Arab States
Asia and the pacific, europe & central asia, latin america & the caribbean.
You’re using an outdated browser. Old browsers are unstable, unsafe and do not support the features of of this website. Please upgrade to continue.
Your browser does not support JavaScript. This site relies on JavaScript to structure its navigation and load images across all pages. Please enable JavaScript to continue.

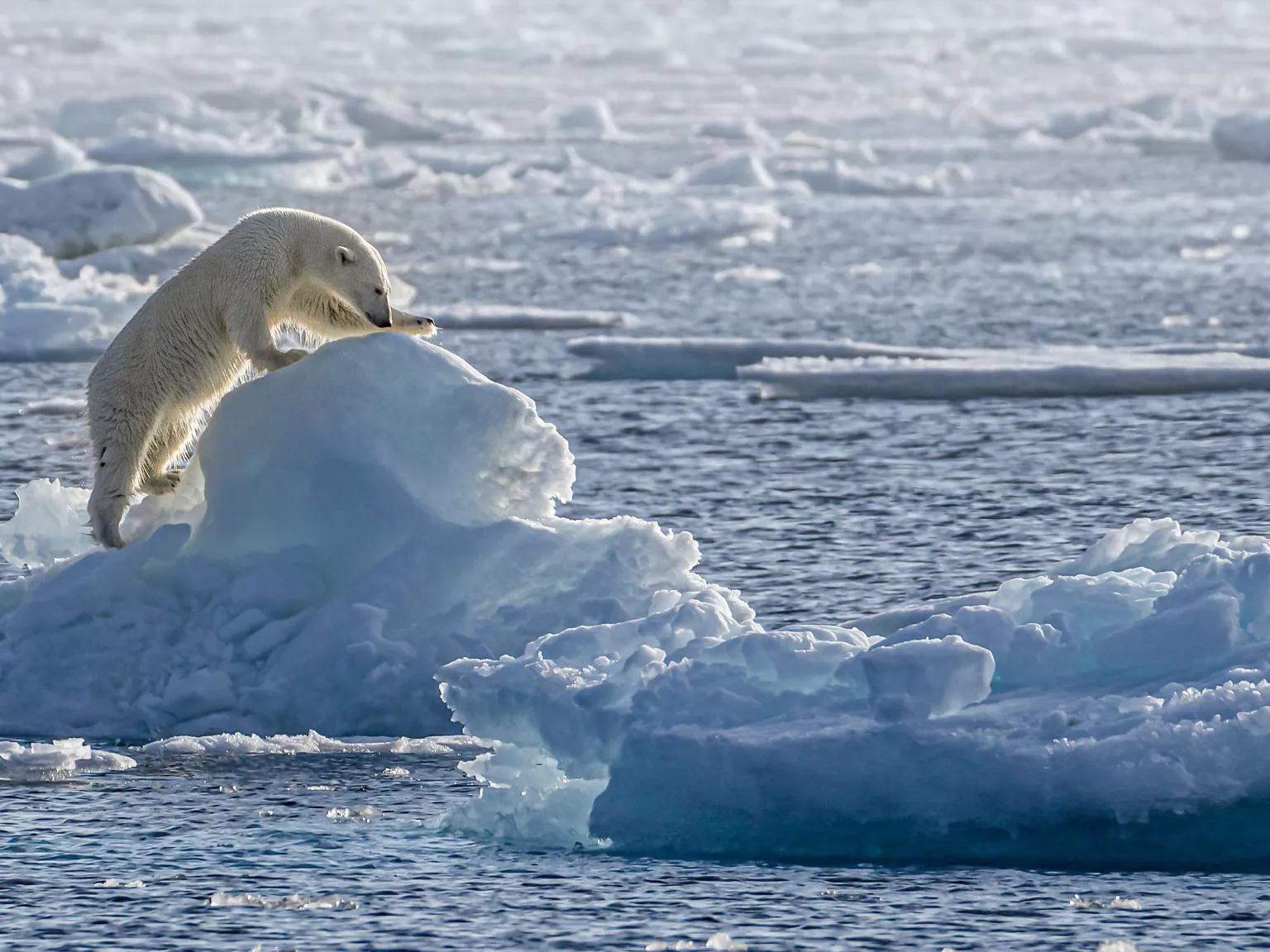
What is climate change mitigation and why is it urgent?
- Share on LinkedIn
- Share on Facebook
- Share on twitter
- Share via email

- Climate change mitigation involves actions to reduce or prevent greenhouse gas emissions from human activities.
- Mitigation efforts include transitioning to renewable energy sources, enhancing energy efficiency, adopting regenerative agricultural practices and protecting and restoring forests and critical ecosystems.
- Effective mitigation requires a whole-of-society approach and structural transformations to reduce emissions and limit global warming to 1.5°C above pre-industrial levels.
- International cooperation, for example through the Paris Agreement, is crucial in guiding and achieving global and national mitigation goals.
- Mitigation efforts face challenges such as the world's deep-rooted dependency on fossil fuels, the increased demand for new mineral resources and the difficulties in revamping our food systems.
- These challenges also offer opportunities to improve resilience and contribute to sustainable development.
What is climate change mitigation?
Climate change mitigation refers to any action taken by governments, businesses or people to reduce or prevent greenhouse gases, or to enhance carbon sinks that remove them from the atmosphere. These gases trap heat from the sun in our planet’s atmosphere, keeping it warm.
Since the industrial era began, human activities have led to the release of dangerous levels of greenhouse gases, causing global warming and climate change. However, despite unequivocal research about the impact of our activities on the planet’s climate and growing awareness of the severe danger climate change poses to our societies, greenhouse gas emissions keep rising. If we can slow down the rise in greenhouse gases, we can slow down the pace of climate change and avoid its worst consequences.
Reducing greenhouse gases can be achieved by:
- Shifting away from fossil fuels : Fossil fuels are the biggest source of greenhouse gases, so transitioning to modern renewable energy sources like solar, wind and geothermal power, and advancing sustainable modes of transportation, is crucial.
- Improving energy efficiency : Using less energy overall – in buildings, industries, public and private spaces, energy generation and transmission, and transportation – helps reduce emissions. This can be achieved by using thermal comfort standards, better insulation and energy efficient appliances, and by improving building design, energy transmission systems and vehicles.
- Changing agricultural practices : Certain farming methods release high amounts of methane and nitrous oxide, which are potent greenhouse gases. Regenerative agricultural practices – including enhancing soil health, reducing livestock-related emissions, direct seeding techniques and using cover crops – support mitigation, improve resilience and decrease the cost burden on farmers.
- The sustainable management and conservation of forests : Forests act as carbon sinks , absorbing carbon dioxide and reducing the overall concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. Measures to reduce deforestation and forest degradation are key for climate mitigation and generate multiple additional benefits such as biodiversity conservation and improved water cycles.
- Restoring and conserving critical ecosystems : In addition to forests, ecosystems such as wetlands, peatlands, and grasslands, as well as coastal biomes such as mangrove forests, also contribute significantly to carbon sequestration, while supporting biodiversity and enhancing climate resilience.
- Creating a supportive environment : Investments, policies and regulations that encourage emission reductions, such as incentives, carbon pricing and limits on emissions from key sectors are crucial to driving climate change mitigation.

Photo: Stephane Bellerose/UNDP Mauritius

Photo: La Incre and Lizeth Jurado/PROAmazonia
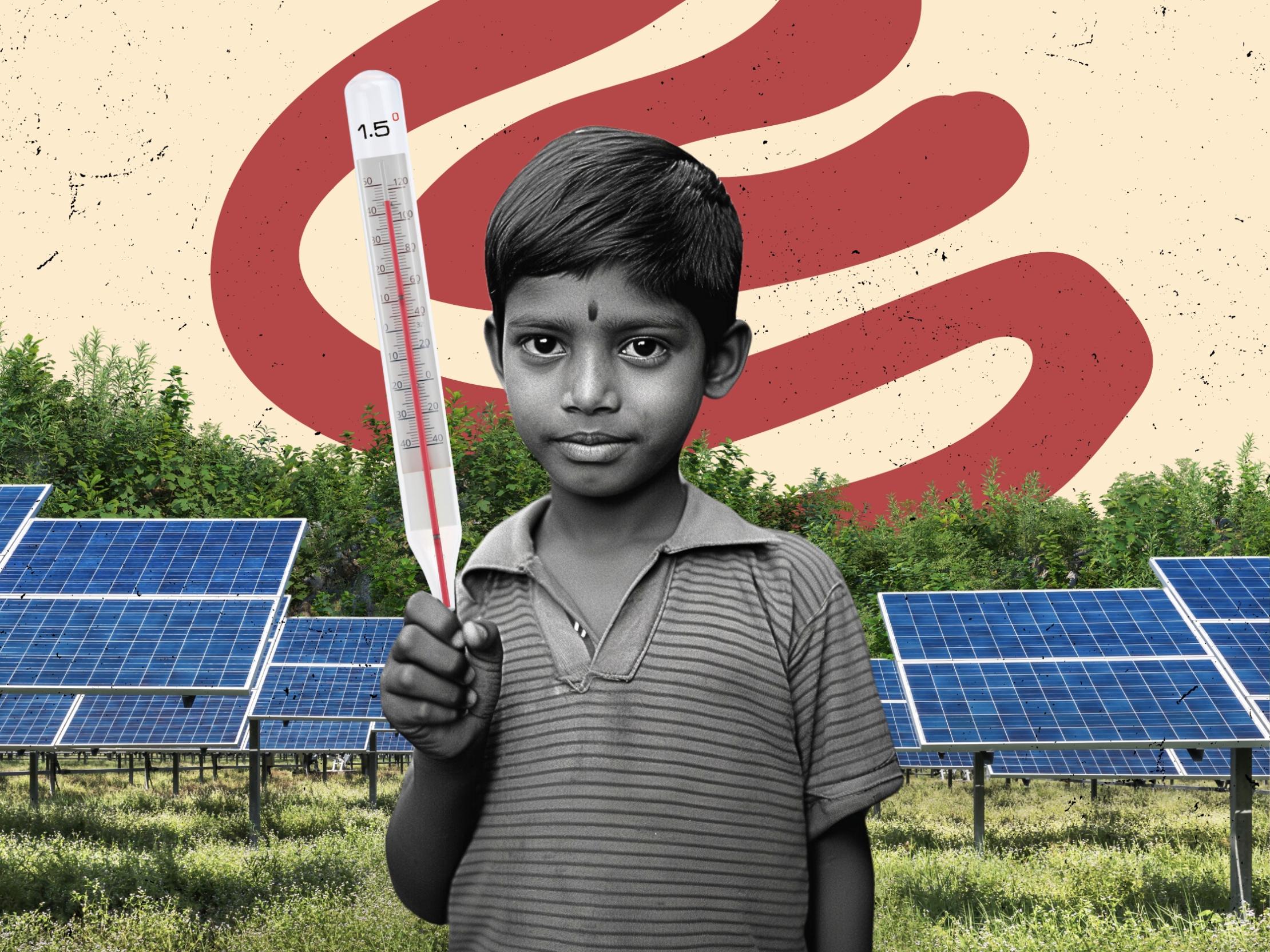
What is the 1.5°C goal and why do we need to stick to it?
In 2015, 196 Parties to the UN Climate Convention in Paris adopted the Paris Agreement , a landmark international treaty, aimed at curbing global warming and addressing the effects of climate change. Its core ambition is to cap the rise in global average temperatures to well below 2°C above levels observed prior to the industrial era, while pursuing efforts to limit the increase to 1.5°C.
The 1.5°C goal is extremely important, especially for vulnerable communities already experiencing severe climate change impacts. Limiting warming below 1.5°C will translate into less extreme weather events and sea level rise, less stress on food production and water access, less biodiversity and ecosystem loss, and a lower chance of irreversible climate consequences.
To limit global warming to the critical threshold of 1.5°C, it is imperative for the world to undertake significant mitigation action. This requires a reduction in greenhouse gas emissions by 45 percent before 2030 and achieving net-zero emissions by mid-century.
What are the policy instruments that countries can use to drive mitigation?
Everyone has a role to play in climate change mitigation, from individuals adopting sustainable habits and advocating for change to governments implementing regulations, providing incentives and facilitating investments. The private sector, particularly those businesses and companies responsible for causing high emissions, should take a leading role in innovating, funding and driving climate change mitigation solutions.
International collaboration and technology transfer is also crucial given the global nature and size of the challenge. As the main platform for international cooperation on climate action, the Paris Agreement has set forth a series of responsibilities and policy tools for its signatories. One of the primary instruments for achieving the goals of the treaty is Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs) . These are the national climate pledges that each Party is required to develop and update every five years. NDCs articulate how each country will contribute to reducing greenhouse gas emissions and enhance climate resilience. While NDCs include short- to medium-term targets, long-term low emission development strategies (LT-LEDS) are policy tools under the Paris Agreement through which countries must show how they plan to achieve carbon neutrality by mid-century. These strategies define a long-term vision that gives coherence and direction to shorter-term national climate targets.

Photo: Mucyo Serge/UNDP Rwanda
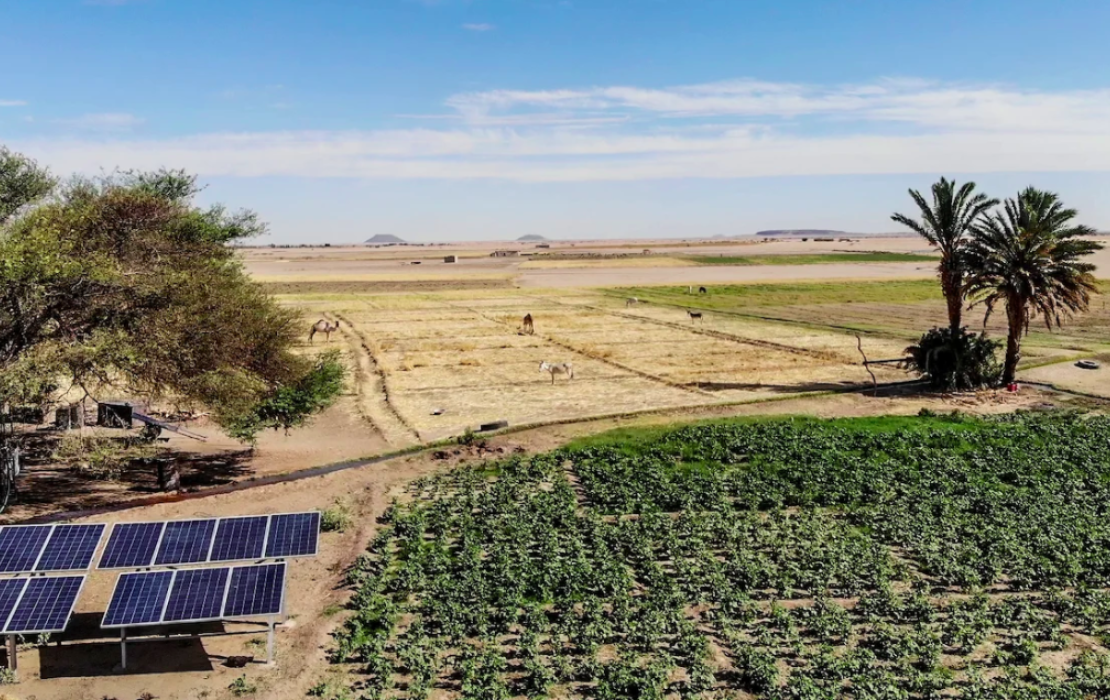

Photo: William Seal/UNDP Sudan
At the same time, the call for climate change mitigation has evolved into a call for reparative action, where high-income countries are urged to rectify past and ongoing contributions to the climate crisis. This approach reflects the UN Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) which advocates for climate justice, recognizing the unequal historical responsibility for the climate crisis, emphasizing that wealthier countries, having profited from high-emission activities, bear a greater obligation to lead in mitigating these impacts. This includes not only reducing their own emissions, but also supporting vulnerable countries in their transition to low-emission development pathways.
Another critical aspect is ensuring a just transition for workers and communities that depend on the fossil fuel industry and its many connected industries. This process must prioritize social equity and create alternative employment opportunities as part of the shift towards renewable energy and more sustainable practices.
For emerging economies, innovation and advancements in technology have now demonstrated that robust economic growth can be achieved with clean, sustainable energy sources. By integrating renewable energy technologies such as solar, wind and geothermal power into their growth strategies, these economies can reduce their emissions, enhance energy security and create new economic opportunities and jobs. This shift not only contributes to global mitigation efforts but also sets a precedent for sustainable development.
What are some of the challenges slowing down climate change mitigation efforts?
Mitigating climate change is fraught with complexities, including the global economy's deep-rooted dependency on fossil fuels and the accompanying challenge of eliminating fossil fuel subsidies. This reliance – and the vested interests that have a stake in maintaining it – presents a significant barrier to transitioning to sustainable energy sources.
The shift towards decarbonization and renewable energy is driving increased demand for critical minerals such as copper, lithium, nickel, cobalt, and rare earth metals. Since new mining projects can take up to 15 years to yield output, mineral supply chains could become a bottleneck for decarbonization efforts. In addition, these minerals are predominantly found in a few, mostly low-income countries, which could heighten supply chain vulnerabilities and geopolitical tensions.
Furthermore, due to the significant demand for these minerals and the urgency of the energy transition, the scaled-up investment in the sector has the potential to exacerbate environmental degradation, economic and governance risks, and social inequalities, affecting the rights of Indigenous Peoples, local communities, and workers. Addressing these concerns necessitates implementing social and environmental safeguards, embracing circular economy principles, and establishing and enforcing responsible policies and regulations .
Agriculture is currently the largest driver of deforestation worldwide. A transformation in our food systems to reverse the impact that agriculture has on forests and biodiversity is undoubtedly a complex challenge. But it is also an important opportunity. The latest IPCC report highlights that adaptation and mitigation options related to land, water and food offer the greatest potential in responding to the climate crisis. Shifting to regenerative agricultural practices will not only ensure a healthy, fair and stable food supply for the world’s population, but also help to significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
Photo: UNDP India

Photo: Nino Zedginidze/UNDP Georgia
What are some examples of climate change mitigation?
In Mauritius , UNDP, with funding from the Green Climate Fund, has supported the government to install battery energy storage capacity that has enabled 50 MW of intermittent renewable energy to be connected to the grid, helping to avoid 81,000 tonnes of carbon dioxide annually.
In Indonesia , UNDP has been working with the government for over a decade to support sustainable palm oil production. In 2019, the country adopted a National Action Plan on Sustainable Palm Oil, which was collaboratively developed by government, industry and civil society representatives. The plan increased the adoption of practices to minimize the adverse social and environmental effects of palm oil production and to protect forests. Since 2015, 37 million tonnes of direct greenhouse gas emissions have been avoided and 824,000 hectares of land with high conservation value have been protected.
In Moldova and Paraguay , UNDP has helped set up Green City Labs that are helping build more sustainable cities. This is achieved by implementing urban land use and mobility planning, prioritizing energy efficiency in residential buildings, introducing low-carbon public transport, implementing resource-efficient waste management, and switching to renewable energy sources.
UNDP has supported the governments of Brazil, Costa Rica, Ecuador and Indonesia to implement results-based payments through the REDD+ (Reducing emissions from deforestation and forest degradation in developing countries) framework. These include payments for environmental services and community forest management programmes that channel international climate finance resources to local actors on the ground, specifically forest communities and Indigenous Peoples.
UNDP is also supporting small island developing states like the Comoros to invest in renewable energy and sustainable infrastructure. Through the Africa Minigrids Program , solar minigrids will be installed in two priority communities, Grand Comore and Moheli, providing energy access through distributed renewable energy solutions to those hardest to reach.
And in South Africa , a UNDP initative to boost energy efficiency awareness among the general population and improve labelling standards has taken over commercial shopping malls.

What is UNDP’s role in supporting climate change mitigation?
UNDP aims to assist countries with their climate change mitigation efforts, guiding them towards sustainable, low-carbon and climate-resilient development. This support is in line with achieving the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), particularly those related to affordable and clean energy (SDG7), sustainable cities and communities (SDG11), and climate action (SDG13). Specifically, UNDP’s offer of support includes developing and improving legislation and policy, standards and regulations, capacity building, knowledge dissemination, and financial mobilization for countries to pilot and scale-up mitigation solutions such as renewable energy projects, energy efficiency initiatives and sustainable land-use practices.
With financial support from the Global Environment Facility and the Green Climate Fund, UNDP has an active portfolio of 94 climate change mitigation projects in 69 countries. These initiatives are not only aimed at reducing greenhouse gas emissions, but also at contributing to sustainable and resilient development pathways.
Explore More Stories
Pacific shores, solar solutions: harnessing renewable energy in the pacific islands.

Photo: Yuichi Ishida/UNDP Timor-Leste
West Africa has great potential for solar energy. It’s time to release it.
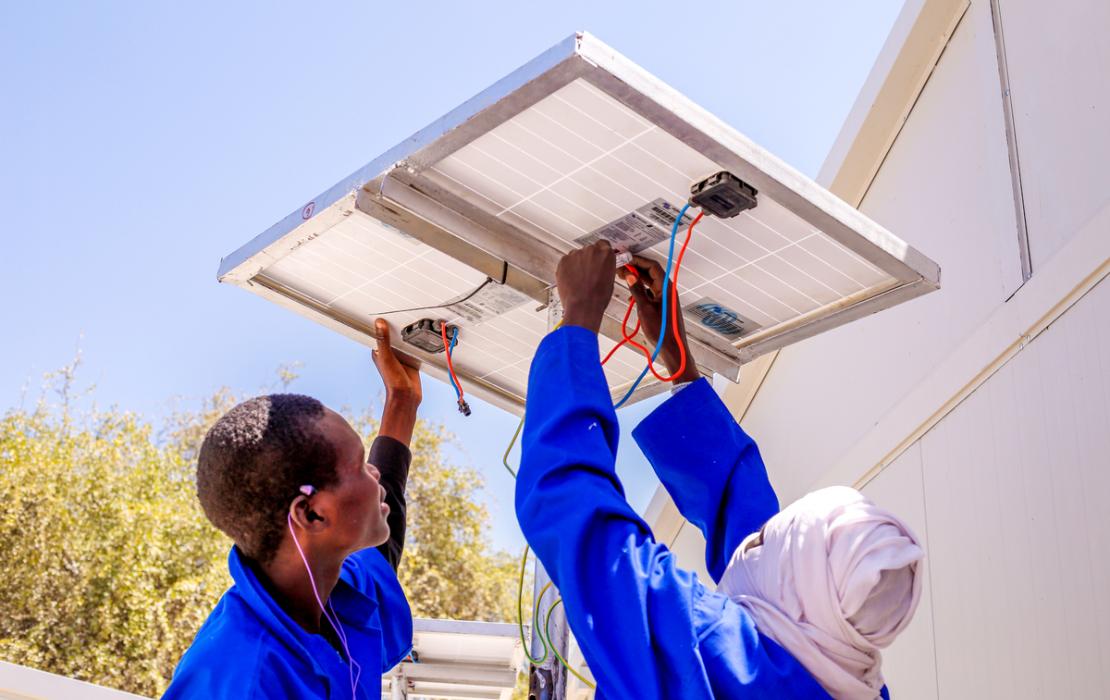

Photo: UNDP Niger
Electric vehicles are driving a greener future in Viet Nam
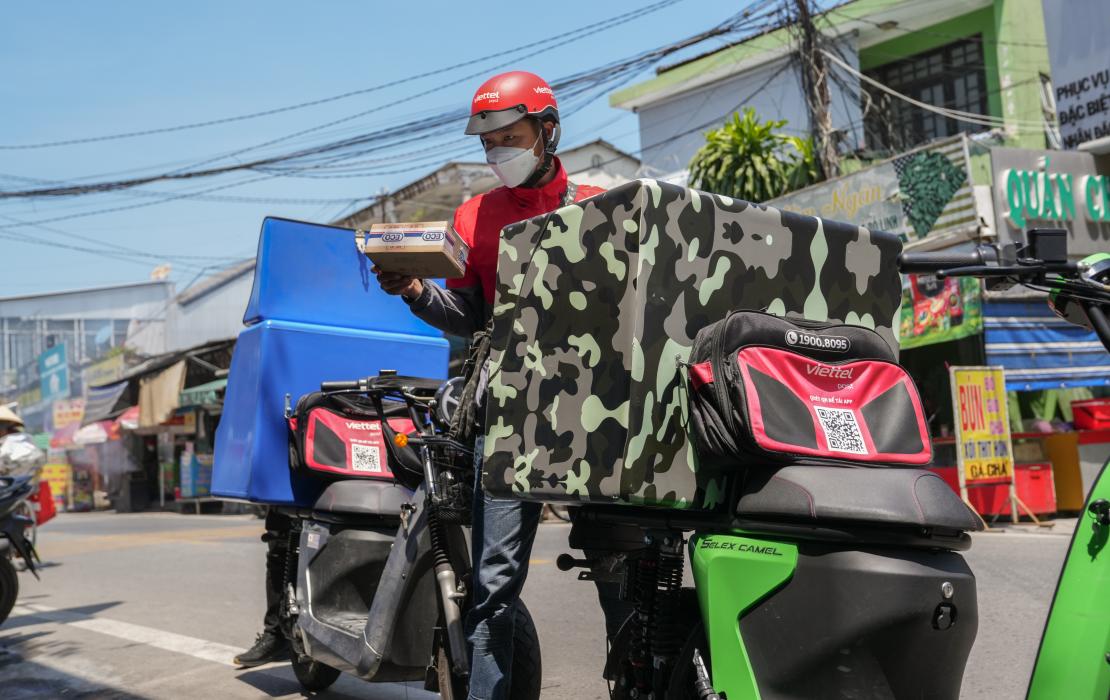

Ho Tuan Anh delivers goods with his new e-motorbike. Photo by: Phan Huong Giang/UNDP Viet Nam
Why the Western Balkans are choosing decarbonization

Photo: UNDP Bosnia and Herzegovina
Six lessons on how to achieve future-smart energy efficient buildings
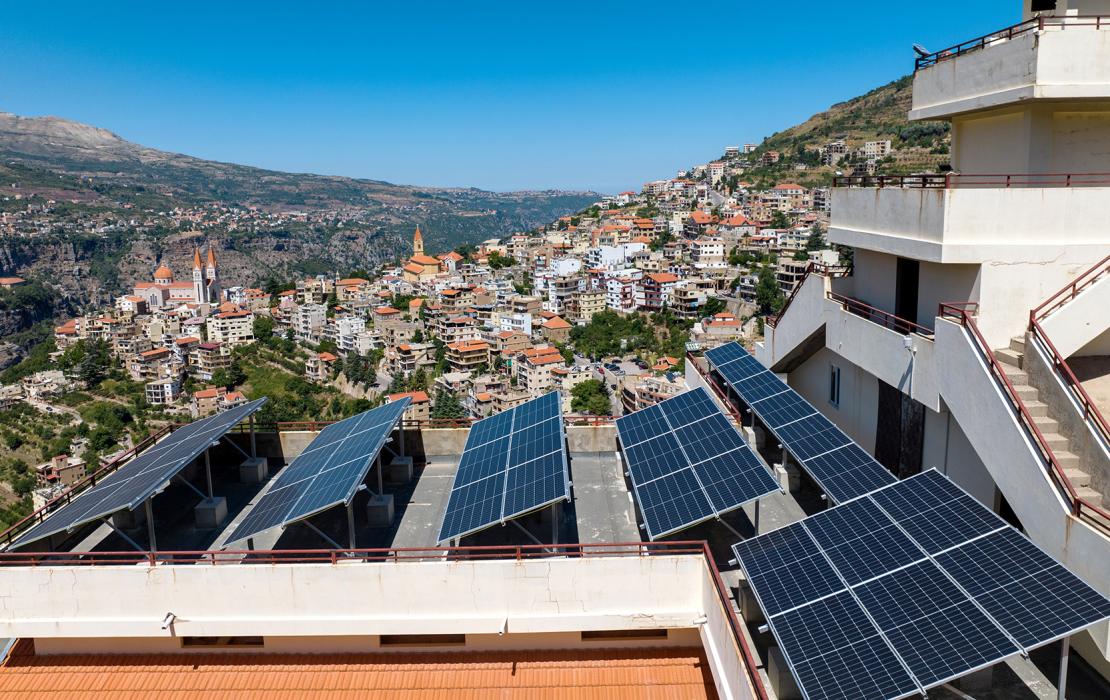

Solar photovoltaic systems on roofs in Lebanon. Photo: Fouad Choufany / UNDP Lebanon
Six ways to achieve sustainable energy for all
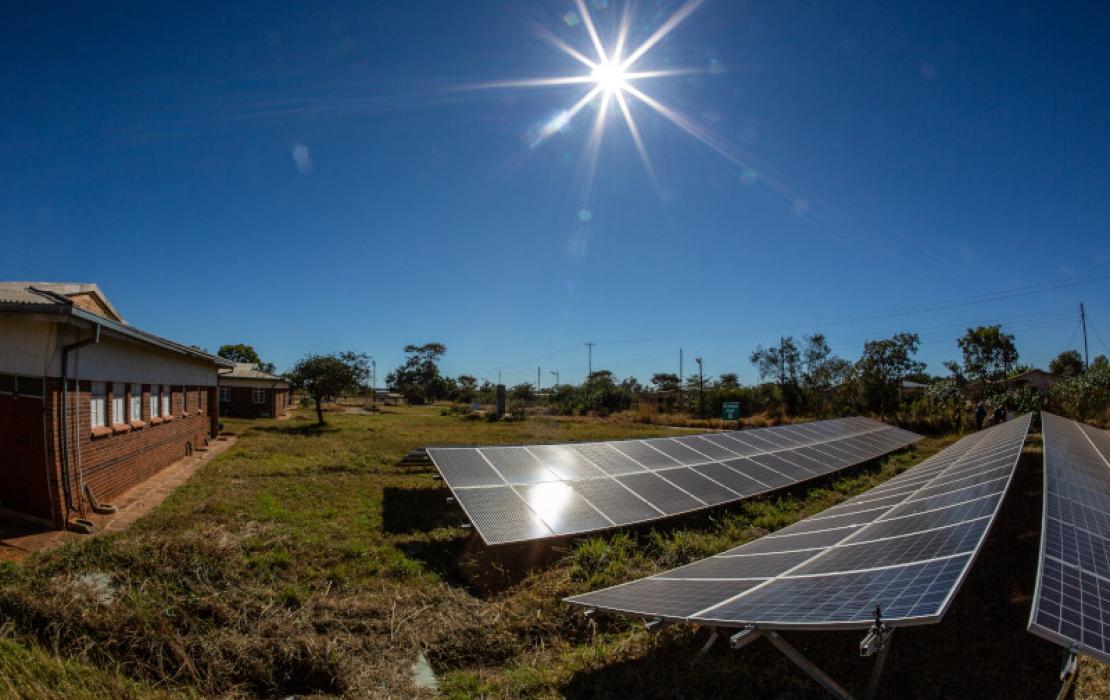

Photo: UNDP Zimbabwe

Climate Action

Tackling Climate Change
Goal 13 calls for urgent action to combat climate change and its impacts. It is intrinsically linked to all 16 of the other Goals of the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development. To address climate change, countries adopted the Paris Agreement to limit global temperature rise to well below 2 degrees Celsius. Learn more about Goal 13 , and for the latest United Nations climate news, visit un.org/climatechange .
Paris Agreement FAQ
Why we need action
Climate change is now affecting every country on every continent. It is disrupting national economies and affecting lives, costing people, communities and countries dearly today and even more tomorrow.
People are experiencing the significant impacts of climate change, which include changing weather patterns, rising sea level, and more extreme weather events. The greenhouse gas emissions from human activities are driving climate change and continue to rise. They are now at their highest levels in history. Without action, the world’s average surface temperature is projected to rise over the 21st century and is likely to surpass 3 degrees Celsius this century—with some areas of the world expected to warm even more. The poorest and most vulnerable people are being affected the most.
A race we can win
Affordable, scalable solutions are now available to enable countries to leapfrog to cleaner, more resilient economies. The pace of change is quickening as more people are turning to renewable energy and a range of other measures that will reduce emissions and increase adaptation efforts.
But climate change is a global challenge that does not respect national borders. Emissions anywhere affect people everywhere. It is an issue that requires solutions that need to be coordinated at the international level and it requires international cooperation to help developing countries move toward a low-carbon economy.
To address climate change, countries adopted the Paris Agreement at the COP21 in Paris on 12 December 2015. The Agreement entered into force less than a year later. In the agreement, all countries agreed to work to limit global temperature rise to well below 2 degrees Celsius, and given the grave risks, to strive for 1.5 degrees Celsius.
Implementation of the Paris Agreement is essential for the achievement of the Sustainable Development Goals , and provides a roadmap for climate actions that will reduce emissions and build climate resilience.
IPCC Climate Report 2022

The Working Group III report provides an updated global assessment of climate change mitigation progress and pledges, and examines the sources of global emissions. It explains developments in emission reduction and mitigation efforts, assessing the impact of national climate pledges in relation to long-term emissions goals. Read more here .
The Paris Agreement on climate change
The UN continues to encourage all stakeholders to take action toward reducing the impacts of climate change.
COP25: Madrid, 2019

The conference was designed to take the next crucial steps in the UN climate change process. The conference served to build ambition ahead of 2020, the year in which countries have committed to submit new and updated national climate action plans. Crucial climate action work was taken forward in areas including finance, the transparency of climate action, forests and agriculture, technology, capacity building, loss and damage, indigenous peoples, cities, oceans and gender.
COP24: Katowice, 2018

The 2018 UN Climate Conference took place in Katowice, Poland from 2-14 December.
The conference finalized the rules for implementation of the Paris Agreement on climate change under the Paris Agreement work programme (PAWP). It also included a number of high-level events, mandated events, action events and roundtables.
COP23: Bonn, 2017

The 2017 UN Climate Conference took place in Bonn, Germany, from 6-18 November. Leaders of national governments, cities, states, business, investors, NGOs and civil society gathered to speed up climate action to meet the goals of the Paris Climate Change Agreement.
COP22: Marrakesh, 2016

High-Level Event Towards Entry into Force: 21 September, 2016

Recap of the High-Level Event Towards Entry into Force
Paris Agreement Signing Ceremony, 22 April 2016

To keep the global spotlight focused on climate change and build on the strong political momentum from Paris, United Nations Secretary-General Ban Ki-moon invited representatives of all countries to sign the Paris Agreement on climate change at a special Ceremony at the United Nations Headquarters on 22 April.
Cop21, 12 December 2015

Paris Agreement – Frequently Asked Questions
What is the present status of the paris agreement on climate change.
The Paris Agreement on climate change officially entered into force on 4 November 2016, after 55 countries accounting for 55 per cent of the total global greenhouse gas emissions, deposited their instruments of ratification, acceptance or approval with the UN Secretary-General.
As of June 2020, 195 signatories and 189 countries have joined the Paris Agreement.
What is the next step towards the implementation of the Paris Agreement?
What are the most significant aspects about the new agreement, is this agreement really going to help, what does the agreement require countries to do, what happens if a country doesn’t live up to its commitments would there be any enforcement, developing countries stressed the need for equity and fairness. does the agreement provide that, how can paris get us to the 2 degree—or even 1.5 degree goal, how are climate change and the paris agreement linked with the sustainable development goals, why is it so urgent that we do something now, related news.

SIDS go forward with ‘new sense of hope, solidarity and determination’
By dpicampaigns | 2024-05-30T08:00:00-04:00 30 May 2024 |
The roadmap towards achieving resilient prosperity for small island States [...]

Cabo Verde beats back climate change through South-South cooperation
The small island developing State of Cabo Verde is fighting [...]

More climate funding needed to ‘transition from rhetoric to decisive action’
By dpicampaigns | 2024-05-29T08:00:00-04:00 29 May 2024 |
Climate action taken so far to help fund efforts in [...]
Related Videos
Launch of secretary-general’s youth advisory group on climate change – 27 july.
Building on the climate action momentum, the Secretary-General will launch his Youth Advisory Group on Climate Change on 27 July to amplify youth voices and to engage young people in an open and transparent dialogue as the UN gears up to raise ambition and accelerate action to address the climate crisis.
ActNow Climate Campaign – Chef Grace Ramirez
Chef Grace Ramirez talks about sustainability and green hacks in support of the UN's ActNow climate campaign.
Angry Birds 2 PSA in support of the ActNow Climate Campaign
The Department of Global Communications is partnering with Sony Pictures Entertainment and the UN Foundation for a second time on an initiative to promote the Sustainable Development Goal 13 – take urgent action against climate change and its impacts.
What can we do to slow or stop global warming?
There is no one-size-fits-all approach to stopping or slowing global warming, and each individual, business, municipal, state, tribal, and federal entity must weigh their options in light of their own unique set of circumstances. Experts say it is likely many strategies working together will be needed. Generally speaking, here are some examples of mitigation strategies we can use to slow or stop the human-caused global warming ( learn more ):
- Where possible, we can switch to renewable sources of energy (such as solar and wind energy) to power our homes and buildings, thus emitting far less heat-trapping gases into the atmosphere.
- Where feasible, we can drive electric vehicles instead of those that burn fossil fuels; or we can use mass transit instead of driving our own cars.
- Where affordable, we can conserve energy by better insulating our homes and buildings, and by replacing old, failing appliances with more energy-efficient models.
- Where practicable, we can counterbalance our annual carbon dioxide emissions by investing in commercial services that draw down an equal amount of carbon out of the atmosphere, such as through planting trees or carbon capture and storage techniques.
- Where practical, we can support more local businesses that use and promote sustainable, climate-smart practices such as those listed above.
- We can consider placing an upper limit on the amount of carbon dioxide we will allow ourselves to emit into the atmosphere within a given timeframe.
Note that NOAA doesn’t advocate for or against particular climate policies. Instead, NOAA’s role is to provide data and scientific information about climate, including how it has changed and is likely to change in the future depending on different climate policies or actions society may or may not take. More guidance on courses of action can be found in the National Academy of Sciences' 2010 report, titled Informing an Effective Response to Climate Change . Also learn more here, here, and here .
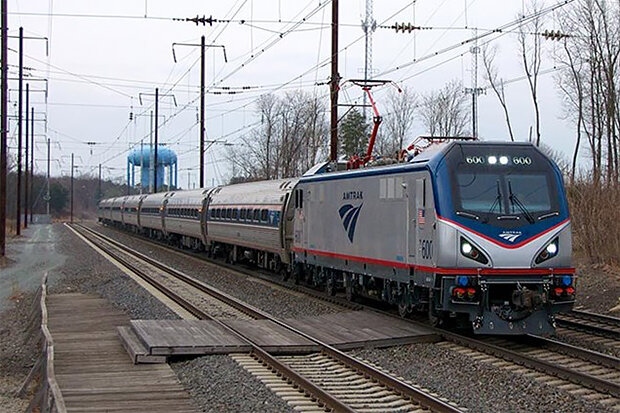

Thanks to low friction between train wheels and tracks, and level train tracks with gradual turns, trains have high energy efficiency. Photo from National Park Service Amtrak Trails and Rails .
Stabilizing global temperature near its current level requires eliminating all emissions of heat-trapping gases or, equivalently, achieving a carbon-neutral society in which people remove as much carbon from the atmosphere as they emit. Achieving this goal will require substantial societal changes in energy technologies and infrastructure that go beyond the collective actions of individuals and households to reduce emissions.
We value your feedback
Help us improve our content
Related Content
News & features, after sandy: changes and choices, national climate assessment: states and cities are already reducing carbon emissions to save lives and dollars, improving models for wind energy, maps & data, land - terrestrial climate variables, climate forcing, sst - sea surface temperature, teaching climate, toolbox for teaching climate & energy, climate youth engagement, young voices for the planet film series, climate resilience toolkit, climate science for water professionals, carbon balance, alaska and the arctic.

