How to Give Assignments to Team Members
Table of Contents
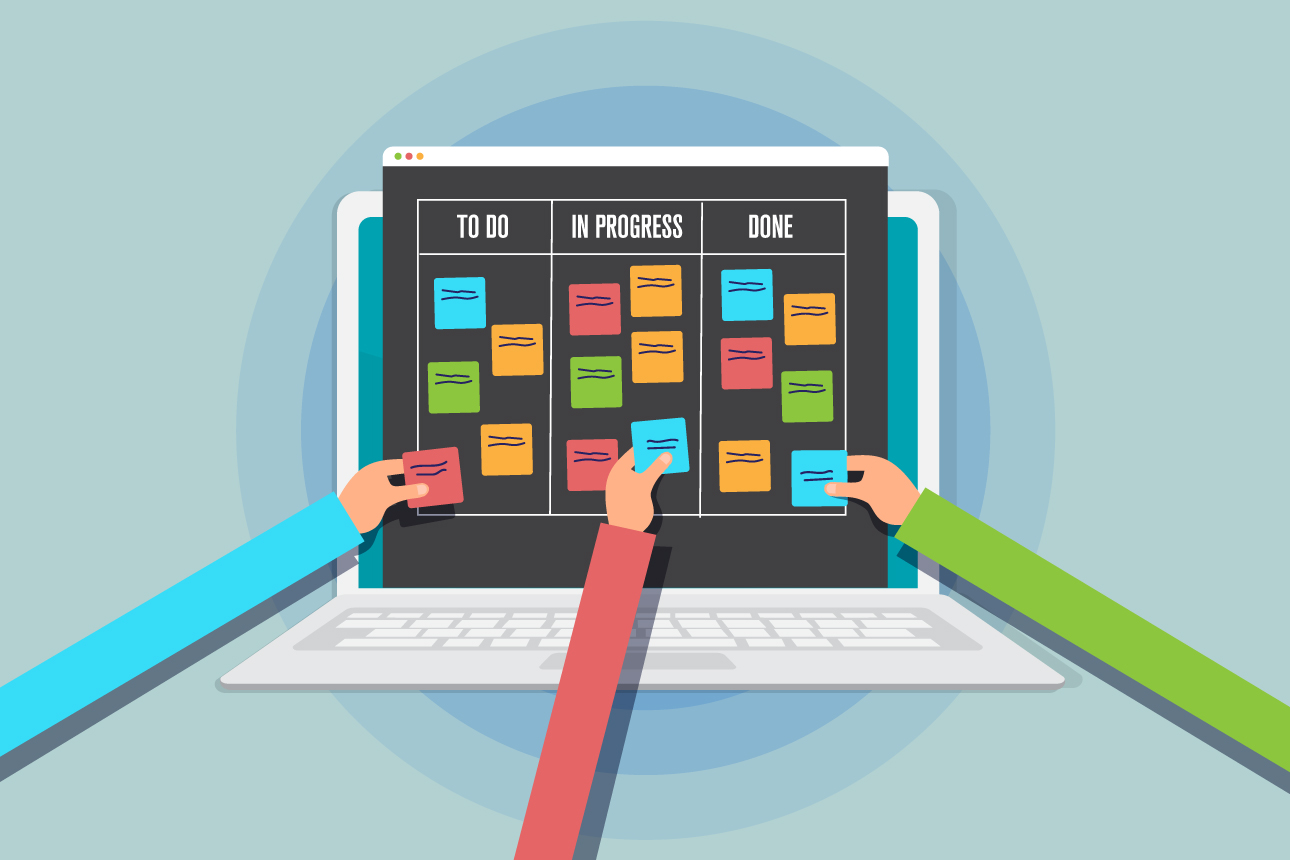
The project has been divided into milestones, goals and objectives broken into tasks, and now it’s time to assign them. But as you open the project management platform, you’re faced with the unflattering process of wording the tasks, and choosing whom to assign them to.
Well, in this article, we offer advice on how to make that jumbled first moment a little clearer. There are actionable tips, learning the difference between allocating and delegating tasks, and suggested criteria on how to choose the best person for the job.
For a more precise overview, here’s a table of contents:

