- Translators
- Graphic Designers
Please enter the email address you used for your account. Your sign in information will be sent to your email address after it has been verified.

17 Thesis Defense Questions and How to Answer Them

A thesis defense gives you the chance to show off your thesis work and demonstrate your expertise in your field of study. During this one- to two-hour discussion with the members of your thesis committee, you'll have some control over how you present your research, but your committee will ask you some prodding questions to test your knowledge and preparedness. They will all have read your thesis beforehand, so their questions will relate to your study, topic, methods, data sample, and other aspects.
A good defense requires mastery of the thesis itself, so before you consider the questions you might face,
1. What is your topic, and why did you choose it?
Give a quick summary in just a few sentences on what you've researched. You could certainly go on for hours about your work, but make sure you prepare a way to give a very brief overview of your thesis. Then, give a quick background on your process for choosing this topic.
2. How does your topic contribute to the existing literature? How is it important?
Many researchers identify a need in the field and choose a topic to bridge the gaps that previous literature has failed to cover. For example, previous studies might not have included a certain population, region, or circumstance. Talk about how your thesis enhances the general understanding of the topic to extend the reach beyond what others have found, and then give examples of why the world needs that increased understanding. For instance, a thesis on romaine lettuce crops in desert climates might bring much-needed knowledge to a region that might not have been represented in previous work.
3. What are the key findings of your study?
When reporting your main results, make sure you have a handle on how detailed your committee wants you to be. Give yourself several options by preparing 1) a very general, quick summary of your findings that takes a minute or less, 2) a more detailed rundown of what your study revealed that is 3-5 minutes long, and 3) a 10- to 15-minute synopsis that delves into your results in detail. With each of these responses prepared, you can gauge which one is most appropriate in the moment, based on what your committee asks you and what has already been requested.
4. What type of background research did you do for your study?
Here you'll describe what you did while you were deciding what to study. This usually includes a literary review to determine what previous researchers have already introduced to the field. You also likely had to look into whether your study was going to be possible and what you would need in order to collect the needed data. Did you need info from databases that require permissions or fees?
5. What was your hypothesis, and how did you form it?
Describe the expected results you had for your study and whether your hypothesis came from previous research experience, long-held expectations, or cultural myths.
6. What limitations did you face when writing your text?
It's inevitable — researchers will face roadblocks or limiting factors during their work. This could be a limited population you had access to, like if you had a great method of surveying university students, but you didn't have a way to reach out to other people who weren't attending that school.
7. Why did you choose your particular method for your study?
Different research methods are more fitting to specific studies than others (e.g., qualitative vs. quantitative ), and knowing this, you applied a method that would present your findings most effectively. What factors led you to choose your method?
8. Who formed the sample group of your study, and why did you choose this population?
Many factors go into the selection of a participant group. Perhaps you were motivated to survey women over 50 who experience burnout in the workplace. Did you take extra measures to target this population? Or perhaps you found a sample group that responded more readily to your request for participation, and after hitting dead ends for months, convenience is what shaped your study population. Make sure to present your reasoning in an honest but favorable way.
9. What obstacles or limitations did you encounter while working with your sample?
Outline the process of pursuing respondents for your study and the difficulties you faced in collecting enough quality data for your thesis. Perhaps the decisions you made took shape based on the participants you ended up interviewing.
10. Was there something specific you were expecting to find during your analysis?
Expectations are natural when you set out to explore a topic, especially one you've been dancing around throughout your academic career. This question can refer to your hypotheses , but it can also touch on your personal feelings and expectations about this topic. What did you believe you would find when you dove deeper into the subject? Was that what you actually found, or were you surprised by your results?
11. What did you learn from your study?
Your response to this question can include not only the basic findings of your work (if you haven't covered this already) but also some personal surprises you might have found that veered away from your expectations. Sometimes these details are not included in the thesis, so these details can add some spice to your defense.
12. What are the recommendations from your study?
With connection to the reasons you chose the topic, your results can address the problems your work is solving. Give specifics on how policymakers, professionals in the field, etc., can improve their service with the knowledge your thesis provides.
13. If given the chance, what would you do differently?
Your response to this one can include the limitations you encountered or dead ends you hit that wasted time and funding. Try not to dwell too long on the annoyances of your study, and consider an area of curiosity; for example, discuss an area that piqued your interest during your exploration that would have been exciting to pursue but didn't directly benefit your outlined study.
14. How did you relate your study to the existing theories in the literature?
Your paper likely ties your ideas into those of other researchers, so this could be an easy one to answer. Point out how similar your work is to some and how it contrasts other works of research; both contribute greatly to the overall body of research.
15. What is the future scope of this study?
This one is pretty easy, since most theses include recommendations for future research within the text. That means you already have this one covered, and since you read over your thesis before your defense, it's already fresh in your mind.
16. What do you plan to do professionally after you complete your study?
This is a question directed more to you and your future professional plans. This might align with the research you performed, and if so, you can direct your question back to your research, maybe mentioning the personal motivations you have for pursuing study of that subject.
17. Do you have any questions?
Although your thesis defense feels like an interrogation, and you're the one in the spotlight, it provides an ideal opportunity to gather input from your committee, if you want it. Possible questions you could ask are: What were your impressions when reading my thesis? Do you believe I missed any important steps or details when conducting my work? Where do you see this work going in the future?
Bonus tip: What if you get asked a question to which you don't know the answer? You can spend weeks preparing to defend your thesis, but you might still be caught off guard when you don't know exactly what's coming. You can be ready for this situation by preparing a general strategy. It's okay to admit that your thesis doesn't offer the answers to everything – your committee won't reasonably expect it to do so. What you can do to sound (and feel!) confident and knowledgeable is to refer to a work of literature you have encountered in your research and draw on that work to give an answer. For example, you could respond, "My thesis doesn't directly address your question, but my study of Dr. Leifsen's work provided some interesting insights on that subject…." By preparing a way to address curveball questions, you can maintain your cool and create the impression that you truly are an expert in your field.
After you're done answering the questions your committee presents to you, they will either approve your thesis or suggest changes you should make to your paper. Regardless of the outcome, your confidence in addressing the questions presented to you will communicate to your thesis committee members that you know your stuff. Preparation can ease a lot of anxiety surrounding this event, so use these possible questions to make sure you can present your thesis feeling relaxed, prepared, and confident.
Header image by Kasto .
Related Posts

How to Write the Perfect Process Analysis Essay (With a Sample Essay)

APA Heading Format: All 5 Levels Explained Plus Examples
- Academic Writing Advice
- All Blog Posts
- Writing Advice
- Admissions Writing Advice
- Book Writing Advice
- Short Story Advice
- Employment Writing Advice
- Business Writing Advice
- Web Content Advice
- Article Writing Advice
- Magazine Writing Advice
- Grammar Advice
- Dialect Advice
- Editing Advice
- Freelance Advice
- Legal Writing Advice
- Poetry Advice
- Graphic Design Advice
- Logo Design Advice
- Translation Advice
- Blog Reviews
- Short Story Award Winners
- Scholarship Winners

Take your thesis to new heights with our expert editing
Want to Get your Dissertation Accepted?
Discover how we've helped doctoral students complete their dissertations and advance their academic careers!
Join 200+ Graduated Students

Get Your Dissertation Accepted On Your Next Submission
Get customized coaching for:.
- Crafting your proposal,
- Collecting and analyzing your data, or
- Preparing your defense.
Trapped in dissertation revisions?
Dissertation proposal defense: 12 tips for effective preparation, published by steve tippins on may 11, 2020 may 11, 2020.
Last Updated on: 2nd February 2024, 02:59 am
The dissertation proposal defense is a nerve-wracking time for even the most hardened of doctoral students.
Even a pirate (writing his dissertation on effective cutlass techniques), will quake a bit in his boots before delivering his dissertation proposal defense.
However, it doesn’t need to be a stressful time.
As a longtime Dissertation Committee Chair and committee member, I’ve overseen more dissertation proposal defenses than I can count. I’ve also helped students through the process as a coach .
If you follow these tips for preparing and delivering your presentation, you shouldn’t have any problem passing your proposal defense.
Dissertation Proposal Defense Tips

Preparing for your Dissertation Proposal Defense
1. anticipate questions. .
In your presentation, try to answer all of the questions you expect your committee to ask. That way, you control the material. Your committee will be more satisfied with your preparation and understanding and it will be less likely that you have to answer questions that you aren’t prepared for.
2. Look for Weaknesses.
If there are potential weaknesses (in your study, proposal, or presentation), address them ahead of time. Ask peers or mentors to review your proposal or presentation for weaknesses. Look at it yourself with a critical eye. Even if you’re not able to eliminate a weakness, take steps to address it as best you can so that your committee can be confident that you’re aware of it and able to handle it.

3. Practice.
Ideally, you would practice with someone who has been a committee member before. They’ll point out the types of questions they would see your committee asking, so you can prepare for those. I can’t understate the value of having this kind of feedback beforehand so that you can properly prepare. I offer this service as part of my dissertation coaching package .
4. Avoid Wordiness on PowerPoint Slides .
Most dissertation proposal defenses have PowerPoints. Don’t put too many words on the slides! People will start reading the slides instead of paying attention to you. Then they’re off somewhere else which will produce questions that you’ve already answered when they weren’t paying attention.
5. Be Able to Pronounce the Words Correctly.
This might sound obvious, but as a dissertation committee member , I’ve heard far too many students struggle through pronunciations of important terminology. This is probably because, up until this point, they’ve only read them and not spoken them out loud.
However, it gives the committee the impression that they don’t know what they’re talking about. Make sure you can properly pronounce all the words you plan on using (like “phenomenological” and “anthropomorphism,”).
6. Watch Recordings of Previous Defenses.

Some schools have recordings of previous defenses. Listen to one or two. See how the procedure goes. Even if it’s not anything in your discipline, it will still help you get familiar with the procedure itself, which will help you be more comfortable when the time comes.
During your Dissertation Proposal Defense:
7. breathe . .
I’ve seen way too many people try to do their dissertation proposal defense seemingly in one breath. Give your committee time to hear and understand what you’re saying. Remember to leave some moments of silence to allow your audience to digest what you say. Also remember that one second of actual time feels like about thirty minutes to someone who’s giving an important presentation. Breathe.

8. Remember: They Want to Pass You.
If you’ve gotten to the point where your committee has scheduled a dissertation proposal defense for you, that means they believe that you can pass it. They want to pass you. Remember that.
They’re not out to screw you, they’re not out for “gotchas.” They’re saying, “we believe you’re ready, show us that’s true.” While they will be rigorous in their evaluation because they have a responsibility to make sure that they don’t allow you to move forward until you are ready to, it’s helpful to remember that they believe you can pass.
9. Answer the Question, No More.
When committee members ask questions, answer only the question–don’t give them anything more than that. Imagine that you’re a witness in a courtroom (or don’t if that makes you more nervous). Committee members value direct, relevant answers and often find tangents irrelevant and frustrating.
10. Dialogue With Your Committee.
If the committee disagrees with something you said, it can be a discussion. You don’t need to just roll over and say “Yes, you’re right. I made a mistake and I’m very bad.” That’s not what your committee wants to hear, either.

A much better response would be, “I hear what you’re saying, however, this is the reason I’m going in this other direction. What do you think about that?” So you’re beginning to engage in discussions as a scholar. Your committee will be impressed by your ability to think critically and your willingness to engage in dialogue.
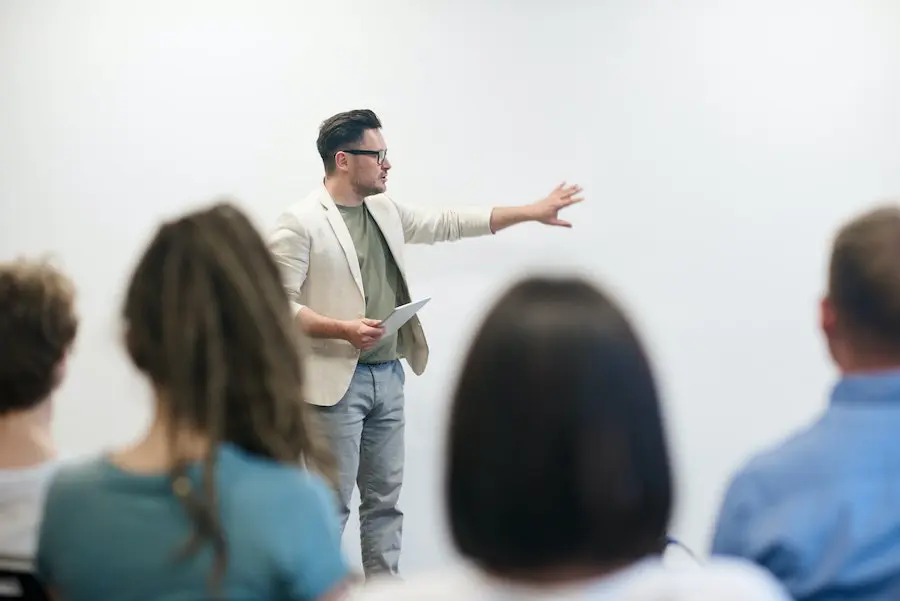

However, do not make it adversarial. It’s incredibly important to be respectful in these conversations. After all, your committee members have significant control over your life for as long as you’re writing your dissertation.
11. Make Life Easy for Your Committee.
It’s always good to send your committee members a copy of your PowerPoint presentation and the most recent copy of your proposal the day before the defense. They likely already have a copy, but when in doubt, make their lives easier. It doesn’t cost you anything. Someone might accidentally have an old copy, or might take them some time to find the copy they have. You want their life to be as easy as possible so they can focus on moving you forward.
12. Pay Attention to Time.
Ask your Chair (in the preparation stage) how long you have to make your presentation. It’s extraordinarily important to stay within this timeframe. If you’re told 25 minutes but you take 50 minutes, committee members are predisposed to say “why isn’t this person better prepared, and why are they wasting my time?”
Likewise, if you run through a 30-minute presentation in ten minutes (nervousness can sometimes lead to very fast talking–that’s why it’s important to practice beforehand), your committee will be wondering why you didn’t use the whole time that was allotted to you. And you’ll likely have to field a lot of questions you weren’t prepared for.
Dissertation Proposal Defense Summary
As long as you prepare properly, your dissertation proposal defense should be nothing to worry about. Your committee thinks you’re ready: all you have to do is show them you’re right.
If you’d like help preparing for your defense, or if you’d like to reduce the amount of time it takes to finish your dissertation, take a look at my Dissertation Coaching Services .
Steve Tippins
Steve Tippins, PhD, has thrived in academia for over thirty years. He continues to love teaching in addition to coaching recent PhD graduates as well as students writing their dissertations. Learn more about his dissertation coaching and career coaching services. Book a Free Consultation with Steve Tippins
Related Posts

Dissertation
What makes a good research question.
Creating a good research question is vital to successfully completing your dissertation. Here are some tips that will help you formulate a good research question. What Makes a Good Research Question? These are the three Read more…

Dissertation Structure
When it comes to writing a dissertation, one of the most fraught questions asked by graduate students is about dissertation structure. A dissertation is the lengthiest writing project that many graduate students ever undertake, and Read more…

Choosing a Dissertation Chair
Choosing your dissertation chair is one of the most important decisions that you’ll make in graduate school. Your dissertation chair will in many ways shape your experience as you undergo the most rigorous intellectual challenge Read more…
Make This Your Last Round of Dissertation Revision.
Learn How to Get Your Dissertation Accepted .
Discover the 5-Step Process in this Free Webinar .
Almost there!
Please verify your email address by clicking the link in the email message we just sent to your address.
If you don't see the message within the next five minutes, be sure to check your spam folder :).
- Graduate School
40 Thesis Defense Questions

