- New QB365-SLMS
- 12th Standard Materials
- 11th Standard Materials
- 10th Standard Materials
- 9th Standard Materials
- 8th Standard Materials
- 7th Standard Materials
- 6th Standard Materials
- 12th Standard CBSE Materials
- 11th Standard CBSE Materials
- 10th Standard CBSE Materials
- 9th Standard CBSE Materials
- 8th Standard CBSE Materials
- 7th Standard CBSE Materials
- 6th Standard CBSE Materials
- Tamilnadu Stateboard
- Scholarship Exams
- Scholarships

CBSE 10th Standard Science Subject Life Processes Chapter Case Study Questions With Solution 2021
By QB365 on 21 May, 2021
QB365 Provides the updated CASE Study Questions for Class 10 , and also provide the detail solution for each and every case study questions . Case study questions are latest updated question pattern from NCERT, QB365 will helps to get more marks in Exams
QB365 - Question Bank Software
Cbse 10th standard science subject life processes case study questions with solution 2021.
10th Standard CBSE
Final Semester - June 2015
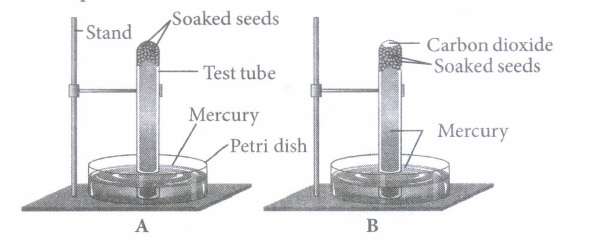
(ii) Fermentation is represented by the equation \(\text { (a) } \mathrm{C}_{6} \mathrm{H}_{12} \mathrm{O}_{6}+6 \mathrm{O}_{2} \rightarrow 6 \mathrm{CO}_{2}+6 \mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}+686 \mathrm{kcal}\) \(\text { (b) } \mathrm{C}_{6} \mathrm{H}_{12} \mathrm{O}_{6} \rightarrow 2 \mathrm{C}_{2} \mathrm{H}_{5} \mathrm{OH}+2 \mathrm{CO}_{2}+59 \mathrm{kcal}\) \(\text { (c) } 6 \mathrm{CO}_{2}+12 \mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O} \frac{\text { Light }}{\text { Chlorophyll }}>\mathrm{C}_{6} \mathrm{H}_{12} \mathrm{O}_{6}+6 \mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}+6 \mathrm{O}_{2}\) \(\text { (d) } 6 \mathrm{CO}_{2}+6 \mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O} \rightarrow \mathrm{C}_{6} \mathrm{H}_{12} \mathrm{O}_{6}+6 \mathrm{O}_{2} \text { . }\) (iii) A test tube containing molasses solution and yeast is kept in a warm place overnight. The gas collected from this mixture
(iv) Ethyl alcohol fermentation occurs in
(v) Though vertebrates are aerobes, but their (i) show anaerobic respiration during (ii) During this (iii) of skeletal muscle fibres is broken down-to release lactic acid and energy. Lactic acid, if accumulates causes muscle fatigue. Fill up the blanks in the above paragraph and select the correct option
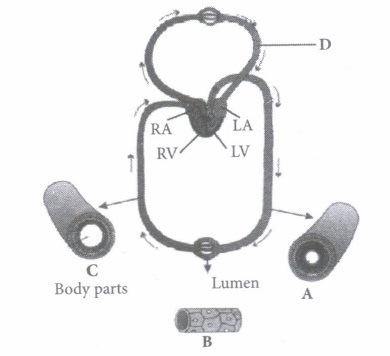
(iii) Which of the following animals shows double circulatory pathway?
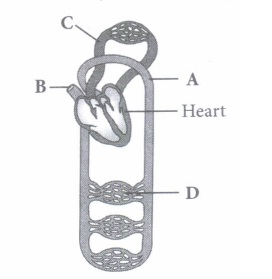
(v) Select the option which properly represents pulmonary circulation in humans. \(\text { (a) Left auricle } \frac{\text { Deoxygenated }}{\text { blood }}{\longrightarrow} \text { Lungs } \frac{\text { Oxygenated }}{\text { blood }} \text { Right ventricle }\) \(\text { (b) Left auricle } \frac{\text { Oxygenated }}{\text { blood }}{\longrightarrow} \text { Lungs } \frac{\text { Deoxygenated }}{\text { blood }}{\longrightarrow} \text { Right ventricle }\) \(\text { (c) Right ventricle } \frac{\text { Deoxygenated }}{\text { blood }}{\longrightarrow} \text { Lungs } \frac{\text { Oxygenated }}{\text { blood }} \rightarrow \text { Left auricle }\) \(\text { (d) Right ventricle } \frac{\text { Oxygenated }}{\text { blood }}>\text { Lungs } \frac{\text { Deoxygenated }}{\text { blood }} \gg \text { Left auricle }\)
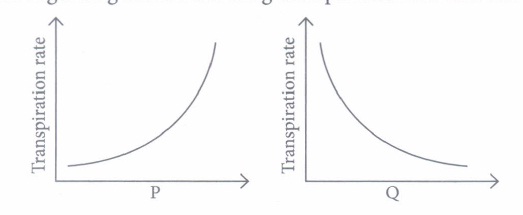
Transpiration is the evaporative loss of water by plants. It occurs mainly through the stoma in the leaves. Besides the loss of water vapour in transpiration, exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the leaf also occurs through pores called stomata. Normally stomata remain open in the day time and close during the night (i) Which of the following will not directly affect transpiration?
|
| |