How do you assign employees tasks?
We normally think that assigning tasks is a time-consuming process that focuses on clearing out task lists to keep the project going. However, task assignment should actually be a more employee-oriented process that requires additional dedication and effort, which yields incredible results. But what do we mean by that?
Properly assigned tasks push your employees, projects, and the overall company forward. Here’s how.
- They strengthen accountability and trust between managers and employees;
- They help teach new skills and perfect old ones;
- They allow employees to get familiar with other teams and avenues of work;
- It becomes easier to make project estimates;
- Makes for great bases for performance reviews, etc.
The list could go on, but we’ll stop there for now.
Of course, such long-term benefits don’t come without some proverbial blood and sweat in the planning stage. Let’s take a look at the general ideas on assigning employee tasks, and specific steps you can take.
Motivation comes from knowing the bigger picture
When we talk about the bigger picture in project management, we talk about each team member’s task affecting their peer’s down the line. Since all tasks are usually small pieces of the puzzle, it helps to remind employees how their work contributes. For example:
- A high-quality draft can make a great foundation for the final version, and it can be completed more quickly.
- A well-prepared presentation can shave time off unnecessary questions and additional email inquiries.
It comes as no surprise that people work better and are more productive, when they know that their work has an impact on the company level.
And so, when you assign tasks, try to emphasize how they fit in the bigger picture. Simply saying: “ You doing X will help with Y and Z ” and how it reflects on the project as a whole will let an employee know that the task they were assigned is important.
Get your employees excited to commit
Telling people about the bigger picture and showing them what’s possible can only get them so far. It’s enough to ignite the initial spark, but for them to fully commit to the task, you need to define what that task entails.
They should be able to picture how to go about the work, what skills to use, and how to reach the desired result. The clearer the instructions, the more motivated they will be to work.
Simply put, give directions on how the task should be done, and make sure they understand. You can’t read each other’s minds, so it’s important everyone is on the same page.
Ask for task transparency
One of the best practices a company can employ is transparency among coworkers.
This is achieved by having everyone input their tasks for the day in a timesheet. The purpose of timesheets is to get an accurate idea of what everyone is working on at any given time.
When people know who works on what tasks, it’s easier for them to know if a person is available or busy, how far along they are with a task, etc.
So, when you give assignments to employees, label them with deadlines. Alternatively, you can ask for employees’ assessments on how long the work would take them, and use those timeframes.
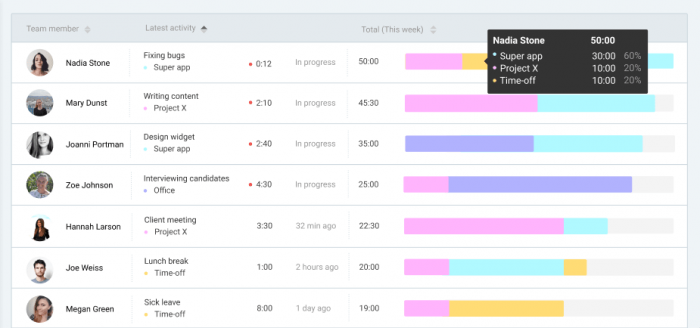
Source: Clockify team timesheet
Timesheets are a great way to keep an eye on tasks and the people doing them. You get to:
- see who struggles with what (helps assess people’s skill sets);
- who burns through their workload and is available for additional tasks;
- whether your time estimates need correction;
- identify any wasted time.
💡 If your employees are insecure about keeping public records of their tasks, here are a few resources that can help:
- How to create order in your daily work tasks
- How to be more efficient with your tasks
Keep a crystal clear timeframe
While we’re discussing timesheets and deadline transparency, it’s important to mention that the times you set for task completions need to be clear-cut.
As we’ve mentioned, the safest way to assign deadlines is to consult the employees. They are better at assessing how long it will take them due to the tasks’ difficulty, overall deadlines, the standards that need to be met, and the skill required to complete it.
When they get a say in how long they should be doing an assignment, people tend to feel more accountable for the whole process. They will do their best to finish in time, since they actively participated in setting the deadline.
Set very clear expectations
Assigning a task should always include your (the supervisor’s) expectations pointed out. For example:
- Does a logo pitch need as many drafts as possible, or just a few finished pieces?
If you ask a designer to make some drafts for a logo pitch, you must specify the kind of quality you’re looking for. Explain whether you are looking for some sketches and drafts for a brainstorming meeting, or if you want clean, presentable pieces to show.
Additionally:
- How many pieces should the designer do?
- Is there a specific color palette they need to follow?
- How important is the task? Is this the day they finally decide on a logo, or is it still in the brainstorming stage? (decides on the quality of the work itself)
Assigning the task using the above questions, you help the designer understand how much effort precisely they need to invest. They become more motivated with clear instructions, as they know what is expected of them. There’s no fear of having their work criticized for something that wasn’t communicated in the beginning. And on your end, it prevents breached deadlines or subpar results.
Avoid creating dependency by being less involved
It’s not unusual for employees to ask their supervisors for their opinion on a certain task, or their performance.
The problem arises when a supervisor makes themselves too involved with the process. When they feel like the project might fall apart if they don’t have their eyes on every moving part all of the time. And when you have, say, 20 people waiting for that person’s approval, advice, or consultation, the workflow runs into a gridlock.
And wait time is wasted time.
Plus, people lose motivation, patience, and grow frustrated, as they could be doing other things.
So, learn not to jump in every time people call for your aid. Assign reliable people who can address smaller issues, while you handle the big picture. Learn how to expend your own energy where it is needed more.
For example – making a pitch presentation for potential investors keeps getting put off because one person needs you to check a client email they want to send, another wants your signature on a form, and the third wants to ask something about employee feedback that’s coming up.
In order to not be stretched thin, and have your time wasted on menial tasks, here’s where you can start:
How to mitigate the risk of being over-involved when assigning
- Remember that you match tasks to people
Which means that, by matching the right people with the right tasks, your involvement will be minimal. Take time to carefully choose who gets to do what. What is the point of assigning tasks if they can’t be done without you?
- Have a 10-point scale to judge the importance of items
How important are certain aspects of your leadership role? Are you absolutely necessary in every meeting, or during every call? Which tasks need your approval, and which ones can be approved by someone under you?
Rank these items on a scale of 0 to 10, based on their importance to you and the project. Top priority tasks should get your undivided attention. And what can be delegated, should be.
- Analyze your schedule
Your energy and time are needed on a much broader scale. The best way to spot if you’re wasting time being too involved is to look at your schedule. Identify how much time you’ve spent on low-priority items, and assess which issues could’ve been solved without you.
- Take into account priorities and deadlines
Step in only when absolutely necessary. You are in charge of things getting done on time, by people most qualified for assigned tasks. Determine what your priorities are for each project, and concern yourself only with those issues, unless there is a risk of breaching a deadline.
- Formulate a list of dependable people
If you know your employees (or team members) well enough, then you should be able to single out those who are more dependable and ready to take on a little more responsibilities. Write out the reasons how they could help by getting involved on low-priority items instead of you. When the time comes, rally them and present them with the idea, keeping in mind that this solution helps push the project forward. When authority is delegated to several people, there’s fewer chances of a hold-up in the workflow.
This also falls into the realm of task delegation , which we’ll get into later.
How do you decide what tasks to assign to which employees?
1. assign based on priority.
Naturally, some tasks will be more important than others. When you break down a project into tasks , spend some time assessing their priority level.
High-priority tasks should be the first on your list to allocate. Whether it’s because they’re time-sensitive, or require more effort and dedication.
Low priority tasks can be allocated as fillers to the first available person.
2. Assign based on employee availability
Another factor to consider when assigning tasks is who is available at the moment.
As the project moves along, new tasks will be added. You will have to allocate new work, but odds are you won’t always be able to pick who you want. Especially if a deadline is approaching, the person with the smallest workload should be your first choice.
Overloading an already busy individual just because they’re more skilled or you have faith in them the most puts an unnecessary strain on them. It’s cause for frustration, poorer results, and decreased productivity.
And as we’ve mentioned, if you have a timesheet with an overview of all the tasks and employees working on them, it’ll be much easier to spot who is free and who isn’t.
3. Assign based on employee skill level
High-priority tasks should go to employees with more experience in a given field or skill. However, you should occasionally give such tasks to other employees as well, to help them grow and become just as dependable. Giving people challenging tasks that can boost their experience is essential to productivity and morale.
Not to mention you get to have multiple high-skilled employees.
Low-priority tasks can be assigned to anyone, despite their experience level. They’re a good opportunity to practice, pick up new skills, or get smaller tasks out of the way to make room for more important ones.
4. Assign based on preference
Last, but not the least, preference can also play a big part in how you assign tasks.
It’s a given that some employees will prefer certain tasks over others. So it could be good to assign tasks at a meeting with the team. As you discuss priorities, deadlines, and availability, ask them which tasks they would like to work on.
If someone shows interest in a specific type of work, they should (with some consideration), be allowed to take it. After all, people are more productive when they’re assigned to something they find new or exciting.
Note: Apply this rule with caution. Letting people do only the tasks they want can stunt their career growth. Getting out of our comfort zones and occasionally doing tasks that we don’t like is how we develop and learn. So, don’t forget to document assignments as you hand them out, to spot these potential issues early on.
Allocating vs delegating tasks
While semantically similar words, delegation and allocation in terms of tasks are two different things.
When you allocate tasks , you are assigning tasks without giving the employees much authority, challenge, or room to grow. It includes you keeping all of the responsibility – writing out the tasks, making deadlines, providing resources, tools, etc. These are usually recurring tasks that can become repetitive.
