Ideas and insights from Harvard Business Publishing Corporate Learning


Powerful and Effective Presentation Skills: More in Demand Now Than Ever

When we talk with our L&D colleagues from around the globe, we often hear that presentation skills training is one of the top opportunities they’re looking to provide their learners. And this holds true whether their learners are individual contributors, people managers, or senior leaders. This is not surprising.
Effective communications skills are a powerful career activator, and most of us are called upon to communicate in some type of formal presentation mode at some point along the way.
For instance, you might be asked to brief management on market research results, walk your team through a new process, lay out the new budget, or explain a new product to a client or prospect. Or you may want to build support for a new idea, bring a new employee into the fold, or even just present your achievements to your manager during your performance review.
And now, with so many employees working from home or in hybrid mode, and business travel in decline, there’s a growing need to find new ways to make effective presentations when the audience may be fully virtual or a combination of in person and remote attendees.
Whether you’re making a standup presentation to a large live audience, or a sit-down one-on-one, whether you’re delivering your presentation face to face or virtually, solid presentation skills matter.
Even the most seasoned and accomplished presenters may need to fine-tune or update their skills. Expectations have changed over the last decade or so. Yesterday’s PowerPoint which primarily relied on bulleted points, broken up by the occasional clip-art image, won’t cut it with today’s audience.
The digital revolution has revolutionized the way people want to receive information. People expect presentations that are more visually interesting. They expect to see data, metrics that support assertions. And now, with so many previously in-person meetings occurring virtually, there’s an entirely new level of technical preparedness required.
The leadership development tools and the individual learning opportunities you’re providing should include presentation skills training that covers both the evergreen fundamentals and the up-to-date capabilities that can make or break a presentation.
So, just what should be included in solid presentation skills training? Here’s what I think.
The fundamentals will always apply When it comes to making a powerful and effective presentation, the fundamentals will always apply. You need to understand your objective. Is it strictly to convey information, so that your audience’s knowledge is increased? Is it to persuade your audience to take some action? Is it to convince people to support your idea? Once you understand what your objective is, you need to define your central message. There may be a lot of things you want to share with your audience during your presentation, but find – and stick with – the core, the most important point you want them to walk away with. And make sure that your message is clear and compelling.
You also need to tailor your presentation to your audience. Who are they and what might they be expecting? Say you’re giving a product pitch to a client. A technical team may be interested in a lot of nitty-gritty product detail. The business side will no doubt be more interested in what returns they can expect on their investment.
Another consideration is the setting: is this a formal presentation to a large audience with questions reserved for the end, or a presentation in a smaller setting where there’s the possibility for conversation throughout? Is your presentation virtual or in-person? To be delivered individually or as a group? What time of the day will you be speaking? Will there be others speaking before you and might that impact how your message will be received?
Once these fundamentals are established, you’re in building mode. What are the specific points you want to share that will help you best meet your objective and get across your core message? Now figure out how to convey those points in the clearest, most straightforward, and succinct way. This doesn’t mean that your presentation has to be a series of clipped bullet points. No one wants to sit through a presentation in which the presenter reads through what’s on the slide. You can get your points across using stories, fact, diagrams, videos, props, and other types of media.
Visual design matters While you don’t want to clutter up your presentation with too many visual elements that don’t serve your objective and can be distracting, using a variety of visual formats to convey your core message will make your presentation more memorable than slides filled with text. A couple of tips: avoid images that are cliched and overdone. Be careful not to mix up too many different types of images. If you’re using photos, stick with photos. If you’re using drawn images, keep the style consistent. When data are presented, stay consistent with colors and fonts from one type of chart to the next. Keep things clear and simple, using data to support key points without overwhelming your audience with too much information. And don’t assume that your audience is composed of statisticians (unless, of course, it is).
When presenting qualitative data, brief videos provide a way to engage your audience and create emotional connection and impact. Word clouds are another way to get qualitative data across.
Practice makes perfect You’ve pulled together a perfect presentation. But it likely won’t be perfect unless it’s well delivered. So don’t forget to practice your presentation ahead of time. Pro tip: record yourself as you practice out loud. This will force you to think through what you’re going to say for each element of your presentation. And watching your recording will help you identify your mistakes—such as fidgeting, using too many fillers (such as “umm,” or “like”), or speaking too fast.
A key element of your preparation should involve anticipating any technical difficulties. If you’ve embedded videos, make sure they work. If you’re presenting virtually, make sure that the lighting is good, and that your speaker and camera are working. Whether presenting in person or virtually, get there early enough to work out any technical glitches before your presentation is scheduled to begin. Few things are a bigger audience turn-off than sitting there watching the presenter struggle with the delivery mechanisms!
Finally, be kind to yourself. Despite thorough preparation and practice, sometimes, things go wrong, and you need to recover in the moment, adapt, and carry on. It’s unlikely that you’ll have caused any lasting damage and the important thing is to learn from your experience, so your next presentation is stronger.
How are you providing presentation skills training for your learners?
Manika Gandhi is Senior Learning Design Manager at Harvard Business Publishing Corporate Learning. Email her at [email protected] .
Let’s talk
Change isn’t easy, but we can help. Together we’ll create informed and inspired leaders ready to shape the future of your business.
© 2024 Harvard Business School Publishing. All rights reserved. Harvard Business Publishing is an affiliate of Harvard Business School.
- Privacy Policy
- Copyright Information
- Terms of Use
- About Harvard Business Publishing
- Higher Education
- Harvard Business Review
- Harvard Business School
We use cookies to understand how you use our site and to improve your experience. By continuing to use our site, you accept our use of cookies and revised Privacy Policy .
Cookie and Privacy Settings
We may request cookies to be set on your device. We use cookies to let us know when you visit our websites, how you interact with us, to enrich your user experience, and to customize your relationship with our website.
Click on the different category headings to find out more. You can also change some of your preferences. Note that blocking some types of cookies may impact your experience on our websites and the services we are able to offer.
These cookies are strictly necessary to provide you with services available through our website and to use some of its features.
Because these cookies are strictly necessary to deliver the website, refusing them will have impact how our site functions. You always can block or delete cookies by changing your browser settings and force blocking all cookies on this website. But this will always prompt you to accept/refuse cookies when revisiting our site.
We fully respect if you want to refuse cookies but to avoid asking you again and again kindly allow us to store a cookie for that. You are free to opt out any time or opt in for other cookies to get a better experience. If you refuse cookies we will remove all set cookies in our domain.
We provide you with a list of stored cookies on your computer in our domain so you can check what we stored. Due to security reasons we are not able to show or modify cookies from other domains. You can check these in your browser security settings.
