
- Tips & Guides

How To Avoid Using “We,” “You,” And “I” in an Essay
- Posted on October 27, 2022 October 27, 2022
Maintaining a formal voice while writing academic essays and papers is essential to sound objective.
One of the main rules of academic or formal writing is to avoid first-person pronouns like “we,” “you,” and “I.” These words pull focus away from the topic and shift it to the speaker – the opposite of your goal.
While it may seem difficult at first, some tricks can help you avoid personal language and keep a professional tone.
Let’s learn how to avoid using “we” in an essay.
What Is a Personal Pronoun?
Pronouns are words used to refer to a noun indirectly. Examples include “he,” “his,” “her,” and “hers.” Any time you refer to a noun – whether a person, object, or animal – without using its name, you use a pronoun.
Personal pronouns are a type of pronoun. A personal pronoun is a pronoun you use whenever you directly refer to the subject of the sentence.
Take the following short paragraph as an example:
“Mr. Smith told the class yesterday to work on our essays. Mr. Smith also said that Mr. Smith lost Mr. Smith’s laptop in the lunchroom.”
The above sentence contains no pronouns at all. There are three places where you would insert a pronoun, but only two where you would put a personal pronoun. See the revised sentence below:
“Mr. Smith told the class yesterday to work on our essays. He also said that he lost his laptop in the lunchroom.”
“He” is a personal pronoun because we are talking directly about Mr. Smith. “His” is not a personal pronoun (it’s a possessive pronoun) because we are not speaking directly about Mr. Smith. Rather, we are talking about Mr. Smith’s laptop.
If later on you talk about Mr. Smith’s laptop, you may say:
“Mr. Smith found it in his car, not the lunchroom!”
In this case, “it” is a personal pronoun because in this point of view we are making a reference to the laptop directly and not as something owned by Mr. Smith.
Why Avoid Personal Pronouns in Essay Writing
We’re teaching you how to avoid using “I” in writing, but why is this necessary? Academic writing aims to focus on a clear topic, sound objective, and paint the writer as a source of authority. Word choice can significantly impact your success in achieving these goals.
Writing that uses personal pronouns can unintentionally shift the reader’s focus onto the writer, pulling their focus away from the topic at hand.
Personal pronouns may also make your work seem less objective.
One of the most challenging parts of essay writing is learning which words to avoid and how to avoid them. Fortunately, following a few simple tricks, you can master the English Language and write like a pro in no time.
Alternatives To Using Personal Pronouns
How to not use “I” in a paper? What are the alternatives? There are many ways to avoid the use of personal pronouns in academic writing. By shifting your word choice and sentence structure, you can keep the overall meaning of your sentences while re-shaping your tone.
Utilize Passive Voice
In conventional writing, students are taught to avoid the passive voice as much as possible, but it can be an excellent way to avoid first-person pronouns in academic writing.
You can use the passive voice to avoid using pronouns. Take this sentence, for example:
“ We used 150 ml of HCl for the experiment.”
Instead of using “we” and the active voice, you can use a passive voice without a pronoun. The sentence above becomes:
“150 ml of HCl were used for the experiment.”
Using the passive voice removes your team from the experiment and makes your work sound more objective.
Take a Third-Person Perspective
Another answer to “how to avoid using ‘we’ in an essay?” is the use of a third-person perspective. Changing the perspective is a good way to take first-person pronouns out of a sentence. A third-person point of view will not use any first-person pronouns because the information is not given from the speaker’s perspective.
A third-person sentence is spoken entirely about the subject where the speaker is outside of the sentence.
Take a look at the sentence below:
“In this article you will learn about formal writing.”
The perspective in that sentence is second person, and it uses the personal pronoun “you.” You can change this sentence to sound more objective by using third-person pronouns:
“In this article the reader will learn about formal writing.”
The use of a third-person point of view makes the second sentence sound more academic and confident. Second-person pronouns, like those used in the first sentence, sound less formal and objective.
Be Specific With Word Choice
You can avoid first-personal pronouns by choosing your words carefully. Often, you may find that you are inserting unnecessary nouns into your work.
Take the following sentence as an example:
“ My research shows the students did poorly on the test.”
In this case, the first-person pronoun ‘my’ can be entirely cut out from the sentence. It then becomes:
“Research shows the students did poorly on the test.”
The second sentence is more succinct and sounds more authoritative without changing the sentence structure.
You should also make sure to watch out for the improper use of adverbs and nouns. Being careful with your word choice regarding nouns, adverbs, verbs, and adjectives can help mitigate your use of personal pronouns.
“They bravely started the French revolution in 1789.”
While this sentence might be fine in a story about the revolution, an essay or academic piece should only focus on the facts. The world ‘bravely’ is a good indicator that you are inserting unnecessary personal pronouns into your work.
We can revise this sentence into:
“The French revolution started in 1789.”
Avoid adverbs (adjectives that describe verbs), and you will find that you avoid personal pronouns by default.
Closing Thoughts
In academic writing, It is crucial to sound objective and focus on the topic. Using personal pronouns pulls the focus away from the subject and makes writing sound subjective.
Hopefully, this article has helped you learn how to avoid using “we” in an essay.
When working on any formal writing assignment, avoid personal pronouns and informal language as much as possible.
While getting the hang of academic writing, you will likely make some mistakes, so revising is vital. Always double-check for personal pronouns, plagiarism , spelling mistakes, and correctly cited pieces.
You can prevent and correct mistakes using a plagiarism checker at any time, completely for free.
Quetext is a platform that helps you with all those tasks. Check out all resources that are available to you today.
Sign Up for Quetext Today!
Click below to find a pricing plan that fits your needs.
You May Also Like

Writing Under Pressure: Strategies for Excelling in Timed Essay Exams
- Posted on October 24, 2024

Writing with Confidence: Strategies for Overcoming Self-Doubt and Imposter Syndrome
- Posted on October 18, 2024 October 22, 2024

Best AI Detector Tools for Content, Images & Videos
- Posted on October 9, 2024

7 Best AI Detectors for Teachers & Professors (+ How To Choose)
- Posted on September 25, 2024 October 9, 2024

How Professors Check for Plagiarism (+Tips for Plagiarism Prevention)
- Posted on September 18, 2024 October 9, 2024

How Accurate Are AI Content Detectors? (+ How They Work)
- Posted on September 6, 2024 October 18, 2024

Best Chat GPT Detector
- Posted on August 22, 2024 October 9, 2024

The Importance of Proofreading: Techniques for Catching Errors and Polishing Your Writing
- Posted on August 16, 2024 August 19, 2024
Input your search keywords and press Enter.
- Have your assignments done by seasoned writers. We work 24/7. Just email us at:
- [email protected]

How to Replace I in Essays: Alternative 3rd Person Pronouns

replacing I in essays
Learning how to write an essay without using ‘I,’ ‘We,’ or ‘You,’ and other personal languages can be challenging for students.
The best writing skills recommend not to use such pronouns. This guide explores how to replace ‘I,’ ‘We,’ or ‘You’ in an essay and the methods to avoid them.
For those of us who have been able to overcome this, you will agree that there was a time when you experienced a challenge when finding alternatives to clauses such as “I will argue” or “I think.”

