakers, the challenge is especially difficult since English is the lingua franca of academia and research.
How does an editing service improve your dissertation or thesis ?
From body spacing and pagination, to font size and citation formatting, the dissertation guidelines are exhaustive. Even worse, they vary by school. So besides the actual English writing and grammar, graduate students must worry about consistency, formatting, nomenclature, and terminology. That’s quite the burden!
This is why it’s very common for graduate students, especially ESL and foreign ones, to seek out dissertation editing services that specifically cater to the academic needs of researchers and students.
Here are just a few reasons why dissertation proofreading is so helpful and what these editors do:
- Correct grammar, punctuation, syntax, and structural errors
- Offer suggestions to rewrite, remove, and revise writing
- Ensure formatting and nomenclature are consistent
- Knowledgeable academic editors with master’s and PhD degrees
- Free up your time to focus on research, revisions, and content instead of looking for mistakes
- Provide a language editing certificate , which may be necessary for non-native English-speaking students
Lastly, most PhD advisors recommend that students seek out professional editing services , specifically thesis editing or dissertation editing , since professors prefer to assess the actual research content of a dissertation, not mundane writing errors. Any graduate student reading this knows professors don’t like their time to be wasted!
Be sure to check out other academic resources on how to improve your academic manuscript and the benefits of proofreading and editing.
And try the Wordvice FREE Citation Generator, which provides citations for four academic formatting styles: APA Citation Generator , MLA Citation Generator , Chicago Citation Generator , and Vancouver Citation Generator .
- Communications
- Computer Science
- Criminal Justice
- Environmental Management
- Forensic Psychology
- Healthcare Admin
- Human Resources
- Project Management
- Social work
- Special Education
- Sports Management
- Supply Chain Management
- Adult Education
- Business Intelligence
- Early Childhood Education
- Educational Technology
- Homeland Security
- Information Systems Security
- Information Technology
- International Business
- Management Information Systems
- Nonprofit Management
- School Counseling
- Academic Publishing Guide
- Building a Graduate School Resume or CV
Choosing Between a Thesis or Non-thesis Master's Degree
- Expert Guide to Studying Abroad
- FAQ: Online Master's Degrees
- Grad School Guide Book
- Graduate School for Students with Disabilities
- Green Graduate Degrees
- How to Be a Successful Grad Student
- How to Choose the Right Graduate Program
- How to Get a Master's Degree in an Unrelated Field
- How to Transfer College Credits in Grad School
- How to Write a Winning Personal Statement
- Inside Graduate Admissions
- Ivy League Grad Schools
- Master's Degrees for Veterans
- Master's Degree for Women
- Mental Health in Grad School
- Progressive LGBTQ Graduate Degrees
- Should You Apply for a Graduate School Assistantship?
- Surviving Grad School with a Family
- Taking a Gap Year Before Grad School
- Women in STEM Graduate Resources
- Writing a Successful Statement of Purpose
- Alternative Ways to Pay for School
- The Best Part-Time Jobs During Grad School
- Company Funded Graduate School
- FAFSA For Grad Students
- Financial Aid Resources
- Graduate Student Loans
- Paying for Your Master's Degree
- Paying Off Student Loans
- Paying for Your PhD
- Fellowship Opportunities
- LGBTQ Scholarships
- MBA Scholarships
- Scholarship Resources
- Scholarships for Veterans
- Scholarships for Women
- Crushing the GRE Guidebook
- GMAT Guidebook
- Guide to the LSAT
- MCAT Prep for Medical School
- Study Guide: Exam Resources
- TOEFL Prep for Non-Native English Speakers
- Resources Choosing Between a Thesis or Non-thesis Master's Degree
As of 2015, approximately 25.4 million Americans held advanced degrees , with more citizens joining these ranks each year. As studies continue to show the career advancement and salary benefits of completing a master's degree, more and more students elect to pursue advanced educations. When considering their options, many question whether to enroll in a master's requiring a thesis or not. The following guide examines some of the reasons degree seekers may want to write a thesis while also highlighting why they might not. Students on the fence about this important decision can find expert advice, actionable tips, and relevant guidance to help them make an informed choice in the guide that follows.
Understanding the Master's Thesis
What is the difference between a thesis & non-thesis master's program, the decision not to do a thesis.
As students research various master's programs in their chosen discipline, it's common to find that many degrees require a thesis – especially if they want to enter a research-heavy field. While this word gets thrown around a lot in academia, some learners may want more information regarding what it entails in order to make an informed decision.
What is a Master's Thesis?
The master's thesis is an original piece of scholarship allowing the student to dig into a topic and produce an expanded document that demonstrates how their knowledge has grown throughout the degree program. These documents require significant independent research of primary and secondary sources and, depending on the subject, may require interviews and/or surveys to support the overarching argument.
Individual schools and departments dictate the length of these documents, but they typically range between 60 and 100 pages – or approximately 20,000 to 40,000 words. While tackling a document of such heft may seem overwhelming at first, learners need not fret. Each master's candidate receives a faculty advisor early in their tenure to provide support, feedback, and guidance throughout the process. Because the final thesis is expected to be of a publishable quality, learners seeking the highest marks typically send their supervisor excerpts of the document as they write to ensure they are on the right track.
When picking a thesis topic, no magical formula exists. Students should consider their interests and read extensively on that topic to get a better sense of existing scholarship. They should also speak to other academics working in that sphere to familiarize themselves with ongoing projects. Only after they feel reasonably well-read should they begin looking for uncovered angles or interesting ways of using emerging methodologies to bring new light to the topic.
When considering formatting, degree seekers should check with their specific schools and departments, as they may have unique requirements. To get a general understanding of what to expect, learners can review Simon Fraser University's guidelines on thesis formatting. After completing the thesis, some programs require an oral defense before a committee while others read the document and provide a grade. Check with your prospective schools to get a better sense of procedure.
Format & Components of a Master's Thesis
While this guide attempts to provide helpful and actionable information about the process of deciding whether to follow a thesis or non-thesis track in a master's program, readers should remember that specific components and requirements of a thesis vary according to discipline, university, and department. That being said, some commonalities exist across all these – especially when it comes to what students must include in their final drafts.
As the first section a reader encounters after moving through the table of contents and other anterior text, the introductory allows the writer to firmly establish what they want to accomplish. Sometimes also called the "research question" section, the introductory must clearly state the goals of the paper and the overarching hypothesis guiding the argument. This should be written in a professional yet accessible tone that allows individuals without specializations in the field to understand the text.
This section allows learners to demonstrate their deep knowledge of the field by providing context to existing texts within their chosen discipline Learners review the main bodies of work, highlighting any issues they find within each. Constructive criticism often centers around shortcomings, blind spots, or outdated hypotheses.
Students use this section to explain how they went about their work. While scientists may point to a specific method used to reach conclusions, historians may reference the use of an emerging framework for understanding history to bring new light to a topic. The point of this section is to demonstrate the thought processes that led to your findings.
This section allows for learners to show what they learned during the research process in a non-biased way. Students should simply state what information they gathered by utilizing a specific framework or methodology and arrange those findings, without interpretation, in an easy-to-read fashion.
After providing readers with all the necessary information, the discussion section exists for candidates to interpret the raw data and demonstrate how their research led to a new understanding or contributed a unique perspective to the field. This section should directly connect to the introduction by reinforcing the hypothesis and showing how you answered the questions posed.
Even though the previous sections give prospective degree seekers a better sense of what to expect if they decide to write a thesis during their master's program, they don't necessarily help learners decide whether to pursue a thesis or non-thesis track. The following section highlights some of the reasons students frequently choose to complete a thesis or bypass the process altogether by providing a pros and cons list.
Why a Thesis Program
- Especially when entering a research-heavy discipline, completing a thesis shows prospective schools and employers that you possess the skills needed for researching and writing long-form reports.
- Students hoping to pursue a Ph.D. stand in better stead with admissions panels if they wrote a thesis during a master's program.
- Individuals hoping to enter a field that values syntax and grammar often better their writing skills by completing a thesis.
- Students who write a thesis can submit the final product to various academic journals, increasing their chances of getting published.
- Theses expand students' understanding of what they're capable of, deepen their ability to carry out an argument, and develop their skills in making connections between ideas.
Why a Non-thesis Program
- Because they don't require a significant written product, non-thesis master's tend to take less time to complete.
- Often mirrors a bachelor's program in terms of structure, allowing learners to complete classes and take exams without a great deal of research or writing.
- Students who excel in project-based assignments can continue building skills in this arena rather than focusing on skills they don't plan to use (e.g. research)
- Provides learners the opportunity to work more closely and more frequently with faculty on real-world projects since they don't spend hundreds of hours researching/writing.
- Allows learners to take more classes and gain hands-on skills to fill the time they would have spent researching and writing a thesis.
How to Choose a Master's Program: FAQs
Within some academic disciplines and professional fields, research and writing plays a key role in work done on a daily basis. Because of this, master's programs in these fields require learners to complete theses to compete against peers and be seen as competent in their work. Other disciplines, conversely, rely on other tools to accomplish work and progress ideas – making theses less important.
Yes. Master's programs focused more on application than research typically don't require a thesis – although they may still give students the option. Examples of common non-thesis master's programs include nursing, business, and education.
Even though non-thesis students won't be writing a 100-page paper, that doesn't mean they avoid completing a significant project. In place of a thesis, most applied master's programs require students to take part in at least one internship or complete a culminating project. These projects typically ask learners to take what they learned throughout coursework and create an expansive final project – examples include case studies, creative works, or portfolios.
While students who followed a non-thesis path routinely receive acceptance to Ph.D. programs, those with theses often find the process easier. Even if a learner pursues a Ph.D. in a discipline that isn't research-heavy, admissions panels still want to get a sense of your academic interests and ability to engage in independent, nuanced thought. Students with theses can provide solid proof of these skills, while those without may struggle to demonstrate preparedness as thoroughly.
The answer to this question depends on many factors, but typically it is okay not to do a thesis if you plan to enter a field that doesn't depend heavily on research or writing, or if you don't plan to complete a Ph.D.
Students wanting to work in academic, research, or writing should always opt for the thesis track. They should also follow this path if they have any doctoral degree aspirations.
Ultimately, the decision of whether or not to complete a thesis rests with the individual student. Figuring out how to proceed on this front requires lots of careful consideration, and learners should ensure they consider various aspects before coming to a final decision. The following section helps students consider how they should and should not come to a conclusion.
Dos and Don'ts of Choosing a Thesis or Non-thesis Program
- Consider the longevity of your decision: will you feel the same in 5-10 years or are you making a decision based on current desires?
- Talk to others who with experience in this area. Ask them questions about their decision-making process and if they regret their choice.
- Research potential thesis topics before starting a program. Going in with a game plan can help you feel more confident and settled about the process than if you're scrambling for a topic while in school.
- Reach out to prospective schools to speak with faculty and/or current students following both tracks. This will provide knowledge specific to the school while also expanding your network if you choose to attend there.
- Research Ph.D. entrance requirements to ascertain if the majority expect learners to possess a thesis when applying. This will give you a sense of whether you may experience issues later on if you do not complete one.
- Decide not to complete a thesis simply because you have never taken on such a task and feel overwhelmed or fearful that you will fail.
- Complete a thesis simply because you think it will look good on your resume. Theses require intense devotion over an extended amount of time; learners who complete them without conviction often find the process miserable.
- Forget to research alternatives to writing a thesis. Just because you don't complete a research paper doesn't mean a non-thesis track lacks rigor or challenging coursework.
- Forget to read examples of theses by previous students. If you feel overwhelmed by the task, reading work other people have done can often make the task at hand feel less scary.
- Let yourself off easy by taking the non-thesis path. If you find you have extra time in the program, talk to your advisor about taking more classes, develop meaningful projects for yourself, or see about presenting at an academic conference.
From the Expert

Sudiksha Joshi, Ph.D. is a learning advocate. Her mission is to empower our youth to think bigger, bolder thoughts and forge a career path that will change the world. She taps into her natural curiosity and ability to identify strengths to help students and those in transition find their path from feeling lost in the traditional ways of achieving success to charting their own path. Her work has been featured in Forbes, Huffington Post, Thrive Global, Medium and LinkedIn.
Why might a student decide to follow a thesis track? Why might they follow a non-thesis track?
A student might decide to take a thesis track if she/he wants to pursue a Ph.D. Also, if the students want to focus on careers where research and writing have a strong focus, the students opt for the thesis option. Research assistantships at the graduate level are also more often available to students who opt for the thesis option.
A student who might feel that writing is not one of their strengths might choose to go the non-thesis track. Likewise, a student who has other work commitments may find a non-thesis option more convenient.
Do you have any tips for deciding on a program?
I chose a thesis option because being able to conduct independent research was a big reason to go to graduate school. Also, showing the ability that I could do research was what afforded me research assistantships which meant that my tuition was paid for and I got a stipend that paid for expenses while I was in graduate school. This also allowed me the opportunity to work closely with the faculty mentor that provided me with the support and the accountability I wanted.
I would not recommend taking a non-thesis option if all the degree requires is for you to take courses. You have little to show in terms of your learning other than your grades unless you are already working on something on the side that does that for you and all you need is a certificate.
Opt for a non-thesis option if you can still work closely with a professor or on a project and if you'd rather be involved in multiple projects rather than focus on a single project. If you already have a good (informed) reason for choosing one over the other, go for it.
What's the most important thing to consider when choosing a program?
The most important thing to consider when choosing a program is getting excited about the projects that at least one of the faculty members are involved in. Do some research and see why you are excited about a particular work that at least one of the faculty members have been involved in.
Who should students talk to when considering options?
Students should talk to other students and also reach out directly to the graduate coordinator and even individual faculty members. This means that students should have done prior homework and have some good questions ready. Asking good questions will get you at least halfway through to make the right decision.
What Is a Master's Thesis?
Are you a Master's student starting your thesis or have you just decided to pursue a graduate degree and are trying to understand what it takes to get one? In this article, we'll explain everything you need to know about a Master's thesis.
- Student Tips