Practicing answering thesis defense questions in a mock thesis defense is the best way to get ready for this challenging step in your academic career. Aside from knowing your research project inside and out, you must have solid strategies for tackling different question types and talking about why you chose your research topic. You might have already answered questions related to your research interests in your research interest statement and grad school interview questions , but now after years for in-depth study, it's time to really test what you have accomplished! Check out some of the hardest thesis defense questions below and read our expert responses!
>> Want us to help you get accepted? Schedule a free strategy call here . <<
Article Contents 11 min read
What to expect in a thesis defense.
A thesis defense is your chance to demonstrate your in-depth knowledge and expertise in the topic of your research thesis. While you will be able to take charge of the narrative and present your research to those on your thesis committee, the professors will prod you to test how well you know and understand your topic. The questions are mostly open-ended and give you the chance to showcase your knowledge and understanding, as well as any future plans you may have regarding your research topic.
A thesis defense usually lasts between one and two hours, depending on the area of your research. It starts with you giving a presentation of your interest, findings, and conclusions. After you have finished, the committee members will ask you questions based not only on your presentation, but also on your written thesis as they will have read it before your presentation. Lastly, the committee might approve your thesis or suggest changes to your paper.
Preparing thesis defense questions requires you to start well in advance. While the duration of your thesis defense might vary as per your institution's requirements, the major idea is to defend your research. Thus, you should go about preparing for your thesis defense questions by taking the following steps.
Interested in a quick overview of the section below? Check out this infographic:
Re-read your thesis for clarity
Your thesis defense questions will be based on what you have written in your research paper. Hence, it is a good idea to re-read your paper. You should be clear on the concepts and understand your research well. It might have been some time since you would have submitted your paper, so a revision should be the starting point of your preparation.
Have an answer strategy and structure
Plan a strategy to answer the panel’s questions. Keep your answers direct, but elaborate on the research details wherever necessary. If you do not know the answer to a question, that is alright. The key is to be able to formulate an answer even if you do not possess enough knowledge to answer at that point in time. For instance, if a question is about the content of your research, you can say something like “I am not certain my research touches on the question you are asking, but my research has led me to Dr. X. Based his evidence, I would have to conclude that…” Having a strategy for answering even the most unexpected questions can be a life saver in these situations!
Most of the thesis defense questions can be easily predicted based on your research. You can prepare a list of possible questions when you are going through your paper. Getting to know the committee can help you in preparing better. Their areas of expertise can help you in determining what they might ask. Once you have a list of questions, you can start brainstorming how you might answer them.
Prepare your slides in advance
If you require visual aids such as slides, it is a good idea to prepare them beforehand. You can double-check the slides and make sure that your presentation will run smoothly on the day of your thesis defense. Make sure your slides are arranged in the correct order.
Attend a thesis defense of other candidates if it is an open event
If your institution allows it, you can visit a thesis defense of other candidates. This will give you an excellent idea of what you can expect in your meeting. If it is not possible to attend the event, you can speak to your peers to find out how their meeting went and what questions were asked.
Dress appropriately for your meeting
The thesis defense meeting is a formal event, and hence you should be dressed in formal clothes. While there are no strict dressing rules, you should consider it something equivalent to a job interview. Don’t just wear your T-shirt and appear in front of the committee. Your formal suit is a better option for the occasion.
Practice speaking for your meeting
Take your preparation to the next level by practicing your presentation. This activity will give you the confidence for the actual meeting and presentation. You can request your academic peers to help you out in the practice task. Based on their feedback in the mock session, you can improve for the actual session. Make sure to prepare well for the mock session as if you are preparing for the actual session. You can also practice your speech and body language in the mock session. If you used thesis writing services , these professionals would also be the ideal people to test you in a mock thesis defense – don’t hesitate to reach out to them again!
Sample Thesis Defense Questions and Answers
1. what is your research study all about.
In your answer, you should summarize your research in a few sentences. The question is simple but requires technical expertise for a better explanation of concepts. For instance, if you completed a thesis in an attempt to explain the constituents of dark matter in the universe and particle accelerators, you could frame your answer like this:
In this research, the different aspects of dark matter and its detection models have been investigated. The cosmic ray positron excess observed by the PAMELA detector has been discussed and explained through the construction of models of decaying dark matter. The cosmic-ray electron and positron spectra were studied assuming a general Dirac structure for the four fermion contact interactions of interest. A supersymmetric leptophilic Higgs model was constructed to explain the possible excess of gamma rays in the galactic center. Finally, by the use of Razor analysis, an improvement on the dark matter collider searches is considered.
2. Why did you choose this study?
This question requires you to answer what motivated you to pursue the study in the first place. Your answers could touch on your interests in the area of the study. For example, if you conducted a study called “Media Combat: The Great War and the Transformation of American Culture” then you can shape your answer like this:
The First World War (1914-1918) has always been a topic of fascination for me, and my prime interest lies in exploring the state of society at that time. I wanted to analyze the formation of a nationalized, wartime cultural apparatus during the United States' involvement in the war and how theatre and music transformed the relationship between the government and American citizens.
3. Why did you choose this particular title for your research?
The title of your thesis captures the main point of your research, which is why it is so important to use an appropriate title. Your committee will want to know how you came to the final decision of naming your work. For example,
I chose the title “Dark matter in the heavens and at colliders: Models and constraints” for my research thesis because my research attempts to explain the constituency of dark matter as it occurs in the universe. “The heavens” is another word for the universe. Dark matter can also be created in particle accelerators such as the CERN collider. I have attempted to provide an explanation for both of the cases through the use of models, along with describing the constraints which exist in the current times due to certain scientific limitations.
4. What is the scope of your study?
In your answer, you have to define the boundaries of your project and define exactly what you are studying. There can be several elements involved but you have to define the parameters that you have chosen to study. For example,
My study is on the efficacy of equity stocks in the US market. For my study, I have chosen 50 companies listed on the NASDAQ. You can review the names of these companies on page 5 of my thesis.
5. What phenomenon were you trying to understand with this research?
Describe the focus concept of your thesis in the answer. For example,
In our study “Motivation to volunteer”, we were looking to study the Theory of Planned Behavior by analyzing the behavioral and normative beliefs that influence attitudes and subjective norms.
Want increase your productivity and mainain a healthy work life balance to help get you through your thesis project? Here are some tips straight from our CEO:
6. Who will be most interested in your research?
You can talk about who may be affected by your research and the parties who can potentially benefit from the research. Take a look at this example:
My sociology thesis on “Impact of social media on youngsters” can be of interest to sociology academics, social media companies, education experts, and parents of youngsters in general.
7. Did your research questions evolve during the process? If so, how?
Often, qualitative research questions change over time with respect to the responses that you might get from your focus group. Or you might just change your question as you do lab research or general text research. You can describe the change to the evaluating committee. For example,
We started our study to understand the impact of the new public policy change on recycling of vinyl waste through installation of garbage bins specifically for vinyl products. However, after interviewing some of the respondents in the target community, we found that the rule is actually irrelevant to their behavior and thoughts because the percentage of vinyl waste in that specific locality was very low and it didn’t need the installation of dedicated bins for the purpose. Going by their frustrations with the current economic insecurity, our study evolved into the impact of costs incurred by public policy changes.
8. What gaps did you intend to bridge with your research?
Your research thesis must eliminate the present gaps in the concepts related to your subject topic.
The relationship between hard water and its effect on the size of the kidney stone is not clear yet, so we analyzed the mineral composition of hard water to determine its impact on the size of the kidney stone.
9. Why is your research significant?
The answer to this research question should outline the impact of your research on your field of study. You may talk about the new insights contributed by your research and its impact on society.
Through my study on “The effect of chamomile in reducing stress and promoting better sleep,” patients with insomnia and anxiety will be able to find alternative treatments without the use of medicinal drugs. The medical abilities of chamomile will promote the usage of ingredients in nature and will encourage the community to plant more herbs and trees.
10. What did you find in your research?
You may describe your research in a few sentences in this answer. For instance,
In our study on “Impact of artificial fluoride in water on the human body,” we found that excessive exposure to high quantities of Fluoride can result in tooth discoloration and bone issues in humans since it has neurotoxic qualities.
11. What research findings surprised you?
When you conduct research, you come across findings that you were not expecting earlier. If you had such an experience, you might describe the same to the evaluation committee when you answer this question. For example,
I was expecting that business promotion through social media would not be a good idea for rural enterprises in developing countries in my comparative analysis of the usage of traditional and contemporary marketing methods. But I was surprised to learn that 68% of rural textile businesses in Nigeria promote their products on Instagram.
12. What is the validity of your findings?
You have to talk about the conditions in which your research findings would be valid.
In my research, I have considered test anxiety to be involving both nervous system activation and negative thoughts. Thus, my measure of test anxiety has included the elements of both nervous feelings and negative thoughts, the conditions in which my findings are valid.
For example,
For studying the differential protein expression, its localization, and distribution at different levels, we used the method of immunostaining in our research.
14. What sources did you use for data collection?
You would have used several sources to search for data for your topic. You may elaborate on those sources. You might have referred to databases, content on the web, or even conducted primary research by interviewing prospects. Thus, you can talk about these sources. Refer to the following answer:
To understand the impact of the current tax regime on skilled workers, we interviewed 150 subjects in 5 months. Additionally, we referred to databases and scholarly works available by authors who had previously conducted such studies for previous tax laws and rates.
15. How can your research be put into practice?
This question talks about the practical implications of your research. You should talk about how your research is beneficial for society and how it can help in eliminating current issues.
In our research titled “Effectiveness of Meditation on Reducing the Anxiety Levels of College Students in the US,” we discovered that students who practiced meditation at least thrice a week were two times more likely to score better in their exams, owing to the positive impact of meditation. So, this research finding can help in the reduction of mental health issues among students. A suitable course of action would be to hold meditating sessions a couple of times a week.
16. How will your findings contribute to the related area of knowledge?
Our study on medicinal analysis of herbs conveys information about various medicinal benefits of chamomile in treating depression and contributes to the area of medicinal botany.
17. Did you experience any limitations in your research?
Our research on “Impact of smoking on β-cell function and risk for type 2 diabetes in US citizens” finds that smoking increases the risk of diabetes among smokers. However, smokers might be affected by some genetic conditions which can protect them from diabetes.
18. What sampling techniques did you use?
When conducting research, it is practically not possible to study the entire number of elements. So, you would be using a method to select a sample population.
In our study “Impact of consumption of soda on the health of teenagers in Corpus Christi”, we used area sampling to divide the city into several areas and then selected some clusters for our sample group.
19. What are the dependent and independent variables in your research?
In research, several variable factors impact your study. You can describe these variables. Independent variables have values which are not affected by other variables in your study. On the other hand, the dependent variables have values that change with changes in the independent variable. For example,
In our study on “Impact of online tutoring on test scores”, the independent variable is the nature of the classes i.e., online and the participants' test score is the dependent variable.
20. What areas do you suggest for further research?
As a researcher, you should be able to describe what further areas are open for research with the addition of your research to the field. This can act as a starting point for future researchers. For example,
In my research on “Effectiveness of Acetaminophen in treating sports induced injuries”, I discovered that administering Acetaminophen is not very effective for treating joint pains such as the knee. This further suggests measures for the regulation of Acetaminophen in the production of painkillers for body pain and the search for alternative compounds.
Practice Questions
After taking a look at the sample answers, now try answering these questions by yourself:
Do you have any closing comments? "}]">
After submitting your research thesis for evaluation, you have to appear before a panel of professors and present your work; afterwards, they will ask you questions about your research.
You have to plan and prepare for your thesis defense. Review your paper and anticipate the questions that the committee can ask. Practice with mock defense sessions using professional servicesand make improvements based on their feedback. Be prepared with a strategy for answering any question asked by the panel.
Your research thesis should be on a topic of your interest. Scan your course syllabus to find something that makes you curious. Or, you can even refer to your grad school career goals statement to review what got you interested in grad school in the first place. Shortlist a few topics and zero down to the one that excites you the most.
The first step in preparing for a master’s thesis defense is to revise your research paper and write down a list of questions that the committee might ask. Find answers to those questions and get ready for your presentation. Practice your presentation beforehand. Try to attend a thesis defense of other candidates to know what you can expect in your session.
You will get questions related to what you have mentioned in your research paper. The most common starting questions are “what is your research about?" and “what was your motivation behind choosing this topic?” Later on, the committee asks you more detailed questions on research methodology, literature review, study variables, research findings, recommendations, and areas of further research.
You can get help from a grad school essay tutor for your research thesis writing. They can help you in developing writing skills and reviewing your work. They can proofread your work and provide recommendations on areas of improvement.
You can include your research thesis on your grad school CV to show your practical knowledge and skills. You can add the details of the study in a separate section for research experience.
Immediately after the thesis defense, the evaluation panel will decide whether to approve your paper as submitted or request some changes, or reject it.
To pass a thesis defense, a majority of the panel members must approve the defense. In case of more than one vote against you, you can fail the thesis.
A thesis defense can last for two hours or longer, depending on your area of research.
Your thesis defense presentation should include the focus concept, findings, recommendation, and conclusion.
The contribution of your thesis towards your degree differs as per institution. You can refer to your course handbook for exact details. In most cases, the committee needs to approve your thesis for you to graduate from your degree.
Want more free tips? Subscribe to our channels for more free and useful content!
Apple Podcasts
Like our blog? Write for us ! >>
Have a question ask our admissions experts below and we'll answer your questions.
why did you choose this place for a research locale
BeMo Academic Consulting
Hi Jeff! Yes, this can also be one of the questions you are asked in a thesis defense!
That is good
Hello Eshetu! Thanks for your comment. Glad you found this helpful!
Very helpful
Thanks, Abel. Glad you found this helpful.
Helpful thank you.
Hi Lagat! Thanks!
As an 11th-grade student, I don't have any experience in thesis or research defense in general. Me and my groupmates will be conducting our research title defense next week, this is invaluable information for us. Thank you!
You are very welcome, Kate!
THANK YOU SO MUCH FOR THIS, I REALLY APPRECIATE.
Hello Stephanie! Thanks for your comment.
EMELDA NAFULA NYONGESA
This is a good guideline to post graduate students (Masters and PhD) CPA:Emelda Nyongesa
Hi Emelda! Thanks!
Get Started Now
Talk to one of our admissions experts
Our site uses cookies. By using our website, you agree with our cookie policy .
FREE Training Webinar:
How to make your grad school application stand out, (and avoid the top 5 mistakes that get most rejected).
Time Sensitive. Limited Spots Available:
We guarantee you'll get into grad school or you don't pay.
Swipe up to see a great offer!
Reference management. Clean and simple.
How to prepare an excellent thesis defense
What is a thesis defense?
How long is a thesis defense, what happens at a thesis defense, your presentation, questions from the committee, 6 tips to help you prepare for your thesis defense, 1. anticipate questions and prepare for them, 2. dress for success, 3. ask for help, as needed, 4. have a backup plan, 5. prepare for the possibility that you might not know an answer, 6. de-stress before, during, and after, frequently asked questions about preparing an excellent thesis defense, related articles.
If you're about to complete, or have ever completed a graduate degree, you have most likely come across the term "thesis defense." In many countries, to finish a graduate degree, you have to write a thesis .
A thesis is a large paper, or multi-chapter work, based on a topic relating to your field of study.
Once you hand in your thesis, you will be assigned a date to defend your work. Your thesis defense meeting usually consists of you and a committee of two or more professors working in your program. It may also include other people, like professionals from other colleges or those who are working in your field.
During your thesis defense, you will be asked questions about your work. The main purpose of your thesis defense is for the committee to make sure that you actually understand your field and focus area.
The questions are usually open-ended and require the student to think critically about their work. By the time of your thesis defense, your paper has already been evaluated. The questions asked are not designed so that you actually have to aggressively "defend" your work; often, your thesis defense is more of a formality required so that you can get your degree.
- Check with your department about requirements and timing.
- Re-read your thesis.
- Anticipate questions and prepare for them.
- Create a back-up plan to deal with technology hiccups.
- Plan de-stressing activities both before, and after, your defense.
How long your oral thesis defense is depends largely on the institution and requirements of your degree. It is best to consult your department or institution about this. In general, a thesis defense may take only 20 minutes, but it may also take two hours or more. The length also depends on how much time is allocated to the presentation and questioning part.
Tip: Check with your department or institution as soon as possible to determine the approved length for a thesis defense.
First of all, be aware that a thesis defense varies from country to country. This is just a general overview, but a thesis defense can take many different formats. Some are closed, others are public defenses. Some take place with two committee members, some with more examiners.
The same goes for the length of your thesis defense, as mentioned above. The most important first step for you is to clarify with your department what the structure of your thesis defense will look like. In general, your thesis defense will include:
- your presentation of around 20-30 minutes
- questions from the committee
- questions from the audience (if the defense is public and the department allows it)
You might have to give a presentation, often with Powerpoint, Google slides, or Keynote slides. Make sure to prepare an appropriate amount of slides. A general rule is to use about 10 slides for a 20-minute presentation.
But that also depends on your specific topic and the way you present. The good news is that there will be plenty of time ahead of your thesis defense to prepare your slides and practice your presentation alone and in front of friends or family.
Tip: Practice delivering your thesis presentation in front of family, friends, or colleagues.
You can prepare your slides by using information from your thesis' first chapter (the overview of your thesis) as a framework or outline. Substantive information in your thesis should correspond with your slides.
Make sure your slides are of good quality— both in terms of the integrity of the information and the appearance. If you need more help with how to prepare your presentation slides, both the ASQ Higher Education Brief and James Hayton have good guidelines on the topic.
The committee will ask questions about your work after you finish your presentation. The questions will most likely be about the core content of your thesis, such as what you learned from the study you conducted. They may also ask you to summarize certain findings and to discuss how your work will contribute to the existing body of knowledge.
Tip: Read your entire thesis in preparation of the questions, so you have a refreshed perspective on your work.
While you are preparing, you can create a list of possible questions and try to answer them. You can foresee many of the questions you will get by simply spending some time rereading your thesis.
Here are a few tips on how to prepare for your thesis defense:
You can absolutely prepare for most of the questions you will be asked. Read through your thesis and while you're reading it, create a list of possible questions. In addition, since you will know who will be on the committee, look at the academic expertise of the committee members. In what areas would they most likely be focused?
If possible, sit at other thesis defenses with these committee members to get a feel for how they ask and what they ask. As a graduate student, you should generally be adept at anticipating test questions, so use this advantage to gather as much information as possible before your thesis defense meeting.
Your thesis defense is a formal event, often the entire department or university is invited to participate. It signals a critical rite of passage for graduate students and faculty who have supported them throughout a long and challenging process.
While most universities don't have specific rules on how to dress for that event, do regard it with dignity and respect. This one might be a no-brainer, but know that you should dress as if you were on a job interview or delivering a paper at a conference.
It might help you deal with your stress before your thesis defense to entrust someone with the smaller but important responsibilities of your defense well ahead of schedule. This trusted person could be responsible for:
- preparing the room of the day of defense
- setting up equipment for the presentation
- preparing and distributing handouts
Technology is unpredictable. Life is too. There are no guarantees that your Powerpoint presentation will work at all or look the way it is supposed to on the big screen. We've all been there. Make sure to have a plan B for these situations. Handouts can help when technology fails, and an additional clean shirt can save the day if you have a spill.
One of the scariest aspects of the defense is the possibility of being asked a question you can't answer. While you can prepare for some questions, you can never know exactly what the committee will ask.
There will always be gaps in your knowledge. But your thesis defense is not about being perfect and knowing everything, it's about how you deal with challenging situations. You are not expected to know everything.
James Hayton writes on his blog that examiners will sometimes even ask questions they don't know the answer to, out of curiosity, or because they want to see how you think. While it is ok sometimes to just say "I don't know", he advises to try something like "I don't know, but I would think [...] because of x and y, but you would need to do [...] in order to find out.” This shows that you have the ability to think as an academic.
You will be nervous. But your examiners will expect you to be nervous. Being well prepared can help minimize your stress, but do know that your examiners have seen this many times before and are willing to help, by repeating questions, for example. Dora Farkas at finishyourthesis.com notes that it’s a myth that thesis committees are out to get you.
Two common symptoms of being nervous are talking really fast and nervous laughs. Try to slow yourself down and take a deep breath. Remember what feels like hours to you are just a few seconds in real life.
- Try meditational breathing right before your defense.
- Get plenty of exercise and sleep in the weeks prior to your defense.
- Have your clothes or other items you need ready to go the night before.
- During your defense, allow yourself to process each question before answering.
- Go to dinner with friends and family, or to a fun activity like mini-golf, after your defense.
Allow yourself to process each question, respond to it, and stop talking once you have responded. While a smile can often help dissolve a difficult situation, remember that nervous laughs can be irritating for your audience.
We all make mistakes and your thesis defense will not be perfect. However, careful preparation, mindfulness, and confidence can help you feel less stressful both before, and during, your defense.
Finally, consider planning something fun that you can look forward to after your defense.
It is completely normal to be nervous. Being well prepared can help minimize your stress, but do know that your examiners have seen this many times before and are willing to help, by repeating questions for example if needed. Slow yourself down, and take a deep breath.
Your thesis defense is not about being perfect and knowing everything, it's about how you deal with challenging situations. James Hayton writes on his blog that it is ok sometimes to just say "I don't know", but he advises to try something like "I don't know, but I would think [...] because of x and y, you would need to do [...] in order to find out".
Your Powerpoint presentation can get stuck or not look the way it is supposed to do on the big screen. It can happen and your supervisors know it. In general, handouts can always save the day when technology fails.
- Dress for success.
- Ask for help setting up.
- Have a backup plan (in case technology fails you).
- Deal with your nerves.