When you delegate tasks , you allow for some of that responsibility to fizzle out from your fingers. All you think about are the objectives, while letting the employees figure out the details and means to get there.
However, that doesn’t mean delegation is right and the allocation is wrong.
Task allocation has its own place. It is just as important, as a lot of tasks come down to repeated processes that are still vital to the project progress. Task delegation is just a good opportunity for employees to learn, challenge themselves, and assess their skills and performance.
When should you allocate tasks?
Management and BizDev consultant Artem Albul shared his concept on task assignment, which he dubbed an “algorithm”. He emphasized how these criteria are useful only and only when you wish that employees perform the tasks based on your guidelines and instructions (aka allocation).
Here is how Albul broke down the algorithm:
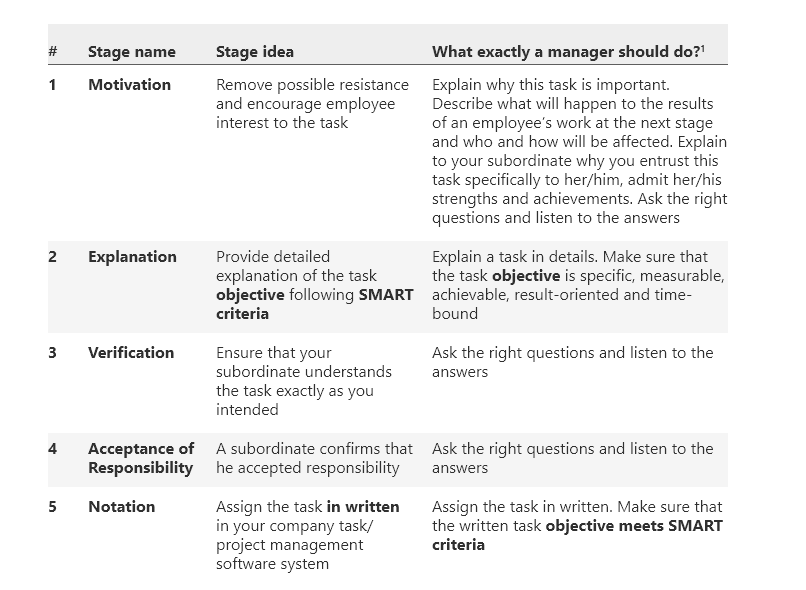
Source: Artem Albul, TWA Consulting
As we can see, task allocation, while the more “controlling” of the two, also gives in-depth instructions and asks for confirmation on task clarity. A lot of it comes down to everyone being on the same page, leaving little to no room for misinterpretation (but also creative freedom).
How should you allocate tasks?
With all that we’ve mentioned in the previous section, here’s how your task allotment could look like, step by step.
- Break down your project
Detail out the goals, objectives, and some individual tasks (not all, be careful not to start micromanaging). Place the most important deadlines.
- Prioritize tasks and sort them
It’s important to know what tasks need to be done faster/better, to properly allocate your resources and manpower from the start.
- Make a list of teams and team members
Assign team leaders (if you don’t have them), and alternatively, ask for their input on individual employees skills, for a more informed decision on who gets what.
- Schedule a meeting
Make a meeting with the team leads and go through the points above. Assign tasks according to each team’s availability, interest, and skill required to successfully push the project forward.
- As team leads – assign tasks further down the pipeline
- Track task completion and make necessary changes along the way
Whether it’s pushing deadlines, reassigning tasks, or shifting around resources. This is perfectly fine and expected, so long as it doesn’t happen on every task you’ve assigned. Then, it is an indicator of poor pre-planning.
- Offer feedback and write performances
Don’t forget to track the progress and make notes of important details that might help the next task allocation/delegation process. It’s also a useful piece of information for the employees on what they need to improve on.
Allocating tasks is somewhat more complicated than we want it to be. But, this kind of thorough research and preparation will make projects run more smoothly. Employees will also be more satisfied with their work, and there will be less hurdles as deadlines approach.
When should you delegate tasks?
Delegation is a great practice in trust for both the employer/supervisor and the employee. The employer learns how to give away some of their control over the process, while the employee learns how to take more accountability for their work.
This lets you focus on big-picture aspects of your job, since you deal less with assignments that are low-priority for you. You save time and energy, while helping others move up in their careers.
How do you effectively delegate tasks as a leader?
As we’ve mentioned, delegating includes more employee independence. There are some additional components which make this type of task assignment more appealing than allocation, with great opportunities for growth.
Focus on delegating objectives instead of actual tasks
When you delegate, you focus on the objective that needs to be done. You shouldn’t give employees a “color by numbers” instruction on how to complete a task.
Communicate clearly what the end result should be and what expectations you (or the higher-ups) have. Leave the means for reaching that end goal to the employees themselves. Because how you solve a task may be completely different to how they will. And that is perfectly fine, so long as the result is the one you are looking for.
Keep the objectives challenging
When the objectives you’re delegating are too easy, chances are the person will either procrastinate, or feel like you don’t trust them enough. And if they’re too difficult, they get frustrated, anxious, and begin to panic.
It’s a good idea to be aware of an employee’s skill level, so you can gauge how much challenge and responsibility they can take on. For them to be the most productive and achieve great results, they need to enter “the state of Flow”.
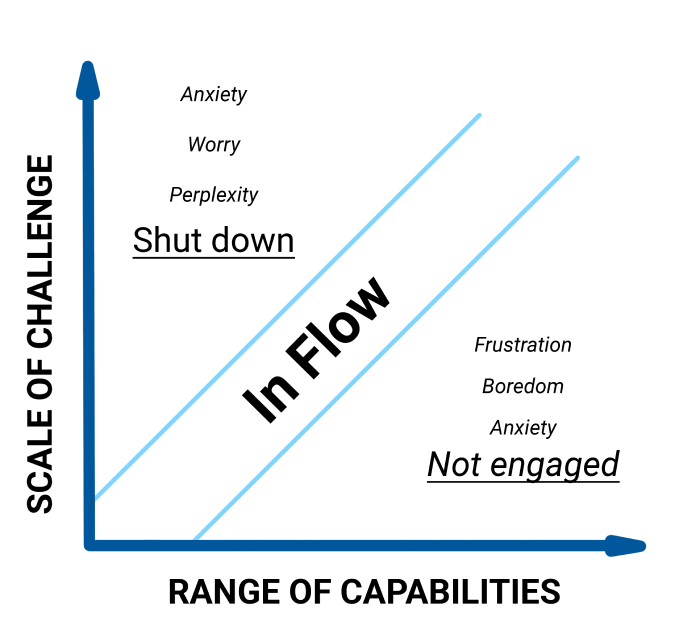
Source: Optimal Experience , M. Csikszentmihalyi
💡 We’ve discussed the state of Flow in more detail in an article on time organization.
Encourage discussion and feedback
Let employees voice their opinions on the topic.
They should ask anything about the task, the goals, or the overall impact their work will have on the later stages or others’ workflow. It means they are interested in the task, and getting involved.
And if they aren’t asking questions themselves, you can always nudge them into proactivity.
- Is there something you’d like me to clarify?
- Do you already have any ideas on how to go about the task?
- Is the time we agreed upon enough for you?
- Will you need other resources, tools, or support?
- Do you see any problems or risks?
Questions like these help them feel valued, their efforts acknowledged, and let them know you care about the task and how well they perform. Just be careful not to overdo it, or you’ll start to look like a micromanager.
Give employees free rein, but offer support
Speaking of micromanaging, delegation means you let people problem-solve their way out on their own. There should be no reason for a manager to step in and control or supervise any step of the process, unless absolutely necessary.
However, what you should do is let them know you’re available for any advice should they feel stuck. Just because employees get authority on a certain task, and are left to their own devices, doesn’t mean the project has to suffer until they pull themselves up.
From time to time, ask them if they need anything from you, and make sure they know you’re there for any kind of support, consultation, or mediation. ANother good practice is to also give them additional learning opportunities – such as training, conferences, courses, etc.
Delegate objectives that move people forward
Choose assignments that boost the skills and employ all of their experiences, instead of something that simply needs to be done. For example:
- Tasks that require they brush up on their team communication skills;
- Learning how to allocate smaller tasks;
- Supervising others’ work and doing quality control;
- Learning to work with a new tool;
- Holding a meeting (or more), etc.
Find out which skills your employees may want or need to develop, and then plan your delegations accordingly. You want them to complete the task while having learned something new at the same time.
How to choose who to delegate to
Paul Beesley, senior director and consultant at Beyond Theory proposed a nifty checklist for when you’re choosing an employee to delegate to. It’s meant to simplify and speed up the process.
To successfully complete the delegated task, your chosen employee needs:
S – the skill to perform and complete a task
T – the time to complete the task, and if needed, learn the required skill
A – the authority to handle everything concerning the task
R – the necessary level of responsibility
R – the recognition for successfully completing the task
This list is a set of important criteria that should be covered when you consider who to assign to a specific task. However, depending on your niche, type of service, company size and the project at hand, the criteria are likely to change. And it should accommodate your needs, not the other way around.
Common task delegation mistakes to avoid
With all being said, there are some common mistakes managers and employers make, sometimes without even realizing it.
- Being too vague concerning deadlines (using: as soon as possible, when you get to it, I need it by yesterday). It creates unnecessary pressure.
- Being unavailable for questions and concerns. While you shouldn’t micromanage, you should still be present for support if an employee feels stuck. Ignoring them or handing them over to someone else could cause distrust. However, if you are usually swamped with work, set consultation hours each day or week.
- Having unclear directions. Specifying the allotted time for task completion and expectations should be the bare minimum when delegating tasks.
- Not providing feedback. No feedback is worse than bad feedback. Employees need to be aware when they’re doing good work, as well. In one company I worked for, the mantra was: “If no one is complaining about your work, that means you’re doing good”. And while it sounds like sound logic, it actually caused a lot of frustration. We were left directionless, and simply “floating” from task to task, never knowing if any of them had a positive impact on our performance.
- Not listening to employees. Take into account how they feel about a task or the objective. Let them give you feedback and if there are potential problems from the get-go.
- Assigning other people to the same task. If you notice a person struggling, the first instinct should be to ask them how they’re faring, and if they need any help. Some managers tend to assign other employees to help them without consultation, which leaves a sore taste. The employee will feel even more incompetent and will be less likely to take on a similar task in the future.
- Assuming people will know what you mean. This is one of the biggest problems. When you’re formulating a task, be as clear as possible about the goals and expectations. Oftentimes managers think that these things are implied, but the truth is – no one is a mind reader. To avoid having information misconstrued or misunderstood, communicate clearly and directly.
There could be more mistakes, especially for every different field and industry. If at all possible, identify the most common ones, made either by you or your peers. Note down all the instances where certain tasks weren’t up to par, and see what you could have changed in your assignment process to fix it. Maybe there wasn’t enough time or resources, you were unclear, or the employee wasn’t ready for such responsibility. Use the same procedure in all future task delegations. It’s the only way to learn and make the process quicker.
Use Clockify to assign tasks with ease
Now you’re a master of task delegation — congrats!
But there’s more to it than meets the eye.
In fact, what if you used a digital tool like Clockify to increase the likelihood that each job would be completed on time and on point?
In Clockify, you can easily create highly descriptive assignments that contain information like:
- Start time,
- Billability status,
- Name of the employee,
- Period for getting the assignment done,
- Hours per day to spend on the assignment, and more.
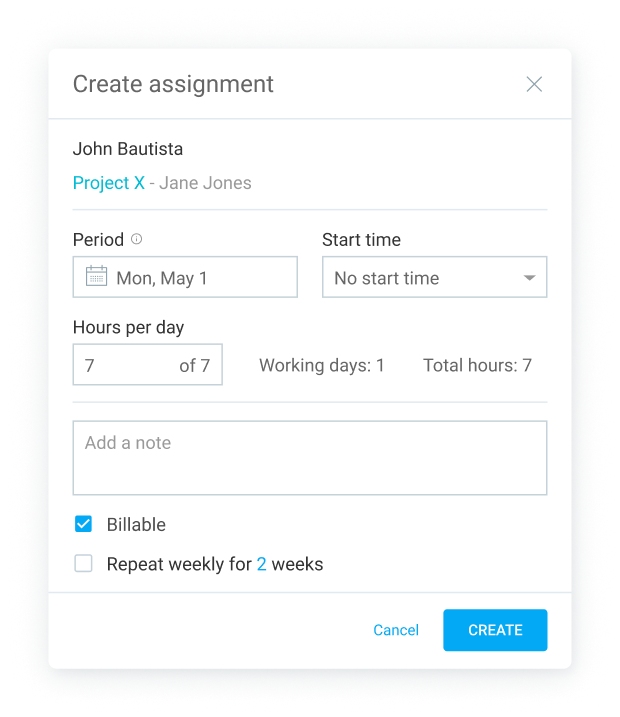
That way, you can plan who works on what, how long, and when.
Similarly, Clockify allows you to create project milestones to achieve results faster.
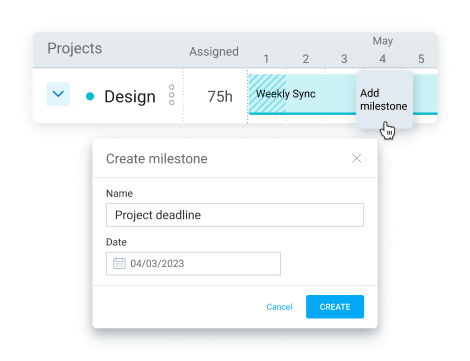
With the Milestones option, you can select dates for deadlines, allowing you to pin down important events in your projects.
For example, if your client expects you to keep them in the loop about developments, you can inform them promptly on whether your team has reached the agreed-upon milestones.
Refocus on your company’s big picture with a project and time tracking tool.