Page Content
As a part of your Master's program, you are going to spend a significant amount of time working on your Master's thesis. It involves thorough research and gives you a chance to demonstrate your abilities in your chosen field. So what is a Master's thesis exactly and what does it mean to write one?
Looking for your perfect graduate program?
Browse over 22,000 master's degrees, what is a master's thesis.
Simply put, a Master's thesis is the last and biggest project you do in the last two semesters as a culminating point of your Master's degree. It's an academic research paper meant to demonstrate a student's competence and mastery of a particular subject within their field of study. These research papers typically combine pre-existing studies with new data . The purpose is to either challenge or support an existing hypothesis, but it can take different forms depending on what your advisor and you decide to do.
Moreover, there are non-thesis Master's programs , like the MBA and the MS in Finance , that don't focus on research but rather on practical skills for you to enter the workforce. These programs normally require you to submit a Master's Degree Capstone project including case studies or program evaluations.
Master's thesis structure

Exact format requirements vary from one program to another, but a Master's thesis generally follows this structure:
- Title page: Your institution will most likely provide you with a template. It should state the name of your institution, the title of your thesis, your name, and the name(s) of your advisor(s).
- Summary: This part will be evaluated by the thesis committee so make sure to write it well. Here you should include your research question, the data you used, the methodology, and the summary of your findings.
- Table of contents
- Introduction: Your goal for the introduction is to state a problem that hasn't been properly addressed, and discuss what your thesis intends to accomplish in terms of the solution - the so-called " research question ".
- Literature review: This section describes the most important and relevant research conducted previously on your topic. It's recommended to include several viewpoints and contrasting opinions.
- Methods: Once you've identified where the existing research falls short in answering the thesis' research question, you should tell the reader your plan to find the solution. In this part, you also explain which methodologies you used to analyze the data you collected.
- Analysis of the results: Here you describe in great detail all your findings - what new information you managed to discover.
- Conclusions: The final chapter of your thesis is meant to determine how well your work answered the research question. Also, you should identify any shortcomings of your own research and discuss future research opportunities.
- List of references: Since the existing research serves as a base for your paper, you should provide a list of all references that were cited in your work.
Most parts can be split into several chapters. Students sometimes also include an acknowledgment, as well as an appendix (or multiple appendices) for additional information, like tables, graphics, or other materials that are not required to understand the main text but can be useful.
How long is a Master's thesis?
A Master's thesis is generally 40-100 pages long , not including the bibliography. However, there is no "correct" number of pages. You are free to make it as long as you need to properly and fully present all the necessary material.
Remember that longer does not mean better, it largely depends on topic complexity and discipline . For example, for a highly mathematical thesis with proof 50 pages can be more than enough, while a sociology thesis relies on a lot of diagrams and may be much longer.
Usually, your institution will have its own guide for the formatting and structure requirements , where you can check if there is a limit for word count, find the length range, font style and size, the number of references, and other useful information.
Getting started on your Master’s thesis
It's better to start thinking about possible topics early in your program. First, you should explore your interests. Then, look up a professor who works in a similar field and ask them to be your thesis advisor . They will be able to help you with forming the research question or offer you to take over an existing project they are already working on.
Don't worry, your thesis advisor will assist you if you have any issues. You can schedule a meeting with them to discuss the outline of your project and create a research plan .
They will also be able to recommend relevant literature so that you know where to begin. Since a literature review in your Master's thesis is a reflection of the existing research on a particular topic, make sure you have enough sources for an in-depth understanding of your subject.
Master’s thesis defense: how does it work?

If the word "defense" scares you, don't worry, no one will actually attack you. Much like what you did for your Bachelor's, a Master's thesis defense is where you present your project and answer a few questions from the thesis committee, which they mainly ask to make sure you understand the subject.
By this time, your paper will already be read, reviewed, and evaluated, so the defense is a formality , and it's highly unlikely you'll fail. The presentation usually takes up to 15 minutes. It's hard to say for the questions part though - it depends on the goal of the committee and the requirements of the program.
After completing your Master's thesis, you can publish the paper if your institution allows it. Research the university's publication process and independent publishing platforms.
If you're considering pursuing a postgraduate degree, your Master's thesis topic can be researched further in the PhD dissertation. Or, in case you want to go into industry after your Master's program, your thesis will say a lot about your abilities to research and analyze information, and experience in a particular field.
Overall, a Master's thesis is a crucial part of your degree , especially if you aim to get more into research and pursue a PhD. It is an independent work designed to back up your academic and professional qualifications , as well as demonstrate your research and even presentation skills.
Writing a Master's thesis is a long and tedious process: it takes about a year from choosing a topic and reviewing the literature to conducting research and submitting your paper. To avoid failing, start early and create a realistic plan with your thesis advisor with many intermediate deadlines to keep you accountable. Take guidance from your advisor and don't hesitate to ask for help.
- The Ultimate Master’s Degree Guide
- After a Master’s Degree: Your Career Options
- How to Get an Internship
- Networking Skills for Master’s Students

Tetiana Sokolova Author
With a Bachelor's degree in System Analysis and Applied Statistics, Tetiana brings a strong analytical foundation to her role as a Content Editor at Keystone Education Group. She is dedicated to researching, producing, and refining content to support students worldwide in their education journey, applying her technical expertise and analytical skills to ensure accuracy and relevance.
Find a program in these categories
Read related articles

How To Look For A Job Across The World
October 2023 Education Study Abroad Student Tips Visa