Here are the most effective things you can do to fight climate change
PhD Student, University of Leeds
Disclosure statement
Max Callaghan does not work for, consult, own shares in or receive funding from any company or organisation that would benefit from this article, and has disclosed no relevant affiliations beyond their academic appointment.
University of Leeds provides funding as a founding partner of The Conversation UK.
View all partners
Limiting global warming to 1.5°C above pre-industrial levels requires reaching net zero emissions by the middle of this century. This means that, in less than three decades, we need to reverse more than a century of rising emissions and bring annual emissions down to near zero, while balancing out all remaining unavoidable emissions by actively removing carbon from the atmosphere.
To help speed this process as individuals, we’ve got to do everything we can to cut down our use of fossil fuels. But many people aren’t aware of the most effective ways to do this. Thankfully, the latest report by the UN climate change panel IPCC devotes a chapter to all the ways in which changes in people’s behaviour can accelerate the transition to net zero.
The chapter includes an analysis of 60 individual actions which can help fight climate change, building on research led by Diana Ivanova at the University of Leeds – and to which I contributed. We grouped these actions into three areas: avoiding consumption, shifting consumption and improving consumption (making it more efficient). The charts below, produced for the IPCC report , show what we found.

What to avoid
By far the most effective things to avoid involve transport. Living without a car reduces greenhouse gas emissions by an average of 2 tonnes of CO₂ emissions per person per year, while avoiding a single long distance return flight cuts emissions by an average of 1.9 tonnes. That’s equivalent to driving a typical EU car more than 16,000km from Hamburg, Germany to Ulaanbaatar, Mongolia and back.

Since the vast majority of the world’s population do not fly at all – and of those who do, only a small percentage fly frequently – fliers can make very substantial reductions to their carbon footprints with each flight they avoid.
What to shift
But living sustainably is not just about giving things up. Large reductions in emissions can be achieved by shifting to a different way of doing things. Because driving is so polluting, for example, shifting to public transport , walking or cycling can make an enormous change, with added benefits for your personal health and local air pollution levels.
Likewise, because of the high emissions associated with meat and dairy – particularly those produced by farming sheep and cows – shifting towards more sustainable diets can substantially reduce your carbon footprint. A totally vegan diet is the most effective way to do this, but sizeable savings can be made simply by switching from beef and lamb to pork and chicken.
What to improve
Finally, the things we do already could be made more efficient by improving carbon efficiency at home: for example by using insulation and heat pumps , or producing your own renewable energy by installing solar panels . Switching from a combustion car to an electric one – ideally a battery EV, which generates much larger reductions in emissions than hybrid or fuel cell EVs – will make your car journeys more efficient. Plus, its effect on emissions will increase as time goes by and the amount of electricity generated by renewables grows.

In the race to net zero, every tonne of CO₂ really does count. If more of us take even a few of these suggestions into account, we’re collectively more likely to be able to achieve the ambitious goals set out in the Paris climate agreement . Of course, these changes will need to be backed by major political action on sustainability at the same time.
If we’re to use less fossil fuel energy, the use of fossil fuels needs to be either restricted or made more expensive. The social consequences of this need to be carefully managed so that carbon pricing schemes can benefit people on lower incomes: which can happen if revenues are redistributed to take the financial burden off poorer households.
But there’s a whole lot more that governments could do to help people to live more sustainably, such as providing better, safer public transport and “ active travel ” infrastructure (such as bike lanes and pedestrian zones) so that people have alternatives to driving and flying.
There’s no avoiding the fact that if political solutions are to address climate change with the urgency our global situation requires, these solutions will limit the extent to which we can indulge in carbon-intensive behaviours. More than anything, we must vote into power those prepared to make such tough decisions for the sake of our planet’s future.

Don’t have time to read about climate change as much as you’d like? Get a weekly roundup in your inbox instead. Every Wednesday, The Conversation’s environment editor writes Imagine, a short email that goes a little deeper into just one climate issue. Join the 10,000+ readers who’ve subscribed so far.
- Fossil fuels
- Climate change
- Renewable energy
- Sustainability
- Public transport
- Sustainable living
- climate mitigation
- Greenhouse gas emissions (GHG)

Data Manager

Research Support Officer

Director, Social Policy

Head, School of Psychology

Senior Research Fellow - Women's Health Services

Russell Millner/Alamy
Defend Our Planet and Most Vulnerable Species
Your donation today will be triple-matched to power NRDC’s next great chapter in protecting our ecosystems and saving imperiled wildlife.
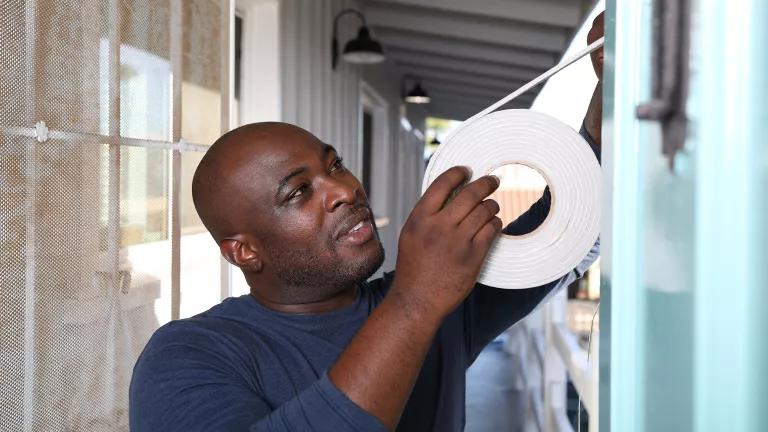
How You Can Stop Global Warming
Healing the planet starts in your garage, in your kitchen, and at your dining room table.

Weatherizing doors and windows by sealing drafts can make your home more energy efficient.
Getty Images
- Share this page block
Rising sea levels. Raging storms. Searing heat. Ferocious fires. Severe drought. Punishing floods. The effects of climate change are already threatening our health, our communities, our economy, our security, and our children’s future.
What can you do? A whole lot, as it turns out. Americans, on average, produce 21 tons of carbon a year, about four times the global average. Personal action is, of course, no substitute for meaningful government policies. We still must limit carbon pollution and aggressively move away from dirty fossil fuels toward cleaner power.
But it’s important to remember the equally vital contributions that can be made by private citizens—which is to say, by you. “Change only happens when individuals take action,” says clean energy advocate Aliya Haq. “There’s no other way, if it doesn’t start with people.”
Here are a dozen easy, effective ways each one of us can make a difference.
1. Speak up!
What’s the single biggest way you can make an impact on global climate change? “Talk to your friends and family, and make sure your representatives are making good decisions,” Haq says. By voicing your concerns—via social media or, better yet, directly to your elected officials —you send a message that you care about the warming world. Encourage Congress to enact new laws that limit carbon emissions and require polluters to pay for the emissions they produce. “The main reason elected officials do anything difficult is because their constituents make them,” Haq says. You can help protect public lands, stop offshore drilling, and more here .
2. Power your home with renewable energy.
Choose a utility company that generates at least half its power from wind or solar and has been certified by Green-e Energy , an organization that vets renewable energy options. If that isn’t possible for you, take a look at your electric bill; many utilities now list other ways to support renewable sources on their monthly statements and websites.
3. Weatherize, weatherize, weatherize.
“Building heating and cooling are among the biggest uses of energy,” Haq says. Indeed, heating and air-conditioning account for almost half of home energy use. You can make your space more energy efficient by sealing drafts and ensuring it’s adequately insulated. You can also claim federal tax credits for many energy efficiency home improvements. To help you figure out where to start, you could also get a home energy audit, which some utilities offer free of charge. (Alternatively, you can hire a professional to come to your home and perform one; the Inflation Reduction Act offers a partial tax credit for this.) The EPA’s Home Energy Yardstick gives you a simple assessment of your home’s annual energy use compared with similar homes.
4. Invest in energy-efficient appliances.
Since they were first implemented nationally in 1987, efficiency standards for dozens of appliances and products have kept 2.3 billion tons of carbon dioxide out of the air. That’s about the same amount as the annual carbon pollution coughed up by nearly 440 million cars. “Energy efficiency is the lowest-cost way to reduce emissions,” Haq says. When shopping for refrigerators, washing machines, heat pump water heaters , and other appliances, look for the Energy Star label. It will tell you which are the most efficient. (There may also be rebates to earn from your purchase of Energy Star–certified products.)
And when you’re ready to swap out your old machines, don’t just put them on the curb: Recycling an old refrigerator through the EPA’s Responsible Appliance Disposal Program can prevent an additional 10,000 pounds of carbon pollution because the global-warming pollutants in the refrigerants and foam would be properly captured rather than vented to the air.
5. Reduce water waste.
Saving water reduces carbon pollution, too. That's because it takes a lot of energy to pump, heat, and treat your water. So take shorter showers, turn off the tap while brushing your teeth, and switch to WaterSense -labeled fixtures and appliances. The EPA estimates that if just one out of every 100 American homes were retrofitted with water-efficient fixtures, about 100 million kilowatt-hours of electricity per year would be saved—avoiding 80,000 tons of global warming pollution .
6. Actually eat the food you buy—and compost what you can’t.
Approximately 10 percent of U.S. energy use goes into growing, processing, packaging, and shipping food—about 40 percent of which winds up in the landfill. “If you’re wasting less food, you’re likely cutting down on energy consumption,” Haq says. As for the scraps you can’t eat or the leftovers you don’t get to, collect them in a compost bin instead of sending them to the landfill where they release methane. Recycling food and other organic waste into compost provides a range of environmental benefits, including improving soil health, reducing greenhouse gas emissions, recycling nutrients, and mitigating the impact of droughts.
7. Buy better bulbs.
LED light bulbs use one-sixth the amount of energy to deliver the same amount of light as conventional incandescents and last at least 10 times longer. They’re also cheaper in the long run: A 10-watt LED that replaces your traditional 60-watt bulb will save you $125 over the light bulb’s life. And because the average American home has around 40 to 50 light bulbs, this is a simple swap that will reap huge rewards. If every household in the United States replaced just one incandescent with an Energy Star–labeled LED, we would prevent seven billion pounds of carbon pollution per year. That’s equivalent to the emissions of about 648,000 cars.
8. Pull the plug(s).
Taken together, the outlets in your home are likely powering about 65 devices—an average load for a home in the United States. Audio and video devices, cordless vacuums and power tools, and other electronics use energy even when they're not charging. This "idle load" across all U.S. households adds up to the output of 50 large power plants in the country . So don't leave fully charged devices plugged into your home's outlets, unplug rarely used devices or plug them into power strips and timers, and adjust your computers and monitors to automatically power down to the lowest power mode when not in use.
9. Drive a fuel-efficient vehicle.
Gas-smart cars, such as hybrids and fully electric vehicles, save fuel and money . And once all cars and light trucks meet 2025’s clean car standards, which means averaging 54.5 miles per gallon, they’ll be a mainstay. For good reason: Relative to a national fleet of vehicles that averaged only 28.3 miles per gallon in 2011, Americans will spend $80 billion less at the pump each year and cut their automotive emissions by half. Before you buy a new set of wheels, compare fuel-economy performance here .
10. Maintain your ride.
If all Americans kept their tires properly inflated, we could save 1.2 billion gallons of gas each year. A simple tune-up can boost miles per gallon anywhere from 4 percent to 40 percent, and a new air filter can get you a 10 percent boost. Also, remove unnecessary accessories from your car roof. Roof racks and clamshell storage containers can reduce fuel efficiency by as much as 5 percent.
11. Rethink planes, trains, and automobiles.
Choosing to live in walkable smart-growth cities and towns with quality public transportation leads to less driving, less money spent on fuel, and less pollution in the air . Less frequent flying can make a big difference, too. “Air transport is a major source of climate pollution,” Haq says. “If you can take a train instead, do that.” If you must fly, consider purchasing carbon offsets to counterbalance the hefty carbon pollution associated with flying. But not all carbon offset companies are alike. Do your homework to find the best supplier.
12. Reduce, reuse, and recycle.
In the United States, the average person generates 4.5 pounds of trash every day. Fortunately, not all the items we discard end up in landfills; we recycle or compost more than one-third of our trash. In 2014 this saved carbon emissions equivalent to the yearly output of 38 million passenger cars . But we could be doing so much more. “ Reduce should always be the number-one priority,” says NRDC senior resource specialist Darby Hoover . And to reap the environmental benefits of “recyclable” goods, you must recycle according to the rules of your municipality, since systems vary widely by location . Search your municipality’s sanitation department (or equivalent) webpage to learn exactly what you can place in the recycling bin, as counties and cities often differ in what they accept.
This story was originally published on April 20, 2022 and has been updated with new information and links.
This NRDC.org story is available for online republication by news media outlets or nonprofits under these conditions: The writer(s) must be credited with a byline; you must note prominently that the story was originally published by NRDC.org and link to the original; the story cannot be edited (beyond simple things such as grammar); you can’t resell the story in any form or grant republishing rights to other outlets; you can’t republish our material wholesale or automatically—you need to select stories individually; you can’t republish the photos or graphics on our site without specific permission; you should drop us a note to let us know when you’ve used one of our stories.
Related Stories

What Are the Solutions to Climate Change?

How to Ditch the Biggest Fossil Fuel Offenders in Your Life

A Consumer Guide to the Inflation Reduction Act
When you sign up, you’ll become a member of NRDC’s Activist Network. We will keep you informed with the latest alerts and progress reports.
- CEO and Chairperson
- Focal Points
- Secretariat Staff
Stakeholder Engagement
- GEF Agencies
- Conventions
- Civil Society Organizations
- Private Sector
- Feature Stories
- Press Releases
- Publications
The GEF sponsors 13 youth ambassadors for COP28 climate summit

Climate Change Mitigation
- Climate Change
- Climate Change Adaptation
- Transparency
Climate change mitigation means reducing the net release of greenhouse gas emissions that are warming our planet. The Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) highlights the urgency of needed climate actions: global emissions will have to decline by 43% from 2019 by 2030, and rapidly decrease to net-zero by 2050 if we are to stay within the safety limits established by the Paris Agreement .
However, the 2023 NDC Synthesis Report prepared by the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) Secretariat shows that while countries have increased individual levels of ambition to reduce emissions, the combined impact still falls short of the emission reduction cuts necessary to meet the Paris Agreement goals.
Achieving net-zero objectives will require a whole-of-economy and whole-of-government strategy, across all sectors and actors. Rapid emissions decline from power generation, transportation, and from the industrial sector will have to be coupled with significant transformations in the way we manage land, forests, coastlines, and wetlands, which currently account for about a quarter of global carbon emissions.

The GEF at UNFCCC COP28
The 2023 UN Climate Change Conference will take place Nov. 30 to Dec. 12, 2023 in Dubai, UAE.
The GEF will co-host a pavilion at COP28 with the Adaptation Fund, Climate Investment Funds, and Green Climate Fund, focusing on the importance of #Finance4Climate and emphasizing collaboration and coordination between the multilateral funds, including the GEF’s Least Developed Countries Fund and Special Climate Change Fund.
Featured Content

The GEF and Climate Change: Catalyzing Transformation

The Africa Minigrids Program

UNFCCC Guidance from the COPs and Responses by the GEF: COP1 - COP27
Climate change affects virtually all natural and socio-economic systems. The interactions between climate change and biodiversity, land degradation, forests, chemicals and waste, and international waters point to the importance of recognizing climate change implications in everything we do.
As the largest multilateral fund focusing on global environmental issues, the GEF has the unique ability to support integrated solutions with systems thinking that look to generate multiple global environmental benefits across several UN Conventions , improving efficiency and reducing trade-offs and duplication. It is also well placed to take risks on innovative and early-stage business models and technologies, using predictable grant funding.
The GEF-8 climate change mitigation strategy aims to support developing countries to make transformational shifts towards net-zero greenhouse gas emissions and climate-resilient development pathways, supporting the objectives of the UNFCCC and the Paris Agreement. Within the evolving landscape of climate finance, the strategy is designed to be as complementary as possible to other sources of climate finance. This is evident for instance through the collaboration with the Green Climate Fund , with which we have established a Long-Term Vision for Complementarity, Coherence and Collaboration .
Building on the GEF's long-standing track record of driving innovation and fostering enabling conditions, the strategy also aims at promoting private sector engagement and increased investment in low-carbon technologies and nature-based solutions with high mitigation potential. This is done by combining technical assistance and investments, to pilot innovative business models, financial mechanisms, supportive policies regulations, strategies and institutional arrangements, in order to trigger systemic transformations while creating or expanding markets for green products and services, generating jobs, and supporting economic growth. Projects will also promote gender-responsive approaches and decision-making built on inclusive stakeholder consultations and aim to empower women and girls in the implementation of the identified solutions and in the promotion of sustainable income generating opportunities.
To achieve the ambitious goal of reducing (or avoiding) emissions of greenhouse gases equivalent to at least 1.8 billion tons of CO2, the mitigation strategy hinges upon two fundamental pillars:
Pillar I. Promoting innovation, technology development and transfer, and enabling policies for mitigation options with systemic impacts : Four entry points have been prioritized for GEF-8 support in the climate mitigation area, in consideration of their innovative and transformative nature and complementary to other financial mechanisms:
- Accelerating the efficient use of energy and materials
- Enabling the transition to decarbonized power systems
- Scaling up zero-emission mobility of people and goods
- Promoting nature-based solutions with high mitigation potential
Pillar II. Fostering enabling conditions to mainstream mitigation concerns into sustainable development strategies : The GEF continues to address the need for enabling conditions to mainstream climate change concerns into the national planning and development agenda through sound data, analysis, and policy frameworks. These activities are supported under two main objectives:
- Supporting capacity-building needs for transparency under the Paris Agreement through the Capacity-building Initiative for Transparency (CBIT)
- Supporting relevant UN Convention obligations and enabling activities, such as National Communications and Biennial Transparency Reports
Climate Change Mitigation Programs
Owing to the integrated nature of GEF support, climate change mitigation benefits are also generated through programmatic approaches at a regional and global level. These include programs such as:
GEF Global Program to Support Electric Mobility
Implemented in collaboration with leading international organizations and partners from the private sector, finance and academia, this program has been developed to support low- and middle- income countries around the world with the shift to electric mobility. Explore the e-Mobility Toolbox >>

Accelerating the Shift to Electric Mobility
Un-led partnership to accelerate electric mobility shift in 27 countries.

'The opportunities add up': lessons from e-mobility in Africa
Gef africa minigrids program.
This technical assistance program aims to to support access to clean energy by increasing the financial viability, and promoting scaled up commercial investment, in low-carbon minigrids in Africa, with a focus on cost reduction levers and innovative business models. Explore the program website >>
New initiative to transform energy markets in over 20 African countries
Gef ceo message for launch of the africa minigrids program at cop27.

GEF Global Cleantech Innovation Programme
This program aims to bring about transformative change in low- and middle-income countries by addressing market and policy shortcomings that prevent the emergence, deployment, and adoption of cleantech solutions in the long term, thus enabling countries to leapfrog to greener economies. Explore the program website >>

Global Cleantech Innovation Programme 2022 Brochure
Global cleantech innovation programme.

Cleantech innovators take on COVID-19 recovery
Gef-8 integrated programs.
The Integrated Programs aim to generate climate change outcomes with systemic impacts, and strengthen interaction and integration between climate change mitigation and the other GEF focal areas. Six of the 11 GEF-8 cross-cutting Integrated Programs will provide key climate contributions:
- Net-Zero Nature-Positive Accelerator
Sustainable Cities
- Food Systems
- Amazon, Congo, and Critical Forest Biomes
- Circular Solutions to Plastic Pollution
- Ecosystem Restoration
In the GEF’s first 30 years, we have provided at least $7.6 billion and leveraged $60.6 billion with other partners for more than 1,100 mitigation projects and programs in over 160 countries. These investments are expected to contribute 9.5 billion metric tons of direct and indirect greenhouse gas emission reductions over time. This includes :
- More than $2.7 billion for 550 renewable energy and energy efficiency projects, contributing to 520 million metric tons of CO2 equivalents of reduction
- 650 projects supporting sustainable forest management
- Over 180 million hectares under sustainable land management, benefiting more than 90 million smallholders
- Protecting carbon sinks and biodiversity in over 4,000 protected areas covering 2,500 million hectares
- Over 650 projects with private sector co-financing, more than 141 of which included equity, loans or risk-mitigation instruments, leveraging an average co-financing ratio of 1:9
- Over $600 million in enabling activities, including support for 210 Biennial Update Reports, 80 Biennial Transparency Reports, and 531 National Communications
- Support to 88 countries to build institutional and technical capacity for enhanced transparency with $146 million through the CBIT
Looking Ahead
The GEF is continuing to provide nimble support to enable developing countries to implement their climate change mitigation priorities, in support of a carbon-neutral, nature-positive, pollution-free, and climate-resilient future.
The GEF has been collaborating closely with the Green Climate Fund (GCF) through coordinated engagement, including joint country dialogues and programming. The GEF-GCF partnership has been enhanced through the launch and implementation of the Long-Term Vision of Complementarity , including identification of major initiatives, building on the successful GEF-GCF investments on the new phase of the Great Green Wall initiative, and the facilitation of national investment planning in five countries. An annual report on the progress made with the implementation of the LTV is presented to the GEF Council each June. Building on this partnership, increased collaboration with other climate funds will be explored in the GEF-8 period to continue to advance the global climate action agenda.
GEF-8 projects and programs aim to work more closely with the private sector on climate change mitigation, including small- and medium-sized enterprises, entrepreneurs, energy suppliers and distributors, vehicle manufacturers, industrial producers and manufacturers, farmers and producers, and financial institutions, among others. Our work will focus on translating the ambition of net-zero commitments into real-economy emissions reductions. In addition, we will work with businesses ready to align with deep decarbonization targets in areas that can transform energy, transport, and land-use systems.
As an operating mechanism of the financial mechanism of the UNFCCC, the GEF is engaged in the UNFCCC process to help raise the level of climate ambition and support ongoing action and progress. An annual report of the GEF to the UNFCCC is submitted in advance of the meetings of the Conference of the Parties.
Related Topics

Sustainable Forest Management

Forest and Landscape Restoration
Responding to the Climate Threat: Essays on Humanity’s Greatest Challenge

A new book co-authored by MIT Joint Program Founding Co-Director Emeritus Henry Jacoby
From the Back Cover
This book demonstrates how robust and evolving science can be relevant to public discourse about climate policy. Fighting climate change is the ultimate societal challenge, and the difficulty is not just in the wrenching adjustments required to cut greenhouse emissions and to respond to change already under way. A second and equally important difficulty is ensuring widespread public understanding of the natural and social science. This understanding is essential for an effective risk management strategy at a planetary scale. The scientific, economic, and policy aspects of climate change are already a challenge to communicate, without factoring in the distractions and deflections from organized programs of misinformation and denial.
Here, four scholars, each with decades of research on the climate threat, take on the task of explaining our current understanding of the climate threat and what can be done about it, in lay language―importantly, without losing critical aspects of the natural and social science. In a series of essays, published during the 2020 presidential election, the COVID pandemic, and through the fall of 2021, they explain the essential components of the challenge, countering the forces of distrust of the science and opposition to a vigorous national response.
Each of the essays provides an opportunity to learn about a particular aspect of climate science and policy within the complex context of current events. The overall volume is more than the sum of its individual articles. Proceeding each essay is an explanation of the context in which it was written, followed by observation of what has happened since its first publication. In addition to its discussion of topical issues in modern climate science, the book also explores science communication to a broad audience. Its authors are not only scientists – they are also teachers, using current events to teach when people are listening. For preserving Earth’s planetary life support system, science and teaching are essential. Advancing both is an unending task.
About the Authors
Gary Yohe is the Huffington Foundation Professor of Economics and Environmental Studies, Emeritus, at Wesleyan University in Connecticut. He served as convening lead author for multiple chapters and the Synthesis Report for the IPCC from 1990 through 2014 and was vice-chair of the Third U.S. National Climate Assessment.
Henry Jacoby is the William F. Pounds Professor of Management, Emeritus, in the MIT Sloan School of Management and former co-director of the MIT Joint Program on the Science and Policy of Global Change, which is focused on the integration of the natural and social sciences and policy analysis in application to the threat of global climate change.
Richard Richels directed climate change research at the Electric Power Research Institute (EPRI). He served as lead author for multiple chapters of the IPCC in the areas of mitigation, impacts and adaptation from 1992 through 2014. He also served on the National Assessment Synthesis Team for the first U.S. National Climate Assessment.
Ben Santer is a climate scientist and John D. and Catherine T. MacArthur Fellow. He contributed to all six IPCC reports. He was the lead author of Chapter 8 of the 1995 IPCC report which concluded that “the balance of evidence suggests a discernible human influence on global climate”. He is currently a Visiting Researcher at UCLA’s Joint Institute for Regional Earth System Science & Engineering.
Access the Book
View the book on the publisher's website here .
Order the book from Amazon here .

Related Posts
E9: slow carbon, fast carbon.

Making steel with electricity

E7: An introduction to carbon capture (re-air)
Elaine liu: charging ahead.
MIT Climate News in Your Inbox
Advertisement
A review of the global climate change impacts, adaptation, and sustainable mitigation measures
- Review Article
- Published: 04 April 2022
- Volume 29 , pages 42539–42559, ( 2022 )
Cite this article