We also use different external services like Google Webfonts, Google Maps, and external Video providers. Since these providers may collect personal data like your IP address we allow you to block them here. Please be aware that this might heavily reduce the functionality and appearance of our site. Changes will take effect once you reload the page.
Google Webfont Settings:
Google Map Settings:
Google reCaptcha Settings:
Vimeo and Youtube video embeds:
You can read about our cookies and privacy settings in detail on our Privacy Policy Page.

- PRESENTATION SKILLS
Top Tips for Effective Presentations
Search SkillsYouNeed:
Presentation Skills:
- A - Z List of Presentation Skills
- General Presentation Skills
- What is a Presentation?
- Preparing for a Presentation
- Organising the Material
- Writing Your Presentation
- Deciding the Presentation Method
- Managing your Presentation Notes
- Working with Visual Aids
- Presenting Data
- Managing the Event
- Coping with Presentation Nerves
- Dealing with Questions
- How to Build Presentations Like a Consultant
- 7 Qualities of Good Speakers That Can Help You Be More Successful
- Self-Presentation in Presentations
- Specific Presentation Events
- Remote Meetings and Presentations
- Giving a Speech
- Presentations in Interviews
- Presenting to Large Groups and Conferences
- Giving Lectures and Seminars
- Managing a Press Conference
- Attending Public Consultation Meetings
- Managing a Public Consultation Meeting
- Crisis Communications
- Elsewhere on Skills You Need:
- Communication Skills
- Facilitation Skills
- Teams, Groups and Meetings
- Effective Speaking
- Question Types
Subscribe to our FREE newsletter and start improving your life in just 5 minutes a day.
You'll get our 5 free 'One Minute Life Skills' and our weekly newsletter.
We'll never share your email address and you can unsubscribe at any time.
How can you make a good presentation even more effective?
This page draws on published advice from expert presenters around the world, which will help to take your presentations from merely ‘good’ to ‘great’.
By bringing together advice from a wide range of people, the aim is to cover a whole range of areas.
Whether you are an experienced presenter, or just starting out, there should be ideas here to help you to improve.
1. Show your Passion and Connect with your Audience
It’s hard to be relaxed and be yourself when you’re nervous.
But time and again, the great presenters say that the most important thing is to connect with your audience, and the best way to do that is to let your passion for the subject shine through.
Be honest with the audience about what is important to you and why it matters.
Be enthusiastic and honest, and the audience will respond.
2. Focus on your Audience’s Needs
Your presentation needs to be built around what your audience is going to get out of the presentation.
As you prepare the presentation, you always need to bear in mind what the audience needs and wants to know, not what you can tell them.
While you’re giving the presentation, you also need to remain focused on your audience’s response, and react to that.
You need to make it easy for your audience to understand and respond.
3. Keep it Simple: Concentrate on your Core Message
When planning your presentation, you should always keep in mind the question:
What is the key message (or three key points) for my audience to take away?
You should be able to communicate that key message very briefly.
Some experts recommend a 30-second ‘elevator summary’, others that you can write it on the back of a business card, or say it in no more than 15 words.
Whichever rule you choose, the important thing is to keep your core message focused and brief.
And if what you are planning to say doesn’t contribute to that core message, don’t say it.
4. Smile and Make Eye Contact with your Audience
This sounds very easy, but a surprisingly large number of presenters fail to do it.
If you smile and make eye contact, you are building rapport , which helps the audience to connect with you and your subject. It also helps you to feel less nervous, because you are talking to individuals, not to a great mass of unknown people.
To help you with this, make sure that you don’t turn down all the lights so that only the slide screen is visible. Your audience needs to see you as well as your slides.
5. Start Strongly
The beginning of your presentation is crucial. You need to grab your audience’s attention and hold it.
They will give you a few minutes’ grace in which to entertain them, before they start to switch off if you’re dull. So don’t waste that on explaining who you are. Start by entertaining them.
Try a story (see tip 7 below), or an attention-grabbing (but useful) image on a slide.
6. Remember the 10-20-30 Rule for Slideshows
This is a tip from Guy Kawasaki of Apple. He suggests that slideshows should:
- Contain no more than 10 slides;
- Last no more than 20 minutes; and
- Use a font size of no less than 30 point.
This last is particularly important as it stops you trying to put too much information on any one slide. This whole approach avoids the dreaded ‘Death by PowerPoint’.
As a general rule, slides should be the sideshow to you, the presenter. A good set of slides should be no use without the presenter, and they should definitely contain less, rather than more, information, expressed simply.
If you need to provide more information, create a bespoke handout and give it out after your presentation.
7. Tell Stories
Human beings are programmed to respond to stories.
Stories help us to pay attention, and also to remember things. If you can use stories in your presentation, your audience is more likely to engage and to remember your points afterwards. It is a good idea to start with a story, but there is a wider point too: you need your presentation to act like a story.
Think about what story you are trying to tell your audience, and create your presentation to tell it.
Finding The Story Behind Your Presentation
To effectively tell a story, focus on using at least one of the two most basic storytelling mechanics in your presentation:
Focusing On Characters – People have stories; things, data, and objects do not. So ask yourself “who” is directly involved in your topic that you can use as the focal point of your story.
For example, instead of talking about cars (your company’s products), you could focus on specific characters like:
- The drivers the car is intended for – people looking for speed and adventure
- The engineers who went out of their way to design the most cost-effective car imaginable
A Changing Dynamic – A story needs something to change along the way. So ask yourself “What is not as it should be?” and answer with what you are going to do about it (or what you did about it).
For example…
- Did hazardous road conditions inspire you to build a rugged, all-terrain jeep that any family could afford?
- Did a complicated and confusing food labelling system lead you to establish a colour-coded nutritional index so that anybody could easily understand it?
8. Use your Voice Effectively
The spoken word is actually a pretty inefficient means of communication, because it uses only one of your audience’s five senses. That’s why presenters tend to use visual aids, too. But you can help to make the spoken word better by using your voice effectively.
Varying the speed at which you talk, and emphasising changes in pitch and tone all help to make your voice more interesting and hold your audience’s attention.
For more about this, see our page on Effective Speaking .
9. Use your Body Too
It has been estimated that more than three quarters of communication is non-verbal.
That means that as well as your tone of voice, your body language is crucial to getting your message across. Make sure that you are giving the right messages: body language to avoid includes crossed arms, hands held behind your back or in your pockets, and pacing the stage.
Make your gestures open and confident, and move naturally around the stage, and among the audience too, if possible.
10. Relax, Breathe and Enjoy
If you find presenting difficult, it can be hard to be calm and relaxed about doing it.