Why You Should Apply To Graduate School Abroad

Why Study Architecture?
October 2023 Education Study Abroad Student Tips International News
Master’s Thesis
Master’s general requirements, types of theses.
Master’s theses submitted by students in partial fulfillment of degree requirements must embody the results of original research and must be successfully defended at oral examinations. Master’s theses shall be on a topic approved by the student’s supervisor and supervisory committee, and shall include submission and approval of a thesis proposal, including appropriate ethics review and approval, in accordance with Faculty and program requirements and procedures.
Master’s theses should demonstrate that the student is familiar with and has an acceptable understanding of the literature in the subject of the thesis; that appropriate research methods have been used, and that appropriate levels of critical analysis have been applied. The research embodied in the thesis should make some original contribution to knowledge in the field.
By submitting a thesis or dissertation, a student is making the representation that it is entirely his or her own work and that it has been done while he or she was a graduate student at York University.
If such is not the case, then the student must indicate in a signed, written statement what part of the thesis or dissertation is solely his or her own or co-authored. If co-authored, the candidate must provide an account of its provenance. The supervisor must produce her or his own corroborative written statement.
If a thesis or dissertation is the result of collaborative work, then the nature of the collaboration and the extent of the candidate’s contribution must be described in a written statement signed by the candidate and approved in writing by the candidate’s supervisor. Where there has been collaboration with others in the collection or preparation of data, materials, or documentation included in the thesis or dissertation, then appropriate acknowledgment must be made in the thesis or dissertation.
If a thesis or dissertation—or any part thereof—has been published prior to submission of the thesis/dissertation, then the candidate must disclose this fact in a signed written statement, and the supervisor must approve in writing the inclusion of such work in the thesis or dissertation. In cases where one or more chapters of the thesis or dissertation have been previously published in a journal or book to which the author has assigned copyright, permission to include the chapter(s) in the thesis or dissertation must be obtained from the copyright holder(s). Please see the section on Copyright for more details.
A thesis or dissertation containing previously published material of which the candidate is the author and/or co-author should also contain a review of the literature that adequately explains the relationship to the literature of the work undertaken. In addition, it should contain a rationale for the study. These elements may form part of the body of the work – normally an introduction or opening chapter – that leads coherently into the publications. Furthermore, there should be a concluding chapter or section that discusses the body of the thesis or dissertation, including all previously published parts.
A false representation or failure to make a disclosure as outlined above is an academic offence and renders the thesis or dissertation ineligible for consideration of the relevant degree.
The general form and style of a thesis/dissertation may differ from program to program, but a thesis/dissertation should be a coherent work. This means that if a thesis/dissertation contains separate manuscripts, there needs also to be introductory and concluding chapters that explain how these separate manuscripts fit together into a unified body of research. If previously published materials are included, then it should be made clear what exactly is the student’s own work and what is the contribution of other researchers, as outlined above under Originality of a Thesis/Dissertation.
All theses and dissertations must contain a written component. Theses and dissertations may, however, include other components in addition to the written component.
A complex electronic thesis/dissertation is a work with a high reliance on slides, film or videos, electronically interactive word/image-based text on CD-ROM or the internet. For complex electronic theses/dissertations, part of the work can be produced in traditional written form, but key elements of the work depend on direct experience with or interaction with a text whose physical form may be changed as a consequence of the interaction. Students producing a multimedia thesis/dissertation should consult with the Theses Canada Portal on the Library and Archives Canada website for advice on formats supportable for preservation. However, a student may work in or submit work in an unsupported format as part of the oral exam as long as the work is readily accessible by the exam committee and the student submits a written component.
A multimodal thesis/dissertation is a work in which the key component is a performance or piece of art. For multimodal theses/dissertations, part of the work can be produced in traditional written form, but key elements of the work depend on direct experience by the exam committee with, for example, displayed artworks or theatrical productions.
For both electronic and multimodal theses/dissertations, students may wish to include supplementary files as part of their final submission (see Final Submission Tab ).
A thesis or dissertation should be written in English, but approval may be given to a written request from a student for a thesis or dissertation to be written in French or in the language of any Aboriginal/First Nations people in North America, subject to confirmation from the director of the graduate program concerned that relevant supervision and sufficient support for the completion of such written work can be provided.
For theses/dissertation written in English, either American or British spelling is acceptable provided that it is used consistently throughout.
Students preparing their thesis/dissertation should follow a single style guide appropriate to their discipline. The York University Libraries provides links to various style guides for various disciplines.
Thesis Proposals
In accordance with program requirements and procedures, all students should prepare a thesis/dissertation proposal, normally in consultation with their supervisor in advance of commencing their proposed inquiry. Each program should have written guidelines and should communicate them to candidates, as and when appropriate.
At a minimum, the proposal should contain a brief statement in non-technical language on the purpose/goals of the thesis/dissertation research, its relationship to existing work in the area, through an abbreviated literature review, the research question(s), the proposed methodology(ies) with rationale, and the contribution which the researcher hopes to make to the advancement of knowledge in the field. In addition, the proposal includes a title, the name of the supervisor and the supervisory committee. The title should indicate as clearly as possible the area of research, but it is understood that this title may change. The recommended maximum length of a proposal is 3,500 words, but individual programs may require proposals of a greater length. Proposals must be reviewed and approved by a student’s thesis or dissertation committee.
Following approval of the proposal by the supervisory committee, students must submit one or more copies of the proposal to the graduate program director. After confirming that the relevant Faculty and internal program requirements have been satisfied, the program director is responsible for submitting the proposals to the Office of the Dean, Graduate Studies using the Form TD1: Thesis/Dissertation Research Submission . As indicated on Form TD1: Thesis/Dissertation Research Submission, submission of the proposal to the Office of the Dean, Graduate Studies, includes submission of the relevant research ethics forms and documentation. For more information on required documentation and submission procedures, please refer to the Research Ethics section of this Handbook.
For a master’s thesis, the supervisory committee must review the student’s research proposal and recommend its approval not less than three months prior to the date set for the oral examination.
Please note that the deadlines outlined above are the Faculty’s minimum requirements, and individual graduate programs may have more specific requirements and timelines with respect to the development, review and approval of thesis/dissertation proposals. Students should consult their program for more details. Further, the Faculty deadlines outlined above may not provide the time necessary for ethics approval, if required. More information regarding research ethics is provided below.
Research Ethics
York University is committed to the highest standards of integrity in research. All projects involving the use of human subjects, animals, and biohazardous materials are subject to review by the appropriate University committee. York has formulated policies and procedures for the conduct of research involving all three of these areas.
As indicated on Form TD1: Thesis/Dissertation Research Submission , submission of the thesis/dissertation proposal to the Office of the Dean, Graduate Studies for approval must include the relevant research ethics forms and documentation.
All research involving human participants is governed by the Senate Policy for the Ethics Review Process for Research Involving Human Participants . The Senate Policy stipulates that all University-based research involving human participants, whether funded or non-funded, faculty or student, scholarly, commercial or consultative, is subject to an ethics review process. The Senate Policy for the Ethics Review Process for Research Involving Human Participants and corresponding review procedures adhere to the published guidelines of the Canadian Institutes of Health Research, the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council, and the Social Sciences and Humanities Research Council, known as the Tri-Council Policy Statement (TCPS).
Please note that in accordance with the TCPS and Senate policy, graduate students undertaking research with human participants may not begin that research until their proposal has received approval from the appropriate body . Further, prior to conducting research involving human participants, graduate students are required to complete the complete the TCPS tutorial .
Details regarding the ethics review procedures for thesis/dissertation research involving human participants is available on the Faculty of Graduate Studies research ethics webpage .
Students conducting research with human participants may be required to submit the Form TD2: Human Participants Research Protocol . Additional forms may be required.
Further details regarding the University policies and ethics review procedures for thesis/dissertation research involving animals and biohazardous materials is available on the Office of Research Ethics web page.
Ethics guidelines for other research situations are also available on the Office of Research Ethics web page, including:
- Invasive Procedures
- Health and Safety Checklist
- Surveys and Research in an Online Environment
- Research Conducted by External Researchers
- Research Conducted in Hospital Clinical Settings
- Research in Educational Settings
- Research Involving Minor Age Participants
- Research with People who are Homeless
Students hold copyright to their theses and dissertations, regardless of the method of submission. Consequently, a student is free to publish his or her thesis/dissertation following a successful oral examination. Please note that if a thesis/dissertation includes any work which is copyrighted to another party, permission may be required to publish the thesis/dissertation.
After a successful oral examination the Library and Archives Canada Thesis Non-Exclusive License (.pdf) must be submitted to the Office of the Dean, Faculty of Graduate Studies. The student must also accept the terms of the York University Copyright License as part of the electronic submission of their thesis/dissertation using the Electronic Thesis and Dissertation (ETD) .
By signing these licenses, a student is confirming that his or her thesis/dissertation is his or her original work, that his or her thesis/dissertation does not infringe any rights of others, and that he or she has the right to make the grant conferred by those copyright licenses. In addition, the student is granting a Licence to York University to make copies including electronically formatted copies, and/or distribute worldwide all or part of the thesis/dissertation, subject to the conditions outlined.
If applicable, the student should submit copies of any required copyright permissions prior to the final thesis/dissertation submission to the Office of the Dean, Graduate Studies. The student should also retain copies of all copyright permission requests and approvals.
The following sections provide guidance and suggestions with respect to when and how to secure copyright permission. It is, however, the responsibility of the student to confirm that if there is copyrighted material in his or her thesis/dissertation, it either complies with the “fair dealing” provisions of the Canadian Copyright Act or documented permission has been obtained to use the copyrighted material. The Office of the Dean, Faculty of Graduate Studies cannot offer legal advice as to whether or not copyright permission is required.
Limit of Copyright Protection : Copyright protection applies to original, literary, musical, dramatic or artistic works in a variety of forms, including written materials, computer software, and web-based formats regardless of whether the work in question is published or not and whether someone has made it available to the public or not. This protection expires 50 years after the death of the originator, regardless of who holds copyright at that time.
Public Domain : A work that is freely available to the public is not necessarily in the public domain. For a work to be in the public domain, the originator must have specifically waived copyright to the work, or copyright must have legally expired. Work that is in the public domain can be used by anyone without copyright being violated.
Fair Dealing : A student is allowed to use copyrighted material in his or her thesis/dissertation provided it falls under the Canadian Copyright Act’s definition of “fair dealing”. Information on York University’s Fair Dealing Guidelines can be reviewed at York University—Copyright .
While it is required academic practice to cite sources, proper citation does not remove the obligation to obtain documented permission to use copyrighted permission that is not covered under the “fair dealing” provisions of the Canadian Copyright Act. If a thesis/dissertation includes any of the following elements, the student should seek copyright permission. (Please note that this is not an exhaustive list. If you require additional information on York’s Copyright Policy or Fair Dealing Guidelines contact the Copyright Office at [email protected] ).
- Material or parts of material written by the thesis/dissertation author which have been previously published in a journal and to which the author has assigned copyright
- Material co-authored with another author(s) who share copyright
- Tables, figures, and all forms of images including photos, maps, graphs, drawings, logos etc. that have been obtained from a copyrighted source, including websites, newspapers, journals, books, brochures, professors’ lecture notes, etc.
- Scripts and recordings of any performance
In cases where a student is not certain that his or her use of copyrighted material is covered under the “fair dealing” provisions of the Canadian Copyright Act, documented permission from the copyright holder(s) must be obtained in order to include the material in the thesis/dissertation. Since securing copyright permission may take some time, it is strongly recommended that students being this process sooner rather than later. Please note that the copyright holder must be aware of and agree to the terms of the York University Copyright License and Library and Archives Canada Thesis Non-Exclusive License.
If seeking permission from a journal, a good first step is to check the journal’s website, which may provide information with respect to copyright, including advance permission to journal authors who have signed over copyright, how to request permission, and uses that are specifically prohibited. There are also a number of websites that may be helpful in determining the copyright policies of particular journals/publishers, including Sherpa Romeo and EPrints . Some journals and publishers provide (on their website or on request) a policy statement granting copyright permission to the author of a thesis/dissertation who signed over copyright to the journal/publisher. In such cases, retain a copy of that policy statement as evidence of documented permission.
Alternatively, a student should contact the copyright holder. Sample text for a copyright permission request is included below. Although email proof of permission is acceptable, please note that an original, signed letter on the copyright holder’s letterhead is the best protection against accusations of copyright violation.
Students should provide copies of any required copyright permissions prior to submission of their final thesis/dissertation to the Graduate Milestones and Progression Coordinator in the Office of the Dean, Graduate Studies. Students should also retain copies of all copyright permission requests and approvals.
[Date] [Name] [Address] Re: Request for Permission to Use Copyrighted Material in a Thesis/Dissertation Dear: I am a York University student preparing my thesis/dissertation for submission as part of the requirements of my master’s/doctoral degree in [program]. The title of my [thesis/dissertation] is: […] The reason I am writing is to ask permission to include the following material in my thesis/dissertation: [Provide standard reference information for the material, including figure/table number, if any, and page numbers. If appropriate, you can also briefly describe the manner/context in which the material will be used in thesis/dissertation.] The material will be fully cited in my thesis/dissertation. In the interest of facilitating research by others, my thesis/dissertation will be available on the internet for reference, study and/or copy. The electronic version of my thesis/dissertation will be accessible through the York University Libraries website and catalogue, and also through various web search engines. I will be granting Library and Archives Canada a non-exclusive license to reproduce, loan, distribute, or sell single copies of my thesis by any means and in any form or format. These rights will in no way restrict republication of the material in any other form by you or by others authorized by you. Could you please confirm in writing or by email that these arrangements meet with your approval. If you do not solely control the copyright in the material, please let me know as soon as possible. I would also appreciate any information you can provide about others to whom I should write to request permission. If you would like to confirm permission in writing, you can do so by signing and completing the information below and returning this signed and completed letter in the enclosed self-addressed stamped envelope by [date]. If you would like to confirm permission by email, my email address is […]. Sincerely, [Your Name and Signature] I, the undersigned, hereby represent and warrant that I have authority to grant the permission requested and do grant the permission. Signature: Name:
Students must include full citations for any copyrighted material used in their thesis/dissertation regardless of source, including photos, pictures, charts, graphs and tables.
Each citation must include the copyright symbol, name of the copyright holder (who may or may not be the author), and, if applicable, a statement that the use of the material or adaptation (in the case of adapted graphics) is by permission of the copyright holder.
In cases where use of copyrighted material is not covered under the “fair dealing” provisions of the Canadian Copyright Act and a student is unable to secure permission from the copyright holder (or there is a charge for obtaining permission), the material in question must be removed from the thesis/dissertation. In its place, the student should indicate that the material has been removed because of copyright restrictions.
Depending upon the nature of the material, the student may want to include additional information. In the case of a figure or image that has been removed, a description of the missing material and a full citation of source material and where it can be found (including, if possible, a link to an online source) would be helpful to those reading the thesis/dissertation. In the case of a chapter that was previously published in a journal, an abstract of the chapter content and link to the journal website where the article can be found could be provided.
Organization & Technical Requirements
Although the form, style, sections, etc. of main body (text) of the thesis/dissertation may differ from program to program, all theses/dissertations must include the following components in the following order.
The front matter of the thesis/dissertation must be numbered with lower case Roman numerals. The page number should be not be included on the title page, although the title page is considered page i. Numbering must be included starting with the abstract, as page ii, and continue until the end of the front matter, as follows:
| Title Page | No number appears |
| Abstract | Numbered as: ii |
| Dedication (optional) | Numbered as: iii |
| Acknowledgments (optional) | Numbered as: iv |
| Table of Contents | Numbered as: v |
| List of Tables, if appropriate | Numbered as: vi |
| List of Figures, if appropriate | Numbered as: vii |
| List of Illustrations, if appropriate | Numbered as: ix |
The main body of the thesis/dissertation, starting with the introduction or chapter one, must be numbered with Arabic numerals, beginning with the number 1. Each chapter of the main body must begin on a separate page. Footnotes and/or endnotes are considered part of the main body of the thesis/dissertation.
The back matter of the thesis/dissertation includes references (or the bibliography), as well as any appendices, glossaries, indexes, where and as applicable. The back matter must be numbered with Arabic numerals, which should follow from the last page of the main body of the thesis/dissertation.
Each appendix must be assigned an alphabetical letter and title, (e.g., Appendix A: Title). Appendices are ordered in the same sequence as they are referred to in the body of the text; that is, the appendix first mentioned in the text is assigned the letter A, the second is B, etc. Materials in the appendices that are copied from other sources must meet the same requirements as the body of the paper, for example, copies or scans from books, maps, etc., must be clear and legible, and must maintain the same margins.
Technical Requirements
A sample title page is provided below. The title page should include the following information:
- Thesis/Dissertation Title: The title should provide a concise and meaningful description of the thesis/dissertation. It is recommended that the title include key words to make the thesis/dissertation more easily searchable. It is also recommended that formulas, Greek letters, symbols and abbreviations be avoided in the title, and that they be written out as words instead.
- Student Name: The name on the title page must be the one under which the student is registered at York University.
- All title pages must include the following statement: A Dissertation* submitted to the Faculty of Graduate Studies in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree of Doctor of Philosophy* [*For a master’s thesis, replace “Dissertation” with “Thesis”, and indicate the master’s degree designation (e.g. Master of Arts, Master of Science, Master of Fine Arts) in place of “Doctor of Philosophy”]
- Program and Institution: Name of Program [e.g. English, Biology, Music], York University, Toronto, Ontario
- Date: The month and year that the Chair of the Examining Committee confirmed successful defense of the thesis/dissertation
- Copyright: The universal copyright symbol ©, followed by the student name (which must be the name under which the student is registered at York University) and year that the Chair of the Examining Committee confirmed successful defense of the thesis/dissertation.
The information on the title page may be centered, as long as all margins are at least 1 inch (25 mm). The font of the title page need not be the same as that used in the sample title page provided below.
Each thesis or dissertation must contain an abstract. The abstract is expected to give a succinct account of the thesis/dissertation so that a reader can decide whether to read the complete work.
For master’s theses, the abstract cannot exceed 150 words, while, for doctoral dissertations, the abstract cannot exceed 350 words. An abstract contains a statement of the problem, the procedure or methods used, the results and the conclusions.
The abstract should be inserted immediately following the Title Page, and should be numbered “ii”.
An acknowledgements page may be included.
The Table of Contents, List of Tables and List of Figures, where applicable, should follow the abstract (or acknowledgements, if any). Curriculum vitae, list of student-authored publications, or conference presentations do not form part of the contents of the thesis/dissertation. A truncated version of the Table of Contents should not precede each chapter.
The document must be formatted using letter-sized pages (8.5 x 11 inches).
The same font type (e.g. Arial or Times New Roman) should be used throughout the thesis/dissertation, particularly the main body.
The font size of the main body of the thesis/dissertation must be a minimum of 10 points, with smaller font sizes permitted for endnotes/footnotes, graphs, formulae, appendices, etc. A font size larger than 12 points is not recommended for the main body of the thesis/dissertation.
The line spacing must be at least one-and-a-half (1.5) spaces or double-spaced. Single spacing may be used for long quotations and foot/endnotes.
All margins must beat least 1 inch (25mm). Margins may be wider but not narrower than the stated requirements. For example, the first page of every chapter may have a top margin of 2.5 inches.
Running headers to put title, name, chapter, etc., on each page are not acceptable.
All page numbers should be in a consistent location, that is either centre bottom, centre top, right top corner, or right bottom corner. They must fall at the 1 inch (25 mm) margin. There should be no blank pages or large blank spaces within the thesis or dissertation.
Each diagram and table should be numbered. Page numbers should appear in the same position on the page as they appear elsewhere in the body of the text. Tables may be horizontal or vertical as long as the required margins are used. Diagrams must be generated by graphic software.
All images included in the thesis or dissertation should be of high quality and sufficient resolution.
- Sample Title Page (.pdf)
- Sample Table of Contents (.pdf)
- Sample List of Tables (.pdf)
Oral Examination
Master’s thesis exam committees.
A thesis examining committee shall consist of at least three voting members, including the Chair, as follows:
- two graduate faculty members chosen from the program and/or supervisory committee, at least one of whom must be from the supervisory committee;
- one graduate faculty member at arm’s length from the thesis 1 , and for whom there is no conflict of interest 2 .
The Chair of the examining committee shall be chosen from among the voting members. Members of the student’s thesis supervisory committee may be members of the examining committee, but the principal supervisor may not serve as the Chair of the examining committee.
These are minimum requirements with respect to the composition of and quorum for thesis examining committees. Individual graduate programs may include one additional voting member on examining committees, in accordance with program requirements and procedures.
In exceptional circumstances, the Dean may approve a program director’s recommendation that a York University faculty member who is not a member of the graduate faculty serve as a member (but not the Chair) of an examining committee. Such recommendations are to be accompanied by a brief rationale and an up-to-date curriculum vitae, which may be attached to the Recommendation for Oral Examination Form .
In addition to the voting members, the thesis examining committee may include the following ex-officio members (non-voting, unless present as one of the voting members named above): Vice-President Academic & Provost, Dean of the Faculty of Graduate Studies or their representative, Graduate Program Director.
The examination may be conducted in person, remotely by videoconference, or in hybrid format, the student’s preference of which is to be considered.
External examiners who would otherwise require local lodging will be asked to participate remotely via videoconference unless there is a demonstrable benefit to in-person participation. Local members of the examination committee are expected to participate in person, on campus.
1 “Arm’s length” refers to a relationship which is “conducted between parties that have no corporate or other direct connections, familial or financial relationships with each other, and thus act each in its own self-interest.”
2 Individuals in the Faculty of Graduate Studies are responsible for ensuring that they do not have a real, perceived, or potential conflict of interest that may impact the integrity of their activities, particularly, involving assessment and evaluation arising from current, previous, or foreseen future relationships. See Conflict of Interest Disclosure with Respect to Graduate Student Education for more information.
The membership of each master’s thesis exam committee, including designation of the Chair, must be recommended by the appropriate graduate program director for approval and appointment by the Dean of Graduate Studies as soon as possible and no later than 15 business days before the date set for the oral examination.
Copies of the master’s thesis approved by the supervisory committee must be provided to the members of the examining committee no less than 15 business days before the date of the oral examination.
Prior to the establishment of a master’s thesis exam committee, the student’s supervisory committee must read the thesis and agree that the version read is ready to proceed to oral examination.
Following agreement by the supervisory committee that the thesis is ready to proceed to oral examination, recommendation for membership of a master’s thesis exam committee (as well as the date and location of the oral exam) is formally initiated by the graduate program director via submission of a Recommendation for Oral Examination Form to the Graduate Milestones and Progression Coordinator in the Office of the Dean, Graduate Studies.