How to Effectively Prepare for Your Thesis Defense

You’ve completed your research study, written your thesis, and think you’re done! If only it were this easy. Before you finish with your thesis, there is one last hurdle to overcome: the thesis defense.
What is a thesis defense?
A thesis defense is an opportunity for you to present your research study before other academic professionals who will evaluate the quality of your academic work. While a thesis defense can sometimes feel like a cross-examination in a court of law, in reality, there is no need to fear your thesis defense as long as you are well-prepared. In this article, we’ll talk about how to prepare for a thesis defense, what to expect at the defense itself, and what comes after your defense.
Why do I have to defend my thesis?
At your thesis defense, you will discuss everything you’ve learned with a group of interested examiners who are eager to hear your thoughts.
The fundamental purpose of a thesis defense is to prove that you have mastered your subject and can be considered as a knowledgeable expert in your field, thereby allowing you to graduate successfully. For many students, a thesis is one of the first attempts at conducting original research and demonstrating that you are equipped to function as an independent expert in your field. If qualified academic professionals can assess your work, question your methods and results, and confirm that your study is sound and novel, then you meet the requirements.
The exact format and expectations for your thesis defense will differ depending on the region you study in and your institution’s rules for the thesis program. The thesis defense meeting may have just two or three examiners or may have a whole panel of examiners along with an audience.
If the thought of facing your professors, peers, and parents to present your research study makes you feel dizzy, you aren’t alone . Moreover, a thesis defense is a great opportunity for you to hone your public speaking skills as well as talk about your research study. At your thesis defense, you will discuss everything you’ve learned with a group of interested examiners who are eager to hear your thoughts.
While the format for a thesis defense will vary, as mentioned above, most thesis defenses consist of:
- Presenting your research study (using PowerPoint or other similar tools)
- Answering questions from your thesis committee
- Receiving feedback from your thesis committee
So how can you prepare for it? Let’s talk about some important tips.
Preparing: Before the defense
It is useful to attend multiple defenses and ask others who have gone through the process what it was like.
The best way to prepare for a thesis defense is to attend other defenses at your institution so that you know what to expect. It is useful to attend multiple defenses and ask others who have gone through the process what it was like. Senior students are often happy to provide advice and can give you specific insights about particular examiners as well as details of the administrative process at your institution.
You should also talk to your thesis advisor well in advance of your defense about what to expect. Ask whether you need to shortlist your own committee, how long your presentation should be, and how long the thesis defense will be. The duration of a thesis defense varies by the degree level as well as the institution. On average, expect your defense to be at least an hour long, possibly longer for a Ph.D.
What should my presentation cover and how can I prepare it?
While preparing your presentation, also prepare a list of questions and answers that you think are likely to be asked by your committee.
You will need to prepare a presentation that will cover the details of your research study. It is wise to rehearse this presentation multiple times in advance of your thesis defense so that you will be comfortable when you actually present in front of your audience. While preparing your presentation, also prepare a list of questions and answers that you think are likely to be asked by your committee. If you can, enlist the help of a classmate or friend to be the examiner. They can ask you questions about your research study so you will be able to practice addressing these questions.
One mistake many students make is assuming that all members of their defense committee will thoroughly read their thesis prior to the defense. This is simply not always the case. For this reason, you should make sure your presentation makes sense to someone who has not actually read your thesis. A typical thesis defense presentation gives:
- An introduction to the topic
- Explains how the study is significant in the field
- Covers the main highlights of the methodology and results of the study
- Picks out the main points from the discussion and conclusion
What should I do the day before my defense?
Before your thesis defense, make sure you have backups of everything you need saved in multiple formats and multiple locations.
Before your thesis defense, make sure you have backups of everything you need to be saved in multiple formats and multiple locations. Put your presentation and your thesis on a USB drive, email it to yourself, upload it to the cloud, and print it out. Leave nothing to chance: you want to be absolutely prepared to defend your thesis short of an act of God obliterating the venue. In addition, make sure you prepare hard copies (printouts) of both your thesis and slideshow for the committee members. It need not be professionally bound at this stage, but they will appreciate having reference material on hand.
Finally, there are some practical steps to take in preparation for the thesis defense. Choose your outfit in advance (you should dress professionally) and practice presenting in it. You should also make sure you know the exact location of the thesis defense venue. Scope out the venue before your defense, if possible, so you can imagine yourself there while you rehearse. If you are presenting virtually, test all your equipment in advance and have a backup plan in case your internet goes out or your computer suddenly crashes. Most importantly, make sure that you eat well and get proper rest the night before. Don’t stay up late rehearsing last minute in the hopes of improving your chances of passing your defense. You will do much better if you are well-rested and alert.
Time to shine: At the defense
Try to stay calm and remember you are not on trial!
What can you expect on the day of the defense?
Typically, you will enter the room, set up, and begin your presentation once the committee indicates that they are ready. As mentioned above, it is always advisable to bring hard copies of both your thesis and slideshow for the committee. That way, they can easily refer to what you are talking about as you present. Make sure you also bring a pencil and notebook with you to take notes, and some water, because you will get thirsty as you talk.
After you are done with the presentation, the committee members will ask questions. Try to stay calm and remember you are not on trial! Your committee generally wants you to succeed, but they also want you to prove that you really know what you’re talking about. Do your best to answer their questions and never be afraid to admit when you don’t know something. It is much better, to be honest than to be caught lying or making something up during your thesis defense.
After the question and answer session, depending on your institution, you may be asked to leave the room while the committee deliberates. You may also be present while they discuss the merits of your defense and make suggestions for how to revise it. Alternatively, they might adjourn to another room if there is a large audience present. After they deliberate, they will usually thank you for your time, and your defense will be over. At some institutions, they will inform you if you passed right away, while at others, you will find out after a few days.
How does my committee decide if my work is good or not?
In general, you can expect your thesis defense and your thesis as a whole to be evaluated based on the below criteria:
- Whether the thesis meets the departmental requirements
- Whether the research study is logical and clear
- Whether the stated objectives are met in the study
- Use of primary and secondary literature
- Use of relevant and up-to-date sources
- Methodological rigor
- Your ability to critically analyze data, facts, relevant literature, and synthesize information into a coherent narrative
- Writing quality and flow
- The validity of your conclusions based on your data and analysis
- The relevance and importance of your research study in the field
- Your ability to clearly and coherently present what your thesis is about
- Your ability to answer questions about your work accurately and in-depth
- Your ability to acknowledge and consider other theories or perspectives and explain why you dismissed one theory in favor of another
In summary, the examining committee want to know:
- Did you meet the thesis criteria set by your institution?
- Did you perform high-quality research work?
- Do you know what you are talking about?
After the defense: What’s next?
After your thesis is approved, you will need to have it professionally bound and then submit copies to your university.
After your thesis defense, you should definitely celebrate and congratulate yourself for all your hard work! Unfortunately, you aren’t quite done yet. Although the committee may notify you about passing, it is also very likely that you will be asked to make some changes to your thesis before you are finally done. You should work with your advisor to finalize and incorporate any comments you received into your work as quickly as possible.
After your thesis is approved, you will need to have it professionally bound and then submit copies to your university. You will also get the chance to order copies for yourself. This process also differs by institution, so make sure you talk to the administration department to figure out what you need to do and when to complete this process.
All in all, while a thesis defense is a scary and overwhelming event, it is also an incredible achievement. Earning your degree is no small feat, and you should definitely feel proud of yourself once you have done it! Check out our site for more tips on how to write a good thesis, where to find the best thesis editing services , and more about thesis editing and proofreading services .
Editor’s pick
Get free updates.
Subscribe to our newsletter for regular insights from the research and publishing industry!
Review Checklist
To prepare for your thesis defense, make sure that you:
Find out your institutional requirements
Talk to your advisor well in advance about what to expect and prepare
Attend defenses of other students to see what they are like
Prepare your presentation early so you can rehearse it
Rehearse your presentation with a timer
Make a list of questions and answers about your research study
Enlist a friend to be the examiner and ask you questions
Prepare multiple backups of your materials (USB drive, Google Drive/Cloud storage, email, hard copy)
Have a plan for computer/internet problems if you are presenting virtually
Eat well and get a good night’s rest before the defense
Arrive at the defense venue early enough to test any IT equipment or internet connection
What should I do to prepare for my thesis defense? +
- Find out your institution’s requirements
- Attend other thesis defenses
- Speak to your advisor
- Prepare and practice your presentation
- Enlist a friend or classmate to act as the examiner and ask you questions while you practice
How long is a typical thesis defense? +
Every institution is different, but most thesis defenses are at least an hour long.
What should my thesis presentation actually contain? +
A typical thesis defense presentation introduces the thesis topic, explains how your study is significant in the field, and covers the main highlights of the methodology and results of the study. It finally picks out the main points from the discussion and conclusion section of your thesis.

What if I fail my thesis defense? +
The odds that you will fail are extremely low! Most advisors and committees do not let a candidate schedule a defense unless they feel the candidate is ready. So, don’t worry about it. However, if you do fail for some reason, your institution will have a process for you to apply to try again.