(v) Which of the following sequences is correct to initiate inspiration? (I) The contraction of intercostal muscles raises the ribs and sternum (II) Volume of thorax increases (III) Intrathoracic pressure of the lungs decreases (IV) Diaphragm contraction (v) Air rushes into lungs
The green plants make their food, through photosynthesis and are therefore called autotrophs. All other organisms depend upon green plants for food and are referred to as heterotrophs. Green plants carry out photosynthesis by using light energy of sun. The first phase of reactions are directly light driven therefore called light reactions. The second phase of reactions are not directly light driven but are dependent on the products of light reactions and are called dark reactions. (i) Which of the following is produced during the light phase of photosynthesis?
(ii) In the overall process of photosynthesis, the number of sugar molecules produced is
(v) Following table summarises the differences between light and dark reactions.
| (I) These are also called biosynthetic phase | These are also called photochemical phase. |
| (II) These reactions occur over thylakoids. | These reactions occur in stroma of chloroplasts |
| (III) These produce assimilatory power i.e NADPH and ATP | These consume NADPH and ATP |
| (IV) These are directly dependent upon light | They depend upon the products synthesised during light reactions |
Which of the following is correct group of differences?
*****************************************
Cbse 10th standard science subject life processes case study questions with solution 2021 answer keys.
(i) (c): In the test tube full of mercury (figure A) there is no air and, therefore, the introduced soaked seeds do not get air for aerobic respiration. But they are capable of respiration in the absence of oxygen as is indicated by the evolution of carbon dioxide (figure B). Therefore, anaerobic respiration takes place in the seeds in the absence of free oxygen. The experiment also shows that CO 2 is evolved in anaerobic respiration of seeds. (ii) (b) (iii) (d): The given process is an example of alcoholic fermentation, thus the gas produced is CO 2 . (iv) (c): Ethyl alcohol fermentation occurs in fungi such as Rhizopus, yeast and bacteria. (v) (a): Muscle fatigue is the reduction in force of contraction of a muscle after prolonged stimulation. In the absence of oxygen, skeletal muscle of human beings can contract for a short time, but it gets fatigued soon. This is due to the fact that in the absence of oxygen, products of glycolysis mainly lactic acid is not disposed off and accumulates in the muscles. This leads to muscle fatigue and pain in the muscles. A muscle gets fatigued sooner after a strenuous exercise than after a mild exercise. Faster breathing for sometime after a strenuous exercise supplies extra oxygen, disposes off excess lactic acid and muscle fatigue disappears.
(i) (c): A- Artery: Carries blood from heart to different body parts. It is thick-walled and elastic. It acts as a "pressure reservoir" for maintaining the blood flow. B - Capillary : Nutrients, hormones, gases, etc. can diffuse into tissue cells through capillaries and vice versa. It is thin-walled, and only one cell layer thick resting on basement membrane. C - Vein: Brings blood from different body parts to the heart. It is thin-walled and act as low-resistance conduct for blood flow. D - Pulmonary vein: Two pulmonary veins from each lung transport the oxygenated blood to the left atrium. (ii) (d): In amphibians, the left atrium receives oxygenated blood from the gills/lungs/skin and the right atrium gets the deoxygenated blood from other body parts. However, they get mixed up in the single ventricle which pumps out mixed blood i.e., incomplete double circulation (iii) (d): Whale is a mammal and in mammals, two separate circulatory pathways are found - systemic circulation and pulmonary circulation. Oxygenated and deoxygenated bloods received by the left and right atria respectively pass on to the left and right ventricles. Thus, oxygenated and deoxygenated bloods are not mixed. This is referred to as double circulation. (iv) (a) (v) (c): Pulmonary circulation is the movement of blood between heart and lungs. During this pathway deoxygenated blood entering the right atrium, moves into the right ventricle. From here it moves through the pulmonary arch into the lungs for oxygenation. Then from lungs the oxygenated blood moves into the left atrium through pulmonary veins.