Final approval of master’s thesis exam committee membership recommendations rests with the Dean of the Faculty of Graduate Studies.
Scheduling of Master’s Thesis Oral Exams
In consultation with the student and the members of the exam committee, the graduate program director will recommend the date, time and location of an oral exam via submission of a Recommendation for Oral Examination Form .
Oral examinations for master’s theses shall be held normally no less than 15 business days from the date on which copies of the completed thesis approved by the supervisory committee are sent to each member of the examining committee.
The student must be registered as active for the term in which the oral exam is scheduled to take place.
Number of Copies The number of copies of a thesis required for an oral exam depends upon the number of members on the exam committee. A thesis exam committee consists of at least three voting members, including the Chair. However, it is often the case that more than three copies of the thesis are required for an oral exam. The thesis supervisor or program director will inform the student how many copies of the thesis are required for the exam.
Nature of Copies The student is responsible for ensuring that all members of the exam committee have an e-copy of the thesis, unless prior approval has been received for the submission of a paper copy. (If paper copies are submitted for the oral exam, the pagination and formatting of each page of the paper copies and the e-copies must match.)
For a complex electronic thesis, the student is responsible for ensuring that all members of the exam committee have an e-copy of the written component of the thesis, unless prior approval has been received for the submission of a paper copy. (If paper copies are submitted for the oral exam, the pagination and formatting of each page of the paper copies and the e-copies must match.) For the remaining component of the work, it is the student’s responsibility to ensure that the work produced for the thesis can be examined by the examining committee. Students producing a multimedia thesis should consult with the Library and Archives Canada website for advice on formats supportable for preservation. However, a student may work in/submit work in an unsupported format as part of the oral exam as long as the work is readily accessible by the exam committee and the student submits a written component.
For a multimodal thesis, the student is responsible for ensuring that all members of the exam committee have an e-copy of the written component of the thesis, unless prior approval has been received for the submission of a paper copy. (If paper copies are submitted for the oral exam, the pagination and formatting of each page of the paper copies and the e-copies must match.) For the remaining component of the work, it is the student’s responsibility to make arrangements for the exam committee to view/engage in the non-written component.
Note: If an examining committee member requests a paper copy of the written component(s) of the thesis, it is the graduate program’s responsibility to make arrangements once an e-copy has been provided by the student.
Before an oral examination can be convened, a majority of the exam committee members must agree that the thesis is examinable. The graduate program director shall poll the members of the exam committee five business days before the scheduled date for the oral. If the student does not receive a majority vote, the members of the examining committee who do not agree that the thesis is examinable are required to give their reasons in writing to the student, the supervisor, and the Dean within five business days after the poll. In such cases, the oral shall be postponed for a period not to exceed 12 months. However, the student has the right to insist that the oral proceed as planned.
External examiners who would otherwise require local lodging will be asked to participate remotely via videoconference unless there is a demonstrable benefit to in-person participation. Local members of the examination committee are expected to participate in person, on campus. For doctoral oral examinations, if more than two participants in the examination in total wish to participate remotely via videoconference, then the candidate and supervisor must consent, with a rationale provided to the Dean of the Faculty of Graduate Studies for approval. The wishes of the examination candidate are paramount to the Dean’s decision.
With the consent of the voting members of the examination committee, the program director and the student, the Dean may approve a recommendation that an oral examination be rescheduled due to exceptional circumstances.
The use of audio-visual (AV) equipment at oral exams is governed by the following principles:
- AV equipment may be used for oral exam presentations but the Faculty of Graduate Studies is not responsible for ordering supplies or equipment (e.g., overhead projectors).
- Audio-taping or videotaping of oral exams is not permitted.
The oral exam is a public academic event. Faculty members, graduate students and others may attend oral exams at the discretion of the Chair of the exam committee. They may, at the discretion of the Chair, participate in the questioning. Only members of the exam committee may be present for the evaluation and for the vote at the conclusion of an oral exam.
Master’s Thesis Oral Exam Evaluation Guidelines and Reporting of Results
- Master’s theses submitted by students in partial fulfillment of degree requirements must be successfully defended at oral examinations. The oral examination will centre on the thesis.
- the committee accepts the thesis with no revisions; or,
- the committee accepts the thesis with specified revisions.
- Specified revisions could range from typographical errors or changes of a minor editorial nature, to specified insertions or deletions which do not radically modify the development/argument of the thesis. The committee must specify such changes with precision. It is the responsibility of the supervisor to ensure that all such changes are made and the Chair will confirm that this is the case. Specified revisions must be completed within six months of the date of the oral examination.
- In cases where there is one vote for major revision, specified revisions are expected.
- the committee agrees that the thesis requires substantive changes in order to be acceptable; or,
- there are a minimum of two votes for major revision; or,
- there is one vote for failure.
- the committee will reconvene within twelve months to continue the oral examination; or,
- the revised thesis will be circulated within twelve months to all members, who will inform the Chair whether they feel the stipulated requirements have been met.
- Detailed reasons for referring pending major revisions must be supplied in writing by the Chair to the Dean, the program director and the student within 10 business days.
- After an adjournment and when the major revisions have been completed, the thesis is failed if there are two or more votes for failure. A thesis cannot be referred for major revisions more than once and no further adjournment is permitted. In the event of failure, detailed reasons must be supplied in writing by the Chair to the Dean, program director and student within 10 business days.
- A thesis is failed if there are a minimum of two votes for failure. In the event of failure, detailed reasons must be supplied in writing by the Chair to the Dean, program director and student within 10 business days.
The results of the oral exam, as determined by the exam committee in accordance with the evaluation guidelines described above, are reported to the Office of the Dean, Graduate Studies, via the Oral Examination Report Form . The form should be signed by the Chair of the exam committee and should include, where appropriate, details regarding any required revisions under “comments”.
In accordance with the evaluation guidelines described above, the Oral Examination Report Form requires that the committee reach one of the following four decisions:
- Accepted with No Revision
- Accepted Pending Specified Revisions The nature of the revisions should be agreed to by the exam committee and reported in detail on Oral Examination Report Form under “comments”. Specified revisions must be completed within six months of the date of the oral exam. It is the responsibility of the supervisor to ensure that all of the specified revisions are made and the Chair will confirm that this is the case. Approval of specified revisions should be reported to the Office of the Dean, Graduate Studies, via the Revisions Approved Memorandum or via email to the appropriate Graduate Milestones and Progression Coordinator .
- Referred Pending Major Revisions In cases involving a referred pending major revisions decisions, one of the following procedures, agreed upon by the committee before the examination is adjourned, must be used to finalize the oral results: a) the committee will reconvene within twelve months to continue the oral examination, or b) the revised thesis will be circulated within twelve months to all members, who will inform the Chair whether they feel the stipulated requirements have been met. Please note that a clear consensus must be reached by the committee as to the extent and nature of the revisions required. Detailed reasons for referring pending major revision must be supplied in writing by the Chair of the exam committee to the Dean, the program director and the candidate concerned within 10 business days. Approval of major revisions should be reported to the Office of the Dean, Graduate Studies, via the Revisions Approved Memorandum or via email to the appropriate Graduate Milestones and Progression Coordinator .
- Failed In the event of failure, detailed reasons must be supplied in writing by the Chair of the exam committee to the Dean, program director and candidate within 10 business days.
Exam Committee Roles and Responsibilities
Before an oral examination can be convened, a majority of the exam committee members must agree that the dissertation is examinable. The graduate program director shall poll the members of the exam committee five business days before the scheduled date for the oral. If the student does not receive a majority vote, the members of the examining committee who do not agree that the thesis is examinable are required to give their reasons in writing to the student, the supervisor, and the Dean within five business days after the poll. In such cases, the oral shall be postponed for a period not to exceed 12 months. However, the student has the right to insist that the oral proceed as planned.
For master’s theses, the Chair of the exam committee shall be chosen from among the voting members. Members of the student’s thesis supervisory committee may be members of the exam committee, but the principal supervisor may not serve as the Chair of the exam committee.
The Chair of the exam committee normally participates fully in the questioning of the candidate, the discussion and the vote.
In general, the role of the Chair of the exam committee is to ensure:
- that the process of oral exam is fair and orderly,
- that the student is truly being examined and challenged, and
- that high standards of scholarship are met.
Prior to the formal start of the oral exam, the Chair should:
- verify that all members of the exam committee are present. (If any member is not in attendance, the examination shall be postponed. Only under rare, exceptional and compelling circumstances can an oral examination proceed in the absence of the external examiner. Please see Role of the External Examiner below for more details.)
- verify that the members of the exam committee are agreed that the thesis/dissertation is “examinable”. (If the thesis/dissertation is found to be unexaminable at this time, the oral exam may be postponed for a period not to exceed 12 months. However, the student has the right to insist that the oral proceed as planned.)
- discuss with the members of the Committee the expected length of the examination, and the order in which the exam committee will question the student.
At the outset of and during the oral exam, the Chair should:
- clarify to both the exam committee and the student the procedures to be followed,
- determine the point at which further questioning will not produce additional useful information for the consideration of the exam committee, and
- monitor the procedures throughout the oral exam.
After the candidate and any observers have left the room, the Chair should:
- assess the committee’s opinion from the discussion, including whether the exam committee considers the work sufficiently outstanding to merit nomination for the Faculty of Graduate Studies Thesis/Dissertation Prize.
- If there is no consensus, the Chair should call for a vote to determine the outcome of the oral exam. The outcome of the vote shall be governed by the master’s thesis oral exam evaluation guidelines.
- In cases of accepted pending specified revisions, the Chair should ensure the nature of the on the Oral Examination Report Form under “comments”. A clear consensus must be reached by the committee as to the extent of the revisions required.
- the revised dissertation will be circulated within twelve months to all members, who will inform the Chair whether they feel the stipulated requirements have been met.
After the exam committee has reached a decision, the Chair should:
- recall the candidate to convey the decision, including a description of any required revisions, as appropriate, and
- inform the program director if the thesis/dissertation has been nominated for the Faculty of Graduate Studies Thesis/Dissertation Prize, where applicable.
If the thesis/dissertation was accepted with no revisions , the Chair should:
- ensure that a properly completed and signed Oral Examination Report Form, is returned to the Graduate Milestones and Progression Coordinator in the Office of the Dean, Graduate Studies.
If the thesis/dissertation was accepted pending specified revisions , the Chair should:
- ensure that a properly completed (including a clear description of the required revisions) and signed Oral Examination Report Form is returned to the Graduate Milestones and Progression Coordinator in the Office of the Dean, Graduate Studies. It is the responsibility of the supervisor to ensure that all of the specified revisions are made and the Chair will confirm that this is the case. Specified revisions must be completed within six months of the date of the oral exam.
- Approval of specified revisions should be reported to the Office of the Dean, Graduate Studies, via the Revisions Approved Memorandum or via email to the Graduate Milestones and Progression Coordinator .
In cases of referred pending major revisions , the Chair should:
- ensure that a properly completed (including a clear description of the required revisions) is returned to the Graduate Milestones and Progression Coordinator in the Office of the Dean, Graduate Studies, and
- provide detailed reasons for the exam committee’s decision in writing to the Dean, program director and student within 10 business days of the oral exam.
When major revisions have been completed satisfactorily as decided by the exam committee, the Chair should:
- Report approval of the major revisions to the Office of the Dean, Graduate Studies, via the Revisions Approved Memorandum or via email to the Graduate Milestones and Progression Coordinator .
In cases of failure , the Chair should:
- ensure that a properly completed and signed Oral Examination Report Form is returned to the Graduate Milestones and Progression Coordinator in the Office of the Dean, Graduate Studies, and
The exam committee members have the responsibility of ensuring that high standards of scholarship are met.
The “at arm’s length from the thesis/dissertation” committee member has a particular responsibility of ensuring that these high standards of scholarship are met from a perspective broader than that of the student’s own program. Such exam committee members who are appointed to the student’s program should be especially mindful of this responsibility.
Note: The following description of external examiner roles and responsibilities applies to those master’s programs that require an external or outside examiner on their exam committee.
External examiners are expected to be established academics, normally members of a graduate Faculty at another university. The assessment of the dissertation provided by the external examiner should be treated as the yardstick by which to measure the quality of the candidate’s work relative to standards at other universities. The external examiner is a voting member of the Committee and must have been at arm’s length from the dissertation. The external examiner does not have a formal power of veto, but the exam committee must have substantial reasons for not accepting an external examiner’s recommendation, especially if the recommendation is negative. The external examiner’s written comments will be provided to the other members of the exam committee prior to the oral exam and, where the exam committee deems advisable and the external examiner agrees, may be made available to the student at the end of the oral exam.
Only under rare, exceptional and compelling circumstances can an oral examination proceed in the absence of the external examiner, and only with the express permission of the Dean. In such circumstances, the following conditions must be met:
- the external’s absence must be unplanned and unavoidable (i.e. it must have been the initial intent that the external would be present);
- a written assessment of the dissertation must be received before the scheduled examination, including certification that the dissertation is examinable, and identification of any areas that need revision, or questioning and clarification at the oral exam. However, if the external examiner feels that the result of the examination depends upon the oral exam, then the external examiner shall be present or the oral exam will be postponed until the external examiner can be present or an alternative external examiner is appointed.
In addition to the voting members, the Vice-President Academic & Provost and Graduate Program Director may along with the Dean of the Faculty of Graduate Studies or his/her representative, participate as ex-officio members (non-voting, unless present as one of the voting members) on master’s thesis exam committees.
As the oral examination is the culmination of a graduate student’s study and advances the mission of York University as a whole, the inclusion of these positions as ex-officio members of the thesis and dissertation exam committees recognizes and emphasizes the importance of the oral exam. Due to the nature of the workload of the incumbents in these positions, they are not expected to attend every oral exam. When they do attend in their capacity as ex-officio members, they are encouraged to be active participants, but they do not vote.
- For those master’s programs that require an external or outside examiner, the written comments provided by the external examiner will be made available to the committee prior to the oral exam.
- At the oral exam, the student may be given the opportunity to present an oral summary of his or her work. If this procedure is followed, the Chair of the exam committee will inform the student and indicate the time available.
- Normally, the first round of questions will refer to general aspects of the work. Subsequent questions will deal with more detailed matters. For all doctoral dissertation oral exams and for those master’s programs that require an external or outside examiner, the external examiner will normally begin each round of questioning and will be followed by the other members of the committee in an order agreed upon before the exam.
- The Chair of the exam committee will ensure that each member of the exam committee has an equal opportunity to pose questions. After the formal rounds of questioning, general discussion and order of further questioning will be at the Chair’s discretion.
- The question period should normally run its natural course, with members of the exam committee indicating when they are satisfied. The Chair of the exam committee will, however use his/her discretion as to the appropriate closing point. For a master’s thesis, a general guideline for the length of the oral exam is approximately 10 to 20 minutes for presentation (if applicable) and 1.5 hours for questioning. For a doctoral dissertation, a general guideline for the length of the oral exam is 20 to 40 minutes for presentation (if applicable) and 2 hours for questioning.
- After the candidate and any observers have left the room, the exam committee will discuss the work and the oral defense of that work, the discussion beginning with the external examiner’s remarks.
- The Chair of the exam committee will then assess the committee’s opinion from the discussion.
- If there is no consensus, the Chair of the exam committee will call for a vote to determine the outcome of the oral exam. The outcome of the vote shall be governed by the master’s thesis oral exam evaluation guidelines and doctoral dissertation oral exam evaluation guidelines.
- In cases of accepted pending specified revisions , the nature of the revisions will be agreed to by the exam committee and reported in detail by the Chair in the “comments” section of the Oral Examination Report Form.
- In cases of major revision , the Chair of the exam committee will confirm which of the following two procedures, agreed upon by the committee before the exam is adjourned, will be used to finalize the oral results: a) the committee will reconvene within twelve months to continue the oral examination; or, b) the revised dissertation will be circulated within twelve months to all members, who will inform the Chair whether they feel the stipulated requirements have been met.
- After the exam committee has reached a decision, the candidate will be recalled and informed by the Chair of the outcome of the examination. Should revisions be required, their exact nature will be transmitted to the student by the Chair.
- The written comments of the external examiner will, with his or her permission, be provided to the student and program director.
- In cases of accepted pending specified revisions , it is the responsibility of the supervisor to ensure that all of the specified revisions are made and the Chair will confirm that this is the case. Specified revisions must be completed within six months of the date of the oral examination. Approval of specified revisions should be reported to the Office of the Dean, Graduate Studies, via the Revisions Approved Memorandum or via email to the Graduate Milestones and Progression Coordinator .
- In cases of referred pending major revisions or failure , the Chair will provide detailed reasons for the exam committee’s decision in writing to the Dean, program director and student within 10 business days of the oral exam. When major revisions have been completed satisfactorily as decided by the exam committee, the Chair should report approval of the major revisions to the Office of the Dean, Graduate Studies, via the Revisions Approved Memorandum or via email to the Graduate Milestones and Progression Coordinator .
Final Submission
Following a successful oral exam (including confirmed approval of any specified revisions or major revisions), submission by the student of the final approved thesis/dissertation is a requirement for graduation and convocation.
The thesis or dissertation is submitted electronically using York University’s Electronic Thesis and Dissertation (ETD) platform. The Graduate Milestones and Progression Coordinator in the Office of the Dean, Graduate Studies, will check that the thesis/dissertation meets the Faculty’s organizational and technical requirements, and has the right to refuse any unacceptable document until it is submitted in acceptable form.
Once the submission is approved and all requirements for graduation are met, the thesis/ dissertation will be transferred to YorkSpace, York University’s institutional repository of research outputs, where it will be accessible to Library and Archives Canada as well as major search engines and other repositories.
The degree completion date is NOT based on the date of the oral examination; it is based on the date of submission to the Electronic Thesis & Dissertation Tool (ETD) and to the Office of the Dean, Graduate Studies of the acceptable final approved copy. Students are responsible for active registration and all tuition fees until the final copy is submitted to and approved by the Office of the Dean, Graduate Studies.
Submission deadlines with respect to convocation can be found under Important Dates .
An ETD record will be created for each student by the Graduate Milestones and Progression Coordinator in the Office of the Dean, Faculty of Graduate Studies once all of the following have been received:
- Oral Examination Report (passed)
- Revisions Approved Memorandum, if applicable
- Library and Archives Canada Theses Non-Exclusive License form, signed and dated
- Copies of copyright permissions (if applicable)
Once an ETD record is opened, the student will receive an email with instructions on how to log in and complete their submission. Students should ensure that they have followed the organization and technical requirements for theses/dissertations prior to making a submission to the Office of the Dean, Graduate Studies through the ETD platform . If, after reading the Organization & Technical Requirements section of this handbook, students have any questions concerning formatting and preparation, they should direct these questions to the appropriate Graduate Milestones and Progression Coordinator . Instructions for the use of the ETD platform are available at Electronic Thesis and Dissertation (ETD) below.
By signing the Library and Archives Canada (LAC) Theses Non-Exclusive License form, the student authorizes LAC to reproduce, publish, archive, preserve, conserve, communicate to the public, loan, distribute and sell the thesis/dissertation for commercial or non-commercial purposes. Further information about the Non-Exclusive License and the Library & Archives Canada thesis program is available on the Library and Archives Canada website.
The student must also accept the terms of the York University Copyright License as part of the electronic submission of their thesis/dissertation using the Electronic Thesis and Dissertation (ETD) application.
If required, students should provide copies of any needed copyright permissions prior to the final thesis/dissertation submission. Students should also retain copies of all copyright permission requests and approvals.
As a publicly funded institution, York University has an obligation to ensure that research produced by its graduate students is available for the benefit of the public, particularly by making successfully defended theses and dissertations available through York University Libraries and Library and Archives Canada. With that in mind, there is normally no restriction on the publication of and access to successfully defended theses and dissertations. However, in some exceptional instances it may be detrimental to the author or sponsor of the thesis/dissertation research to have the thesis/dissertation publicly available immediately following a successful defence. Valid reasons to delay publication/restrict access to a successfully defended thesis/dissertation may include:
- approved intellectual property contract between a research sponsor and the University that specifies a period of confidentiality;
- that public distribution of the thesis/dissertation would invalidate a patent application;
- that public distribution of the thesis/dissertation would invalidate a publication contract; and,
- that public distribution of the thesis/dissertation would pose a risk to the personal safety of the author.
Prior to submission of the final version of their thesis being accepted on the Electronic Thesis & Dissertation Tool (ETD), students may request to delay (or to extend a previously approved delay) publication of/restrict access to their thesis/dissertation for a maximum of three years. Requests for embargo must be made to the Office of the Dean, Faculty of Graduate Studies, through the Request for a Delay of Publication (Embargo) on a Thesis or Dissertation form , prior to the submission of the final version of the thesis/dissertation. Requests will only be considered with the recommendation of the student’s supervisor and graduate program director. If approved, the body of the thesis/dissertation will be withheld from York University Libraries and Library and Archives Canada for the approved period. At the end of the approved period, the body of the thesis/dissertation will be released to York University Libraries and Library and Archives Canada via YorkSpace. To submit a request for an embargo/delay of publication, including extension requests, please do so using the Request for a Delay of Publication (Embargo) on a Thesis or Dissertation Form . Your request will be reviewed by the Faculty of Graduate Studies and a decision will be communicated to you by email. For more information on the Delay of Publication/Embargo Processes, please contact the Graduate Record & Enrolment Coordinator for your Faculty.
Students who wish to have personal copies of the thesis/dissertation bound must make their own arrangements.
How to Submit
Submitting your thesis/dissertation using York University’s Electronic Theses and Dissertations (ETD) application is a quick and easy process.
The instructions below outline the step-by-step process of using the application. Please refer to the Thesis, Dissertation and Submission Guidelines above for details on the policies and process leading up to the point of final submission, including formatting and other requirements. To view the York University ETD collection, visit the Faculty of Graduate Studies section on YorkSpace .
You can access the ETD application from any computer with an internet connection. Recommended browsers include Google Chrome, Firefox, Safari or Opera.
Instructions for converting your thesis to a PDF file are available on the YorkSpace Resources Site .
An ETD record will be set up for you by a staff member in the Office of the Dean, Faculty of Graduate Studies (FGS). FGS will need to receive the following before you will be able to access your record:
- Oral Examination Report (normally provided by the Dean’s representative on your Examining Committee as soon as possible following your defense);
- Revisions Approved Memorandum, if applicable (if your thesis/dissertation was approved with specified revisions). A blank form is usually provided to you by FGS prior to your defense. You will need to ensure it is completed and returned to FGS;
- Library and Archives Canada Theses Non–Exclusive License form (.pdf) , signed and dated;
- Copies of copyright permissions, if applicable.
Once all of the above items have been received, you will receive an email from a Graduate Milestones and Progression Coordinator letting you know that your ETD record has been created and inviting you to log in using your Passport York ID . Click on the link provided in the email to take you to etd.library.yorku.ca .
You’ll notice that there is a navigation bar across the top of the screen. You can click on any of the “tabs” to move back and forth through the process.
At the bottom right of each screen there are also arrows you can click on to move on to the next step (or move back).