Marijana Stojanovic is a writer and researcher who specializes in the topics of productivity and time management.
Where does the time go?
START TRACKING TIME
with Clockify
How to create a PTO policy
Everything you need to know about creating a PTO policy — from the basics of PTO to choosing a PTO tracking system that suits your workflow.
Working Overtime Without Pay – Know Your Rights and Options
Discover the legal and financial aspects of working overtime without pay. Learn your rights and how to handle common concerns regarding off-clock work.
PTO vs. Vacation: What Is the Difference?
Learn the difference between PTO and vacation and find out the answers to the most frequently asked questions regarding paid leave!
Best methods for tracking team productivity
Find out the most useful methods of tracking team productivity, followed by actual examples of how different teams measure their effectiveness.
Difference between a freelancer, a contractor, and an employee
Learn which work category you fall into, to better protect your rights as a worker and avoid worker exploitation.
10+ Life-changing tips to increase office productivity in 2023
Workplace distractions, stress, and poor performance are everywhere. Read this guide with life-changing tips to increase office productivity now!
FREE FOREVER • UNLIMITED USERS
Free time tracker
Time tracking software used by millions. Clockify is a time tracker and timesheet app that lets you track work hours across projects.
- Book a Speaker
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Vivamus convallis sem tellus, vitae egestas felis vestibule ut.
Error message details.
Reuse Permissions
Request permission to republish or redistribute SHRM content and materials.
How do I conduct a job analysis to ensure the job description matches the duties performed by the employee in the job?
Job analysis is the process of gathering, examining and interpreting data about a job's tasks and responsibilities. It generally includes tracking an employee's duties and the duration of each task, observing the employee performing his or her job, interviewing the employee, managers and others who interact with the employee, and comparing the job to other jobs in the same department and job grade or job family. An important concept in job analysis is that it is an evaluation of the job, not the person doing the job. The final product from a job analysis includes a thorough understanding of the essential functions of the job, a list of all duties and responsibilities, a percentage of time spent for each group of tasks, the job's relative importance in comparison with other jobs, the knowledge, skills and abilities (KSAs) needed to perform the job, and the conditions under which the work is completed.
There are many ways to perform a job analysis, but all require the cooperation of the employee in the position, his or her manager(s) and others the employee works closely with while performing his or her job duties.
The following steps will help provide the best analysis of a particular job:
- Have employees complete a job analysis questionnaire.
- Interview employees, asking them specific questions about their job duties and responsibilities.
- Obtain log sheets from employees with information about each of their tasks and the time spent on each task for at least one full work week.
- Complete desk audits where you observe employees doing their jobs at different times of the day and days of the week and track what they do and for how long.
- Interview supervisors and managers, and other employees, clients and customers the employee may interact with while performing the job.
- Compare the job to other jobs in the department as well as the job grade or job family to show where it falls on the pay scale.
If there is more than one person doing the same job, make sure to observe and obtain feedback and information from more than one person. You will want to review your findings with the employees who do the job as well as their supervisors and managers to tweak your findings until you have an accurate reflection of the job duties and responsibilities.
Once an accurate overview of a position is developed, employers should update the job description to match the results of the job analysis.
Job descriptions can be used as a tool for recruiting, determining salary ranges and levels or grades, establishing job titles, creating employee's job goals and objectives, and conducting performance reviews. They can also be used for career planning, creating reasonable accommodations and meeting legal requirements for compliance purposes. Because of this, it is important to have written job descriptions that accurately reflect the employees' current job duties and responsibilities.
Related Content

A 4-Day Workweek? AI-Fueled Efficiencies Could Make It Happen
The proliferation of artificial intelligence in the workplace, and the ensuing expected increase in productivity and efficiency, could help usher in the four-day workweek, some experts predict.