The good thing is that there are several methods of communicating your point and writing an essay without using ‘I’ or related personal language.
Let us Write your Essays! No Plagiarism
Get an expert writer to score an A in your next essay assignment. Place your order today, and you will enjoy it.
Why Avoid Using Pronouns in Formal Writing
Before identifying the communication methods without using personal language like “I,” it is best to know why we should avoid such language while writing essays.
The most important reason for avoiding such language is because it is not suitable for formal writing such as essays. Appropriate professional English should not include any form of personal pronouns or language.

The second and equally important reason to avoid using personal language while writing an essay is to sound impersonal, functional, and objective.
In formal English, personal pronouns conflict with the idea of being impersonal, functional, and objective because they make redundant references to the writer and other people.
Personal pronouns will make an essay seem to contain only the writer’s perspectives and others they have deliberately selected. Again, they will make the work appear subjective.
Another reason to avoid personal language while coming up with an essay is to avoid sounding as if you have an urgent need to impress the reader through wording.
Personal pronouns like “you” and “I” tend to suggest something important that is away from what the writing is all about.
By continually using “I,” “we,” or “you,” you are taking the reader’s attention from the essay to other personal issues. The essay becomes all about the writer.
That being said, let’s explore how to replace “I” in an essay.
Custom Essay Writing Service by vetted writers
Ways of avoiding pronouns “i,” “you,” and “we” in an essay.
You can replace the pronouns ‘I’, ‘You’, and ‘We’ by replacing them with acceptable wording, applying passive voice instead of pronouns, Using a third-person perspective, adopting an objective language, and including strong verbs and adjectives.
In our other guide, we explained the best practices to avoid using ‘you’ in essay writing and use academically sound words. Let us explore each of these strategies in detail.
1. Replacing it with an Acceptable Wording
This is a very good strategy for replacing “I” in an essay. The problem is that it is often difficult to find the right word to replace the personal pronoun. Though this is the case, “I” has some alternatives.
For example, if the verb that follows it revolves around writing and research, such as “…will present” or “…have described”, it is best to replace “I” with text-referencing nouns such as “the essay.”
If you wanted to say “I will present” or “I have described”, then the alternative will be “the essay will present,” or “as described in the essay.”
Another method of replacing “I” in an essay is using appropriate wording like “this writer” if the verb’s action is not within the text.
While this is sometimes acceptable, it is often advised to have no words here by using passive verbs or their equivalents.
A wording that may also be used but rarely suitable is “the researcher”. This alternative can only be used when your actions as a writer are completely detached from the writing.
2. Using Passive voice Instead of Pronouns
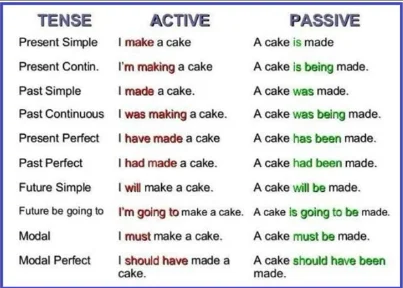
Another way to replace “I” and other personal pronouns in an essay is to use passive voice. This is achieved by transforming an active verb passive.
Though this is the case, the strategy is often difficult, and it may create sentence structures that are not acceptable in formal writing and language.
The sentences in which “I” can be successfully changed using this strategy is when an active verb describing an object is transformed into its passive form.
3. Using a Third-Person Perspective
This is a very important and applicable strategy when replacing “I” in an essay. This is where you avoid using first-person and second-person perspectives.
When referring to the subject matter, refer directly to them using the third person. For example, if you were to write, “I think regular exercise is good for mind and body”, you can replace it with “Regular exercise is good for mind and body”.
4. Use of Objective Language
Objective language is lost when a person uses informal expressions like colloquialisms, slang, contractions, and clichés. It is the reason why we discourage the use of contractions in essay writing so that you can keep things formal.
While informal language can be applicable in casual writing and speeches, it is not acceptable when writing essays. This is because you will be tempted to use a first-person perspective to convey your message.
5. Being Specific and using Strong Verbs and Adjectives
In most cases, essays that have been written using a lot of personal pronouns tend to be imprecise. When you want to avoid using “I” in your essay, try to be exact and straight to the point.
Personal pronouns tend to convey a subjective message, and it is up to the writer to explain their perspectives through writing.
Here, a writer will use a lot of “I think…” or “I believe…” to express their opinion. By doing so, the writer will end up wasting a lot of time explaining a concept.
Instead of doing that, it is best to look for appropriate verbs and adjectives to explain the points. Also, use objective language. Refer to the suggestions given by credible evidence instead of basing your arguments on what you think.
Get an essay written by a Team
Our team avoids plagiarism and ensures checks to guarantee a quality and ORIGINAL paper
Words to use Instead of Personal Pronouns like “You” and “I”
As noted, it is important to avoid using personal pronouns such as “You” and “I” when writing an essay.
By eliminating them or finding alternatives to them, your essay will be formal and objective. You can decide to eliminate them in a sentence.

For example, you could be having a sentence like “I think the author makes a valid point concerning capitalism.”
In this example, you can eliminate the personal language and write, “The author makes a valid point concerning capitalism.”
The second sentence goes straight to the point and is objective.
Other words to use instead of personal pronouns, like “You” and “I,” can be created when personal judgment words are avoided.
Instead, it is best to replace those words with those that refer to the evidence.
Examples of Ways to Replace Personal Pronouns
Below are examples of how personal judgment words can be replaced by words referring to the evidence.
- I feel – In light of the evidence
- From I think – According to the findings
- I agree – It is evident from the data that
- I am convinced – Considering the results
- You can see that – From the results, it is evident that
Using the third-person or “it” constructions can be used to replace personal pronouns like “You” and “I.” Such words also help to reduce the word count of your essay and make it short and precise.
For example, if you write “I conclude that, “replace those words with “it could be concluded that. ” Here, “it” constructions are helping replace personal pronouns to make the sentence more objective and precise.
To be more specific, words to replace personal pronouns like “I” include “one,” the viewer,” “the author,” “the reader,” “readers,” or something similar.
However, avoid overusing those words because your essay will seem stiff and awkward. For example, if you write, “I can perceive the plot’s confusion,” you can replace “I” by writing, “Readers can perceive the plot’s confusion.”
Words that can be used instead of personal pronouns like “You” include “one,” “the viewer,” reader,” “readers,” or any other similar phrases. It is similar to words that replace first-person pronouns.
For example, if you write “you can see that the poet’s tone is serious and urgent,” you can replace “You” by writing “readers/one can see that the poet’s tone is serious and urgent.”
Words to use Instead of “My” in an Essay
Since “My” demonstrates the possessiveness of something, in this case, the contents or thoughts within an essay, it makes the writing subjective. According to experts, writing should take an objective language . To do this, it is important to replace it.