You will not lose data by moving back and forth.
You can stop and save your work at any point in the process, and resume your submission simply by logging back in. To save your work, click on the navigation arrow at the bottom right of your screen. The information you have entered will be stored until you log back in.
As long as the status of your ETD record is “Open”, you can continue to make edits, updates and changes. Only once you have clicked on “I accept and send for review” on the “Submit for Review” tab will your record be closed.
If for some reason you need to request that your submission be re-opened (for example if you notice a mistake or forgot to add something), please email a Graduate Milestones and Progression Coordinator .
If you’d like more information or instructions for any of the fields you are being asked to fill out, just click on the question mark icon next to the field.
If you still have questions, you may wish to contact:
- A Graduate Milestones and Progression Coordinator in the Office of the Dean, Faculty of Graduate Studies;
- Your Graduate Program Assistant.
Step by Step Instructions
On the first screen you will find welcome text, along with the title of your thesis/dissertation and some other information from your student record (such as your degree name and program).
To begin entering your details, click on the title of your thesis/dissertation. Alternatively, you can click on the “Update Details” button on the bottom right, or on the “Update Details” tab in the navigation bar.
On the second screen, “Update Details”, you’ll notice that there are some fields already filled in, and others that you will need to complete.
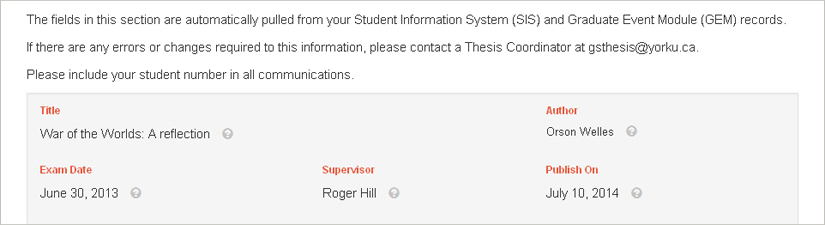
The fields that are already filled in are automatically pulled from your Student Information System (SIS) and Graduate Event Module (GEM) records. You cannot edit these fields yourself, so if you notice an error, please contact a Graduate Milestones and Progression Coordinator at a Graduate Milestones and Progression Coordinator . In the second section, you’ll find the following fields for you to complete:
Language : Click on the arrow to see the drop down menu. You will be able to select English, French, or Other (a thesis or dissertation normally should be written in English, but approval may be given to write in French or the language of any Aboriginal/First Nations people in North America).
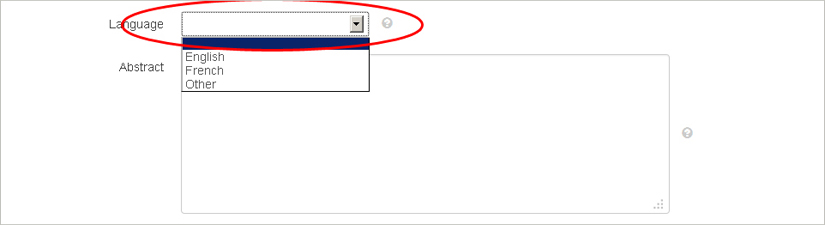
Abstract: Copy and paste your abstract into this field (the abstract must be provided in English regardless of the language of your thesis or dissertation). Please note the maximum number of words allowed (Master’s thesis 150 words; doctoral dissertation 350 words). Subjects: Click on the arrow to see the drop down menu. You must select at least one subject that best describes the overall subject of your thesis or dissertation. You have the option of selecting up to two additional secondary subjects from the other drop down menu boxes.
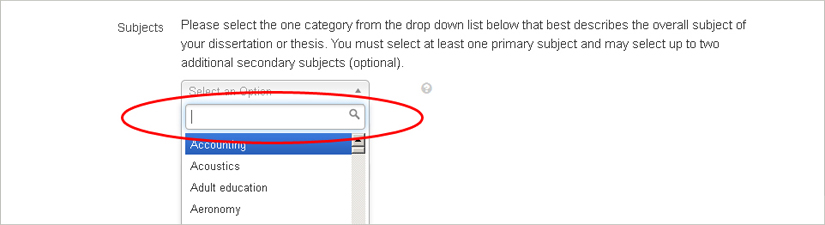
Keywords: Enter as many terms or search phrases as you like. Please use a comma to separate each keyword or string of keywords. Tip: the more terms you provide, the more likely it is that users will find your work in their searches.
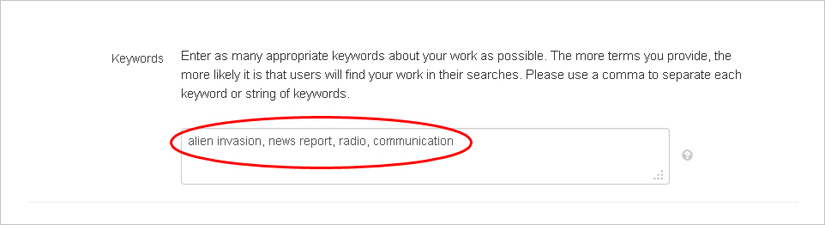
When you are finished updating your details, click “Save Details” on the bottom right to move to the next screen, or to save and return later to make further updates.
Uploading Files
Before uploading your files, you will need to save your thesis or dissertation as a PDF file (.pdf), which must be compatible with Adobe Acrobat version 5.0 or higher
This PDF document should contain the full body of your thesis/dissertation, including:
- title page;
- dedication (optional);
- acknowledgements (optional);
- table of contents;
- list of tables, figures and illustrations (if applicable);
- all chapters and written body of the thesis/dissertation;
- references or bibliography;
- all appendices.
You may upload only ONE PDF file.
Your document must be saved using the following naming convention:
Lastname_Firstname_MiddleInitial_yearofcopyright_PhDORMasters
Replace “Lastname” with your last name and “Firstname” with your first name. So, for example, if Jane Smith completed her PhD in 2014, she would save her documents as
Smith_Jane_E_2014_PhD.pdf
The “year of copyright” refers to the date that appears on the title page of your thesis/dissertation (this is the year you successfully defended).
To upload your file, simply click on the “upload primary file” button.