How One Company Uses Digital Tools to Boost Employee Well-Being
Learn how Marsh McLennan successfully boosts staff well-being with digital tools, improving productivity and work satisfaction for more than 20,000 employees.
Advertisement
Artificial Intelligence in the Workplace
An organization run by AI is not a futuristic concept. Such technology is already a part of many workplaces and will continue to shape the labor market and HR. Here's how employers and employees can successfully manage generative AI and other AI-powered systems.
HR Daily Newsletter
New, trends and analysis, as well as breaking news alerts, to help HR professionals do their jobs better each business day.
Success title
Success caption
- Data, AI, & Machine Learning
- Managing Technology
- Social Responsibility
- Workplace, Teams, & Culture
- AI & Machine Learning
- Diversity & Inclusion
- Big ideas Research Projects
- Artificial Intelligence and Business Strategy
- Responsible AI
- Future of the Workforce
- Future of Leadership
- All Research Projects
- AI in Action
- Most Popular
- The Truth Behind the Nursing Crisis
- Work/23: The Big Shift
- Coaching for the Future-Forward Leader
- Measuring Culture

The spring 2024 issue’s special report looks at how to take advantage of market opportunities in the digital space, and provides advice on building culture and friendships at work; maximizing the benefits of LLMs, corporate venture capital initiatives, and innovation contests; and scaling automation and digital health platform.
- Past Issues
- Upcoming Events
- Video Archive
- Me, Myself, and AI
- Three Big Points

Assignments Are Critical Tools to Achieve Workplace Gender Equity
Work assignments can be a powerful means of propelling employees’ growth but — unless managed deliberately — they can also undermine efforts to build a diverse workforce.
- Workplace, Teams, & Culture
- Organizational Behavior

Facing unprecedented levels of employee burnout and historic quit rates , how can companies lead with a model that attracts and retains talent? This period of transition, and the lessons learned from the pandemic, offer organizations a unique opportunity to improve and refine their diversity, equity, and inclusion (DEI) strategies. 1 It is imperative that leaders consider the landscape of work assignments at their companies as a foundation for greater workforce equity.
“Assignments” can comprise work tasks, activities, or projects. Scholars have long identified a gender gap in access to the kinds of assignments — large in scope, highly visible, and strategically important — that are seen as essential to career advancement. An estimated 70% of leadership development occurs through experiential learning , especially the kind offered by these challenging stretch assignments.
Get Updates on Transformative Leadership
Evidence-based resources that can help you lead your team more effectively, delivered to your inbox monthly.
Please enter a valid email address
Thank you for signing up
Privacy Policy
Yet women are largely overlooked for challenging work assignments. One factor is that women typically have fewer ties to influential decision makers who connect people to assignment opportunities . Biased performance evaluations also may play a role, with women seeing no gains in their performance scores for the very behaviors (such as “taking charge”) for which men are rewarded. 2 One study showed how promotability depends on having had challenging past projects — setting up a vicious cycle in which women never get ahead. 3 Women of color, tasked with the additional burden of “fitting in” at predominantly White organizations, may find channels to career-advancing work blocked entirely. 4
Historically, companies have not tracked assignment processes. In one 2010 report, when HR leaders were asked the percentage of “business-critical/important” assignments held by women, the top two responses were “1% to 10%” and “not measured.” Both career-advancing work and meaningful work are cornerstones of positive professional experiences. But leaders may know little about who has access to significant assignments, or they may be unaware of how a lack of access drives burnout, turnover, and dwindling diversity on the leadership bench. 5
These many unknowns about assignments drive an information gap that grows riskier as countless organizations head into new hybrid work arrangements. To quantify this risk, our team at the Stanford VMware Women’s Leadership Innovation Lab ran a study of assignments, using data that many companies collect and managers review at least yearly: employee engagement survey (EES) data. We examined pre-pandemic EES results for a midsized global technology company. 6 Only one question on the survey asked about employees’ perceptions of access to career-advancing assignments.
The company did not track assignments by gender, but our analysis showed a statistically significant gender difference. Relative to men, women were 15% less likely to report opportunities for career-advancing assignments. 7 This gender difference held even after we adjusted for employee and job characteristics. That is, women were less likely than men to perceive their assignment opportunities as having career value. This was the case even among women and men in the same department and role.
We then supplemented this analysis with a descriptive look at two related survey questions on our case company’s EES: one about making meaningful contributions, and another about receiving recognition for one’s work. Of women, 39% saw greater contribution opportunities than recognition opportunities, compared with 34% of men. While this particular gender gap may seem small, limited opportunities can accumulate over the course of a career and contribute to the persistent underrepresentation of women in leadership. Imagine how these results could inform today’s leaders in an economy recalibrating during an ongoing global pandemic.
An Equity-Minded Assignment Framework
Unseen assignment disparities can destabilize efforts to build a diverse workforce all the way up the ladder, so we propose an equity-minded assignment framework for leaders and managers to implement in the short, medium, and long terms, starting today . The purpose of this framework is to better identify and strengthen the role of work assignments in meeting DEI goals.
In the short term, embed assignment conversations in the “return to office” tools for managers. Many companies are deploying managerial tools to support employees and teams in their decision-making about hybrid work arrangements. These one-on-one meetings offer a promising context for managers to discuss assignments with their direct reports. These discussions are critical, as will be the consequences of not talking about assignments: Hybrid work arrangements, where some employees are in the office while others are working from home, run the risk of creating inequality in employees’ visibility to leaders and thus who might be seen as the right person for a particular assignment.
These conversations present a unique opportunity to explore assignments and have a forward-looking career discussion. Managers may ask, for example:
- What are you currently working on that you see as critical to your career development and advancement? What work do you find especially meaningful? How do these areas overlap?
- As we return to the office, how can we align your work with your career advancement goals and your sense of fulfillment? Which assignments do you need in order to get there, and to whom do you need to be visible?
- How will your hybrid work arrangement give you exposure to the right people and workstreams?
These questions will encourage managers and employees to think through not just the where of the hybrid workplace, but the what and with what career outcomes . Answering them can push employees to think beyond work-life factors in their ideal hybrid design — and can nudge everyone in the organization to view assignments as a core tool in employee development.
In the medium term, develop a broader view of the assignments landscape in the organization. In the wake of workforce disruption and heightened attention to racism, sexism, and inequality, leaders have been called on to accelerate their DEI efforts. To achieve real change, assignments need to be embedded in DEI strategy. The first step is to get a better handle on the baseline landscape of assignments by identifying the most important assignments for career advancement and meaning. Conducting focus groups with employees across all organizational functions can help inform the strategy by identifying common assignment-related themes and persistent problems to tackle.
Once the landscape is understood, leaders can create accountability mechanisms for more equitable assignment allocations and outcomes. Leaders need to ensure that top assignments are made available across organizational functions and that supports are in place for people to execute them successfully. For example, the former CEO of Jamba Juice, James White, changed how high-profile work was assigned by deliberately giving defined strategic projects to people who were rarely selected for them and providing them with dedicated time to meet project goals. Rethinking these channels diversified the internal pipeline of people ready to advance to leadership roles .
In performance evaluation and talent calibration meetings, leaders must explicitly account for assignments — those assigned to employees who are promoted and, just as importantly, to employees who are not. Managers should consider whether promotion gaps between women and men, for instance, would shift if assignments were changed. Internal audits and assignment dashboards, which visually clarify who on which teams is doing what, can inform data-driven managerial decision-making about assignments. The goal is not to decrease managerial autonomy but rather to empower managers with a broad view of the landscape, to increase assignment transparency and build opportunities for connection.
Finally, the range of assignments needs to be balanced fairly within units and across different roles. In mapping and building on this landscape, leaders must not overlook “low-promotability” work. Linda Babcock and colleagues have shown that women are more often asked to volunteer for lower-leverage assignments than are men, and they agree to do this work more often, too. 8 Expectations about women’s propensity to volunteer for tasks that everyone wants completed but no one wants to do themselves can route women away from career-advancing work and ultimately deepen gender stereotypes and inequity in the workplace. Leaders must engage managers, HR professionals, and staff members focused on DEI efforts in building a more equitable assignment space to support the advancement of all workforce groups.
Over the long term, make assignments a core part of your employee engagement surveys, and link the results to your talent strategy. The EES has long been a tool for organizations to take the temperature of their workforces by collecting engagement data and identifying employee needs. But work assignments are rarely measured on EESs, despite their significance for motivation, engagement, and equitable advancement. (In examining EESs at four large multinational companies in various sectors, we found that, of nearly 200 total questions, only five explicitly mentioned work assignments.) Including even a few questions about assignments will allow for new insights, and running gap analyses that integrate EES data can lead to even more significant change. (A gap analysis is a tool that allows an organization to diagnose gaps between an organizational goal and an actual outcome.)
Questions included on a survey define what information leaders can know about their workforces. “What is not measured is critically important to consider,” said Molly Anderson, CEO of Exponential Talent, a diversity and inclusion consulting firm. She also noted that “companies often draw the wrong conclusions … through an error of omission.” We suggest using one question as a starting point for study: “To what extent do you have sufficient opportunities to work on assignments that are important to your career development?” Gathering information about access to critical assignments and their connections to particular employees’ goals is a good jumping-off point that organizations can track in real time.
After you ask questions, it’s crucial to examine group differences in the responses as part of conducting a larger gap analysis into which EES data can factor directly. 9 Say, for example, that an organization sets a DEI goal to increase the representation of women and people of color in leadership roles. Collected EES data might show that these groups perceive access to leadership development assignments differently than White men do. With assignment-specific EES data, leaders can then act to meet their DEI goal, equipped with information to open dialogue, inspire interventions, and course-correct.
Assignments Looking Forward
Related articles.
The best approach to incorporating assignments in your talent strategy is multipronged. As organizations prepare for hybrid work arrangements, assignments should be discussed in managers’ one-on-ones with their direct reports; embedded in DEI goals, performance evaluations, and promotion conversations; explored in focus groups; and measured on EESs and in gap analyses. When any of these approaches reveals potential disparities in the experiences or perceptions of assignments between groups, leaders should focus on revamping their processes.
Leaders don’t have to tackle all of these approaches at once. Any increase in understanding the state of assignments in an organization, and in beginning to act on these insights, will in fact be a talent differentiator. After the pandemic-driven exodus of women — especially women of color — from the workforce, companies cannot afford to lose more of them to the additional burnout wrought by unfairly allocated assignments. By keeping steady tabs on their workforces when change is both inevitable and highly uncertain, forward-looking leaders can quickly identify and intervene in emergent negative trends and drive positive changes to empower their workforces equitably.
About the Authors
Erin Macke is a Ph.D. candidate in sociology at Stanford University and a graduate research assistant at Stanford’s VMware Women’s Leadership Innovation Lab. Gabriela Gall Rosa is a research data analyst at the VMware Women’s Leadership Innovation Lab. Shannon Gilmartin is a senior research scholar at the VMware Women’s Leadership Innovation Lab. Caroline Simard is managing director of the VMware Women’s Leadership Innovation Lab.
1. “ Hybrid Working Is Here to Stay Post-Pandemic: Stanford’s Nicholas Bloom ,” Bloomberg TV, Dec. 30, 2020, video, 6:34, www.bloomberg.com; and J.M. Barrero, N. Bloom, and S.J. Davis, “ Why Working From Home Will Stick ,” working paper 28731, National Bureau of Economic Research, Cambridge, Massachusetts, April 2021.
2. S.J. Correll, K.R. Weisshaar, A.T. Wynn, et al., “Inside the Black Box of Organizational Life: The Gendered Language of Performance Assessment,” American Sociological Review 85, no. 6 (December 2020): 1022-1050.
3. I.E. De Pater, A.E.M. van Vianen, M.N. Bechtoldt, et al., “Employees’ Challenging Job Experiences and Supervisors’ Evaluations of Promotability,” Personnel Psychology 62, no. 2 (May 2009): 297-325.
4. T.M. Melaku, “You Don’t Look Like a Lawyer: Black Women and Systemic Gendered Racism,” (Lanham, Maryland: Rowman & Littlefield Publishers, 2019).
5. P.T.Y. Preenan, I.E. De Pater, A.E. van Vianen, et al., “Managing Voluntary Turnover Through Challenging Assignments,” Group & Organization Management 36, no.3 (April 2011): 3088-344; C. Maslach and M. Leiter, “Early Predictors of Job Burnout and Engagement,” Journal of Applied Psychology 93, no. 3 (June 2008): 489-512; and J.M. Hoobler, G. Lemmon, and S.J. Wayne, “Women’s Managerial Aspirations: An Organizational Development Perspective,” Journal of Management 40, no. 3 (March 2014): 703-730.
6. This EES data was collected in 2015 from over 4,000 respondents at this company.
7. For this analysis, we calculated predicted probabilities (57% for women and 67% for men, p<0.0001) from a logistic regression in which the dependent measure, agreement with “having opportunities,” is dichotomized into levels of agreement: “great/very great” and “very little/some/moderate.” A series of ordinary least squares regressions on a nondichotomized dependent measure yielded similar results.
8. L. Babcock, M.P. Recalde, L. Vesterlund, et al., “Gender Differences in Accepting and Receiving Requests for Tasks With Low Promotability,” American Economic Review 107, no. 3 (March 2017): 714-747.
9. It is worth noting that we could not conduct our case study analyses by employees’ race and ethnicity because this information was not collected on the company’s EES, so our analyses cannot speak to both gender and race assignment inequities. While legal and privacy considerations in different geographies may constrain what can be measured, companies should strive to examine such data by race and ethnicity, geography, and other social dimensions based on their diversity strategies.
Acknowledgments
More like this, add a comment cancel reply.
You must sign in to post a comment. First time here? Sign up for a free account : Comment on articles and get access to many more articles.
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
Make Sure Your Team’s Workload Is Divided Fairly
- Rebecca Knight
It’ll save your top performer from burnout.
An important part of your job as a manager is making sure everyone on your team has the right amount of work. It’s tempting to give the workhorse more projects than others (especially if she’ll get them done the fastest) or to ease up on someone who is struggling, but you also need to be fair. How do you make sure that work on your team is evenly distributed? What do you do about the person who’s great at saying no and the one who can’t say no?
- RK Rebecca Knight is a journalist who writes about all things related to the changing nature of careers and the workplace. Her essays and reported stories have been featured in The Boston Globe, Business Insider, The New York Times, BBC, and The Christian Science Monitor. She was shortlisted as a Reuters Institute Fellow at Oxford University in 2023. Earlier in her career, she spent a decade as an editor and reporter at the Financial Times in New York, London, and Boston.
Partner Center
Academic Assignment Writing Jobs Let Enjoy Freedom
Monetize your time and efforts
- WritingCreek is a freelance academic writing company which can offer you a trustworthy long-term cooperation.
- A simple application process, continuous career growth, a wide range of disciplines and subjects, are among the benefits of WritingCreek