(i) (d) (ii) (d) (iii) (b): The epidermal surface of the leaf exhibits a large number of minute openings called stomata. The stomata are bordered by two specialized epidermal cells - the guard cells which in some cases are accompanied by subsidiary cells. The walls of guard cells are unevenly thickened. Each guard cell has thick, inelastic inner wall and thin, elastic outer wall. Stomatal aperture is present in between the guard cells. Guard cells are not always surrounded by accessory cells or subsidiary cells. (iv) (b) (v) (a)
(i) (c) : Number of RBCs per cubic millimetre of blood is likely to be higher in people living at high altitudes. This is in response to the air being less dense at high altitude and thus more RBCs (and hence more Hb) are needed to absorb the required amount of O 2 from the air having low pO 2 (partial pressure of O 2 ). (ii) (c): The change from II to III indicates decrease in the volume of lungs and thus, increase in the pressure of air inside the lungs. This results in movement of air out of the lungs. (iii) (c) (iv) (b): p-pharynx, q-trachea, r-alveoli, s-diaphragm, t-ribs (v) (c)
(i) (d): In light reaction of photosynthesis assimilatory power is produced, i.e., energy rich ATP molecules and reduced coenzyme NADPH. (ii) (d): The equation of photosynthesis may be represented as \(6 \mathrm{CO}_{2}+12 \mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O} \rightarrow \mathrm{C}_{6} \mathrm{H}_{12} \mathrm{O}_{6}+6 \mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}+6 \mathrm{O}_{2}\) No. of C 6 H 12 O 6 (sugar) molecules produced =1 (iii) (c) (iv) (b): Light reactions (or photochemical phase) of photosynthesis mainly occur on the grana thylakoids. Dark reactions (or biosynthetic phase) which involve synthesis of carbohydrates by CO 2 fixation, occur inthe stroma (or matrix) of chloroplasts. The chloroplast matrix of higher plants stores starch temporarily in the form of starch granules. (v) (b): Light reactions are also called photochemical phase whereas dark reactions are also called biochemical phase.
Related 10th Standard CBSE Science Materials
10th standard cbse syllabus & materials, cbse 10th maths probability chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths statistics chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths surface areas and volumes chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths areas related to circles chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths circles chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths some applications of trigonometry chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths introduction to trigonometry chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths coordinate geometry chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths triangles chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths arithmetic progressions chapter case study questions with answers, cbse 10th maths quadratic equations chapter case study questions with answers, cbse 10th social science the making of a global world chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th social science nationalism in india chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th social science the rise of nationalism in europe chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths pair of linear equation in two variables chapter case study question with answers.