Defending Your Dissertation: A Guide

Written by Luke Wink-Moran | Photo by insta_photos
Dissertation defenses are daunting, and no wonder; it’s not a “dissertation discussion,” or a “dissertation dialogue.” The name alone implies that the dissertation you’ve spent the last x number of years working on is subject to attack. And if you don’t feel trepidation for semantic reasons, you might be nervous because you don’t know what to expect. Our imaginations are great at making The Unknown scarier than reality. The good news is that you’ll find in this newsletter article experts who can shed light on what dissertations defenses are really like, and what you can do to prepare for them.
The first thing you should know is that your defense has already begun. It started the minute you began working on your dissertation— maybe even in some of the classes you took beforehand that helped you formulate your ideas. This, according to Dr. Celeste Atkins, is why it’s so important to identify a good mentor early in graduate school.
“To me,” noted Dr. Atkins, who wrote her dissertation on how sociology faculty from traditionally marginalized backgrounds teach about privilege and inequality, “the most important part of the doctoral journey was finding an advisor who understood and supported what I wanted from my education and who was willing to challenge me and push me, while not delaying me. I would encourage future PhDs to really take the time to get to know the faculty before choosing an advisor and to make sure that the members of their committee work well together.”
Your advisor will be the one who helps you refine arguments and strengthen your work so that by the time it reaches your dissertation committee, it’s ready. Next comes the writing process, which many students have said was the hardest part of their PhD. I’ve included this section on the writing process because this is where you’ll create all the material you’ll present during your defense, so it’s important to navigate it successfully. The writing process is intellectually grueling, it eats time and energy, and it’s where many students find themselves paddling frantically to avoid languishing in the “All-But-Dissertation” doldrums. The writing process is also likely to encroach on other parts of your life. For instance, Dr. Cynthia Trejo wrote her dissertation on college preparation for Latin American students while caring for a twelve-year-old, two adult children, and her aging parents—in the middle of a pandemic. When I asked Dr. Trejo how she did this, she replied:
“I don’t take the privilege of education for granted. My son knew I got up at 4:00 a.m. every morning, even on weekends, even on holidays; and it’s a blessing that he’s seen that work ethic and that dedication and the end result.”
Importantly, Dr. Trejo also exercised regularly and joined several online writing groups at UArizona. She mobilized her support network— her partner, parents, and even friends from high school to help care for her son.
The challenges you face during the writing process can vary by discipline. Jessika Iwanski is an MD/PhD student who in 2022 defended her dissertation on genetic mutations in sarcomeric proteins that lead to severe, neonatal dilated cardiomyopathy. She described her writing experience as “an intricate process of balancing many things at once with a deadline (defense day) that seems to be creeping up faster and faster— finishing up experiments, drafting the dissertation, preparing your presentation, filling out all the necessary documents for your defense and also, for MD/PhD students, beginning to reintegrate into the clinical world (reviewing your clinical knowledge and skill sets)!”
But no matter what your unique challenges are, writing a dissertation can take a toll on your mental health. Almost every student I spoke with said they saw a therapist and found their sessions enormously helpful. They also looked to the people in their lives for support. Dr. Betsy Labiner, who wrote her dissertation on Interiority, Truth, and Violence in Early Modern Drama, recommended, “Keep your loved ones close! This is so hard – the dissertation lends itself to isolation, especially in the final stages. Plus, a huge number of your family and friends simply won’t understand what you’re going through. But they love you and want to help and are great for getting you out of your head and into a space where you can enjoy life even when you feel like your dissertation is a flaming heap of trash.”
While you might sometimes feel like your dissertation is a flaming heap of trash, remember: a) no it’s not, you brilliant scholar, and b) the best dissertations aren’t necessarily perfect dissertations. According to Dr. Trejo, “The best dissertation is a done dissertation.” So don’t get hung up on perfecting every detail of your work. Think of your dissertation as a long-form assignment that you need to finish in order to move onto the next stage of your career. Many students continue revising after graduation and submit their work for publication or other professional objectives.
When you do finish writing your dissertation, it’s time to schedule your defense and invite friends and family to the part of the exam that’s open to the public. When that moment comes, how do you prepare to present your work and field questions about it?
“I reread my dissertation in full in one sitting,” said Dr. Labiner. “During all my time writing it, I’d never read more than one complete chapter at a time! It was a huge confidence boost to read my work in full and realize that I had produced a compelling, engaging, original argument.”
There are many other ways to prepare: create presentation slides and practice presenting them to friends or alone; think of questions you might be asked and answer them; think about what you want to wear or where you might want to sit (if you’re presenting on Zoom) that might give you a confidence boost. Iwanksi practiced presenting with her mentor and reviewed current papers to anticipate what questions her committee might ask. If you want to really get in the zone, you can emulate Dr. Labiner and do a full dress rehearsal on Zoom the day before your defense.
But no matter what you do, you’ll still be nervous:
“I had a sense of the logistics, the timing, and so on, but I didn’t really have clear expectations outside of the structure. It was a sort of nebulous three hours in which I expected to be nauseatingly terrified,” recalled Dr. Labiner.
“I expected it to be terrifying, with lots of difficult questions and constructive criticism/comments given,” agreed Iwanski.
“I expected it to be very scary,” said Dr. Trejo.
“I expected it to be like I was on trial, and I’d have to defend myself and prove I deserved a PhD,” said Dr Atkins.
And, eventually, inexorably, it will be time to present.
“It was actually very enjoyable” said Iwanski. “It was more of a celebration of years of work put into this project—not only by me but by my mentor, colleagues, lab members and collaborators! I felt very supported by all my committee members and, rather than it being a rapid fire of questions, it was more of a scientific discussion amongst colleagues who are passionate about heart disease and muscle biology.”
“I was anxious right when I logged on to the Zoom call for it,” said Dr. Labiner, “but I was blown away by the number of family and friends that showed up to support me. I had invited a lot of people who I didn’t at all think would come, but every single person I invited was there! Having about 40 guests – many of them joining from different states and several from different countries! – made me feel so loved and celebrated that my nerves were steadied very quickly. It also helped me go into ‘teaching mode’ about my work, so it felt like getting to lead a seminar on my most favorite literature.”
“In reality, my dissertation defense was similar to presenting at an academic conference,” said Dr. Atkins. “I went over my research in a practiced and organized way, and I fielded questions from the audience.
“It was a celebration and an important benchmark for me,” said Dr. Trejo. “It was a pretty happy day. Like the punctuation at the end of your sentence: this sentence is done; this journey is done. You can start the next sentence.”
If you want to learn more about dissertations in your own discipline, don’t hesitate to reach out to graduates from your program and ask them about their experiences. If you’d like to avail yourself of some of the resources that helped students in this article while they wrote and defended their dissertations, check out these links:
The Graduate Writing Lab
https://thinktank.arizona.edu/writing-center/graduate-writing-lab
The Writing Skills Improvement Program
https://wsip.arizona.edu
Campus Health Counseling and Psych Services
https://caps.arizona.edu
https://www.scribbr.com/
The top 10 thesis defense questions (+ how to prepare strong answers)
Crafting a thesis is significant, but defending it often feels like the ultimate test. While nerve-wracking, proper preparation can make it manageable. Prepare for your thesis defense with insights on the top questions you can expect, including strategies for answering convincingly.
Mastering the thesis defense: cultivate a success mindset
Question 1: why did you choose this particular topic for your research, question 2: how does your research contribute to the existing body of knowledge, question 3: what are the key findings of your research, question 4: can you defend your research methodology, question 5: how did you analyze the data and what challenges did you encounter, question 6: what theoretical frameworks or references underpin your research, question 7: how did you address ethical considerations in your research, question 8: in what ways does your research contribute to the field, question 9: how did you ensure your research was free from bias, question 10: where can future research go from here.
Nurturing a success mindset for your defense is pivotal. This means adopting a mental outlook geared towards achieving favorable outcomes during your thesis defense. To truly excel in this pivotal academic moment, it’s imperative to cultivate both confidence and composure.
Confidence enables you to present your research with conviction, while composure allows you to navigate any challenges with grace and clarity.
Remember, you know your thesis best, so trust in your expertise.
In essence, a success mindset encompasses the belief in your abilities, coupled with the ability to remain calm and focused under pressure.
Stay composed and focused, relying on your thorough preparation. If you encounter a question you can’t answer, gracefully guide the conversation back to familiar topics.
Use strategic responses when needed. For example, if a question goes beyond your thesis scope, acknowledge its relevance but steer back to your focused areas. Similarly, if you’re unfamiliar with a theory or literature, admit it but offer related insights or perspectives.
By embracing these principles and staying confident and adaptable, you’ll navigate your thesis defense with ease.
This question delves into the origins of your academic journey, aiming to understand not just what you studied, but the underlying motivations and processes that drove your exploration. It’s not merely about the superficial aspects of your research, but rather about the deeper intellectual curiosity that ignited your quest.
To effectively respond, take the opportunity to elaborate on the intricacies of your journey. Begin by unpacking the specific interests or questions that sparked your intellectual curiosity in the subject matter. What events, experiences, or influences led you to delve into this particular area of study? Providing an anecdote or example that vividly illustrates the genesis of your scholarly pursuit can be helpful.
Moreover, discuss the gaps you identified in the existing literature that motivated you to contribute to your field. What deficiencies or unanswered questions did you observe? How did these gaps inspire you to embark on your research journey with the aim of filling these voids? By articulating the specific shortcomings in the current body of knowledge, you demonstrate a nuanced understanding of your research area and underscore the significance of your work.
Additionally, highlight any personal or academic experiences that played a pivotal role in steering you towards your chosen topic. Whether it was a transformative educational experience, a profound personal interest, or a meaningful encounter, these experiences can offer valuable insights into the origins of your scholarly pursuits.
In summary, when articulating your narrative, consider the following key points:
- Unpack the specific interests or questions that sparked your intellectual curiosity.
- Discuss the gaps in the existing literature that motivated your research.
- Highlight any personal or academic experiences that influenced your choice of topic.
This question delves into the vital role your research plays within the existing body of knowledge, urging you to articulate its significance and impact. It’s not merely about the subject matter you’ve studied, but also about the unique contributions and advancements your research brings to your field. To effectively respond, delve into the intricacies of your work and its implications for the broader academic landscape.
Begin by emphasizing the novelties and breakthroughs your research introduces. Highlight specific aspects of your study that represent advancements in understanding or methodologies. Whether it’s a novel approach to a longstanding problem, the discovery of new phenomena, or the development of innovative methodologies, these contributions underscore the significance of your research within the academic community.
Next, describe how your work engages with or challenges current conversations in your field. Discuss the existing paradigms or theories your research builds upon or critiques. Articulate how your findings contribute to ongoing debates or reshape prevailing understandings. By positioning your research within the broader context of scholarly discourse, you showcase its relevance and impact on the evolving landscape of your field.
Illuminate how your findings could influence future research trajectories. Explore potential avenues for further inquiry that emerge from your research findings. Consider how your work opens up new questions or areas of exploration for future researchers. By identifying these potential research directions, you demonstrate the forward-looking nature of your work and its potential to shape the future trajectory of your field.
In summary, when addressing how your research contributes to the existing body of knowledge, consider the following key points:
- Emphasize the novelties and breakthroughs your research introduces.
- Describe the conversations in your field that your work engages with or challenges.
- Illuminate how your findings could influence future research trajectories.
Addressing the question of your research’s key findings demands skill, as it necessitates succinctly summarizing your work while conveying its significance. To effectively respond, distill your findings into digestible takeaways that encapsulate the essence of your research. Identify the central discoveries or outcomes of your study, ensuring clarity and conciseness in your presentation.
Furthermore, relate these findings to the broader implications they hold for your field. Articulate how your research contributes to advancing knowledge or addressing pressing issues within your academic discipline. Consider the potential impact of your findings on theory, practice, or policy, highlighting their relevance and significance within the larger scholarly community.
Additionally, be prepared to elucidate the nuances and complexities involved in your results. While providing a concise summary of your findings is essential, it’s equally important to acknowledge the intricacies and limitations of your research. Discuss any methodological considerations, unexpected outcomes, or areas for further investigation, demonstrating a nuanced understanding of your work.
In summary, when addressing the key findings of your research, consider the following key points:
- Distill your findings into digestible takeaways.
- Relate the outcomes to the broader implications they hold for your field.
- Be prepared to shed light on the nuances and complexities involved in your results.
Defending your research methodology entails a comprehensive understanding of its rationale, alignment with research objectives, and acknowledgment of potential limitations. It’s not merely about explaining the methods employed but also justifying why they were chosen over alternative approaches. To effectively respond, delve into the intricacies of your methodology and its implications for the study.
Begin by elucidating the reasons for selecting the chosen methodology over alternatives. Discuss the specific advantages or suitability of the selected approach in addressing the research questions or objectives. Consider factors such as feasibility, appropriateness for the research context, and compatibility with the theoretical framework guiding your study.
Furthermore, explain how your chosen methods align with your research objectives. Articulate how the selected methodology enables you to achieve the intended outcomes and contribute to answering the research questions. Discuss how each methodological choice supports the overall research design and furthers the overarching goals of the study.
Be prepared to discuss the limitations inherent in your chosen methodology and how you mitigated them. Acknowledge any constraints or shortcomings associated with the selected approach, such as potential biases, sample size limitations, or data collection challenges. Demonstrate your awareness of these limitations and discuss the strategies implemented to address or minimize their impact on the validity and reliability of your findings.
In summary, when defending your research methodology, consider the following key points:
- Justify the methodology with reasons for selecting it over alternatives.
- Explain the methods’ alignment with your research objectives.
- Be ready to discuss the limitations and how you mitigated them.
Addressing the intricacies of data analysis involves not only outlining the techniques employed but also navigating the challenges encountered and evaluating the reliability and validity of the interpretations drawn. When responding to inquiries about data analysis, it’s essential to provide a comprehensive understanding of the methodologies employed, the obstacles faced, and the strategies utilized to ensure the accuracy and credibility of the findings.
Begin by outlining the techniques used for data analysis. Describe the specific methods, tools, and software employed to process and interpret the data collected. Whether it involved quantitative statistical analysis, qualitative coding techniques, or a combination of both, provide insights into the analytical framework guiding your study. Additionally, discuss the rationale behind the chosen analytical approach and how it aligns with the research objectives and questions.
Next, share the hurdles faced during the data analysis process and how you overcame them. Reflect on any challenges encountered, such as data cleaning issues, missing data, or unexpected patterns in the dataset. Discuss the steps taken to address these challenges, whether through iterative refinement of analytical techniques, consultation with peers or supervisors, or adaptation of the research design. Highlighting your ability to navigate obstacles demonstrates resilience and resourcefulness in overcoming methodological challenges.
Furthermore, discuss the reliability and validity of your data interpretation. Evaluate the rigor and credibility of your analytical process, considering factors such as data integrity, consistency, and relevance to the research objectives. Discuss any measures taken to ensure the trustworthiness of the findings, such as inter-coder reliability checks, triangulation of data sources, or member checking with participants. By critically examining the reliability and validity of your data interpretation, you provide insights into the robustness of your analytical approach and the credibility of the conclusions drawn.
In summary, when addressing inquiries about data analysis, consider the following key points:
- Outline the techniques used for data analysis.
- Share the hurdles faced during the process and how you overcame them.
- Discuss the reliability and validity of your data interpretation.
Exploring the theoretical underpinnings of your research involves delving into the foundational frameworks and seminal works that informed your study’s conceptual framework and analytical approach. When responding to inquiries about theoretical frameworks , it’s essential to provide a comprehensive understanding of the theories and references that shaped your research, elucidate their influence on your hypothesis and analysis, and reflect on the potential contributions or revisions your study may offer to existing theoretical foundations.
Begin by naming the key theories and seminal works that guided your research. Identify the theoretical frameworks that provided the conceptual scaffolding for your study, as well as the seminal works that shaped your understanding of the research area. Discuss how these theories and references informed your research design, methodology, and analytical approach, providing a theoretical lens through which to interpret your findings.
Elucidate on how these frameworks shaped your hypothesis and analysis. Describe how the theoretical perspectives and insights gleaned from seminal works informed the development of your research questions, hypotheses, and analytical framework. Discuss the ways in which these theoretical frameworks guided your data collection and interpretation, influencing the selection of variables, measures, and analytical techniques employed in your study.
Reflect on how your research may contribute to or revise these theoretical foundations. Consider the implications of your findings for advancing existing theoretical frameworks or revising established paradigms within your field. Discuss how your research extends or challenges current theoretical perspectives, offering new insights, conceptual refinements, or empirical evidence that may enrich or reshape prevailing theories. By critically examining the relationship between your research and existing theoretical frameworks, you provide insights into the broader theoretical implications and contributions of your study.
In summary, when addressing inquiries about theoretical frameworks, consider the following key points:
- Name the key theories and seminal works that guided your research.
- Elucidate on how these frameworks shaped your hypothesis and analysis.
- Reflect on how your research may contribute to or revise these theoretical foundations.
When addressing ethical considerations in your research, it’s essential to demonstrate a commitment to upholding ethical standards and protecting the rights and well-being of participants. Responding to inquiries about ethical protocols involves explaining the steps taken to ensure ethical conduct throughout the research process, describing the consent process and data protection measures implemented, and mentioning any institutional review board (IRB) approvals obtained.
Begin by explaining the ethical protocols you followed. Detail the ethical guidelines, codes of conduct, or regulatory frameworks that informed your research design and conduct. Discuss how these guidelines influenced decisions regarding participant recruitment, data collection methods, confidentiality protocols, and data storage procedures, emphasizing your adherence to ethical principles throughout the research process.
Describe the consent process, if applicable, and how you protected participants’ data. Provide insights into how informed consent was obtained from participants, including the procedures used to inform participants about the research purpose, risks, benefits, and their rights. Discuss any measures taken to safeguard participants’ privacy and confidentiality, such as anonymizing data, securing data storage, and limiting access to sensitive information, ensuring the protection of participants’ identities and personal information.
Mention any institutional ethics review board approvals you obtained. Highlight any formal ethical review processes or approvals obtained from relevant regulatory bodies, such as IRBs or ethics committees. Discuss how the research protocol was reviewed for compliance with ethical guidelines and standards, including considerations of participant welfare, informed consent procedures, and data protection measures. By acknowledging the oversight and approval of institutional review bodies, you demonstrate your commitment to ethical integrity and accountability in conducting research involving human subjects.
In summary, when addressing inquiries about ethical considerations in your research, consider the following key points:
- Explain the ethical protocols you followed.
- Describe the consent process and data protection measures implemented.
- Mention any institutional ethics review board approvals obtained.
When discussing the contributions of your research to the field, it’s essential to highlight the novel insights and potential impact your thesis offers. Responding to inquiries about your research’s significance involves detailing the unique perspectives and fresh understanding it brings to the academic discourse, as well as considering its implications for future research or practice and arguing its relevance within the broader academic community.
Begin by detailing the novel insights your thesis provides. Articulate the key findings, discoveries, or perspectives that distinguish your research from existing literature and contribute to advancing knowledge within your field. Discuss how your study fills gaps in current understanding, challenges established assumptions, or offers innovative approaches to addressing pressing issues, highlighting its potential to generate new avenues of inquiry and broaden the scope of scholarly discourse.
Discuss how your findings might influence future research or practice. Consider the implications of your research for shaping future scholarship, informing policy decisions, or guiding professional practice within relevant domains. Reflect on the potential practical applications, theoretical advancements, or methodological innovations stemming from your findings, highlighting their significance for advancing the field and addressing real-world challenges.
Be prepared to argue the relevance of your research within the broader academic community. Articulate the broader significance of your study within the context of current debates, trends, or priorities within your discipline. Discuss how your research aligns with existing scholarly agendas, contributes to interdisciplinary dialogue, or addresses pressing societal concerns, underscoring its relevance and potential impact on shaping the direction of future research and practice.
In summary, when addressing inquiries about the contributions of your research to the field, consider the following key points:
- Detail the novel insights your thesis provides.
- Discuss how your findings might influence future research or practice.
- Be prepared to argue the relevance of your research within the broader academic community.
When ensuring the integrity of your research and minimizing bias, it’s crucial to maintain objectivity and rigor throughout the study. Responding to inquiries about bias involves discussing the steps taken to uphold objectivity, describing any blind or double-blind procedures employed, and acknowledging and mitigating any unavoidable biases that may have arisen during the research process.
Begin by discussing the steps taken to maintain objectivity and rigor. Detail the strategies implemented to minimize the influence of personal biases, preconceptions, or external factors on the research outcomes. This may include adhering to a predetermined research protocol, using standardized procedures for data collection and analysis, and engaging in peer review or validation processes to ensure the reliability and validity of the findings.
Describe any blind or double-blind procedures employed in the study. Explain how blinding techniques were used to prevent bias in data collection, analysis, or interpretation. This may involve withholding certain information from researchers or participants to minimize the potential for conscious or unconscious bias to influence the results. Discuss how these procedures were implemented and their impact on enhancing the credibility and impartiality of the research outcomes.
Acknowledge any unavoidable biases that may have emerged during the research process and discuss how they were mitigated. Reflect on the inherent limitations or sources of bias in the study design, data collection methods, or participant selection criteria. Discuss the steps taken to minimize the impact of these biases, such as conducting sensitivity analyses, controlling for confounding variables, or triangulating data sources to corroborate findings.
In summary, when addressing inquiries about bias in your research, consider the following key points:
- Discuss steps taken to maintain objectivity and rigor.
- Describe any blind or double-blind procedures employed.
- Acknowledge any unavoidable biases and discuss how they were mitigated.
When considering the potential trajectory of your research topic, it’s essential to identify areas where further investigation could yield valuable insights, discuss unexplored questions that emerged from your research, and reflect on the limitations of your study as starting points for future research endeavors. Responding to inquiries about the future direction of research involves suggesting fruitful areas for further investigation, highlighting unresolved questions, and leveraging the limitations of your study as opportunities for future exploration.
Begin by suggesting areas where further investigation could be fruitful. Identify specific gaps, ambiguities, or unanswered questions within the existing literature that warrant additional inquiry. Consider emerging trends, advancements in technology or methodology, or pressing societal issues that may inform potential research directions. Propose research topics or hypotheses that build upon the findings of your study and extend the boundaries of current knowledge within your field.
Discuss unexplored questions that arose from your research. Reflect on any unexpected findings, anomalies, or areas of ambiguity that emerged during the course of your study. Consider how these unanswered questions or unresolved issues could serve as catalysts for future research endeavors, prompting further investigation into related phenomena, alternative explanations, or novel research methodologies.
Reflect on the limitations of your study as starting points for future research. Acknowledge any constraints, biases, or methodological shortcomings that may have influenced the outcomes or interpretations of your study. Discuss how these limitations provide opportunities for future research to refine methodologies, address confounding variables, or explore alternative theoretical frameworks. Consider how addressing these limitations could enhance the validity, reliability, and generalizability of future research findings within your field.
In summary, when addressing inquiries about the potential trajectory of your research topic, consider the following key points:
- Suggest areas where further investigation could be fruitful.
- Discuss unexplored questions that arose from your research.
- Reflect on the limitations of your study as starting points for future research.
Master Academia
Get new content delivered directly to your inbox.
Subscribe and receive Master Academia's quarterly newsletter.
How to harness theoretical and conceptual frameworks for groundbreaking research
25 short graduation quotes: inspiration in four words or less, related articles.