Get decent freelance job
Simple application process.
Begin earning money in 3 days!

We believe you have all it takes
- Excellent communication skills
- Proficiency in the particular area of study
- Ability to conduct a research
- Original content writing
- Advanced level of English
Continuous career growth
Earn from $ 4 - 12 per page
- 1+ completed orders
- 5+ completed orders
- 80% + Success Rate
- 30+ completed orders
- 90% + Success Rate
- 50+ completed orders
- 95% + Success Rate

Reveal your skillset in academic writing
- Humanities 0 %
- Applied sciences 0 %
- Social sciences 0 %
- Formal sciences 0 %
- Natural sciences 0 %
- Other academic fields 0 %
Share of orders in the system for this branch of science

Some of the latest orders
Find the one that fits your expertise
You must have heard plenty of times about perks of specific jobs allowing to work without leaving your house on a permanent basis. They are true. Freelance occupation lets:
Determine your workload yourself. Due to this factor, you will not face the extreme fatigue when any amount of money for one more task doesn’t represent any interest because all you want to do is to fall asleep for a couple of days. With freelance writing jobs online, you are your own boss. You know how many regular duties you need to fulfill. You know how much time you need to devote to your significant other, your family, friends, hobby, sports, sleep, healthy lifestyle, etc. You are fully aware of how much time you need to spend on anything else but work to be happy. And only you can determine the golden middle!
Set the working hours. Striving to optimization of working process, you can set the hours when you feel like working most of all to focus on your tasks easier. When you have chosen one of the freelance writing jobs online , you are free to set the working hours. It is a very useful prerogative! You don’t have to ask if you can go home earlier today because you need to take your child from school or because you have a competition. You don’t need to provide explanations for being late for 15 minutes at the beginning of the day. You are the boss. Being one of the essay writers or those who accepted an offer of grant writing jobs, you become independent.
Choose tasks yourself. Having joined the team of freelance writers, you are given an opportunity to select your assignments: take the one you like and reject the one that seems not your cup of tea. You will no longer have to deal with a bundle of tasks you’d wish to burn. Freelance writing jobs give you a chance deal only with the tasks that are of interest to you. Thus, you will easily boost your knowledge and skills in professional sphere.
Such is a kind of position we gladly offer to experts in the wide variety of spheres:
- Human and social sciences. We invite for collaboration experts in Sociology, Psychology, Arts, Political science, Economics, Law, Management, Journalism, Pedagogics, Philosophy, Aesthetics, Linguistics, Law, and many other areas belonging to this group. On our website, you will find grant writing jobs to make use of your knowledge.
- Natural sciences. We are looking for freelance writers in Biology, Physics, Chemistry, Geology, Geography, Ecology, and Astronomy. If you have in-depth knowledge in Quantum or Cell biology, Space physics, or Nuclear chemistry (just as well as the rest of domains), and are looking for a position that gives you freedom in organizing your working hours – choose freelance writing jobs at biz.
- Technical studies. We are looking for specialists in Engineering, Informatics, Transport, Telecommunication, Architecture, Technology, Avionics, Food manufacturing industry, Computer science, Electronics, etc. We assume, we need writers specialized in any area of listed studies. Taking grant writing jobs at our website, you take your chance for independence. On our list, we include both the most common and the rarest spheres: from Radio electronics, Electrical engineering, and Modern architecture to Space syntax, Biological engineering, and Sumerian architecture.
- Exact studies. The connoisseurs of this group are always in high demand: due to the difficulties with assignments related to the subjects of this kind, every second student is looking for assistance with exact studies. Choose our freelance writing jobs! Make use of favorable terms of collaboration with a trustworthy website. Freelance experts in Algebra, Mathematical analysis, Geometry, Accounting, Trigonometry, Calculus, Discrete math, and Algorithms, welcome to biz.
Are you still hesitating? It’s high time to speed up your success with freelance writing.
You need to Log in or Sign up for a new account in order to create account
Please enter your email to proceed
By clicking "Continue", you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy. We`ll occasionally send you promo and account related emails.
- Branch and Bound Tutorial
- Backtracking Vs Branch-N-Bound
- 0/1 Knapsack
- 8 Puzzle Problem
- Job Assignment Problem
- N-Queen Problem
- Travelling Salesman Problem
- Branch and Bound Algorithm
- Introduction to Branch and Bound - Data Structures and Algorithms Tutorial
- 0/1 Knapsack using Branch and Bound
- Implementation of 0/1 Knapsack using Branch and Bound
- 8 puzzle Problem using Branch And Bound
Job Assignment Problem using Branch And Bound
- N Queen Problem using Branch And Bound
- Traveling Salesman Problem using Branch And Bound
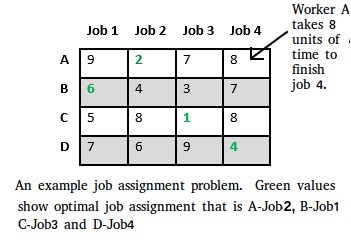
Let there be N workers and N jobs. Any worker can be assigned to perform any job, incurring some cost that may vary depending on the work-job assignment. It is required to perform all jobs by assigning exactly one worker to each job and exactly one job to each agent in such a way that the total cost of the assignment is minimized.
Let us explore all approaches for this problem.
Solution 1: Brute Force
We generate n! possible job assignments and for each such assignment, we compute its total cost and return the less expensive assignment. Since the solution is a permutation of the n jobs, its complexity is O(n!).
Solution 2: Hungarian Algorithm
The optimal assignment can be found using the Hungarian algorithm. The Hungarian algorithm has worst case run-time complexity of O(n^3).
Solution 3: DFS/BFS on state space tree
A state space tree is a N-ary tree with property that any path from root to leaf node holds one of many solutions to given problem. We can perform depth-first search on state space tree and but successive moves can take us away from the goal rather than bringing closer. The search of state space tree follows leftmost path from the root regardless of initial state. An answer node may never be found in this approach. We can also perform a Breadth-first search on state space tree. But no matter what the initial state is, the algorithm attempts the same sequence of moves like DFS.
Solution 4: Finding Optimal Solution using Branch and Bound
The selection rule for the next node in BFS and DFS is “blind”. i.e. the selection rule does not give any preference to a node that has a very good chance of getting the search to an answer node quickly. The search for an optimal solution can often be speeded by using an “intelligent” ranking function, also called an approximate cost function to avoid searching in sub-trees that do not contain an optimal solution. It is similar to BFS-like search but with one major optimization. Instead of following FIFO order, we choose a live node with least cost. We may not get optimal solution by following node with least promising cost, but it will provide very good chance of getting the search to an answer node quickly.
There are two approaches to calculate the cost function:
- For each worker, we choose job with minimum cost from list of unassigned jobs (take minimum entry from each row).
- For each job, we choose a worker with lowest cost for that job from list of unassigned workers (take minimum entry from each column).
In this article, the first approach is followed.
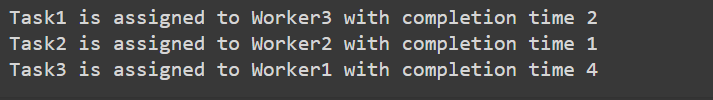
Let’s take below example and try to calculate promising cost when Job 2 is assigned to worker A.
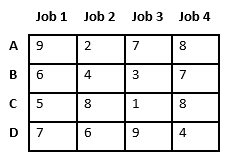
Since Job 2 is assigned to worker A (marked in green), cost becomes 2 and Job 2 and worker A becomes unavailable (marked in red).
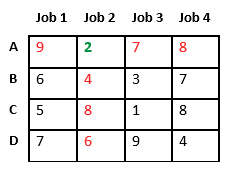
Now we assign job 3 to worker B as it has minimum cost from list of unassigned jobs. Cost becomes 2 + 3 = 5 and Job 3 and worker B also becomes unavailable.
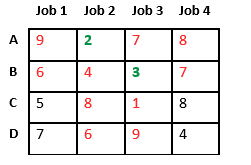
Finally, job 1 gets assigned to worker C as it has minimum cost among unassigned jobs and job 4 gets assigned to worker D as it is only Job left. Total cost becomes 2 + 3 + 5 + 4 = 14.
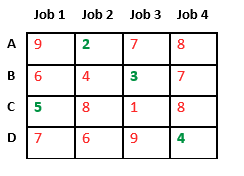
Below diagram shows complete search space diagram showing optimal solution path in green.
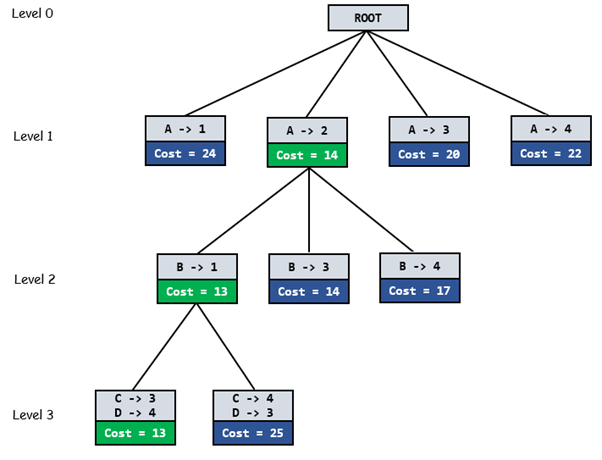
Complete Algorithm:
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
Time Complexity: O(M*N). This is because the algorithm uses a double for loop to iterate through the M x N matrix. Auxiliary Space: O(M+N). This is because it uses two arrays of size M and N to track the applicants and jobs.
Please Login to comment...
Similar reads.
- Branch and Bound
Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?
Optimizing Job Assignments with Python: A Greedy Approach

In this article, we will learn the skill of job assignment which is a very important topic in the field of Operations Research. For this, we will utilize Python programming language and the Numpy library for the same. We will also solve a small case on a job assignment.
Job assignment involves allocating tasks to workers while minimizing overall completion time or cost. Python’s greedy algorithm, combined with NumPy, can solve such problems by iteratively assigning jobs based on worker skills and constraints, enabling efficient resource management in various industries.
Recommended: Maximizing Cost Savings Through Offshore Development: A Comprehensive Guide
Recommended: Delivery Route Optimization using Python: A Step-by-Step Guide
What is a Job Assignment?
Let us understand what a job assignment is with an example. In our example, three tasks have to be completed. Three workers have different sets of skills and take different amounts of time to complete the above-mentioned tasks. Now our goal is to assign the jobs to the workers to minimize the period of completing the three tasks.
Now, we solve the above problem using the concepts of Linear programming. Now there are certain constraints as well, each worker can be assigned only a single job at a time. Our objective function is the sum of all the time taken by the workers and minimize it. Let us now solve this problem using the power of the Numpy library of Python programming language.
Let us now look at the output of the problem.
From the output, we can see that The assignment is complete and optimized. Let us now look at a small case and understand the job assignment further.
A Real-World Job Assignment Scenario
Continuing with the example of assigning workers some jobs, in this case, a company is looking to get some work done with the help of some freelancers. There are 15 jobs and we have 10 freelancers. We have to assign jobs to workers in such a way, that we minimize the time as well as the cost of the whole operation. Let us now model this in the Python programming language.
This problem is solved using the greedy algorithm. In short, the greedy algorithm selects the most optimal choice available and does not consider what will happen in the future while making this choice. In the above code, we have randomly generated data on freelancer details. Let us now look at the output of the code.
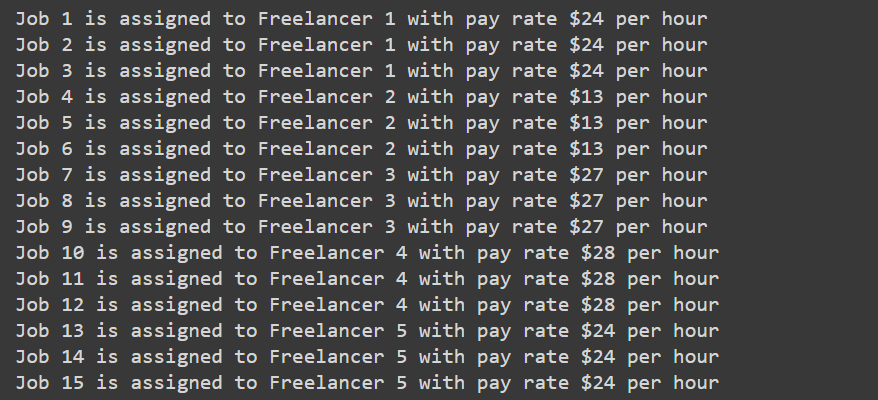
Thus, we complete our agenda of job assignment while minimizing costs as evidenced by the output.
Assigning jobs optimally is crucial for maximizing productivity and minimizing costs in today’s competitive landscape. Python’s powerful libraries like NumPy make it easy to implement greedy algorithms and solve complex job assignment problems, even with larger sets of jobs and workers. How could you adapt this approach to accommodate dynamic changes in job requirements or worker availability?
Recommended: Splitting Lists into Sub-Lists in Python: Techniques and Advantages
Recommended: Object Detection with OpenCV: A Step-by-Step Tutorial
Job Descriptions .
How to write a job description (with examples), how to write a job description.
Job descriptions are the cornerstone of the recruiting process. They help to attract top talent, set expectations for qualified candidates, inform prospects about the role and company, and streamline the search process. Plus, a well-written job description gives companies a chance to make a great first impression. So while writing accurate and compelling job descriptions can be frustrating, finding the time and resources to do so is well worth it.