Class VI to XII
Tn state board / cbse, 3000+ q&a's per subject, score high marks.

10th Standard CBSE Study Materials

10th Standard CBSE Subjects

Gurukul of Excellence
Classes for Physics, Chemistry and Mathematics by IITians
Join our Telegram Channel for Free PDF Download
Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Life Processes
- Last modified on: 3 years ago
- Reading Time: 7 Minutes
In CBSE Class 10 Science Paper, Students will have to answer some questions based on Assertion and Reason . There will be a few questions based on case studies and passage based as well. In that, a paragraph will be given, and then the MCQ questions based on it will be asked.
Here, we have provided case based/passage based questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Life Processes .
Question 1:
Read the following and answer any four questions from (i) to (v).
All living cells need nutrients, O, and other essential substances. Also, the waste and harmful substances need to be removed continuously for healthy functioning of cells. So, a well developed transport system is mandatory for living organisms. Complex organisms have special fluids within their bodies to transport such materials. Blood is the most commonly used body fluid by most of the higher organisms. Lymph also helps in the transport of certain substances.
(i) Which of the following does not exhibit phagocytic activity? (a) Monocytes (b) Neutrophils (c) Basophil (d) Macrophage
(ii) Amount of blood corpusles in changed in dengue fever. One of the common symptoms observed in people infected with dengue fever is (a) significant decrease in RBC count (b) significant decrease in WBC count (c) significant decrease in platelets count (d) significant increase in platelets count.
(iii) Why are WBCs called soldiers of the body? (a) They are capable of squeezing out of blood capillaries. (b) They are manufactured in bone marrow. (c) They fight against disease causing germs. (d) They have granular cytoplasm with lobed nucleus.
(iv) Name the blood cells, whose reduction in number can cause clotting disorder, leading to excessive loss of blood from the body. (a) Erythrocytes (b) Neutrophils (c) Leucocytes (d) Thrombocytes
(v) Which of the following is the correct feature of lymph? (a) It is similar to the plasma of blood, but is colourless and contains less proteins. (b) It is similar to the WBCs of blood, but is colourless and contain more proteins. (c) It is similar to the RBCs of blood and red in colour. (d) It contains more fats.
Question 2:
Heterotrophic nutrition is a mode of nutrition in which organisms obtain readymade organic food from outside sources. The organisms that depend upon outside sources for obtaining organic nutrients are called heterotrophs. Heterotrophic nutrition is of three types: saprophytic, parasitic and holozoic nutrition.
(i) In which of the following groups of organisms food material is broken outside the body and absorbed? (a) Mushroom, green plants, Amoeba (b) Yeast, mushroom, bread mould (c) Paramecium, Amoeba, Cuscuta (d) Cuscuta, lice, tapeworm
(ii) Which of the following is a parasite? (a) Yeast (b) Taenia (c) Amoeba (d) Earthworm
(iii) Which of the following is an example of saprotroph? (a) Grass (b) Mushroom (c) Amoeba (d) Paramecium
(iv) Heterotrophic nutrition involves (a) production of simple sugar from inorganic compounds (b) utilisation of chemical energy to prepare food (c) utilisation of energy obtained by plants (d) all of these.
(v) In Paramecium, food enters the body through (a) mouth (b) pseudopodia (c) cilia (d) cytostome
Download Books – Exam Special
Sample Papers for CBSE 2025 Exams
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 8 All Subjects (for 2025 Exams)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 9 All Subjects (for 2025 Exams)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 10 All Subjects (for 2025 Exams)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 All Subjects (for 2025 Exams)
CBSE Class 10 Most Downloaded Books
- CBSE Important Numerical Problems Class 10 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Practical Based Questions for Class 10 Science Board Exams
- CBSE Important Diagram Based Questions Class 10 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Most Repeated Questions for Class 10 Science Board Exams
CBSE Class 12 Most Downloaded Books
- CBSE Important Diagrams & Graphs Asked in Board Exams Class 12 Physics
- CBSE Important Numericals Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Laws & Principles Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Definitions Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- Master Organic Conversions CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Board Exams
- CBSE Class 12 Physics Chapterwise Important Questions
CBSE Class 8 Most Downloaded Books
- Worksheets for CBSE Class 8 Maths – Chapterwise
ICSE Class 10
- ICSE Important Numericals Class 10 Physics BOARD Exams (215 Numericals)
- ICSE Important Figure Based Questions Class 10 Physics BOARD Exams (230 Questions)
- ICSE Mole Concept and Stoichiometry Numericals Class 10 Chemistry (65 Numericals)
- ICSE Reasoning Based Questions Class 10 Chemistry BOARD Exams (150 Qs)
- ICSE Important Functions and Locations Based Questions Class 10 Biology
- ICSE Reasoning Based Questions Class 10 Biology BOARD Exams (100 Qs)
- ICSE Reasoning Based Questions Class 10 Geography BOARD Exams
- ICSE Revision Notes for Class 10 Chemistry BOARD Exams
- ICSE Revision Notes for Class 10 Physics BOARD Exams
ICSE Class 9
- ICSE Important Figure Based Questions Class 9 Physics Exams
- ICSE Important Numerical Problems for Class 9 Physics Exams
- ICSE Reasoning Based Questions Class 9 Geography BOARD Exams (150 Qs)
CBSE Chapter-Wise Test Papers
- CBSE Class 9 Science Chapterwise Test Papers
- CBSE Class 10 Science Chapterwise Test Papers
- CBSE Class 10 Maths Chapterwise Test Papers
- CBSE Class 10 Social Science Chapterwise Test Papers
- CBSE Class 12 Physics Chapterwise Test Papers
- CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Chapterwise Test papers
✨ Join our Online NEET Test Series for 499/- Only for 1 Year
Leave a Reply Cancel reply