One option is to start by concentrating on your breathing. Slow it down, and make sure that you’re breathing fully. Make sure that you continue to pause for breath occasionally during your presentation too.
For more ideas, see our page on Coping with Presentation Nerves .
If you can bring yourself to relax, you will almost certainly present better. If you can actually start to enjoy yourself, your audience will respond to that, and engage better. Your presentations will improve exponentially, and so will your confidence. It’s well worth a try.
Improve your Presentation Skills
Follow our guide to boost your presentation skills learning about preparation, delivery, questions and all other aspects of giving effective presentations.
Start with: What is a Presentation?
Continue to: How to Give a Speech Self Presentation
See also: Five Ways You Can Do Visual Marketing on a Budget Can Presentation Science Improve Your Presentation? Typography – It’s All About the Message in Your Slides
Home Blog Education Presentation Skills 101: A Guide to Presentation Success
Presentation Skills 101: A Guide to Presentation Success

Getting the perfect presentation design is just a step toward a successful presentation. For the experienced user, building presentation skills is the answer to elevating the power of your message and showing expertise on any subject. Still, one can ask: is it the same set of skills, or are they dependable on the type of presentation?
In this article, we will introduce the different types of presentations accompanied by the skillset required to master them. The purpose, as always, is to retain the audience’s interest for a long-lasting and convincing message.
Table of Contents
The Importance of Presentation Skills
Persuasive presentations, instructional presentations, informative presentations, inspirational presentations, basic presentation skills, presentation techniques, what are the main difficulties when giving a presentation, recommendations to improve your presentation skills, closing statement.
Effective communication is the answer to reaching business and academic goals. The scenarios in which we can be required to deliver a presentation are as diverse as one can imagine. Still, some core concepts apply to all presentations.
We define presentation skills as a compendium of soft skills that directly affect your presentation performance and contribute to creating a great presentation. These are not qualities acquired by birth but skills you ought to train and master to delve into professional environments.
You may ask: is it really that evident when a presenter is not prepared? Here are some common signs people can experience during presentations:
- Evasive body language: Not making eye contact with the audience, arms closed tightly to the body, hands in pockets all the time.
- Lack of interest in the presenter’s voice: dull tone, not putting an effort to articulate the topics.
- Doubting when asked to answer a question
- Irksome mood
The list can go on about common presenter mistakes , and most certainly, it will affect the performance of any presented data if the lack of interest by the presenter is blatantly obvious. Another element to consider is anxiety, and according to research by the National Institute of Mental Health, 73% of the population in the USA is affected by glossophobia , which is the fear of public speaking, judgment, or negative evaluation by other people.
Therefore, presentation skills training is essential for any business professional who wants to achieve effective communication . It will remove the anxiety from presentation performance and help users effectively deliver their message and connect with the audience.
Archetypes of presentations
Persuasive presentations aim to convince the audience – often in short periods – to acquire a product or service, adhere to a cause, or invest in a company. For business entrepreneurs or politicians, persuasive presentations are their tool for the trade.
Unless you aim to be perceived as an imposter, a proper persuasive presentation has the elements of facts, empathy, and logic, balanced under a well-crafted narrative. The central pillar of these presentations is to identify the single factor that gathered your audience: it could be a market need, a social cause, or a revolutionary concept for today’s society. It has to be something with enough power to gather critiques – both good and bad.
That single factor has to be backed up by facts. Research that builds your hypothesis on how to solve that problem. A deep understanding of the target audience’s needs , concerns, and social position regarding the solution your means can offer. When those elements are in place, building a pitch becomes an easy task.
Graphics can help you introduce information in a compelling format, lowering the need for lengthy presentations. Good presentation skills for persuasive presentations go by the hand of filtering relevant data and creating the visual cues that resonate with what your audience demands.
One powerful example of a persuasive presentation is the technique known as the elevator pitch . You must introduce your idea or product convincingly to the audience in a timeframe between 30 seconds and less than 2 minutes. You have to expose:
- What do you do
- What’s the problem to solve
- Why is your solution different from others
- Why should the audience care about your expertise
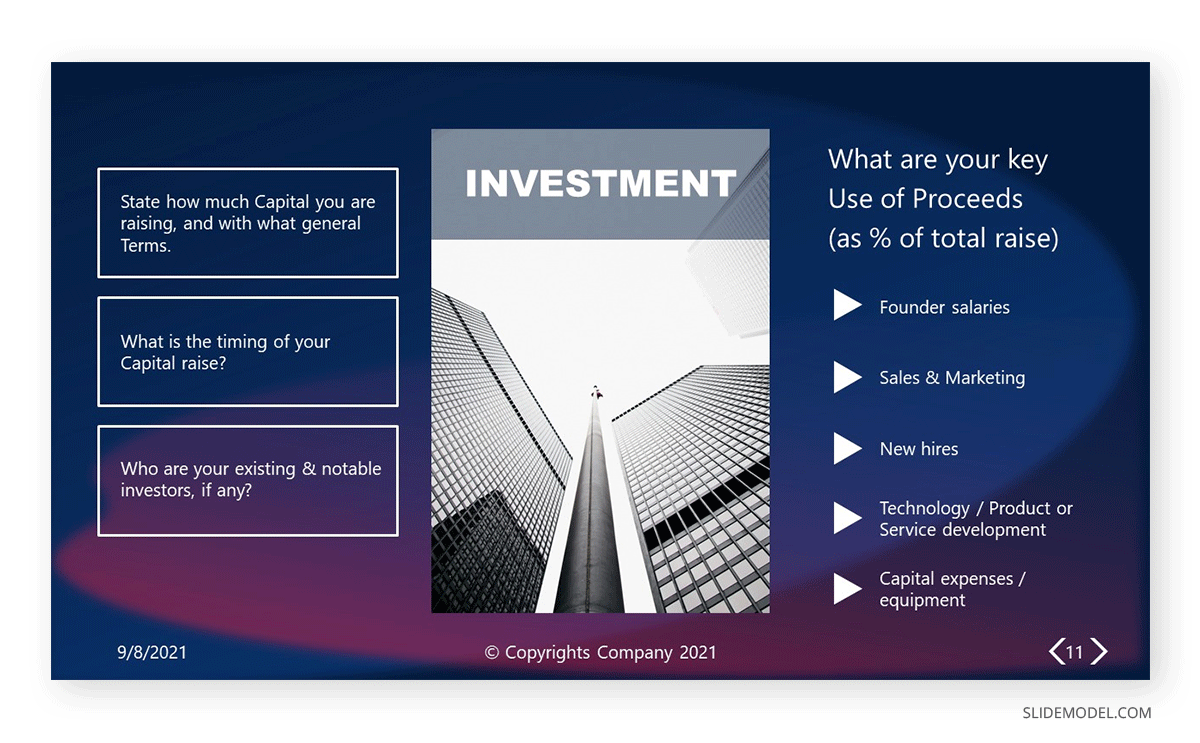
For that very purpose, using engaging graphics with contrasting colors elevates the potential power of your message. It speaks professionalism, care for details, and out-of-the-box thinking. Knowing how to end a presentation is also critical, as your CTAs should be placed with care.