Importance of Job Descriptions
No matter how many job descriptions you write, they never seem to get any easier, especially if you are writing them for roles you know little about. We’re here to help. For starters, let’s discuss the importance of job descriptions, and then we’ll tackle how to write them.
Job descriptions are helpful for both prospective candidates and employers. Here’s why:
Attract Prospective Candidates
A concise and compelling job description will play a major role in attracting qualified candidates. With resources like LinkedIn, Facebook, Twitter and email, the ability to post and share jobs is instantaneous and has exponential reachability.
Set Expectations
A clear job description will set everyone up for success. Prospects will understand what is expected of them, more-qualified candidates will apply, under-qualified applicants will move on and you will save loads of time sifting through applications and communicating with potential candidates.
Prepare for Interviews
A well-crafted job description can help both applicants and interviewers prep for the big day . Applicants will be able to prepare for likely topics of conversation and interview teams will be equipped to ask questions that will accurately gauge the candidate’s qualifications.
Make a Stellar First Impression
Job descriptions are often the first point of contact candidates will have with your company and can shape their first impression. Just like resumes and CVs, any jargon or grammatical errors will turn a candidate off and leave a lasting negative impression.
Simplify the Search
Searching for jobs is incredibly time-consuming, especially for the 73 percent of candidates who are passive and currently employed. Clear and concise job descriptions help prospects compare salaries, benefits, perks and even company culture to determine what roles are worth applying to.
Establish a Baseline
Once a candidate is hired, the job description will stand as a baseline to measure growth, reference during performance reviews and consider future training opportunities.
Recommended Reading 29 Recruitment Strategies With Real Examples
Great job descriptions are thorough yet concise. They use specific terms and keep a professional tone. It’s OK to be a little quirky, but don’t overdo it. If you don’t take the job description seriously, top candidates will move on to other opportunities.
Important Parts of a Job Description
- Company Bio/Mission
Role Summary
- Role Responsibilities
- Role Requirements (Must-Have Skills)
- Time/Location
- Next Steps (How to Apply)
Here’s an outline of the main sections every job description should include.
Make the job title clear, concise and industry-specific.
43 percent of job seekers look for career opportunities on job boards that use search engine optimization (SEO) techniques. Job seekers are also likely to search based on the terms they know, so don’t stray from the standard industry language of common job titles. Be sure to include specific terms, like the programs required for the role. The title Lead Front End AngularJS Engineer is much more descriptive than Developer and will attract more qualified candidates. If your job can’t be found, it can’t be applied to.
Company Mission
Include a company description or mission, but keep it to about two to four sentences.
72 percent of job seekers noted they would be more likely to apply to a job posting with a company description. At the same time, don’t get too lost in the details. Most companies have a lengthy mission statement with core values and a culture code. For candidates looking at multiple companies and open roles, the missions start to sound the same. If candidates decide to pursue the position, they can read about the company’s full profile on the website.
Consider writing a templated version that can be repurposed whenever you need to write a new job post. It’s also more common to include the company description or mission at the beginning of the post.
Write a brief three to five sentence summary about what the candidate will do in their role, who they’ll work with and any general qualities your team is looking for in the individual.
Job Responsibilities
90 percent of top-performing job descriptions include clear responsibilities and duties, according to Built In research. Responsibilities and duties are essential in order for a candidate to understand the role. They also set expectations for the hired employee and can be used as a baseline for performance reviews down the line.
Give five to 10 bullet points on what the candidate can expect to do in the role. Here are a few tips:
- Write in complete sentences.
- Be thorough. Candidates will be better prepared for the interview and role if they know what is expected of them.
- Don’t be excessive. You don’t need to include every single possible thing a person might encounter during the work day.
Must-Have Skills
Job descriptions include an average of eight distinct qualifications per job post (including must-have and nice-to-have skills), according to Built In research. List five to seven bullet points that are absolutely necessary for a candidate to be successful in the role they are applying to.
- Include quantities when applicable, like years of experience.
- Be sure to clarify what the application requires, like a portfolio, writing sample, video recording, resume, CV, cover letter, etc.
- Other important information includes education, experience, certifications and knowledge of specific platforms.
Nice-to-Have Skills
If there are any other qualities that are nice to have, include those here. Don’t feel like you have to include this section, but it may help candidates know what to include in the application or interview to stand out. This section is lower priority and should have fewer bullet points.
Compensation
61 percent consider compensation information to be the most important part of a job description. However, 99 percent of top-performing job descriptions don’t include compensation information, according to Built In research. Many companies still refuse to provide this information in job descriptions, but it’s time to get over this discomfort to garner a larger applicant pool.
It’s best to be upfront about the time frame you need employees to work. Flexible work hours are more common for full-time employees, time zones may play a role, and certain industries and markets work around different schedules.
Candidates will consider commute time or relocation efforts in their employment decision, so help them determine fit before they embark on the application process. Embedding a Google Map onto your website is really quite simple and can be done with this guide .
Working Conditions
Keep working conditions and workplace expectations clear. People want to know what to expect in their future work environment. Are there any physical requirements for the role? What is the expected dress code?
Call to Action
Make sure it is blatantly obvious where a candidate is supposed to apply. Do not make it complicated or frustrating to apply because that’s just going to reduce your applicant pool for the wrong reasons. This is one area that companies should customize to the location the job is being posted. Make sure they know where to click or who to email to get the process started.
Disclaimer Statements
Most companies include an equal opportunity employer statement and that the employee may be required to perform additional job functions beyond the description. Do your research because disclaimers can help companies prevent serious lawsuits .
Elements to Improve Job Descriptions
Some companies include additional details in their job descriptions to help differentiate them from other employers. There’s certainly a balance between writing a thorough job description and being excessive, and that’s up to your team to decide. Here are a few additional sections to consider including in your job description. While these items are optional, they may turn a good job description into a great one.
Non-financial benefits are often a deciding factor for prospective candidates — 61 percent of job seekers expect to see benefits packages in job descriptions, yet only 43 percent of top-performing job descriptions included such information, according to Built In research.
Things to include are your company’s:
- Health insurance and wellness plans
- Retirement and stock options offerings
- Childcare and parental leave options
- Vacation and PTO policies
Remember that perks are not the same thing as benefits. Perks are nice add-ons the company offers its employees to improve work-life balance and help them live happier, more productive lives.
Company Culture
Sure, it’s a buzzword, but the people have spoken and the best candidates expect a strong company culture . In fact, 47 percent say that company culture is the main reason they’re searching for new opportunities.
Word Count
It’s best to keep your job description in the 250 to 500 word count range, as supported by a study that found the majority of job postings had a similar word count trend. Top-performing job descriptions contain an average word count of 457 words, based on Built In findings.
Average word count also correlates with average time on page for job descriptions. Job descriptions with a word count between 251 to 500 words see an average time on page of one minute and 39 seconds (1:39), which is closest to the average job description reading time of one minute and 41 seconds (1:41). It’s clear that job descriptions which adhere to word count best practices are much more engaging than their lower-performing counterparts.
16 percent of job descriptions as analyzed by Built In contain obvious typos, which could be detrimental to applicant reach and a company trustworthiness. Similar to how many recruiters disregard applicants with typos on their resume or application, candidates may come away with a negative impression of your company for not doing its due diligence. Remember to always have at least one other person read your job description before posting.
Job Description Examples
Job descriptions aren’t one-size-fits-all. While the company bio and mission statement sections may remain the same for each role a company posts, the main sections — which include role responsibilities and requirements — should be uniquely tailored to the job at hand.
For instance, a job description for a highly specialized role will usually go into more detail about the types of tools and software programs qualified candidates are expected to possess, while a JD for an entry-level role may spend more time broadly discussing the mentality or passions a candidate should have. In any case, job descriptions that have enough detail specific to the role gives job-seekers a better sense of the position and it gives you an opportunity to make a positive first impression.
Below we’ve rounded up some in-depth guides and job description templates for several roles:
Creative Roles
- Art Director Job Description
- Technical Writer Job Description
- UX Designer Job Description
Data and Analytics Roles
- Business Intelligence Analyst Job Description
- Data Analyst Job Description
- Data Scientist Job Description
Developer Roles
- Front End Developer Job Description
- iOS Developer Job Description
- Java Developer Job Description
- PHP Developer Job Description
- Product Manager Job Description
- Salesforce Developer Job Description
Operations Roles
- Operations Manager Job Description
- DevOp Job Description
- Project Manager Job Description
Marketing Roles
- Marketing Manager Job Description
Sales Roles
- Account Executive Job Description
- Account Manager Job Description
- Customer Success Manager Job Description
- Sales Development Representative Job Description
- Sales Engineer Job Description
- Sales Operations Manager Job Description
How to Write a Job Description: Data-Driven Results
We gathered cold, hard facts from a sample of the top performing job descriptions across our seven markets. Here’s what we found out.

FREE DOWNLOAD: JOB DESCRIPTION TEMPLATES
7 interview questions that will reveal a company’s culture.

These Careers Are at the Forefront of the Deep Tech Revolution

Skills-Based Hiring: What It Is and Why It Works

How to Write a Marketing Manager Job Description: Important Skills and Role Responsibilities

How to Write a UX Designer Job Description: Important Skills and Role Responsibilities
How to write an art director job description: important skills and role responsibilities.
Art Directors integrate design with strategy. Get examples, a template & salary information for an Art Director job description.

How to Write a Customer Success Manager Job Description: Important Skills and Role Responsibilities

How to Write a Data Analyst Job Description: Important Skills and Role Responsibilities

How to Write an Account Manager Job Description: Important Skills and Role Responsibilities

How to Write a Project Manager Job Description: Important Skills and Role Responsibilities
How to write job requirements.
Learn how to write job requirements and understand the recruiting potential of doing it well.

How Tech Can Get More Women Into Software Engineering
Great companies need great people. that's where we come in..