You can replace the word “My” with “the”. For example, if you write, “My final thoughts concerning the issue are”, you can write, “The final thoughts concerning the issues are”.
In this case, the article “The” makes the sentence formal and objective.
Another method is eliminating the word “My” from the sentence to make it more objective and straight to the point.
In the same example above, if you write “My final thoughts concerning the issue are”, you can write “Final thoughts concerning the issue are”.
The major difference here is that the word “my” in the first example makes it subjective, and eliminating it from the sentence makes it sound formal and objective.
Final Advice
Therefore, when writing an essay, it is important to avoid personal pronouns like “You”, “I,” and “My.” Not all papers use third-person language. Different types of essays are formatted differently, a 5-paragraph essay is different from a 4-page paper , but all use third-person tones.
This is because an essay should be written in formal language, and using personal pronouns makes it appear and sound informal. Therefore, writing an essay without using ‘I’ is good.
Formal language makes your essay sound objective and precise. However, do not remove the first-person language when writing personal experiences in an essay or a paper. This is because it is acceptable and formal that way.
Order an Excellent Essay today!
Let us help you get that A in your next assignment. Place your order today, and you will enjoy the benefits.

With over 10 years in academia and academic assistance, Alicia Smart is the epitome of excellence in the writing industry. She is our managing editor and is in charge of the writing operations at Grade Bees.
Related posts

essay writing problems
10 Essay Writing Problems and their Easy Solutions

writing essay on your phone
How to Write an Essay or paper on your Phone: 3 Easy Ways

essay writing is important
7 reasons why Writing is Important in College & in Life

10 Better Ways To Say “Our” And “We” In Formal Essays
When writing formal essays, there are rules of English grammar that we need to follow. Sometimes, we need to change perspective, and instead of writing in the first person and saying ‘we,’ we need to stay in the third person. So, what are the best alternatives to saying ‘we?’

There are many alternatives to saying ‘we.’ The most preferred alternatives we use are ‘they,’ ‘the group,’ and ‘the team.’ These three alternatives are the more general alternatives that seem to be applicable in almost all contexts, especially ‘they’ as we simply remove ourselves from the narrative by using it.
‘They’ is the most general and preferred alternative to ‘we’ and ‘us.’ By using ‘they,’ we replace our first-person pronoun with a third-person pronoun that simply excludes ourselves from the narrative, making the essay sound more objective and formal. ‘They’ is also a pronoun that is applicable in all contexts.
Take a look at these examples below.
- Original: Humans are incredible creatures. We have so much creativity.
- Alternative: Humans are incredible creatures. They have so much creativity.
- Original: Our group will report tomorrow. We will talk about this month’s sales.
- Alternative: Their group will report tomorrow. They will talk about this month’s sales.
- Original: We simply hope the audience learned something from us.
- Alternative: They simply hope the audience learned something from them.
- Original: We’ve done our research, but we don’t have precise predictions yet.
- Alternative: They’ve done their research, but they don’t have precise predictions yet.
‘The group’ is a good, general alternative to saying ‘we’ in formal essays. However, this alternative specifies that we refer to ‘we’ as a group of individuals. Therefore, this alternative does not apply to populations of large scale like nations, humans, or races.
- Original: We were able to conclude the following findings.
- Alternative: The group was able to conclude the following findings.
- Original: We could not administer the test today due to certain circumstances.
- Alternative: The group could not administer the test today due to certain circumstances?
- Original: Our experimental set-ups did not yield any significant difference.
- Alternative: The group’s experimental set-ups did not yield any significant difference.
- Original: It is beneficial for us if more people participate in the study.
- Alternative: It is beneficial for the group if more people participate in the study.
‘The team’ is synonymous with ‘the group.’ It is another alternative to saying ‘we’ but implies that ‘we’ refers to a team or a group of individuals that are together for the same purpose. However, ‘the team’ does not apply to bigger populations, like an entire race or human population.
- Original: We are composed of individuals with a passion for learning.
- Alternative: The team is composed of individuals with a passion for learning.
- Original: The results of our work do not define our identity.
- Alternative: The results of the team’s work do not define the team’s identity.
- Original: We poured our best efforts into this project.
- Alternative: The team poured their best efforts into this project.
- Original: We do not tolerate any misconduct and violent behavior.
- Alternative: The team does not tolerate any misconduct and violent behavior.
‘The body’ is another alternative for saying ‘we’ in formal essays. We mostly use ‘body’ when referring to large groups of individuals like the audience, spectators, or students. However, we do not use it for extreme scales such as a race population, and the like.
- Original: We didn’t find the presentation interesting.
- Alternative: The body didn’t find the presentation interesting.
- Original: We have a lot of questions we want to ask the speaker after the talk.
- Alternative: The body has a lot of questions they want to ask the speaker after the talk.
- Original: We listened to different opinions on the issue.
- Alternative: The body listened to different opinions on the issue.
- Original: We were only able to watch the latter part of the program.
- Alternative: The body was only able to watch the latter part of the program.
The Organization
‘The organization’ is a more specific alternative for ‘we.’ In using this alternative, we refer to ‘we’ as an organization in the context we are talking or writing. This alternative is most applicable for organization-related things. However, do not use this alternative if the context does not involve an organization.
- Original: We will push through with the planned fundraising project.
- Alternative: The organization will push through with the planned fundraising project.
- Original: Our accomplishments this year are something we should be proud of.
- Alternative: The organization’s accomplishments this year are something they should be proud of.
- Original: We plan on collaborating with other organizations to plan the event.
- Alternative: The organization plans on collaborating with other organizations to plan the event.
- Original: We only accept people who have a passion for our advocacy.
- Alternative: The organization only accepts people who have a passion for their advocacy.
The Researchers
‘The researchers’ is a specific alternative to ‘we’ that we only use when we refer to ‘we’ as a group of researchers. We mostly use this alternative in writing research papers that need to be in the third-person perspective. However, we don’t use this alternative outside the scope of research.
- Original: We administered a total of three set-ups for the study.
- Alternative: The researchers administered a total of three set-ups for the study.
- Original: We encountered circumstances that provided the limitations of our research.
- Alternative: The researchers encountered circumstances that provided the limitations of their research.
- Original: After three months of observation, our conclusion is as follows.
- Alternative: After three months of observation, the researchers’ conclusion is as follows.
- Original: Our study would not be successful if not for the help of our research adviser.
- Alternative: The researchers’ study would not be successful if not for the help of their research adviser.
The Company
‘The company’ is another specific alternative for ‘we.’ We only use this alternative, if we are in the context that ‘we’ refers to a company. We use this mostly in business-related reports or presentations. Other than that, we don’t use this alternative for purposes that do not involve a company.
- Original: Our sales for this month are higher than last month.
- Alternative: The company’s sales for this month are higher than last month.
- Original: We only sell organic, vegan-friendly, and cruelty-free products.
- Alternative: The company only sells organic, vegan-friendly, and cruelty-free products.
- Original: We need to continuously track our demand and supply levels.
- Alternative: The company needs to continuously track its demand and supply levels.
- Original: Our vision and mission should guide us in all our endeavors.
- Alternative: The company’s vision and mission should guide the company in all its endeavors.
The Association
‘The association’ is also a specific alternative to ‘we.’ We only use this alternative if we are in a context to talk as part of or within an association. However, we do not use this alternative if we are not talking about, for, or as part of an association.
- Original: We will hold meetings every Friday to discuss weekly matters.
- Alternative: The association will hold meetings every Friday to discuss weekly matters.
- Original: Our job is to advocate and uphold democracy in our country.
- Alternative: The association’s job is to advocate and uphold democracy in our country.
- Original: Our goal directs the objectives of every endeavor we take care of.
- Alternative: The association’s goal directs the objectives of every endeavor it takes care of.
- Original: We are open to expanding the scope of its initiatives.
- Alternative: The association is open to expanding the scope of its initiatives.
‘Humans’ is a specific alternative for ‘we’ that we use only when we refer to ‘we’ as the entire human population. We cannot use ‘humans’ for small-scale groups like researchers or a company. We use this alternative only when we regard ‘we’ as the entire human population.
Take a look at the examples below.
- Original: We have so much potential inside us.
- Alternative: Humans have so much potential inside them.
- Original: Sometimes, even 24 hours isn’t enough for what we want to do in a day.
- Alternative: Sometimes, even 24 hours isn’t enough for what humans want to do in a day.
- Original: All of us have a desire to accomplish something in our lives.
- Alternative: All humans have a desire to accomplish something in their lives.
- Original: We cannot live without one another.
- Alternative: Humans cannot live without one another.
‘Society’ or ‘the society’ is an alternative to ‘we’ that we use when referring to ‘we’ as the society we are part of, or we are in. Like ‘humans,’ we do not use ‘society’ for small-scale groups, and we can only use this alternative for anything that involves our society.
- Original: We are so cruel towards others sometimes.
- Alternative: Society is so cruel towards others sometimes.
- Original: We have reached far and accomplished a lot collectively.
- Alternative: Society has reached far and accomplished a lot collectively.
- Original: Sometimes, we put up unrealistic standards for ourselves and for others.
- Alternative: Sometimes, society puts up unrealistic standards for oneself and for others.
- Original: We should start accepting everyone for who they are.
- Alternative: Society should start accepting everyone for who they are.
Is It Appropriate To Use ‘Our’ And ‘We’ In Formal Essays?
Whether to use ‘we’ or not depends on how formal you want your essay to be or how formal it needs to be. Some formal essays allow the use of first-person pronouns like ‘we’ and ‘us.’ However, omitting these pronouns do make your essays sound more professional, formal, and objective.
- Onward or Onwards – Difference Explained (Helpful Examples)
- Instructions On or Instructions For – Which Is Correct?
- 10 Better Ways To Say “A Lot Of Work To Do”
- Can You Call a Man “Sweetheart”? (8 Better Nicknames)
KathySteinemann.com: Free Resources for Writers
Word lists, cheat sheets, and sometimes irreverent reviews of writing rules. kathy steinemann is the author of the writer's lexicon series..