- Kashif Abbass 1 ,
- Muhammad Zeeshan Qasim 2 ,
- Huaming Song 1 ,
- Muntasir Murshed ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-9872-8742 3 , 4 ,
- Haider Mahmood ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-6474-4338 5 &
- Ijaz Younis 1
210k Accesses
426 Citations
31 Altmetric
Explore all metrics
Climate change is a long-lasting change in the weather arrays across tropics to polls. It is a global threat that has embarked on to put stress on various sectors. This study is aimed to conceptually engineer how climate variability is deteriorating the sustainability of diverse sectors worldwide. Specifically, the agricultural sector’s vulnerability is a globally concerning scenario, as sufficient production and food supplies are threatened due to irreversible weather fluctuations. In turn, it is challenging the global feeding patterns, particularly in countries with agriculture as an integral part of their economy and total productivity. Climate change has also put the integrity and survival of many species at stake due to shifts in optimum temperature ranges, thereby accelerating biodiversity loss by progressively changing the ecosystem structures. Climate variations increase the likelihood of particular food and waterborne and vector-borne diseases, and a recent example is a coronavirus pandemic. Climate change also accelerates the enigma of antimicrobial resistance, another threat to human health due to the increasing incidence of resistant pathogenic infections. Besides, the global tourism industry is devastated as climate change impacts unfavorable tourism spots. The methodology investigates hypothetical scenarios of climate variability and attempts to describe the quality of evidence to facilitate readers’ careful, critical engagement. Secondary data is used to identify sustainability issues such as environmental, social, and economic viability. To better understand the problem, gathered the information in this report from various media outlets, research agencies, policy papers, newspapers, and other sources. This review is a sectorial assessment of climate change mitigation and adaptation approaches worldwide in the aforementioned sectors and the associated economic costs. According to the findings, government involvement is necessary for the country’s long-term development through strict accountability of resources and regulations implemented in the past to generate cutting-edge climate policy. Therefore, mitigating the impacts of climate change must be of the utmost importance, and hence, this global threat requires global commitment to address its dreadful implications to ensure global sustenance.
Similar content being viewed by others
Morocco’s climate change impacts, adaptation and mitigation—a stocktake
Climate change adaptation (CCA) research in Nepal: implications for the advancement of adaptation planning
A comprehensive review of climate change impacts, adaptation, and mitigation on environmental and natural calamities in Pakistan
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
Worldwide observed and anticipated climatic changes for the twenty-first century and global warming are significant global changes that have been encountered during the past 65 years. Climate change (CC) is an inter-governmental complex challenge globally with its influence over various components of the ecological, environmental, socio-political, and socio-economic disciplines (Adger et al. 2005 ; Leal Filho et al. 2021 ; Feliciano et al. 2022 ). Climate change involves heightened temperatures across numerous worlds (Battisti and Naylor 2009 ; Schuurmans 2021 ; Weisheimer and Palmer 2005 ; Yadav et al. 2015 ). With the onset of the industrial revolution, the problem of earth climate was amplified manifold (Leppänen et al. 2014 ). It is reported that the immediate attention and due steps might increase the probability of overcoming its devastating impacts. It is not plausible to interpret the exact consequences of climate change (CC) on a sectoral basis (Izaguirre et al. 2021 ; Jurgilevich et al. 2017 ), which is evident by the emerging level of recognition plus the inclusion of climatic uncertainties at both local and national level of policymaking (Ayers et al. 2014 ).
Climate change is characterized based on the comprehensive long-haul temperature and precipitation trends and other components such as pressure and humidity level in the surrounding environment. Besides, the irregular weather patterns, retreating of global ice sheets, and the corresponding elevated sea level rise are among the most renowned international and domestic effects of climate change (Lipczynska-Kochany 2018 ; Michel et al. 2021 ; Murshed and Dao 2020 ). Before the industrial revolution, natural sources, including volcanoes, forest fires, and seismic activities, were regarded as the distinct sources of greenhouse gases (GHGs) such as CO 2 , CH 4 , N 2 O, and H 2 O into the atmosphere (Murshed et al. 2020 ; Hussain et al. 2020 ; Sovacool et al. 2021 ; Usman and Balsalobre-Lorente 2022 ; Murshed 2022 ). United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) struck a major agreement to tackle climate change and accelerate and intensify the actions and investments required for a sustainable low-carbon future at Conference of the Parties (COP-21) in Paris on December 12, 2015. The Paris Agreement expands on the Convention by bringing all nations together for the first time in a single cause to undertake ambitious measures to prevent climate change and adapt to its impacts, with increased funding to assist developing countries in doing so. As so, it marks a turning point in the global climate fight. The core goal of the Paris Agreement is to improve the global response to the threat of climate change by keeping the global temperature rise this century well below 2 °C over pre-industrial levels and to pursue efforts to limit the temperature increase to 1.5° C (Sharma et al. 2020 ; Sharif et al. 2020 ; Chien et al. 2021 .
Furthermore, the agreement aspires to strengthen nations’ ability to deal with the effects of climate change and align financing flows with low GHG emissions and climate-resilient paths (Shahbaz et al. 2019 ; Anwar et al. 2021 ; Usman et al. 2022a ). To achieve these lofty goals, adequate financial resources must be mobilized and provided, as well as a new technology framework and expanded capacity building, allowing developing countries and the most vulnerable countries to act under their respective national objectives. The agreement also establishes a more transparent action and support mechanism. All Parties are required by the Paris Agreement to do their best through “nationally determined contributions” (NDCs) and to strengthen these efforts in the coming years (Balsalobre-Lorente et al. 2020 ). It includes obligations that all Parties regularly report on their emissions and implementation activities. A global stock-take will be conducted every five years to review collective progress toward the agreement’s goal and inform the Parties’ future individual actions. The Paris Agreement became available for signature on April 22, 2016, Earth Day, at the United Nations Headquarters in New York. On November 4, 2016, it went into effect 30 days after the so-called double threshold was met (ratification by 55 nations accounting for at least 55% of world emissions). More countries have ratified and continue to ratify the agreement since then, bringing 125 Parties in early 2017. To fully operationalize the Paris Agreement, a work program was initiated in Paris to define mechanisms, processes, and recommendations on a wide range of concerns (Murshed et al. 2021 ). Since 2016, Parties have collaborated in subsidiary bodies (APA, SBSTA, and SBI) and numerous formed entities. The Conference of the Parties functioning as the meeting of the Parties to the Paris Agreement (CMA) convened for the first time in November 2016 in Marrakesh in conjunction with COP22 and made its first two resolutions. The work plan is scheduled to be finished by 2018. Some mitigation and adaptation strategies to reduce the emission in the prospective of Paris agreement are following firstly, a long-term goal of keeping the increase in global average temperature to well below 2 °C above pre-industrial levels, secondly, to aim to limit the rise to 1.5 °C, since this would significantly reduce risks and the impacts of climate change, thirdly, on the need for global emissions to peak as soon as possible, recognizing that this will take longer for developing countries, lastly, to undertake rapid reductions after that under the best available science, to achieve a balance between emissions and removals in the second half of the century. On the other side, some adaptation strategies are; strengthening societies’ ability to deal with the effects of climate change and to continue & expand international assistance for developing nations’ adaptation.
However, anthropogenic activities are currently regarded as most accountable for CC (Murshed et al. 2022 ). Apart from the industrial revolution, other anthropogenic activities include excessive agricultural operations, which further involve the high use of fuel-based mechanization, burning of agricultural residues, burning fossil fuels, deforestation, national and domestic transportation sectors, etc. (Huang et al. 2016 ). Consequently, these anthropogenic activities lead to climatic catastrophes, damaging local and global infrastructure, human health, and total productivity. Energy consumption has mounted GHGs levels concerning warming temperatures as most of the energy production in developing countries comes from fossil fuels (Balsalobre-Lorente et al. 2022 ; Usman et al. 2022b ; Abbass et al. 2021a ; Ishikawa-Ishiwata and Furuya 2022 ).
This review aims to highlight the effects of climate change in a socio-scientific aspect by analyzing the existing literature on various sectorial pieces of evidence globally that influence the environment. Although this review provides a thorough examination of climate change and its severe affected sectors that pose a grave danger for global agriculture, biodiversity, health, economy, forestry, and tourism, and to purpose some practical prophylactic measures and mitigation strategies to be adapted as sound substitutes to survive from climate change (CC) impacts. The societal implications of irregular weather patterns and other effects of climate changes are discussed in detail. Some numerous sustainable mitigation measures and adaptation practices and techniques at the global level are discussed in this review with an in-depth focus on its economic, social, and environmental aspects. Methods of data collection section are included in the supplementary information.
Review methodology
Related study and its objectives.
Today, we live an ordinary life in the beautiful digital, globalized world where climate change has a decisive role. What happens in one country has a massive influence on geographically far apart countries, which points to the current crisis known as COVID-19 (Sarkar et al. 2021 ). The most dangerous disease like COVID-19 has affected the world’s climate changes and economic conditions (Abbass et al. 2022 ; Pirasteh-Anosheh et al. 2021 ). The purpose of the present study is to review the status of research on the subject, which is based on “Global Climate Change Impacts, adaptation, and sustainable mitigation measures” by systematically reviewing past published and unpublished research work. Furthermore, the current study seeks to comment on research on the same topic and suggest future research on the same topic. Specifically, the present study aims: The first one is, organize publications to make them easy and quick to find. Secondly, to explore issues in this area, propose an outline of research for future work. The third aim of the study is to synthesize the previous literature on climate change, various sectors, and their mitigation measurement. Lastly , classify the articles according to the different methods and procedures that have been adopted.
Review methodology for reviewers
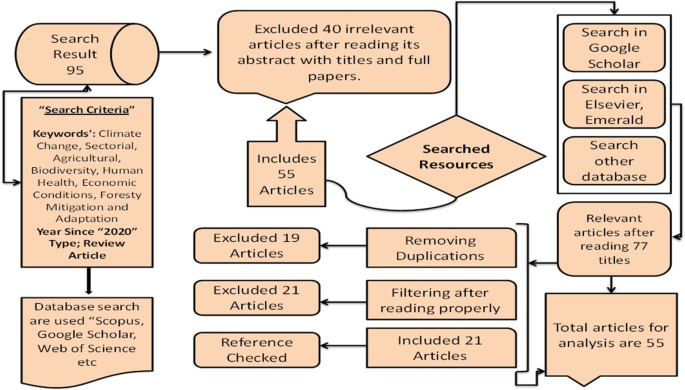
This review-based article followed systematic literature review techniques that have proved the literature review as a rigorous framework (Benita 2021 ; Tranfield et al. 2003 ). Moreover, we illustrate in Fig. 1 the search method that we have started for this research. First, finalized the research theme to search literature (Cooper et al. 2018 ). Second, used numerous research databases to search related articles and download from the database (Web of Science, Google Scholar, Scopus Index Journals, Emerald, Elsevier Science Direct, Springer, and Sciverse). We focused on various articles, with research articles, feedback pieces, short notes, debates, and review articles published in scholarly journals. Reports used to search for multiple keywords such as “Climate Change,” “Mitigation and Adaptation,” “Department of Agriculture and Human Health,” “Department of Biodiversity and Forestry,” etc.; in summary, keyword list and full text have been made. Initially, the search for keywords yielded a large amount of literature.
Source : constructed by authors
Methodology search for finalized articles for investigations.
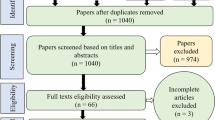
Since 2020, it has been impossible to review all the articles found; some restrictions have been set for the literature exhibition. The study searched 95 articles on a different database mentioned above based on the nature of the study. It excluded 40 irrelevant papers due to copied from a previous search after readings tiles, abstract and full pieces. The criteria for inclusion were: (i) articles focused on “Global Climate Change Impacts, adaptation, and sustainable mitigation measures,” and (ii) the search key terms related to study requirements. The complete procedure yielded 55 articles for our study. We repeat our search on the “Web of Science and Google Scholars” database to enhance the search results and check the referenced articles.
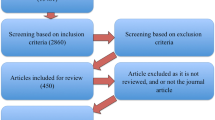
In this study, 55 articles are reviewed systematically and analyzed for research topics and other aspects, such as the methods, contexts, and theories used in these studies. Furthermore, this study analyzes closely related areas to provide unique research opportunities in the future. The study also discussed future direction opportunities and research questions by understanding the research findings climate changes and other affected sectors. The reviewed paper framework analysis process is outlined in Fig. 2 .
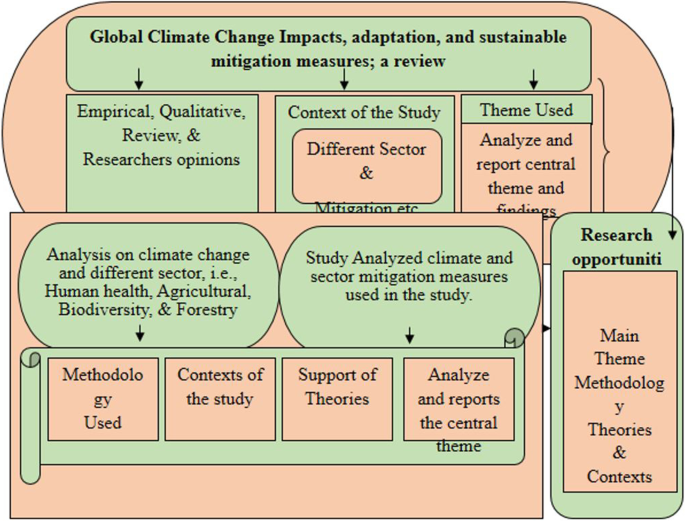
Framework of the analysis Process.
Natural disasters and climate change’s socio-economic consequences
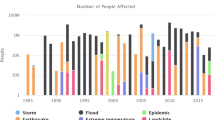
Natural and environmental disasters can be highly variable from year to year; some years pass with very few deaths before a significant disaster event claims many lives (Symanski et al. 2021 ). Approximately 60,000 people globally died from natural disasters each year on average over the past decade (Ritchie and Roser 2014 ; Wiranata and Simbolon 2021 ). So, according to the report, around 0.1% of global deaths. Annual variability in the number and share of deaths from natural disasters in recent decades are shown in Fig. 3 . The number of fatalities can be meager—sometimes less than 10,000, and as few as 0.01% of all deaths. But shock events have a devastating impact: the 1983–1985 famine and drought in Ethiopia; the 2004 Indian Ocean earthquake and tsunami; Cyclone Nargis, which struck Myanmar in 2008; and the 2010 Port-au-Prince earthquake in Haiti and now recent example is COVID-19 pandemic (Erman et al. 2021 ). These events pushed global disaster deaths to over 200,000—more than 0.4% of deaths in these years. Low-frequency, high-impact events such as earthquakes and tsunamis are not preventable, but such high losses of human life are. Historical evidence shows that earlier disaster detection, more robust infrastructure, emergency preparedness, and response programmers have substantially reduced disaster deaths worldwide. Low-income is also the most vulnerable to disasters; improving living conditions, facilities, and response services in these areas would be critical in reducing natural disaster deaths in the coming decades.
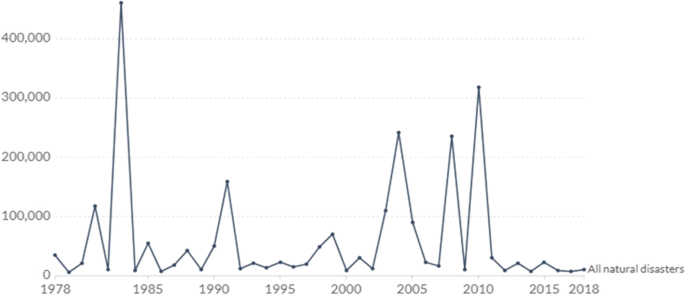
Source EMDAT ( 2020 )
Global deaths from natural disasters, 1978 to 2020.
The interior regions of the continent are likely to be impacted by rising temperatures (Dimri et al. 2018 ; Goes et al. 2020 ; Mannig et al. 2018 ; Schuurmans 2021 ). Weather patterns change due to the shortage of natural resources (water), increase in glacier melting, and rising mercury are likely to cause extinction to many planted species (Gampe et al. 2016 ; Mihiretu et al. 2021 ; Shaffril et al. 2018 ).On the other hand, the coastal ecosystem is on the verge of devastation (Perera et al. 2018 ; Phillips 2018 ). The temperature rises, insect disease outbreaks, health-related problems, and seasonal and lifestyle changes are persistent, with a strong probability of these patterns continuing in the future (Abbass et al. 2021c ; Hussain et al. 2018 ). At the global level, a shortage of good infrastructure and insufficient adaptive capacity are hammering the most (IPCC 2013 ). In addition to the above concerns, a lack of environmental education and knowledge, outdated consumer behavior, a scarcity of incentives, a lack of legislation, and the government’s lack of commitment to climate change contribute to the general public’s concerns. By 2050, a 2 to 3% rise in mercury and a drastic shift in rainfall patterns may have serious consequences (Huang et al. 2022 ; Gorst et al. 2018 ). Natural and environmental calamities caused huge losses globally, such as decreased agriculture outputs, rehabilitation of the system, and rebuilding necessary technologies (Ali and Erenstein 2017 ; Ramankutty et al. 2018 ; Yu et al. 2021 ) (Table 1 ). Furthermore, in the last 3 or 4 years, the world has been plagued by smog-related eye and skin diseases, as well as a rise in road accidents due to poor visibility.
Climate change and agriculture
Global agriculture is the ultimate sector responsible for 30–40% of all greenhouse emissions, which makes it a leading industry predominantly contributing to climate warming and significantly impacted by it (Grieg; Mishra et al. 2021 ; Ortiz et al. 2021 ; Thornton and Lipper 2014 ). Numerous agro-environmental and climatic factors that have a dominant influence on agriculture productivity (Pautasso et al. 2012 ) are significantly impacted in response to precipitation extremes including floods, forest fires, and droughts (Huang 2004 ). Besides, the immense dependency on exhaustible resources also fuels the fire and leads global agriculture to become prone to devastation. Godfray et al. ( 2010 ) mentioned that decline in agriculture challenges the farmer’s quality of life and thus a significant factor to poverty as the food and water supplies are critically impacted by CC (Ortiz et al. 2021 ; Rosenzweig et al. 2014 ). As an essential part of the economic systems, especially in developing countries, agricultural systems affect the overall economy and potentially the well-being of households (Schlenker and Roberts 2009 ). According to the report published by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), atmospheric concentrations of greenhouse gases, i.e., CH 4, CO 2 , and N 2 O, are increased in the air to extraordinary levels over the last few centuries (Usman and Makhdum 2021 ; Stocker et al. 2013 ). Climate change is the composite outcome of two different factors. The first is the natural causes, and the second is the anthropogenic actions (Karami 2012 ). It is also forecasted that the world may experience a typical rise in temperature stretching from 1 to 3.7 °C at the end of this century (Pachauri et al. 2014 ). The world’s crop production is also highly vulnerable to these global temperature-changing trends as raised temperatures will pose severe negative impacts on crop growth (Reidsma et al. 2009 ). Some of the recent modeling about the fate of global agriculture is briefly described below.
Decline in cereal productivity
Crop productivity will also be affected dramatically in the next few decades due to variations in integral abiotic factors such as temperature, solar radiation, precipitation, and CO 2 . These all factors are included in various regulatory instruments like progress and growth, weather-tempted changes, pest invasions (Cammell and Knight 1992 ), accompanying disease snags (Fand et al. 2012 ), water supplies (Panda et al. 2003 ), high prices of agro-products in world’s agriculture industry, and preeminent quantity of fertilizer consumption. Lobell and field ( 2007 ) claimed that from 1962 to 2002, wheat crop output had condensed significantly due to rising temperatures. Therefore, during 1980–2011, the common wheat productivity trends endorsed extreme temperature events confirmed by Gourdji et al. ( 2013 ) around South Asia, South America, and Central Asia. Various other studies (Asseng, Cao, Zhang, and Ludwig 2009 ; Asseng et al. 2013 ; García et al. 2015 ; Ortiz et al. 2021 ) also proved that wheat output is negatively affected by the rising temperatures and also caused adverse effects on biomass productivity (Calderini et al. 1999 ; Sadras and Slafer 2012 ). Hereafter, the rice crop is also influenced by the high temperatures at night. These difficulties will worsen because the temperature will be rising further in the future owing to CC (Tebaldi et al. 2006 ). Another research conducted in China revealed that a 4.6% of rice production per 1 °C has happened connected with the advancement in night temperatures (Tao et al. 2006 ). Moreover, the average night temperature growth also affected rice indicia cultivar’s output pragmatically during 25 years in the Philippines (Peng et al. 2004 ). It is anticipated that the increase in world average temperature will also cause a substantial reduction in yield (Hatfield et al. 2011 ; Lobell and Gourdji 2012 ). In the southern hemisphere, Parry et al. ( 2007 ) noted a rise of 1–4 °C in average daily temperatures at the end of spring season unti the middle of summers, and this raised temperature reduced crop output by cutting down the time length for phenophases eventually reduce the yield (Hatfield and Prueger 2015 ; R. Ortiz 2008 ). Also, world climate models have recommended that humid and subtropical regions expect to be plentiful prey to the upcoming heat strokes (Battisti and Naylor 2009 ). Grain production is the amalgamation of two constituents: the average weight and the grain output/m 2 , however, in crop production. Crop output is mainly accredited to the grain quantity (Araus et al. 2008 ; Gambín and Borrás 2010 ). In the times of grain set, yield resources are mainly strewn between hitherto defined components, i.e., grain usual weight and grain output, which presents a trade-off between them (Gambín and Borrás 2010 ) beside disparities in per grain integration (B. L. Gambín et al. 2006 ). In addition to this, the maize crop is also susceptible to raised temperatures, principally in the flowering stage (Edreira and Otegui 2013 ). In reality, the lower grain number is associated with insufficient acclimatization due to intense photosynthesis and higher respiration and the high-temperature effect on the reproduction phenomena (Edreira and Otegui 2013 ). During the flowering phase, maize visible to heat (30–36 °C) seemed less anthesis-silking intermissions (Edreira et al. 2011 ). Another research by Dupuis and Dumas ( 1990 ) proved that a drop in spikelet when directly visible to high temperatures above 35 °C in vitro pollination. Abnormalities in kernel number claimed by Vega et al. ( 2001 ) is related to conceded plant development during a flowering phase that is linked with the active ear growth phase and categorized as a critical phase for approximation of kernel number during silking (Otegui and Bonhomme 1998 ).
The retort of rice output to high temperature presents disparities in flowering patterns, and seed set lessens and lessens grain weight (Qasim et al. 2020 ; Qasim, Hammad, Maqsood, Tariq, & Chawla). During the daytime, heat directly impacts flowers which lessens the thesis period and quickens the earlier peak flowering (Tao et al. 2006 ). Antagonistic effect of higher daytime temperature d on pollen sprouting proposed seed set decay, whereas, seed set was lengthily reduced than could be explicated by pollen growing at high temperatures 40◦C (Matsui et al. 2001 ).
The decline in wheat output is linked with higher temperatures, confirmed in numerous studies (Semenov 2009 ; Stone and Nicolas 1994 ). High temperatures fast-track the arrangements of plant expansion (Blum et al. 2001 ), diminution photosynthetic process (Salvucci and Crafts‐Brandner 2004 ), and also considerably affect the reproductive operations (Farooq et al. 2011 ).
The destructive impacts of CC induced weather extremes to deteriorate the integrity of crops (Chaudhary et al. 2011 ), e.g., Spartan cold and extreme fog cause falling and discoloration of betel leaves (Rosenzweig et al. 2001 ), giving them a somehow reddish appearance, squeezing of lemon leaves (Pautasso et al. 2012 ), as well as root rot of pineapple, have reported (Vedwan and Rhoades 2001 ). Henceforth, in tackling the disruptive effects of CC, several short-term and long-term management approaches are the crucial need of time (Fig. 4 ). Moreover, various studies (Chaudhary et al. 2011 ; Patz et al. 2005 ; Pautasso et al. 2012 ) have demonstrated adapting trends such as ameliorating crop diversity can yield better adaptability towards CC.
Schematic description of potential impacts of climate change on the agriculture sector and the appropriate mitigation and adaptation measures to overcome its impact.
Climate change impacts on biodiversity
Global biodiversity is among the severe victims of CC because it is the fastest emerging cause of species loss. Studies demonstrated that the massive scale species dynamics are considerably associated with diverse climatic events (Abraham and Chain 1988 ; Manes et al. 2021 ; A. M. D. Ortiz et al. 2021 ). Both the pace and magnitude of CC are altering the compatible habitat ranges for living entities of marine, freshwater, and terrestrial regions. Alterations in general climate regimes influence the integrity of ecosystems in numerous ways, such as variation in the relative abundance of species, range shifts, changes in activity timing, and microhabitat use (Bates et al. 2014 ). The geographic distribution of any species often depends upon its ability to tolerate environmental stresses, biological interactions, and dispersal constraints. Hence, instead of the CC, the local species must only accept, adapt, move, or face extinction (Berg et al. 2010 ). So, the best performer species have a better survival capacity for adjusting to new ecosystems or a decreased perseverance to survive where they are already situated (Bates et al. 2014 ). An important aspect here is the inadequate habitat connectivity and access to microclimates, also crucial in raising the exposure to climate warming and extreme heatwave episodes. For example, the carbon sequestration rates are undergoing fluctuations due to climate-driven expansion in the range of global mangroves (Cavanaugh et al. 2014 ).
Similarly, the loss of kelp-forest ecosystems in various regions and its occupancy by the seaweed turfs has set the track for elevated herbivory by the high influx of tropical fish populations. Not only this, the increased water temperatures have exacerbated the conditions far away from the physiological tolerance level of the kelp communities (Vergés et al. 2016 ; Wernberg et al. 2016 ). Another pertinent danger is the devastation of keystone species, which even has more pervasive effects on the entire communities in that habitat (Zarnetske et al. 2012 ). It is particularly important as CC does not specify specific populations or communities. Eventually, this CC-induced redistribution of species may deteriorate carbon storage and the net ecosystem productivity (Weed et al. 2013 ). Among the typical disruptions, the prominent ones include impacts on marine and terrestrial productivity, marine community assembly, and the extended invasion of toxic cyanobacteria bloom (Fossheim et al. 2015 ).
The CC-impacted species extinction is widely reported in the literature (Beesley et al. 2019 ; Urban 2015 ), and the predictions of demise until the twenty-first century are dreadful (Abbass et al. 2019 ; Pereira et al. 2013 ). In a few cases, northward shifting of species may not be formidable as it allows mountain-dwelling species to find optimum climates. However, the migrant species may be trapped in isolated and incompatible habitats due to losing topography and range (Dullinger et al. 2012 ). For example, a study indicated that the American pika has been extirpated or intensely diminished in some regions, primarily attributed to the CC-impacted extinction or at least local extirpation (Stewart et al. 2015 ). Besides, the anticipation of persistent responses to the impacts of CC often requires data records of several decades to rigorously analyze the critical pre and post CC patterns at species and ecosystem levels (Manes et al. 2021 ; Testa et al. 2018 ).
Nonetheless, the availability of such long-term data records is rare; hence, attempts are needed to focus on these profound aspects. Biodiversity is also vulnerable to the other associated impacts of CC, such as rising temperatures, droughts, and certain invasive pest species. For instance, a study revealed the changes in the composition of plankton communities attributed to rising temperatures. Henceforth, alterations in such aquatic producer communities, i.e., diatoms and calcareous plants, can ultimately lead to variation in the recycling of biological carbon. Moreover, such changes are characterized as a potential contributor to CO 2 differences between the Pleistocene glacial and interglacial periods (Kohfeld et al. 2005 ).
Climate change implications on human health
It is an understood corporality that human health is a significant victim of CC (Costello et al. 2009 ). According to the WHO, CC might be responsible for 250,000 additional deaths per year during 2030–2050 (Watts et al. 2015 ). These deaths are attributed to extreme weather-induced mortality and morbidity and the global expansion of vector-borne diseases (Lemery et al. 2021; Yang and Usman 2021 ; Meierrieks 2021 ; UNEP 2017 ). Here, some of the emerging health issues pertinent to this global problem are briefly described.
Climate change and antimicrobial resistance with corresponding economic costs
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) is an up-surging complex global health challenge (Garner et al. 2019 ; Lemery et al. 2021 ). Health professionals across the globe are extremely worried due to this phenomenon that has critical potential to reverse almost all the progress that has been achieved so far in the health discipline (Gosling and Arnell 2016 ). A massive amount of antibiotics is produced by many pharmaceutical industries worldwide, and the pathogenic microorganisms are gradually developing resistance to them, which can be comprehended how strongly this aspect can shake the foundations of national and global economies (UNEP 2017 ). This statement is supported by the fact that AMR is not developing in a particular region or country. Instead, it is flourishing in every continent of the world (WHO 2018 ). This plague is heavily pushing humanity to the post-antibiotic era, in which currently antibiotic-susceptible pathogens will once again lead to certain endemics and pandemics after being resistant(WHO 2018 ). Undesirably, if this statement would become a factuality, there might emerge certain risks in undertaking sophisticated interventions such as chemotherapy, joint replacement cases, and organ transplantation (Su et al. 2018 ). Presently, the amplification of drug resistance cases has made common illnesses like pneumonia, post-surgical infections, HIV/AIDS, tuberculosis, malaria, etc., too difficult and costly to be treated or cure well (WHO 2018 ). From a simple example, it can be assumed how easily antibiotic-resistant strains can be transmitted from one person to another and ultimately travel across the boundaries (Berendonk et al. 2015 ). Talking about the second- and third-generation classes of antibiotics, e.g., most renowned generations of cephalosporin antibiotics that are more expensive, broad-spectrum, more toxic, and usually require more extended periods whenever prescribed to patients (Lemery et al. 2021 ; Pärnänen et al. 2019 ). This scenario has also revealed that the abundance of resistant strains of pathogens was also higher in the Southern part (WHO 2018 ). As southern parts are generally warmer than their counterparts, it is evident from this example how CC-induced global warming can augment the spread of antibiotic-resistant strains within the biosphere, eventually putting additional economic burden in the face of developing new and costlier antibiotics. The ARG exchange to susceptible bacteria through one of the potential mechanisms, transformation, transduction, and conjugation; Selection pressure can be caused by certain antibiotics, metals or pesticides, etc., as shown in Fig. 5 .
Source: Elsayed et al. ( 2021 ); Karkman et al. ( 2018 )
A typical interaction between the susceptible and resistant strains.
Certain studies highlighted that conventional urban wastewater treatment plants are typical hotspots where most bacterial strains exchange genetic material through horizontal gene transfer (Fig. 5 ). Although at present, the extent of risks associated with the antibiotic resistance found in wastewater is complicated; environmental scientists and engineers have particular concerns about the potential impacts of these antibiotic resistance genes on human health (Ashbolt 2015 ). At most undesirable and worst case, these antibiotic-resistant genes containing bacteria can make their way to enter into the environment (Pruden et al. 2013 ), irrigation water used for crops and public water supplies and ultimately become a part of food chains and food webs (Ma et al. 2019 ; D. Wu et al. 2019 ). This problem has been reported manifold in several countries (Hendriksen et al. 2019 ), where wastewater as a means of irrigated water is quite common.