The Path to Reassignment as an Accommodation
From the desk of tracie defreitas, m.s., program leader, director of training and outreach.
Engaging in the interactive process under the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) requires navigating a range of reasonable accommodation pathways. Some trails lead to familiar places, like making the workplace accessible, job restructuring, or modifying a schedule. Some paths are bumpy, flanked by twists and turns, and require time and patience to reach the destination, like purchasing equipment, modifying workplace policies, or providing access to leave. Sometimes the process requires navigating an entirely different path than was initially mapped-out, like changing lanes and taking the ramp that leads to reassigning an employee to a vacant position. This accommodation pathway is reasonably well-marked under the ADA, but can still lead those responsible for considering the accommodation to second-guess whether it’s the best route – kind of like when you’re relying on your GPS to get you home, but it generates a different route every time and you’re not sure if you can trust it.
The reassignment path can be trusted when exploring job accommodations under the ADA, provided certain rules are followed. The duty to consider reassignment as a form of reasonable accommodation is clearly articulated in the ADA regulations and enforcement guidance. The title I regulations of the ADA specifically include reassignment as an accommodation, and the Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC) formal enforcement guidance on Reasonable Accommodation and Undue Hardship Under the ADA notes that this form of accommodation must be considered and provided, when reasonable. Interestingly, even the courts mostly agree with the EEOC position on this accommodation issue. Then why do employers still stumble when they reach the reassignment path as part of the accommodation process?
Likely for a number of reasons, but for one, it probably doesn’t seem logical to give an employee a different job when they can’t perform the essential functions of their current job. But, it’s important to remember that the ADA is meant to facilitate positive employment outcomes for individuals with disabilities. This means that, when a disability prevents an employee from performing the essential job duties of their original position, the possibility of maintaining employment by being placed in a vacant position the employer seeks to fill can lead to a successful employment outcome for all parties. When the interactive process reveals that reassignment is a possible accommodation solution, employers are expected to make that last ditch effort to keep the employee on the path of continued employment.
Reassignment is commonly known as the accommodation of last resort. This is because accommodations that will enable an employee to remain in their current position should, under ordinary circumstances, be considered first. However, this accommodation strategy should not be misinterpreted to mean that it’s only possible to consider reassignment when the search for accommodations in the original position is exhausted. Reassignment can be considered when:
- there is no reasonable accommodation that will enable an employee with a disability to perform the essential functions of their current position;
- both the employee and employer agree that an alternative position is a more preferable accommodation solution, in light of the employee’s limitations and ability to perform essential functions, with or without accommodation;
- an employee is on a leave of absence and their position cannot be held open during the entire leave period without posing an undue hardship, and if there is a vacant position to which the employee can be reassigned to continue the leave; or
- the location where work is performed causes a work-related barrier due to limitations affecting an employee’s commute, or the need to access specialized healthcare, and there is a vacant position at a different location that meets the employee’s disability-related needs.
What makes reassignment an accommodation under the ADA? The opportunity to be transferred to a new job with the same employer without having to go through the competitive hiring process. An individual with a disability who will be accommodated through reassignment shall not be required to compete for the alternative position. But, while a competitive bid for the vacancy is not required, the individual must be minimally qualified, though not necessarily the best qualified, for any vacant position under consideration, and must be capable of performing the essential functions of the job, with or without accommodation.
The path to reassignment can be bumpy when it’s not clear whose responsibility it is to identify vacant positions, and for what duration the parties will search. This is where it can be useful to have a procedure for processing this type of accommodation request. A procedure can assign organizational responsibility for the job search, and also make clear that the individual is invited to assist in identifying vacancies. The EEOC offers tips for drafting and implementing accommodation procedures, including reassignment procedures, in their guidance on Practical Advice for Drafting and Implementing Reasonable Accommodation Procedures Under Executive Order 13164 . The information in this guidance informs the reasonable accommodation practices of federal government employers, but is a useful resource for other types of employers that must engage in the interactive accommodation process under the ADA.
Employers sometimes ask if an individual who will be reassigned as an accommodation can be expected to formally apply for vacant positions, or to interview for jobs that are selected. The answer to this question probably depends on why the employer wants to require this of someone who is not expected to compete for the job. For example, if the objective of asking the individual interview questions, or to complete an application, is simply to gather information to assess their qualifications and interest in the job, this may be possible. But, if the individual is minimally qualified for the position, they get the job regardless of the interview outcome. An interview may be useful when more than one vacancy has been identified and both the individual and the employer believe the process will present an opportunity to learn more information to determine which position is the best fit.
Upon making the decision to explore reassignment as the accommodation of choice, employers should be mindful of several points. First, reassignment will only be available as an accommodation if a vacant position is available, or will be in the reasonably near future. There is no duty to create a vacancy. The search for vacant positions should include those that are equivalent to the employee’s original position, in terms of pay and status, and does not have to be limited to positions within the employee’s original department or location. When an equivalent vacant position is not available, an individual may be reassigned to a vacant lower level position. In this situation, there is no duty to carry-over the employee’s original rate of pay, unless this is done for others in a similar situation.
Generally, employers are in the best position to know about potential vacancies, but the interactive process is collaborative and so both parties can take part in the job search. The duration of the job search may depend on the size of the employer, but should begin without delay and should be completed in a reasonable period of time. For example, smaller employers may have fewer available positions, and in-turn, may require a shorter duration of time to complete a thorough search. The duration could be days or weeks. Some employers have a policy of searching for a certain number of days (e.g., 30 to 60 days). According to the EEOC, upon the end of a reasonable search period, if no appropriate vacancies have been identified, the employer will have fulfilled its obligation to consider reassignment as an accommodation.
The idea of reassignment as an accommodation raises a number of questions for employers. A lot of ground was covered on this topic in this brief article, but there can be many twists and turns while navigating this path during the interactive process. You may have more questions about reassignment now. The REASSIGNMENT section of the EEOC formal enforcement guidance on Reasonable Accommodation and Undue Hardship Under the ADA is a good place to start for more information. If you still have questions, Ask JAN , we can help!
> Back to Newsletter

Add Page to MyJAN

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Job interview assignments vary for each type of job. Here are a few examples of job interview assignments: Example 1 ... Stratus Software Solutions is hiring a software engineer for their cloud-based platform. The hiring manager provides candidates with a coding issue, limited instructions and access to the company's training source code ...
Work assignments are most common in creative and technical fields of work. For example, writers may need to complete a trial piece before being hired, and marketing professionals may have to create a campaign pitch and outline as part of their interview process. For more technical work, like information technology or computer science, the ...
3. Outline Main Points, Only Tease the Details. More often than not, the primary reason companies dole out homework is to get a better sense of your thought process, as well as how you structure and convey your thoughts and ideas. There's not necessarily a "right" answer, nor is there a need to get way down in the weeds.
Choose a career based on your career interests. Want a simple recipe for job satisfaction and success? Choose work that includes mostly what you like to do, and not too much of what you dislike. ... 1-877-US2-JOBS (1-877-872-5627) or TTY 1-877-889-5627 For help using the CareerOneStop website: [email protected]. CareerOneStop is sponsored ...
The job analysis gave us the ability to ensure the assessment would measure relevant characteristics based on the job. A pre-employment assessment cannot predict success without a job analysis," Brandstetter explains. "By completing a job analysis with our pre-employment assessment vendor, we were able to build an assessment that would help ...
Make a meeting with the team leads and go through the points above. Assign tasks according to each team's availability, interest, and skill required to successfully push the project forward. As team leads - assign tasks further down the pipeline. Track task completion and make necessary changes along the way.
Job analysis is the process of gathering, examining and interpreting data about a job's tasks and responsibilities. It generally includes tracking an employee's duties and the duration of each ...
Scholars have long identified a gender gap in access to the kinds of assignments — large in scope, highly visible, and strategically important — that are seen as essential to career advancement. An estimated 70% of leadership development occurs through experiential learning, especially the kind offered by these challenging stretch assignments.
An important part of your job as a manager is making sure everyone on your team has the right amount of work. It's tempting to give the workhorse more projects than others (especially if she ...
Review Employee Job Responsibilities. The first step is to review the roles and responsibilities for the specific position. Interview employees, supervisors and HR personnel to get an idea of ...
Literature Creative Writing "The Veldt" by Ray Bradbury Using the module literature on the 'division of labour', analyse and assess the relationship between the demise, or growth, of individual knowledge and the overall expansion of knowledge within society and its implication for social hierarchy. 4 Pages. $16-46 Rate.
Solution 1: Brute Force. We generate n! possible job assignments and for each such assignment, we compute its total cost and return the less expensive assignment. Since the solution is a permutation of the n jobs, its complexity is O (n!). Solution 2: Hungarian Algorithm. The optimal assignment can be found using the Hungarian algorithm.
For this, we will utilize Python programming language and the Numpy library for the same. We will also solve a small case on a job assignment. Job assignment involves allocating tasks to workers while minimizing overall completion time or cost. Python's greedy algorithm, combined with NumPy, can solve such problems by iteratively assigning ...
Word Count. It's best to keep your job description in the 250 to 500 word count range, as supported by a study that found the majority of job postings had a similar word count trend. Top-performing job descriptions contain an average word count of 457 words, based on Built In findings.
Open the desired task, click "Assignee", and choose the right team member (s). Keyboard shortcuts: Hover over the task and press "A" to open the Assignee picker. Press the space bar to assign yourself. This way makes assigning tasks easier and quicker!
It is illegal for an employer to make decisions about job assignments and promotions based on an employee's race, color, religion, sex (including gender identity, sexual orientation, and pregnancy), national origin, age (40 or older), disability or genetic information. For example, an employer may not give preference to employees of a certain ...
1000+ job description templates. Better job descriptions attract better candidates. Optimized for job board approval and SEO, our 1000+ job description templates boost exposure, provide inspiration and speed up hiring. Rich in the right kind of content, they also lead to more qualified applicants.
When the interactive process reveals that reassignment is a possible accommodation solution, employers are expected to make that last ditch effort to keep the employee on the path of continued employment. Reassignment is commonly known as the accommodation of last resort. This is because accommodations that will enable an employee to remain in ...
say having a sense of purpose is very or somewhat important to their overall job satisfaction and well-being. 44%. ... have rejected an assignment or project based on their personal beliefs. Download the 2024 Gen Z and Millennial Report. Climate action. Environmental sustainability is everyone's responsibility ...