Editable Study Materials for Your Institute - CBSE, ICSE, State Boards (Maharashtra & Karnataka), JEE, NEET, FOUNDATION, OLYMPIADS, PPTs
Discover more from Gurukul of Excellence
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Type your email…
Continue reading
- Life Processes Class 10 Case Study Questions Science Chapter 6

Last Updated on September 13, 2024 by XAM CONTENT
Hello students, we are providing case study questions for class 10 science. Case study questions are the new question format that is introduced in CBSE board. The resources for case study questions are very less. So, to help students we have created chapterwise case study questions for class 10 science. In this article, you will find case study questions for cbse class 10 science chapter 6 Life Processes.
| Life Processes | |
| Case Study Questions | |
| Competency Based Questions | |
| CBSE | |
| 10 | |
| Science | |
| Class 10 Studying Students | |
| Yes | |
| Mentioned | |

Table of Contents
Case Study Questions on Life Processes
Question 1:
Read the following and answer the questions given below:
Heterotrophic nutrition is a mode of nutrition in which organisms obtain readymade organic food from outside sources. The organisms that depend upon outside sources for obtaining organic nutrients are called heterotrophs. Heterotrophic nutrition is of three types: saprophytic, parasitic and holozoic nutrition.
(i) In which of the following groups of organisms food material is broken outside the body and absorbed? (a) Mushroom, green plants, Amoeba (b) Yeast, mushroom, bread mould (c) Paramecium, Amoeba, Cuscuta (d) Cuscuta, lice, tapeworm
Difficulty Level: Medium
Ans. Option (b) is correct. Explanation: Yeast, mushroom and bread mould have a saprophytic mode of nutrition which is chemoheterotrophic in nature. They breakdown complex organic substances by secreting digestive enzyme outside their body and absorb simple molecules as nutrients.
(ii) Which of the following is a parasite? (a) Yeast (b) Taenia (c) Amoeba (d) Earthworm
Ans. Option (b) is correct.
(iii) Which of the following is an example of saprotroph? (a) Grass (b) Mushroom (c) Amoeba (d) Paramecium
(iv) Heterotrophic nutrition involves (a) production of simple sugar from inorganic compounds (b) utilisation of chemical energy to prepare food (c) utilisation of energy obtained by plants (d) all of these.
Ans. Option (c) is correct. Explanation: Heterotrophic nutrition is mode of nutrition in which an organism depends on other living organisms for food.
(v) In Paramecium, food enters the body through (a) mouth (b) pseudopodia (c) cilia (d) cytostome.
Ans. Option (d) is correct. Explanation: Feeding apparatus in Paramecium consists of peristome, vestibule, buccal cavity, cytostome (cell mouth) and cytopharynx.
- Electricity Class 10 Case Study Questions Science Chapter 12
- The Human Eye and the Colourful World Class 10 Case Study Questions Science Chapter 11
- Metals and Non-metals Class 10 Case Study Questions Science Chapter 3
- Light – Reflection and Refraction Class 10 Case Study Questions Science Chapter 10
Acids Bases and Salts Class 10 Case Study Questions Science Chapter 2
Chemical reactions and equations class 10 case study questions science chapter 1, topics from which case study questions may be asked.
- Basic concept of nutrition, respiration, transport and excretion in plants and animals.
- Autotrophic Nutrition
- Heterotrophic Nutrition
- Photosynthesis
- Nutrition in Unicellular Organisms
- Human Digestive System
This chapter deals with the basic understanding of nutrition, respiration, transport and excretion in plants and animals. Life Processes are maintenance processes, which sustain orderly structure of living beings e.g. Plants use CO2, animals consume carbohydrate, fats, proteins etc. Continuous supply of energy and materials is needed for maintenance of life by these processes. Life on earth depends on carbon-based molecules, therefore, the sources of energy and materials are carbon-based. The way of life of different organisms depends on complexity of the carbon source. All living organisms use ATP as a source of energy, required for molecular movements, growth and maintenance of living structure.
Helpful Links for CBSE Class 10 Science Preparation
- Download 125 Important Case Study Questions for CBSE Class 10 Science
- Download 220 Important Assertion Reason Questions for CBSE Class 10 Science
- Download 225 Practical Based Questions for CBSE Class 10 Science
- Download 65 Important Numerical Problems for CBSE Class 10 Physics
- Download 60 Important Diagram Based Questions for CBSE Class 10 Physics
- Download 150 Most Repeated Questions for CBSE Class 10 Science
- Download Chapter Test for CBSE Class 10 Science