30+ Ways to Avoid Repetition of “I” in First-Person Writing

First-person narrative engages readers, who experience the world from your narrator’s perspective — including intimate thoughts and feelings. However, it’s easy to overplay constructions such as I did this and I thought that and I wanted something else.
Many people claim the I, I, I approach is permissible because I is an invisible word like said .
Don’t believe them.
Prose or poetry with an overabundance of the same words or structures will seem off. Readers might not be able to tell you what’s wrong, but they know they’re unsettled by something .
Consider the Following Two Story Snippets
I answered the irresistible beckoning of the backyard. I watched brightly colored birds there frolicking in the breeze as they fluttered toward the creek. I closed my eyes and felt the warmth of the sun . I smelled the fragrance of the clover underneath my feet, a fragrance so sweet I could almost taste it. I heard fledgling robins twittering in a nearby tree.
I thought to myself , This is the life. I knew I never wanted to leave this place.
I decided to phone the real estate agent and tell her to take the FOR SALE sign off my lawn. She acted as though she had expected my call.
I told her in a firm voice that my mind was made up, and yes, I understood she would still receive her full commission.
I realized I didn’t care about the money.
The backyard beckoned with its irresistible sights and sounds. Frolicking in the breeze, brightly colored birds fluttered toward the creek. The sun warmed my closed eyelids, and my nostrils were flooded by the sweet fragrance of clover underneath my feet, a fragrance so sweet it almost sugared the taste buds. In a nearby tree, fledgling robins twittered.
This is the life. Who in their right mind would ever leave this place?
The real estate agent acted as though she had expected my call when asked to take the FOR SALE sign off the lawn.
My voice was firm. “Yes, my mind is made up. … Understood. … You’ll still receive your full commission.”
Hah! Who cares about the money?
Beware Verbosity
Rewrites could result in bloat, and the wrong words could make you seem pretentious or long-winded.
The second snippet reduces, rather than increases, word count.
The first example would be even shorter with the removal of to myself. Who else would you think to? Your editor? Your cat? Or maybe your dictation software?
Did You Notice the Changes?
Almost every sentence in the first example begins with I.
In the rewrite, note the removal of several filtering phrases:
I watched I … felt I smelled I could … taste I heard I thought I knew I decided I told I understood I realized
Whenever you filter thoughts and senses through your narrator’s eyes, you distance readers from your story — like a selfie of a selfie. Use the direct approach instead.
Passive voice appeared once to vary sentence structure. “I smelled the fragrance of the clover underneath my feet ” became “my nostrils were flooded by the sweet fragrance of clover underneath my feet.”
A so-called rule of writing is not to use passive voice. However, you’ll find times such as this when it’s warranted.
The phrase could also have been written as “my nostrils flooded with the sweet fragrance of clover underneath my feet.”
Reread the examples. Compare again. You’ll notice subtle changes that make the text flow smoother.
A Partial List of Filter Words
Watch for these or their equivalents. They all have the potential to weaken your writing:
A to W assume, be able to, believe, can, decide, experience, feel (or feel like) , hear, know, look, note, notice, realize, remember, see, seem, sound (or sound like), taste, think, touch, watch, wonder
Change the Focus
Just because you’re writing in first person doesn’t mean you, the storyteller, should be the most important character in the piece.
If you concentrate on the activities of other characters, readers will feel as though they are you. They still know you’re the narrator, but you become invisible.
Try These I Alternatives
I agree: We are in agreement
I am convinced that: In my opinion
I am sure that: Correct me if my opinion is wrong
I believe: The experts say (or, in Dothraki , “It is known”)
I decided: It was my intention
I disagree: You are wrong
I dislike that: That’s not for me
I don’t know: That’s an excellent question
I feel: In light of the evidence
I have experience in: My experience includes
I interpret the results: The results indicate
I like: It’s one of my favorites
I was nearly hit by a car: A car nearly hit me
I’ll show you: The report will show you
I’m hungry: My stomach is growling
Beware the Me-My Snare
In an attempt to remove instances of I, you might introduce excessive repetition of me and my .
For instance, “I felt an irresistible urge to buy the shoes” could become “An irresistible urge to buy the shoes came over me .”
“I saw three chickadees sitting on the fence” could end up as “Three chickadees sitting on the fence came into my view.”
As shown by the strikeout, you can often omit my .
Rely on Your Ears
They’re excellent critics.
Read your text out loud or harness your computer’s text-to-speech capabilities and listen to your writing . Repetitions that hide from notice during a silent read often become obvious and irritating when processed by the ears .
Discover more from KathySteinemann.com: Free Resources for Writers
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
Type your email…
28 thoughts on “ 30+ Ways to Avoid Repetition of “I” in First-Person Writing ”
how can we replace i in this sentence i had a dream to spend a beautiful day at an island
Sleep, peaceful sleep, filled the night, interrupted only by the dream of an idyllic day on a tiny island.
Hello Kathy,
Me again. Since reading your article, I have made a greater conscious effort in avoiding the use of “I” in my first-person stories. However, in doing so, I’m noticing I am starting to use “-ing” words to begin sentences more often, and I understand that’s something to use sparingly in fiction writing.
I may be over-analysing my works (that’s a bad habit of mine), but if using “I” in a sentence, whether it’s beginning a sentence or in the middle of it, creates a clearer structured sentence when compared to using a “-ing” word, would you say it’s okay to use “I”, or to try and figure out another way of structuring the sentence to avoid either?
On a side note, sometimes when I do avoid both, the sentence gets written in passive voice, as that seems to be the only way to structure it, while keeping it clear and precise. For example, a sentence within a story of mine read: “Rather than wasting time on breakfast, I can use it for more important things, such as training.” After re-editing it, it became: “Rather than wasting time on breakfast, it can be used for more important things, such as training.”
I’m really just trying to determine out of “I”, “-ing”, or passive voice, which is the best to use. Apologies if this is unclear. Sometimes that’s my thought process for you. There’s logic in there, but you’ve gotta dig past all the dribble to find it.
Kind regards, Footrot Flats
Phrases such as the following can help eliminate some instances of “I”:
– experience has shown – statistics indicate – events suggest – circumstances often require
Regarding your sentence: “Rather than wasting time on breakfast, it can be used for more important things, such as training.”
Try something like: “[Whatever ‘it’ is] can focus on activities, such as training, which are more important than breakfast.”
Remember: The goal is not to eliminate words but to eliminate their overuse.
Thank you for the response, Kathy!
I’ll keep those phrases in mind and see if they can be used anywhere that fits. Thank you for the suggestion as well.