Climate change and vector borne-diseases
Temperature is a fundamental factor for the sustenance of living entities regardless of an ecosystem. So, a specific living being, especially a pathogen, requires a sophisticated temperature range to exist on earth. The second essential component of CC is precipitation, which also impacts numerous infectious agents’ transport and dissemination patterns. Global rising temperature is a significant cause of many species extinction. On the one hand, this changing environmental temperature may be causing species extinction, and on the other, this warming temperature might favor the thriving of some new organisms. Here, it was evident that some pathogens may also upraise once non-evident or reported (Patz et al. 2000 ). This concept can be exemplified through certain pathogenic strains of microorganisms that how the likelihood of various diseases increases in response to climate warming-induced environmental changes (Table 2 ).
A recent example is an outburst of coronavirus (COVID-19) in the Republic of China, causing pneumonia and severe acute respiratory complications (Cui et al. 2021 ; Song et al. 2021 ). The large family of viruses is harbored in numerous animals, bats, and snakes in particular (livescience.com) with the subsequent transfer into human beings. Hence, it is worth noting that the thriving of numerous vectors involved in spreading various diseases is influenced by Climate change (Ogden 2018 ; Santos et al. 2021 ).
Psychological impacts of climate change
Climate change (CC) is responsible for the rapid dissemination and exaggeration of certain epidemics and pandemics. In addition to the vast apparent impacts of climate change on health, forestry, agriculture, etc., it may also have psychological implications on vulnerable societies. It can be exemplified through the recent outburst of (COVID-19) in various countries around the world (Pal 2021 ). Besides, the victims of this viral infection have made healthy beings scarier and terrified. In the wake of such epidemics, people with common colds or fever are also frightened and must pass specific regulatory protocols. Living in such situations continuously terrifies the public and makes the stress familiar, which eventually makes them psychologically weak (npr.org).
CC boosts the extent of anxiety, distress, and other issues in public, pushing them to develop various mental-related problems. Besides, frequent exposure to extreme climatic catastrophes such as geological disasters also imprints post-traumatic disorder, and their ubiquitous occurrence paves the way to developing chronic psychological dysfunction. Moreover, repetitive listening from media also causes an increase in the person’s stress level (Association 2020 ). Similarly, communities living in flood-prone areas constantly live in extreme fear of drowning and die by floods. In addition to human lives, the flood-induced destruction of physical infrastructure is a specific reason for putting pressure on these communities (Ogden 2018 ). For instance, Ogden ( 2018 ) comprehensively denoted that Katrina’s Hurricane augmented the mental health issues in the victim communities.
Climate change impacts on the forestry sector
Forests are the global regulators of the world’s climate (FAO 2018 ) and have an indispensable role in regulating global carbon and nitrogen cycles (Rehman et al. 2021 ; Reichstein and Carvalhais 2019 ). Hence, disturbances in forest ecology affect the micro and macro-climates (Ellison et al. 2017 ). Climate warming, in return, has profound impacts on the growth and productivity of transboundary forests by influencing the temperature and precipitation patterns, etc. As CC induces specific changes in the typical structure and functions of ecosystems (Zhang et al. 2017 ) as well impacts forest health, climate change also has several devastating consequences such as forest fires, droughts, pest outbreaks (EPA 2018 ), and last but not the least is the livelihoods of forest-dependent communities. The rising frequency and intensity of another CC product, i.e., droughts, pose plenty of challenges to the well-being of global forests (Diffenbaugh et al. 2017 ), which is further projected to increase soon (Hartmann et al. 2018 ; Lehner et al. 2017 ; Rehman et al. 2021 ). Hence, CC induces storms, with more significant impacts also put extra pressure on the survival of the global forests (Martínez-Alvarado et al. 2018 ), significantly since their influences are augmented during higher winter precipitations with corresponding wetter soils causing weak root anchorage of trees (Brázdil et al. 2018 ). Surging temperature regimes causes alterations in usual precipitation patterns, which is a significant hurdle for the survival of temperate forests (Allen et al. 2010 ; Flannigan et al. 2013 ), letting them encounter severe stress and disturbances which adversely affects the local tree species (Hubbart et al. 2016 ; Millar and Stephenson 2015 ; Rehman et al. 2021 ).
Climate change impacts on forest-dependent communities
Forests are the fundamental livelihood resource for about 1.6 billion people worldwide; out of them, 350 million are distinguished with relatively higher reliance (Bank 2008 ). Agro-forestry-dependent communities comprise 1.2 billion, and 60 million indigenous people solely rely on forests and their products to sustain their lives (Sunderlin et al. 2005 ). For example, in the entire African continent, more than 2/3rd of inhabitants depend on forest resources and woodlands for their alimonies, e.g., food, fuelwood and grazing (Wasiq and Ahmad 2004 ). The livings of these people are more intensely affected by the climatic disruptions making their lives harder (Brown et al. 2014 ). On the one hand, forest communities are incredibly vulnerable to CC due to their livelihoods, cultural and spiritual ties as well as socio-ecological connections, and on the other, they are not familiar with the term “climate change.” (Rahman and Alam 2016 ). Among the destructive impacts of temperature and rainfall, disruption of the agroforestry crops with resultant downscale growth and yield (Macchi et al. 2008 ). Cruz ( 2015 ) ascribed that forest-dependent smallholder farmers in the Philippines face the enigma of delayed fruiting, more severe damages by insect and pest incidences due to unfavorable temperature regimes, and changed rainfall patterns.
Among these series of challenges to forest communities, their well-being is also distinctly vulnerable to CC. Though the detailed climate change impacts on human health have been comprehensively mentioned in the previous section, some studies have listed a few more devastating effects on the prosperity of forest-dependent communities. For instance, the Himalayan people have been experiencing frequent skin-borne diseases such as malaria and other skin diseases due to increasing mosquitoes, wild boar as well, and new wasps species, particularly in higher altitudes that were almost non-existent before last 5–10 years (Xu et al. 2008 ). Similarly, people living at high altitudes in Bangladesh have experienced frequent mosquito-borne calamities (Fardous; Sharma 2012 ). In addition, the pace of other waterborne diseases such as infectious diarrhea, cholera, pathogenic induced abdominal complications and dengue has also been boosted in other distinguished regions of Bangladesh (Cell 2009 ; Gunter et al. 2008 ).
Pest outbreak
Upscaling hotter climate may positively affect the mobile organisms with shorter generation times because they can scurry from harsh conditions than the immobile species (Fettig et al. 2013 ; Schoene and Bernier 2012 ) and are also relatively more capable of adapting to new environments (Jactel et al. 2019 ). It reveals that insects adapt quickly to global warming due to their mobility advantages. Due to past outbreaks, the trees (forests) are relatively more susceptible victims (Kurz et al. 2008 ). Before CC, the influence of factors mentioned earlier, i.e., droughts and storms, was existent and made the forests susceptible to insect pest interventions; however, the global forests remain steadfast, assiduous, and green (Jactel et al. 2019 ). The typical reasons could be the insect herbivores were regulated by several tree defenses and pressures of predation (Wilkinson and Sherratt 2016 ). As climate greatly influences these phenomena, the global forests cannot be so sedulous against such challenges (Jactel et al. 2019 ). Table 3 demonstrates some of the particular considerations with practical examples that are essential while mitigating the impacts of CC in the forestry sector.
Climate change impacts on tourism
Tourism is a commercial activity that has roots in multi-dimensions and an efficient tool with adequate job generation potential, revenue creation, earning of spectacular foreign exchange, enhancement in cross-cultural promulgation and cooperation, a business tool for entrepreneurs and eventually for the country’s national development (Arshad et al. 2018 ; Scott 2021 ). Among a plethora of other disciplines, the tourism industry is also a distinct victim of climate warming (Gössling et al. 2012 ; Hall et al. 2015 ) as the climate is among the essential resources that enable tourism in particular regions as most preferred locations. Different places at different times of the year attract tourists both within and across the countries depending upon the feasibility and compatibility of particular weather patterns. Hence, the massive variations in these weather patterns resulting from CC will eventually lead to monumental challenges to the local economy in that specific area’s particular and national economy (Bujosa et al. 2015 ). For instance, the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) report demonstrated that the global tourism industry had faced a considerable decline in the duration of ski season, including the loss of some ski areas and the dramatic shifts in tourist destinations’ climate warming.
Furthermore, different studies (Neuvonen et al. 2015 ; Scott et al. 2004 ) indicated that various currently perfect tourist spots, e.g., coastal areas, splendid islands, and ski resorts, will suffer consequences of CC. It is also worth noting that the quality and potential of administrative management potential to cope with the influence of CC on the tourism industry is of crucial significance, which renders specific strengths of resiliency to numerous destinations to withstand against it (Füssel and Hildén 2014 ). Similarly, in the partial or complete absence of adequate socio-economic and socio-political capital, the high-demanding tourist sites scurry towards the verge of vulnerability. The susceptibility of tourism is based on different components such as the extent of exposure, sensitivity, life-supporting sectors, and capacity assessment factors (Füssel and Hildén 2014 ). It is obvious corporality that sectors such as health, food, ecosystems, human habitat, infrastructure, water availability, and the accessibility of a particular region are prone to CC. Henceforth, the sensitivity of these critical sectors to CC and, in return, the adaptive measures are a hallmark in determining the composite vulnerability of climate warming (Ionescu et al. 2009 ).
Moreover, the dependence on imported food items, poor hygienic conditions, and inadequate health professionals are dominant aspects affecting the local terrestrial and aquatic biodiversity. Meanwhile, the greater dependency on ecosystem services and its products also makes a destination more fragile to become a prey of CC (Rizvi et al. 2015 ). Some significant non-climatic factors are important indicators of a particular ecosystem’s typical health and functioning, e.g., resource richness and abundance portray the picture of ecosystem stability. Similarly, the species abundance is also a productive tool that ensures that the ecosystem has a higher buffering capacity, which is terrific in terms of resiliency (Roscher et al. 2013 ).
Climate change impacts on the economic sector
Climate plays a significant role in overall productivity and economic growth. Due to its increasingly global existence and its effect on economic growth, CC has become one of the major concerns of both local and international environmental policymakers (Ferreira et al. 2020 ; Gleditsch 2021 ; Abbass et al. 2021b ; Lamperti et al. 2021 ). The adverse effects of CC on the overall productivity factor of the agricultural sector are therefore significant for understanding the creation of local adaptation policies and the composition of productive climate policy contracts. Previous studies on CC in the world have already forecasted its effects on the agricultural sector. Researchers have found that global CC will impact the agricultural sector in different world regions. The study of the impacts of CC on various agrarian activities in other demographic areas and the development of relative strategies to respond to effects has become a focal point for researchers (Chandioet al. 2020 ; Gleditsch 2021 ; Mosavi et al. 2020 ).
With the rapid growth of global warming since the 1980s, the temperature has started increasing globally, which resulted in the incredible transformation of rain and evaporation in the countries. The agricultural development of many countries has been reliant, delicate, and susceptible to CC for a long time, and it is on the development of agriculture total factor productivity (ATFP) influence different crops and yields of farmers (Alhassan 2021 ; Wu 2020 ).
Food security and natural disasters are increasing rapidly in the world. Several major climatic/natural disasters have impacted local crop production in the countries concerned. The effects of these natural disasters have been poorly controlled by the development of the economies and populations and may affect human life as well. One example is China, which is among the world’s most affected countries, vulnerable to natural disasters due to its large population, harsh environmental conditions, rapid CC, low environmental stability, and disaster power. According to the January 2016 statistical survey, China experienced an economic loss of 298.3 billion Yuan, and about 137 million Chinese people were severely affected by various natural disasters (Xie et al. 2018 ).
Mitigation and adaptation strategies of climate changes
Adaptation and mitigation are the crucial factors to address the response to CC (Jahanzad et al. 2020 ). Researchers define mitigation on climate changes, and on the other hand, adaptation directly impacts climate changes like floods. To some extent, mitigation reduces or moderates greenhouse gas emission, and it becomes a critical issue both economically and environmentally (Botzen et al. 2021 ; Jahanzad et al. 2020 ; Kongsager 2018 ; Smit et al. 2000 ; Vale et al. 2021 ; Usman et al. 2021 ; Verheyen 2005 ).
Researchers have deep concern about the adaptation and mitigation methodologies in sectoral and geographical contexts. Agriculture, industry, forestry, transport, and land use are the main sectors to adapt and mitigate policies(Kärkkäinen et al. 2020 ; Waheed et al. 2021 ). Adaptation and mitigation require particular concern both at the national and international levels. The world has faced a significant problem of climate change in the last decades, and adaptation to these effects is compulsory for economic and social development. To adapt and mitigate against CC, one should develop policies and strategies at the international level (Hussain et al. 2020 ). Figure 6 depicts the list of current studies on sectoral impacts of CC with adaptation and mitigation measures globally.
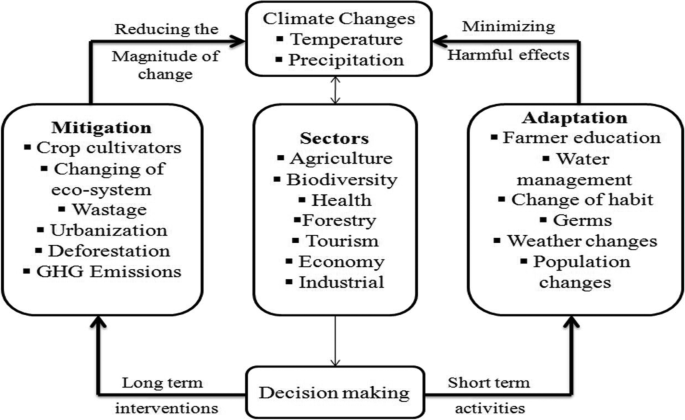
Sectoral impacts of climate change with adaptation and mitigation measures.
Conclusion and future perspectives
Specific socio-agricultural, socio-economic, and physical systems are the cornerstone of psychological well-being, and the alteration in these systems by CC will have disastrous impacts. Climate variability, alongside other anthropogenic and natural stressors, influences human and environmental health sustainability. Food security is another concerning scenario that may lead to compromised food quality, higher food prices, and inadequate food distribution systems. Global forests are challenged by different climatic factors such as storms, droughts, flash floods, and intense precipitation. On the other hand, their anthropogenic wiping is aggrandizing their existence. Undoubtedly, the vulnerability scale of the world’s regions differs; however, appropriate mitigation and adaptation measures can aid the decision-making bodies in developing effective policies to tackle its impacts. Presently, modern life on earth has tailored to consistent climatic patterns, and accordingly, adapting to such considerable variations is of paramount importance. Because the faster changes in climate will make it harder to survive and adjust, this globally-raising enigma calls for immediate attention at every scale ranging from elementary community level to international level. Still, much effort, research, and dedication are required, which is the most critical time. Some policy implications can help us to mitigate the consequences of climate change, especially the most affected sectors like the agriculture sector;
Seasonal variations and cultivation practices
Warming might lengthen the season in frost-prone growing regions (temperate and arctic zones), allowing for longer-maturing seasonal cultivars with better yields (Pfadenhauer 2020 ; Bonacci 2019 ). Extending the planting season may allow additional crops each year; when warming leads to frequent warmer months highs over critical thresholds, a split season with a brief summer fallow may be conceivable for short-period crops such as wheat barley, cereals, and many other vegetable crops. The capacity to prolong the planting season in tropical and subtropical places where the harvest season is constrained by precipitation or agriculture farming occurs after the year may be more limited and dependent on how precipitation patterns vary (Wu et al. 2017 ).
New varieties of crops
The genetic component is comprehensive for many yields, but it is restricted like kiwi fruit for a few. Ali et al. ( 2017 ) investigated how new crops will react to climatic changes (also stated in Mall et al. 2017 ). Hot temperature, drought, insect resistance; salt tolerance; and overall crop production and product quality increases would all be advantageous (Akkari 2016 ). Genetic mapping and engineering can introduce a greater spectrum of features. The adoption of genetically altered cultivars has been slowed, particularly in the early forecasts owing to the complexity in ensuring features are expediently expressed throughout the entire plant, customer concerns, economic profitability, and regulatory impediments (Wirehn 2018 ; Davidson et al. 2016 ).
Changes in management and other input factors
To get the full benefit of the CO 2 would certainly require additional nitrogen and other fertilizers. Nitrogen not consumed by the plants may be excreted into groundwater, discharged into water surface, or emitted from the land, soil nitrous oxide when large doses of fertilizer are sprayed. Increased nitrogen levels in groundwater sources have been related to human chronic illnesses and impact marine ecosystems. Cultivation, grain drying, and other field activities have all been examined in depth in the studies (Barua et al. 2018 ).
The technological and socio-economic adaptation
The policy consequence of the causative conclusion is that as a source of alternative energy, biofuel production is one of the routes that explain oil price volatility separate from international macroeconomic factors. Even though biofuel production has just begun in a few sample nations, there is still a tremendous worldwide need for feedstock to satisfy industrial expansion in China and the USA, which explains the food price relationship to the global oil price. Essentially, oil-exporting countries may create incentives in their economies to increase food production. It may accomplish by giving farmers financing, seedlings, fertilizers, and farming equipment. Because of the declining global oil price and, as a result, their earnings from oil export, oil-producing nations may be unable to subsidize food imports even in the near term. As a result, these countries can boost the agricultural value chain for export. It may be accomplished through R&D and adding value to their food products to increase income by correcting exchange rate misalignment and adverse trade terms. These nations may also diversify their economies away from oil, as dependence on oil exports alone is no longer economically viable given the extreme volatility of global oil prices. Finally, resource-rich and oil-exporting countries can convert to non-food renewable energy sources such as solar, hydro, coal, wind, wave, and tidal energy. By doing so, both world food and oil supplies would be maintained rather than harmed.
IRENA’s modeling work shows that, if a comprehensive policy framework is in place, efforts toward decarbonizing the energy future will benefit economic activity, jobs (outweighing losses in the fossil fuel industry), and welfare. Countries with weak domestic supply chains and a large reliance on fossil fuel income, in particular, must undertake structural reforms to capitalize on the opportunities inherent in the energy transition. Governments continue to give major policy assistance to extract fossil fuels, including tax incentives, financing, direct infrastructure expenditures, exemptions from environmental regulations, and other measures. The majority of major oil and gas producing countries intend to increase output. Some countries intend to cut coal output, while others plan to maintain or expand it. While some nations are beginning to explore and execute policies aimed at a just and equitable transition away from fossil fuel production, these efforts have yet to impact major producing countries’ plans and goals. Verifiable and comparable data on fossil fuel output and assistance from governments and industries are critical to closing the production gap. Governments could increase openness by declaring their production intentions in their climate obligations under the Paris Agreement.
It is firmly believed that achieving the Paris Agreement commitments is doubtlful without undergoing renewable energy transition across the globe (Murshed 2020 ; Zhao et al. 2022 ). Policy instruments play the most important role in determining the degree of investment in renewable energy technology. This study examines the efficacy of various policy strategies in the renewable energy industry of multiple nations. Although its impact is more visible in established renewable energy markets, a renewable portfolio standard is also a useful policy instrument. The cost of producing renewable energy is still greater than other traditional energy sources. Furthermore, government incentives in the R&D sector can foster innovation in this field, resulting in cost reductions in the renewable energy industry. These nations may export their technologies and share their policy experiences by forming networks among their renewable energy-focused organizations. All policy measures aim to reduce production costs while increasing the proportion of renewables to a country’s energy system. Meanwhile, long-term contracts with renewable energy providers, government commitment and control, and the establishment of long-term goals can assist developing nations in deploying renewable energy technology in their energy sector.
Availability of data and material
Data sources and relevant links are provided in the paper to access data.
Abbass K, Begum H, Alam ASA, Awang AH, Abdelsalam MK, Egdair IMM, Wahid R (2022) Fresh Insight through a Keynesian Theory Approach to Investigate the Economic Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic in Pakistan. Sustain 14(3):1054
Abbass K, Niazi AAK, Qazi TF, Basit A, Song H (2021a) The aftermath of COVID-19 pandemic period: barriers in implementation of social distancing at workplace. Library Hi Tech
Abbass K, Song H, Khan F, Begum H, Asif M (2021b) Fresh insight through the VAR approach to investigate the effects of fiscal policy on environmental pollution in Pakistan. Environ Scie Poll Res 1–14
Abbass K, Song H, Shah SM, Aziz B (2019) Determinants of Stock Return for Non-Financial Sector: Evidence from Energy Sector of Pakistan. J Bus Fin Aff 8(370):2167–0234
Google Scholar
Abbass K, Tanveer A, Huaming S, Khatiya AA (2021c) Impact of financial resources utilization on firm performance: a case of SMEs working in Pakistan
Abraham E, Chain E (1988) An enzyme from bacteria able to destroy penicillin. 1940. Rev Infect Dis 10(4):677
CAS Google Scholar
Adger WN, Arnell NW, Tompkins EL (2005) Successful adaptation to climate change across scales. Glob Environ Chang 15(2):77–86
Article Google Scholar
Akkari C, Bryant CR (2016) The co-construction approach as approach to developing adaptation strategies in the face of climate change and variability: A conceptual framework. Agricultural Research 5(2):162–173
Alhassan H (2021) The effect of agricultural total factor productivity on environmental degradation in sub-Saharan Africa. Sci Afr 12:e00740
Ali A, Erenstein O (2017) Assessing farmer use of climate change adaptation practices and impacts on food security and poverty in Pakistan. Clim Risk Manag 16:183–194
Allen CD, Macalady AK, Chenchouni H, Bachelet D, McDowell N, Vennetier M, Hogg ET (2010) A global overview of drought and heat-induced tree mortality reveals emerging climate change risks for forests. For Ecol Manag 259(4):660–684
Anwar A, Sinha A, Sharif A, Siddique M, Irshad S, Anwar W, Malik S (2021) The nexus between urbanization, renewable energy consumption, financial development, and CO2 emissions: evidence from selected Asian countries. Environ Dev Sust. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-021-01716-2
Araus JL, Slafer GA, Royo C, Serret MD (2008) Breeding for yield potential and stress adaptation in cereals. Crit Rev Plant Sci 27(6):377–412
Aron JL, Patz J (2001) Ecosystem change and public health: a global perspective: JHU Press
Arshad MI, Iqbal MA, Shahbaz M (2018) Pakistan tourism industry and challenges: a review. Asia Pacific Journal of Tourism Research 23(2):121–132
Ashbolt NJ (2015) Microbial contamination of drinking water and human health from community water systems. Current Environmental Health Reports 2(1):95–106
Article CAS Google Scholar
Asseng S, Cao W, Zhang W, Ludwig F (2009) Crop physiology, modelling and climate change: impact and adaptation strategies. Crop Physiol 511–543
Asseng S, Ewert F, Rosenzweig C, Jones JW, Hatfield JL, Ruane AC, Cammarano D (2013) Uncertainty in simulating wheat yields under climate change. Nat Clim Chang 3(9):827–832
Association A (2020) Climate change is threatening mental health, American Psychological Association, “Kirsten Weir, . from < https://www.apa.org/monitor/2016/07-08/climate-change >, Accessed on 26 Jan 2020.
Ayers J, Huq S, Wright H, Faisal A, Hussain S (2014) Mainstreaming climate change adaptation into development in Bangladesh. Clim Dev 6:293–305
Balsalobre-Lorente D, Driha OM, Bekun FV, Sinha A, Adedoyin FF (2020) Consequences of COVID-19 on the social isolation of the Chinese economy: accounting for the role of reduction in carbon emissions. Air Qual Atmos Health 13(12):1439–1451
Balsalobre-Lorente D, Ibáñez-Luzón L, Usman M, Shahbaz M (2022) The environmental Kuznets curve, based on the economic complexity, and the pollution haven hypothesis in PIIGS countries. Renew Energy 185:1441–1455
Bank W (2008) Forests sourcebook: practical guidance for sustaining forests in development cooperation: World Bank
Barua S, Valenzuela E (2018) Climate change impacts on global agricultural trade patterns: evidence from the past 50 years. In Proceedings of the Sixth International Conference on Sustainable Development (pp. 26–28)
Bates AE, Pecl GT, Frusher S, Hobday AJ, Wernberg T, Smale DA, Colwell RK (2014) Defining and observing stages of climate-mediated range shifts in marine systems. Glob Environ Chang 26:27–38
Battisti DS, Naylor RL (2009) Historical warnings of future food insecurity with unprecedented seasonal heat. Science 323(5911):240–244
Beesley L, Close PG, Gwinn DC, Long M, Moroz M, Koster WM, Storer T (2019) Flow-mediated movement of freshwater catfish, Tandanus bostocki, in a regulated semi-urban river, to inform environmental water releases. Ecol Freshw Fish 28(3):434–445
Benita F (2021) Human mobility behavior in COVID-19: A systematic literature review and bibliometric analysis. Sustain Cities Soc 70:102916
Berendonk TU, Manaia CM, Merlin C, Fatta-Kassinos D, Cytryn E, Walsh F, Pons M-N (2015) Tackling antibiotic resistance: the environmental framework. Nat Rev Microbiol 13(5):310–317
Berg MP, Kiers ET, Driessen G, Van DerHEIJDEN M, Kooi BW, Kuenen F, Ellers J (2010) Adapt or disperse: understanding species persistence in a changing world. Glob Change Biol 16(2):587–598
Blum A, Klueva N, Nguyen H (2001) Wheat cellular thermotolerance is related to yield under heat stress. Euphytica 117(2):117–123
Bonacci O (2019) Air temperature and precipitation analyses on a small Mediterranean island: the case of the remote island of Lastovo (Adriatic Sea, Croatia). Acta Hydrotechnica 32(57):135–150
Botzen W, Duijndam S, van Beukering P (2021) Lessons for climate policy from behavioral biases towards COVID-19 and climate change risks. World Dev 137:105214
Brázdil R, Stucki P, Szabó P, Řezníčková L, Dolák L, Dobrovolný P, Suchánková S (2018) Windstorms and forest disturbances in the Czech Lands: 1801–2015. Agric for Meteorol 250:47–63
Brown HCP, Smit B, Somorin OA, Sonwa DJ, Nkem JN (2014) Climate change and forest communities: prospects for building institutional adaptive capacity in the Congo Basin forests. Ambio 43(6):759–769
Bujosa A, Riera A, Torres CM (2015) Valuing tourism demand attributes to guide climate change adaptation measures efficiently: the case of the Spanish domestic travel market. Tour Manage 47:233–239
Calderini D, Abeledo L, Savin R, Slafer GA (1999) Effect of temperature and carpel size during pre-anthesis on potential grain weight in wheat. J Agric Sci 132(4):453–459
Cammell M, Knight J (1992) Effects of climatic change on the population dynamics of crop pests. Adv Ecol Res 22:117–162
Cavanaugh KC, Kellner JR, Forde AJ, Gruner DS, Parker JD, Rodriguez W, Feller IC (2014) Poleward expansion of mangroves is a threshold response to decreased frequency of extreme cold events. Proc Natl Acad Sci 111(2):723–727
Cell CC (2009) Climate change and health impacts in Bangladesh. Clima Chang Cell DoE MoEF
Chandio AA, Jiang Y, Rehman A, Rauf A (2020) Short and long-run impacts of climate change on agriculture: an empirical evidence from China. Int J Clim Chang Strat Manag
Chaudhary P, Rai S, Wangdi S, Mao A, Rehman N, Chettri S, Bawa KS (2011) Consistency of local perceptions of climate change in the Kangchenjunga Himalaya landscape. Curr Sci 504–513
Chien F, Anwar A, Hsu CC, Sharif A, Razzaq A, Sinha A (2021) The role of information and communication technology in encountering environmental degradation: proposing an SDG framework for the BRICS countries. Technol Soc 65:101587
Cooper C, Booth A, Varley-Campbell J, Britten N, Garside R (2018) Defining the process to literature searching in systematic reviews: a literature review of guidance and supporting studies. BMC Med Res Methodol 18(1):1–14
Costello A, Abbas M, Allen A, Ball S, Bell S, Bellamy R, Kett M (2009) Managing the health effects of climate change: lancet and University College London Institute for Global Health Commission. The Lancet 373(9676):1693–1733
Cruz DLA (2015) Mother Figured. University of Chicago Press. Retrieved from, https://doi.org/10.7208/9780226315072
Cui W, Ouyang T, Qiu Y, Cui D (2021) Literature Review of the Implications of Exercise Rehabilitation Strategies for SARS Patients on the Recovery of COVID-19 Patients. Paper presented at the Healthcare
Davidson D (2016) Gaps in agricultural climate adaptation research. Nat Clim Chang 6(5):433–435
Diffenbaugh NS, Singh D, Mankin JS, Horton DE, Swain DL, Touma D, Tsiang M (2017) Quantifying the influence of global warming on unprecedented extreme climate events. Proc Natl Acad Sci 114(19):4881–4886
Dimri A, Kumar D, Choudhary A, Maharana P (2018) Future changes over the Himalayas: mean temperature. Global Planet Change 162:235–251
Dullinger S, Gattringer A, Thuiller W, Moser D, Zimmermann N, Guisan A (2012) Extinction debt of high-mountain plants under twenty-first-century climate change. Nature Publishing Group, Nat Clim Chang
Book Google Scholar
Dupuis I, Dumas C (1990) Influence of temperature stress on in vitro fertilization and heat shock protein synthesis in maize (Zea mays L.) reproductive tissues. Plant Physiol 94(2):665–670
Edreira JR, Otegui ME (2013) Heat stress in temperate and tropical maize hybrids: a novel approach for assessing sources of kernel loss in field conditions. Field Crop Res 142:58–67
Edreira JR, Carpici EB, Sammarro D, Otegui M (2011) Heat stress effects around flowering on kernel set of temperate and tropical maize hybrids. Field Crop Res 123(2):62–73
Ellison D, Morris CE, Locatelli B, Sheil D, Cohen J, Murdiyarso D, Pokorny J (2017) Trees, forests and water: Cool insights for a hot world. Glob Environ Chang 43:51–61
Elsayed ZM, Eldehna WM, Abdel-Aziz MM, El Hassab MA, Elkaeed EB, Al-Warhi T, Mohammed ER (2021) Development of novel isatin–nicotinohydrazide hybrids with potent activity against susceptible/resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis and bronchitis causing–bacteria. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem 36(1):384–393
EM-DAT (2020) EMDAT: OFDA/CRED International Disaster Database, Université catholique de Louvain – Brussels – Belgium. from http://www.emdat.be
EPA U (2018) United States Environmental Protection Agency, EPA Year in Review
Erman A, De Vries Robbe SA, Thies SF, Kabir K, Maruo M (2021) Gender Dimensions of Disaster Risk and Resilience
Fand BB, Kamble AL, Kumar M (2012) Will climate change pose serious threat to crop pest management: a critical review. Int J Sci Res Publ 2(11):1–14
FAO (2018).The State of the World’s Forests 2018 - Forest Pathways to Sustainable Development.
Fardous S Perception of climate change in Kaptai National Park. Rural Livelihoods and Protected Landscape: Co-Management in the Wetlands and Forests of Bangladesh, 186–204
Farooq M, Bramley H, Palta JA, Siddique KH (2011) Heat stress in wheat during reproductive and grain-filling phases. Crit Rev Plant Sci 30(6):491–507
Feliciano D, Recha J, Ambaw G, MacSween K, Solomon D, Wollenberg E (2022) Assessment of agricultural emissions, climate change mitigation and adaptation practices in Ethiopia. Clim Policy 1–18
Ferreira JJ, Fernandes CI, Ferreira FA (2020) Technology transfer, climate change mitigation, and environmental patent impact on sustainability and economic growth: a comparison of European countries. Technol Forecast Soc Change 150:119770
Fettig CJ, Reid ML, Bentz BJ, Sevanto S, Spittlehouse DL, Wang T (2013) Changing climates, changing forests: a western North American perspective. J Forest 111(3):214–228
Fischer AP (2019) Characterizing behavioral adaptation to climate change in temperate forests. Landsc Urban Plan 188:72–79
Flannigan M, Cantin AS, De Groot WJ, Wotton M, Newbery A, Gowman LM (2013) Global wildland fire season severity in the 21st century. For Ecol Manage 294:54–61
Fossheim M, Primicerio R, Johannesen E, Ingvaldsen RB, Aschan MM, Dolgov AV (2015) Recent warming leads to a rapid borealization of fish communities in the Arctic. Nat Clim Chang 5(7):673–677
Füssel HM, Hildén M (2014) How is uncertainty addressed in the knowledge base for national adaptation planning? Adapting to an Uncertain Climate (pp. 41–66): Springer
Gambín BL, Borrás L, Otegui ME (2006) Source–sink relations and kernel weight differences in maize temperate hybrids. Field Crop Res 95(2–3):316–326
Gambín B, Borrás L (2010) Resource distribution and the trade-off between seed number and seed weight: a comparison across crop species. Annals of Applied Biology 156(1):91–102
Gampe D, Nikulin G, Ludwig R (2016) Using an ensemble of regional climate models to assess climate change impacts on water scarcity in European river basins. Sci Total Environ 573:1503–1518
García GA, Dreccer MF, Miralles DJ, Serrago RA (2015) High night temperatures during grain number determination reduce wheat and barley grain yield: a field study. Glob Change Biol 21(11):4153–4164
Garner E, Inyang M, Garvey E, Parks J, Glover C, Grimaldi A, Edwards MA (2019) Impact of blending for direct potable reuse on premise plumbing microbial ecology and regrowth of opportunistic pathogens and antibiotic resistant bacteria. Water Res 151:75–86
Gleditsch NP (2021) This time is different! Or is it? NeoMalthusians and environmental optimists in the age of climate change. J Peace Res 0022343320969785
Godfray HCJ, Beddington JR, Crute IR, Haddad L, Lawrence D, Muir JF, Toulmin C (2010) Food security: the challenge of feeding 9 billion people. Science 327(5967):812–818
Goes S, Hasterok D, Schutt DL, Klöcking M (2020) Continental lithospheric temperatures: A review. Phys Earth Planet Inter 106509
Gorst A, Dehlavi A, Groom B (2018) Crop productivity and adaptation to climate change in Pakistan. Environ Dev Econ 23(6):679–701
Gosling SN, Arnell NW (2016) A global assessment of the impact of climate change on water scarcity. Clim Change 134(3):371–385
Gössling S, Scott D, Hall CM, Ceron J-P, Dubois G (2012) Consumer behaviour and demand response of tourists to climate change. Ann Tour Res 39(1):36–58
Gourdji SM, Sibley AM, Lobell DB (2013) Global crop exposure to critical high temperatures in the reproductive period: historical trends and future projections. Environ Res Lett 8(2):024041
Grieg E Responsible Consumption and Production
Gunter BG, Rahman A, Rahman A (2008) How Vulnerable are Bangladesh’s Indigenous People to Climate Change? Bangladesh Development Research Center (BDRC)
Hall CM, Amelung B, Cohen S, Eijgelaar E, Gössling S, Higham J, Scott D (2015) On climate change skepticism and denial in tourism. J Sustain Tour 23(1):4–25
Hartmann H, Moura CF, Anderegg WR, Ruehr NK, Salmon Y, Allen CD, Galbraith D (2018) Research frontiers for improving our understanding of drought-induced tree and forest mortality. New Phytol 218(1):15–28
Hatfield JL, Prueger JH (2015) Temperature extremes: Effect on plant growth and development. Weather and Climate Extremes 10:4–10
Hatfield JL, Boote KJ, Kimball B, Ziska L, Izaurralde RC, Ort D, Wolfe D (2011) Climate impacts on agriculture: implications for crop production. Agron J 103(2):351–370
Hendriksen RS, Munk P, Njage P, Van Bunnik B, McNally L, Lukjancenko O, Kjeldgaard J (2019) Global monitoring of antimicrobial resistance based on metagenomics analyses of urban sewage. Nat Commun 10(1):1124
Huang S (2004) Global trade patterns in fruits and vegetables. USDA-ERS Agriculture and Trade Report No. WRS-04–06
Huang W, Gao Q-X, Cao G-L, Ma Z-Y, Zhang W-D, Chao Q-C (2016) Effect of urban symbiosis development in China on GHG emissions reduction. Adv Clim Chang Res 7(4):247–252
Huang Y, Haseeb M, Usman M, Ozturk I (2022) Dynamic association between ICT, renewable energy, economic complexity and ecological footprint: Is there any difference between E-7 (developing) and G-7 (developed) countries? Tech Soc 68:101853
Hubbart JA, Guyette R, Muzika R-M (2016) More than drought: precipitation variance, excessive wetness, pathogens and the future of the western edge of the eastern deciduous forest. Sci Total Environ 566:463–467
Hussain M, Butt AR, Uzma F, Ahmed R, Irshad S, Rehman A, Yousaf B (2020) A comprehensive review of climate change impacts, adaptation, and mitigation on environmental and natural calamities in Pakistan. Environ Monit Assess 192(1):48
Hussain M, Liu G, Yousaf B, Ahmed R, Uzma F, Ali MU, Butt AR (2018) Regional and sectoral assessment on climate-change in Pakistan: social norms and indigenous perceptions on climate-change adaptation and mitigation in relation to global context. J Clean Prod 200:791–808
Intergov. Panel Clim Chang 33 from https://doi.org/10.1017/CBO9781107415324
Ionescu C, Klein RJ, Hinkel J, Kumar KK, Klein R (2009) Towards a formal framework of vulnerability to climate change. Environ Model Assess 14(1):1–16
IPCC (2013) Summary for policymakers. Clim Chang Phys Sci Basis Contrib Work Gr I Fifth Assess Rep
Ishikawa-Ishiwata Y, Furuya J (2022) Economic evaluation and climate change adaptation measures for rice production in vietnam using a supply and demand model: special emphasis on the Mekong River Delta region in Vietnam. In Interlocal Adaptations to Climate Change in East and Southeast Asia (pp. 45–53). Springer, Cham
Izaguirre C, Losada I, Camus P, Vigh J, Stenek V (2021) Climate change risk to global port operations. Nat Clim Chang 11(1):14–20
Jactel H, Koricheva J, Castagneyrol B (2019) Responses of forest insect pests to climate change: not so simple. Current opinion in insect science
Jahanzad E, Holtz BA, Zuber CA, Doll D, Brewer KM, Hogan S, Gaudin AC (2020) Orchard recycling improves climate change adaptation and mitigation potential of almond production systems. PLoS ONE 15(3):e0229588
Jurgilevich A, Räsänen A, Groundstroem F, Juhola S (2017) A systematic review of dynamics in climate risk and vulnerability assessments. Environ Res Lett 12(1):013002
Karami E (2012) Climate change, resilience and poverty in the developing world. Paper presented at the Culture, Politics and Climate change conference
Kärkkäinen L, Lehtonen H, Helin J, Lintunen J, Peltonen-Sainio P, Regina K, . . . Packalen T (2020) Evaluation of policy instruments for supporting greenhouse gas mitigation efforts in agricultural and urban land use. Land Use Policy 99:104991
Karkman A, Do TT, Walsh F, Virta MP (2018) Antibiotic-resistance genes in waste water. Trends Microbiol 26(3):220–228
Kohfeld KE, Le Quéré C, Harrison SP, Anderson RF (2005) Role of marine biology in glacial-interglacial CO2 cycles. Science 308(5718):74–78
Kongsager R (2018) Linking climate change adaptation and mitigation: a review with evidence from the land-use sectors. Land 7(4):158
Kurz WA, Dymond C, Stinson G, Rampley G, Neilson E, Carroll A, Safranyik L (2008) Mountain pine beetle and forest carbon feedback to climate change. Nature 452(7190):987
Lamperti F, Bosetti V, Roventini A, Tavoni M, Treibich T (2021) Three green financial policies to address climate risks. J Financial Stab 54:100875
Leal Filho W, Azeiteiro UM, Balogun AL, Setti AFF, Mucova SA, Ayal D, . . . Oguge NO (2021) The influence of ecosystems services depletion to climate change adaptation efforts in Africa. Sci Total Environ 146414
Lehner F, Coats S, Stocker TF, Pendergrass AG, Sanderson BM, Raible CC, Smerdon JE (2017) Projected drought risk in 1.5 C and 2 C warmer climates. Geophys Res Lett 44(14):7419–7428
Lemery J, Knowlton K, Sorensen C (2021) Global climate change and human health: from science to practice: John Wiley & Sons
Leppänen S, Saikkonen L, Ollikainen M (2014) Impact of Climate Change on cereal grain production in Russia: Mimeo
Lipczynska-Kochany E (2018) Effect of climate change on humic substances and associated impacts on the quality of surface water and groundwater: a review. Sci Total Environ 640:1548–1565
livescience.com. New coronavirus may have ‘jumped’ to humans from snakes, study finds, live science,. from < https://www.livescience.com/new-coronavirus-origin-snakes.html > accessed on Jan 2020
Lobell DB, Field CB (2007) Global scale climate–crop yield relationships and the impacts of recent warming. Environ Res Lett 2(1):014002
Lobell DB, Gourdji SM (2012) The influence of climate change on global crop productivity. Plant Physiol 160(4):1686–1697
Ma L, Li B, Zhang T (2019) New insights into antibiotic resistome in drinking water and management perspectives: a metagenomic based study of small-sized microbes. Water Res 152:191–201
Macchi M, Oviedo G, Gotheil S, Cross K, Boedhihartono A, Wolfangel C, Howell M (2008) Indigenous and traditional peoples and climate change. International Union for the Conservation of Nature, Gland, Suiza
Mall RK, Gupta A, Sonkar G (2017) Effect of climate change on agricultural crops. In Current developments in biotechnology and bioengineering (pp. 23–46). Elsevier
Manes S, Costello MJ, Beckett H, Debnath A, Devenish-Nelson E, Grey KA, . . . Krause C (2021) Endemism increases species’ climate change risk in areas of global biodiversity importance. Biol Conserv 257:109070
Mannig B, Pollinger F, Gafurov A, Vorogushyn S, Unger-Shayesteh K (2018) Impacts of climate change in Central Asia Encyclopedia of the Anthropocene (pp. 195–203): Elsevier
Martínez-Alvarado O, Gray SL, Hart NC, Clark PA, Hodges K, Roberts MJ (2018) Increased wind risk from sting-jet windstorms with climate change. Environ Res Lett 13(4):044002
Matsui T, Omasa K, Horie T (2001) The difference in sterility due to high temperatures during the flowering period among japonica-rice varieties. Plant Production Science 4(2):90–93
Meierrieks D (2021) Weather shocks, climate change and human health. World Dev 138:105228
Michel D, Eriksson M, Klimes M (2021) Climate change and (in) security in transboundary river basins Handbook of Security and the Environment: Edward Elgar Publishing
Mihiretu A, Okoyo EN, Lemma T (2021) Awareness of climate change and its associated risks jointly explain context-specific adaptation in the Arid-tropics. Northeast Ethiopia SN Social Sciences 1(2):1–18
Millar CI, Stephenson NL (2015) Temperate forest health in an era of emerging megadisturbance. Science 349(6250):823–826
Mishra A, Bruno E, Zilberman D (2021) Compound natural and human disasters: Managing drought and COVID-19 to sustain global agriculture and food sectors. Sci Total Environ 754:142210
Mosavi SH, Soltani S, Khalilian S (2020) Coping with climate change in agriculture: Evidence from Hamadan-Bahar plain in Iran. Agric Water Manag 241:106332
Murshed M (2020) An empirical analysis of the non-linear impacts of ICT-trade openness on renewable energy transition, energy efficiency, clean cooking fuel access and environmental sustainability in South Asia. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(29):36254–36281. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-09497-3
Murshed M (2022) Pathways to clean cooking fuel transition in low and middle income Sub-Saharan African countries: the relevance of improving energy use efficiency. Sustainable Production and Consumption 30:396–412. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spc.2021.12.016
Murshed M, Dao NTT (2020) Revisiting the CO2 emission-induced EKC hypothesis in South Asia: the role of Export Quality Improvement. GeoJournal. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10708-020-10270-9
Murshed M, Abbass K, Rashid S (2021) Modelling renewable energy adoption across south Asian economies: Empirical evidence from Bangladesh, India, Pakistan and Sri Lanka. Int J Finan Eco 26(4):5425–5450
Murshed M, Nurmakhanova M, Elheddad M, Ahmed R (2020) Value addition in the services sector and its heterogeneous impacts on CO2 emissions: revisiting the EKC hypothesis for the OPEC using panel spatial estimation techniques. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(31):38951–38973. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-09593-4
Murshed M, Nurmakhanova M, Al-Tal R, Mahmood H, Elheddad M, Ahmed R (2022) Can intra-regional trade, renewable energy use, foreign direct investments, and economic growth reduce ecological footprints in South Asia? Energy Sources, Part B: Economics, Planning, and Policy. https://doi.org/10.1080/15567249.2022.2038730
Neuvonen M, Sievänen T, Fronzek S, Lahtinen I, Veijalainen N, Carter TR (2015) Vulnerability of cross-country skiing to climate change in Finland–an interactive mapping tool. J Outdoor Recreat Tour 11:64–79
npr.org. Please Help Me.’ What people in China are saying about the outbreak on social media, npr.org, . from < https://www.npr.org/sections/goatsandsoda/2020/01/24/799000379/please-help-me-what-people-in-china-are-saying-about-the-outbreak-on-social-medi >, Accessed on 26 Jan 2020.
Ogden LE (2018) Climate change, pathogens, and people: the challenges of monitoring a moving target. Bioscience 68(10):733–739
Ortiz AMD, Outhwaite CL, Dalin C, Newbold T (2021) A review of the interactions between biodiversity, agriculture, climate change, and international trade: research and policy priorities. One Earth 4(1):88–101
Ortiz R (2008) Crop genetic engineering under global climate change. Ann Arid Zone 47(3):343
Otegui MAE, Bonhomme R (1998) Grain yield components in maize: I. Ear growth and kernel set. Field Crop Res 56(3):247–256
Pachauri RK, Allen MR, Barros VR, Broome J, Cramer W, Christ R, . . . Dasgupta P (2014) Climate change 2014: synthesis report. Contribution of Working Groups I, II and III to the fifth assessment report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change: Ipcc
Pal JK (2021) Visualizing the knowledge outburst in global research on COVID-19. Scientometrics 126(5):4173–4193
Panda R, Behera S, Kashyap P (2003) Effective management of irrigation water for wheat under stressed conditions. Agric Water Manag 63(1):37–56
Pärnänen KM, Narciso-da-Rocha C, Kneis D, Berendonk TU, Cacace D, Do TT, Jaeger T (2019) Antibiotic resistance in European wastewater treatment plants mirrors the pattern of clinical antibiotic resistance prevalence. Sci Adv 5(3):eaau9124
Parry M, Parry ML, Canziani O, Palutikof J, Van der Linden P, Hanson C (2007) Climate change 2007-impacts, adaptation and vulnerability: Working group II contribution to the fourth assessment report of the IPCC (Vol. 4): Cambridge University Press
Patz JA, Campbell-Lendrum D, Holloway T, Foley JA (2005) Impact of regional climate change on human health. Nature 438(7066):310–317
Patz JA, Graczyk TK, Geller N, Vittor AY (2000) Effects of environmental change on emerging parasitic diseases. Int J Parasitol 30(12–13):1395–1405
Pautasso M, Döring TF, Garbelotto M, Pellis L, Jeger MJ (2012) Impacts of climate change on plant diseases—opinions and trends. Eur J Plant Pathol 133(1):295–313
Peng S, Huang J, Sheehy JE, Laza RC, Visperas RM, Zhong X, Cassman KG (2004) Rice yields decline with higher night temperature from global warming. Proc Natl Acad Sci 101(27):9971–9975
Pereira HM, Ferrier S, Walters M, Geller GN, Jongman R, Scholes RJ, Cardoso A (2013) Essential biodiversity variables. Science 339(6117):277–278
Perera K, De Silva K, Amarasinghe M (2018) Potential impact of predicted sea level rise on carbon sink function of mangrove ecosystems with special reference to Negombo estuary, Sri Lanka. Global Planet Change 161:162–171
Pfadenhauer JS, Klötzli FA (2020) Zonal Vegetation of the Subtropical (Warm–Temperate) Zone with Winter Rain. In Global Vegetation (pp. 455–514). Springer, Cham
Phillips JD (2018) Environmental gradients and complexity in coastal landscape response to sea level rise. CATENA 169:107–118
Pirasteh-Anosheh H, Parnian A, Spasiano D, Race M, Ashraf M (2021) Haloculture: A system to mitigate the negative impacts of pandemics on the environment, society and economy, emphasizing COVID-19. Environ Res 111228
Pruden A, Larsson DJ, Amézquita A, Collignon P, Brandt KK, Graham DW, Snape JR (2013) Management options for reducing the release of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes to the environment. Environ Health Perspect 121(8):878–885
Qasim MZ, Hammad HM, Abbas F, Saeed S, Bakhat HF, Nasim W, Fahad S (2020) The potential applications of picotechnology in biomedical and environmental sciences. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(1):133–142
Qasim MZ, Hammad HM, Maqsood F, Tariq T, Chawla MS Climate Change Implication on Cereal Crop Productivity
Rahman M, Alam K (2016) Forest dependent indigenous communities’ perception and adaptation to climate change through local knowledge in the protected area—a Bangladesh case study. Climate 4(1):12
Ramankutty N, Mehrabi Z, Waha K, Jarvis L, Kremen C, Herrero M, Rieseberg LH (2018) Trends in global agricultural land use: implications for environmental health and food security. Annu Rev Plant Biol 69:789–815
Rehman A, Ma H, Ahmad M, Irfan M, Traore O, Chandio AA (2021) Towards environmental Sustainability: devolving the influence of carbon dioxide emission to population growth, climate change, Forestry, livestock and crops production in Pakistan. Ecol Indic 125:107460
Reichstein M, Carvalhais N (2019) Aspects of forest biomass in the Earth system: its role and major unknowns. Surv Geophys 40(4):693–707
Reidsma P, Ewert F, Boogaard H, van Diepen K (2009) Regional crop modelling in Europe: the impact of climatic conditions and farm characteristics on maize yields. Agric Syst 100(1–3):51–60
Ritchie H, Roser M (2014) Natural disasters. Our World in Data
Rizvi AR, Baig S, Verdone M (2015) Ecosystems based adaptation: knowledge gaps in making an economic case for investing in nature based solutions for climate change. IUCN, Gland, Switzerland, p 48
Roscher C, Fergus AJ, Petermann JS, Buchmann N, Schmid B, Schulze E-D (2013) What happens to the sown species if a biodiversity experiment is not weeded? Basic Appl Ecol 14(3):187–198
Rosenzweig C, Elliott J, Deryng D, Ruane AC, Müller C, Arneth A, Khabarov N (2014) Assessing agricultural risks of climate change in the 21st century in a global gridded crop model intercomparison. Proc Natl Acad Sci 111(9):3268–3273
Rosenzweig C, Iglesius A, Yang XB, Epstein PR, Chivian E (2001) Climate change and extreme weather events-implications for food production, plant diseases, and pests
Sadras VO, Slafer GA (2012) Environmental modulation of yield components in cereals: heritabilities reveal a hierarchy of phenotypic plasticities. Field Crop Res 127:215–224
Salvucci ME, Crafts-Brandner SJ (2004) Inhibition of photosynthesis by heat stress: the activation state of Rubisco as a limiting factor in photosynthesis. Physiol Plant 120(2):179–186
Santos WS, Gurgel-Gonçalves R, Garcez LM, Abad-Franch F (2021) Deforestation effects on Attalea palms and their resident Rhodnius, vectors of Chagas disease, in eastern Amazonia. PLoS ONE 16(5):e0252071
Sarkar P, Debnath N, Reang D (2021) Coupled human-environment system amid COVID-19 crisis: a conceptual model to understand the nexus. Sci Total Environ 753:141757
Schlenker W, Roberts MJ (2009) Nonlinear temperature effects indicate severe damages to US crop yields under climate change. Proc Natl Acad Sci 106(37):15594–15598
Schoene DH, Bernier PY (2012) Adapting forestry and forests to climate change: a challenge to change the paradigm. Forest Policy Econ 24:12–19
Schuurmans C (2021) The world heat budget: expected changes Climate Change (pp. 1–15): CRC Press
Scott D (2021) Sustainable Tourism and the Grand Challenge of Climate Change. Sustainability 13(4):1966
Scott D, McBoyle G, Schwartzentruber M (2004) Climate change and the distribution of climatic resources for tourism in North America. Climate Res 27(2):105–117
Semenov MA (2009) Impacts of climate change on wheat in England and Wales. J R Soc Interface 6(33):343–350
Shaffril HAM, Krauss SE, Samsuddin SF (2018) A systematic review on Asian’s farmers’ adaptation practices towards climate change. Sci Total Environ 644:683–695
Shahbaz M, Balsalobre-Lorente D, Sinha A (2019) Foreign direct Investment–CO2 emissions nexus in Middle East and North African countries: Importance of biomass energy consumption. J Clean Product 217:603–614
Sharif A, Mishra S, Sinha A, Jiao Z, Shahbaz M, Afshan S (2020) The renewable energy consumption-environmental degradation nexus in Top-10 polluted countries: Fresh insights from quantile-on-quantile regression approach. Renew Energy 150:670–690
Sharma R (2012) Impacts on human health of climate and land use change in the Hindu Kush-Himalayan region. Mt Res Dev 32(4):480–486
Sharma R, Sinha A, Kautish P (2020) Examining the impacts of economic and demographic aspects on the ecological footprint in South and Southeast Asian countries. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(29):36970–36982
Smit B, Burton I, Klein RJ, Wandel J (2000) An anatomy of adaptation to climate change and variability Societal adaptation to climate variability and change (pp. 223–251): Springer
Song Y, Fan H, Tang X, Luo Y, Liu P, Chen Y (2021) The effects of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) on ischemic stroke and the possible underlying mechanisms. Int J Neurosci 1–20
Sovacool BK, Griffiths S, Kim J, Bazilian M (2021) Climate change and industrial F-gases: a critical and systematic review of developments, sociotechnical systems and policy options for reducing synthetic greenhouse gas emissions. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 141:110759
Stewart JA, Perrine JD, Nichols LB, Thorne JH, Millar CI, Goehring KE, Wright DH (2015) Revisiting the past to foretell the future: summer temperature and habitat area predict pika extirpations in California. J Biogeogr 42(5):880–890
Stocker T, Qin D, Plattner G, Tignor M, Allen S, Boschung J, . . . Midgley P (2013) Climate change 2013: The physical science basis. Working group I contribution to the IPCC Fifth assessment report: Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. 1535p
Stone P, Nicolas M (1994) Wheat cultivars vary widely in their responses of grain yield and quality to short periods of post-anthesis heat stress. Funct Plant Biol 21(6):887–900
Su H-C, Liu Y-S, Pan C-G, Chen J, He L-Y, Ying G-G (2018) Persistence of antibiotic resistance genes and bacterial community changes in drinking water treatment system: from drinking water source to tap water. Sci Total Environ 616:453–461
Sunderlin WD, Angelsen A, Belcher B, Burgers P, Nasi R, Santoso L, Wunder S (2005) Livelihoods, forests, and conservation in developing countries: an overview. World Dev 33(9):1383–1402
Symanski E, Han HA, Han I, McDaniel M, Whitworth KW, McCurdy S, . . . Delclos GL (2021) Responding to natural and industrial disasters: partnerships and lessons learned. Disaster medicine and public health preparedness 1–4
Tao F, Yokozawa M, Xu Y, Hayashi Y, Zhang Z (2006) Climate changes and trends in phenology and yields of field crops in China, 1981–2000. Agric for Meteorol 138(1–4):82–92
Tebaldi C, Hayhoe K, Arblaster JM, Meehl GA (2006) Going to the extremes. Clim Change 79(3–4):185–211
Testa G, Koon E, Johannesson L, McKenna G, Anthony T, Klintmalm G, Gunby R (2018) This article has been accepted for publication and undergone full peer review but has not been through the copyediting, typesetting, pagination and proofreading process, which may lead to differences between this version and the Version of Record. Please cite this article as
Thornton PK, Lipper L (2014) How does climate change alter agricultural strategies to support food security? (Vol. 1340): Intl Food Policy Res Inst
Tranfield D, Denyer D, Smart P (2003) Towards a methodology for developing evidence-informed management knowledge by means of systematic review. Br J Manag 14(3):207–222
UNEP (2017) United nations environment programme: frontiers 2017. from https://www.unenvironment.org/news-and-stories/press-release/antimicrobial-resistance - environmental-pollution-among-biggest
Usman M, Balsalobre-Lorente D (2022) Environmental concern in the era of industrialization: Can financial development, renewable energy and natural resources alleviate some load? Ene Policy 162:112780
Usman M, Makhdum MSA (2021) What abates ecological footprint in BRICS-T region? Exploring the influence of renewable energy, non-renewable energy, agriculture, forest area and financial development. Renew Energy 179:12–28
Usman M, Balsalobre-Lorente D, Jahanger A, Ahmad P (2022b) Pollution concern during globalization mode in financially resource-rich countries: Do financial development, natural resources, and renewable energy consumption matter? Rene. Energy 183:90–102
Usman M, Jahanger A, Makhdum MSA, Balsalobre-Lorente D, Bashir A (2022a) How do financial development, energy consumption, natural resources, and globalization affect Arctic countries’ economic growth and environmental quality? An advanced panel data simulation. Energy 241:122515
Usman M, Khalid K, Mehdi MA (2021) What determines environmental deficit in Asia? Embossing the role of renewable and non-renewable energy utilization. Renew Energy 168:1165–1176
Urban MC (2015) Accelerating extinction risk from climate change. Science 348(6234):571–573
Vale MM, Arias PA, Ortega G, Cardoso M, Oliveira BF, Loyola R, Scarano FR (2021) Climate change and biodiversity in the Atlantic Forest: best climatic models, predicted changes and impacts, and adaptation options The Atlantic Forest (pp. 253–267): Springer
Vedwan N, Rhoades RE (2001) Climate change in the Western Himalayas of India: a study of local perception and response. Climate Res 19(2):109–117
Vega CR, Andrade FH, Sadras VO, Uhart SA, Valentinuz OR (2001) Seed number as a function of growth. A comparative study in soybean, sunflower, and maize. Crop Sci 41(3):748–754
Vergés A, Doropoulos C, Malcolm HA, Skye M, Garcia-Pizá M, Marzinelli EM, Vila-Concejo A (2016) Long-term empirical evidence of ocean warming leading to tropicalization of fish communities, increased herbivory, and loss of kelp. Proc Natl Acad Sci 113(48):13791–13796
Verheyen R (2005) Climate change damage and international law: prevention duties and state responsibility (Vol. 54): Martinus Nijhoff Publishers
Waheed A, Fischer TB, Khan MI (2021) Climate Change Policy Coherence across Policies, Plans, and Strategies in Pakistan—implications for the China-Pakistan Economic Corridor Plan. Environ Manage 67(5):793–810
Wasiq M, Ahmad M (2004) Sustaining forests: a development strategy: The World Bank
Watts N, Adger WN, Agnolucci P, Blackstock J, Byass P, Cai W, Cooper A (2015) Health and climate change: policy responses to protect public health. The Lancet 386(10006):1861–1914
Weed AS, Ayres MP, Hicke JA (2013) Consequences of climate change for biotic disturbances in North American forests. Ecol Monogr 83(4):441–470
Weisheimer A, Palmer T (2005) Changing frequency of occurrence of extreme seasonal temperatures under global warming. Geophys Res Lett 32(20)
Wernberg T, Bennett S, Babcock RC, De Bettignies T, Cure K, Depczynski M, Hovey RK (2016) Climate-driven regime shift of a temperate marine ecosystem. Science 353(6295):169–172
WHO (2018) WHO, 2018. Antimicrobial resistance
Wilkinson DM, Sherratt TN (2016) Why is the world green? The interactions of top–down and bottom–up processes in terrestrial vegetation ecology. Plant Ecolog Divers 9(2):127–140
Wiranata IJ, Simbolon K (2021) Increasing awareness capacity of disaster potential as a support to achieve sustainable development goal (sdg) 13 in lampung province. Jurnal Pir: Power in International Relations 5(2):129–146
Wiréhn L (2018) Nordic agriculture under climate change: a systematic review of challenges, opportunities and adaptation strategies for crop production. Land Use Policy 77:63–74
Wu D, Su Y, Xi H, Chen X, Xie B (2019) Urban and agriculturally influenced water contribute differently to the spread of antibiotic resistance genes in a mega-city river network. Water Res 158:11–21
Wu HX (2020) Losing Steam?—An industry origin analysis of China’s productivity slowdown Measuring Economic Growth and Productivity (pp. 137–167): Elsevier
Wu H, Qian H, Chen J, Huo C (2017) Assessment of agricultural drought vulnerability in the Guanzhong Plain. China Water Resources Management 31(5):1557–1574
Xie W, Huang J, Wang J, Cui Q, Robertson R, Chen K (2018) Climate change impacts on China’s agriculture: the responses from market and trade. China Econ Rev
Xu J, Sharma R, Fang J, Xu Y (2008) Critical linkages between land-use transition and human health in the Himalayan region. Environ Int 34(2):239–247
Yadav MK, Singh R, Singh K, Mall R, Patel C, Yadav S, Singh M (2015) Assessment of climate change impact on productivity of different cereal crops in Varanasi. India J Agrometeorol 17(2):179–184
Yang B, Usman M (2021) Do industrialization, economic growth and globalization processes influence the ecological footprint and healthcare expenditures? Fresh insights based on the STIRPAT model for countries with the highest healthcare expenditures. Sust Prod Cons 28:893–910
Yu Z, Razzaq A, Rehman A, Shah A, Jameel K, Mor RS (2021) Disruption in global supply chain and socio-economic shocks: a lesson from COVID-19 for sustainable production and consumption. Oper Manag Res 1–16
Zarnetske PL, Skelly DK, Urban MC (2012) Biotic multipliers of climate change. Science 336(6088):1516–1518
Zhang M, Liu N, Harper R, Li Q, Liu K, Wei X, Liu S (2017) A global review on hydrological responses to forest change across multiple spatial scales: importance of scale, climate, forest type and hydrological regime. J Hydrol 546:44–59
Zhao J, Sinha A, Inuwa N, Wang Y, Murshed M, Abbasi KR (2022) Does Structural Transformation in Economy Impact Inequality in Renewable Energy Productivity? Implications for Sustainable Development. Renew Energy 189:853–864. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2022.03.050
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
School of Economics and Management, Nanjing University of Science and Technology, Nanjing, 210094, People’s Republic of China
Kashif Abbass, Huaming Song & Ijaz Younis
Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Chemical Pollution Control and Resources Reuse, School of Environmental and Biological Engineering, Nanjing University of Science and Technology, Xiaolingwei 200, Nanjing, 210094, People’s Republic of China
Muhammad Zeeshan Qasim
School of Business and Economics, North South University, Dhaka, 1229, Bangladesh
Muntasir Murshed
Department of Journalism, Media and Communications, Daffodil International University, Dhaka, Bangladesh
Department of Finance, College of Business Administration, Prince Sattam Bin Abdulaziz University, 173, Alkharj, 11942, Saudi Arabia
Haider Mahmood
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
KA: Writing the original manuscript, data collection, data analysis, Study design, Formal analysis, Visualization, Revised draft, Writing-review, and editing. MZQ: Writing the original manuscript, data collection, data analysis, Writing-review, and editing. HS: Contribution to the contextualization of the theme, Conceptualization, Validation, Supervision, literature review, Revised drapt, and writing review and editing. MM: Writing review and editing, compiling the literature review, language editing. HM: Writing review and editing, compiling the literature review, language editing. IY: Contribution to the contextualization of the theme, literature review, and writing review and editing.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Huaming Song .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Philippe Garrigues.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Abbass, K., Qasim, M.Z., Song, H. et al. A review of the global climate change impacts, adaptation, and sustainable mitigation measures. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29 , 42539–42559 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-19718-6
Download citation
Received : 26 August 2021
Accepted : 10 March 2022
Published : 04 April 2022
Issue Date : June 2022
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-19718-6
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Climate change
- Antimicrobial resistance
- Biodiversity
- Mitigation measures
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- Perspective
- Published: 09 June 2022
Aligning artificial intelligence with climate change mitigation
- Lynn H. Kaack ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-3630-3102 1 , 2 , 3 ,
- Priya L. Donti ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-8503-7464 4 , 5 ,
- Emma Strubell ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-2798-0726 4 ,
- George Kamiya ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-4376-0790 6 ,
- Felix Creutzig ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-5710-3348 7 , 8 &
- David Rolnick ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-2855-393X 9 , 10
Nature Climate Change volume 12 , pages 518–527 ( 2022 ) Cite this article
13k Accesses
82 Citations
411 Altmetric
Metrics details
- Energy policy
There is great interest in how the growth of artificial intelligence and machine learning may affect global GHG emissions. However, such emissions impacts remain uncertain, owing in part to the diverse mechanisms through which they occur, posing difficulties for measurement and forecasting. Here we introduce a systematic framework for describing the effects of machine learning (ML) on GHG emissions, encompassing three categories: computing-related impacts, immediate impacts of applying ML and system-level impacts. Using this framework, we identify priorities for impact assessment and scenario analysis, and suggest policy levers for better understanding and shaping the effects of ML on climate change mitigation.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
24,99 € / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
195,33 € per year
only 16,28 € per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others