Better thesis writing with the Pomodoro® technique

Minimalist writing for a better thesis

75 linking words for academic writing (+examples)

How to write a unique thesis acknowledgement (+ FAQs)
What (Exactly) Is A Research Proposal?
A simple explainer with examples + free template.
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Reviewed By: Dr Eunice Rautenbach | June 2020 (Updated April 2023)
Whether you’re nearing the end of your degree and your dissertation is on the horizon, or you’re planning to apply for a PhD program, chances are you’ll need to craft a convincing research proposal . If you’re on this page, you’re probably unsure exactly what the research proposal is all about. Well, you’ve come to the right place.
Overview: Research Proposal Basics
- What a research proposal is
- What a research proposal needs to cover
- How to structure your research proposal
- Example /sample proposals
- Proposal writing FAQs
- Key takeaways & additional resources
What is a research proposal?
Simply put, a research proposal is a structured, formal document that explains what you plan to research (your research topic), why it’s worth researching (your justification), and how you plan to investigate it (your methodology).
The purpose of the research proposal (its job, so to speak) is to convince your research supervisor, committee or university that your research is suitable (for the requirements of the degree program) and manageable (given the time and resource constraints you will face).
The most important word here is “ convince ” – in other words, your research proposal needs to sell your research idea (to whoever is going to approve it). If it doesn’t convince them (of its suitability and manageability), you’ll need to revise and resubmit . This will cost you valuable time, which will either delay the start of your research or eat into its time allowance (which is bad news).

What goes into a research proposal?
A good dissertation or thesis proposal needs to cover the “ what “, “ why ” and” how ” of the proposed study. Let’s look at each of these attributes in a little more detail:
Your proposal needs to clearly articulate your research topic . This needs to be specific and unambiguous . Your research topic should make it clear exactly what you plan to research and in what context. Here’s an example of a well-articulated research topic:
An investigation into the factors which impact female Generation Y consumer’s likelihood to promote a specific makeup brand to their peers: a British context
As you can see, this topic is extremely clear. From this one line we can see exactly:
- What’s being investigated – factors that make people promote or advocate for a brand of a specific makeup brand
- Who it involves – female Gen-Y consumers
- In what context – the United Kingdom
So, make sure that your research proposal provides a detailed explanation of your research topic . If possible, also briefly outline your research aims and objectives , and perhaps even your research questions (although in some cases you’ll only develop these at a later stage). Needless to say, don’t start writing your proposal until you have a clear topic in mind , or you’ll end up waffling and your research proposal will suffer as a result of this.
Need a helping hand?
As we touched on earlier, it’s not good enough to simply propose a research topic – you need to justify why your topic is original . In other words, what makes it unique ? What gap in the current literature does it fill? If it’s simply a rehash of the existing research, it’s probably not going to get approval – it needs to be fresh.
But, originality alone is not enough. Once you’ve ticked that box, you also need to justify why your proposed topic is important . In other words, what value will it add to the world if you achieve your research aims?
As an example, let’s look at the sample research topic we mentioned earlier (factors impacting brand advocacy). In this case, if the research could uncover relevant factors, these findings would be very useful to marketers in the cosmetics industry, and would, therefore, have commercial value . That is a clear justification for the research.
So, when you’re crafting your research proposal, remember that it’s not enough for a topic to simply be unique. It needs to be useful and value-creating – and you need to convey that value in your proposal. If you’re struggling to find a research topic that makes the cut, watch our video covering how to find a research topic .

It’s all good and well to have a great topic that’s original and valuable, but you’re not going to convince anyone to approve it without discussing the practicalities – in other words:
- How will you actually undertake your research (i.e., your methodology)?
- Is your research methodology appropriate given your research aims?
- Is your approach manageable given your constraints (time, money, etc.)?
While it’s generally not expected that you’ll have a fully fleshed-out methodology at the proposal stage, you’ll likely still need to provide a high-level overview of your research methodology . Here are some important questions you’ll need to address in your research proposal:
- Will you take a qualitative , quantitative or mixed -method approach?
- What sampling strategy will you adopt?
- How will you collect your data (e.g., interviews, surveys, etc)?
- How will you analyse your data (e.g., descriptive and inferential statistics , content analysis, discourse analysis, etc, .)?
- What potential limitations will your methodology carry?
So, be sure to give some thought to the practicalities of your research and have at least a basic methodological plan before you start writing up your proposal. If this all sounds rather intimidating, the video below provides a good introduction to research methodology and the key choices you’ll need to make.
How To Structure A Research Proposal
Now that we’ve covered the key points that need to be addressed in a proposal, you may be wondering, “ But how is a research proposal structured? “.
While the exact structure and format required for a research proposal differs from university to university, there are four “essential ingredients” that commonly make up the structure of a research proposal:
- A rich introduction and background to the proposed research
- An initial literature review covering the existing research
- An overview of the proposed research methodology
- A discussion regarding the practicalities (project plans, timelines, etc.)
In the video below, we unpack each of these four sections, step by step.
Research Proposal Examples/Samples
In the video below, we provide a detailed walkthrough of two successful research proposals (Master’s and PhD-level), as well as our popular free proposal template.
Proposal Writing FAQs
How long should a research proposal be.
This varies tremendously, depending on the university, the field of study (e.g., social sciences vs natural sciences), and the level of the degree (e.g. undergraduate, Masters or PhD) – so it’s always best to check with your university what their specific requirements are before you start planning your proposal.
As a rough guide, a formal research proposal at Masters-level often ranges between 2000-3000 words, while a PhD-level proposal can be far more detailed, ranging from 5000-8000 words. In some cases, a rough outline of the topic is all that’s needed, while in other cases, universities expect a very detailed proposal that essentially forms the first three chapters of the dissertation or thesis.
The takeaway – be sure to check with your institution before you start writing.
How do I choose a topic for my research proposal?
Finding a good research topic is a process that involves multiple steps. We cover the topic ideation process in this video post.
How do I write a literature review for my proposal?
While you typically won’t need a comprehensive literature review at the proposal stage, you still need to demonstrate that you’re familiar with the key literature and are able to synthesise it. We explain the literature review process here.
How do I create a timeline and budget for my proposal?
We explain how to craft a project plan/timeline and budget in Research Proposal Bootcamp .
Which referencing format should I use in my research proposal?
The expectations and requirements regarding formatting and referencing vary from institution to institution. Therefore, you’ll need to check this information with your university.
What common proposal writing mistakes do I need to look out for?
We’ve create a video post about some of the most common mistakes students make when writing a proposal – you can access that here . If you’re short on time, here’s a quick summary:
- The research topic is too broad (or just poorly articulated).
- The research aims, objectives and questions don’t align.
- The research topic is not well justified.
- The study has a weak theoretical foundation.
- The research design is not well articulated well enough.
- Poor writing and sloppy presentation.
- Poor project planning and risk management.
- Not following the university’s specific criteria.
Key Takeaways & Additional Resources
As you write up your research proposal, remember the all-important core purpose: to convince . Your research proposal needs to sell your study in terms of suitability and viability. So, focus on crafting a convincing narrative to ensure a strong proposal.
At the same time, pay close attention to your university’s requirements. While we’ve covered the essentials here, every institution has its own set of expectations and it’s essential that you follow these to maximise your chances of approval.
By the way, we’ve got plenty more resources to help you fast-track your research proposal. Here are some of our most popular resources to get you started:
- Proposal Writing 101 : A Introductory Webinar
- Research Proposal Bootcamp : The Ultimate Online Course
- Template : A basic template to help you craft your proposal
If you’re looking for 1-on-1 support with your research proposal, be sure to check out our private coaching service , where we hold your hand through the proposal development process (and the entire research journey), step by step.

Psst… there’s more!
This post is an extract from our bestselling short course, Research Proposal Bootcamp . If you want to work smart, you don't want to miss this .
You Might Also Like:

51 Comments
I truly enjoyed this video, as it was eye-opening to what I have to do in the preparation of preparing a Research proposal.
I would be interested in getting some coaching.
I real appreciate on your elaboration on how to develop research proposal,the video explains each steps clearly.
Thank you for the video. It really assisted me and my niece. I am a PhD candidate and she is an undergraduate student. It is at times, very difficult to guide a family member but with this video, my job is done.
In view of the above, I welcome more coaching.
Wonderful guidelines, thanks
This is very helpful. Would love to continue even as I prepare for starting my masters next year.
Thanks for the work done, the text was helpful to me
Bundle of thanks to you for the research proposal guide it was really good and useful if it is possible please send me the sample of research proposal
You’re most welcome. We don’t have any research proposals that we can share (the students own the intellectual property), but you might find our research proposal template useful: https://gradcoach.com/research-proposal-template/
Cheruiyot Moses Kipyegon
Thanks alot. It was an eye opener that came timely enough before my imminent proposal defense. Thanks, again
thank you very much your lesson is very interested may God be with you
I am an undergraduate student (First Degree) preparing to write my project,this video and explanation had shed more light to me thanks for your efforts keep it up.
Very useful. I am grateful.
this is a very a good guidance on research proposal, for sure i have learnt something
Wonderful guidelines for writing a research proposal, I am a student of m.phil( education), this guideline is suitable for me. Thanks
You’re welcome 🙂
Thank you, this was so helpful.
A really great and insightful video. It opened my eyes as to how to write a research paper. I would like to receive more guidance for writing my research paper from your esteemed faculty.
Thank you, great insights
Thank you, great insights, thank you so much, feeling edified
Wow thank you, great insights, thanks a lot
Thank you. This is a great insight. I am a student preparing for a PhD program. I am requested to write my Research Proposal as part of what I am required to submit before my unconditional admission. I am grateful having listened to this video which will go a long way in helping me to actually choose a topic of interest and not just any topic as well as to narrow down the topic and be specific about it. I indeed need more of this especially as am trying to choose a topic suitable for a DBA am about embarking on. Thank you once more. The video is indeed helpful.
Have learnt a lot just at the right time. Thank you so much.
thank you very much ,because have learn a lot things concerning research proposal and be blessed u for your time that you providing to help us
Hi. For my MSc medical education research, please evaluate this topic for me: Training Needs Assessment of Faculty in Medical Training Institutions in Kericho and Bomet Counties
I have really learnt a lot based on research proposal and it’s formulation
Thank you. I learn much from the proposal since it is applied
Your effort is much appreciated – you have good articulation.
You have good articulation.
I do applaud your simplified method of explaining the subject matter, which indeed has broaden my understanding of the subject matter. Definitely this would enable me writing a sellable research proposal.
This really helping
Great! I liked your tutoring on how to find a research topic and how to write a research proposal. Precise and concise. Thank you very much. Will certainly share this with my students. Research made simple indeed.
Thank you very much. I an now assist my students effectively.
Thank you very much. I can now assist my students effectively.
I need any research proposal
Thank you for these videos. I will need chapter by chapter assistance in writing my MSc dissertation
Very helpfull
the videos are very good and straight forward
thanks so much for this wonderful presentations, i really enjoyed it to the fullest wish to learn more from you
Thank you very much. I learned a lot from your lecture.
I really enjoy the in-depth knowledge on research proposal you have given. me. You have indeed broaden my understanding and skills. Thank you
interesting session this has equipped me with knowledge as i head for exams in an hour’s time, am sure i get A++
This article was most informative and easy to understand. I now have a good idea of how to write my research proposal.
Thank you very much.
Wow, this literature is very resourceful and interesting to read. I enjoyed it and I intend reading it every now then.
Thank you for the clarity
Thank you. Very helpful.
Thank you very much for this essential piece. I need 1o1 coaching, unfortunately, your service is not available in my country. Anyways, a very important eye-opener. I really enjoyed it. A thumb up to Gradcoach
What is JAM? Please explain.
Thank you so much for these videos. They are extremely helpful! God bless!
very very wonderful…
thank you for the video but i need a written example
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
How Should I Shape and Defend My Proposal?
- First Online: 28 June 2019
Cite this chapter

- Ray Cooksey 3 &
- Gael McDonald 4
1716 Accesses
This chapter discusses considerations surrounding the production of your research proposal. Your proposal will be required in the early stages of your candidature and is, essentially, a detailed plan of your anticipated postgraduate research journey in the context of the degree program you are enrolled in. In your proposal, you detail ‘ what ’ you intend to study in the form of the topic and research questions and ‘ why ’ (contextualisation and positioning, anticipated contribution(s), potential limitations), and ‘ how ’ (guiding assumptions, research frame, research configuration, sampling and data gathering and analysis strategies) you will obtain the answers to your questions. Your goal is to convince relevant stakeholders that your planned research has a high likelihood of achieving its goals, will add value as an original contribution, will demonstrate your capabilities as a competent researcher, and, most importantly, will likely lead to successful completion of the postgraduate program in which you are enrolled.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Durable hardcover edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Cooksey, R. W. (2008). Paradigm-independent meta-criteria for social & behavioural research. Proceedings of the 2nd Annual Postgraduate Research Conference , University of New England, Armidale, NSW, pp. 4–17.
Google Scholar
Dadich, A., & Fitzgerald, A. (2006). Qualitative research in the making: A practical guide to project design . Paper presented at the ACSPRI Social Science Methodology Conference, Sydney, Australia.
Finn, J. A. (2005). Getting a PhD: An action plan to help manage your research, your supervisor and your project . London: Routledge.
Book Google Scholar
Hamper, R. J., & Baugh, L. (2010). Handbook for writing proposals (2nd ed.). New York: McGraw-Hill Education.
Jay, R. (2000). How to write proposals and reports that get results: Master the skills of business writing (Rev. ed.). London: Prentice Hall.
Kilbourn, B. (2006). The qualitative doctoral dissertation proposal. Teachers College Record, 108 (4), 529–576.
Article Google Scholar
Krathwohl, D. R., & Smith, N. L. (2005). How to prepare a dissertation proposal . Syracuse, NY: Syracuse University Press.
Locke, L., Spirduso, W., & Silverman, S. (2014). Proposals that work: A guide for planning dissertations and grant proposals (6th ed.). Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications.
Lockhart, J. C., & Stablein, R. E. (2002). Spanning the academy-practice divide with doctoral education in business. Higher Education Research & Development, 21 (2), 191–202.
O’Leary, Z. (2017). Doing your research project (3rd ed.). Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications.
Panda, A., & Gupta, R. K. (2014). Making academic research more relevant: A few suggestions. IIMB Management Review, 26 (3), 156–169.
Peters, R. (1997). Getting what you came for: The smart student’s guide to earning a Master’s or a Ph.D. (Rev. ed.). New York: Noonday Press.
Polonsky, J. M., & Waller, S. D. (2015). Designing and managing a research project: A business student’s guide (3rd ed.). Los Angeles: Sage Publications.
Punch, K. F. (2016). Developing effective research proposals (3rd ed.). Los Angeles: Sage Publications.
Sternberg, R. (2014). Writing successful grant proposals from the top down and the bottom up . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications.
Stewart, A. L., & Stewart, R. D. (1993). Proposal preparation (2nd ed.). New Jersey: Wiley.
Stokes, P., & Wall, T. (2014). Research methods . London: Palgrave.
Tammemagi, H. (2010). Winning proposals: How to write them and get better results (3rd ed.). North Vancouver, CA: Self-Counsel Press Inc.
Walker, R. (2014). Writing a research proposal . Retrieved October 27, 2018, from http://transnationalteachingteams.org/documents/Toolbox%207/Writing_A_Research_Proposal.pdf .
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
UNE Business School, University of New England, Armidale, NSW, Australia
Ray Cooksey
RMIT University Vietnam, Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam
Gael McDonald
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Ray Cooksey .
Appendix: Research Proposal Check List
To recap, the intention of your research proposal is to cover a number of key questions, including:
What are the purpose and aims of the research?
What is your broad research problem?
What are your specific research questions/hypotheses?
What prior research is relevant to the area of study?
What areas of theory inform those research questions?
What is the underlying epistemology and guiding assumptions?
How are you positioning your research?
What is the theoretical or conceptual framework (where appropriate to have one)?
What data gathering strategies are you are going to use (and do you have a Plan B)?
How will you pilot test or trial your research approach?
How will you go about addressing each research question?
How will you approach the sampling of data sources, including how you will negotiate access via relevant gatekeepers (and do you have a Plan B)?
How will you address any ethical concerns and expectations?
What form of analysis and data displays are you considering?
What do you think are the intended outcomes?
What are the potential strengths and weaknesses of the data sources and what does this mean for your research plan?
What might be the benefit or value of this research and for whom?
What do you anticipate might be the limitations of the research plan?
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2019 Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this chapter
Cooksey, R., McDonald, G. (2019). How Should I Shape and Defend My Proposal?. In: Surviving and Thriving in Postgraduate Research. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-7747-1_16
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-7747-1_16
Published : 28 June 2019
Publisher Name : Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN : 978-981-13-7746-4
Online ISBN : 978-981-13-7747-1
eBook Packages : Education Education (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
- The Open University
- Guest user / Sign out
- Study with The Open University
My OpenLearn Profile
Personalise your OpenLearn profile, save your favourite content and get recognition for your learning

Addressing ethical issues in your research proposal
This article explores the ethical issues that may arise in your proposed study during your doctoral research degree.
What ethical principles apply when planning and conducting research?
Research ethics are the moral principles that govern how researchers conduct their studies (Wellcome Trust, 2014). As there are elements of uncertainty and risk involved in any study, every researcher has to consider how they can uphold these ethical principles and conduct the research in a way that protects the interests and welfare of participants and other stakeholders (such as organisations).
You will need to consider the ethical issues that might arise in your proposed study. Consideration of the fundamental ethical principles that underpin all research will help you to identify the key issues and how these could be addressed. As you are probably a practitioner who wants to undertake research within your workplace, consider how your role as an ‘insider’ influences how you will conduct your study. Think about the ethical issues that might arise when you become an insider researcher (for example, relating to trust, confidentiality and anonymity).
What key ethical principles do you think will be important when planning or conducting your research, particularly as an insider? Principles that come to mind might include autonomy, respect, dignity, privacy, informed consent and confidentiality. You may also have identified principles such as competence, integrity, wellbeing, justice and non-discrimination.
Key ethical issues that you will address as an insider researcher include:
- Gaining trust
- Avoiding coercion when recruiting colleagues or other participants (such as students or service users)
- Practical challenges relating to ensuring the confidentiality and anonymity of organisations and staff or other participants.
(Heslop et al, 2018)
A fuller discussion of ethical principles is available from the British Psychological Society’s Code of Human Research Ethics (BPS, 2021).
You can also refer to guidance from the British Educational Research Association and the British Association for Applied Linguistics .