A box will open giving you the option to choose a file from your computer or a disk, USB key or other source.
Once you have chosen the file, click on “upload.”
In addition to the PDF of your thesis or dissertation, you may have supplementary files to add. Supplementary files refer to items that are part of the approved, examined thesis/dissertation that cannot be included in the PDF, such as multi–media, sound, video or hypertext
A list of acceptable file formats includes:
- Documents: Portable Document Format (.pdf), Text (.txt), Hypertext Markup Language (.html, .htm), Open Document Format (.odt, .odp, .ods);
- Images: Portable Network Graphics format (.png), Tagged Image File format (.tif), JPEG (.jpg);
- Data: Comma–separated values (.csv) or other delimited text, Extensible Markup Language (.xml);
- Video: 8–10 bit uncompressed AVI (.avi);
- Audio: Free Lossless Audio Codec or WAVE (.flac or .wav).
If you wish to upload a type of file that you do not see on this list, please email Digital Initiatives @ York .
Keep in mind that a supplementary file is NOT an appendix. Regular appendices can be included in the PDF document of your thesis/dissertation.
To upload your file, simply click on the “upload supplementary files“ button.

A box will open giving you the option to choose a file from your computer or a disk, USB key or other source. You may upload as many files as necessary, but no single file can exceed 500 MB. If you have a file that exceeds this size, please contact a Graduate Milestones and Progression Coordinator.
Once you have chosen the file, click on “upload.” To upload more than one file, simply click on the “upload supplementary files” button as many times as necessary.
When you have finished uploading all files, click “Review Details” on the bottom right to move to the next screen, or to save and return later to make further updates.
This is an opportunity for you to do a final confirmation that all of the details are accurate and your record is complete. Please make sure that all uploaded files are attached (they will be listed at the bottom of this screen).
As always, you can use the navigation bar at the top or arrows in the bottom right corner to go back and update any information.
When you are certain that all the information is correct and complete, click on “Submit for Review” at bottom right.
The final step in submitting your thesis or dissertation is agreeing to the York University Copyright License.
By clicking on “I Accept and Send for Review,” you are confirming that your thesis/dissertation is your original work, that your thesis/dissertation does not infringe on any rights of others and that you have the right to make the grant conferred by this copyright license. In addition, you are granting a license to York University to make copies, including electronically formatted copies, and/or distribute worldwide all or part of your thesis or dissertation, subject to the conditions outlined.
You retain copyright to your thesis/dissertation and may make it available on a personal website and pursue other sources of publication as well.
If you have questions or concerns about this license, please contact your supervisor or a Graduate Milestones and Progression Coordinator in the Faculty of Graduate Studies. You can then log back in to agree to the terms and make your submission once any queries you have are resolved.
Please carefully read this information and click on “I Accept and Send for Review” to send your thesis/dissertation to the Faculty of Graduate Studies.
Congratulations! You have completed your submission.
What Happens Next?
Once you send your thesis/dissertation for review, the status of your ETD record will change from “Open” to “Under Review” and you will not be able to make further changes. You will receive a confirmation email letting you know it is being reviewed.
If for some reason you realize you have made an error or forgotten to add something, you can email a Graduate Milestones and Progression Coordinator to request that your record be re–opened. Please remember to include your student ID number in all correspondence
After your submission has been reviewed by a Graduate Milestones and Progression Coordinator in FGS, you will receive an email notifying you of one of two outcomes:
- Your submission has been approved and will be deposited in YorkSpace upon conferral of your degree; or,
- Your submission has formatting or other errors and has been returned to you for modification.
If your submission is returned to you for modification, your ETD record will be reopened to enable you to make the required changes and resubmit. The required changes will be outlined in the email you receive from the Graduate Milestones and Progression Coordinator. If you are asked to make changes to your PDF thesis/dissertation document, simply replace the previously uploaded file with the updated one. Make sure you click on “I Accept and Send for Review” on the “Submit for Review” tab to resubmit your thesis/dissertation to FGS.
At any time you can log in to your ETD record to check on the status of your submission. Simply click on the “Check Status” tab in the navigation bar.
YorkSpace is York University’s Open Access Institutional Repository (IR). It is a platform that enables York community members to post, organize and preserve their research online in an institutional context. It showcases the scholarship of the York University community through the use of a special standards–based software platform that collects usage statistics and promotes visibility on the web.
Once your submission is approved by the Graduate Milestones and Progression Coordinator and all required forms received and fees paid, your thesis/dissertation will be deposited in YorkSpace at the time of conferral of your degree, according to the publication date listed on your ETD record (normally either November 1 or July 1).
Once the thesis/dissertation is deposited in YorkSpace, it will be available for harvesting by Library and Archives Canada (LAC) Theses Portal , other Open Archives Initiative (OAI) metadata harvesters, and major search engines such as Google Scholar . You retain copyright to your thesis/dissertation and may make it available on a personal website and pursue other sources of publication as well.
Students who wish to have personal copies of their thesis/dissertation bound must make their own arrangements. One options availabe includes:
- Wallaceburg Bookbinding
Please note that you may be required to make minor formatting adjustments to your document to prepare it for binding. For example, many binders will require that the top and left margins are at least 1.5 inches.
Graduate students who are members of CUPE 3903 (Unit 1) may submit reimbursement requests for thesis, dissertation or MRP production costs to the Office of the Dean, Faculty of Graduate Studies, using the Reimbursement of Thesis/Dissertation Production Costs Form .
- Theses Canada
- Theses and Dissertations in YorkSpace
Connect with FGS
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Happiness Hub Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- Happiness Hub
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- College University and Postgraduate
- Academic Degrees
- Doctoral Studies
- Theses and Dissertations
How to Write a Master's Thesis
Last Updated: June 1, 2023 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Christopher Taylor, PhD . Christopher Taylor is an Adjunct Assistant Professor of English at Austin Community College in Texas. He received his PhD in English Literature and Medieval Studies from the University of Texas at Austin in 2014. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 616,355 times.
Students learning how to write a Master's Thesis will first learn that a central thesis question must be presented and subsequently answered. A Master's Thesis will be the most prominent piece of your graduate work up to this point, and a pertinent thesis question that forms the spine of this work elevates it from the prosaic to the significant.
Choosing a Topic

- To get a degree - topic should be difficult enough, but manageable too.
- To enjoy the work - topic that you are truly interested in, something that you will not grow bored of after a short period of time.
- To get a job afterward - if you know what specifically you want to do after your studies and/or for which company, it might be useful to choose a topic, that will help with this goal.
- To be useful - thesis might actually be useful to help to make the world a little better place.
- Try thinking about your favorite subject of study - it may be a particular author, theory, time period, etc. Imagine how you might further the study of that subject.
- You might consider skimming through papers you wrote for your graduate courses and see if there is any apparent topic that you tend to gravitate towards.
- Consult with faculty members, favorite professors. They might have some good suggestions to write about. Generally, you'll be required to meet with your thesis advisor at least once before you start working.
- Consider consulting with industry partners. Your favorite company might have some work to do which might be done as a master's thesis. This might also help you get a job within the company afterward and maybe even some money for the thesis.
- If you want to help the world to be a better place, you might want to consult with your local non-profits and charities or check the Internet for possible thesis topics to write about.
- 3 Choose the right topic. From the possible topics generated in the previous step, find the one which best fits the objectives from the first step, especially the objectives most important to you. Make sure that you have a clear, specific, and organized plan on how to write a master's thesis which you will be able to then defend.

- Make sure that your question and the answers provided will provide original content to the body of research in existence. A judicious question will also keep research focused, organized, and interesting.
- Once you've formulated your topic and direction of inquiry, try formulating 5-10 different questions around your intended research. This forces you to think flexibly about your topic and visualize how small changes in wording can change the trajectory of your research.

- Usually, your committee chair will be in place before you formally start your thesis. They can help guide you and provide input into your project, so the earlier you can get their commitment, the better.
- Nothing is more frustrating than your thesis progress being held up by a professor who has too many obligations to make time to meet with you.
Selecting Your Texts

- For example, a novel written by Ernest Hemingway or a scientific journal article in which new results are documented for the first time would both be considered primary sources.

- For example, a book written about Ernest Hemingway's novel or a scientific journal article examining the findings of someone else's experiment would both be considered secondary sources.

- Use the in-text citation format appropriate to your discipline. [3] X Research source The most common formats are MLA, APA, and Chicago.
- Create a coordinating works cited or reference entry for each source you cite in the text of your document or in a footnote.
- Consider using a citation management software such as EndNote, Mendeley, or Zotero. These will enable you to insert and move citations within your word processor program and will automatically populate a works cited or reference page for you.
Planning an Outline

- Qualitative. This type of thesis involves completing a project that is exploratory, analytical, or creative in some way. Usually, students in the humanities will complete this kind of thesis.
- Quantitative. This type of thesis involves conducting experiments, measuring data, and recording results. Students in the sciences usually complete this kind of thesis.

- Signature page (with the completed signatures of your advising committee - usually attained at the defense, or after the project is deemed complete )
- Abstract - this is a short (one paragraph or so) description/summary of the work completed in your thesis
- Table of Contents (with page numbers)
- Introduction
- Body of paper
- Works Cited or Bibliography
- Any necessary appendices or endnotes
Moving through the Writing Process

- If you do not already have a review of literature written, it’s time to do your research! The review of literature is essentially a summary of all of the existing scholarship about your topic with plenty of direct quotations from the primary and secondary sources that you’re referencing.

Finalizing Your Thesis

- Many departments or programs provide a document template for theses and dissertations. If you have one of these, it may be easiest to use such a template from the beginning of your work (rather than copying and pasting your writing into it).

- Alternatively, ask a trusted colleague or friend to read over your thesis to help you catch any minor grammar/spelling/punctuation errors and typos.

- Some institutions require you to submit your thesis for a formatting check prior to uploading the document to ProQuest. Be sure to check with your department’s Director of Graduate Studies for specific instructions.
- Be aware of thesis submission deadlines, which are often well in advance of your graduation date. Late submission of your thesis may force you to push back your graduation date, which may affect your employment or continuing graduate studies.
Masters Thesis Outline

Expert Q&A

- Remember why you are writing a Master's thesis and who will want to read and use the material. You write a Master's thesis for members of your community, so keep in mind that they will have extensive knowledge and experience before reading your work. Don't bore them with unnecessary material. Thanks Helpful 2 Not Helpful 0
- Choosing the perfect question before starting research will prevent frustration and save time. Rigorous effort on finding the perfect question is probably the most important task when learning how to write a Master's thesis. Thanks Helpful 2 Not Helpful 0
- Consult other people who have completed a Master's thesis and obtained a Master's degree. It can be a long, grueling process, and having the support and advice of someone who has already done it can be very valuable. Thanks Helpful 1 Not Helpful 0

You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://umb.libguides.com/PrimarySources/secondary
- ↑ https://www.scribbr.com/citing-sources/in-text-citation-styles/
- ↑ https://www.unk.edu/academics/gradstudies/admissions/grad-files/Grad%20Files/ThesisGdlnsFinal08.pdf
- ↑ https://u.osu.edu/hackingthethesis/managing-stuff/your-content/outline/
- ↑ http://www.imm.dtu.dk/~janba/MastersThesisAdvice.pdf
About This Article

To write a master's thesis, make it a goal to write 500 words every day, which will help you meet your deadline without having to rush at the last minute. It's also helpful if you work in 25-minute increments and take a 5-minute break in between, which will make your work sessions less overwhelming. Also, figure out a writing time that works best for you, whether it's in the morning or at night, and stick with it so you're more productive. For more help writing your master's thesis, like how to make an outline, keep reading! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Joseph Pertey
Aug 24, 2018
Did this article help you?
Jackson Kwakwa
Nov 21, 2017
Genc Zhushi
Apr 18, 2016
İsmail Binmasudi
Jul 20, 2016
Sep 30, 2017

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
wikiHow Tech Help Pro:
Develop the tech skills you need for work and life

How To Write A Dissertation Introduction
A Simple Explainer With Examples + Free Template
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Reviewed By Dr Eunice Rautenbach (D. Tech) | March 2020
If you’re reading this, you’re probably at the daunting early phases of writing up the introduction chapter of your dissertation or thesis. It can be intimidating, I know.
In this post, we’ll look at the 7 essential ingredients of a strong dissertation or thesis introduction chapter, as well as the essential things you need to keep in mind as you craft each section. We’ll also share some useful tips to help you optimize your approach.
Overview: Writing An Introduction Chapter
- The purpose and function of the intro chapter
- Craft an enticing and engaging opening section
- Provide a background and context to the study
- Clearly define the research problem
- State your research aims, objectives and questions
- Explain the significance of your study
- Identify the limitations of your research
- Outline the structure of your dissertation or thesis
A quick sidenote:
You’ll notice that I’ve used the words dissertation and thesis interchangeably. While these terms reflect different levels of research – for example, Masters vs PhD-level research – the introduction chapter generally contains the same 7 essential ingredients regardless of level. So, in this post, dissertation introduction equals thesis introduction.

Start with why.
To craft a high-quality dissertation or thesis introduction chapter, you need to understand exactly what this chapter needs to achieve. In other words, what’s its purpose ? As the name suggests, the introduction chapter needs to introduce the reader to your research so that they understand what you’re trying to figure out, or what problem you’re trying to solve. More specifically, you need to answer four important questions in your introduction chapter.
These questions are:
- What will you be researching? (in other words, your research topic)
- Why is that worthwhile? (in other words, your justification)
- What will the scope of your research be? (in other words, what will you cover and what won’t you cover)
- What will the limitations of your research be? (in other words, what will the potential shortcomings of your research be?)
Simply put, your dissertation’s introduction chapter needs to provide an overview of your planned research , as well as a clear rationale for it. In other words, this chapter has to explain the “what” and the “why” of your research – what’s it all about and why’s that important.
Simple enough, right?
Well, the trick is finding the appropriate depth of information. As the researcher, you’ll be extremely close to your topic and this makes it easy to get caught up in the minor details. While these intricate details might be interesting, you need to write your introduction chapter on more of a “need-to-know” type basis, or it will end up way too lengthy and dense. You need to balance painting a clear picture with keeping things concise. Don’t worry though – you’ll be able to explore all the intricate details in later chapters.