Predicting European cities’ climate mitigation performance using machine learning
Predicting global patterns of long-term climate change from short-term simulations using machine learning

A machine learning approach to rapidly project climate responses under a multitude of net-zero emission pathways
Zhang, D. et al. Artificial Intelligence Index Report 2021 (AI Index Steering Committee, Human-Centered AI Institute, 2021).
Digital Technology and the Planet: Harnessing Computing to Achieve Net Zero (Royal Society, 2020); https://royalsociety.org/-/media/policy/projects/digital-technology-and-the-planet/digital-technology-and-the-planet-report.pdf
Kaack, L. H., Donti, P. L., Strubell, E. & Rolnick, D. Artificial Intelligence and Climate Change: Opportunities, Considerations, and Policy Levers to Align AI with Climate Change Goals (Heinrich-Böll-Stiftung, 2020); https://eu.boell.org/en/2020/12/03/artificial-intelligence-and-climate-change
Harnessing Artificial Intelligence to Accelerate the Energy Transition (World Economic Forum, 2021); https://www.weforum.org/whitepapers/harnessing-artificial-intelligence-to-accelerate-the-energy-transition
Berkhout, F. & Hertin, J. De-materialising and re-materialising: digital technologies and the environment. Futures 36 , 903–920 (2004).
Article Google Scholar
Hilty, L. M. & Aebischer, B. in ICT Innovations for Sustainability (eds Hilty, L. M. & Aebischer, B) 3–36 (Springer, 2015).
Rolnick, D. et al. Tackling climate change with machine learning. ACM Comput. Surv . https://doi.org/10.1145/3485128 (2022).
Oil in the Cloud: How Tech Companies are Helping Big Oil Profit from Climate Destruction (Greenpeace, 2019); https://www.greenpeace.org/usa/reports/oil-in-the-cloud/
Dobbe, R. & Whittaker, M. AI and climate change: how they’re connected, and what we can do about it. Medium https://medium.com/@AINowInstitute/ai-and-climate-change-how-theyre-connected-and-what-we-can-do-about-it-6aa8d0f5b32c (2019).
Strubell, E., Ganesh, A. & McCallum, A. Energy and policy considerations for deep learning in NLP. In Proc. 57th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics 3645–3650 (Association for Computational Linguistics, 2019); https://doi.org/10.18653/v1/P19-1355
Schwartz, R., Dodge, J., Smith, N. A. & Etzioni, O. Green AI. Commun. ACM 63 , 54–63 (2020).
Dauvergne, P. Is artificial intelligence greening global supply chains? Exposing the political economy of environmental costs. Rev. Int. Polit. Econ. https://doi.org/10.1080/09692290.2020.1814381 (2020).
Coeckelbergh, M. AI for climate: freedom, justice, and other ethical and political challenges. AI Ethics 1 , 67–72 (2021).
Gunther, H. & Rose, J. Governing AI: the importance of environmentally sustainable and equitable innovation. Environ. Law Rep. 50 , 10888 (2020).
Stein, A. L. Artificial intelligence and climate change. Yale J. Reg . 37 , 890–939 (2020).
Google Scholar
Cowls, J., Tsamados, A., Taddeo, M. & Floridi, L. The AI gambit-leveraging artificial intelligence to combat climate change: opportunities, challenges, and recommendations. SSRN https://ssrn.com/abstract=3804983 (2021).
FAccT ’21: Proceedings of the 2021 ACM Conference on Fairness, Accountability, and Transparency (ACM, 2021).
Recommendation on the Ethics of Artificial Intelligence (UNESCO, 2021); https://unesdoc.unesco.org/ark:/48223/pf0000380455
Areas for Future Action in the Responsible AI Ecosystem (The Future Society, GPAI Responsible Development, Use and Governance of AI Working Group & CEIMIA, 2020); https://www.gpai.ai/projects/responsible-ai/areas-for-future-action-in-responsible-ai.pdf
Horner, N. C., Shehabi, A. & Azevedo, I. L. Known unknowns: indirect energy effects of information and communication technology. Environ. Res. Lett. 11 , 103001 (2016).
Bieser, J. & Hilty, L. Indirect effects of the digital transformation on environmental sustainability: methodological challenges in assessing the greenhouse gas abatement potential of ICT. In 5th International Conference on Information and Communication Technology for Sustainability 68–81 (EasyChair, 2018); https://doi.org/10.29007/lx7q
Pohl, J., Hilty, L. M. & Finkbeiner, M. How LCA contributes to the environmental assessment of higher order effects of ICT application: a review of different approaches. J. Clean. Prod. 219 , 698–712 (2019).
Digitalization & Energy (OECD/IEA, 2017); https://www.iea.org/reports/digitalisation-and-energy
Sivaram, V. et al. Digital Decarbonization Promoting Digital Innovations to Advance Clean Energy Systems (Council on Foreign Relations, 2018); https://www.cfr.org/report/digital-decarbonization
Wilson, C., Kerr, L., Sprei, F., Vrain, E. & Wilson, M. Potential climate benefits of digital consumer innovations. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 45 , 113–144 (2020).
Canziani, A., Paszke, A. & Culurciello, E. An analysis of deep neural network models for practical applications. Preprint at https://arxiv.org/abs/1605.07678 (2017).
AI and compute. OpenAI https://openai.com/blog/ai-and-compute (16 May 2018).
Bommasani, R. et al. On the opportunities and risks of foundation models. Preprint at https://arxiv.org/abs/2108.07258 (2021).
Joulin, A., Grave, E., Bojanowski, P. & Mikolov, T. Bag of tricks for efficient text classification. In Proc. 15th Conference of the European Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Volume 2 427–431 (Association for Computational Linguistics, 2017); https://www.aclweb.org/anthology/E17-2068
Hazelwood, K. et al. Applied machine learning at Facebook: a datacenter infrastructure perspective. In 2018 IEEE International Symposium on High Performance Computer Architecture 620–629 (IEEE, 2018); https://doi.org/10.1109/HPCA.2018.00059
Sandler, M., Howard, A., Zhu, M., Zhmoginov, A. & Chen, L.-C. MobileNetV2: inverted residuals and linear bottlenecks. In IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (IEEE, 2018).
Turovsky, B. Ten years of Google Translate. The Keyword https://blog.google/products/translate/ten-years-of-google-translate (2016).
Wu, C. J. et al. Sustainable AI: environmental implications, challenges and opportunities. In Proc. Machine Learning and Systems 4 795–813 (MLSys, 2022).
Jiang, A. H. et al. Accelerating deep learning by focusing on the biggest losers. Preprint at https://arxiv.org/abs/1910.00762 (2019).
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S. & Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition 770–778 (IEEE, 2016); https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2016.90
Albanie, S. ConvNet-Burden: estimates of memory consumption and FLOP counts for various convolutional neural networks. GitHub https://github.com/albanie/convnet-burden (2019).
Bender, E. M., Gebru, T., McMillan-Major, A. & Shmitchell, S. On the dangers of stochastic parrots: can language models be too big? In Proc. 2021 ACM Conference on Fairness, Accountability, and Transparenc y 610–623 (ACM, 2021).
Gupta, A., Lanteigne, C. & Kingsley, S. SECure: a social and environmental certificate for AI Systems. Preprint at https://arxiv.org/abs/2006.06217 (2020).
Tomašev, N. et al. AI for social good: unlocking the opportunity for positive impact. Nat. Commun. 11 , 2468 (2020).
Henderson, P. et al. Towards the systematic reporting of the energy and carbon footprints of machine learning. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 21 , 1–43 (2020).
Schmidt, V. et al. CodeCarbon: estimate and track carbon emissions from machine learning computing. Zenodo https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.4658424 (2021).
Anthony, L. F. W., Kanding, B. & Selvan, R. Carbontracker: tracking and predicting the carbon footprint of training deep learning models. Preprint at https://arxiv.org/abs/2007.03051 (2020).
Cai, E., Juan, D., Stamoulis, D. & Marculescu, D. NeuralPower: predict and deploy energy-efficient convolutional neural networks. In 9 th Asian Conference on Machine Learning (ACML, 2017).
Dodge, J., Gururangan, S., Card, D., Schwartz, R. & Smith, N. A. Show your work: improved reporting of experimental results. In Proc. 2019 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing and 9th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing 2185–2194 (Association for Computational Linguistics, 2019); https://doi.org/10.18653/v1/D19-1224
Mattson, P. et al. (eds) Proc. Machine Learning and Systems 2 336–349 (MLSys, 2020).
Reddi, V. J. et al. MLPerf inference benchmark. In 2020 ACM/IEEE 47th Annual International Symposium on Computer Architecture 446–459 (IEEE, 2020); https://doi.org/10.1109/ISCA45697.2020.00045
Hinton, G., Vinyals, O. & Dean, J. Distilling the knowledge in a neural network. In NeurIPS Deep Learning Workshop (NeurIPS, 2014).
Schaul, T., Quan, J., Antonoglou, I. & Silver, D. Prioritized experience replay. In International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR, 2016).
Hubara, I., Courbariaux, M., Soudry, D., El-Yaniv, R. & Bengio, Y. Quantized neural networks: training neural networks with low precision weights and activations. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 18 , 1–30 (2018).
Pfeiffer, J. et al. Adapterhub: a framework for adapting transformers. In Proc. 2020 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing: System Demonstrations 46–54 (Association for Computational Linguistics, 2020).
Cai, H., Gan, C., Wang, T., Zhang, Z. & Han, S. Once-for-all: train one network and specialize it for efficient deployment. In International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR, 2020).
Lepikhin, D. et al. GShard: scaling giant models with conditional computation and automatic sharding. In International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR, 2021).
Hooker, S., Moorosi, N., Clark, G., Bengio, S. & Denton, E. Characterizing and mitigating bias in compact models. In ICML Workshop on Human Interpretability in Machine Learning (ICML, 2020).
Greenhouse Gas Emissions Trajectories for the Information and Communication Technology Sector Compatible with the UNFCCC Paris Agreement (International Telecommunication Union, 2020); http://handle.itu.int/11.1002/1000/14084
Malmodin, J. & Lundén, D. The energy and carbon footprint of the global ICT and E&M sectors 2010–2015. Sustainability 10 , 3027 (2018).
Masanet, E., Shehabi, A., Lei, N., Smith, S. & Koomey, J. Recalibrating global data center energy-use estimates. Science 367 , 984–986 (2020).
Article CAS Google Scholar
Data Centres and Data Transmission Networks (International Energy Agency, 2021); https://www.iea.org/reports/data-centres-and-data-transmission-networks
Montevecchi, F., Stickler, T., Hintemann, R. & Hinterholzer, S. Energy-Efficient Cloud Computing Technologies and Policies for an Eco-Friendly Cloud Market (2020); https://ec.europa.eu/newsroom/dae/document.cfm?doc_id=71330
Cisco Global Cloud Index: Forecast and Methodology, 2016–2021 (Cisco, 2018); https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/solutions/collateral/service-provider/global-cloud-index-gci/white-paper-c11-738085.pdf
Compton, C. Cisco’s Global Cloud Index study: acceleration of the multicloud era. Cisco Blogs https://blogs.cisco.com/news/acceleration-of-multicloud-era (2018).
Wu, C. et al. Machine learning at Facebook: understanding inference at the edge. In 2019 IEEE International Symposium on High Performance Computer Architecture 331–344 (IEEE, 2019).
Koomey, J., Berard, S., Sanchez, M. & Wong, H. Implications of historical trends in the electrical efficiency of computing. IEEE Ann. Hist. Comput. 33 , 46–54 (2010).
Koomey, J. & Naffziger, S. Moore's law might be slowing down, but not energy efficiency. IEEE Spectrum 52 , 35 (2015).
Facebook Sustainability Data 2020 (Facebook, 2021); https://sustainability.fb.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/06/2020_FB_Sustainability-Data.pdf
Naumov, M. et al. Deep learning training in Facebook data centers: design of scale-up and scale-out systems. Preprint at https://arxiv.org/abs/2003.09518 (2020).
Park, J. et al. Deep learning inference in Facebook data centers: characterization, performance optimizations and hardware implications. Preprint at https://arxiv.org/abs/1811.09886 (2018).
Shehabi, A. et al. United States Data Center Energy Usage Report (Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, 2016); https://eta.lbl.gov/publications/united-states-data-center-energy
Jouppi, N. P. et al. In-datacenter performance analysis of a tensor processing unit. In Proc. 44th Annual International Symposium on Computer Architecture 1–12 (ACM, 2017).
Radovanovic, A. Our data centers now work harder when the sun shines and wind blows. The Keyword https://blog.google/inside-google/infrastructure/data-centers-work-harder-sun-shines-wind-blows (2020).
Whitehead, B., Andrews, D. & Shah, A. The life cycle assessment of a UK data centre. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 20 , 332–349 (2015).
Masanet, E., Shehabi, A. & Koomey, J. Characteristics of low-carbon data centres. Nat. Clim. Change 3 , 627–630 (2013).
Hischier, R., Coroama, V. C., Schien, D. & Achachlouei, M. A. in ICT Innovations for Sustainability (eds Hilty, L. M. & Aebischer, B.) 171–189 (Springer, 2015).
André Barroso, L., Clidaras, J. & Hölzle, U. The datacenter as a computer: an introduction to the design of warehouse-scale machines. Synth. Lect. Comput. Arch. 8 , 1–154 (2013).
Gupta, U. et al. Chasing carbon: the elusive environmental footprint of computing. In IEEE International Symposium on High-Performance Computer Architecture 854–867 (IEEE, 2021).
Finer, M. et al. Combating deforestation: from satellite to intervention. Science 360 , 1303–1305 (2018).
Kulp, S. A. & Strauss, B. H. New elevation data triple estimates of global vulnerability to sea-level rise and coastal flooding. Nat. Commun. 10 , 4844 (2019).
Friederich, D., Kaack, L. H., Luccioni, A. & Steffen, B. Automated identification of climate risk disclosures in annual corporate reports. Preprint at https://arxiv.org/abs/2108.01415 (2021).
Liu, Y., Guo, B., Zou, X., Li, Y. & Shi, S. Machine learning assisted materials design and discovery for rechargeable batteries. Energy Storage Mater . 31 , 434–450 (2020).
Ahmed, R., Sreeram, V., Mishra, Y. & Arif, M. D. A review and evaluation of the state-of-the-art in PV solar power forecasting: techniques and optimization. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 124 , 109792 (2020).
You, J., Li, X., Low, M., Lobell, D. & Ermon, S. Deep Gaussian process for crop yield prediction based on remote sensing data. In Thirty-First AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence 4559–4565 (ACM, 2017).
Toqué, F., Khouadjia, M., Come, E., Trepanier, M. & Oukhellou, L. Short & long term forecasting of multimodal transport passenger flows with machine learning methods. In 2017 IEEE 20th International Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems 560–566 (IEEE, 2017).
Evans, R. & Gao, J. DeepMind AI reduces Google data centre cooling bill by 40%. DeepMind https://www.deepmind.com/blog/deepmind-ai-reduces-google-data-centre-cooling-bill-by-40 (2016).
Roman, N. D., Bre, F., Fachinotti, V. D. & Lamberts, R. Application and characterization of metamodels based on artificial neural networks for building performance simulation: a systematic review. Energy Build. 217 , 109972 (2020).
Irrgang, C. et al. Towards neural Earth system modelling by integrating artificial intelligence in Earth system science. Nat. Mach. Intell. 3 , 667–674 (2021).
Jenssen, R. et al. Automatic autonomous vision-based power line inspection: a review of current status and the potential role of deep learning. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 99 , 107–120 (2018).
Rudin, C. et al. Interpretable machine learning: fundamental principles and 10 grand challenges. Stat. Surv. 16 , 1–85 (2022).
Ghahramani, Z. Probabilistic machine learning and artificial intelligence. Nature 521 , 452–459 (2015).
Willard, J., Jia, X., Xu, S., Steinbach, M. & Kumar, V. Integrating physics-based modeling with machine learning: a survey. Preprint at https://arxiv.org/abs/2003.04919 (2020).
Zhuang, F. et al. A comprehensive survey on transfer learning. Proc. IEEE 109 , 43–76 (2020).
Adams-Progar, A., Fink, G.A.,Walker, E. & Llewellyn, D. in Security and Privacy in Cyber‐Physical Systems: Foundations, Principles and Applications (eds Song, H. et al.) Ch. 18 (Wiley, 2017); https://doi.org/10.1002/9781119226079.ch18
Charles, H. et al. Meat consumption, health, and the environment. Science 361 , eaam5324 (2018).
Herweijer, C., Combes, B. & Gillham, J. How AI Can Enable a Sustainable Future (Microsoft & PWC, 2018); https://www.pwc.co.uk/services/sustainability-climate-change/insights/how-ai-future-can-enable-sustainable-future.html
Climate AI: How Artificial Intelligence Can Power Your Climate Action Strategy (Capgemini, 2020); https://www.capgemini.com/research/climate-ai/
Degot, C., Duranton, S., Frédeau, M. & Hutchinson, R. Reduce carbon and costs with the power of AI. BCG https://www.bcg.com/en-us/publications/2021/ai-to-reduce-carbon-emissions (2021).
Azevedo, I. M. L. Consumer end-use energy efficiency and rebound effects. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 39 , 393–418 (2014).
Lange, S., Pohl, J. & Santarius, T. Digitalization and energy consumption. Does ICT reduce energy demand? Ecol. Econ. 176 , 106760 (2020).
Anderson, J. M. et al. Autonomous Vehicle Technology: A Guide for Policymakers (RAND Corporation, 2016); https://doi.org/10.7249/RR443-2
Creutzig, F. et al. Leveraging digitalization for sustainability in urban transport. Glob. Sustain. 2 , e14 (2019).
Wadud, Z., MacKenzie, D. & Leiby, P. Help or hindrance? The travel, energy and carbon impacts of highly automated vehicles. Transport. Res. A 86 , 1–18 (2016).
Chase, N., Maples, J. & Schipper, M. Autonomous Vehicles: Uncertainties and Energy Implications (EIA, 2018); https://www.eia.gov/outlooks/aeo/av.php
Arthur, W. B. Competing technologies, increasing returns, and lock-in by historical events. Econ. J. 99 , 116–131 (1989).
Cox, E., Royston, S. & Selby, J. Impact of Non-Energy Policies on Energy Systems (UK Energy Research Centre, 2016); https://ukerc.ac.uk/publications/impact-of-non-energy-policies-on-energy-systems/
Stilgoe, J., Owen, R. & Macnaghten, P. Developing a framework for responsible innovation. Res. Policy 42 , 1568–1580 (2013).
Jirotka, M., Grimpe, B., Stahl, B., Eden, G. & Hartswood, M. Responsible research and innovation in the digital age. Commun. ACM 60 , 62–68 (2017).
Itten, R. et al. Digital transformation-life cycle assessment of digital services, multifunctional devices and cloud computing. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 25 , 2093–2098 (2020).
Coroamă, V. C., Bergmark, P., Höjer, M. & Malmodin, J. A methodology for assessing the environmental effects induced by ICT services: part I. Single services. In Proc. 7th International Conference on ICT for Sustainability 36–45 (ACM, 2020).
Bergmark, P., Coroamă, V. C., Höjer, M. & Donovan, C. A Methodology for assessing the environmental effects induced by ICT services: part I. Multiple services and companies. In Proc. 7th International Conference on ICT for Sustainability 46–55 (ACM, 2020).
Haataja, M. & Bryson, J. J. What costs should we expect from the EU’s AI Act? Preprint at SocArXiv https://osf.io/preprints/socarxiv/8nzb4 (2021).
Mytton, D. Hiding greenhouse gas emissions in the cloud. Nat. Clim. Change 10 , 701–701 (2020).
Proposal for a Regulation of the European Parliament and of the Council Laying Down Harmonised Rules on Artificial Intelligence (Artificial Intelligence Act) and Amending Certain Union Legislative Acts (European Commission, 2021); https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=CELEX:52021PC0206
Hilbert, M. Big data for development: a review of promises and challenges. Dev. Policy Rev. 34 , 135–174 (2016).
Mehrabi, N., Morstatter, F., Saxena, N., Lerman, K. & Galstyan, A. A survey on bias and fairness in machine learning. in ACM Computing Surveys Vol. 54, 1–35 (ACM, 2021).
Bondi, E., Xu, L., Acosta-Navas, D. & Killian, J. A. Envisioning communities: a participatory approach towards AI for social good. In Proc. 2021 AAAI/ACM Conference on AI, Ethics, and Society 425–436 (ACM, 2021).
Pinch, T. J. & Bijker, W. E. The social construction of facts and artefacts: or how the sociology of science and the sociology of technology might benefit each other. Soc. Stud. Sci. 14 , 399–441 (1984).
Klein, H. K. & Lee Kleinman, D. The social construction of technology: structural considerations. Sci. Technol. Human Values 27 , 28–52 (2002).
Download references
Acknowledgements
We thank the Environmental Law Institute and Alfred P. Sloan Foundation for their support of this work. P.L.D. was also supported by a US Department of Energy Computational Science Graduate Fellowship (DE-FG02-97ER25308), the Center for Climate and Energy Decision Making through a cooperative agreement between the US National Science Foundation and Carnegie Mellon University (grant number SES-00949710) and the Siebel Scholars programme. D.R. was supported by the Canada CIFAR AI Chairs programme. We are grateful to W.Y. for assistance with the figures. We thank P. Bergmark, V. Coroama, D. Daniels, J. Dunietz, L. Klaaβen, S. Luccioni, J. Malmodin, D. Rejeski, C. Samaras, N. Schmid, T. S. Schmidt, M. Scheutz, S. Sewerin, B. Steffen and M. Voss for their input and comments on the manuscript. Opinions are G.K.’s own and do not reflect those of the OECD, the IEA or their member countries.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Data Science Lab, Hertie School, Berlin, Germany
Lynn H. Kaack
Energy and Technology Policy Group, Department of Humanities, Social and Political Sciences, ETH Zurich, Zurich, Switzerland
Institute of Science, Technology, and Policy, ETH Zurich, Zurich, Switzerland
School of Computer Science, Carnegie Mellon University, Pittsburgh, PA, USA
Priya L. Donti & Emma Strubell
Department of Engineering and Public Policy, Carnegie Mellon University, Pittsburgh, PA, USA
Priya L. Donti
International Energy Agency, Paris, France
George Kamiya
Mercator Research Institute on Global Commons and Climate Change, Berlin, Germany
Felix Creutzig
Sustainability Economics of Human Settlements, Technical University Berlin, Berlin, Germany
School of Computer Science, McGill University, Montreal, Quebec, Canada
David Rolnick
Mila – Quebec AI Institute, Montreal, Quebec, Canada
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
P.L.D., L.H.K. and D.R. conceived the idea for this manuscript. All authors wrote and edited the manuscript text and figures, with primary contributions from E.S. and G.K. to the section on computing-related impacts, from D.R., F.C. and L.H.K. to the sections on application-related impacts, from P.L.D. to the section on shaping ML’s impacts and from L.H.K. to the introduction, roadmap for assessing impacts and overall conceptual framing.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Lynn H. Kaack .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information.
Nature Climate Change thanks Lorenz Hilty, Christopher Irrgang and Yang Yu for their contribution to the peer review of this work.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Kaack, L.H., Donti, P.L., Strubell, E. et al. Aligning artificial intelligence with climate change mitigation. Nat. Clim. Chang. 12 , 518–527 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41558-022-01377-7
Download citation
Received : 07 April 2021
Accepted : 27 April 2022
Published : 09 June 2022
Issue Date : June 2022
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1038/s41558-022-01377-7
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
This article is cited by
Assessing the current landscape of ai and sustainability literature: identifying key trends, addressing gaps and challenges.
- Shailesh Tripathi
- Nadine Bachmann
- Herbert Jodlbauer
Journal of Big Data (2024)
The environmental sustainability of digital content consumption
- Robert Istrate
- Victor Tulus
- Gonzalo Guillén-Gosálbez
Nature Communications (2024)
Will AI accelerate or delay the race to net-zero emissions?
- Jonathan Koomey
- Eric Horvitz
Nature (2024)
Generative AI’s environmental costs are soaring — and mostly secret
- Kate Crawford
ChatGPT Needs SPADE (Sustainability, PrivAcy, Digital divide, and Ethics) Evaluation: A Review
- Sunder Ali Khowaja
- Parus Khuwaja
- Lewis Nkenyereye
Cognitive Computation (2024)
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Springer Nature - PMC COVID-19 Collection

A review of the global climate change impacts, adaptation, and sustainable mitigation measures
Kashif abbass.
1 School of Economics and Management, Nanjing University of Science and Technology, Nanjing, 210094 People’s Republic of China
Muhammad Zeeshan Qasim
2 Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Chemical Pollution Control and Resources Reuse, School of Environmental and Biological Engineering, Nanjing University of Science and Technology, Xiaolingwei 200, Nanjing, 210094 People’s Republic of China
Huaming Song
Muntasir murshed.
3 School of Business and Economics, North South University, Dhaka, 1229 Bangladesh
4 Department of Journalism, Media and Communications, Daffodil International University, Dhaka, Bangladesh
Haider Mahmood
5 Department of Finance, College of Business Administration, Prince Sattam Bin Abdulaziz University, 173, Alkharj, 11942 Saudi Arabia
Ijaz Younis
Associated data.
Data sources and relevant links are provided in the paper to access data.
Climate change is a long-lasting change in the weather arrays across tropics to polls. It is a global threat that has embarked on to put stress on various sectors. This study is aimed to conceptually engineer how climate variability is deteriorating the sustainability of diverse sectors worldwide. Specifically, the agricultural sector’s vulnerability is a globally concerning scenario, as sufficient production and food supplies are threatened due to irreversible weather fluctuations. In turn, it is challenging the global feeding patterns, particularly in countries with agriculture as an integral part of their economy and total productivity. Climate change has also put the integrity and survival of many species at stake due to shifts in optimum temperature ranges, thereby accelerating biodiversity loss by progressively changing the ecosystem structures. Climate variations increase the likelihood of particular food and waterborne and vector-borne diseases, and a recent example is a coronavirus pandemic. Climate change also accelerates the enigma of antimicrobial resistance, another threat to human health due to the increasing incidence of resistant pathogenic infections. Besides, the global tourism industry is devastated as climate change impacts unfavorable tourism spots. The methodology investigates hypothetical scenarios of climate variability and attempts to describe the quality of evidence to facilitate readers’ careful, critical engagement. Secondary data is used to identify sustainability issues such as environmental, social, and economic viability. To better understand the problem, gathered the information in this report from various media outlets, research agencies, policy papers, newspapers, and other sources. This review is a sectorial assessment of climate change mitigation and adaptation approaches worldwide in the aforementioned sectors and the associated economic costs. According to the findings, government involvement is necessary for the country’s long-term development through strict accountability of resources and regulations implemented in the past to generate cutting-edge climate policy. Therefore, mitigating the impacts of climate change must be of the utmost importance, and hence, this global threat requires global commitment to address its dreadful implications to ensure global sustenance.
Introduction
Worldwide observed and anticipated climatic changes for the twenty-first century and global warming are significant global changes that have been encountered during the past 65 years. Climate change (CC) is an inter-governmental complex challenge globally with its influence over various components of the ecological, environmental, socio-political, and socio-economic disciplines (Adger et al. 2005 ; Leal Filho et al. 2021 ; Feliciano et al. 2022 ). Climate change involves heightened temperatures across numerous worlds (Battisti and Naylor 2009 ; Schuurmans 2021 ; Weisheimer and Palmer 2005 ; Yadav et al. 2015 ). With the onset of the industrial revolution, the problem of earth climate was amplified manifold (Leppänen et al. 2014 ). It is reported that the immediate attention and due steps might increase the probability of overcoming its devastating impacts. It is not plausible to interpret the exact consequences of climate change (CC) on a sectoral basis (Izaguirre et al. 2021 ; Jurgilevich et al. 2017 ), which is evident by the emerging level of recognition plus the inclusion of climatic uncertainties at both local and national level of policymaking (Ayers et al. 2014 ).
Climate change is characterized based on the comprehensive long-haul temperature and precipitation trends and other components such as pressure and humidity level in the surrounding environment. Besides, the irregular weather patterns, retreating of global ice sheets, and the corresponding elevated sea level rise are among the most renowned international and domestic effects of climate change (Lipczynska-Kochany 2018 ; Michel et al. 2021 ; Murshed and Dao 2020 ). Before the industrial revolution, natural sources, including volcanoes, forest fires, and seismic activities, were regarded as the distinct sources of greenhouse gases (GHGs) such as CO 2 , CH 4 , N 2 O, and H 2 O into the atmosphere (Murshed et al. 2020 ; Hussain et al. 2020 ; Sovacool et al. 2021 ; Usman and Balsalobre-Lorente 2022 ; Murshed 2022 ). United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) struck a major agreement to tackle climate change and accelerate and intensify the actions and investments required for a sustainable low-carbon future at Conference of the Parties (COP-21) in Paris on December 12, 2015. The Paris Agreement expands on the Convention by bringing all nations together for the first time in a single cause to undertake ambitious measures to prevent climate change and adapt to its impacts, with increased funding to assist developing countries in doing so. As so, it marks a turning point in the global climate fight. The core goal of the Paris Agreement is to improve the global response to the threat of climate change by keeping the global temperature rise this century well below 2 °C over pre-industrial levels and to pursue efforts to limit the temperature increase to 1.5° C (Sharma et al. 2020 ; Sharif et al. 2020 ; Chien et al. 2021 .
Furthermore, the agreement aspires to strengthen nations’ ability to deal with the effects of climate change and align financing flows with low GHG emissions and climate-resilient paths (Shahbaz et al. 2019 ; Anwar et al. 2021 ; Usman et al. 2022a ). To achieve these lofty goals, adequate financial resources must be mobilized and provided, as well as a new technology framework and expanded capacity building, allowing developing countries and the most vulnerable countries to act under their respective national objectives. The agreement also establishes a more transparent action and support mechanism. All Parties are required by the Paris Agreement to do their best through “nationally determined contributions” (NDCs) and to strengthen these efforts in the coming years (Balsalobre-Lorente et al. 2020 ). It includes obligations that all Parties regularly report on their emissions and implementation activities. A global stock-take will be conducted every five years to review collective progress toward the agreement’s goal and inform the Parties’ future individual actions. The Paris Agreement became available for signature on April 22, 2016, Earth Day, at the United Nations Headquarters in New York. On November 4, 2016, it went into effect 30 days after the so-called double threshold was met (ratification by 55 nations accounting for at least 55% of world emissions). More countries have ratified and continue to ratify the agreement since then, bringing 125 Parties in early 2017. To fully operationalize the Paris Agreement, a work program was initiated in Paris to define mechanisms, processes, and recommendations on a wide range of concerns (Murshed et al. 2021 ). Since 2016, Parties have collaborated in subsidiary bodies (APA, SBSTA, and SBI) and numerous formed entities. The Conference of the Parties functioning as the meeting of the Parties to the Paris Agreement (CMA) convened for the first time in November 2016 in Marrakesh in conjunction with COP22 and made its first two resolutions. The work plan is scheduled to be finished by 2018. Some mitigation and adaptation strategies to reduce the emission in the prospective of Paris agreement are following firstly, a long-term goal of keeping the increase in global average temperature to well below 2 °C above pre-industrial levels, secondly, to aim to limit the rise to 1.5 °C, since this would significantly reduce risks and the impacts of climate change, thirdly, on the need for global emissions to peak as soon as possible, recognizing that this will take longer for developing countries, lastly, to undertake rapid reductions after that under the best available science, to achieve a balance between emissions and removals in the second half of the century. On the other side, some adaptation strategies are; strengthening societies’ ability to deal with the effects of climate change and to continue & expand international assistance for developing nations’ adaptation.
However, anthropogenic activities are currently regarded as most accountable for CC (Murshed et al. 2022 ). Apart from the industrial revolution, other anthropogenic activities include excessive agricultural operations, which further involve the high use of fuel-based mechanization, burning of agricultural residues, burning fossil fuels, deforestation, national and domestic transportation sectors, etc. (Huang et al. 2016 ). Consequently, these anthropogenic activities lead to climatic catastrophes, damaging local and global infrastructure, human health, and total productivity. Energy consumption has mounted GHGs levels concerning warming temperatures as most of the energy production in developing countries comes from fossil fuels (Balsalobre-Lorente et al. 2022 ; Usman et al. 2022b ; Abbass et al. 2021a ; Ishikawa-Ishiwata and Furuya 2022 ).
This review aims to highlight the effects of climate change in a socio-scientific aspect by analyzing the existing literature on various sectorial pieces of evidence globally that influence the environment. Although this review provides a thorough examination of climate change and its severe affected sectors that pose a grave danger for global agriculture, biodiversity, health, economy, forestry, and tourism, and to purpose some practical prophylactic measures and mitigation strategies to be adapted as sound substitutes to survive from climate change (CC) impacts. The societal implications of irregular weather patterns and other effects of climate changes are discussed in detail. Some numerous sustainable mitigation measures and adaptation practices and techniques at the global level are discussed in this review with an in-depth focus on its economic, social, and environmental aspects. Methods of data collection section are included in the supplementary information.
Review methodology
Related study and its objectives.
Today, we live an ordinary life in the beautiful digital, globalized world where climate change has a decisive role. What happens in one country has a massive influence on geographically far apart countries, which points to the current crisis known as COVID-19 (Sarkar et al. 2021 ). The most dangerous disease like COVID-19 has affected the world’s climate changes and economic conditions (Abbass et al. 2022 ; Pirasteh-Anosheh et al. 2021 ). The purpose of the present study is to review the status of research on the subject, which is based on “Global Climate Change Impacts, adaptation, and sustainable mitigation measures” by systematically reviewing past published and unpublished research work. Furthermore, the current study seeks to comment on research on the same topic and suggest future research on the same topic. Specifically, the present study aims: The first one is, organize publications to make them easy and quick to find. Secondly, to explore issues in this area, propose an outline of research for future work. The third aim of the study is to synthesize the previous literature on climate change, various sectors, and their mitigation measurement. Lastly , classify the articles according to the different methods and procedures that have been adopted.
Review methodology for reviewers
This review-based article followed systematic literature review techniques that have proved the literature review as a rigorous framework (Benita 2021 ; Tranfield et al. 2003 ). Moreover, we illustrate in Fig. 1 the search method that we have started for this research. First, finalized the research theme to search literature (Cooper et al. 2018 ). Second, used numerous research databases to search related articles and download from the database (Web of Science, Google Scholar, Scopus Index Journals, Emerald, Elsevier Science Direct, Springer, and Sciverse). We focused on various articles, with research articles, feedback pieces, short notes, debates, and review articles published in scholarly journals. Reports used to search for multiple keywords such as “Climate Change,” “Mitigation and Adaptation,” “Department of Agriculture and Human Health,” “Department of Biodiversity and Forestry,” etc.; in summary, keyword list and full text have been made. Initially, the search for keywords yielded a large amount of literature.