Ethical principles are essential for protecting the interests of research participants, including maximising the benefits and minimising any risks associated with taking part in a study. These principles describe ethical conduct which reflects the integrity of the researcher, promotes the wellbeing of participants and ensures high-quality research is conducted (Health Research Authority, 2022).
Research ethics is therefore not simply about gaining ethical approval for your study to be conducted. Research ethics relates to your moral conduct as a doctoral researcher and will apply throughout your study from design to dissemination (British Psychological Society, 2021). When you apply to undertake a doctorate, you will need to clearly indicate in your proposal that you understand these ethical principles and are committed to upholding them.
Where can I find ethical guidance and resources?
Professional bodies, learned societies, health and social care authorities, academic publications, Research Ethics Committees and research organisations provide a range of ethical guidance and resources. International codes such as the Universal Declaration of Human Rights underpin ethical frameworks (United Nations, 1948).
You may be aware of key legislation in your own country or the country where you plan to undertake the research, including laws relating to consent, data protection and decision-making capacity, for example, the Data Protection Act, 2018 (UK). If you want to find out more about becoming an ethical researcher, check out this Open University short course: Becoming an ethical researcher: Introduction and guidance: What is a badged course? - OpenLearn - Open University
You should be able to justify the research decisions you make. Utilising these resources will guide your ethical judgements when writing your proposal and ultimately when designing and conducting your research study. The Ethical Guidelines for Educational Research (British Educational Research Association, 2018) identifies the key responsibilities you will have when you conduct your research, including the range of stakeholders that you will have responsibilities to, as follows:
- to your participants (e.g. to appropriately inform them, facilitate their participation and support them)
- clients, stakeholders and sponsors
- the community of educational or health and social care researchers
- for publication and dissemination
- your wellbeing and development
The National Institute for Health and Care Research (no date) has emphasised the need to promote equality, diversity and inclusion when undertaking research, particularly to address long-standing social and health inequalities. Research should be informed by the diversity of people’s experiences and insights, so that it will lead to the development of practice that addresses genuine need. A commitment to equality, diversity and inclusion aims to eradicate prejudice and discrimination on the basis of an individual or group of individuals' protected characteristics such as sex (gender), disability, race, sexual orientation, in line with the Equality Act 2010.
The NIHR has produced guidance for enhancing the inclusion of ‘under-served groups’ when designing a research study (2020). Although the guidance refers to clinical research it is relevant to research more broadly.
You should consider how you will promote equality and diversity in your planned study, including through aspects such as your research topic or question, the methodology you will use, the participants you plan to recruit and how you will analyse and interpret your data.
What ethical issues do I need to consider when writing my research proposal?

You might be planning to undertake research in a health, social care, educational or other setting, including observations and interviews. The following prompts should help you to identify key ethical issues that you need to bear in mind when undertaking research in such settings.
1. Imagine you are a potential participant. Think about the questions and concerns that you might have:
- How would you feel if a researcher sat in your space and took notes, completed a checklist, or made an audio or film recording?
- What harm might a researcher cause by observing or interviewing you and others?
- What would you want to know about the researcher and ask them about the study before giving consent?
- When imagining you are the participant, how could the researcher make you feel more comfortable to be observed or interviewed?
2. Having considered the perspective of your potential participant, how would you take account of concerns such as privacy, consent, wellbeing and power in your research proposal?
[Adapted from OpenLearn course: Becoming an ethical researcher, Week 2 Activity 3: Becoming an ethical researcher - OpenLearn - Open University ]
The ethical issues to be considered will vary depending on your organisational context/role, the types of participants you plan to recruit (for example, children, adults with mental health problems), the research methods you will use, and the types of data you will collect. You will need to decide how to recruit your participants so you do not inappropriately exclude anyone. Consider what methods may be necessary to facilitate their voice and how you can obtain their consent to taking part or ensure that consent is obtained from someone else as necessary, for example, a parent in the case of a child.
You should also think about how to avoid imposing an unnecessary burden or costs on your participants. For example, by minimising the length of time they will have to commit to the study and by providing travel or other expenses. Identify the measures that you will take to store your participants’ data safely and maintain their confidentiality and anonymity when you report your findings. You could do this by storing interview and video recordings in a secure server and anonymising their names and those of their organisations using pseudonyms.
Professional codes such as the Code of Human Research Ethics (BPS, 2021) provide guidance on undertaking research with children. Being an ‘insider’ researching within your own organisation has advantages. However, you should also consider how this might impact on your research, such as power dynamics, consent, potential bias and any conflict of interest between your professional and researcher roles (Sapiro and Matthews, 2020).
How have other researchers addressed any ethical challenges?
The literature provides researchers’ accounts explaining how they addressed ethical challenges when undertaking studies. For example, Turcotte-Tremblay and McSween-Cadieux (2018) discuss strategies for protecting participants’ confidentiality when disseminating findings locally, such as undertaking fieldwork in multiple sites and providing findings in a generalised form. In addition, professional guidance includes case studies illustrating how ethical issues can be addressed, including when researching online forums (British Sociological Association, no date).
Watch the videos below and consider what insights the postgraduate researcher and supervisor provide regarding issues such as being an ‘insider researcher’, power relations, avoiding intrusion, maintaining participant anonymity and complying with research ethics and professional standards. How might their experiences inform the design and conduct of your own study?
Postgraduate researcher and supervisor talk about ethical considerations
Your thoughtful consideration of the ethical issues that might arise and how you would address these should enable you to propose an ethically informed study and conduct it in a responsible, fair and sensitive manner.
British Educational Research Association (2018) Ethical Guidelines for Educational Research. Available at: https://www.bera.ac.uk/publication/ethical-guidelines-for-educational-research-2018 (Accessed: 9 June 2023).
British Psychological Society (2021) Code of Human Research Ethics . Available at: https://cms.bps.org.uk/sites/default/files/2022-06/BPS%20Code%20of%20Human%20Research%20Ethics%20%281%29.pdf (Accessed: 9 June 2023).
British Sociological Association (2016) Researching online forums . Available at: https://www.britsoc.co.uk/media/24834/j000208_researching_online_forums_-cs1-_v3.pdf (Accessed: 9 June 2023).
Health Research Authority (2022) UK Policy Framework for Health and Social Care Research . Available at: https://www.hra.nhs.uk/planning-and-improving-research/policies-standards-legislation/uk-policy-framework-health-social-care-research/uk-policy-framework-health-and-social-care-research/#chiefinvestigators (Accessed: 9 June 2023).
Heslop, C., Burns, S., Lobo, R. (2018) ‘Managing qualitative research as insider-research in small rural communities’, Rural and Remote Health , 18: pp. 4576.
Equality Act 2010, c. 15. Available at: https://www.legislation.gov.uk/ukpga/2010/15/introduction (Accessed: 9 June 2023).
National Institute for Health and Care Research (no date) Equality, Diversity and Inclusion (EDI) . Available at: https://arc-kss.nihr.ac.uk/public-and-community-involvement/pcie-guide/how-to-do-pcie/equality-diversity-and-inclusion-edi (Accessed: 9 June 2023).
National Institute for Health and Care Research (2020) Improving inclusion of under-served groups in clinical research: Guidance from INCLUDE project. Available at: https://www.nihr.ac.uk/documents/improving-inclusion-of-under-served-groups-in-clinical-research-guidance-from-include-project/25435 (Accessed: 9 June 2023).
Sapiro, B. and Matthews, E. (2020) ‘Both Insider and Outsider. On Conducting Social Work Research in Mental Health Settings’, Advances in Social Work , 20(3). Available at: https://doi.org/10.18060/23926
Turcotte-Tremblay, A. and McSween-Cadieux, E. (2018) ‘A reflection on the challenge of protecting confidentiality of participants when disseminating research results locally’, BMC Medical Ethics, 19(supplement 1), no. 45. Available at: https://bmcmedethics.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12910-018-0279-0
United Nations General Assembly (1948) The Universal Declaration of Human Rights . Resolution A/RES/217/A. Available at: https://www.un.org/en/about-us/universal-declaration-of-human-rights#:~:text=Drafted%20by%20representatives%20with%20different,all%20peoples%20and%20all%20nations . (Accessed: 9 June 2023).
Wellcome Trust (2014) Ensuring your research is ethical: A guide for Extended Project Qualification students . Available at: https://wellcome.org/sites/default/files/wtp057673_0.pdf (Accessed: 9 June 2023).
More articles from the research proposal collection

Writing your research proposal
A doctoral research degree is the highest academic qualification that a student can achieve. The guidance provided in these articles will help you apply for one of the two main types of research degree offered by The Open University.
Level: 1 Introductory

Defining your research methodology
Your research methodology is the approach you will take to guide your research process and explain why you use particular methods. This article explains more.

Writing your proposal and preparing for your interview
The final article looks at writing your research proposal - from the introduction through to citations and referencing - as well as preparing for your interview.
Free courses on postgraduate study

Are you ready for postgraduate study?
This free course, Are you ready for postgraduate study, will help you to become familiar with the requirements and demands of postgraduate study and ensure you are ready to develop the skills and confidence to pursue your learning further.

Succeeding in postgraduate study
This free course, Succeeding in postgraduate study, will help you to become familiar with the requirements and demands of postgraduate study and to develop the skills and confidence to pursue your learning further.

Applying to study for a PhD in psychology
This free OpenLearn course is for psychology students and graduates who are interested in PhD study at some future point. Even if you have met PhD students and heard about their projects, it is likely that you have only a vague idea of what PhD study entails. This course is intended to give you more information.
Become an OU student
Ratings & comments, share this free course, copyright information, publication details.
- Originally published: Tuesday, 27 June 2023
- Body text - Creative Commons BY-NC-SA 4.0 : The Open University
- Image 'Pebbles balance on a stone see-saw' - Copyright: Photo 51106733 / Balance © Anatoli Styf | Dreamstime.com
- Image 'Camera equipment set up filming a man talking' - Copyright: Photo 42631221 © Gabriel Robledo | Dreamstime.com
- Image 'Applying to study for a PhD in psychology' - Copyright free
- Image 'Succeeding in postgraduate study' - Copyright: © Everste/Getty Images
- Image 'Addressing ethical issues in your research proposal' - Copyright: Photo 50384175 / Children Playing © Lenutaidi | Dreamstime.com
- Image 'Writing your proposal and preparing for your interview' - Copyright: Photo 133038259 / Black Student © Fizkes | Dreamstime.com
- Image 'Defining your research methodology' - Copyright free
- Image 'Writing your research proposal' - Copyright free
- Image 'Are you ready for postgraduate study?' - Copyright free
Rate and Review
Rate this article, review this article.
Log into OpenLearn to leave reviews and join in the conversation.
Article reviews
For further information, take a look at our frequently asked questions which may give you the support you need.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- PLoS Comput Biol
- v.16(4); 2020 Apr

Ten simple rules for innovative dissemination of research
Tony ross-hellauer.
1 Open and Reproducible Research Group, Institute of Interactive Systems and Data Science, Graz University of Technology and Know-Center GmbH, Graz, Austria
Jonathan P. Tennant
2 Center for Research and Interdisciplinarity, University of Paris, Paris, France
Viltė Banelytė
3 Freelance Researcher, Vilnius, Lithuania
Edit Gorogh
4 University and National Library, University of Debrecen, Debrecen, Hungary
Daniela Luzi
5 Institute for Research on Population and Social Policies, National Research Council, Rome, Italy
Peter Kraker
6 Open Knowledge Maps, Vienna, Austria
Lucio Pisacane
Roberta ruggieri, electra sifacaki.
7 National and Kapodistrian University of Athens, Athens, Greece
Michela Vignoli
8 Center for Digital Safety and Security, AIT Austrian Institute of Technology, Vienna, Austria
Author summary
How we communicate research is changing because of new (especially digital) possibilities. This article sets out 10 easy steps researchers can take to disseminate their work in novel and engaging ways, and hence increase the impact of their research on science and society.
Introduction
As with virtually all areas of life, research dissemination has been disrupted by the internet and digitally networked technologies. The last two decades have seen the majority of scholarly journals move online, and scholarly books are increasingly found online as well as in print. However, these traditional communication vehicles have largely retained similar functions and formats during this transition. But digital dissemination can happen in a variety of ways beyond the traditional modes: social media have become more widely used among researchers [ 1 , 2 , 3 ], and the use of blogs and wikis as a specific form of ‘open notebook science’ has been popular for more than a decade [ 4 ].
Professional academic social networks such as ResearchGate and Academia.edu boast millions of users. New online formats for interaction with the wider public, such as TED talks broadcast via YouTube, often receive millions of views. Some researchers have even decided to make all of their research findings public in real time by keeping open notebooks [ 5 , 6 ]. In particular, digital technologies invoke new ways of reaching and involving audiences beyond their usual primary dissemination targets (i.e., other scholars) to actively involve peers or citizens who would otherwise remain out of reach for traditional methods of communication [ 7 ]. Adoption of these outlets and methods can also lead to new cross-disciplinary collaborations, helping to create new research, publication, and funding opportunities [ 8 ].
Beyond the increase in the use of web-based and computational technologies, other trends in research cultures have had a profound effect on dissemination. The push towards greater public understanding of science and research since the 1980s, and an emphasis on engagement and participation of non-research audiences have brought about new forms of dissemination [ 9 ]. These approaches include popular science magazines and science shows on television and the radio. In recent years, new types of events have emerged that aim at involving the general public within the research process itself, including science slams and open lab days. With science cafés and hackerspaces, novel, participatory spaces for research production and dissemination are emerging—both online and offline. Powerful trends towards responsible research and innovation, the increasing globalisation of research, and the emergence and inclusion of new or previously excluded stakeholders or communities are also reshaping the purposes of dissemination as well as the scope and nature of its audiences.
Many now view wider dissemination and public engagement with science to be a fundamental element of open science [ 10 ]. However, there is a paradox at play here, for while there have never been more avenues for the widespread dissemination of research, researchers tend nonetheless to value and focus upon just a few traditional outputs: journal articles, books, and conference presentations [ 11 ].
Following Wilson and colleagues [ 12 ], we here define research dissemination as a planned process that involves consideration of target audiences, consideration of the settings in which research findings are to be received, and communicating and interacting with wider audiences in ways that will facilitate research uptake and understanding. Innovative dissemination, then, means dissemination that goes beyond traditional academic publishing (e.g., academic journals, books, or monographs) and meetings (conferences and workshops) to achieve more widespread research uptake and understanding. Hence, a citizen science project, which involves citizens in data collection but does not otherwise educate them about the research, is not here considered innovative dissemination.
We here present 10 steps researchers can take to embrace innovative dissemination practices in their research, either as individuals or groups ( Fig 1 ). They represent the synthesis of multidimensional research activities undertaken within the OpenUP project ( https://www.openuphub.eu/ ). This European Coordination and Support Action grant award addressed key aspects and challenges of the currently transforming science landscape and proposed recommendations and solutions addressing the needs of researchers, innovators, the public, and funding bodies. The goal is to provide stakeholders (primarily researchers but also intermediaries) with an entry point to innovative dissemination, so that they can choose methods and tools based on their audience, their skills, and their requirements. The advice is directed towards both individual researchers and research teams or projects. It is similar to other entries in the Ten Simple Rules series (e.g., [ 13 , 14 ]). Ultimately, the benefit here for researchers is increased recognition and social impact of their work.