Therefore, let’s resume the requirements of persuasive presentations in terms of good presentation skills:
- Identifying problems and needs
- Elaborating “the hook” (the element that grabs the audience’s attention)
- Knowing how to “tie” your audience (introducing a piece of information related to the hook that causes an emotional impact)
- Broad knowledge of body language and hand gestures to quickly convey your message
- Being prepared to argue a defense of your point of view
- Handling rejection
- Having a proactive attitude to convert opportunities into new projects
- Using humor, surprise, or personal anecdotes as elements to sympathize with the audience
- Having confidence
- Be able to summarize facts and information in visually appealing ways

You can learn more about persuasive presentation techniques by clicking here .
In the case of instructional presentations, we ought to differentiate two distinctive types:
- Lecture Presentations : Presentations being held at universities or any other educative institution. Those presentations cover, topic by topic, and the contents of a syllabus and are created by the team of teachers in charge of the course.
- Training Presentations : These presentations take place during in-company training sessions and usually comprise a good amount of content that is resumed into easy-to-take solutions. They are aimed to coach employees over certain topics relevant to their work performance. The 70-20-10 Model is frequently used to address these training situations.
Lecture presentations appeal to the gradual introduction of complex concepts , following a structure set in the course’s syllabus. These presentations often have a similar aesthetic as a group of professors or researchers created to share their knowledge about a topic. Personal experience does tell that course presentations often rely on factual data, adequately documented, and on the theoretical side.
An example of a presentation that lies under this concept is a Syllabus Presentation, used by the teaching team to introduce the subject to new students, evaluation methods, concepts to be learned, and expectations to pass the course.
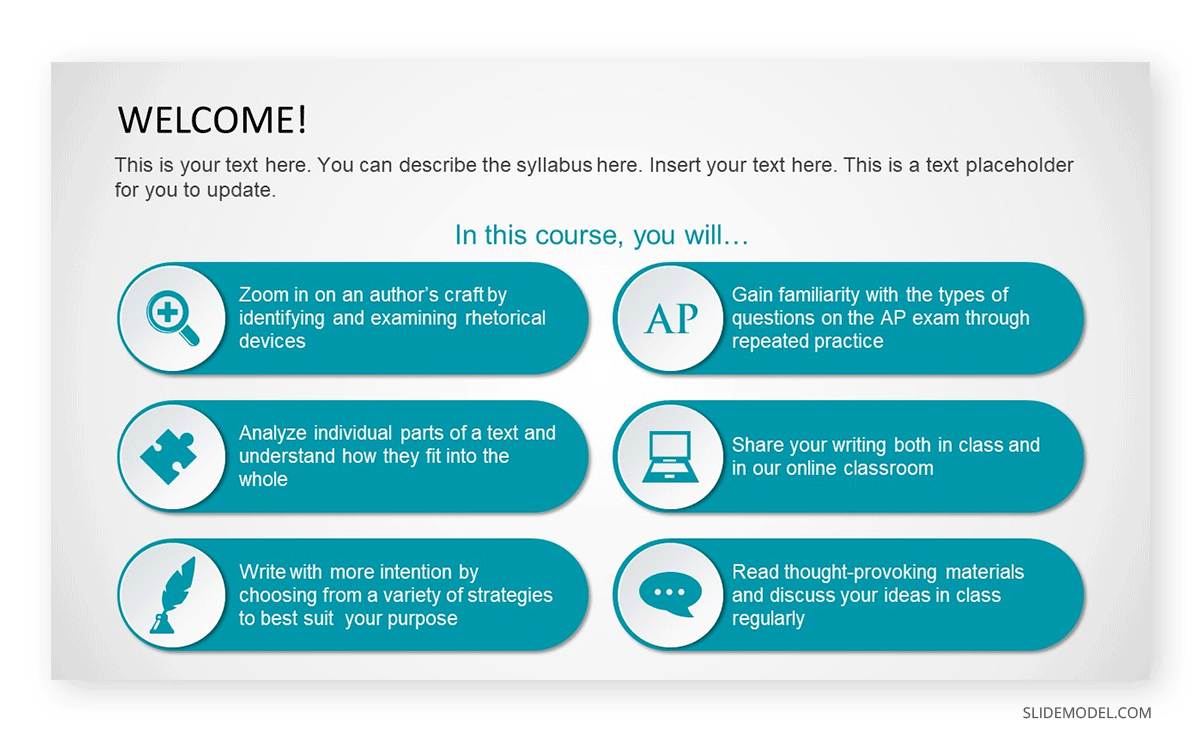
On the other hand, training presentations are slide decks designed to meet an organization’s specific needs in the formal education of their personnel. Commonly known as “continuous education,” plenty of companies invest resources in coaching their employees to achieve higher performance results. These presentations have the trademark of being concise since their idea is to introduce the concepts that shall be applied in practice sessions.
Ideally, the training presentations are introduced with little text and easy-to-recognize visual cues. Since the idea is to summarize as much as possible, these are visually appealing for the audience. They must be dynamic enough to allow the presenter to convey the message.

Those key takeaways remind employees when they revisit their learning resources and allow them to ruminate on questions that fellow workers raise.