Methodology search for finalized articles for investigations.
Source : constructed by authors
Since 2020, it has been impossible to review all the articles found; some restrictions have been set for the literature exhibition. The study searched 95 articles on a different database mentioned above based on the nature of the study. It excluded 40 irrelevant papers due to copied from a previous search after readings tiles, abstract and full pieces. The criteria for inclusion were: (i) articles focused on “Global Climate Change Impacts, adaptation, and sustainable mitigation measures,” and (ii) the search key terms related to study requirements. The complete procedure yielded 55 articles for our study. We repeat our search on the “Web of Science and Google Scholars” database to enhance the search results and check the referenced articles.
In this study, 55 articles are reviewed systematically and analyzed for research topics and other aspects, such as the methods, contexts, and theories used in these studies. Furthermore, this study analyzes closely related areas to provide unique research opportunities in the future. The study also discussed future direction opportunities and research questions by understanding the research findings climate changes and other affected sectors. The reviewed paper framework analysis process is outlined in Fig. 2 .

Framework of the analysis Process.
Natural disasters and climate change’s socio-economic consequences
Natural and environmental disasters can be highly variable from year to year; some years pass with very few deaths before a significant disaster event claims many lives (Symanski et al. 2021 ). Approximately 60,000 people globally died from natural disasters each year on average over the past decade (Ritchie and Roser 2014 ; Wiranata and Simbolon 2021 ). So, according to the report, around 0.1% of global deaths. Annual variability in the number and share of deaths from natural disasters in recent decades are shown in Fig. 3 . The number of fatalities can be meager—sometimes less than 10,000, and as few as 0.01% of all deaths. But shock events have a devastating impact: the 1983–1985 famine and drought in Ethiopia; the 2004 Indian Ocean earthquake and tsunami; Cyclone Nargis, which struck Myanmar in 2008; and the 2010 Port-au-Prince earthquake in Haiti and now recent example is COVID-19 pandemic (Erman et al. 2021 ). These events pushed global disaster deaths to over 200,000—more than 0.4% of deaths in these years. Low-frequency, high-impact events such as earthquakes and tsunamis are not preventable, but such high losses of human life are. Historical evidence shows that earlier disaster detection, more robust infrastructure, emergency preparedness, and response programmers have substantially reduced disaster deaths worldwide. Low-income is also the most vulnerable to disasters; improving living conditions, facilities, and response services in these areas would be critical in reducing natural disaster deaths in the coming decades.

Global deaths from natural disasters, 1978 to 2020.
Source EMDAT ( 2020 )
The interior regions of the continent are likely to be impacted by rising temperatures (Dimri et al. 2018 ; Goes et al. 2020 ; Mannig et al. 2018 ; Schuurmans 2021 ). Weather patterns change due to the shortage of natural resources (water), increase in glacier melting, and rising mercury are likely to cause extinction to many planted species (Gampe et al. 2016 ; Mihiretu et al. 2021 ; Shaffril et al. 2018 ).On the other hand, the coastal ecosystem is on the verge of devastation (Perera et al. 2018 ; Phillips 2018 ). The temperature rises, insect disease outbreaks, health-related problems, and seasonal and lifestyle changes are persistent, with a strong probability of these patterns continuing in the future (Abbass et al. 2021c ; Hussain et al. 2018 ). At the global level, a shortage of good infrastructure and insufficient adaptive capacity are hammering the most (IPCC 2013 ). In addition to the above concerns, a lack of environmental education and knowledge, outdated consumer behavior, a scarcity of incentives, a lack of legislation, and the government’s lack of commitment to climate change contribute to the general public’s concerns. By 2050, a 2 to 3% rise in mercury and a drastic shift in rainfall patterns may have serious consequences (Huang et al. 2022 ; Gorst et al. 2018 ). Natural and environmental calamities caused huge losses globally, such as decreased agriculture outputs, rehabilitation of the system, and rebuilding necessary technologies (Ali and Erenstein 2017 ; Ramankutty et al. 2018 ; Yu et al. 2021 ) (Table (Table1). 1 ). Furthermore, in the last 3 or 4 years, the world has been plagued by smog-related eye and skin diseases, as well as a rise in road accidents due to poor visibility.
Main natural danger statistics for 1985–2020 at the global level
Source: EM-DAT ( 2020 )
Climate change and agriculture
Global agriculture is the ultimate sector responsible for 30–40% of all greenhouse emissions, which makes it a leading industry predominantly contributing to climate warming and significantly impacted by it (Grieg; Mishra et al. 2021 ; Ortiz et al. 2021 ; Thornton and Lipper 2014 ). Numerous agro-environmental and climatic factors that have a dominant influence on agriculture productivity (Pautasso et al. 2012 ) are significantly impacted in response to precipitation extremes including floods, forest fires, and droughts (Huang 2004 ). Besides, the immense dependency on exhaustible resources also fuels the fire and leads global agriculture to become prone to devastation. Godfray et al. ( 2010 ) mentioned that decline in agriculture challenges the farmer’s quality of life and thus a significant factor to poverty as the food and water supplies are critically impacted by CC (Ortiz et al. 2021 ; Rosenzweig et al. 2014 ). As an essential part of the economic systems, especially in developing countries, agricultural systems affect the overall economy and potentially the well-being of households (Schlenker and Roberts 2009 ). According to the report published by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), atmospheric concentrations of greenhouse gases, i.e., CH 4, CO 2 , and N 2 O, are increased in the air to extraordinary levels over the last few centuries (Usman and Makhdum 2021 ; Stocker et al. 2013 ). Climate change is the composite outcome of two different factors. The first is the natural causes, and the second is the anthropogenic actions (Karami 2012 ). It is also forecasted that the world may experience a typical rise in temperature stretching from 1 to 3.7 °C at the end of this century (Pachauri et al. 2014 ). The world’s crop production is also highly vulnerable to these global temperature-changing trends as raised temperatures will pose severe negative impacts on crop growth (Reidsma et al. 2009 ). Some of the recent modeling about the fate of global agriculture is briefly described below.
Decline in cereal productivity
Crop productivity will also be affected dramatically in the next few decades due to variations in integral abiotic factors such as temperature, solar radiation, precipitation, and CO 2 . These all factors are included in various regulatory instruments like progress and growth, weather-tempted changes, pest invasions (Cammell and Knight 1992 ), accompanying disease snags (Fand et al. 2012 ), water supplies (Panda et al. 2003 ), high prices of agro-products in world’s agriculture industry, and preeminent quantity of fertilizer consumption. Lobell and field ( 2007 ) claimed that from 1962 to 2002, wheat crop output had condensed significantly due to rising temperatures. Therefore, during 1980–2011, the common wheat productivity trends endorsed extreme temperature events confirmed by Gourdji et al. ( 2013 ) around South Asia, South America, and Central Asia. Various other studies (Asseng, Cao, Zhang, and Ludwig 2009 ; Asseng et al. 2013 ; García et al. 2015 ; Ortiz et al. 2021 ) also proved that wheat output is negatively affected by the rising temperatures and also caused adverse effects on biomass productivity (Calderini et al. 1999 ; Sadras and Slafer 2012 ). Hereafter, the rice crop is also influenced by the high temperatures at night. These difficulties will worsen because the temperature will be rising further in the future owing to CC (Tebaldi et al. 2006 ). Another research conducted in China revealed that a 4.6% of rice production per 1 °C has happened connected with the advancement in night temperatures (Tao et al. 2006 ). Moreover, the average night temperature growth also affected rice indicia cultivar’s output pragmatically during 25 years in the Philippines (Peng et al. 2004 ). It is anticipated that the increase in world average temperature will also cause a substantial reduction in yield (Hatfield et al. 2011 ; Lobell and Gourdji 2012 ). In the southern hemisphere, Parry et al. ( 2007 ) noted a rise of 1–4 °C in average daily temperatures at the end of spring season unti the middle of summers, and this raised temperature reduced crop output by cutting down the time length for phenophases eventually reduce the yield (Hatfield and Prueger 2015 ; R. Ortiz 2008 ). Also, world climate models have recommended that humid and subtropical regions expect to be plentiful prey to the upcoming heat strokes (Battisti and Naylor 2009 ). Grain production is the amalgamation of two constituents: the average weight and the grain output/m 2 , however, in crop production. Crop output is mainly accredited to the grain quantity (Araus et al. 2008 ; Gambín and Borrás 2010 ). In the times of grain set, yield resources are mainly strewn between hitherto defined components, i.e., grain usual weight and grain output, which presents a trade-off between them (Gambín and Borrás 2010 ) beside disparities in per grain integration (B. L. Gambín et al. 2006 ). In addition to this, the maize crop is also susceptible to raised temperatures, principally in the flowering stage (Edreira and Otegui 2013 ). In reality, the lower grain number is associated with insufficient acclimatization due to intense photosynthesis and higher respiration and the high-temperature effect on the reproduction phenomena (Edreira and Otegui 2013 ). During the flowering phase, maize visible to heat (30–36 °C) seemed less anthesis-silking intermissions (Edreira et al. 2011 ). Another research by Dupuis and Dumas ( 1990 ) proved that a drop in spikelet when directly visible to high temperatures above 35 °C in vitro pollination. Abnormalities in kernel number claimed by Vega et al. ( 2001 ) is related to conceded plant development during a flowering phase that is linked with the active ear growth phase and categorized as a critical phase for approximation of kernel number during silking (Otegui and Bonhomme 1998 ).
The retort of rice output to high temperature presents disparities in flowering patterns, and seed set lessens and lessens grain weight (Qasim et al. 2020 ; Qasim, Hammad, Maqsood, Tariq, & Chawla). During the daytime, heat directly impacts flowers which lessens the thesis period and quickens the earlier peak flowering (Tao et al. 2006 ). Antagonistic effect of higher daytime temperature d on pollen sprouting proposed seed set decay, whereas, seed set was lengthily reduced than could be explicated by pollen growing at high temperatures 40◦C (Matsui et al. 2001 ).
The decline in wheat output is linked with higher temperatures, confirmed in numerous studies (Semenov 2009 ; Stone and Nicolas 1994 ). High temperatures fast-track the arrangements of plant expansion (Blum et al. 2001 ), diminution photosynthetic process (Salvucci and Crafts‐Brandner 2004 ), and also considerably affect the reproductive operations (Farooq et al. 2011 ).
The destructive impacts of CC induced weather extremes to deteriorate the integrity of crops (Chaudhary et al. 2011 ), e.g., Spartan cold and extreme fog cause falling and discoloration of betel leaves (Rosenzweig et al. 2001 ), giving them a somehow reddish appearance, squeezing of lemon leaves (Pautasso et al. 2012 ), as well as root rot of pineapple, have reported (Vedwan and Rhoades 2001 ). Henceforth, in tackling the disruptive effects of CC, several short-term and long-term management approaches are the crucial need of time (Fig. 4 ). Moreover, various studies (Chaudhary et al. 2011 ; Patz et al. 2005 ; Pautasso et al. 2012 ) have demonstrated adapting trends such as ameliorating crop diversity can yield better adaptability towards CC.

Schematic description of potential impacts of climate change on the agriculture sector and the appropriate mitigation and adaptation measures to overcome its impact.
Climate change impacts on biodiversity
Global biodiversity is among the severe victims of CC because it is the fastest emerging cause of species loss. Studies demonstrated that the massive scale species dynamics are considerably associated with diverse climatic events (Abraham and Chain 1988 ; Manes et al. 2021 ; A. M. D. Ortiz et al. 2021 ). Both the pace and magnitude of CC are altering the compatible habitat ranges for living entities of marine, freshwater, and terrestrial regions. Alterations in general climate regimes influence the integrity of ecosystems in numerous ways, such as variation in the relative abundance of species, range shifts, changes in activity timing, and microhabitat use (Bates et al. 2014 ). The geographic distribution of any species often depends upon its ability to tolerate environmental stresses, biological interactions, and dispersal constraints. Hence, instead of the CC, the local species must only accept, adapt, move, or face extinction (Berg et al. 2010 ). So, the best performer species have a better survival capacity for adjusting to new ecosystems or a decreased perseverance to survive where they are already situated (Bates et al. 2014 ). An important aspect here is the inadequate habitat connectivity and access to microclimates, also crucial in raising the exposure to climate warming and extreme heatwave episodes. For example, the carbon sequestration rates are undergoing fluctuations due to climate-driven expansion in the range of global mangroves (Cavanaugh et al. 2014 ).
Similarly, the loss of kelp-forest ecosystems in various regions and its occupancy by the seaweed turfs has set the track for elevated herbivory by the high influx of tropical fish populations. Not only this, the increased water temperatures have exacerbated the conditions far away from the physiological tolerance level of the kelp communities (Vergés et al. 2016 ; Wernberg et al. 2016 ). Another pertinent danger is the devastation of keystone species, which even has more pervasive effects on the entire communities in that habitat (Zarnetske et al. 2012 ). It is particularly important as CC does not specify specific populations or communities. Eventually, this CC-induced redistribution of species may deteriorate carbon storage and the net ecosystem productivity (Weed et al. 2013 ). Among the typical disruptions, the prominent ones include impacts on marine and terrestrial productivity, marine community assembly, and the extended invasion of toxic cyanobacteria bloom (Fossheim et al. 2015 ).
The CC-impacted species extinction is widely reported in the literature (Beesley et al. 2019 ; Urban 2015 ), and the predictions of demise until the twenty-first century are dreadful (Abbass et al. 2019 ; Pereira et al. 2013 ). In a few cases, northward shifting of species may not be formidable as it allows mountain-dwelling species to find optimum climates. However, the migrant species may be trapped in isolated and incompatible habitats due to losing topography and range (Dullinger et al. 2012 ). For example, a study indicated that the American pika has been extirpated or intensely diminished in some regions, primarily attributed to the CC-impacted extinction or at least local extirpation (Stewart et al. 2015 ). Besides, the anticipation of persistent responses to the impacts of CC often requires data records of several decades to rigorously analyze the critical pre and post CC patterns at species and ecosystem levels (Manes et al. 2021 ; Testa et al. 2018 ).
Nonetheless, the availability of such long-term data records is rare; hence, attempts are needed to focus on these profound aspects. Biodiversity is also vulnerable to the other associated impacts of CC, such as rising temperatures, droughts, and certain invasive pest species. For instance, a study revealed the changes in the composition of plankton communities attributed to rising temperatures. Henceforth, alterations in such aquatic producer communities, i.e., diatoms and calcareous plants, can ultimately lead to variation in the recycling of biological carbon. Moreover, such changes are characterized as a potential contributor to CO 2 differences between the Pleistocene glacial and interglacial periods (Kohfeld et al. 2005 ).
Climate change implications on human health
It is an understood corporality that human health is a significant victim of CC (Costello et al. 2009 ). According to the WHO, CC might be responsible for 250,000 additional deaths per year during 2030–2050 (Watts et al. 2015 ). These deaths are attributed to extreme weather-induced mortality and morbidity and the global expansion of vector-borne diseases (Lemery et al. 2021; Yang and Usman 2021 ; Meierrieks 2021 ; UNEP 2017 ). Here, some of the emerging health issues pertinent to this global problem are briefly described.
Climate change and antimicrobial resistance with corresponding economic costs
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) is an up-surging complex global health challenge (Garner et al. 2019 ; Lemery et al. 2021 ). Health professionals across the globe are extremely worried due to this phenomenon that has critical potential to reverse almost all the progress that has been achieved so far in the health discipline (Gosling and Arnell 2016 ). A massive amount of antibiotics is produced by many pharmaceutical industries worldwide, and the pathogenic microorganisms are gradually developing resistance to them, which can be comprehended how strongly this aspect can shake the foundations of national and global economies (UNEP 2017 ). This statement is supported by the fact that AMR is not developing in a particular region or country. Instead, it is flourishing in every continent of the world (WHO 2018 ). This plague is heavily pushing humanity to the post-antibiotic era, in which currently antibiotic-susceptible pathogens will once again lead to certain endemics and pandemics after being resistant(WHO 2018 ). Undesirably, if this statement would become a factuality, there might emerge certain risks in undertaking sophisticated interventions such as chemotherapy, joint replacement cases, and organ transplantation (Su et al. 2018 ). Presently, the amplification of drug resistance cases has made common illnesses like pneumonia, post-surgical infections, HIV/AIDS, tuberculosis, malaria, etc., too difficult and costly to be treated or cure well (WHO 2018 ). From a simple example, it can be assumed how easily antibiotic-resistant strains can be transmitted from one person to another and ultimately travel across the boundaries (Berendonk et al. 2015 ). Talking about the second- and third-generation classes of antibiotics, e.g., most renowned generations of cephalosporin antibiotics that are more expensive, broad-spectrum, more toxic, and usually require more extended periods whenever prescribed to patients (Lemery et al. 2021 ; Pärnänen et al. 2019 ). This scenario has also revealed that the abundance of resistant strains of pathogens was also higher in the Southern part (WHO 2018 ). As southern parts are generally warmer than their counterparts, it is evident from this example how CC-induced global warming can augment the spread of antibiotic-resistant strains within the biosphere, eventually putting additional economic burden in the face of developing new and costlier antibiotics. The ARG exchange to susceptible bacteria through one of the potential mechanisms, transformation, transduction, and conjugation; Selection pressure can be caused by certain antibiotics, metals or pesticides, etc., as shown in Fig. 5 .

A typical interaction between the susceptible and resistant strains.
Source: Elsayed et al. ( 2021 ); Karkman et al. ( 2018 )
Certain studies highlighted that conventional urban wastewater treatment plants are typical hotspots where most bacterial strains exchange genetic material through horizontal gene transfer (Fig. 5 ). Although at present, the extent of risks associated with the antibiotic resistance found in wastewater is complicated; environmental scientists and engineers have particular concerns about the potential impacts of these antibiotic resistance genes on human health (Ashbolt 2015 ). At most undesirable and worst case, these antibiotic-resistant genes containing bacteria can make their way to enter into the environment (Pruden et al. 2013 ), irrigation water used for crops and public water supplies and ultimately become a part of food chains and food webs (Ma et al. 2019 ; D. Wu et al. 2019 ). This problem has been reported manifold in several countries (Hendriksen et al. 2019 ), where wastewater as a means of irrigated water is quite common.
Climate change and vector borne-diseases
Temperature is a fundamental factor for the sustenance of living entities regardless of an ecosystem. So, a specific living being, especially a pathogen, requires a sophisticated temperature range to exist on earth. The second essential component of CC is precipitation, which also impacts numerous infectious agents’ transport and dissemination patterns. Global rising temperature is a significant cause of many species extinction. On the one hand, this changing environmental temperature may be causing species extinction, and on the other, this warming temperature might favor the thriving of some new organisms. Here, it was evident that some pathogens may also upraise once non-evident or reported (Patz et al. 2000 ). This concept can be exemplified through certain pathogenic strains of microorganisms that how the likelihood of various diseases increases in response to climate warming-induced environmental changes (Table (Table2 2 ).
Examples of how various environmental changes affect various infectious diseases in humans
Source: Aron and Patz ( 2001 )
A recent example is an outburst of coronavirus (COVID-19) in the Republic of China, causing pneumonia and severe acute respiratory complications (Cui et al. 2021 ; Song et al. 2021 ). The large family of viruses is harbored in numerous animals, bats, and snakes in particular (livescience.com) with the subsequent transfer into human beings. Hence, it is worth noting that the thriving of numerous vectors involved in spreading various diseases is influenced by Climate change (Ogden 2018 ; Santos et al. 2021 ).
Psychological impacts of climate change
Climate change (CC) is responsible for the rapid dissemination and exaggeration of certain epidemics and pandemics. In addition to the vast apparent impacts of climate change on health, forestry, agriculture, etc., it may also have psychological implications on vulnerable societies. It can be exemplified through the recent outburst of (COVID-19) in various countries around the world (Pal 2021 ). Besides, the victims of this viral infection have made healthy beings scarier and terrified. In the wake of such epidemics, people with common colds or fever are also frightened and must pass specific regulatory protocols. Living in such situations continuously terrifies the public and makes the stress familiar, which eventually makes them psychologically weak (npr.org).
CC boosts the extent of anxiety, distress, and other issues in public, pushing them to develop various mental-related problems. Besides, frequent exposure to extreme climatic catastrophes such as geological disasters also imprints post-traumatic disorder, and their ubiquitous occurrence paves the way to developing chronic psychological dysfunction. Moreover, repetitive listening from media also causes an increase in the person’s stress level (Association 2020 ). Similarly, communities living in flood-prone areas constantly live in extreme fear of drowning and die by floods. In addition to human lives, the flood-induced destruction of physical infrastructure is a specific reason for putting pressure on these communities (Ogden 2018 ). For instance, Ogden ( 2018 ) comprehensively denoted that Katrina’s Hurricane augmented the mental health issues in the victim communities.
Climate change impacts on the forestry sector
Forests are the global regulators of the world’s climate (FAO 2018 ) and have an indispensable role in regulating global carbon and nitrogen cycles (Rehman et al. 2021 ; Reichstein and Carvalhais 2019 ). Hence, disturbances in forest ecology affect the micro and macro-climates (Ellison et al. 2017 ). Climate warming, in return, has profound impacts on the growth and productivity of transboundary forests by influencing the temperature and precipitation patterns, etc. As CC induces specific changes in the typical structure and functions of ecosystems (Zhang et al. 2017 ) as well impacts forest health, climate change also has several devastating consequences such as forest fires, droughts, pest outbreaks (EPA 2018 ), and last but not the least is the livelihoods of forest-dependent communities. The rising frequency and intensity of another CC product, i.e., droughts, pose plenty of challenges to the well-being of global forests (Diffenbaugh et al. 2017 ), which is further projected to increase soon (Hartmann et al. 2018 ; Lehner et al. 2017 ; Rehman et al. 2021 ). Hence, CC induces storms, with more significant impacts also put extra pressure on the survival of the global forests (Martínez-Alvarado et al. 2018 ), significantly since their influences are augmented during higher winter precipitations with corresponding wetter soils causing weak root anchorage of trees (Brázdil et al. 2018 ). Surging temperature regimes causes alterations in usual precipitation patterns, which is a significant hurdle for the survival of temperate forests (Allen et al. 2010 ; Flannigan et al. 2013 ), letting them encounter severe stress and disturbances which adversely affects the local tree species (Hubbart et al. 2016 ; Millar and Stephenson 2015 ; Rehman et al. 2021 ).
Climate change impacts on forest-dependent communities
Forests are the fundamental livelihood resource for about 1.6 billion people worldwide; out of them, 350 million are distinguished with relatively higher reliance (Bank 2008 ). Agro-forestry-dependent communities comprise 1.2 billion, and 60 million indigenous people solely rely on forests and their products to sustain their lives (Sunderlin et al. 2005 ). For example, in the entire African continent, more than 2/3rd of inhabitants depend on forest resources and woodlands for their alimonies, e.g., food, fuelwood and grazing (Wasiq and Ahmad 2004 ). The livings of these people are more intensely affected by the climatic disruptions making their lives harder (Brown et al. 2014 ). On the one hand, forest communities are incredibly vulnerable to CC due to their livelihoods, cultural and spiritual ties as well as socio-ecological connections, and on the other, they are not familiar with the term “climate change.” (Rahman and Alam 2016 ). Among the destructive impacts of temperature and rainfall, disruption of the agroforestry crops with resultant downscale growth and yield (Macchi et al. 2008 ). Cruz ( 2015 ) ascribed that forest-dependent smallholder farmers in the Philippines face the enigma of delayed fruiting, more severe damages by insect and pest incidences due to unfavorable temperature regimes, and changed rainfall patterns.
Among these series of challenges to forest communities, their well-being is also distinctly vulnerable to CC. Though the detailed climate change impacts on human health have been comprehensively mentioned in the previous section, some studies have listed a few more devastating effects on the prosperity of forest-dependent communities. For instance, the Himalayan people have been experiencing frequent skin-borne diseases such as malaria and other skin diseases due to increasing mosquitoes, wild boar as well, and new wasps species, particularly in higher altitudes that were almost non-existent before last 5–10 years (Xu et al. 2008 ). Similarly, people living at high altitudes in Bangladesh have experienced frequent mosquito-borne calamities (Fardous; Sharma 2012 ). In addition, the pace of other waterborne diseases such as infectious diarrhea, cholera, pathogenic induced abdominal complications and dengue has also been boosted in other distinguished regions of Bangladesh (Cell 2009 ; Gunter et al. 2008 ).
Pest outbreak
Upscaling hotter climate may positively affect the mobile organisms with shorter generation times because they can scurry from harsh conditions than the immobile species (Fettig et al. 2013 ; Schoene and Bernier 2012 ) and are also relatively more capable of adapting to new environments (Jactel et al. 2019 ). It reveals that insects adapt quickly to global warming due to their mobility advantages. Due to past outbreaks, the trees (forests) are relatively more susceptible victims (Kurz et al. 2008 ). Before CC, the influence of factors mentioned earlier, i.e., droughts and storms, was existent and made the forests susceptible to insect pest interventions; however, the global forests remain steadfast, assiduous, and green (Jactel et al. 2019 ). The typical reasons could be the insect herbivores were regulated by several tree defenses and pressures of predation (Wilkinson and Sherratt 2016 ). As climate greatly influences these phenomena, the global forests cannot be so sedulous against such challenges (Jactel et al. 2019 ). Table Table3 3 demonstrates some of the particular considerations with practical examples that are essential while mitigating the impacts of CC in the forestry sector.
Essential considerations while mitigating the climate change impacts on the forestry sector
Source : Fischer ( 2019 )
Climate change impacts on tourism
Tourism is a commercial activity that has roots in multi-dimensions and an efficient tool with adequate job generation potential, revenue creation, earning of spectacular foreign exchange, enhancement in cross-cultural promulgation and cooperation, a business tool for entrepreneurs and eventually for the country’s national development (Arshad et al. 2018 ; Scott 2021 ). Among a plethora of other disciplines, the tourism industry is also a distinct victim of climate warming (Gössling et al. 2012 ; Hall et al. 2015 ) as the climate is among the essential resources that enable tourism in particular regions as most preferred locations. Different places at different times of the year attract tourists both within and across the countries depending upon the feasibility and compatibility of particular weather patterns. Hence, the massive variations in these weather patterns resulting from CC will eventually lead to monumental challenges to the local economy in that specific area’s particular and national economy (Bujosa et al. 2015 ). For instance, the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) report demonstrated that the global tourism industry had faced a considerable decline in the duration of ski season, including the loss of some ski areas and the dramatic shifts in tourist destinations’ climate warming.
Furthermore, different studies (Neuvonen et al. 2015 ; Scott et al. 2004 ) indicated that various currently perfect tourist spots, e.g., coastal areas, splendid islands, and ski resorts, will suffer consequences of CC. It is also worth noting that the quality and potential of administrative management potential to cope with the influence of CC on the tourism industry is of crucial significance, which renders specific strengths of resiliency to numerous destinations to withstand against it (Füssel and Hildén 2014 ). Similarly, in the partial or complete absence of adequate socio-economic and socio-political capital, the high-demanding tourist sites scurry towards the verge of vulnerability. The susceptibility of tourism is based on different components such as the extent of exposure, sensitivity, life-supporting sectors, and capacity assessment factors (Füssel and Hildén 2014 ). It is obvious corporality that sectors such as health, food, ecosystems, human habitat, infrastructure, water availability, and the accessibility of a particular region are prone to CC. Henceforth, the sensitivity of these critical sectors to CC and, in return, the adaptive measures are a hallmark in determining the composite vulnerability of climate warming (Ionescu et al. 2009 ).
Moreover, the dependence on imported food items, poor hygienic conditions, and inadequate health professionals are dominant aspects affecting the local terrestrial and aquatic biodiversity. Meanwhile, the greater dependency on ecosystem services and its products also makes a destination more fragile to become a prey of CC (Rizvi et al. 2015 ). Some significant non-climatic factors are important indicators of a particular ecosystem’s typical health and functioning, e.g., resource richness and abundance portray the picture of ecosystem stability. Similarly, the species abundance is also a productive tool that ensures that the ecosystem has a higher buffering capacity, which is terrific in terms of resiliency (Roscher et al. 2013 ).
Climate change impacts on the economic sector
Climate plays a significant role in overall productivity and economic growth. Due to its increasingly global existence and its effect on economic growth, CC has become one of the major concerns of both local and international environmental policymakers (Ferreira et al. 2020 ; Gleditsch 2021 ; Abbass et al. 2021b ; Lamperti et al. 2021 ). The adverse effects of CC on the overall productivity factor of the agricultural sector are therefore significant for understanding the creation of local adaptation policies and the composition of productive climate policy contracts. Previous studies on CC in the world have already forecasted its effects on the agricultural sector. Researchers have found that global CC will impact the agricultural sector in different world regions. The study of the impacts of CC on various agrarian activities in other demographic areas and the development of relative strategies to respond to effects has become a focal point for researchers (Chandioet al. 2020 ; Gleditsch 2021 ; Mosavi et al. 2020 ).
With the rapid growth of global warming since the 1980s, the temperature has started increasing globally, which resulted in the incredible transformation of rain and evaporation in the countries. The agricultural development of many countries has been reliant, delicate, and susceptible to CC for a long time, and it is on the development of agriculture total factor productivity (ATFP) influence different crops and yields of farmers (Alhassan 2021 ; Wu 2020 ).
Food security and natural disasters are increasing rapidly in the world. Several major climatic/natural disasters have impacted local crop production in the countries concerned. The effects of these natural disasters have been poorly controlled by the development of the economies and populations and may affect human life as well. One example is China, which is among the world’s most affected countries, vulnerable to natural disasters due to its large population, harsh environmental conditions, rapid CC, low environmental stability, and disaster power. According to the January 2016 statistical survey, China experienced an economic loss of 298.3 billion Yuan, and about 137 million Chinese people were severely affected by various natural disasters (Xie et al. 2018 ).
Mitigation and adaptation strategies of climate changes
Adaptation and mitigation are the crucial factors to address the response to CC (Jahanzad et al. 2020 ). Researchers define mitigation on climate changes, and on the other hand, adaptation directly impacts climate changes like floods. To some extent, mitigation reduces or moderates greenhouse gas emission, and it becomes a critical issue both economically and environmentally (Botzen et al. 2021 ; Jahanzad et al. 2020 ; Kongsager 2018 ; Smit et al. 2000 ; Vale et al. 2021 ; Usman et al. 2021 ; Verheyen 2005 ).
Researchers have deep concern about the adaptation and mitigation methodologies in sectoral and geographical contexts. Agriculture, industry, forestry, transport, and land use are the main sectors to adapt and mitigate policies(Kärkkäinen et al. 2020 ; Waheed et al. 2021 ). Adaptation and mitigation require particular concern both at the national and international levels. The world has faced a significant problem of climate change in the last decades, and adaptation to these effects is compulsory for economic and social development. To adapt and mitigate against CC, one should develop policies and strategies at the international level (Hussain et al. 2020 ). Figure 6 depicts the list of current studies on sectoral impacts of CC with adaptation and mitigation measures globally.