Rule 1: Get the basics right
Despite changes in communication technologies and models, there are some basic organisational aspects of dissemination that remain important: to define objectives, map potential target audience(s), target messages, define mode of communication/engagement, and create a dissemination plan. These might seem a bit obvious or laborious but are critical first steps towards strategically planning a project.
Define objectives
The motivation to disseminate research can come in many forms. You might want to share your findings with wider nonacademic audiences to raise awareness of particular issues or invite audience engagement, participation, and feedback. Start by asking yourself what you want to achieve with your dissemination. This first strategic step will make all other subsequent steps much simpler, as well as guide how you define the success of your activities.
Map your audience
Specify who exactly you want your research results to reach, for which purposes, and what their general characteristics might be (e.g., policy makers, patient groups, non-governmental organisations). Individuals are not just ‘empty vessels’ to be filled with new knowledge, and having a deeper contextual understanding of your audience can make a real difference to the success of your engagement practices. Who is most affected by your research? Who might find it most valuable? What is it that you want them to take away? Get to know your target audiences, their needs and expectations of the research outcomes, as well as their preferred communication channels to develop a detailed understanding of their interests and align your messages and media with their needs and priorities. Keep in mind, too, that intermediaries such as journalists or science communication organisations can support or mediate the dissemination process.
Target/frame your messages
Target and frame the key messages that you want to communicate to specific groups. Think first from the perspective of what they might want or need to hear from you, rather than what you want to tell them. Choosing media and format of your communication strongly depends on your communication objectives, i.e., what you want to achieve. There are many ways to communicate your research; for example, direct messages, blog/vlog posts, tweeting about it, or putting your research on Instagram. Form and content go hand in hand. Engage intermediaries and leverage any relevant existing networks to help amplify messages.
Create a dissemination plan
Many funded research projects require a dissemination plan. However, even if not, the formal exercise of creating a plan at the outset that organises dissemination around distinct milestones in the research life cycle will help you to assign roles, structure activities, as well as plan funds to be allocated in your dissemination. This will ultimately save you time and make future work easier. If working in groups, distribute tasks and effort to ensure regular updates of content targeted to different communities. Engage those with special specific skills in the use and/or development of appropriate communication tools, to help you in using the right language and support you in finding the suitable occasions to reach your identified audience. Research is not linear, however, and so you might find it best to treat the plan as a living document to be flexibly adapted as the direction of research changes.
Rule 2: Keep the right profile
Whether communicating as an individual researcher, a research project, or a research organisation, establishing a prominent and unique identity online and offline is essential for communicating. Use personal websites, social media accounts, researcher identifiers, and academic social networks to help make you and your research visible. When doing this, try to avoid any explicit self-promotion—your personal profile naturally will develop based on your ability to be an effective and impactful communicator.
Academia is a prestige economy, where individual researchers are often evaluated based on their perceived esteem or standing within their communities [ 15 ]. Remaining visible is an essential part of accumulating esteem. An online presence maintained via personal websites, social media accounts (e.g., Facebook, Twitter, LinkedIn), researcher identifiers (e.g., ORCID), and academic social networks (e.g., ResearchGate, institutional researcher profiles) can be a personal calling card, where you can highlight experience and demonstrate your expertise in certain topics. Being active on important mailing lists, forums, and social media is not only a good chance to disseminate your findings to those communities but also offers you the chance to engage with your community and potentially spark new ideas and collaborations.
Using researcher identifiers like ORCID when disseminating outputs will ensure that those outputs will be unambiguously linked back to the individual researcher (and even automatically updated to their ORCID profile). The OpenUP survey showed that nearly half of the respondents (41%) use academic social networks as a medium to disseminate their research, and a quarter of respondents (26%) said that these networks informed their professional work [ 16 ].
Create a brand by giving your project a unique name, ideally with some intuitive relation to the issue you are investigating. Create a striking visual identity, with a compelling logo, core colours, and a project slogan. Create a website that leverages this visual identity and is as simple and intuitive as possible, both in its layout and in the way content is formulated (limit insider jargon). Create associated appropriate social media accounts (e.g., Twitter, Facebook, LinkedIn, SlideShare, YouTube) and link to this from the project website. Aim for a sustained presence with new and engaging content to reinforce project messaging, and this can help to establish a core following group or user base within different platforms. Include links to other project online presences such as social media accounts, or a rolling feed of updates if possible. Consider including a blog to disseminate core findings or give important project updates. A periodical newsletter could be released in order to provide project updates and other news, to keep the community informed and activated regarding project issues. Depending on the size of your project and budget, you might want to produce hard copy material such as leaflets or fact sheets, as well as branded giveaways to increase awareness of your project. Finally, and perhaps most importantly, try not to come across as a ‘scientific robot’, and make sure to communicate the more human personality side of research.
Rule 3: Encourage participation
In the age of open research, don’t just broadcast. Invite and engage others to foster participation and collaboration with research audiences. Scholarship is a collective endeavour, and so we should not expect its dissemination to be unidirectional, especially not in the digital age. Dissemination is increasingly done at earlier stages of the research life cycle, and such wider and more interactive engagement is becoming an integral part of the whole research workflow.
Such participative activities can be as creative as you wish; for example, through games, such as Foldit for protein folding ( https://fold.it/portal/ ). You might even find it useful to actively engage ‘citizen scientists’ in research projects; for example, to collect data or analyse findings. Initiatives such as Zooniverse ( https://www.zooniverse.org/ ) serve as great examples of allowing anyone to freely participate in cutting-edge ‘people-powered research’.
Disseminating early and often showcases the progress of your work and demonstrates productivity and engagement as part of an agile development workflow. People like to see progress and react positively to narrative, so give regular updates to followers on social media, for example, blogging or tweeting early research findings for early feedback. Alternatively, involving businesses early on can align research to industry requirements and expectations, thus potentially increasing commercial impact. In any case, active involvement of citizens and other target audiences beyond academia can help increase the societal impact of your research [ 17 ].
Rule 4: Open science for impact
Open science is ‘transparent and accessible knowledge that is shared and developed through collaborative networks’, as defined by one systematic review [ 18 ]. It encompasses a variety of practices covering a range of research processes and outputs, including areas like open access (OA) to publications, open research data, open source software/tools, open workflows, citizen science, open educational resources, and alternative methods for research evaluation including open peer review [ 19 ]. Open science is rooted in principles of equitable participation and transparency, enabling others to collaborate in, contribute to, scrutinise and reuse research, and spread knowledge as widely as possible [ 20 ]. As such, innovative dissemination is a core element of open science.
Embracing open science principles can boost the impact of research. Firstly, OA publications seem to accrue more citations than their closed counterparts, as well as having a variety of possible wider economic and societal benefits [ 21 ]. There are a number of ways to make research papers OA, including at the journal site itself, or self-archiving an accepted manuscript in a repository or personal website.
Disseminating publications as preprints in advance of or parallel to journal submission can increase impact, as measured by relative citation counts [ 22 ]. Very often, traditional publishing takes a long time, with the waiting time between submission and acceptance of a paper being in excess of 100 days [ 23 ]. Preprinting speeds up dissemination, meaning that findings are available sooner for sharing and reuse. Potential platforms for disseminating preprints include the Open Science Framework, biorXiv, or arXiv.
Dissemination of other open science outputs that would usually remain hidden also not only helps to ensure the transparency and increased reproducibility of research [ 24 ], but also means that more research elements are released that can potentially impact upon others by creating network effects through reuse. Making FAIR (Findable, Accessible, Interoperable, Reusable) research data and code available enables reuse and remixing of core research outputs, which can also lead to further citations for projects [ 25 , 26 , 27 ]. Published research proposals, protocols, and open notebooks act as advertisements for ongoing research and enable others to reuse methods, exposing the continuous and collaborative nature of scholarship.
To enable reuse, embrace open licenses. When it comes to innovative dissemination, the goal is usually that the materials are accessible to as large an audience as possible. If appropriate open licenses are not used, while materials may be free to access, they cannot be widely used, modified, or shared. The best in this case is the widely adopted Creative Commons licenses, CC BY or CC 0. Variations of these licenses are less permissive and can constrain reuse for commercial or derivative purposes. This limitation, however, prevents the use of materials in many forms of (open) educational resources and other open projects, including Wikipedia. Careful consideration should be given to licensing of materials, depending on what your intended outcomes from the project are (see Rule 1). Research institutes and funding bodies typically have a variety of policies and guidance about the use and licensing of such materials, and should be consulted prior to releasing any materials.
Rule 5: Remix traditional outputs
Traditional research outputs like research articles and books can be complemented with innovative dissemination to boost impact; for example, by preparing accompanying nonspecialist summaries, press releases, blog posts, and visual/video abstracts to better reach your target audiences. Free media coverage can be an easy way to get results out to as many people as possible. There are countless media outlets interested in science-related stories. Most universities and large research organisations have an office for public affairs or communication: liaise with these experts to disseminate research findings widely through public media. Consider writing a press release for manuscripts that have been accepted for publication in journals or books and use sample forms and tools available online to assist you in the process. Some journals also have dedicated press teams that might be able to help you with this.
Another useful tool to disseminate traditional research outputs is to release a research summary document. This one- or two-page document clearly and concisely summarises the key conclusions from a research initiative. It can combine several studies by the same investigator or by a research group and should integrate two main components: key findings and fact sheets (preferably with graphical images to illustrate your point). This can be published on your institutional website as well as on research blogs, thematic hubs, or simply posted on your social media profiles. Other platforms such as ScienceOpen and Kudos allow authors to attach nonspecialist summaries to each of their research papers.
To maximise the impact of your conference presentations or posters, there are several steps that can be taken. For instance, you can upload your slides to a general-purpose repository such as Figshare or Zenodo and add a digital object identifier (DOI) to your presentation. This also makes it easier to integrate such outputs with other services like ORCID. You can also schedule tweets before and during any conferences, and use the conference hashtag to publicise your talk or poster. Finally, you can also add information about your contributions to email signatures or out-of-office messages [ 28 ].
Rule 6: Go live
In-person dissemination does not just have to be at stuffy conferences. With research moving beyond the walls of universities, there are several types of places for more participatory events. Next to classic scientific conferences, different types of events addressing wider audiences have emerged. It is possible to hit the road and take part in science festivals, science slams, TEDx talks, or road shows.
Science slams are short talks in which researchers explain a scientific topic to a typically nonexpert audience. Similar to other short talk formats like TED talks, they lend themselves to being spread over YouTube and other video channels. A prominent example from the German-speaking area is Giulia Enders, who won the first prize in a science slam that took place in 2012 in Berlin. The YouTube video of her fascinating talk about the gut has received over 1 million views. After this success, she got an offer to write a book about the gut and the digestive system, which has since been published and translated into many languages. You never know how these small steps might end up having a wider impact on your research and career.
Another example is Science Shops, small entities which provide independent, participatory research support to civil society. While they are usually linked to universities, hacker and maker spaces tend to be community-run locations, where people with an interest in science, engineering, and art meet and collaborate on projects. Science festivals are community-based showcases of science and technology that take place over large areas for several days or weeks and directly involve researchers and practitioners in public outreach. Less formally, Science Cafés or similar events like Pint of Science are public engagement events in casual settings like pubs and coffeehouses.
Alternatively, for a more personal approach, consider reaching out to key stakeholders who might be affected by your research and requesting a meeting, or participating in relevant calls for policy consultations. Such an approach can be especially powerful in getting the message across to decision-makers and thought-leaders, although the resources required to schedule and potentially travel to such meetings means you should target such activities very carefully. And don’t forget the value of serendipity—who knows who you’ll meet in the course of your everyday meetings and travels. Always be prepared with a 30 second ‘elevator pitch’ that sums up your project in a confident and concise manner—such encounters may be the gateways to greater engagement or opportunities.
Rule 7: Think visual
Dissemination of research is still largely ruled by the written or spoken word. However, there are many ways to introduce visual elements that can act as attractive means to help your audience understand and interpret your research. Disseminate findings through art or multimedia interpretations. Let your artistic side loose or use new visualisation techniques to produce intuitive, attractive data displays. Of course, not everyone is a trained artist, and this will be dependent on your personal skills.
Most obviously, this could take the form of data visualisation. Graphic representation of quantitative information reaches back to ‘earliest map-making and visual depiction’ [ 29 ]. As technologies have advanced, so have our means of visually representing data.
If your data visualisations could be considered too technical and not easily understandable by a nonexpert reader, consider creating an ad hoc image for this document; sometimes this can also take the form of a graphical abstract or infographic. Use online tools to upload a sample of your data and develop smart graphs and infographics (e.g., Infogr.am, Datawrapper, Easel.ly, or Venngage).
Science comics can be used, in the words of McDermott, Partridge, and Bromberg [ 30 ], to ‘communicate difficult ideas efficiently, illuminate obscure concepts, and create a metaphor that can be much more memorable than a straightforward description of the concept itself’. McDermott and colleagues continue that comics can be used to punctuate or introduce papers or presentations and to capture and share the content of conference talks, and that some journals even have a ‘cartoon’ publication category. They advise that such content has a high chance of being ‘virally’ spread via social media.
As previously discussed, you may also consider creating a video abstract for a paper or project. However, as with all possible methods, it is worth considering the relative costs versus benefits of such an approach. Creating a high-quality video might have more impact than, say, a blog post but could be more costly to produce.
Projects have even successfully disseminated scientific findings through art. For example, The Civilians—a New York–based investigative theatre company—received a three-year grant to develop The Great Immensity , a play addressing the complexity of climate change. AstroDance tells the story of the search for gravitational waves through a combination of dance, multimedia, sound, and computer simulations. The annual Dance Your PhD contest, which began in 2007 and is sponsored by Science magazine, even asks scientists to interpret their PhD research as dance. This initiative receives approximately 50 submissions a year, demonstrating the popularity of novel forms of research dissemination.
Rule 8: Respect diversity
The academic discourse on diversity has always included discussions on gender, ethnic and cultural backgrounds, digital literacy, and epistemic, ideological, or economic diversity. An approach that is often taken is to include as many diverse groups into research teams as possible; for example, more women, underrepresented minorities, or persons from developing countries. In terms of scientific communication, however, not only raising awareness about diversity issues but also increasing visibility of underrepresented minorities in research or including more women in science communication teams should be considered, and embedded in projects from the outset. Another important aspect is assessing how the communication messages are framed, and if the chosen format and content is appropriate to address and respect all audiences. Research should reach all who might be affected by it. Respect inclusion in scientific dissemination by creating messages that reflect and respect diversity regarding factors like gender, demography, and ability. Overcoming geographic barriers is also important, as well as the consideration of differences in time zones and the other commitments that participants might have. As part of this, it is a key responsibility to create a healthy and welcoming environment for participation. Having things such as a code of conduct, diversity statement, and contributing guidelines can really help provide this for projects.
The 2017 Progression Framework benchmarking report of the Scientific Council made several recommendations on how to make progress on diversity and inclusion in science: (1) A strategy and action plan for diversity should developed that requires action from all members included and (2) diversity should be included in a wide range of scientific activities, such as building diversity into prizes, awards, or creating guidance on building diversity and inclusion across a range of demographics groups into communications, and building diversity and inclusion into education and training.
Rule 9: Find the right tools
Innovative dissemination practices often require different resources and skills than traditional dissemination methods. As a result of different skills and tools needed, there may be higher costs associated with some aspects of innovative dissemination. You can find tools via a more-complete range of sources, including the OpenUP Hub. The Hub lists a catalogue of innovative dissemination services, organised according to the following categories, with some suggested tools:
- Visualising data: tools to help create innovative visual representations of data (e.g., Nodegoat, DataHero, Plot.ly)
- Sharing notebooks, protocols, and workflows: ways to share outputs that document and share research processes, including notebooks, protocols, and workflows (e.g., HiveBench, Protocols.io, Open Notebook Science Network)
- Crowdsourcing and collaboration: platforms that help researchers and those outside academia to come together to perform research and share ideas (e.g., Thinklab, Linknovate, Just One Giant Lab)
- Profiles and networking: platforms to raise academic profile and find collaboration and funding opportunities with new partners (e.g., Humanities Commons, ORCID, ImpactStory)
- Organiding events: tools to help plan, facilitate, and publicise academic events (e.g., Open Conference Systems, Sched, ConfTool)
- Outreach to wider public: channels to help broadcast your research to audiences beyond academia, including policy makers, young people, industry, and broader society (e.g., Famelab, Kudos, Pint of Science)
- Publishing: platforms, tools, and services to help you publish your research (e.g., Open Science Framework, dokieli, ScienceMatters)
- Archive and share: preprint servers and repositories to help you archive and share your texts, data, software, posters, and more (e.g., BitBucket, GitHub, RunMyCode)
The Hub here represents just one attempt to create a registry of resources related to scholarly communication. A similar project is the 101 Innovations in Scholarly Communication project, which contains different tools and services for all parts of a generalised research workflow, including dissemination and outreach. This can be broadly broken down into services for communication through social media (e.g., Twitter), as well as those designed for sharing of scholarly outputs, including posters and presentations (e.g., Zenodo or Figshare). The Open Science MOOC has also curated a list of resources for its module on Public Engagement with Science, and includes key research articles, organisations, and services to help with wider scientific engagement.
Rule 10: Evaluate, evaluate, evaluate
Assess your dissemination activities. Are they having the right impact? If not, why not? Evaluation of dissemination efforts is an essential part of the process. In order to know what worked and which strategies did not generate the desired outcomes, all the research activities should be rigorously assessed. Such evaluation should be measured via the use of a combination of quantitative and qualitative indicators (which should be already foreseen in the planning stage of dissemination; see Rule 1). Questionnaires, interviews, observations, and assessments could also be used to measure the impact. Assessing and identifying the most successful practices will give you the evidence for the most effective strategies to reach your audience. In addition, the evaluation can help you plan your further budget and minimise the spending and dedicating efforts on ineffective dissemination methods.
Some examples of quantitative indicators include the following:
- Citations of publications;
- alternative metrics related to websites and social media platforms (updates, visits, interactions, likes, and reposts);
- numbers of events held for specific audiences;
- numbers of participants in those events;
- production and circulation of printed materials;
- media coverage (articles in specialised press newsletters, press releases, interviews, etc.); and
- how much time and effort were spent on activities.
Some examples of qualitative indicators include the following:
- Visibility in the social media and attractiveness of website;
- newly established contacts with networks and partners and the outcomes of these contacts;
- feedback from the target groups; and
- share feedback within your group on what dissemination strategies seemed to be the most effective in conveying your messages and reaching your target audiences.
We recognise that researchers are usually already very busy, and we do not seek to pressurise them further by increasing their burdens. Our recommendations, however, come at a time when there are shifting norms in how researchers are expected to engage with society through new technologies. Researchers are now often partially evaluated based on such, or expected to include dissemination plans in grant applications. We also do not want to encourage the further fragmentation of scholarship across different platforms and ‘silos’, and therefore we strongly encourage researchers to be highly strategic in how they engage with different methods of innovative dissemination. We hope that these simple rules provide guidance for researchers and their future projects, especially as the tools and services available evolve through time. Some of these suggestions or platforms might not work across all project types, and it is important for researchers to find which methods work best for them.
Acknowledgments
Many thanks to everyone who engaged with the workshops we conducted as part of this grant award.
Funding Statement
This work was partly funded by the OpenUP project, which received funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under grant agreement No. 710722. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Home » Feature » Thesis » 11 Possible Questions in Research Title Defense
11 Possible Questions in Research Title Defense
The research title defense is a part where you will face a panel of evaluators to defend or explain to them what you want to learn about your thesis or proposed research titles. Some schools and institutions organize committees to screen and criticize research titles before they are allowed to proceed with the actual research. Here, you will have a question-and-answer session with a panel of evaluators. This session aims to demonstrate the importance of carrying out the research you have chosen and to determine if you, as a researcher, are truly capable of accomplishing it.
In this post, we will look at the types of questions that may be asked during a research title defense. Understanding these potential questions can help you fully prepare for the first defense of your research journey. Without further ado, here are the possible questions in your research title defense.
Possible Questions and Answers in Research Title Defense
Here are the possible questions that you may encounter during your research title defense and their possible answers.
1. Among the three proposed titles, which one do you highly prefer?
Suppose your research professor asks you to submit three possible titles for your project. During your presentation to the panel, they will ask you: Which of the three titles do you prefer the most?
Some researchers rank their titles according to their preferences. The first one is their top choice, the second one is their backup option, and the third one is their least favorite. So when the panel asks you which title you prefer, you should be honest. Tell them what you really want and why you are passionate about it.
What if you can only submit one title for your project? Well, then you have no choice. You have to defend it and explain why you chose that title for your research.
Sample Answer:
Among the three proposed titles, I highly prefer the title “Exploring the Impact of Renewable Energy Policies on Economic Growth: A Comparative Study.” This title stands out because it focuses on an important and timely topic, the relationship between renewable energy policies and economic growth, which has significant implications for sustainable development. Additionally, the title suggests a research approach that involves a comparative study, indicating a comprehensive analysis of multiple cases or regions. By examining the impact of renewable energy policies on economic growth, this study has the potential to provide valuable insights for policymakers and contribute to the ongoing discourse on the transition to a greener economy.
2. What problem prompted you to propose such study?
The panel will ask you about the source and significance of the problem that you want to address with your research title. You should be able to explain that clearly. If you don’t have a strong justification for your research title and you just say, “I just feel like it,” you may risk getting rejected. Be careful with this question, and make sure you know why you are interested in this topic. You cannot say, “Sir, I don’t have any ideas or inspiration.” That is not an acceptable answer, and it may lead to disapproval.
The problem that prompted me to propose this study is the increasing prevalence of mental health disorders among adolescents. According to the World Health Organization, approximately 10–20% of children and adolescents worldwide experience mental health disorders. This has significant implications for their overall well-being, academic performance, and long-term functioning. The lack of early intervention and effective strategies to address these disorders has contributed to their persistence and negative impact. Therefore, it is crucial to investigate the factors contributing to mental health disorders in adolescents and develop appropriate interventions to mitigate their effects. By understanding the underlying causes and implementing targeted interventions, we can promote the mental well-being of adolescents and enhance their overall quality of life.
3. What possible contributions can this study yield?
The panel wants to know how your study can contribute to the field of knowledge and society. What are the expected outcomes and implications of your research? Who are the stakeholders or beneficiaries of your findings? You should be able to articulate these points clearly. A good proposal should demonstrate the value and significance of your study.
The possible contributions of this study are multi-fold and can significantly advance the existing knowledge in the field. Firstly, this research addresses a critical gap in the literature by investigating [insert specific research focus], thereby expanding the understanding of [insert relevant subject]. This study’s findings will contribute to theoretical frameworks by offering novel insights and perspectives, paving the way for future research, and refining existing theories.
Secondly, the practical implications of this study are noteworthy. The outcomes can inform policymakers, practitioners, and stakeholders involved in [insert relevant field] to make informed decisions and develop effective strategies. By identifying and addressing key issues, this research can potentially improve [insert specific area or practice] and enhance outcomes in [insert relevant domain].
4. What legal bases can you cite to support the proposed study?
You need to cite relevant laws, Republic Acts, or executive orders that back up your research. How can you find those legal bases? You have to search the internet, read, and remember them.
In conducting this research, there are several legal bases that can be cited to support the proposed study. The study aligns with the principle of academic freedom, which is protected under international and national laws, emphasizing the right to pursue research and express ideas freely. It adheres to ethical guidelines and institutional review board regulations, ensuring the protection of human subjects and ethical research practices. Additionally, the study may be supported by specific legal frameworks or regulations that govern the subject matter being investigated, such as Republic Act 10173, the Data Privacy Act of 2012, Republic Act No. 8293, the Intellectual Property Code, or industry-specific regulations. Lastly, the research may be conducted in accordance with the provisions of any relevant local, national, or international laws that govern research activities in the respective field.
5. What do you mean by _______?
The panel asks for meaning or details about the words you used in your title. Be prepared for this question. Whatever words you have used in your title, it is a must that you be able to explain the meaning of these words or phrases.
Cloud computing is a model that enables convenient, on-demand access to a shared pool of computing resources, including networks, servers, storage, applications, and services, that can be rapidly provisioned and released with minimal management effort. It allows users to access and utilize computing resources from anywhere, at any time, using internet connectivity.
6. On what theoretical foundation can you base this study?
Mention a theory or theories to support your title proposal. For example, the Social Identity Theory, the Second Language Acquisition Theory, or perhaps the laws of learning? Prepare one, two, or maybe three theories that you can use to support your proposed study.
The theoretical foundation for this study is grounded in social cognitive theory. Bandura’s social cognitive theory emphasizes the reciprocal interaction between individuals, their environment, and their behavior, highlighting the role of cognitive processes in shaping human actions. This theory provides a framework to understand how individuals acquire knowledge, develop skills, and engage in behaviors through observational learning, self-regulation, and self-efficacy beliefs. By adopting this theoretical perspective, the study aims to explore the cognitive and behavioral mechanisms underlying the phenomenon under investigation, contributing to a comprehensive understanding of the topic.
7. What are your variables?
In our research, we have variables. These variables refer to the factors or attributes that can vary or change throughout the study. They are the measurable or manipulable elements that have an impact on the research outcomes. The variables can be classified into independent variables (manipulated or controlled factors) and dependent variables (measured or observed outcomes).
Check your study which one is the dependent variable and which one is the independent variable. Remember, the independent variable is the cause, and the dependent variable is the effect. As a result, whatever changes take place in your independent variable also affect your dependent variable.
The variables in my study on the effects of exercise on cardiovascular health are exercise and cardiovascular health. The independent variable in this study is exercise, specifically the type, duration, intensity, and frequency of exercise. The dependent variable is cardiovascular health, measured through indicators such as blood pressure, heart rate, cholesterol levels, and aerobic capacity.
8. What findings/results do you intend to gather?
In your defense, if you are asked the question, “What findings/results do you intend to gather?” you can provide a strong answer by emphasizing the specific goals and objectives of your research. Here’s an example response:
“In my research, I aim to gather significant findings and results that contribute to our understanding of [insert your research topic]. By conducting a comprehensive analysis of [describe the data, variables, or sources you will be studying], I anticipate uncovering valuable insights regarding [highlight the key aspects or phenomena you will be investigating]. Through rigorous data collection and analysis methods, I intend to identify patterns, correlations, or trends that shed light on [specific research questions or hypotheses]. Ultimately, my goal is to generate new knowledge and contribute to the existing body of literature in the field of [your research area]. I anticipate that my findings will provide valuable implications for [mention potential applications or implications of your research], offering practical benefits to [identify the stakeholders or beneficiaries].”
Remember to tailor your response to your specific research topic and objectives. This answer showcases your intention to make meaningful contributions to the field and highlights the potential impact of your findings.
9. What is the essence of your proposed study?
When asked about the essence of your proposed study, you can provide a comprehensive and concise answer that highlights the significance and purpose of your research. Here’s an example of a good answer:
“The essence of my proposed study lies in addressing a critical gap in our understanding of [insert your research topic]. By examining [briefly describe the main focus or objectives of your study], my research aims to contribute to the existing body of knowledge in this field and provide valuable insights into [mention the potential impact or implications of your study]. Through rigorous data collection, analysis, and interpretation, I intend to shed light on [specific research questions or issues] and offer evidence-based recommendations for [relevant stakeholders or areas of application]. Ultimately, this study seeks to advance our understanding of [research topic] and has the potential to make a meaningful contribution to academia, industry, or society as a whole.”
10. Who will be your respondents? Do you think they will cooperate?
If you are not prepared for this question, you might be caught off guard. When it comes to the question of “Who will be your respondents?” in your research, it refers to the individuals or groups of people who will participate in your study and provide data or information based on your research objectives. The selection of appropriate respondents is crucial as they should be representative of the target population or have the knowledge and experiences relevant to your research topic.
In order to provide a good answer to this question during your defense, consider the following points:
- Clearly define your target population: Specify the characteristics and criteria that define the group of people who are most relevant to your research. This may include demographics, professional backgrounds, or specific expertise.
- Justify the selection of your respondents: Explain the rationale behind choosing these particular individuals or groups. Discuss how their perspectives, experiences, or expertise align with your research objectives and can contribute valuable insights to your study.
- Describe your recruitment strategy: Outline the methods you will use to identify and approach potential respondents. This could involve using random sampling techniques, seeking participants through professional networks, or utilizing existing databases.
- Address potential challenges: Acknowledge any potential obstacles or difficulties that may arise when recruiting respondents. These could include time constraints, reluctance to participate, or other factors that may affect cooperation.
- Outline measures to ensure cooperation: Discuss the steps you will take to encourage cooperation and participation from your chosen respondents. This could involve clear communication, informed consent procedures, confidentiality assurances, or incentives for their involvement.
By addressing these points, you can demonstrate your thoughtful consideration in selecting appropriate respondents for your research and provide assurance that you have considered potential challenges and strategies to ensure cooperation.
“My respondents will be teachers and students from three public high schools in Quezon City. I chose these respondents because they are directly involved in the implementation and evaluation of the K-12 curriculum, which is the focus of my research. I want to explore their perceptions, challenges, and recommendations regarding the curriculum.
To recruit my respondents, I will use stratified random sampling to select 10 teachers and 20 students from each school. This will ensure that I have a representative sample of different grade levels, subject areas, and academic performances. I will contact the school administrators to obtain their consent and assistance in identifying and inviting potential respondents.
One of the challenges that I may face is the limited availability and willingness of the respondents to participate in my study. Since they are busy with their teaching and learning activities, they may not have enough time or interest to join my study. To address this challenge, I will schedule the data collection at their convenience and offer incentives such as snacks, certificates, or tokens of appreciation. I will also explain the purpose and benefits of my study and assure them of confidentiality and anonymity.”
11. If approved, how many months would it take you to finish this study?
You should always be ready for this question. It is not acceptable to start thinking about the timeframe for your research only during the defense. You should also know why you will spend that much time on the study. The panel wants to see how prepared you are and if your planning for this study is good. You have to let them know that you are systematic and strategic and that you have well-thought-out plans for this study.
Based on the proposed methodology and scope of the study, I anticipate that it will take approximately six months to complete the research. This estimation takes into account factors such as data collection, analysis, interpretation, write-up of findings, and potential revisions. Similar studies in the field have typically been required around this timeframe to ensure thoroughness and rigor in the research process. However, the actual timeline may be adjusted depending on unforeseen challenges and resource availability.
The research title defense is the first level of your research journey. The success of the other two levels is dependent on the success of your title defense. Being prepared for the questions that may arise during this defense can greatly enhance one’s chances of success. By anticipating and addressing potential queries related to the research objective, research questions, methodology, data collection and analysis, expected outcomes, and feasibility, researchers can demonstrate their competence and passion for their chosen topic. Embracing the defense as an opportunity to showcase knowledge and capabilities will enable you to confidently navigate this critical stage and move closer to realizing your research aspirations.
- Civil Service Exam Reviewer
- L TO Portal Registration Guide
- How to Renew a Driver's License
- National ID Tracker
- Civil Service Exam Application
- Privacy Policy
- Terms of Service
All content provided on this website is for informational purposes only. The owner of this website makes no representations as to the accuracy or completeness of any information on this site or found by following any link on this site. The owner will not be liable for any errors or omissions in this information or for the availability of this information. The owner will not be liable for any losses, injuries, or damages from the display or use of this information.
You may not use the content of this blog for commercial purposes without prior formal written consent from us. These terms and conditions of use are subject to change at any time and without notice.
TOPNOTCHER PH is a participant in the Shopee Affiliate Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for us to earn advertising fees by linking to SHOPEE.PH. As a Shopee Affiliate, we earn from your qualifying purchases through our links without extra cost to you.
© 2024 TOPNOTCHER.PH