I understand it’s okay to use “I”, just not too often, which is what I’m trying to do, but also figuring out how often “I” is fine to use. Finding that ‘Goldilocks Zone’ is my next challenge. If it’s used once every few paragraphs, it doesn’t stick out at me, but if I see two (or more) I’s in the same field of view, that’s when I tend to change it.
I may or may not pop up again sometime in the future. If I don’t, your article and advise has helped me immensely, so thank you for the time and effort you have put in. It’s much appreciated.
All the best, and stay safe too! Footrot Flats
When writing stories, I’ve always tried avoiding the usage of I’s (same goes for adverbs). 95% of the time, there’s an alternative way of describing a scene, whether it’s action, thoughts or dialogue, but something, every now and then, there just doesn’t seem to be a way to avoid using I (or an adverb).
Like adverbs, would you say it’s okay to use ‘I’ sparingly?
In some cases, the word ‘I’ gets replaced with an adverb, and then I enter a never-ending cycle.
Your approach is astute, FF.
Words exist for a reason, including adverbs and I . The goal is not to eliminate them but to reduce their frequency and make them “invisible” to readers. That turns them into useful tools.
Good luck with your writing, and please stay safe! (Exclamation points, em dashes, and parentheses are more useful tools — when used sparingly. 🙂 )
Thank you for the reply Kathy.
I agree that making them “invisible” rather than eliminating them completely is the better approach. Everything would provide a greater impact when used sparingly.
All the best, and stay safe too. Footrot Flats
Hello Kathy, the article above really helped me but i am still just a little confused. . . . would it be alright if you could un-I-ify my story. i haven’t written much and i probably wont be using it, but just to get a rough idea on how i could do it.
I was sitting on the train minding my own business and reading a book, when I casually looked out the window. It was pretty dark and rainy, but I could still see the blurry silhouette of the woods turning into a dim lighted village. As I was about to turn away, I started to sweat and felt a pounding in my head. My heart felt as if I had just run a marathon 3 times and I could hear my blood rushing through my ears. My hands shook and my breathing turned uneven. My vision went all blurry. I had to get away. I did not want to be on a train while having a panic attack. I stood up and hit my knee on the table but I ignored the pain. I grabbed my book and backpack and yelled for assistance. An assistant quickly rushed over and asked if I needed anything. I told her to stop the train. “But ma’am, we don’t have a station here, we can’t stop here-” “Just stop the train. NOW! Please!” I cut her off. “Ma’am, are you feeling ok? You should probably sit down.” She offers. “STOP THE TRAIN! NOW!” I shout. She nodded to me and swiveled around and quickly rushed to the front of the train. My mouth started to feel dry and I could feel tears coming starting to form at the corners of my eyes. By this time I was shaking. I turned to the nearest compartment and grabbed the glass of water on the table. I took one big sip and looked up at the young bloke who was sitting there. My mouth felt a bit better knowing it was hydrated and I could say my words without them sounding raspy. “I am so sorry. I really needed that drink.” I grabbed my backpack and took out £2 and put it down on the table. “I’m really sorry about the drink, I know you paid for that so here’s the money. I know it was 3 pound but this is all I can find right now.” I blurted out. I could feel the train slowing down and felt nauseous. I sat down in the young blokes compartment seat and looked down. I could feel the guy’s eyes staring at the top of my head which made me feel uncomfortable.
sorry if thats too much. thank you 🙂
Thanks for stopping by, Astoria.
I’ve retired from editing, but you can join online critique groups free of charge.
Scribophile and Critique Circle are two popular sites.
Good luck with your writing, and stay safe!
Undertaking a short story/flash fiction assignment for Open University. Word count is up to 800 words. The premise is in hand, and I’ve done a plan.
Really want to do it in First POV, though I know third is easy to fall back on. Your advice is brilliant, I am just so nervous of the structure and grammar. I don’t envision that creative writing is for me, as the strain of English Lit etc scares me.
You can do this, Louise. I hope you’ll be able to use some of the advice in this post.
Good luck, and stay safe!
This is so frustrating, As I edit my work I can’t think of anything to replace my ‘I’ overuse!!!
Think less of how you control the action and more about how the action happens, period. The suggestions in this article will help.
Thanks for stopping by, Max!
Great article. Chuck Palahnuik is an expert at submerging the ‘I’, and I’m constantly perplexed about how to avoid the pitfalls you mentioned when following his advice. This has helped a great deal.
Thanks, Tom. May your muse be ever with you — and stay safe.
I get it, I just don’t know how to repair the problem. Online English class?
There’s no magic one-size-fits-all approach. You have to examine each occurrence to determine a suitable remedy. This requires time and effort; but as you edit, you become more proficient at creating solutions.
Thanks for stopping by!
Can you please give me some examples of books written in first person, without the overuse of ‘I’? My 13 year old daughter is in an Academic Excellence class and has had her eyes opened and mind blown buy how removing the ‘I’s, it makes you live the story. She has Aspergers and dyslexia and has always loved writing, it is her get away. We would be truly grateful for some guidance.
Warmest wishes Michelle Australia
Hi, Michelle. Thanks for stopping by.
The books that stand out in my mind are To Kill a Mockingbird by Harper Lee, all The Hunger Games books by Suzanne Collins, and Ready Player One by Ernest Cline. They should keep your daughter busy for a while.
Thank you very much Kathy. I am truly grateful.
May you too keep safe.
Warmest wishes Michelle
Thank you so much. I always put I’s in my stories and it bothered me because ‘I’ use it repeatedly. That’s when ‘I’ started to notice it also want to thank you for the alternatives to making my story look as if a professional wrote it. Well I’m no professional but hopefully one day. 4 years later and came across this website. Thank you btw. (PS I was embarrassed now because I used my I’s a lot in this comment lolz so I had to fix it to make it right ) Anyways I’m forever grateful and have a good year in 2020!
Thanks for stopping by, Nora. Yes, those Is can be slippery little creatures. You’ve made the most important step by recognizing the problem.
You have a great 2020 too, and may the muses favor your writing!
Excellent, as per usual. 🙂
Thanks, Jenn!
Another excellent post, Kathy. This is exactly what I was looking for. As an added bonus, I now know what filter words are. Time for another edit on my latest WIP. (Heck – I’ve just noticed two I’s in the above comment. Oh no, there’s another two!)
Thanks, Tom. I laughed out loud as I was reading your reply. Next week I’ll be posting an open letter to book pirates. Arrgh! Three I ‘s.
Let’s see …
As my eyes scrutinized your reply, a humongous LOL burst from my lips. Next week’s blog post will feature an open letter to book pirates.
Doesn’t have the same snap, does it?
Comments are closed.
Coming Soon: New Courses for 2025. Register Your Interest
- 40 Useful Words and Phrases for Top-Notch Essays