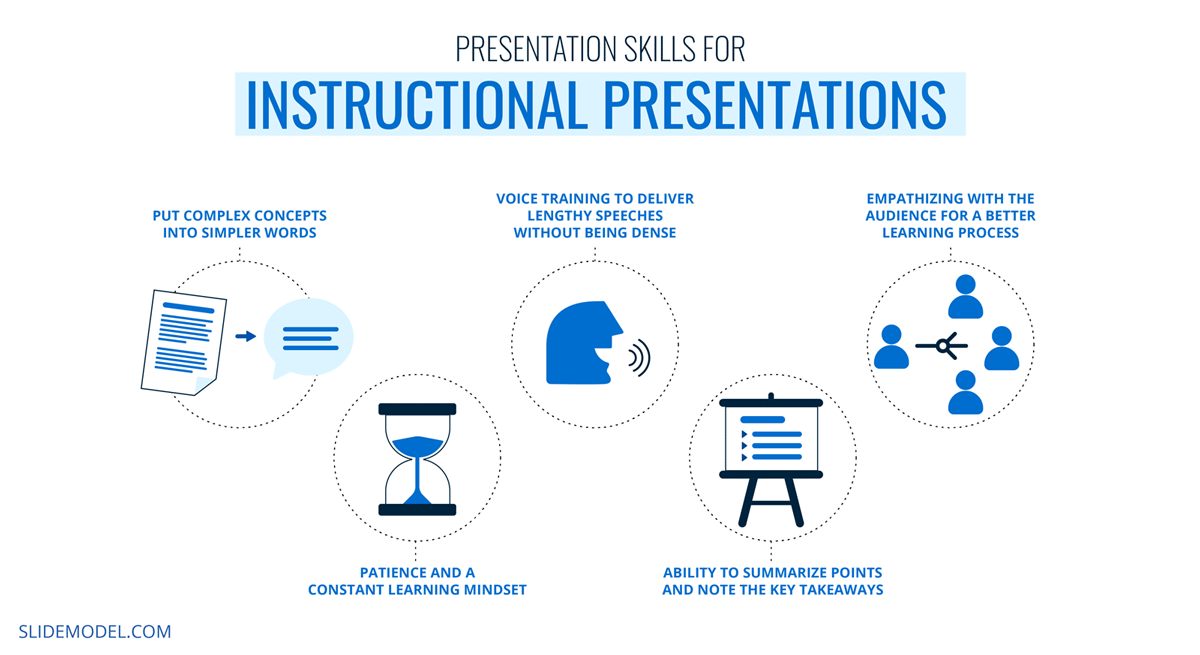
To sum up this point, building presentation skills for instructional presentations requires:
- Ability to put complex concepts into simpler words
- Patience and a constant learning mindset
- Voice training to deliver lengthy speeches without being too dense
- Ability to summarize points and note the key takeaways
- Empathizing with the audience to understand their challenges in the learning process
The informative presentations take place in business situations, such as when to present project reports from different departments to the management. Another potential usage of these presentations is in SCRUM or other Agile methodologies, when a sprint is completed, to discuss the advance of the project with the Product Owner.
As they are presentations heavily dependent on data insights, it’s common to see the usage of infographics and charts to express usually dense data in simpler terms and easy to remember.
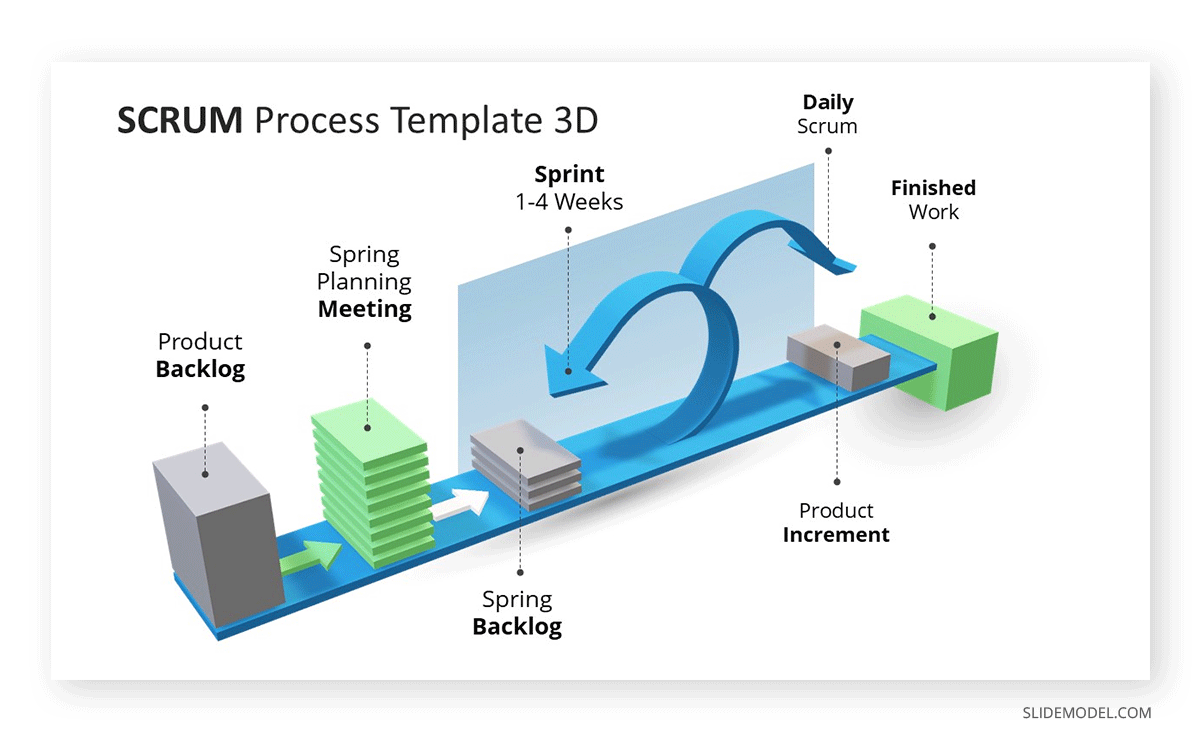
Informative presentations don’t just fall into the business category. Ph.D. Dissertation and Thesis presentations are topics that belong to the informative presentations category as they condense countless research hours into manageable reports for the academic jury.