Now that you understand what you need to achieve from your introduction chapter, we can get into the details. While the exact requirements for this chapter can vary from university to university, there are seven core components that most universities will require. We call these the seven essential ingredients .
The 7 Essential Ingredients
- The opening section – where you’ll introduce the reader to your research in high-level terms
- The background to the study – where you’ll explain the context of your project
- The research problem – where you’ll explain the “gap” that exists in the current research
- The research aims , objectives and questions – where you’ll clearly state what your research will aim to achieve
- The significance (or justification) – where you’ll explain why your research is worth doing and the value it will provide to the world
- The limitations – where you’ll acknowledge the potential limitations of your project and approach
- The structure – where you’ll briefly outline the structure of your dissertation or thesis to help orient the reader
By incorporating these seven essential ingredients into your introduction chapter, you’ll comprehensively cover both the “ what ” and the “ why ” I mentioned earlier – in other words, you’ll achieve the purpose of the chapter.
Side note – you can also use these 7 ingredients in this order as the structure for your chapter to ensure a smooth, logical flow. This isn’t essential, but, generally speaking, it helps create an engaging narrative that’s easy for your reader to understand. If you’d like, you can also download our free introduction chapter template here.
Alright – let’s look at each of the ingredients now.

#1 – The Opening Section
The very first essential ingredient for your dissertation introduction is, well, an introduction or opening section. Just like every other chapter, your introduction chapter needs to start by providing a brief overview of what you’ll be covering in the chapter.
This section needs to engage the reader with clear, concise language that can be easily understood and digested. If the reader (your marker!) has to struggle through it, they’ll lose interest, which will make it harder for you to earn marks. Just because you’re writing an academic paper doesn’t mean you can ignore the basic principles of engaging writing used by marketers, bloggers, and journalists. At the end of the day, you’re all trying to sell an idea – yours is just a research idea.
So, what goes into this opening section?
Well, while there’s no set formula, it’s a good idea to include the following four foundational sentences in your opening section:
1 – A sentence or two introducing the overall field of your research.
For example:
“Organisational skills development involves identifying current or potential skills gaps within a business and developing programs to resolve these gaps. Management research, including X, Y and Z, has clearly established that organisational skills development is an essential contributor to business growth.”
2 – A sentence introducing your specific research problem.
“However, there are conflicting views and an overall lack of research regarding how best to manage skills development initiatives in highly dynamic environments where subject knowledge is rapidly and continuously evolving – for example, in the website development industry.”
3 – A sentence stating your research aims and objectives.
“This research aims to identify and evaluate skills development approaches and strategies for highly dynamic industries in which subject knowledge is continuously evolving.”.
4 – A sentence outlining the layout of the chapter.
“This chapter will provide an introduction to the study by first discussing the background and context, followed by the research problem, the research aims, objectives and questions, the significance and finally, the limitations.”
As I mentioned, this opening section of your introduction chapter shouldn’t be lengthy . Typically, these four sentences should fit neatly into one or two paragraphs, max. What you’re aiming for here is a clear, concise introduction to your research – not a detailed account.
PS – If some of this terminology sounds unfamiliar, don’t stress – I’ll explain each of the concepts later in this post.
#2 – Background to the study
Now that you’ve provided a high-level overview of your dissertation or thesis, it’s time to go a little deeper and lay a foundation for your research topic. This foundation is what the second ingredient is all about – the background to your study.
So, what is the background section all about?
Well, this section of your introduction chapter should provide a broad overview of the topic area that you’ll be researching, as well as the current contextual factors . This could include, for example, a brief history of the topic, recent developments in the area, key pieces of research in the area and so on. In other words, in this section, you need to provide the relevant background information to give the reader a decent foundational understanding of your research area.
Let’s look at an example to make this a little more concrete.
If we stick with the skills development topic I mentioned earlier, the background to the study section would start by providing an overview of the skills development area and outline the key existing research. Then, it would go on to discuss how the modern-day context has created a new challenge for traditional skills development strategies and approaches. Specifically, that in many industries, technical knowledge is constantly and rapidly evolving, and traditional education providers struggle to keep up with the pace of new technologies.
Importantly, you need to write this section with the assumption that the reader is not an expert in your topic area. So, if there are industry-specific jargon and complex terminology, you should briefly explain that here , so that the reader can understand the rest of your document.
Don’t make assumptions about the reader’s knowledge – in most cases, your markers will not be able to ask you questions if they don’t understand something. So, always err on the safe side and explain anything that’s not common knowledge.

#3 – The research problem
Now that you’ve given your reader an overview of your research area, it’s time to get specific about the research problem that you’ll address in your dissertation or thesis. While the background section would have alluded to a potential research problem (or even multiple research problems), the purpose of this section is to narrow the focus and highlight the specific research problem you’ll focus on.
But, what exactly is a research problem, you ask?
Well, a research problem can be any issue or question for which there isn’t already a well-established and agreed-upon answer in the existing research. In other words, a research problem exists when there’s a need to answer a question (or set of questions), but there’s a gap in the existing literature , or the existing research is conflicting and/or inconsistent.
So, to present your research problem, you need to make it clear what exactly is missing in the current literature and why this is a problem . It’s usually a good idea to structure this discussion into three sections – specifically:
- What’s already well-established in the literature (in other words, the current state of research)
- What’s missing in the literature (in other words, the literature gap)
- Why this is a problem (in other words, why it’s important to fill this gap)
Let’s look at an example of this structure using the skills development topic.
Organisational skills development is critically important for employee satisfaction and company performance (reference). Numerous studies have investigated strategies and approaches to manage skills development programs within organisations (reference).
(this paragraph explains what’s already well-established in the literature)
However, these studies have traditionally focused on relatively slow-paced industries where key skills and knowledge do not change particularly often. This body of theory presents a problem for industries that face a rapidly changing skills landscape – for example, the website development industry – where new platforms, languages and best practices emerge on an extremely frequent basis.
(this paragraph explains what’s missing from the literature)
As a result, the existing research is inadequate for industries in which essential knowledge and skills are constantly and rapidly evolving, as it assumes a slow pace of knowledge development. Industries in such environments, therefore, find themselves ill-equipped in terms of skills development strategies and approaches.
(this paragraph explains why the research gap is problematic)
As you can see in this example, in a few lines, we’ve explained (1) the current state of research, (2) the literature gap and (3) why that gap is problematic. By doing this, the research problem is made crystal clear, which lays the foundation for the next ingredient.
#4 – The research aims, objectives and questions
Now that you’ve clearly identified your research problem, it’s time to identify your research aims and objectives , as well as your research questions . In other words, it’s time to explain what you’re going to do about the research problem.
So, what do you need to do here?
Well, the starting point is to clearly state your research aim (or aims) . The research aim is the main goal or the overarching purpose of your dissertation or thesis. In other words, it’s a high-level statement of what you’re aiming to achieve.
Let’s look at an example, sticking with the skills development topic:
“Given the lack of research regarding organisational skills development in fast-moving industries, this study will aim to identify and evaluate the skills development approaches utilised by web development companies in the UK”.
As you can see in this example, the research aim is clearly outlined, as well as the specific context in which the research will be undertaken (in other words, web development companies in the UK).
Next up is the research objective (or objectives) . While the research aims cover the high-level “what”, the research objectives are a bit more practically oriented, looking at specific things you’ll be doing to achieve those research aims.
Let’s take a look at an example of some research objectives (ROs) to fit the research aim.
- RO1 – To identify common skills development strategies and approaches utilised by web development companies in the UK.
- RO2 – To evaluate the effectiveness of these strategies and approaches.
- RO3 – To compare and contrast these strategies and approaches in terms of their strengths and weaknesses.
As you can see from this example, these objectives describe the actions you’ll take and the specific things you’ll investigate in order to achieve your research aims. They break down the research aims into more specific, actionable objectives.
The final step is to state your research questions . Your research questions bring the aims and objectives another level “down to earth”. These are the specific questions that your dissertation or theses will seek to answer. They’re not fluffy, ambiguous or conceptual – they’re very specific and you’ll need to directly answer them in your conclusions chapter .
The research questions typically relate directly to the research objectives and sometimes can look a bit obvious, but they are still extremely important. Let’s take a look at an example of the research questions (RQs) that would flow from the research objectives I mentioned earlier.
- RQ1 – What skills development strategies and approaches are currently being used by web development companies in the UK?
- RQ2 – How effective are each of these strategies and approaches?
- RQ3 – What are the strengths and weaknesses of each of these strategies and approaches?
As you can see, the research questions mimic the research objectives , but they are presented in question format. These questions will act as the driving force throughout your dissertation or thesis – from the literature review to the methodology and onward – so they’re really important.
A final note about this section – it’s really important to be clear about the scope of your study (more technically, the delimitations ). In other words, what you WILL cover and what you WON’T cover. If your research aims, objectives and questions are too broad, you’ll risk losing focus or investigating a problem that is too big to solve within a single dissertation.
Simply put, you need to establish clear boundaries in your research. You can do this, for example, by limiting it to a specific industry, country or time period. That way, you’ll ringfence your research, which will allow you to investigate your topic deeply and thoroughly – which is what earns marks!
Need a helping hand?
#5 – Significance
Now that you’ve made it clear what you’ll be researching, it’s time to make a strong argument regarding your study’s importance and significance . In other words, now that you’ve covered the what, it’s time to cover the why – enter essential ingredient number 5 – significance.
Of course, by this stage, you’ve already briefly alluded to the importance of your study in your background and research problem sections, but you haven’t explicitly stated how your research findings will benefit the world . So, now’s your chance to clearly state how your study will benefit either industry , academia , or – ideally – both . In other words, you need to explain how your research will make a difference and what implications it will have .
Let’s take a look at an example.
“This study will contribute to the body of knowledge on skills development by incorporating skills development strategies and approaches for industries in which knowledge and skills are rapidly and constantly changing. This will help address the current shortage of research in this area and provide real-world value to organisations operating in such dynamic environments.”
As you can see in this example, the paragraph clearly explains how the research will help fill a gap in the literature and also provide practical real-world value to organisations.
This section doesn’t need to be particularly lengthy, but it does need to be convincing . You need to “sell” the value of your research here so that the reader understands why it’s worth committing an entire dissertation or thesis to it. This section needs to be the salesman of your research. So, spend some time thinking about the ways in which your research will make a unique contribution to the world and how the knowledge you create could benefit both academia and industry – and then “sell it” in this section.

#6 – The limitations
Now that you’ve “sold” your research to the reader and hopefully got them excited about what’s coming up in the rest of your dissertation, it’s time to briefly discuss the potential limitations of your research.
But you’re probably thinking, hold up – what limitations? My research is well thought out and carefully designed – why would there be limitations?
Well, no piece of research is perfect . This is especially true for a dissertation or thesis – which typically has a very low or zero budget, tight time constraints and limited researcher experience. Generally, your dissertation will be the first or second formal research project you’ve ever undertaken, so it’s unlikely to win any research awards…
Simply put, your research will invariably have limitations. Don’t stress yourself out though – this is completely acceptable (and expected). Even “professional” research has limitations – as I said, no piece of research is perfect. The key is to recognise the limitations upfront and be completely transparent about them, so that future researchers are aware of them and can improve the study’s design to minimise the limitations and strengthen the findings.
Generally, you’ll want to consider at least the following four common limitations. These are:
- Your scope – for example, perhaps your focus is very narrow and doesn’t consider how certain variables interact with each other.
- Your research methodology – for example, a qualitative methodology could be criticised for being overly subjective, or a quantitative methodology could be criticised for oversimplifying the situation (learn more about methodologies here ).
- Your resources – for example, a lack of time, money, equipment and your own research experience.
- The generalisability of your findings – for example, the findings from the study of a specific industry or country can’t necessarily be generalised to other industries or countries.
Don’t be shy here. There’s no use trying to hide the limitations or weaknesses of your research. In fact, the more critical you can be of your study, the better. The markers want to see that you are aware of the limitations as this demonstrates your understanding of research design – so be brutal.
#7 – The structural outline
Now that you’ve clearly communicated what your research is going to be about, why it’s important and what the limitations of your research will be, the final ingredient is the structural outline.The purpose of this section is simply to provide your reader with a roadmap of what to expect in terms of the structure of your dissertation or thesis.
In this section, you’ll need to provide a brief summary of each chapter’s purpose and contents (including the introduction chapter). A sentence or two explaining what you’ll do in each chapter is generally enough to orient the reader. You don’t want to get too detailed here – it’s purely an outline, not a summary of your research.
Let’s look at an example:
In Chapter One, the context of the study has been introduced. The research objectives and questions have been identified, and the value of such research argued. The limitations of the study have also been discussed.
In Chapter Two, the existing literature will be reviewed and a foundation of theory will be laid out to identify key skills development approaches and strategies within the context of fast-moving industries, especially technology-intensive industries.
In Chapter Three, the methodological choices will be explored. Specifically, the adoption of a qualitative, inductive research approach will be justified, and the broader research design will be discussed, including the limitations thereof.
So, as you can see from the example, this section is simply an outline of the chapter structure, allocating a short paragraph to each chapter. Done correctly, the outline will help your reader understand what to expect and reassure them that you’ll address the multiple facets of the study.
By the way – if you’re unsure of how to structure your dissertation or thesis, be sure to check out our video post which explains dissertation structure .
Keep calm and carry on.
Hopefully you feel a bit more prepared for this challenge of crafting your dissertation or thesis introduction chapter now. Take a deep breath and remember that Rome wasn’t built in a day – conquer one ingredient at a time and you’ll be firmly on the path to success.
Let’s quickly recap – the 7 ingredients are:
- The opening section – where you give a brief, high-level overview of what your research will be about.
- The study background – where you introduce the reader to key theory, concepts and terminology, as well as the context of your study.
- The research problem – where you explain what the problem with the current research is. In other words, the research gap.
- The research aims , objectives and questions – where you clearly state what your dissertation will investigate.
- The significance – where you explain what value your research will provide to the world.
- The limitations – where you explain what the potential shortcomings and limitations of your research may be.
- The structural outline – where you provide a high-level overview of the structure of your document
If you bake these ingredients into your dissertation introduction chapter, you’ll be well on your way to building an engaging introduction chapter that lays a rock-solid foundation for the rest of your document.
Remember, while we’ve covered the essential ingredients here, there may be some additional components that your university requires, so be sure to double-check your project brief!