To be truly brilliant, an essay needs to utilise the right language. You could make a great point, but if it’s not intelligently articulated, you almost needn’t have bothered.
Developing the language skills to build an argument and to write persuasively is crucial if you’re to write outstanding essays every time. In this article, we’re going to equip you with the words and phrases you need to write a top-notch essay, along with examples of how to utilise them.
It’s by no means an exhaustive list, and there will often be other ways of using the words and phrases we describe that we won’t have room to include, but there should be more than enough below to help you make an instant improvement to your essay-writing skills.
If you’re interested in developing your language and persuasive skills, Oxford Royale offers summer courses at its Oxford Summer School , Cambridge Summer School , London Summer School , San Francisco Summer School and Yale Summer School . You can study courses to learn english , prepare for careers in law , medicine , business , engineering and leadership.
General explaining
Let’s start by looking at language for general explanations of complex points.
1. In order to
Usage: “In order to” can be used to introduce an explanation for the purpose of an argument. Example: “In order to understand X, we need first to understand Y.”
2. In other words
Usage: Use “in other words” when you want to express something in a different way (more simply), to make it easier to understand, or to emphasise or expand on a point. Example: “Frogs are amphibians. In other words, they live on the land and in the water.”
3. To put it another way
Usage: This phrase is another way of saying “in other words”, and can be used in particularly complex points, when you feel that an alternative way of wording a problem may help the reader achieve a better understanding of its significance. Example: “Plants rely on photosynthesis. To put it another way, they will die without the sun.”
4. That is to say
Usage: “That is” and “that is to say” can be used to add further detail to your explanation, or to be more precise. Example: “Whales are mammals. That is to say, they must breathe air.”
5. To that end
Usage: Use “to that end” or “to this end” in a similar way to “in order to” or “so”. Example: “Zoologists have long sought to understand how animals communicate with each other. To that end, a new study has been launched that looks at elephant sounds and their possible meanings.”
Adding additional information to support a point
Students often make the mistake of using synonyms of “and” each time they want to add further information in support of a point they’re making, or to build an argument. Here are some cleverer ways of doing this.
6. Moreover
Usage: Employ “moreover” at the start of a sentence to add extra information in support of a point you’re making. Example: “Moreover, the results of a recent piece of research provide compelling evidence in support of…”