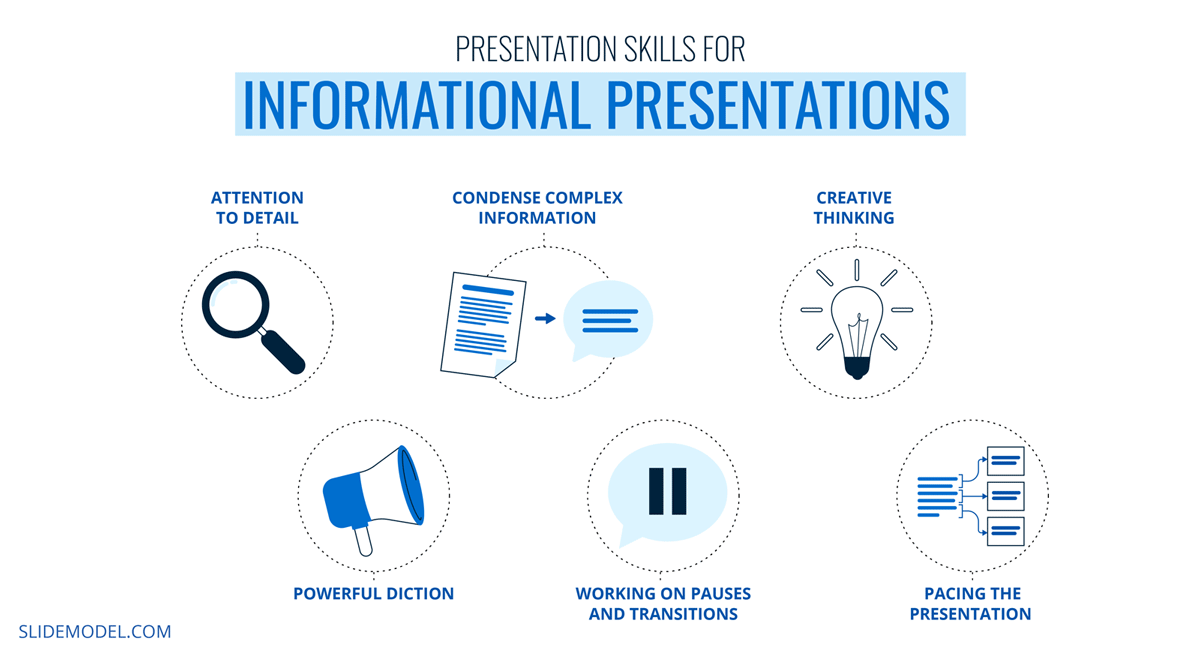
Since these informational presentations can be perceived as lengthy and data-filled, it is important to learn the following professional presentation skills:
- Attention to detail
- Be able to explain complex information in simpler terms
- Creative thinking
- Powerful diction
- Working on pauses and transitions
- Pacing the presentation, so not too much information is divulged per slide
The leading inspirational platform, TEDx, comes to mind when talking about inspirational presentations. This presentation format has the peculiarity of maximizing the engagement with the audience to divulge a message, and due to that, it has specific requirements any presenter must meet.
This presentation format usually involves a speaker on a stage, either sitting or better standing, in which the presenter engages with the audience with a storytelling format about a life experience, a job done that provided a remarkable improvement for society, etc.

Empathizing with the audience is the key ingredient for these inspirational presentations. Still, creativity is what shapes the outcome of your performance as people are constantly looking for different experiences – not the same recipe rephrased with personal touches. The human factor is what matters here, way above data and research. What has your experience to offer to others? How can it motivate another human being to pursue a similar path or discover their true calling?
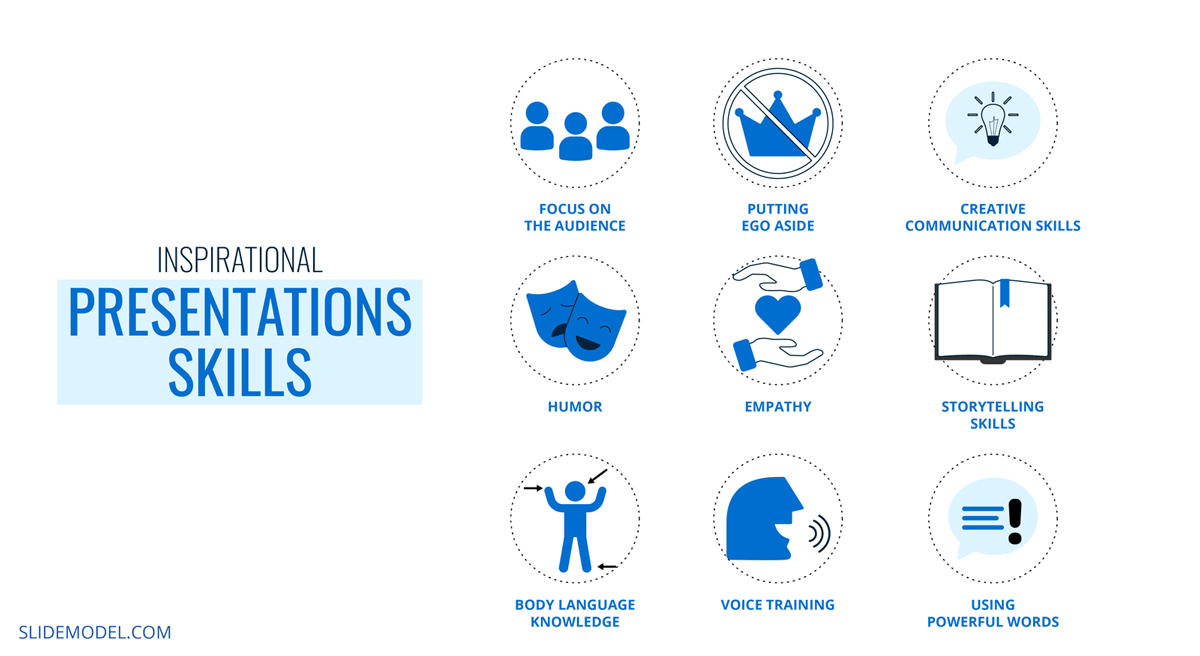
To achieve success in terms of communication skills presentation, these inspirational presentations have the following requirements:
- Focus on the audience (engage, consider their interests, and make them a part of your story)
- Putting ego aside
- Creative communication skills
- Storytelling skills
- Body language knowledge to apply the correct gestures to accompany your story
- Voice training
- Using powerful words
After discussing the different kinds of presentations we can come across at any stage of our lives, a group of presentation skills is standard in any type of presentation. See below what makes a good presentation and which skills you must count on to succeed as a presenter.
Punctuality
Punctuality is a crucial aspect of giving an effective presentation. Nothing says more about respect for your audience and the organization you represent than delivering the presentation on time . Arriving last minute puts pressure on the tech team behind audiovisuals, as they don’t have enough preparation to test microphones, stage lights, and projector settings, which can lead to a less powerful presentation Even when discussing presentations hosted in small rooms for a reduced audience, testing the equipment becomes essential for an effective presentation.
A solution for this is to arrive at least 30 minutes early. Ideally, one hour is a sweet spot since the AV crew has time to check the gear and requirements for your presentation. Another benefit of this, for example, in inspirational presentations, is measuring the previous presenter’s impact on the audience. This gives insights about how to resonate with the public, and their interest, and how to accommodate your presentation for maximum impact.
Body Language
Our bodies can make emotions transparent for others, even when we are unaware of such a fact. Proper training for body language skills reduces performance anxiety, giving the audience a sense of expertise about the presented topic.
Give your presentation and the audience the respect they deserve by watching over these potential mistakes:
- Turning your back to the audience for extended periods : It’s okay to do so when introducing an important piece of information or explaining a graph, but it is considered rude to give your back to the audience constantly.