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Life Processes Case Study Questions
Q1: what are case study questions for cbse examinations.
A1: Case study questions in CBSE examinations typically involve scenarios or real-life examples, requiring students to apply their understanding of concepts to solve problems or analyze situations.
Q2: Why are case study questions important for understanding class 10 science chapters?
A2: Case study questions provide a practical context for students to apply theoretical knowledge to real-world situations, fostering deeper understanding and critical thinking skills.
Q3: How should students approach answering case study questions for CBSE?
A3: Students should carefully read the case study, identify the key issues or problems presented, analyze the information provided, apply relevant concepts and principles of chemical reactions and equations, and formulate well-supported solutions or responses.
Q4: Are there any resources available online for students to practice case study questions on class 10 science chapters for CBSE exams?
A4: Yes, several educational websites offer case study questions for CBSE students preparing for science examinations. We also offer a collection of case study questions for all classes and subject on our website. Visit our website to access these questions and enhance your learning experience. If you need more case study questions for your preparation, then you visit Physics Gurukul website.
Q5: How can students effectively prepare for case study questions on Life Processes for CBSE exams?
A5: Effective preparation strategies include regular revision of concepts, solving practice questions, analyzing case studies from previous exams, seeking clarification on doubts, and consulting with teachers or peers for guidance and support.
Q6: How can teachers incorporate case study questions on Life Processes class 10 science into classroom teaching?
A6: Teachers can integrate case studies into lesson plans, group discussions, or interactive activities to engage students in active learning, promote problem-solving skills, and facilitate a deeper understanding of Life Processes.
Q7: What is transportation?
A7: Transportation is the life process by which substances absorbed or synthesised in one part of the body are carried to other parts where they are consumed.
Q8: What is circulatory system?
A8: It is the system for transportation of substances within the body consisting of organs and fluids.
Q9: Name the instrument used to measure blood pressure.
A9: Sphygmomanometer
Q10: Why do the ventricles have thicker muscular walls as compared to the atria?
A10: Auricles collect the blood coming from veins with very low pressure and pass it to ventricles. Ventricles pump the blood into various organs of the body. They have thicker muscular walls to create sufficient pressure for pumping the blood.
Q11: What is lymph?
A11: Lymph is the tissue fluid formed by a part of blood that comes out of capillaries into extracellular space. It contains plasma, proteins and blood cells. It serves as a medium for transport of materials to and from individual cells.
Q12: What would be the consequences of deficiency of haemolglobin in our bodies?
A12: Haemoglobin present in red blood corpuscles serves as the respiratory pigment for transport of oxygen. If there is deficiency of haemoglobin in our body, the blood will not be able to carry sufficient oxygen. This will cause tiredness, shortness of breath and dizziness.
Q13: Why is it necessary to separate oxygenated and deoxygenated blood in mammals and birds?
A13: Mammals and birds are warm-blooded animals. To maintain their body temperature they need energy constantly. To release more energy by aerobic respiration they need more supply of oxygenated blood. Separation of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood in the heart allows a highly efficient supply of oxygen to the body.

Related Posts


IMAGES
VIDEO