Sectoral impacts of climate change with adaptation and mitigation measures.
Conclusion and future perspectives
Specific socio-agricultural, socio-economic, and physical systems are the cornerstone of psychological well-being, and the alteration in these systems by CC will have disastrous impacts. Climate variability, alongside other anthropogenic and natural stressors, influences human and environmental health sustainability. Food security is another concerning scenario that may lead to compromised food quality, higher food prices, and inadequate food distribution systems. Global forests are challenged by different climatic factors such as storms, droughts, flash floods, and intense precipitation. On the other hand, their anthropogenic wiping is aggrandizing their existence. Undoubtedly, the vulnerability scale of the world’s regions differs; however, appropriate mitigation and adaptation measures can aid the decision-making bodies in developing effective policies to tackle its impacts. Presently, modern life on earth has tailored to consistent climatic patterns, and accordingly, adapting to such considerable variations is of paramount importance. Because the faster changes in climate will make it harder to survive and adjust, this globally-raising enigma calls for immediate attention at every scale ranging from elementary community level to international level. Still, much effort, research, and dedication are required, which is the most critical time. Some policy implications can help us to mitigate the consequences of climate change, especially the most affected sectors like the agriculture sector;
Warming might lengthen the season in frost-prone growing regions (temperate and arctic zones), allowing for longer-maturing seasonal cultivars with better yields (Pfadenhauer 2020 ; Bonacci 2019 ). Extending the planting season may allow additional crops each year; when warming leads to frequent warmer months highs over critical thresholds, a split season with a brief summer fallow may be conceivable for short-period crops such as wheat barley, cereals, and many other vegetable crops. The capacity to prolong the planting season in tropical and subtropical places where the harvest season is constrained by precipitation or agriculture farming occurs after the year may be more limited and dependent on how precipitation patterns vary (Wu et al. 2017 ).
The genetic component is comprehensive for many yields, but it is restricted like kiwi fruit for a few. Ali et al. ( 2017 ) investigated how new crops will react to climatic changes (also stated in Mall et al. 2017 ). Hot temperature, drought, insect resistance; salt tolerance; and overall crop production and product quality increases would all be advantageous (Akkari 2016 ). Genetic mapping and engineering can introduce a greater spectrum of features. The adoption of genetically altered cultivars has been slowed, particularly in the early forecasts owing to the complexity in ensuring features are expediently expressed throughout the entire plant, customer concerns, economic profitability, and regulatory impediments (Wirehn 2018 ; Davidson et al. 2016 ).
To get the full benefit of the CO 2 would certainly require additional nitrogen and other fertilizers. Nitrogen not consumed by the plants may be excreted into groundwater, discharged into water surface, or emitted from the land, soil nitrous oxide when large doses of fertilizer are sprayed. Increased nitrogen levels in groundwater sources have been related to human chronic illnesses and impact marine ecosystems. Cultivation, grain drying, and other field activities have all been examined in depth in the studies (Barua et al. 2018 ).
- The technological and socio-economic adaptation
The policy consequence of the causative conclusion is that as a source of alternative energy, biofuel production is one of the routes that explain oil price volatility separate from international macroeconomic factors. Even though biofuel production has just begun in a few sample nations, there is still a tremendous worldwide need for feedstock to satisfy industrial expansion in China and the USA, which explains the food price relationship to the global oil price. Essentially, oil-exporting countries may create incentives in their economies to increase food production. It may accomplish by giving farmers financing, seedlings, fertilizers, and farming equipment. Because of the declining global oil price and, as a result, their earnings from oil export, oil-producing nations may be unable to subsidize food imports even in the near term. As a result, these countries can boost the agricultural value chain for export. It may be accomplished through R&D and adding value to their food products to increase income by correcting exchange rate misalignment and adverse trade terms. These nations may also diversify their economies away from oil, as dependence on oil exports alone is no longer economically viable given the extreme volatility of global oil prices. Finally, resource-rich and oil-exporting countries can convert to non-food renewable energy sources such as solar, hydro, coal, wind, wave, and tidal energy. By doing so, both world food and oil supplies would be maintained rather than harmed.
IRENA’s modeling work shows that, if a comprehensive policy framework is in place, efforts toward decarbonizing the energy future will benefit economic activity, jobs (outweighing losses in the fossil fuel industry), and welfare. Countries with weak domestic supply chains and a large reliance on fossil fuel income, in particular, must undertake structural reforms to capitalize on the opportunities inherent in the energy transition. Governments continue to give major policy assistance to extract fossil fuels, including tax incentives, financing, direct infrastructure expenditures, exemptions from environmental regulations, and other measures. The majority of major oil and gas producing countries intend to increase output. Some countries intend to cut coal output, while others plan to maintain or expand it. While some nations are beginning to explore and execute policies aimed at a just and equitable transition away from fossil fuel production, these efforts have yet to impact major producing countries’ plans and goals. Verifiable and comparable data on fossil fuel output and assistance from governments and industries are critical to closing the production gap. Governments could increase openness by declaring their production intentions in their climate obligations under the Paris Agreement.
It is firmly believed that achieving the Paris Agreement commitments is doubtlful without undergoing renewable energy transition across the globe (Murshed 2020 ; Zhao et al. 2022 ). Policy instruments play the most important role in determining the degree of investment in renewable energy technology. This study examines the efficacy of various policy strategies in the renewable energy industry of multiple nations. Although its impact is more visible in established renewable energy markets, a renewable portfolio standard is also a useful policy instrument. The cost of producing renewable energy is still greater than other traditional energy sources. Furthermore, government incentives in the R&D sector can foster innovation in this field, resulting in cost reductions in the renewable energy industry. These nations may export their technologies and share their policy experiences by forming networks among their renewable energy-focused organizations. All policy measures aim to reduce production costs while increasing the proportion of renewables to a country’s energy system. Meanwhile, long-term contracts with renewable energy providers, government commitment and control, and the establishment of long-term goals can assist developing nations in deploying renewable energy technology in their energy sector.
Author contribution
KA: Writing the original manuscript, data collection, data analysis, Study design, Formal analysis, Visualization, Revised draft, Writing-review, and editing. MZQ: Writing the original manuscript, data collection, data analysis, Writing-review, and editing. HS: Contribution to the contextualization of the theme, Conceptualization, Validation, Supervision, literature review, Revised drapt, and writing review and editing. MM: Writing review and editing, compiling the literature review, language editing. HM: Writing review and editing, compiling the literature review, language editing. IY: Contribution to the contextualization of the theme, literature review, and writing review and editing.
Availability of data and material
Declarations.
Not applicable.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Contributor Information
Kashif Abbass, Email: nc.ude.tsujn@ssabbafihsak .
Muhammad Zeeshan Qasim, Email: moc.kooltuo@888misaqnahseez .
Huaming Song, Email: nc.ude.tsujn@gnimauh .
Muntasir Murshed, Email: [email protected] .
Haider Mahmood, Email: moc.liamtoh@doomhamrediah .
Ijaz Younis, Email: nc.ude.tsujn@sinuoyzaji .
- Abbass K, Begum H, Alam ASA, Awang AH, Abdelsalam MK, Egdair IMM, Wahid R (2022) Fresh Insight through a Keynesian Theory Approach to Investigate the Economic Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic in Pakistan. Sustain 14(3):1054
- Abbass K, Niazi AAK, Qazi TF, Basit A, Song H (2021a) The aftermath of COVID-19 pandemic period: barriers in implementation of social distancing at workplace. Library Hi Tech
- Abbass K, Song H, Khan F, Begum H, Asif M (2021b) Fresh insight through the VAR approach to investigate the effects of fiscal policy on environmental pollution in Pakistan. Environ Scie Poll Res 1–14 [ PubMed ]
- Abbass K, Song H, Shah SM, Aziz B. Determinants of Stock Return for Non-Financial Sector: Evidence from Energy Sector of Pakistan. J Bus Fin Aff. 2019; 8 (370):2167–0234. [ Google Scholar ]
- Abbass K, Tanveer A, Huaming S, Khatiya AA (2021c) Impact of financial resources utilization on firm performance: a case of SMEs working in Pakistan
- Abraham E, Chain E. An enzyme from bacteria able to destroy penicillin. 1940. Rev Infect Dis. 1988; 10 (4):677. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Adger WN, Arnell NW, Tompkins EL. Successful adaptation to climate change across scales. Glob Environ Chang. 2005; 15 (2):77–86. doi: 10.1016/j.gloenvcha.2004.12.005. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Akkari C, Bryant CR. The co-construction approach as approach to developing adaptation strategies in the face of climate change and variability: A conceptual framework. Agricultural Research. 2016; 5 (2):162–173. doi: 10.1007/s40003-016-0208-8. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Alhassan H (2021) The effect of agricultural total factor productivity on environmental degradation in sub-Saharan Africa. Sci Afr 12:e00740
- Ali A, Erenstein O. Assessing farmer use of climate change adaptation practices and impacts on food security and poverty in Pakistan. Clim Risk Manag. 2017; 16 :183–194. doi: 10.1016/j.crm.2016.12.001. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Allen CD, Macalady AK, Chenchouni H, Bachelet D, McDowell N, Vennetier M, Hogg ET. A global overview of drought and heat-induced tree mortality reveals emerging climate change risks for forests. For Ecol Manag. 2010; 259 (4):660–684. doi: 10.1016/j.foreco.2009.09.001. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Anwar A, Sinha A, Sharif A, Siddique M, Irshad S, Anwar W, Malik S (2021) The nexus between urbanization, renewable energy consumption, financial development, and CO2 emissions: evidence from selected Asian countries. Environ Dev Sust. 10.1007/s10668-021-01716-2
- Araus JL, Slafer GA, Royo C, Serret MD. Breeding for yield potential and stress adaptation in cereals. Crit Rev Plant Sci. 2008; 27 (6):377–412. doi: 10.1080/07352680802467736. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Aron JL, Patz J (2001) Ecosystem change and public health: a global perspective: JHU Press
- Arshad MI, Iqbal MA, Shahbaz M. Pakistan tourism industry and challenges: a review. Asia Pacific Journal of Tourism Research. 2018; 23 (2):121–132. doi: 10.1080/10941665.2017.1410192. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ashbolt NJ. Microbial contamination of drinking water and human health from community water systems. Current Environmental Health Reports. 2015; 2 (1):95–106. doi: 10.1007/s40572-014-0037-5. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Asseng S, Cao W, Zhang W, Ludwig F (2009) Crop physiology, modelling and climate change: impact and adaptation strategies. Crop Physiol 511–543
- Asseng S, Ewert F, Rosenzweig C, Jones JW, Hatfield JL, Ruane AC, Cammarano D. Uncertainty in simulating wheat yields under climate change. Nat Clim Chang. 2013; 3 (9):827–832. doi: 10.1038/nclimate1916. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Association A (2020) Climate change is threatening mental health, American Psychological Association, “Kirsten Weir, . from < https://www.apa.org/monitor/2016/07-08/climate-change >, Accessed on 26 Jan 2020.
- Ayers J, Huq S, Wright H, Faisal A, Hussain S. Mainstreaming climate change adaptation into development in Bangladesh. Clim Dev. 2014; 6 :293–305. doi: 10.1080/17565529.2014.977761. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Balsalobre-Lorente D, Driha OM, Bekun FV, Sinha A, Adedoyin FF (2020) Consequences of COVID-19 on the social isolation of the Chinese economy: accounting for the role of reduction in carbon emissions. Air Qual Atmos Health 13(12):1439–1451
- Balsalobre-Lorente D, Ibáñez-Luzón L, Usman M, Shahbaz M. The environmental Kuznets curve, based on the economic complexity, and the pollution haven hypothesis in PIIGS countries. Renew Energy. 2022; 185 :1441–1455. doi: 10.1016/j.renene.2021.10.059. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bank W (2008) Forests sourcebook: practical guidance for sustaining forests in development cooperation: World Bank
- Barua S, Valenzuela E (2018) Climate change impacts on global agricultural trade patterns: evidence from the past 50 years. In Proceedings of the Sixth International Conference on Sustainable Development (pp. 26–28)
- Bates AE, Pecl GT, Frusher S, Hobday AJ, Wernberg T, Smale DA, Colwell RK. Defining and observing stages of climate-mediated range shifts in marine systems. Glob Environ Chang. 2014; 26 :27–38. doi: 10.1016/j.gloenvcha.2014.03.009. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Battisti DS, Naylor RL. Historical warnings of future food insecurity with unprecedented seasonal heat. Science. 2009; 323 (5911):240–244. doi: 10.1126/science.1164363. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Beesley L, Close PG, Gwinn DC, Long M, Moroz M, Koster WM, Storer T. Flow-mediated movement of freshwater catfish, Tandanus bostocki, in a regulated semi-urban river, to inform environmental water releases. Ecol Freshw Fish. 2019; 28 (3):434–445. doi: 10.1111/eff.12466. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Benita F (2021) Human mobility behavior in COVID-19: A systematic literature review and bibliometric analysis. Sustain Cities Soc 70:102916 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ]
- Berendonk TU, Manaia CM, Merlin C, Fatta-Kassinos D, Cytryn E, Walsh F, Pons M-N. Tackling antibiotic resistance: the environmental framework. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2015; 13 (5):310–317. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro3439. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Berg MP, Kiers ET, Driessen G, Van DerHEIJDEN M, Kooi BW, Kuenen F, Ellers J. Adapt or disperse: understanding species persistence in a changing world. Glob Change Biol. 2010; 16 (2):587–598. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2486.2009.02014.x. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Blum A, Klueva N, Nguyen H. Wheat cellular thermotolerance is related to yield under heat stress. Euphytica. 2001; 117 (2):117–123. doi: 10.1023/A:1004083305905. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bonacci O. Air temperature and precipitation analyses on a small Mediterranean island: the case of the remote island of Lastovo (Adriatic Sea, Croatia) Acta Hydrotechnica. 2019; 32 (57):135–150. doi: 10.15292/acta.hydro.2019.10. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Botzen W, Duijndam S, van Beukering P (2021) Lessons for climate policy from behavioral biases towards COVID-19 and climate change risks. World Dev 137:105214 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ]
- Brázdil R, Stucki P, Szabó P, Řezníčková L, Dolák L, Dobrovolný P, Suchánková S. Windstorms and forest disturbances in the Czech Lands: 1801–2015. Agric for Meteorol. 2018; 250 :47–63. doi: 10.1016/j.agrformet.2017.11.036. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Brown HCP, Smit B, Somorin OA, Sonwa DJ, Nkem JN. Climate change and forest communities: prospects for building institutional adaptive capacity in the Congo Basin forests. Ambio. 2014; 43 (6):759–769. doi: 10.1007/s13280-014-0493-z. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bujosa A, Riera A, Torres CM. Valuing tourism demand attributes to guide climate change adaptation measures efficiently: the case of the Spanish domestic travel market. Tour Manage. 2015; 47 :233–239. doi: 10.1016/j.tourman.2014.09.023. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Calderini D, Abeledo L, Savin R, Slafer GA. Effect of temperature and carpel size during pre-anthesis on potential grain weight in wheat. J Agric Sci. 1999; 132 (4):453–459. doi: 10.1017/S0021859699006504. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Cammell M, Knight J. Effects of climatic change on the population dynamics of crop pests. Adv Ecol Res. 1992; 22 :117–162. doi: 10.1016/S0065-2504(08)60135-X. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Cavanaugh KC, Kellner JR, Forde AJ, Gruner DS, Parker JD, Rodriguez W, Feller IC. Poleward expansion of mangroves is a threshold response to decreased frequency of extreme cold events. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2014; 111 (2):723–727. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1315800111. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Cell CC (2009) Climate change and health impacts in Bangladesh. Clima Chang Cell DoE MoEF
- Chandio AA, Jiang Y, Rehman A, Rauf A (2020) Short and long-run impacts of climate change on agriculture: an empirical evidence from China. Int J Clim Chang Strat Manag
- Chaudhary P, Rai S, Wangdi S, Mao A, Rehman N, Chettri S, Bawa KS (2011) Consistency of local perceptions of climate change in the Kangchenjunga Himalaya landscape. Curr Sci 504–513
- Chien F, Anwar A, Hsu CC, Sharif A, Razzaq A, Sinha A (2021) The role of information and communication technology in encountering environmental degradation: proposing an SDG framework for the BRICS countries. Technol Soc 65:101587
- Cooper C, Booth A, Varley-Campbell J, Britten N, Garside R. Defining the process to literature searching in systematic reviews: a literature review of guidance and supporting studies. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2018; 18 (1):1–14. doi: 10.1186/s12874-018-0545-3. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Costello A, Abbas M, Allen A, Ball S, Bell S, Bellamy R, Kett M. Managing the health effects of climate change: lancet and University College London Institute for Global Health Commission. The Lancet. 2009; 373 (9676):1693–1733. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(09)60935-1. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Cruz DLA (2015) Mother Figured. University of Chicago Press. Retrieved from, 10.7208/9780226315072
- Cui W, Ouyang T, Qiu Y, Cui D (2021) Literature Review of the Implications of Exercise Rehabilitation Strategies for SARS Patients on the Recovery of COVID-19 Patients. Paper presented at the Healthcare [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ]
- Davidson D. Gaps in agricultural climate adaptation research. Nat Clim Chang. 2016; 6 (5):433–435. doi: 10.1038/nclimate3007. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Diffenbaugh NS, Singh D, Mankin JS, Horton DE, Swain DL, Touma D, Tsiang M. Quantifying the influence of global warming on unprecedented extreme climate events. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2017; 114 (19):4881–4886. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1618082114. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Dimri A, Kumar D, Choudhary A, Maharana P. Future changes over the Himalayas: mean temperature. Global Planet Change. 2018; 162 :235–251. doi: 10.1016/j.gloplacha.2018.01.014. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Dullinger S, Gattringer A, Thuiller W, Moser D, Zimmermann N, Guisan A. Extinction debt of high-mountain plants under twenty-first-century climate change. Nat Clim Chang: Nature Publishing Group; 2012. [ Google Scholar ]
- Dupuis I, Dumas C. Influence of temperature stress on in vitro fertilization and heat shock protein synthesis in maize (Zea mays L.) reproductive tissues. Plant Physiol. 1990; 94 (2):665–670. doi: 10.1104/pp.94.2.665. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Edreira JR, Otegui ME. Heat stress in temperate and tropical maize hybrids: a novel approach for assessing sources of kernel loss in field conditions. Field Crop Res. 2013; 142 :58–67. doi: 10.1016/j.fcr.2012.11.009. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Edreira JR, Carpici EB, Sammarro D, Otegui M. Heat stress effects around flowering on kernel set of temperate and tropical maize hybrids. Field Crop Res. 2011; 123 (2):62–73. doi: 10.1016/j.fcr.2011.04.015. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ellison D, Morris CE, Locatelli B, Sheil D, Cohen J, Murdiyarso D, Pokorny J. Trees, forests and water: Cool insights for a hot world. Glob Environ Chang. 2017; 43 :51–61. doi: 10.1016/j.gloenvcha.2017.01.002. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Elsayed ZM, Eldehna WM, Abdel-Aziz MM, El Hassab MA, Elkaeed EB, Al-Warhi T, Mohammed ER. Development of novel isatin–nicotinohydrazide hybrids with potent activity against susceptible/resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis and bronchitis causing–bacteria. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2021; 36 (1):384–393. doi: 10.1080/14756366.2020.1868450. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- EM-DAT (2020) EMDAT: OFDA/CRED International Disaster Database, Université catholique de Louvain – Brussels – Belgium. from http://www.emdat.be
- EPA U (2018) United States Environmental Protection Agency, EPA Year in Review
- Erman A, De Vries Robbe SA, Thies SF, Kabir K, Maruo M (2021) Gender Dimensions of Disaster Risk and Resilience
- Fand BB, Kamble AL, Kumar M. Will climate change pose serious threat to crop pest management: a critical review. Int J Sci Res Publ. 2012; 2 (11):1–14. [ Google Scholar ]
- FAO (2018).The State of the World’s Forests 2018 - Forest Pathways to Sustainable Development.
- Fardous S Perception of climate change in Kaptai National Park. Rural Livelihoods and Protected Landscape: Co-Management in the Wetlands and Forests of Bangladesh, 186–204
- Farooq M, Bramley H, Palta JA, Siddique KH. Heat stress in wheat during reproductive and grain-filling phases. Crit Rev Plant Sci. 2011; 30 (6):491–507. doi: 10.1080/07352689.2011.615687. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Feliciano D, Recha J, Ambaw G, MacSween K, Solomon D, Wollenberg E (2022) Assessment of agricultural emissions, climate change mitigation and adaptation practices in Ethiopia. Clim Policy 1–18
- Ferreira JJ, Fernandes CI, Ferreira FA (2020) Technology transfer, climate change mitigation, and environmental patent impact on sustainability and economic growth: a comparison of European countries. Technol Forecast Soc Change 150:119770
- Fettig CJ, Reid ML, Bentz BJ, Sevanto S, Spittlehouse DL, Wang T. Changing climates, changing forests: a western North American perspective. J Forest. 2013; 111 (3):214–228. doi: 10.5849/jof.12-085. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Fischer AP. Characterizing behavioral adaptation to climate change in temperate forests. Landsc Urban Plan. 2019; 188 :72–79. doi: 10.1016/j.landurbplan.2018.09.024. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Flannigan M, Cantin AS, De Groot WJ, Wotton M, Newbery A, Gowman LM. Global wildland fire season severity in the 21st century. For Ecol Manage. 2013; 294 :54–61. doi: 10.1016/j.foreco.2012.10.022. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Fossheim M, Primicerio R, Johannesen E, Ingvaldsen RB, Aschan MM, Dolgov AV. Recent warming leads to a rapid borealization of fish communities in the Arctic. Nat Clim Chang. 2015; 5 (7):673–677. doi: 10.1038/nclimate2647. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Füssel HM, Hildén M (2014) How is uncertainty addressed in the knowledge base for national adaptation planning? Adapting to an Uncertain Climate (pp. 41–66): Springer
- Gambín BL, Borrás L, Otegui ME. Source–sink relations and kernel weight differences in maize temperate hybrids. Field Crop Res. 2006; 95 (2–3):316–326. doi: 10.1016/j.fcr.2005.04.002. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gambín B, Borrás L. Resource distribution and the trade-off between seed number and seed weight: a comparison across crop species. Annals of Applied Biology. 2010; 156 (1):91–102. doi: 10.1111/j.1744-7348.2009.00367.x. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gampe D, Nikulin G, Ludwig R. Using an ensemble of regional climate models to assess climate change impacts on water scarcity in European river basins. Sci Total Environ. 2016; 573 :1503–1518. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.08.053. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- García GA, Dreccer MF, Miralles DJ, Serrago RA. High night temperatures during grain number determination reduce wheat and barley grain yield: a field study. Glob Change Biol. 2015; 21 (11):4153–4164. doi: 10.1111/gcb.13009. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Garner E, Inyang M, Garvey E, Parks J, Glover C, Grimaldi A, Edwards MA. Impact of blending for direct potable reuse on premise plumbing microbial ecology and regrowth of opportunistic pathogens and antibiotic resistant bacteria. Water Res. 2019; 151 :75–86. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2018.12.003. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gleditsch NP (2021) This time is different! Or is it? NeoMalthusians and environmental optimists in the age of climate change. J Peace Res 0022343320969785
- Godfray HCJ, Beddington JR, Crute IR, Haddad L, Lawrence D, Muir JF, Toulmin C. Food security: the challenge of feeding 9 billion people. Science. 2010; 327 (5967):812–818. doi: 10.1126/science.1185383. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Goes S, Hasterok D, Schutt DL, Klöcking M (2020) Continental lithospheric temperatures: A review. Phys Earth Planet Inter 106509
- Gorst A, Dehlavi A, Groom B. Crop productivity and adaptation to climate change in Pakistan. Environ Dev Econ. 2018; 23 (6):679–701. doi: 10.1017/S1355770X18000232. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gosling SN, Arnell NW. A global assessment of the impact of climate change on water scarcity. Clim Change. 2016; 134 (3):371–385. doi: 10.1007/s10584-013-0853-x. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gössling S, Scott D, Hall CM, Ceron J-P, Dubois G. Consumer behaviour and demand response of tourists to climate change. Ann Tour Res. 2012; 39 (1):36–58. doi: 10.1016/j.annals.2011.11.002. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gourdji SM, Sibley AM, Lobell DB. Global crop exposure to critical high temperatures in the reproductive period: historical trends and future projections. Environ Res Lett. 2013; 8 (2):024041. doi: 10.1088/1748-9326/8/2/024041. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Grieg E Responsible Consumption and Production
- Gunter BG, Rahman A, Rahman A (2008) How Vulnerable are Bangladesh’s Indigenous People to Climate Change? Bangladesh Development Research Center (BDRC)
- Hall CM, Amelung B, Cohen S, Eijgelaar E, Gössling S, Higham J, Scott D. On climate change skepticism and denial in tourism. J Sustain Tour. 2015; 23 (1):4–25. doi: 10.1080/09669582.2014.953544. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hartmann H, Moura CF, Anderegg WR, Ruehr NK, Salmon Y, Allen CD, Galbraith D. Research frontiers for improving our understanding of drought-induced tree and forest mortality. New Phytol. 2018; 218 (1):15–28. doi: 10.1111/nph.15048. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hatfield JL, Prueger JH. Temperature extremes: Effect on plant growth and development. Weather and Climate Extremes. 2015; 10 :4–10. doi: 10.1016/j.wace.2015.08.001. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hatfield JL, Boote KJ, Kimball B, Ziska L, Izaurralde RC, Ort D, Wolfe D. Climate impacts on agriculture: implications for crop production. Agron J. 2011; 103 (2):351–370. doi: 10.2134/agronj2010.0303. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hendriksen RS, Munk P, Njage P, Van Bunnik B, McNally L, Lukjancenko O, Kjeldgaard J. Global monitoring of antimicrobial resistance based on metagenomics analyses of urban sewage. Nat Commun. 2019; 10 (1):1124. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-08853-3. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Huang S (2004) Global trade patterns in fruits and vegetables. USDA-ERS Agriculture and Trade Report No. WRS-04–06
- Huang W, Gao Q-X, Cao G-L, Ma Z-Y, Zhang W-D, Chao Q-C. Effect of urban symbiosis development in China on GHG emissions reduction. Adv Clim Chang Res. 2016; 7 (4):247–252. doi: 10.1016/j.accre.2016.12.003. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Huang Y, Haseeb M, Usman M, Ozturk I (2022) Dynamic association between ICT, renewable energy, economic complexity and ecological footprint: Is there any difference between E-7 (developing) and G-7 (developed) countries? Tech Soc 68:101853
- Hubbart JA, Guyette R, Muzika R-M. More than drought: precipitation variance, excessive wetness, pathogens and the future of the western edge of the eastern deciduous forest. Sci Total Environ. 2016; 566 :463–467. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.05.108. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hussain M, Butt AR, Uzma F, Ahmed R, Irshad S, Rehman A, Yousaf B. A comprehensive review of climate change impacts, adaptation, and mitigation on environmental and natural calamities in Pakistan. Environ Monit Assess. 2020; 192 (1):48. doi: 10.1007/s10661-019-7956-4. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hussain M, Liu G, Yousaf B, Ahmed R, Uzma F, Ali MU, Butt AR. Regional and sectoral assessment on climate-change in Pakistan: social norms and indigenous perceptions on climate-change adaptation and mitigation in relation to global context. J Clean Prod. 2018; 200 :791–808. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.07.272. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Intergov. Panel Clim Chang 33 from 10.1017/CBO9781107415324
- Ionescu C, Klein RJ, Hinkel J, Kumar KK, Klein R. Towards a formal framework of vulnerability to climate change. Environ Model Assess. 2009; 14 (1):1–16. doi: 10.1007/s10666-008-9179-x. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- IPCC (2013) Summary for policymakers. Clim Chang Phys Sci Basis Contrib Work Gr I Fifth Assess Rep
- Ishikawa-Ishiwata Y, Furuya J (2022) Economic evaluation and climate change adaptation measures for rice production in vietnam using a supply and demand model: special emphasis on the Mekong River Delta region in Vietnam. In Interlocal Adaptations to Climate Change in East and Southeast Asia (pp. 45–53). Springer, Cham
- Izaguirre C, Losada I, Camus P, Vigh J, Stenek V. Climate change risk to global port operations. Nat Clim Chang. 2021; 11 (1):14–20. doi: 10.1038/s41558-020-00937-z. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Jactel H, Koricheva J, Castagneyrol B (2019) Responses of forest insect pests to climate change: not so simple. Current opinion in insect science [ PubMed ]
- Jahanzad E, Holtz BA, Zuber CA, Doll D, Brewer KM, Hogan S, Gaudin AC. Orchard recycling improves climate change adaptation and mitigation potential of almond production systems. PLoS ONE. 2020; 15 (3):e0229588. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0229588. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Jurgilevich A, Räsänen A, Groundstroem F, Juhola S. A systematic review of dynamics in climate risk and vulnerability assessments. Environ Res Lett. 2017; 12 (1):013002. doi: 10.1088/1748-9326/aa5508. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Karami E (2012) Climate change, resilience and poverty in the developing world. Paper presented at the Culture, Politics and Climate change conference
- Kärkkäinen L, Lehtonen H, Helin J, Lintunen J, Peltonen-Sainio P, Regina K, . . . Packalen T (2020) Evaluation of policy instruments for supporting greenhouse gas mitigation efforts in agricultural and urban land use. Land Use Policy 99:104991
- Karkman A, Do TT, Walsh F, Virta MP. Antibiotic-resistance genes in waste water. Trends Microbiol. 2018; 26 (3):220–228. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2017.09.005. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kohfeld KE, Le Quéré C, Harrison SP, Anderson RF. Role of marine biology in glacial-interglacial CO2 cycles. Science. 2005; 308 (5718):74–78. doi: 10.1126/science.1105375. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kongsager R. Linking climate change adaptation and mitigation: a review with evidence from the land-use sectors. Land. 2018; 7 (4):158. doi: 10.3390/land7040158. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kurz WA, Dymond C, Stinson G, Rampley G, Neilson E, Carroll A, Safranyik L. Mountain pine beetle and forest carbon feedback to climate change. Nature. 2008; 452 (7190):987. doi: 10.1038/nature06777. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lamperti F, Bosetti V, Roventini A, Tavoni M, Treibich T (2021) Three green financial policies to address climate risks. J Financial Stab 54:100875
- Leal Filho W, Azeiteiro UM, Balogun AL, Setti AFF, Mucova SA, Ayal D, . . . Oguge NO (2021) The influence of ecosystems services depletion to climate change adaptation efforts in Africa. Sci Total Environ 146414 [ PubMed ]
- Lehner F, Coats S, Stocker TF, Pendergrass AG, Sanderson BM, Raible CC, Smerdon JE. Projected drought risk in 1.5 C and 2 C warmer climates. Geophys Res Lett. 2017; 44 (14):7419–7428. doi: 10.1002/2017GL074117. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lemery J, Knowlton K, Sorensen C (2021) Global climate change and human health: from science to practice: John Wiley & Sons
- Leppänen S, Saikkonen L, Ollikainen M (2014) Impact of Climate Change on cereal grain production in Russia: Mimeo
- Lipczynska-Kochany E. Effect of climate change on humic substances and associated impacts on the quality of surface water and groundwater: a review. Sci Total Environ. 2018; 640 :1548–1565. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.05.376. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- livescience.com. New coronavirus may have ‘jumped’ to humans from snakes, study finds, live science,. from < https://www.livescience.com/new-coronavirus-origin-snakes.html > accessed on Jan 2020
- Lobell DB, Field CB. Global scale climate–crop yield relationships and the impacts of recent warming. Environ Res Lett. 2007; 2 (1):014002. doi: 10.1088/1748-9326/2/1/014002. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lobell DB, Gourdji SM. The influence of climate change on global crop productivity. Plant Physiol. 2012; 160 (4):1686–1697. doi: 10.1104/pp.112.208298. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ma L, Li B, Zhang T. New insights into antibiotic resistome in drinking water and management perspectives: a metagenomic based study of small-sized microbes. Water Res. 2019; 152 :191–201. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2018.12.069. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Macchi M, Oviedo G, Gotheil S, Cross K, Boedhihartono A, Wolfangel C, Howell M (2008) Indigenous and traditional peoples and climate change. International Union for the Conservation of Nature, Gland, Suiza
- Mall RK, Gupta A, Sonkar G (2017) Effect of climate change on agricultural crops. In Current developments in biotechnology and bioengineering (pp. 23–46). Elsevier
- Manes S, Costello MJ, Beckett H, Debnath A, Devenish-Nelson E, Grey KA, . . . Krause C (2021) Endemism increases species’ climate change risk in areas of global biodiversity importance. Biol Conserv 257:109070
- Mannig B, Pollinger F, Gafurov A, Vorogushyn S, Unger-Shayesteh K (2018) Impacts of climate change in Central Asia Encyclopedia of the Anthropocene (pp. 195–203): Elsevier
- Martínez-Alvarado O, Gray SL, Hart NC, Clark PA, Hodges K, Roberts MJ. Increased wind risk from sting-jet windstorms with climate change. Environ Res Lett. 2018; 13 (4):044002. doi: 10.1088/1748-9326/aaae3a. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Matsui T, Omasa K, Horie T. The difference in sterility due to high temperatures during the flowering period among japonica-rice varieties. Plant Production Science. 2001; 4 (2):90–93. doi: 10.1626/pps.4.90. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Meierrieks D (2021) Weather shocks, climate change and human health. World Dev 138:105228
- Michel D, Eriksson M, Klimes M (2021) Climate change and (in) security in transboundary river basins Handbook of Security and the Environment: Edward Elgar Publishing
- Mihiretu A, Okoyo EN, Lemma T. Awareness of climate change and its associated risks jointly explain context-specific adaptation in the Arid-tropics. Northeast Ethiopia SN Social Sciences. 2021; 1 (2):1–18. [ Google Scholar ]
- Millar CI, Stephenson NL. Temperate forest health in an era of emerging megadisturbance. Science. 2015; 349 (6250):823–826. doi: 10.1126/science.aaa9933. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Mishra A, Bruno E, Zilberman D (2021) Compound natural and human disasters: Managing drought and COVID-19 to sustain global agriculture and food sectors. Sci Total Environ 754:142210 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ]
- Mosavi SH, Soltani S, Khalilian S (2020) Coping with climate change in agriculture: Evidence from Hamadan-Bahar plain in Iran. Agric Water Manag 241:106332
- Murshed M (2020) An empirical analysis of the non-linear impacts of ICT-trade openness on renewable energy transition, energy efficiency, clean cooking fuel access and environmental sustainability in South Asia. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(29):36254–36281. 10.1007/s11356-020-09497-3 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ]
- Murshed M. Pathways to clean cooking fuel transition in low and middle income Sub-Saharan African countries: the relevance of improving energy use efficiency. Sustainable Production and Consumption. 2022; 30 :396–412. doi: 10.1016/j.spc.2021.12.016. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Murshed M, Dao NTT. Revisiting the CO2 emission-induced EKC hypothesis in South Asia: the role of Export Quality Improvement. GeoJournal. 2020 doi: 10.1007/s10708-020-10270-9. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Murshed M, Abbass K, Rashid S. Modelling renewable energy adoption across south Asian economies: Empirical evidence from Bangladesh, India, Pakistan and Sri Lanka. Int J Finan Eco. 2021; 26 (4):5425–5450. doi: 10.1002/ijfe.2073. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Murshed M, Nurmakhanova M, Elheddad M, Ahmed R. Value addition in the services sector and its heterogeneous impacts on CO2 emissions: revisiting the EKC hypothesis for the OPEC using panel spatial estimation techniques. Environ Sci Pollut Res. 2020; 27 (31):38951–38973. doi: 10.1007/s11356-020-09593-4. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Murshed M, Nurmakhanova M, Al-Tal R, Mahmood H, Elheddad M, Ahmed R (2022) Can intra-regional trade, renewable energy use, foreign direct investments, and economic growth reduce ecological footprints in South Asia? Energy Sources, Part B: Economics, Planning, and Policy. 10.1080/15567249.2022.2038730
- Neuvonen M, Sievänen T, Fronzek S, Lahtinen I, Veijalainen N, Carter TR. Vulnerability of cross-country skiing to climate change in Finland–an interactive mapping tool. J Outdoor Recreat Tour. 2015; 11 :64–79. doi: 10.1016/j.jort.2015.06.010. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- npr.org. Please Help Me.’ What people in China are saying about the outbreak on social media, npr.org, . from < https://www.npr.org/sections/goatsandsoda/2020/01/24/799000379/please-help-me-what-people-in-china-are-saying-about-the-outbreak-on-social-medi >, Accessed on 26 Jan 2020.
- Ogden LE. Climate change, pathogens, and people: the challenges of monitoring a moving target. Bioscience. 2018; 68 (10):733–739. doi: 10.1093/biosci/biy101. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ortiz AMD, Outhwaite CL, Dalin C, Newbold T. A review of the interactions between biodiversity, agriculture, climate change, and international trade: research and policy priorities. One Earth. 2021; 4 (1):88–101. doi: 10.1016/j.oneear.2020.12.008. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ortiz R. Crop genetic engineering under global climate change. Ann Arid Zone. 2008; 47 (3):343. [ Google Scholar ]
- Otegui MAE, Bonhomme R. Grain yield components in maize: I. Ear growth and kernel set. Field Crop Res. 1998; 56 (3):247–256. doi: 10.1016/S0378-4290(97)00093-2. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Pachauri RK, Allen MR, Barros VR, Broome J, Cramer W, Christ R, . . . Dasgupta P (2014) Climate change 2014: synthesis report. Contribution of Working Groups I, II and III to the fifth assessment report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change: Ipcc
- Pal JK. Visualizing the knowledge outburst in global research on COVID-19. Scientometrics. 2021; 126 (5):4173–4193. doi: 10.1007/s11192-021-03912-3. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Panda R, Behera S, Kashyap P. Effective management of irrigation water for wheat under stressed conditions. Agric Water Manag. 2003; 63 (1):37–56. doi: 10.1016/S0378-3774(03)00099-4. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Pärnänen KM, Narciso-da-Rocha C, Kneis D, Berendonk TU, Cacace D, Do TT, Jaeger T. Antibiotic resistance in European wastewater treatment plants mirrors the pattern of clinical antibiotic resistance prevalence. Sci Adv. 2019; 5 (3):eaau9124. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aau9124. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Parry M, Parry ML, Canziani O, Palutikof J, Van der Linden P, Hanson C (2007) Climate change 2007-impacts, adaptation and vulnerability: Working group II contribution to the fourth assessment report of the IPCC (Vol. 4): Cambridge University Press
- Patz JA, Campbell-Lendrum D, Holloway T, Foley JA. Impact of regional climate change on human health. Nature. 2005; 438 (7066):310–317. doi: 10.1038/nature04188. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Patz JA, Graczyk TK, Geller N, Vittor AY. Effects of environmental change on emerging parasitic diseases. Int J Parasitol. 2000; 30 (12–13):1395–1405. doi: 10.1016/S0020-7519(00)00141-7. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Pautasso M, Döring TF, Garbelotto M, Pellis L, Jeger MJ. Impacts of climate change on plant diseases—opinions and trends. Eur J Plant Pathol. 2012; 133 (1):295–313. doi: 10.1007/s10658-012-9936-1. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Peng S, Huang J, Sheehy JE, Laza RC, Visperas RM, Zhong X, Cassman KG. Rice yields decline with higher night temperature from global warming. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2004; 101 (27):9971–9975. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0403720101. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Pereira HM, Ferrier S, Walters M, Geller GN, Jongman R, Scholes RJ, Cardoso A. Essential biodiversity variables. Science. 2013; 339 (6117):277–278. doi: 10.1126/science.1229931. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Perera K, De Silva K, Amarasinghe M. Potential impact of predicted sea level rise on carbon sink function of mangrove ecosystems with special reference to Negombo estuary, Sri Lanka. Global Planet Change. 2018; 161 :162–171. doi: 10.1016/j.gloplacha.2017.12.016. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Pfadenhauer JS, Klötzli FA (2020) Zonal Vegetation of the Subtropical (Warm–Temperate) Zone with Winter Rain. In Global Vegetation (pp. 455–514). Springer, Cham
- Phillips JD. Environmental gradients and complexity in coastal landscape response to sea level rise. CATENA. 2018; 169 :107–118. doi: 10.1016/j.catena.2018.05.036. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Pirasteh-Anosheh H, Parnian A, Spasiano D, Race M, Ashraf M (2021) Haloculture: A system to mitigate the negative impacts of pandemics on the environment, society and economy, emphasizing COVID-19. Environ Res 111228 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ]
- Pruden A, Larsson DJ, Amézquita A, Collignon P, Brandt KK, Graham DW, Snape JR. Management options for reducing the release of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes to the environment. Environ Health Perspect. 2013; 121 (8):878–885. doi: 10.1289/ehp.1206446. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Qasim MZ, Hammad HM, Abbas F, Saeed S, Bakhat HF, Nasim W, Fahad S. The potential applications of picotechnology in biomedical and environmental sciences. Environ Sci Pollut Res. 2020; 27 (1):133–142. doi: 10.1007/s11356-019-06554-4. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Qasim MZ, Hammad HM, Maqsood F, Tariq T, Chawla MS Climate Change Implication on Cereal Crop Productivity
- Rahman M, Alam K. Forest dependent indigenous communities’ perception and adaptation to climate change through local knowledge in the protected area—a Bangladesh case study. Climate. 2016; 4 (1):12. doi: 10.3390/cli4010012. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ramankutty N, Mehrabi Z, Waha K, Jarvis L, Kremen C, Herrero M, Rieseberg LH. Trends in global agricultural land use: implications for environmental health and food security. Annu Rev Plant Biol. 2018; 69 :789–815. doi: 10.1146/annurev-arplant-042817-040256. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Rehman A, Ma H, Ahmad M, Irfan M, Traore O, Chandio AA (2021) Towards environmental Sustainability: devolving the influence of carbon dioxide emission to population growth, climate change, Forestry, livestock and crops production in Pakistan. Ecol Indic 125:107460
- Reichstein M, Carvalhais N. Aspects of forest biomass in the Earth system: its role and major unknowns. Surv Geophys. 2019; 40 (4):693–707. doi: 10.1007/s10712-019-09551-x. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Reidsma P, Ewert F, Boogaard H, van Diepen K. Regional crop modelling in Europe: the impact of climatic conditions and farm characteristics on maize yields. Agric Syst. 2009; 100 (1–3):51–60. doi: 10.1016/j.agsy.2008.12.009. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ritchie H, Roser M (2014) Natural disasters. Our World in Data
- Rizvi AR, Baig S, Verdone M. Ecosystems based adaptation: knowledge gaps in making an economic case for investing in nature based solutions for climate change. Gland, Switzerland: IUCN; 2015. p. 48. [ Google Scholar ]
- Roscher C, Fergus AJ, Petermann JS, Buchmann N, Schmid B, Schulze E-D. What happens to the sown species if a biodiversity experiment is not weeded? Basic Appl Ecol. 2013; 14 (3):187–198. doi: 10.1016/j.baae.2013.01.003. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Rosenzweig C, Elliott J, Deryng D, Ruane AC, Müller C, Arneth A, Khabarov N. Assessing agricultural risks of climate change in the 21st century in a global gridded crop model intercomparison. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2014; 111 (9):3268–3273. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1222463110. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Rosenzweig C, Iglesius A, Yang XB, Epstein PR, Chivian E (2001) Climate change and extreme weather events-implications for food production, plant diseases, and pests
- Sadras VO, Slafer GA. Environmental modulation of yield components in cereals: heritabilities reveal a hierarchy of phenotypic plasticities. Field Crop Res. 2012; 127 :215–224. doi: 10.1016/j.fcr.2011.11.014. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Salvucci ME, Crafts-Brandner SJ. Inhibition of photosynthesis by heat stress: the activation state of Rubisco as a limiting factor in photosynthesis. Physiol Plant. 2004; 120 (2):179–186. doi: 10.1111/j.0031-9317.2004.0173.x. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Santos WS, Gurgel-Gonçalves R, Garcez LM, Abad-Franch F. Deforestation effects on Attalea palms and their resident Rhodnius, vectors of Chagas disease, in eastern Amazonia. PLoS ONE. 2021; 16 (5):e0252071. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0252071. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Sarkar P, Debnath N, Reang D (2021) Coupled human-environment system amid COVID-19 crisis: a conceptual model to understand the nexus. Sci Total Environ 753:141757 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ]
- Schlenker W, Roberts MJ. Nonlinear temperature effects indicate severe damages to US crop yields under climate change. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2009; 106 (37):15594–15598. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0906865106. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Schoene DH, Bernier PY. Adapting forestry and forests to climate change: a challenge to change the paradigm. Forest Policy Econ. 2012; 24 :12–19. doi: 10.1016/j.forpol.2011.04.007. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Schuurmans C (2021) The world heat budget: expected changes Climate Change (pp. 1–15): CRC Press
- Scott D. Sustainable Tourism and the Grand Challenge of Climate Change. Sustainability. 2021; 13 (4):1966. doi: 10.3390/su13041966. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Scott D, McBoyle G, Schwartzentruber M. Climate change and the distribution of climatic resources for tourism in North America. Climate Res. 2004; 27 (2):105–117. doi: 10.3354/cr027105. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Semenov MA. Impacts of climate change on wheat in England and Wales. J R Soc Interface. 2009; 6 (33):343–350. doi: 10.1098/rsif.2008.0285. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Shaffril HAM, Krauss SE, Samsuddin SF. A systematic review on Asian’s farmers’ adaptation practices towards climate change. Sci Total Environ. 2018; 644 :683–695. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.06.349. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Shahbaz M, Balsalobre-Lorente D, Sinha A (2019) Foreign direct Investment–CO2 emissions nexus in Middle East and North African countries: Importance of biomass energy consumption. J Clean Product 217:603–614
- Sharif A, Mishra S, Sinha A, Jiao Z, Shahbaz M, Afshan S (2020) The renewable energy consumption-environmental degradation nexus in Top-10 polluted countries: Fresh insights from quantile-on-quantile regression approach. Renew Energy 150:670–690
- Sharma R. Impacts on human health of climate and land use change in the Hindu Kush-Himalayan region. Mt Res Dev. 2012; 32 (4):480–486. doi: 10.1659/MRD-JOURNAL-D-12-00068.1. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Sharma R, Sinha A, Kautish P. Examining the impacts of economic and demographic aspects on the ecological footprint in South and Southeast Asian countries. Environ Sci Pollut Res. 2020; 27 (29):36970–36982. doi: 10.1007/s11356-020-09659-3. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Smit B, Burton I, Klein RJ, Wandel J (2000) An anatomy of adaptation to climate change and variability Societal adaptation to climate variability and change (pp. 223–251): Springer
- Song Y, Fan H, Tang X, Luo Y, Liu P, Chen Y (2021) The effects of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) on ischemic stroke and the possible underlying mechanisms. Int J Neurosci 1–20 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ]
- Sovacool BK, Griffiths S, Kim J, Bazilian M (2021) Climate change and industrial F-gases: a critical and systematic review of developments, sociotechnical systems and policy options for reducing synthetic greenhouse gas emissions. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 141:110759
- Stewart JA, Perrine JD, Nichols LB, Thorne JH, Millar CI, Goehring KE, Wright DH. Revisiting the past to foretell the future: summer temperature and habitat area predict pika extirpations in California. J Biogeogr. 2015; 42 (5):880–890. doi: 10.1111/jbi.12466. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Stocker T, Qin D, Plattner G, Tignor M, Allen S, Boschung J, . . . Midgley P (2013) Climate change 2013: The physical science basis. Working group I contribution to the IPCC Fifth assessment report: Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. 1535p
- Stone P, Nicolas M. Wheat cultivars vary widely in their responses of grain yield and quality to short periods of post-anthesis heat stress. Funct Plant Biol. 1994; 21 (6):887–900. doi: 10.1071/PP9940887. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Su H-C, Liu Y-S, Pan C-G, Chen J, He L-Y, Ying G-G. Persistence of antibiotic resistance genes and bacterial community changes in drinking water treatment system: from drinking water source to tap water. Sci Total Environ. 2018; 616 :453–461. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.10.318. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Sunderlin WD, Angelsen A, Belcher B, Burgers P, Nasi R, Santoso L, Wunder S. Livelihoods, forests, and conservation in developing countries: an overview. World Dev. 2005; 33 (9):1383–1402. doi: 10.1016/j.worlddev.2004.10.004. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Symanski E, Han HA, Han I, McDaniel M, Whitworth KW, McCurdy S, . . . Delclos GL (2021) Responding to natural and industrial disasters: partnerships and lessons learned. Disaster medicine and public health preparedness 1–4 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ]
- Tao F, Yokozawa M, Xu Y, Hayashi Y, Zhang Z. Climate changes and trends in phenology and yields of field crops in China, 1981–2000. Agric for Meteorol. 2006; 138 (1–4):82–92. doi: 10.1016/j.agrformet.2006.03.014. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Tebaldi C, Hayhoe K, Arblaster JM, Meehl GA. Going to the extremes. Clim Change. 2006; 79 (3–4):185–211. doi: 10.1007/s10584-006-9051-4. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Testa G, Koon E, Johannesson L, McKenna G, Anthony T, Klintmalm G, Gunby R (2018) This article has been accepted for publication and undergone full peer review but has not been through the copyediting, typesetting, pagination and proofreading process, which may lead to differences between this version and the Version of Record. Please cite this article as
- Thornton PK, Lipper L (2014) How does climate change alter agricultural strategies to support food security? (Vol. 1340): Intl Food Policy Res Inst
- Tranfield D, Denyer D, Smart P. Towards a methodology for developing evidence-informed management knowledge by means of systematic review. Br J Manag. 2003; 14 (3):207–222. doi: 10.1111/1467-8551.00375. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- UNEP (2017) United nations environment programme: frontiers 2017. from https://www.unenvironment.org/news-and-stories/press-release/antimicrobial-resistance - environmental-pollution-among-biggest
- Usman M, Balsalobre-Lorente D (2022) Environmental concern in the era of industrialization: Can financial development, renewable energy and natural resources alleviate some load? Ene Policy 162:112780
- Usman M, Makhdum MSA (2021) What abates ecological footprint in BRICS-T region? Exploring the influence of renewable energy, non-renewable energy, agriculture, forest area and financial development. Renew Energy 179:12–28
- Usman M, Balsalobre-Lorente D, Jahanger A, Ahmad P. Pollution concern during globalization mode in financially resource-rich countries: Do financial development, natural resources, and renewable energy consumption matter? Rene. Energy. 2022; 183 :90–102. doi: 10.1016/j.renene.2021.10.067. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Usman M, Jahanger A, Makhdum MSA, Balsalobre-Lorente D, Bashir A (2022a) How do financial development, energy consumption, natural resources, and globalization affect Arctic countries’ economic growth and environmental quality? An advanced panel data simulation. Energy 241:122515
- Usman M, Khalid K, Mehdi MA. What determines environmental deficit in Asia? Embossing the role of renewable and non-renewable energy utilization. Renew Energy. 2021; 168 :1165–1176. doi: 10.1016/j.renene.2021.01.012. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Urban MC. Accelerating extinction risk from climate change. Science. 2015; 348 (6234):571–573. doi: 10.1126/science.aaa4984. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Vale MM, Arias PA, Ortega G, Cardoso M, Oliveira BF, Loyola R, Scarano FR (2021) Climate change and biodiversity in the Atlantic Forest: best climatic models, predicted changes and impacts, and adaptation options The Atlantic Forest (pp. 253–267): Springer
- Vedwan N, Rhoades RE. Climate change in the Western Himalayas of India: a study of local perception and response. Climate Res. 2001; 19 (2):109–117. doi: 10.3354/cr019109. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Vega CR, Andrade FH, Sadras VO, Uhart SA, Valentinuz OR. Seed number as a function of growth. A comparative study in soybean, sunflower, and maize. Crop Sci. 2001; 41 (3):748–754. doi: 10.2135/cropsci2001.413748x. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Vergés A, Doropoulos C, Malcolm HA, Skye M, Garcia-Pizá M, Marzinelli EM, Vila-Concejo A. Long-term empirical evidence of ocean warming leading to tropicalization of fish communities, increased herbivory, and loss of kelp. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2016; 113 (48):13791–13796. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1610725113. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Verheyen R (2005) Climate change damage and international law: prevention duties and state responsibility (Vol. 54): Martinus Nijhoff Publishers
- Waheed A, Fischer TB, Khan MI. Climate Change Policy Coherence across Policies, Plans, and Strategies in Pakistan—implications for the China-Pakistan Economic Corridor Plan. Environ Manage. 2021; 67 (5):793–810. doi: 10.1007/s00267-021-01449-y. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Wasiq M, Ahmad M (2004) Sustaining forests: a development strategy: The World Bank
- Watts N, Adger WN, Agnolucci P, Blackstock J, Byass P, Cai W, Cooper A. Health and climate change: policy responses to protect public health. The Lancet. 2015; 386 (10006):1861–1914. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(15)60854-6. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Weed AS, Ayres MP, Hicke JA. Consequences of climate change for biotic disturbances in North American forests. Ecol Monogr. 2013; 83 (4):441–470. doi: 10.1890/13-0160.1. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Weisheimer A, Palmer T (2005) Changing frequency of occurrence of extreme seasonal temperatures under global warming. Geophys Res Lett 32(20)
- Wernberg T, Bennett S, Babcock RC, De Bettignies T, Cure K, Depczynski M, Hovey RK. Climate-driven regime shift of a temperate marine ecosystem. Science. 2016; 353 (6295):169–172. doi: 10.1126/science.aad8745. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- WHO (2018) WHO, 2018. Antimicrobial resistance
- Wilkinson DM, Sherratt TN. Why is the world green? The interactions of top–down and bottom–up processes in terrestrial vegetation ecology. Plant Ecolog Divers. 2016; 9 (2):127–140. doi: 10.1080/17550874.2016.1178353. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Wiranata IJ, Simbolon K. Increasing awareness capacity of disaster potential as a support to achieve sustainable development goal (sdg) 13 in lampung province. Jurnal Pir: Power in International Relations. 2021; 5 (2):129–146. doi: 10.22303/pir.5.2.2021.129-146. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Wiréhn L. Nordic agriculture under climate change: a systematic review of challenges, opportunities and adaptation strategies for crop production. Land Use Policy. 2018; 77 :63–74. doi: 10.1016/j.landusepol.2018.04.059. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Wu D, Su Y, Xi H, Chen X, Xie B. Urban and agriculturally influenced water contribute differently to the spread of antibiotic resistance genes in a mega-city river network. Water Res. 2019; 158 :11–21. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2019.03.010. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Wu HX (2020) Losing Steam?—An industry origin analysis of China’s productivity slowdown Measuring Economic Growth and Productivity (pp. 137–167): Elsevier
- Wu H, Qian H, Chen J, Huo C. Assessment of agricultural drought vulnerability in the Guanzhong Plain. China Water Resources Management. 2017; 31 (5):1557–1574. doi: 10.1007/s11269-017-1594-9. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Xie W, Huang J, Wang J, Cui Q, Robertson R, Chen K (2018) Climate change impacts on China’s agriculture: the responses from market and trade. China Econ Rev
- Xu J, Sharma R, Fang J, Xu Y. Critical linkages between land-use transition and human health in the Himalayan region. Environ Int. 2008; 34 (2):239–247. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2007.08.004. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Yadav MK, Singh R, Singh K, Mall R, Patel C, Yadav S, Singh M. Assessment of climate change impact on productivity of different cereal crops in Varanasi. India J Agrometeorol. 2015; 17 (2):179–184. doi: 10.54386/jam.v17i2.1000. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Yang B, Usman M. Do industrialization, economic growth and globalization processes influence the ecological footprint and healthcare expenditures? Fresh insights based on the STIRPAT model for countries with the highest healthcare expenditures. Sust Prod Cons. 2021; 28 :893–910. [ Google Scholar ]
- Yu Z, Razzaq A, Rehman A, Shah A, Jameel K, Mor RS (2021) Disruption in global supply chain and socio-economic shocks: a lesson from COVID-19 for sustainable production and consumption. Oper Manag Res 1–16
- Zarnetske PL, Skelly DK, Urban MC. Biotic multipliers of climate change. Science. 2012; 336 (6088):1516–1518. doi: 10.1126/science.1222732. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Zhang M, Liu N, Harper R, Li Q, Liu K, Wei X, Liu S. A global review on hydrological responses to forest change across multiple spatial scales: importance of scale, climate, forest type and hydrological regime. J Hydrol. 2017; 546 :44–59. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2016.12.040. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Zhao J, Sinha A, Inuwa N, Wang Y, Murshed M, Abbasi KR (2022) Does Structural Transformation in Economy Impact Inequality in Renewable Energy Productivity? Implications for Sustainable Development. Renew Energy 189:853–864. 10.1016/j.renene.2022.03.050
'Every fraction of a degree matters': Why climate action needs a new narrative