- Fidgeting : We are all nervous in the presence of strangers, even more, if we are the center of attention for that moment. Instead of playing with your hair or making weird hand gestures, take a deep breath to center yourself before the presentation and remember that everything you could do to prepare is already done. Trust your instincts and give your best.
- Intense eye contact : Have you watched a video where the presenter stared at the camera the entire time? That’s the feeling you transmit to spectators through intense eye contact. It’s a practice often used by politicians to persuade.
- Swearing : This is a no-brainer. Even when you see influencers swearing on camera or in podcasts or live presentations, it is considered an informal and lousy practice for business and academic situations. If you have a habit to break when it comes to this point, find the humor in these situations and replace your swear words with funny alternatives (if the presentation allows for it).
Voice Tone plays a crucial role in delivering effective presentations and knowing how to give a good presentation. Your voice is a powerful tool for exposing your ideas and feelings . Your voice can articulate the message you are telling, briefing the audience if you feel excited about what you are sharing or, in contrast, if you feel the presentation is a burden you ought to complete.
Remember, passion is a primary ingredient in convincing people. Therefore, transmitting such passion with a vibrant voice may help gather potential business partners’ interest.
But what if you feel sick prior to the presentation? If, by chance, your throat is sore minutes before setting foot on the stage, try this: when introducing yourself, mention that you are feeling a bit under the weather. This resonates with the audience to pay more attention to your efforts. In case you don’t feel comfortable about that, ask the organizers for a cup of tea, as it will settle your throat and relax your nerves.
Tech Skills
Believe it or not, people still feel challenged by technology these days. Maybe that’s the reason why presentation giants like Tony Robbins opt not to use PowerPoint presentations . The reality is that there are plenty of elements involved in a presentation that can go wrong from the tech side:
- A PDF not opening
- Saving your presentation in a too-recent PowerPoint version
- A computer not booting up
- Mac laptops and their never-ending compatibility nightmare
- Not knowing how to change between slides
- Not knowing how to use a laser pointer
- Internet not working
- Audio not working
We can come up with a pretty long list of potential tech pitfalls, and yet more than half of them fall in presenters not being knowledgeable about technology.
If computers aren’t your thing, let the organization know about this beforehand. There is always a crew member available to help presenters switch between slides or configure the presentation for streaming. This takes the pressure off your shoulders, allowing you to concentrate on the content to present. Remember, even Bill Gates can get a BSOD during a presentation .
In this section, we will list some of the most useful presentation skills presenters should hone. Remember, none of these techniques are expected to come naturally; they result from effort and practice.
Be passionate
Passion engages audiences, making your message resonate. Presenting with genuine enthusiasm elevates your energy and improves delivery, capturing attention and inspiring trust – an effect commonly seen in inspirational presentations. To convey passion, know the subject well enough to feel confident and excited to share insights.
Expressing strong belief in your message encourages listeners to feel the same. Avoid overacting—natural enthusiasm goes further than forced energy. To hone this, practice until you’re comfortable with the material and can easily express why it matters. A passionate approach is contagious; if you’re invested in the subject, the audience will likely stay engaged and leave a lasting impression.

Be yourself
Authenticity is critical for making a genuine connection with your audience. Being yourself while presenting builds credibility and helps you appear approachable and trustworthy. Staying true to yourself reduces nerves and makes you more engaging since audiences appreciate sincerity over a rehearsed facade.
Focus on what you naturally bring rather than trying to imitate another speaker’s style. This could be a sense of humor, calm, collected presence, or relatable anecdotes. To achieve this, practice speaking in a conversational tone and avoid rehearsing too rigidly; you want to sound prepared yet spontaneous.
Greet the audience
Starting with a warm greeting sets the tone for a welcoming and engaging presentation. A simple “Hello” or “Good morning” is often enough, but make it authentic and with a smile. Introducing yourself and perhaps adding a light remark about the setting or a shared experience builds rapport.
Acknowledge the audience for taking the time to be there, which shows respect and creates a positive connection. This initial interaction establishes your presence as friendly and prepared, making people more receptive to your message. It also lets you settle into your environment, easing initial nervousness.
Ask rhetorical questions
Rhetorical questions engage your audience by prompting them to think without expecting verbal responses. This technique draws listeners into your narrative, creating mental engagement as they consider the answers privately.
Use rhetorical questions strategically to highlight important points or to introduce a topic. Questions like, “Have you ever wondered…?” or “What would you do if…?” encourage reflection and make your points more relatable. Avoid overusing them, as it can disrupt the flow. Instead, use them as subtle engagement tools to keep your audience thinking and invested in the subject.
Backup plan
A backup plan prevents unexpected disruptions from derailing your presentation. Technology issues, unforeseen delays, or lost materials can occur, so preparing alternatives is essential. Bring printed slides, a PDF of your presentation, and any necessary files on a flash drive.
Familiarize yourself with alternate ways to deliver your content, such as verbal summaries if visual aids fail. Practicing flexibility also enhances your confidence since you’re prepared for the unexpected. A solid backup plan keeps you calm and professional, ensuring small setbacks don’t compromise the presentation’s quality.
Adding humor to your presentation lightens the atmosphere and keeps the audience engaged. A well-placed joke or light-hearted comment can make you appear approachable and relatable when appropriate.
To use humor effectively, understand your audience’s comfort level with different styles of humor and avoid jokes that might be inappropriate. Focus on subtle, universal humor that aligns with the presentation theme, like a playful observation or funny anecdote. Overuse can detract from your message, so keep it balanced. Humor should support the presentation’s flow, not become the main focus.
Data can make your points credible and concrete, showing that your claims are backed by evidence. However, presenting data effectively means more than just listing numbers. Use visuals like charts or graphs to simplify complex information, allowing the audience to grasp the core message quickly.
Avoid overwhelming them with too much data; focus on the most relevant figures that support your argument. Introduce the data in context, explaining why it’s significant, and always keep your core message in mind. Well-presented data can strengthen your case, while too much can distract you.
Interactivity
Interactive elements increase engagement by actively involving the audience. Asking for a show of hands, incorporating small group discussions, or even live polling makes the experience dynamic and personalized. Interactive presentations help break up one-way communication’s monotony and keep listeners attentive.
Plan interactivity at key points in your presentation to reinforce essential concepts or check understanding. Compelling interactivity adapts to the size and type of audience—keep it simple with larger groups. Inviting participation creates a more memorable experience and enhances the audience’s connection with your message.