7. Furthermore
Usage:This is also generally used at the start of a sentence, to add extra information. Example: “Furthermore, there is evidence to suggest that…”
8. What’s more
Usage: This is used in the same way as “moreover” and “furthermore”. Example: “What’s more, this isn’t the only evidence that supports this hypothesis.”
9. Likewise
Usage: Use “likewise” when you want to talk about something that agrees with what you’ve just mentioned. Example: “Scholar A believes X. Likewise, Scholar B argues compellingly in favour of this point of view.”
10. Similarly
Usage: Use “similarly” in the same way as “likewise”. Example: “Audiences at the time reacted with shock to Beethoven’s new work, because it was very different to what they were used to. Similarly, we have a tendency to react with surprise to the unfamiliar.”
11. Another key thing to remember
Usage: Use the phrase “another key point to remember” or “another key fact to remember” to introduce additional facts without using the word “also”. Example: “As a Romantic, Blake was a proponent of a closer relationship between humans and nature. Another key point to remember is that Blake was writing during the Industrial Revolution, which had a major impact on the world around him.”
12. As well as
Usage: Use “as well as” instead of “also” or “and”. Example: “Scholar A argued that this was due to X, as well as Y.”
13. Not only… but also
Usage: This wording is used to add an extra piece of information, often something that’s in some way more surprising or unexpected than the first piece of information. Example: “Not only did Edmund Hillary have the honour of being the first to reach the summit of Everest, but he was also appointed Knight Commander of the Order of the British Empire.”
14. Coupled with
Usage: Used when considering two or more arguments at a time. Example: “Coupled with the literary evidence, the statistics paint a compelling view of…”
15. Firstly, secondly, thirdly…
Usage: This can be used to structure an argument, presenting facts clearly one after the other. Example: “There are many points in support of this view. Firstly, X. Secondly, Y. And thirdly, Z.
16. Not to mention/to say nothing of
Usage: “Not to mention” and “to say nothing of” can be used to add extra information with a bit of emphasis. Example: “The war caused unprecedented suffering to millions of people, not to mention its impact on the country’s economy.”
Words and phrases for demonstrating contrast
When you’re developing an argument, you will often need to present contrasting or opposing opinions or evidence – “it could show this, but it could also show this”, or “X says this, but Y disagrees”. This section covers words you can use instead of the “but” in these examples, to make your writing sound more intelligent and interesting.
17. However
Usage: Use “however” to introduce a point that disagrees with what you’ve just said. Example: “Scholar A thinks this. However, Scholar B reached a different conclusion.”
18. On the other hand
Usage: Usage of this phrase includes introducing a contrasting interpretation of the same piece of evidence, a different piece of evidence that suggests something else, or an opposing opinion. Example: “The historical evidence appears to suggest a clear-cut situation. On the other hand, the archaeological evidence presents a somewhat less straightforward picture of what happened that day.”
19. Having said that
Usage: Used in a similar manner to “on the other hand” or “but”. Example: “The historians are unanimous in telling us X, an agreement that suggests that this version of events must be an accurate account. Having said that, the archaeology tells a different story.”
20. By contrast/in comparison
Usage: Use “by contrast” or “in comparison” when you’re comparing and contrasting pieces of evidence. Example: “Scholar A’s opinion, then, is based on insufficient evidence. By contrast, Scholar B’s opinion seems more plausible.”
21. Then again
Usage: Use this to cast doubt on an assertion. Example: “Writer A asserts that this was the reason for what happened. Then again, it’s possible that he was being paid to say this.”
22. That said
Usage: This is used in the same way as “then again”. Example: “The evidence ostensibly appears to point to this conclusion. That said, much of the evidence is unreliable at best.”
Usage: Use this when you want to introduce a contrasting idea. Example: “Much of scholarship has focused on this evidence. Yet not everyone agrees that this is the most important aspect of the situation.”
Adding a proviso or acknowledging reservations
Sometimes, you may need to acknowledge a shortfalling in a piece of evidence, or add a proviso. Here are some ways of doing so.
24. Despite this
Usage: Use “despite this” or “in spite of this” when you want to outline a point that stands regardless of a shortfalling in the evidence. Example: “The sample size was small, but the results were important despite this.”
25. With this in mind
Usage: Use this when you want your reader to consider a point in the knowledge of something else. Example: “We’ve seen that the methods used in the 19th century study did not always live up to the rigorous standards expected in scientific research today, which makes it difficult to draw definite conclusions. With this in mind, let’s look at a more recent study to see how the results compare.”
26. Provided that
Usage: This means “on condition that”. You can also say “providing that” or just “providing” to mean the same thing. Example: “We may use this as evidence to support our argument, provided that we bear in mind the limitations of the methods used to obtain it.”
27. In view of/in light of
Usage: These phrases are used when something has shed light on something else. Example: “In light of the evidence from the 2013 study, we have a better understanding of…”
28. Nonetheless
Usage: This is similar to “despite this”. Example: “The study had its limitations, but it was nonetheless groundbreaking for its day.”
29. Nevertheless
Usage: This is the same as “nonetheless”. Example: “The study was flawed, but it was important nevertheless.”
30. Notwithstanding
Usage: This is another way of saying “nonetheless”. Example: “Notwithstanding the limitations of the methodology used, it was an important study in the development of how we view the workings of the human mind.”
Giving examples
Good essays always back up points with examples, but it’s going to get boring if you use the expression “for example” every time. Here are a couple of other ways of saying the same thing.
31. For instance
Example: “Some birds migrate to avoid harsher winter climates. Swallows, for instance, leave the UK in early winter and fly south…”
32. To give an illustration
Example: “To give an illustration of what I mean, let’s look at the case of…”
Signifying importance
When you want to demonstrate that a point is particularly important, there are several ways of highlighting it as such.
33. Significantly
Usage: Used to introduce a point that is loaded with meaning that might not be immediately apparent. Example: “Significantly, Tacitus omits to tell us the kind of gossip prevalent in Suetonius’ accounts of the same period.”
34. Notably
Usage: This can be used to mean “significantly” (as above), and it can also be used interchangeably with “in particular” (the example below demonstrates the first of these ways of using it). Example: “Actual figures are notably absent from Scholar A’s analysis.”
35. Importantly
Usage: Use “importantly” interchangeably with “significantly”. Example: “Importantly, Scholar A was being employed by X when he wrote this work, and was presumably therefore under pressure to portray the situation more favourably than he perhaps might otherwise have done.”
Summarising
You’ve almost made it to the end of the essay, but your work isn’t over yet. You need to end by wrapping up everything you’ve talked about, showing that you’ve considered the arguments on both sides and reached the most likely conclusion. Here are some words and phrases to help you.
36. In conclusion
Usage: Typically used to introduce the concluding paragraph or sentence of an essay, summarising what you’ve discussed in a broad overview. Example: “In conclusion, the evidence points almost exclusively to Argument A.”
37. Above all
Usage: Used to signify what you believe to be the most significant point, and the main takeaway from the essay. Example: “Above all, it seems pertinent to remember that…”
38. Persuasive
Usage: This is a useful word to use when summarising which argument you find most convincing. Example: “Scholar A’s point – that Constanze Mozart was motivated by financial gain – seems to me to be the most persuasive argument for her actions following Mozart’s death.”
39. Compelling
Usage: Use in the same way as “persuasive” above. Example: “The most compelling argument is presented by Scholar A.”
40. All things considered
Usage: This means “taking everything into account”. Example: “All things considered, it seems reasonable to assume that…”
How many of these words and phrases will you get into your next essay? And are any of your favourite essay terms missing from our list? Let us know in the comments below, or get in touch here to find out more about courses that can help you with your essays.
At Oxford Royale Academy, we offer a number of summer school courses for young people who are keen to improve their essay writing skills. Click here to apply for one of our courses today, including law , business , medicine and engineering .
Comments are closed.