Psst... there’s more!
This post was based on one of our popular Research Bootcamps . If you're working on a research project, you'll definitely want to check this out ...
46 Comments
Thanks very much for such an insight. I feel confident enough in undertaking my thesis on the survey;The future of facial recognition and learning non verbal interaction
Glad to hear that. Good luck with your thesis!
Thanks very much for such an insight. I feel confident now undertaking my thesis; The future of facial recognition and learning non verbal interaction.
Thanks so much for this article. I found myself struggling and wasting a lot of time in my thesis writing but after reading this article and watching some of your youtube videos, I now have a clear understanding of what is required for a thesis.
Thank you Derek, i find your each post so useful. Keep it up.
Thank you so much Derek ,for shedding the light and making it easier for me to handle the daunting task of academic writing .
Thanks do much Dereck for the comprehensive guide. It will assist me queit a lot in my thesis.
thanks a lot for helping
i LOVE the gifs, such a fun way to engage readers. thanks for the advice, much appreciated
Thanks a lot Derek! It will be really useful to the beginner in research!
You’re welcome
This is a well written, easily comprehensible, simple introduction to the basics of a Research Dissertation../the need to keep the reader in mind while writing the dissertation is an important point that is covered../ I appreciate the efforts of the author../
The instruction given are perfect and clear. I was supposed to take the course , unfortunately in Nepal the service is not avaialble.However, I am much more hopeful that you will provide require documents whatever you have produced so far.
Thank you very much
Thanks so much ❤️😘 I feel am ready to start writing my research methodology
This is genuinely the most effective advice I have ever been given regarding academia. Thank you so much!
This is one of the best write up I have seen in my road to PhD thesis. regards, this write up update my knowledge of research
I was looking for some good blogs related to Education hopefully your article will help. Thanks for sharing.
This is an awesome masterpiece. It is one of the most comprehensive guides to writing a Dissertation/Thesis I have seen and read.
You just saved me from going astray in writing a Dissertation for my undergraduate studies. I could not be more grateful for such a relevant guide like this. Thank you so much.
Thank you so much Derek, this has been extremely helpful!!
I do have one question though, in the limitations part do you refer to the scope as the focus of the research on a specific industry/country/chronological period? I assume that in order to talk about whether or not the research could be generalized, the above would need to be already presented and described in the introduction.
Thank you again!
Phew! You have genuinely rescued me. I was stuck how to go about my thesis. Now l have started. Thank you.
This is the very best guide in anything that has to do with thesis or dissertation writing. The numerous blends of examples and detailed insights make it worth a read and in fact, a treasure that is worthy to be bookmarked.
Thanks a lot for this masterpiece!
Powerful insight. I can now take a step
Thank you very much for these valuable introductions to thesis chapters. I saw all your videos about writing the introduction, discussion, and conclusion chapter. Then, I am wondering if we need to explain our research limitations in all three chapters, introduction, discussion, and conclusion? Isn’t it a bit redundant? If not, could you please explain how can we write in different ways? Thank you.
Excellent!!! Thank you…
Thanks for this informative content. I have a question. The research gap is mentioned in both the introduction and literature section. I would like to know how can I demonstrate the research gap in both sections without repeating the contents?
I’m incredibly grateful for this invaluable content. I’ve been dreading compiling my postgrad thesis but breaking each chapter down into sections has made it so much easier for me to engage with the material without feeling overwhelmed. After relying on your guidance, I’m really happy with how I’ve laid out my introduction.
Thank you for the informative content you provided
Hi Derrick and Team, thank you so much for the comprehensive guide on how to write a dissertation or a thesis introduction section. For some of us first-timers, it is a daunting task. However, the instruction with relevant examples makes it clear and easy to follow through. Much appreciated.
It was so helpful. God Bless you. Thanks very much
I thank you Grad coach for your priceless help. I have two questions I have learned from your video the limitations of the research presented in chapter one. but in another video also presented in chapter five. which chapter limitation should be included? If possible, I need your answer since I am doing my thesis. how can I explain If I am asked what is my motivation for this research?
You explain what moment in life caused you to have a peaked interest in the thesis topic. Personal experiences? Or something that had an impact on your life, or others. Something would have caused your drive of topic. Dig deep inside, the answer is within you!
Thank you guys for the great work you are doing. Honestly, you have made the research to be interesting and simplified. Even a novice will easily grasp the ideas you put forward, Thank you once again.
Excellent piece!
I feel like just settling for a good topic is usually the hardest part.
Thank you so much. My confidence has been completely destroyed during my first year of PhD and you have helped me pull myself together again
Happy to help 🙂
I am so glad I ran into your resources and did not waste time doing the wrong this. Research is now making so much sense now.
Gratitude to Derrick and the team I was looking for a solid article that would aid me in drafting the thesis’ introduction. I felt quite happy when I came across the piece you wrote because it was so well-written and insightful. I wish you success in the future.
thank you so much. God Bless you
Thank you so much Grad Coach for these helpful insights. Now I can get started, with a great deal of confidence.
It’s ‘alluded to’ not ‘eluded to’.
This is great!
Thank you for all this information. I feel very confident to complete my dissertation with all the help given. This is awesome and very helpful; I was studying alone with very little supervision and feedback of my thoughts. feelings. aspirations and experiences, with my topic or Kaupapa. It is a topic that very little or few researchers have written a thesis about (from personal experiences). As John Burke said ” unless you are sitting in the front seat and row, up close and personal, you will not understand the difficulties of growing up and living with hearing loss (caused by swimmer’s ears infection, resulting in burst eardrums, unless one denies having a hearing loss. This is from a Māori woman’s cultural perspective. Nga mihi nui kia koutou.
Thanks a lot for this information. The concepts are explained in a simple yet powerful way. They are easy to understand and adopt. Your team played an important role in writing my thesis. A big thank you !!!
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
- Thesis & Dissertation Title Page | Free Templates & Examples
Thesis & Dissertation Title Page | Free Templates & Examples
Published on May 19, 2022 by Tegan George . Revised on July 18, 2023.
The title page (or cover page) of your thesis , dissertation , or research paper should contain all the key information about your document. It usually includes:
- Dissertation or thesis title
- The type of document (e.g., dissertation, research paper)
- The department and institution
- The degree program (e.g., Master of Arts)
- The date of submission
It sometimes also includes your dissertation topic or field of study, your student number, your supervisor’s name, and your university’s logo.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Title page format, title page templates, title page example, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions.
Your department will usually tell you exactly what should be included on your title page and how it should be formatted. Be sure to check whether there are specific guidelines for margins, spacing, and font size.
Title pages for APA and MLA style
The format of your title page can also depend on the citation style you’re using. There may be guidelines in regards to alignment, page numbering, and mandatory elements.
- MLA guidelines for formatting the title page
- APA guidelines for formatting the title page
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

We’ve created a few templates to help you design the title page for your thesis, dissertation, or research paper. You can download them in the format of your choice by clicking on the corresponding button.
Research paper Google Doc
Dissertation Google Doc
Thesis Google Doc
A typical example of a thesis title page looks like this:

If you want to know more about AI for academic writing, AI tools, or research bias, make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
Research bias
- Anchoring bias
- Halo effect
- The Baader–Meinhof phenomenon
- The placebo effect
- Nonresponse bias
- Deep learning
- Generative AI
- Machine learning
- Reinforcement learning
- Supervised vs. unsupervised learning
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
The title page of your thesis or dissertation should include your name, department, institution, degree program, and submission date.
Usually, no title page is needed in an MLA paper . A header is generally included at the top of the first page instead. The exceptions are when:
- Your instructor requires one, or
- Your paper is a group project
In those cases, you should use a title page instead of a header, listing the same information but on a separate page.
The title page of your thesis or dissertation goes first, before all other content or lists that you may choose to include.
In most styles, the title page is used purely to provide information and doesn’t include any images. Ask your supervisor if you are allowed to include an image on the title page before doing so. If you do decide to include one, make sure to check whether you need permission from the creator of the image.
Include a note directly beneath the image acknowledging where it comes from, beginning with the word “ Note .” (italicized and followed by a period). Include a citation and copyright attribution . Don’t title, number, or label the image as a figure , since it doesn’t appear in your main text.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
George, T. (2023, July 18). Thesis & Dissertation Title Page | Free Templates & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved September 27, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/dissertation/title-page/
Is this article helpful?
Tegan George
Other students also liked, thesis & dissertation acknowledgements | tips & examples, dissertation table of contents in word | instructions & examples, figure and table lists | word instructions, template & examples, what is your plagiarism score.

COMMENTS
As stated above, a thesis is the final project required in the completion of many master's degrees. The thesis is a research paper, but it only involves using research from others and crafting your own analytical points. On the other hand, the dissertation is a more in-depth scholarly research paper completed mostly by doctoral students.
Tip #2: Begin Work on the Thesis Statement and Break Up the Thesis into Manageable Sections. After selecting an appropriate topic and developing a central research question for the thesis statement, it is then necessary to apply the research and writing skills you have learned throughout your degree program.
Part 2: Form an Initial Thesis Question, and Find a Supervisor When to Begin Forming Your Initial Thesis Question. Some fields, such as history, may require you to have already formed your thesis question and to have used it to create a statement of intent (outlining the nature of your research) prior to applying to a master's program. Others ...
Learn about the definition, formatting, and submission of your thesis or dissertation at Cornell University. Find out if you can use the papers option and how to access ProQuest and eCommons databases.
minimum of ten days for all members of the thesis committee to review the thesis. Step 1: Prepare the content of your presentation. The content of your presentation is the mirror of your thesis ...
Revised on April 16, 2024. A thesis is a type of research paper based on your original research. It is usually submitted as the final step of a master's program or a capstone to a bachelor's degree. Writing a thesis can be a daunting experience. Other than a dissertation, it is one of the longest pieces of writing students typically complete.
Conclusion. In conclusion, the structure of a master thesis is a critical component that ensures the clarity, coherence, and academic rigor of the research presented. Each section, from the introduction to the conclusion, plays a vital role in guiding the reader through the research journey, providing context, methodology, findings, and ...
Writing a masters dissertation or thesis is a sizable task. It takes a considerable amount of research, studying and writing. Usually, students need to write around 10,000 to 15,000 words. It is completely normal to find the idea of writing a masters thesis or dissertation slightly daunting, even for students who have written one before at ...
Find out how to write a masteral thesis or dissertation by looking at previous work done by other students on similar topics. Browse a list of award-winning theses and dissertations from various disciplines and universities.
While the standard length of a master's thesis is around 100 pages, a doctoral dissertation can be upwards of 400-500 pages. While most students can finish their PhD dissertation or thesis in as little as 1-2 years, it can take as long as 7 years depending on the school, program, and dissertation topic. As doctoral programs have their own ...
Choosing Between a Thesis or Non-thesis Master's Degree. As of 2015, approximately 25.4 million Americans held advanced degrees, with more citizens joining these ranks each year. As studies continue to show the career advancement and salary benefits of completing a master's degree, more and more students elect to pursue advanced educations ...
Simply put, a Master's thesis is the last and biggest project you do in the last two semesters as a culminating point of your Master's degree. It's an academic research paper meant to demonstrate a student's competence and mastery of a particular subject within their field of study. These research papers typically combine pre-existing studies ...
Dissertation & Thesis Outline | Example & Free Templates. Published on June 7, 2022 by Tegan George.Revised on November 21, 2023. A thesis or dissertation outline is one of the most critical early steps in your writing process.It helps you to lay out and organize your ideas and can provide you with a roadmap for deciding the specifics of your dissertation topic and showcasing its relevance to ...
A thesis could consist of an average of 70 to 100 pages, including a bibliography, citations, and various sections. It is written under the guidance of a faculty advisor and should be publishable as an article. Your master's thesis reflects the literature in your field, challenges, evidence, and arguments around your writing topics.
THE MASTER'S THESIS. DIVISION OF EMERGING MEDIA STUDIES. COLLEGE OF COMMUNICATION BOSTON UNIVERSITY. Revised, January 2019. This guide has been prepared to assist students in completing their Master's Theses in a form that is acceptable to the faculty of the Division of Emerging Media Studies and also acceptable within the requirements of ...
Foreword. This guidebook summarizes the procedures followed by the Office of Graduate Studies and Research for students who are planning to write theses for their master's degree. This manual also is intended to guide students in the elements and structure generally contained in a thesis as well as to provide a reference to the appropriate ...
Craft a convincing dissertation or thesis research proposal. Write a clear, compelling introduction chapter. Undertake a thorough review of the existing research and write up a literature review. Undertake your own research. Present and interpret your findings. Draw a conclusion and discuss the implications.
Master's theses submitted by students in partial fulfillment of degree requirements must embody the results of original research and must be successfully defended at oral examinations. Master's theses shall be on a topic approved by the student's supervisor and supervisory committee, and shall include submission and approval of a thesis proposal, including appropriate ethics review and ...
First, you need to find a topic (or "thesis question"), often with the help and/or approval of your faculty-led thesis committee. Next comes the process of research, which is often the most time-intensive. Then, you must take the time to analyze your research. Lastly, you outline and write the actual thesis.
How to Write a Thesis or Dissertation Introduction. Published on September 7, 2022 by Tegan George and Shona McCombes. Revised on November 21, 2023. The introduction is the first section of your thesis or dissertation, appearing right after the table of contents.Your introduction draws your reader in, setting the stage for your research with a clear focus, purpose, and direction on a relevant ...
Keep an idea file where you jot down potential research ideas. Be on the look out for new data that might help provide new insights into a topic, or for past research that might be productively replicated in other circumstances. In order to write a master's thesis you must find a faculty member who is willing to be your thesis advisor.
Craft an enticing and engaging opening section. Provide a background and context to the study. Clearly define the research problem. State your research aims, objectives and questions. Explain the significance of your study. Identify the limitations of your research. Outline the structure of your dissertation or thesis.
Revised on July 18, 2023. The title page (or cover page) of your thesis, dissertation, or research paper should contain all the key information about your document. It usually includes: Dissertation or thesis title. Your name. The type of document (e.g., dissertation, research paper) The department and institution.