Presentations, while valuable for conveying information and ideas, can be daunting for many individuals. Here are some common difficulties people encounter when giving presentations:
Public Speaking Anxiety
Glossophobia, the fear of public speaking, affects a significant portion of the population. This anxiety can lead to nervousness, trembling, and forgetfulness during a presentation.
Lack of Confidence
Many presenters struggle with self-doubt, fearing that they may not be knowledgeable or skilled enough to engage their audience effectively.
Content Organization
Organizing information in a coherent and engaging manner can be challenging. Presenters often grapple with how to structure their content to make it easily digestible for the audience. Artificial Intelligence can help us significantly reduce the content arrangement time when you work with tools like our AI Presentation Maker (made for presenters by experts in presentation design).
Audience Engagement
Keeping the audience’s attention and interest throughout the presentation can be difficult. Distractions, disengaged attendees, or lack of interaction can pose challenges.
Technical Issues
Technology glitches, such as malfunctioning equipment, incompatible file formats, or poor internet connectivity, can disrupt presentations and increase stress.
Time Management
Striking the right balance between providing enough information and staying within time limits is a common challenge. Going over or under the allotted time can affect the effectiveness of the presentation.
Handling Questions and Challenges
Responding to unexpected questions, criticism, or challenges from the audience can be difficult, especially when presenters are unprepared or lack confidence in their subject matter.
Visual Aids and Technology
Creating and effectively using visual aids like slides or multimedia can be a struggle for some presenters. Technical competence is essential in this aspect.
Language and Articulation
Poor language skills or unclear articulation can hinder effective communication. Presenters may worry about stumbling over words or failing to convey their message clearly.
Maintaining appropriate and confident body language can be challenging. Avoiding nervous habits, maintaining eye contact, and using gestures effectively requires practice.
Overcoming Impersonal Delivery
In virtual presentations, maintaining a personal connection with the audience can be difficult. The absence of face-to-face interaction can make it challenging to engage and read the audience.
Cultural and Diversity Awareness
Presenting to diverse audiences requires sensitivity to cultural differences and varying levels of familiarity with the topic.
In this section, we gathered some tips on how to improve presentation skills that can certainly make an impact if applied to your presentation skills. We believe these skills can be cultivated to transform into habits for your work routine.
Tip #1: Build a narrative
One memorable way to guarantee presentation success is by writing a story of all the points you desire to cover. This statement is based on the logic behind storytelling and its power to connect with people .
Don’t waste time memorizing slides or reading your presentation to the audience. It feels unnatural, and any question that diverts from the topic in discussion certainly puts you in jeopardy or, worse, exposes you as a fraud in the eyes of the audience. And before you ask, it is really evident when a presenter has a memorized speech.
Build and rehearse the presentation as if telling a story to a group of interested people. Lower the language barrier by avoiding complex terms that maybe even you aren’t fully aware of their meaning. Consider the ramifications of that story, what it could lead to, and which are the opportunities to explore. Then, visualize yourself giving the presentation in a natural way.
Applying this technique makes the presentation feel like second nature to you. It broadens the spectrum in which you can show expertise over a topic or even build the basis for new interesting points of view about the project.
Tip #2: Don’t talk for more than 3 minutes per slide
It is a common practice of presenters to bombard the audience with facts and information whilst retaining the same slide on the screen. Why can this happen? It could be because the presenter condensed the talk into very few slides and preferred to talk. The reality is that your spectators won’t retain the information you are giving unless you give visual cues to help that process.
Opt to prepare more slides and pace your speech to match the topics shown on each slide. Don’t spend more than 3 minutes per slide unless you have to introduce a complex piece of data. Use visual cues to direct the spectators about what you talk about, and summarize the principal concepts discussed at the end of each section.
Tip #3: Practice meditation daily
Anxiety is the number one enemy of professional presenters. It slowly builds without you being aware of your doubts and can hinder your performance in multiple ways: making you feel paralyzed, fidgeting, making you forget language skills or concepts, affecting your health, etc.
Meditation is an ancient practice taken from Buddhist teachings that train your mind to be here in the present. We often see the concepts of meditation and mindfulness as synonyms, whereas you should be aware that meditation is a practice that sets the blocks to reach a state of mindfulness. For presenters, being in the here and now is essential to retain focus, but meditation techniques also teach us to control our breathing and be in touch with our body signals when stress builds up.
The customary practice of meditation has an impact on imagination and creativity but also helps to build patience – a skill much needed for connecting with your audience in instructional presentations.
Having the proper set of presentation skills can be quite subjective. It goes beyond presentation tips and deepens into how flexible we can be in our ability to communicate ideas.
Different presentations and different audiences shape the outcome of our efforts. Therefore, having a basic understanding of how to connect, raise awareness, and empathize with people can be key ingredients for your career as a presenter. A word of advice: success doesn’t happen overnight. It takes dedication and patience to build communication skills . Don’t condition your work to believe you will be ready “someday”; it’s best to practice and experience failure as part of the learning process.
Like this article? Please share
Business Presentations, Presentation Approaches, Presentation Skills Filed under Education
Related Articles

Filed under Business • October 31st, 2024
How to Create a Construction Proposal Presentation
Learn how to create winning construction proposal presentations with clear visuals, detailed information, and structured insights.

Filed under Presentation Ideas • October 23rd, 2024
Formal vs Informal Presentation: Understanding the Differences
Learn the differences between formal and informal presentations and how to transition smoothly. PPT templates and tips here!
Filed under Design • October 17th, 2024
Architecture Project Presentation: Must-Know Secrets for Creative Slides
Impress your audience by mastering the art of architectural project presentations. This detailed guide will give you the insights for this craft.
Leave a Reply

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Effective presentation skills help you get your point across and connect with the people you’re communicating with, which is why nearly every employer requires them. Understanding what presentation skills are is only half the battle.
Here are a few tips for business professionals who want to move from being good speakers to great ones: be concise (the fewer words, the better); never use bullet points (photos and images paired...
Whether you’re pitching an idea, reporting market research, or sharing something else, a great presentation can give you a competitive advantage, and be a powerful tool when aiming to persuade ...
Whether you’re making a standup presentation to a large live audience, or a sit-down one-on-one, whether you’re delivering your presentation face to face or virtually, solid presentation skills matter. Even the most seasoned and accomplished presenters may need to fine-tune or update their skills.
Learn how to connect with your audience, keep it simple, start strongly, and use stories and slides effectively. This page draws on expert advice from around the world to help you improve your presentation skills.
We define presentation skills as a compendium of soft skills that directly affect your presentation performance and contribute to creating a great presentation. These are not qualities acquired by birth but skills you ought to train and master to delve into professional environments.