Using You in Academic Writing

Using You in Academic Writing Podcast
Using you in academic writing transcript.
This is Kurtis Clements with another effective writing podcast. In this episode, I am going to talk about using the second person, you and your, in academic writing.
Many folks are confused when it comes to using the second person pronouns “you” and “your” in their academic writing, in large part because such pronouns are used often in other kinds of writing, so it seems natural to use such words in academic writing.
What is “academic writing”? Academic writing is writing that is generally formal; by and large, it’s the kind of writing produced in school when you are writing a report or an essay. Academic writing usually does not contain contractions or slang, nor does academic writing use emoticons or exclamation points. Academic writing sticks to a fairly objective point of view and avoids personal pronouns such as “I, we, us, our, you,” and “your,” for example. Now this is not to say that academic writing will never use such pronouns, but as a guiding general principle such pronouns are not used often in academic writing.
I don’t want to confuse you, but not all writing produced in school is “academic.” For example, if you were taking a creative writing course, while you may write essays that require a formal approach to writing, you will also be writing “creatively”—short stories and poems and other genres that would not require you to use “academic writing.”
Imagine a poem like Gwendolyn Brook’s “We Real Cool” in which the speaker, a thug without much of a future, says, “We real cool. We left school. We lurk late” written in formal academic writing like this: “They were indifferent to the conventional values of society. They left school. They lurked late at night.” Big difference, right? Of course. Academic writing is not the kind of writing to use when writing creatively.
Ok, so back to our discussion of second person. Second person is the use of the pronouns “you” and “your” in writing. In this podcast, I sometimes relate what I am talking about to my audience—to you folks listening right now—so I will make statements like “I don’t want to confuse you, but…” In my podcast, which is not a formal writing situation, it’s fine to use the pronouns “you” and “your.”
As a guiding principle, the second person pronouns “you” and “your” should not be used in academic writing. Using “you and your” is informal and lacks the kind of professional tone found in academic writing. “You” may work fine in some situations (like this podcast, for example), but in academic writing, such usage can be downright confusing. When I use “you” in my podcast, it’s clear that I am addressing my listeners.
But let’s say you were reading a paper about recycling, something that you already do. What would your reaction be if every now and then the writer included a sentence like “All you would need to do is set up a few extra bins in your home for glass, paper, metal, and plastic, and then put each item into its respective bin.” What would your response be? You would likely be confused, right? After all, you already recycle. And imagine other instances of the writer referring to “you” in a sentence. Every time you read “you,” you stop in your tracks and think, “Me?”
Let’s say the recycling paper’s purpose is to persuade and thus the logical audience would be folks who don’t recycle. Would “you” be appropriate then? No. While there would clearly be less confusion on the part of readers, writing of a more formal nature should be as objective as possible and not refer directly to readers.
Imagine reading a formal academic essay that is arguing for greater individual effort to recycle, and throughout the paper the writer uses the objective third person point of view, making such statements as “Individuals have a responsibility to future generations to do what they can to cut down on waste” and “Individuals must be proactive in recycling at home and work,” and then all of a sudden, out of the blue, the writing shifts to second person and makes a statement like “You might be busy, but if you make recycling a top priority then you would probably be successful.”
Whoa, right?
Where did that sentence come from? As a reader, you were engaged in the persuasive but objective discussion of the need to recycle, when all of a sudden the writing shifts to second person, and it seems like the writer is pointing a finger at you.
The use of second person can be confusing, awkward, and off-putting in academic writing, so it’s best to avoid the pronouns “you” and “your.”
A good way to ensure such pronouns don’t appear in your paper is to read your work slowly aloud. Mark each “you” or “your” you find and revise accordingly. With a little practice, keeping the second person out of your writing will come naturally.
Thanks for listening, everyone. Happy writing.
Share this:
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window)
- Click to print (Opens in new window)
Follow Blog via Email
Enter your email address to follow this blog and receive email notifications of new posts.
Email Address
- RSS - Posts
- RSS - Comments
- COLLEGE WRITING
- USING SOURCES & APA STYLE
- EFFECTIVE WRITING PODCASTS
- LEARNING FOR SUCCESS
- PLAGIARISM INFORMATION
- FACULTY RESOURCES
- Student Webinar Calendar
- Academic Success Center
- Writing Center
- About the ASC Tutors
- DIVERSITY TRAINING
- PG Peer Tutors
- PG Student Access
Subscribe to Blog via Email
Enter your email address to subscribe to this blog and receive notifications of new posts by email.
- College Writing
- Using Sources & APA Style
- Learning for Success
- Effective Writing Podcasts
- Plagiarism Information
- Faculty Resources
- Tutor Training
Twitter feed
Using “I” in Academic Writing
Traditionally, some fields have frowned on the use of the first-person singular in an academic essay and others have encouraged that use, and both the frowning and the encouraging persist today—and there are good reasons for both positions (see “Should I”).
I recommend that you not look on the question of using “I” in an academic paper as a matter of a rule to follow, as part of a political agenda (see webb), or even as the need to create a strategy to avoid falling into Scylla-or-Charybdis error. Let the first-person singular be, instead, a tool that you take out when you think it’s needed and that you leave in the toolbox when you think it’s not.
Examples of When “I” May Be Needed
- You are narrating how you made a discovery, and the process of your discovering is important or at the very least entertaining.
- You are describing how you teach something and how your students have responded or respond.
- You disagree with another scholar and want to stress that you are not waving the banner of absolute truth.
- You need “I” for rhetorical effect, to be clear, simple, or direct.
Examples of When “I” Should Be Given a Rest
- It’s off-putting to readers, generally, when “I” appears too often. You may not feel one bit modest, but remember the advice of Benjamin Franklin, still excellent, on the wisdom of preserving the semblance of modesty when your purpose is to convince others.
- You are the author of your paper, so if an opinion is expressed in it, it is usually clear that this opinion is yours. You don’t have to add a phrase like, “I believe” or “it seems to me.”
Works Cited
Franklin, Benjamin. The Autobiography of Benjamin Franklin . Project Gutenberg , 28 Dec. 2006, www.gutenberg.org/app/uploads/sites/3/20203/20203-h/20203-h.htm#I.
“Should I Use “I”?” The Writing Center at UNC—Chapel Hill , writingcenter.unc.edu/handouts/should-i-use-i/.
webb, Christine. “The Use of the First Person in Academic Writing: Objectivity, Language, and Gatekeeping.” ResearchGate , July 1992, doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2648.1992.tb01974.x.
J.S.Beniwal 05 August 2017 AT 09:08 AM
I have borrowed MLA only yesterday, did my MAEnglish in May 2017.MLA is of immense help for scholars.An overview of the book really enlightened me.I should have read it at bachelor's degree level.
Your e-mail address will not be published
Dr. Raymond Harter 25 September 2017 AT 02:09 PM
I discourage the use of "I" in essays for undergraduates to reinforce a conversational tone and to "self-recognize" the writer as an authority or at least a thorough researcher. Writing a play is different than an essay with a purpose.
Osayimwense Osa 22 March 2023 AT 05:03 PM
When a student or writer is strongly and passionately interested in his or her stance and argument to persuade his or her audience, the use of personal pronoun srenghtens his or her passion for the subject. This passion should be clear in his/her expression. However, I encourage the use of the first-person, I, sparingly -- only when and where absolutely necessary.
Eleanor 25 March 2023 AT 04:03 PM
I once had a student use the word "eye" when writing about how to use pronouns. Her peers did not catch it. I made comments, but I think she never understood what eye was saying!
Join the Conversation
We invite you to comment on this post and exchange ideas with other site visitors. Comments are moderated and subject to terms of service.
If you have a question for the MLA's editors, submit it to Ask the MLA!

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
One of the main rules of academic or formal writing is to avoid first-person pronouns like “we,” “you,” and “I.” These words pull focus away from the topic and shift it to the speaker – the opposite of your goal. While it may seem difficult at first, some tricks can help you avoid personal language and keep a professional tone.
You can replace the pronouns ‘I’, ‘You’, and ‘We’ by replacing them with acceptable wording, applying passive voice instead of pronouns, Using a third-person perspective, adopting an objective language, and including strong verbs and adjectives.
The most preferred alternatives we use are ‘they,’ ‘the group,’ and ‘the team.’. These three alternatives are the more general alternatives that seem to be applicable in almost all contexts, especially ‘they’ as we simply remove ourselves from the narrative by using it.
If you concentrate on the activities of other characters, readers will feel as though they are you. They still know you’re the narrator, but you become invisible. Try These I Alternatives
Moreover, you can use essay transition words to start a paragraph, sentence, or clause more naturally. Additionally, essay transition words can connect new information to the previous statement so you don’t have to say everything at once. This guide looks at how to use transition words in essays.
Developing the language skills to build an argument and to write persuasively is crucial if you’re to write outstanding essays every time. In this article, we’re going to equip you with the words and phrases you need to write a top-notch essay, along with examples of how to utilise them.
Using “you and your” is informal and lacks the kind of professional tone found in academic writing. “You” may work fine in some situations (like this podcast, for example), but in academic writing, such usage can be downright confusing. When I use “you” in my podcast, it’s clear that I am addressing my listeners.
Positioning yourself in the essay: In some projects, you need to explain how your research or ideas build on or depart from the work of others, in which case you’ll need to say “I,” “we,” “my,” or “our”; if you wish to claim some kind of authority on the topic, first person may help you do so. Deciding whether “I” will help your style.
When you are writing a dissertation, thesis, or research paper, many words and phrases that are acceptable in conversations or informal writing are considered inappropriate in academic writing. You should try to avoid expressions that are too informal, unsophisticated, vague, exaggerated, or subjective, as well as those that are generally ...
Traditionally, some fields have frowned on the use of the first-person singular in an academic essay and others have encouraged that use, and both the frowning and the encouraging persist today—and there are good reasons for both positions (see “Should I”).