Experts suggest that positive stories of climate action can inspire change and motivate individuals and communities to get involved. Image: Pexels/Pixabay

.chakra .wef-9dduvl{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;font-size:1.25rem;}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-9dduvl{font-size:1.125rem;}} Explore and monitor how .chakra .wef-15eoq1r{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;font-size:1.25rem;color:#F7DB5E;}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-15eoq1r{font-size:1.125rem;}} SDG 13: Climate Action is affecting economies, industries and global issues

.chakra .wef-1nk5u5d{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;color:#2846F8;font-size:1.25rem;}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-1nk5u5d{font-size:1.125rem;}} Get involved with our crowdsourced digital platform to deliver impact at scale
Stay up to date:, sdg 13: climate action.
- Global warming has exceeded 1.5°C for over 10 months, raising concerns about reaching the Paris Agreement target.
- Although scientists acknowledge exceeding the 1.5°C limit may be temporary and inevitable, they emphasize continued climate action to minimize warming.
- Current "1.5°C-aligned" corporate goals might be flawed as they may not account for supply chain emissions or rely on unreliable carbon offsets.
- Highlighting successful initiatives and focusing on solutions can motivate individuals and communities to get involved in climate action efforts.
The climate fight is not going well, according to the numbers. Global warming has exceeded 1.5°C above pre-industrial times for 10 months and counting. A year-long breach of the temperature limit relative to the years before 1900 has already happened in January, according to the European Union’s earth observatory.
Warming limits have been a core tenet of climate action for years. World leaders aimed to stay “well below 2°C” in the landmark 2015 Paris Agreement. In 2018, the rallying cry changed to 1.5°C after experts said anything warmer would be too unlivable.
What’s the World Economic Forum doing about climate change?
Climate change poses an urgent threat demanding decisive action. Communities around the world are already experiencing increased climate impacts, from droughts to floods to rising seas. The World Economic Forum's Global Risks Report continues to rank these environmental threats at the top of the list.
To limit global temperature rise to well below 2°C and as close as possible to 1.5°C above pre-industrial levels, it is essential that businesses, policy-makers, and civil society advance comprehensive near- and long-term climate actions in line with the goals of the Paris Agreement on climate change.
The World Economic Forum's Climate Initiative supports the scaling and acceleration of global climate action through public and private-sector collaboration. The Initiative works across several workstreams to develop and implement inclusive and ambitious solutions.
This includes the Alliance of CEO Climate Leaders, a global network of business leaders from various industries developing cost-effective solutions to transitioning to a low-carbon, climate-resilient economy. CEOs use their position and influence with policy-makers and corporate partners to accelerate the transition and realize the economic benefits of delivering a safer climate.
Contact us to get involved.
Businesses have followed suit. Corporate climate action watchdog Science Based Targets Initiative (SBTi) called on firms to cut emissions fast to help keep global warming to 1.5°C, generally by avoiding fossil fuels and reaching net-zero emissions by 2050. Thousands of organisations have signed up to this goal.
Scientists say droughts, floods and storms will get more severe past the 1.5°C global warming limit. Vulnerable communities worldwide are already reeling from climate disasters, such as floods in 2022 that killed over 1,700 people in Pakistan, to record heatwaves in the 40-50°C range across Asia last year.
Generally, the 1.5°C limit refers to temperature averages that occur longer than a year, and the world still has marginal leeway according to decadal metrics. Beyond stepping harder on the emissions reduction brakes, some sustainability professionals say a broader framing of climate targets and action could be more relatable and effective in driving action.

“As scientists, we recognise that limiting the global average temperature rise to 1.5°C is probably not realistic without first overshooting the goal,” said Dr Angel Hsu, environmental expert and associate professor at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill.
Hsu said global warming should still be limited as much as possible, as small temperature rises could still result in unexpected risks to people and nature.
“How we frame the goal now, along the lines of ‘every fraction of a degree matters’ is important to keeping people motivated to continue pursuing climate action,” she said.
Pakistan climate advocate Hafiz Jawad Sohail likewise thinks keeping to the 1.5°C target limit is unlikely.
“The consequences should be highlighted in bold for people to take it very seriously. If [we] miss 2°C, it will be the climate boiling age where [the chances of] survival will be very thin,” Sohail said.
Scientists have said that moving from the 1.5°C limit to 2°C in temperature rise will essentially wipe out coral reefs that support fish stocks. Millions more would also be exposed to extreme heatwaves at the upper limit.
Focusing on the consequences of global warming could better help drive the point across for politicians, since they are driven by “profits and interests” that are also vulnerable to temperature rise, Sohail added.
The 1.5°C target is still very much in vogue in global negotiating fora. Mukhtar Babayev, incoming COP29 president this year, has stressed he wants to keep the temperature target “within reach”, by getting countries to set more ambitious climate action targets and unlocking more climate money to support developing nations.
“The temperature target has not yet been breached. That target does not relate to single years. It refers to longer-term averages, which are currently above 1.2°C.
“But there is a narrowing window of opportunity to act,” Mukhtar, who is Azerbaijan’s ecology and natural resources minister, said last month.
Temporary breach not a failure
Experts warn against treating the ongoing year-long breach as a failure. Woo Qiyun, a Singapore climate advocate, said the difference between short and long-term 1.5°C threshold breaches should be made clear, even as people are already feeling the effects of record warming globally.
“Without the differentiation, people might get confused and feel like [the] 1.5°C [limit] has been breached, when actually we still need to do a lot more to ensure this long-term temperature change does not hit 1.5°C,” Woo explained.
It could be hard to agree on when the 1.5°C warming limit is officially breached. While the latest monthly and one-year averages have exceeded the limit, the World Meteorological Organisation stated the 10-year mean up till 2023 was 1.2°C – the figure Babayev referenced. The United Nations’ Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) uses a 20-year range, which for 2003-2022 is 1.03°C.
The 1.5°C breach is only “temporary”, said Rosa Perez, a Philippines-based lead author for the 2022 IPCC report.
This happens when areas like the Philippines enter the warm phase of the El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO), a recurring climate pattern involving changes in the temperature of waters in the central and eastern tropical Pacific Ocean, Perez told Eco-Business.
“But countries really need to step up their nationally determined contributions (NDCs), make rapid and drastic energy use transformations, to a combination of renewables and vastly expanded energy efficiency.”
“Moving close to the 1.5 C limit is seen as the unwillingness of some countries not to heed the call of our scientists,” Perez added.
While experts say temporary blips shouldn’t count, there is no agreement on which figure actually matters, at least for the Paris Agreement.
“This is likely to result in distraction and delay just at the point when climate action is most urgent,” said a commentary published in the peer-reviewed Nature journal last December. The article’s authors recommended a 20-year metric, though based equally on a decade each of historical data and projections – bringing the 2022 figure to 1.26°C.
But as it stands, the world is headed for over 2.5°C of warming this century, as countries lag on climate targets. In recent years, communications around 1.5°C has shifted, with scientists calling for more ambitious action to pull temperatures back down after a likely overshoot.
Such efforts have largely not yet materialised. Man-made carbon dioxide levels are still creeping up, in parallel with fossil fuel use, despite realistic pathways calling for emissions to drop by over 40 per cent by 2030. Carbon dioxide sequestration – methods to suck up the gas from the atmosphere – needs to scale up by over 1,300 times by 2050, a 2023 report estimated , although many technologies remain nascent today.
The looming threshold aside, Hsu thinks there are other issues with how people relate to the 1.5°C figure today. Aligning corporate green goals to the target conceptually allocates the entire carbon budget to existing businesses and none to sustainability innovators, who may need emitting room to develop solutions against the climate crisis. Many companies’ “1.5°C-aligned” targets are also not credible, for omitting value chain emissions or using often flawed carbon offsets, she noted.
How to better frame climate action targets is “the million dollar question”, Hsu said. In an op-ed for Science journal last month, Hsu and a group of scientists argued that climate progress should be measured more broadly, including in job creation, renewable energy generation and lives saved through transitioning away from fossil fuels.
“We certainly need a broader dashboard of indicators and metrics to measure these benchmarks that can indicate progress is being made [and] in a way to better motivate climate action, since 1.5°C is pretty abstract and also seems insignificant,” Hsu said.
Have you read?
.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo{-webkit-transition:all 0.15s ease-out;transition:all 0.15s ease-out;cursor:pointer;-webkit-text-decoration:none;text-decoration:none;outline:none;color:inherit;}.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo:hover,.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo[data-hover]{-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;}.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo:focus,.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo[data-focus]{box-shadow:0 0 0 3px rgba(168,203,251,0.5);} this is how carbon capture could help us meet key paris agreement goals, what role does climate justice play in the paris agreement, what’s the difference between 1.5 and 2 degrees of global warming, the 1.5°c global warming limit is still within grasp – here's how we can reach it.
Suzy Goulding, head of sustainability for Asia Pacific and Middle East at public relations firm MSL, would agree. It was hard for most people to understand the complexities of climate change and its effects at a macro level, she said.
“I don’t think talking about the temperature limit and targets was ever that helpful in motivating businesses and policymakers to make sustainable changes.”
“Much more effective is to stress how these temperature changes are likely to impact businesses, communities and individuals,” Goulding said.
People understood how the weather affected their daily lives, and would be motivated to act if they believed they could help to improve their communities directly, she said, adding that the focus should be on targets around innovation, investment and awareness-building.
Goulding said there should be “a constant stream of good news stories” of positive change globally to show that the climate challenges can be overcome to spur action, rather than communicating on targets which are “pretty meaningless to the vast majority”.
Don't miss any update on this topic
Create a free account and access your personalized content collection with our latest publications and analyses.
License and Republishing
World Economic Forum articles may be republished in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International Public License, and in accordance with our Terms of Use.
The views expressed in this article are those of the author alone and not the World Economic Forum.
Related topics:
The agenda .chakra .wef-n7bacu{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;font-weight:400;} weekly.
A weekly update of the most important issues driving the global agenda
.chakra .wef-1dtnjt5{display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;-webkit-flex-wrap:wrap;-ms-flex-wrap:wrap;flex-wrap:wrap;} More on Climate Action .chakra .wef-17xejub{-webkit-flex:1;-ms-flex:1;flex:1;justify-self:stretch;-webkit-align-self:stretch;-ms-flex-item-align:stretch;align-self:stretch;} .chakra .wef-nr1rr4{display:-webkit-inline-box;display:-webkit-inline-flex;display:-ms-inline-flexbox;display:inline-flex;white-space:normal;vertical-align:middle;text-transform:uppercase;font-size:0.75rem;border-radius:0.25rem;font-weight:700;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;line-height:1.2;-webkit-letter-spacing:1.25px;-moz-letter-spacing:1.25px;-ms-letter-spacing:1.25px;letter-spacing:1.25px;background:none;padding:0px;color:#B3B3B3;-webkit-box-decoration-break:clone;box-decoration-break:clone;-webkit-box-decoration-break:clone;}@media screen and (min-width:37.5rem){.chakra .wef-nr1rr4{font-size:0.875rem;}}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-nr1rr4{font-size:1rem;}} See all

Climate anxiety is on the rise — here's what we do about it
Britt Wray and Kyle McKinley
May 31, 2024

Is public mobility the next public transport revolution?
Lars Christian Grødem-Olsen and Nils Fearnley
May 30, 2024

Frugal innovation: 3 principles to help improve food production
Navi Radjou
May 29, 2024

Post breakthrough: How AI can lift climate research out of the lab and into the real world
Joe Wegener, Mehdi Ghissassi and Hamid Maher

How MENA’s biggest actors can help the region’s suppliers and SMEs to decarbonize
Akram Alami and Kelsey Goodman
May 27, 2024

3 key ways to meaningfully engage Indigenous peoples in climate action
Amanda Young and Ginelle Greene-Dewasmes
share this!
May 28, 2024
This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies . Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
Health risks from global warming can help drive city climate action, study finds
by Hayley Dunning, Imperial College London
Cities around the world were more likely to maintain climate action and enact "green recovery" long-term plans after the pandemic if local decision-makers were more alert to the health risks of climate change, a new global study has shown.
The health benefits of tackling climate change, such as cleaner air and more access to green spaces , were key drivers in city officials' decisions to continue with climate plans despite funding shortfalls caused by the COVID-19 crisis.
Overall, the study showed that enduring and ambitious climate action during the pandemic was more common in cities in the Global South than in Europe or North America, despite greater funding challenges.
Officials in these cities were also more likely to employ successful practices such as partnering with other cities to strengthen climate action plans, or with businesses to bolster sustainability initiatives.
Study first author Dr. Tanya O'Garra, from the Center for Environmental Policy at Imperial College London, and Middlesex University, said, "Nearly 60% of people live in cities worldwide, which can be economically beneficial for them, but city-dwellers are increasingly vulnerable to multiple crises caused by pandemics, conflict and climate change itself.
"City leaders often pave the way with ambitious climate action until calls to tackle these other threats can draw funds away from their climate goals. Because these major challenges are so intertwined, this leaves their populations more vulnerable to all risks.
"If we find out how city officials can maintain action in the face of such challenges, we can help large populations, especially the poorest and most vulnerable to these interconnected risks, avoid the most serious consequences of climate change ."
The research, conducted by researchers in Canada, Germany, the Netherlands, the United States and the U.K., is published in the journal Nature Cities .
Driving climate action
The team analyzed survey data provided by city officials on the Carbon Disclosure Platform (CDP) from 2021, and other sources, to assess how 793 cities globally responded to the COVID-19 crisis in terms of their climate actions, funding and green recovery efforts.
While they found that in the short term, the majority of city decision-makers kept up their climate commitments, green recovery plans were set up in only 43% of cities, suggesting the remainder of the cities are not investing in longer-term climate plans.
Many previous studies of local city-based climate plans have focused on North America and Europe, but in this study 48% of the cities assessed were in the Global South. The results show that, in general, decision-makers for Global South cities have higher ambition in climate action and promoted more green recovery efforts despite facing greater funding shortfalls than cities in Europe and North America.
The team identified two broad reasons underlying city officials' commitments to climate action. The first is exposure to environmental stress: in cities where citizens experience more climate-related issues (for example, climate hazards like floods or droughts, or persistent issues like air pollution) officials are more motivated to pursue sustained climate action.
The second was early engagement with climate and sustainability: the more that city officials had already engaged in addressing climate and sustainability issues (for example, by joining climate networks, or by aligning economic development with sustainability), the more likely these issues had become embedded in city policies, processes and interactions, making them more likely to continue even under a crisis scenario.
Measuring motivations
The team are now conducting in-depth interviews with city planning and administration officials in a selection of the cities. Preliminary interviews with officials in Kochi, India, confirmed the credit for their resilience was due to many of the factors the team had identified in the data.
For example, interviewees identified the benefits of existing coordination between state and local bodies and engagement with different stakeholders in planning, including academics, entrepreneurs, civil society organizations and the public.
They noted that the pandemic also led to an increased focus on climate action in the city, which has also occurred after other natural disasters.
Journal information: Nature Cities
Provided by Imperial College London
Explore further
Feedback to editors
Study investigates a massive 'spider' pulsar
38 minutes ago

Greener, more effective termite control: Natural compound attracts wood eaters
2 hours ago

Shear genius: Researchers find way to scale up wonder material, which could do wonders for the Earth

New vestiges of the first life on Earth discovered in Saudi Arabia
16 hours ago

Mussels downstream of wastewater treatment plant contain radium, study reports
18 hours ago

A new way to see viruses in action: Super-resolution microscopy provides a nano-scale look

Martian meteorites deliver a trove of information on red planet's structure

New imager acquires amplitude and phase information without digital processing
19 hours ago

AI helps scientists understand cosmic explosions

'Forever chemical' discovery can aid drinking water treatment
Relevant physicsforums posts, iceland warming up again - quakes swarming.
20 hours ago
Mount Ibu, Indonesia erupts
May 29, 2024
Adirondack Mountains and earthquakes
May 23, 2024
The Secrets of Prof. Verschure's Rosetta Stones
Mt. vesuvius 1944 eruption light show -- static electricity.
May 22, 2024
Can a glass of water be filled to its edge?
May 21, 2024
More from Earth Sciences
Related Stories

Sister cities can help communities better navigate the climate crisis, research suggests
May 3, 2024
What makes people tick environmentally?
May 7, 2024
Transforming urban sustainability: New study reveals cities' crucial contribution to meeting decarbonization goals
Aug 31, 2023

North American cities may see a major species turnover by the end of the century
Mar 27, 2024

African cities can do more to protect children from climate change
Apr 21, 2022

Scientists create framework to guide development and assessment of urban climate action plans
Nov 30, 2023
Recommended for you

No new fossil fuel projects needed in the transition to Net Zero, researchers say
21 hours ago

Study of radioiodine sorption and transport could help protect groundwater

Reduced sulfur content in shipping fuel associated with increased maritime atmospheric warming
May 30, 2024
A local bright spot among melting glaciers: 2,000 km of Antarctic ice-covered coastline has been stable for 85 years
Let us know if there is a problem with our content.
Use this form if you have come across a typo, inaccuracy or would like to send an edit request for the content on this page. For general inquiries, please use our contact form . For general feedback, use the public comments section below (please adhere to guidelines ).
Please select the most appropriate category to facilitate processing of your request
Thank you for taking time to provide your feedback to the editors.
Your feedback is important to us. However, we do not guarantee individual replies due to the high volume of messages.
E-mail the story
Your email address is used only to let the recipient know who sent the email. Neither your address nor the recipient's address will be used for any other purpose. The information you enter will appear in your e-mail message and is not retained by Phys.org in any form.
Newsletter sign up
Get weekly and/or daily updates delivered to your inbox. You can unsubscribe at any time and we'll never share your details to third parties.
More information Privacy policy
Donate and enjoy an ad-free experience
We keep our content available to everyone. Consider supporting Science X's mission by getting a premium account.
E-mail newsletter

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Here are 10 ways you can be part of the climate solution: 1. Spread the word. Encourage your friends, family and co-workers to reduce their carbon pollution. Join a global movement like Count Us In, which aims to inspire 1 billion people to take practical steps and challenge their leaders to act more boldly on climate.
Climate change mitigation refers to any action taken by governments, businesses or people to reduce or prevent greenhouse gases, or to enhance carbon sinks that remove them from the atmosphere. These gases trap heat from the sun in our planet's atmosphere, keeping it warm. Since the industrial era began, human activities have led to the ...
Mitigation is action to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and limit the amount of warming our planet will experience. Adaptation is action to help people adjust to the current and future effects of climate change. 1. These two prongs of climate action work together to protect people from the harms of climate change: one to make future climate ...
Tackling Climate Change Goal 13 calls for urgent action to combat climate change and its impacts. ... of climate change mitigation progress and pledges, and examines the sources of global ...
Generally speaking, here are some examples of mitigation strategies we can use to slow or stop the human-caused global warming ( learn more ): Where possible, we can switch to renewable sources of energy (such as solar and wind energy) to power our homes and buildings, thus emitting far less heat-trapping gases into the atmosphere.
The chapter includes an analysis of 60 individual actions which can help fight climate change, building on research led by Diana Ivanova at the University of Leeds - and to which I contributed ...
Climate change is defined as the shift in climate patterns mainly caused by greenhouse gas emissions from natural systems and human activities. So far, anthropogenic activities have caused about 1.0 °C of global warming above the pre-industrial level and this is likely to reach 1.5 °C between 2030 and 2052 if the current emission rates persist. In 2018, the world encountered 315 cases of ...
5. Reduce water waste. Saving water reduces carbon pollution, too. That's because it takes a lot of energy to pump, heat, and treat your water. So take shorter showers, turn off the tap while ...
The MIT community fundamentally agrees that climate change presents grave risks that demand society's urgent attention. The challenge requires an aggressive and pragmatic plan to achieve a net zero carbon global energy system, the sooner the better, for all of humankind. If academia, business, government, and citizens act together toward this ...
Climate change mitigation means reducing the net release of greenhouse gas emissions that are warming our planet. The Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) highlights the urgency of needed climate actions: global emissions will have to decline by 43% from 2019 by 2030, and rapidly decrease to net-zero by 2050 if we are to stay within the safety limits ...
Be Fashion 'Smart'. The global fashion industry - particularly fast fashion - contributes to climate change in multiple ways, especially in terms of the emissions pumped into the atmosphere during every stage of the process (from manufacturing to shipping). With emissions from textile manufacturing alone projected to rise by 60% by 2030 ...
The dashed circles indicate the global maximum mitigation potential and the solid circles indicate the mitigation potential at ≤US$100 tCO 2 e −1 with numbers to indicate estimated GtCO 2 e yr ...
The scientific, economic, and policy aspects of climate change are already a challenge to communicate, without factoring in the distractions and deflections from organized programs of misinformation and denial. Here, four scholars, each with decades of research on the climate threat, take on the task of explaining our current understanding of ...
Here are 16 actions: These actions, derived from experts and research by the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) alongside others, are featured as part the Count Us In campaign, a diverse coalition of culture, faith, sport, cities and businesses. Organizers hope the activities and support of the partners will inspire one billion people ...
A spark of change. "Most human beings have an almost infinite capacity for taking things for granted," says Aldous Huxley in one of his books. He perfectly summarises the biggest cause of the issues the world of today struggles with, the issues that are created by humans' tendency to ignore the consequences of their actions.
The potential to protect, restore and use ecosystems as tools to tackle climate change has gained increasing traction under the broad/overarching framework of NbS, or 'natural climate solutions' (NCS) where the context is mitigation of climate change . NbS can make a partial contribution to slowing and limiting global warming, while also ...
Integrating adaptation and mitigation can accelerate climate action in a fair way that has multiple co-benefits and mitigate potential trade-offs. ... R. & Dahlman, L. Climate Change: Global ...
Climate change is a long-lasting change in the weather arrays across tropics to polls. It is a global threat that has embarked on to put stress on various sectors. This study is aimed to conceptually engineer how climate variability is deteriorating the sustainability of diverse sectors worldwide. Specifically, the agricultural sector's vulnerability is a globally concerning scenario, as ...
Most global climate change mitigation pathways to limit warming to 1.5 °C and 2 °C, modeled by Integrated Assessment Models (IAMs), rely heavily on large-scale land-related CDR, including the ...
The rapid growth of artificial intelligence (AI) is reshaping our society in many ways, and climate change is no exception. This Perspective presents a framework to assess how AI affects GHG ...
When it comes to the science of climate change, psychology has long taken a back seat to the geophysical sciences. Now, more organizations and policymakers are recognizing the vital role that psychology can play in finding solutions to mitigate global warming—and helping people adapt to the inevitable changes to come.
It excluded 40 irrelevant papers due to copied from a previous search after readings tiles, abstract and full pieces. The criteria for inclusion were: (i) articles focused on "Global Climate Change Impacts, adaptation, and sustainable mitigation measures," and (ii) the search key terms related to study requirements.
To limit global temperature rise to well below 2°C and as close as possible to 1.5°C above pre-industrial levels, it is essential that businesses, policy-makers, and civil society advance comprehensive near- and long-term climate actions in line with the goals of the Paris Agreement on climate change.
As climate change and environmental degradation became a top priority for the Chinese government, it participated more in global climate talks, eventually becoming "a leader on climate change ...
A UNEP report released last year revealed the number of climate change litigation cases rose to 2,180 in 2022 from 884 in 2017. The type of cases has varied, with some plaintiffs challenging the lack of enforcement of climate-related laws. Other litigants are seeking to keep fossil fuels in the ground and hold corporations liable for damage to ...
Actions could include: Campaigning to produce behavioral change. Developing more sustainable commuting. Producing products and food locally. Providing services to people affected by climate change. Reducing the use of energy in buildings. Local solutions for sustainable energy access and transformation. Creating wealth from waste.
A demonstrator at the People's Climate March (2017). Individual action on climate change can include personal choices with regards to diet, travel, lifestyle, consumption of goods and services, family size and so on.Individuals can also get active in local and political advocacy work around climate action.People who wish to reduce their carbon footprint (particularly those in high income ...
Local governments are expected now more than ever to lead climate action planning as climate change intensifies and urbanization increases rapidly. However, studies indicate limitations in the comprehensiveness and level of integration of adaptation and mitigation in existing climate action plans. To develop suitable climate action plans that are comprehensive and consistent with globally ...
Effects of climate change are well documented and growing for Earth's natural environment and human societies. Changes to the climate system include an overall warming trend, changes to precipitation patterns, and more extreme weather.As the climate changes it impacts the natural environment with effects such as more intense forest fires, thawing permafrost, and desertification.
Health risks from global warming can help drive city climate action, study finds. by Hayley Dunning, Imperial College London. Count of green recovery Interventions in cities by CDP geographic ...