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
In this article, we will discuss the essential components that you need to include in your defense seminar, from the introduction to the literature review, research gap, problem statement, aim of ...
A thesis defense gives you the chance to show off your thesis work and demonstrate your expertise in your field of study. During this one- to two-hour discussion with the members of your thesis committee, you'll have some control over how you present your research, but your committee will ask you some prodding questions to test your knowledge and preparedness. They will all have read your ...
Preparing for your Dissertation Proposal Defense. 1. Anticipate Questions. In your presentation, try to answer all of the questions you expect your committee to ask. That way, you control the material. Your committee will be more satisfied with your preparation and understanding and it will be less likely that you have to answer questions that ...
Preparing for your dissertation or thesis defense (also called a "viva voce") is a formidable task. All your hard work over the years leads you to this one point, and you'll need to defend yourself against some of the most experienced researchers you've encountered so far. It's natural to feel a little nervous.
After submitting your research thesis for evaluation, you have to appear before a panel of professors and present your work; afterwards, they will ask you questions about your research. 2. How do you defend a thesis? You have to plan and prepare for your thesis defense. Review your paper and anticipate the questions that the committee can ask.
Here are a few tips on how to prepare for your thesis defense: 1. Anticipate questions and prepare for them. You can absolutely prepare for most of the questions you will be asked. Read through your thesis and while you're reading it, create a list of possible questions.
Answer: It is not clear what you mean by "defend research.". It could mean either defending your thesis (during the thesis defense) or defending or justifying your research in a research paper. If you mean defending your thesis, here are some broad strategies you can employ: Know your thesis very well. As you have spent considerable time ...
Have a plan for computer/internet problems if you are presenting virtually. Eat well and get a good night's rest before the defense. Arrive at the defense venue early enough to test any IT equipment or internet connection. For more tips on how to write a good thesis, where to find the best thesis editing services.
•For Successful Post-Proposal: Your committee will suggest any necessary revisions. Your committee chair should have you, the committee members, and the deans of the colleges sign the Proposal Cover Sheet. Your committee chair should pass along appropriate material to deans, members, and the appropriate colleges. Be sure to continuously check ...
The first thing you should know is that your defense has already begun. It started the minute you began working on your dissertation— maybe even in some of the classes you took beforehand that helped you formulate your ideas. This, according to Dr. Celeste Atkins, is why it's so important to identify a good mentor early in graduate school.
Crafting a thesis is significant, but defending it often feels like the ultimate test. While nerve-wracking, proper preparation can make it manageable. Prepare for your thesis defense with insights on the top questions you can expect, including strategies for answering convincingly. Contents Mastering the thesis defense: cultivate a success mindsetQuestion 1: Why did you choose
Writing a research proposal can be quite challenging, but a good starting point could be to look at some examples. We've included a few for you below. Example research proposal #1: "A Conceptual Framework for Scheduling Constraint Management" Example research proposal #2: "Medical Students as Mediators of Change in Tobacco Use" Title page
How-to: Prepare for your best Proposal or Defense* Before your talk Remind your committee members the day before the talk of the date and time of your presentation Make sure a member of the exams committee will be present. Treat him/her just like a thesis committee member (i.e.; similar reminders)
The purpose of the research proposal (its job, so to speak) is to convince your research supervisor, committee or university that your research is suitable (for the requirements of the degree program) and manageable (given the time and resource constraints you will face). The most important word here is "convince" - in other words, your ...
The proposal, which will be required in the early stages of your candidature, is, essentially, a detailed plan of your anticipated postgraduate research journey in the context of the degree program you are enrolled in. You will have discussed all elements of this with your supervisor (s) and, in the proposal, your intention is to communicate ...
Principles that come to mind might include autonomy, respect, dignity, privacy, informed consent and confidentiality. You may also have identified principles such as competence, integrity, wellbeing, justice and non-discrimination. Key ethical issues that you will address as an insider researcher include: Gaining trust.
In this video, Prof Jocelyn Gagalang talks about the common research title defense questions and the potential answers plus tips. Watch also How to write the...
How to defend your research project proposal explained in 5 minutesSeries: 5 Minutes with CyrillCyrill Stachniss, 2022Credits:Video by Cyrill StachnissSpecia...
Published research proposals, protocols, and open notebooks act as advertisements for ongoing research and enable others to reuse methods, exposing the continuous and collaborative nature of scholarship. To enable reuse, embrace open licenses. When it comes to innovative dissemination, the goal is usually that the materials are accessible to as ...
11 Possible Questions in Research Title Defense. September 11, 2023 by Draven Cueva. The research title defense is a part where you will face a panel of evaluators to defend or explain to them what you want to learn about your thesis or proposed research titles. Some schools and institutions organize committees to screen and criticize research ...
Research proposal is a mirror of research Research proposal is a blue print of research. Research proposal can serve as a document of contract for the project. Types of research proposal There are two major types of research proposal; Academic: • An academic proposal is the first step in producing a thesis or major project.