- For educators
- English (US)
- English (India)
- English (UK)
- Greek Alphabet

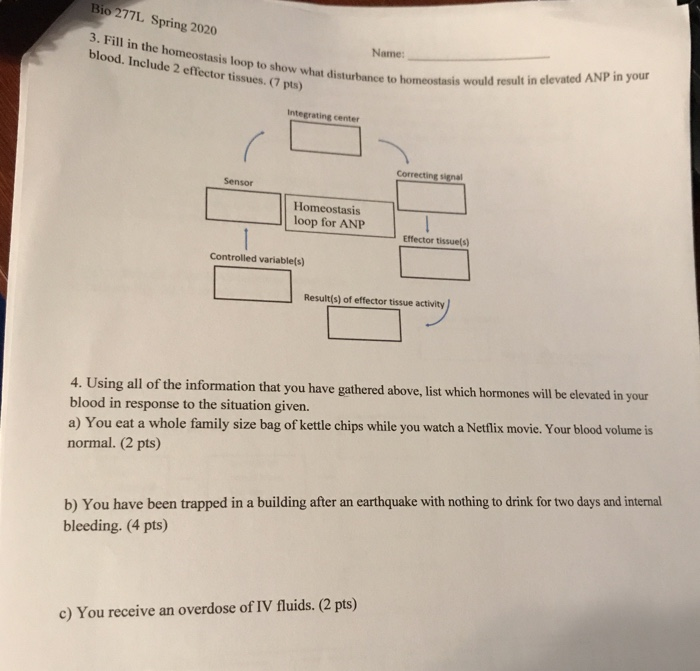
Question: Bio 277L Spring 2020 3. Fill in the homeostasis loop to show what disturbance to ho blood. Include 2 effector tissues. (7 pts) Name: ice to homeostasis would result in elevated ANP in your Integrating center Correcting sinal Sensor Homeostasis loop for ANP Effector tissues) Controlled variable(s) Result(s) of effector tissue activity 4. Using all of the
Not the question you’re looking for?
Post any question and get expert help quickly.
- by Academic Documents
- Access the best Study Guides Lecture Notes and Practice Exams Log In Sign Up
This preview shows page 1-2 out of 5 pages .
BIO 277 1st Edition Final Exam Study Guide Work through all of the specific learning objectives for each unit 6 Questions Principles of biology and chemistry eg diffusion carrier mediated transport osmosis pH etc o Simple diffusion small lipid soluble steroids o Facilitated diffusion requires carrier protein glucose o Primary active transport ATP directly consumed Na K ATPase o Secondary active transport energy of ion gradient usually Na used to move 2nd solute Cell signaling o Epinephrine EPI adrenaline Binds with adrenergic receptors on smooth muscle cells of bronchioles dilate and open up airways to deliver more oxygen Binds with adrenergic receptors on the pacemaker cells of the heart speeds up heart rat Blood vessels delivering blood to kindeys or digestive tract constrict and diverting blood away from those organs o Norepinephrine Binds with adrenergic receptors vascular smooth muscle contracts Receptor on the outside of the cell is connected to a G protein on the inside of the cell Binds with a beta adrenergic receptor vascular smooth muscle relaxes Receptor on the outside of the cell is connected to a different set of proteins on the inside of the cell o Antagonistic control Different signals bind with different receptors to cause different response Example Pacemaker cells o Tonic control the tissue response varies with the amount of signal that binds with the receptor Blood vessels the amount of contraction varies with how much EPI NE is applied 10 Questions Neurobiology GHK equation know values for equilibrium potentials of Na K Cl Ca o E Na 60mV o E K 90mV o E Ca 122 mV o E Cl 63 mV These notes represent a detailed interpretation of the professor s lecture GradeBuddy is best used as a supplement to your own notes not as a substitute autonomic nervous system o Central nervous system includes brain and spinal cord o Peripheral nervous system Afferent branch neurons bringing information into the central nervous system Efferent branch neurons taking information away from the central nervous system sensory biology Touch stimulus bending of membrane Smell binding of odorant molecules Taste binding of sweet bitter umami tastants maybe movement of Na or H through ion channels Hearing Mechanical bending of hair cell in cochlea o 4 Questions Muscles Skeletal muscles contract on an all or none basis meaning that if a fiber is stimulated Smooth muscles o Contraction depends on how much calcium is in the cytosol Gating mechanisms Stretch gated channels present bladder as bladder fills muscle contracts Voltage gates channels exist on smooth muscle of the gut facilitating waves of contraction Differences between muscle types o Skeletal muscle striated has sacromeres fastest contraction speed o Smooth muscle smooth no sacromeres slowest contraction speed 7 Questions Cardiovascular topics MAP o The pumps heart this is the force generator Increased force leads to higher MAP o The plumbing blood vessels increased length or decreased radius leads to higher MAP o Blood increased blood volume leads to higher MAP Heart rate and Stroke volume Cardiac Output the capacity of the heart to pump blood and measured in L min It is a product of heart rate HR in beats min X stroke volume SV in L beat o Starling s law cardiac muscle o States that the stroke volume of the heart increases in response to an increase in the volume of blood filling the heart the end diastolic volume when all other factors remain constant 3 Questions Respiratory Gas exchange occurs between the alveolar space and the blood o O2 far more in alveolar space then in the blood in exchange moves into blood o CO2 more in the blood leaves the blood in exchange Ventilation air flows pressure gradients it moves from high to low o Palv alveolar pressure o Pip intrapleural space Always less than the other two pressures to help keep the lungs expanded o Patm atmospheric pressure o Pneumothorax puncture lung Pip Palv Patm Alveoli collapse and stick together cannot perform gas exchange o Expiration Palv Patm Volume of the thoracic cavity is going to decrease Increase Palv Diaphragm relaxes and move upward abdominals and internal intercostal contact o Inspiration Pip Palv Patm Volume of thoracic cavity increase Decrease Palv Diaphragm contracts and moves down and flattens external intercostal can contact respiratory system including HB O2 saturation curve o Saturation hemoglobin it is carrying all of the oxygen that it is capable of holding Saturation on the partial pressure of O2 Hb changes shape Decrease affinity of Hb for O2 related to working cells o Decrease pH o Increase temp o Increase CO2 o Increase 2 3 DPG hypoxia Increase affinity of Hb for O2 typical of pulmonary capillaries o Increase pH o Decrease temp o Decrease CO2 o Decrease 2 3 DPG Fetal Hb left shift fetus has the ability to take Hb from the mother o Cell types Type I cells very large thin Main site of gas exchange Type II cells secret surfactant important to reduce the surface tension of alveoli Cells have glucorticold receptors and are stimulated by cortisol 8 Questions Kidney Renal system hormonal regulation GFR Glomerular filtration rate or the amount of filtrate per unit time o Factors increase GFR vasodilators get rid of excess fluid ANP makes you pee increase urine output o Factors decrease GFR vasoconstrictors conserve fluid volume if plasma osmolarity gets too high or MAP gets too low Increase ADH due to decrease MAP or increase plasma osmolarity Increase ANG II decrease renal blood pressure which increase renin Increase sympathetic output at adrenergic receptors o Tubuloglomerular feedback renal autoregulation Maintains constant glomerular filtration despite small fluctuations in MAP Increase DCT flow due to small increase in MAP sensed by macula densa in DCT release of a paracrine signal decrease NO contraction of afferent arteriole to decrease GFR Decrease DCT flow due to small decrease in MAP sensed by macula densa in DCT release of a paracrine signal increase NO relaxation of afferent arteriole to increase GFR glucose reabsorption facilitated diffusion at proximal tubule 6 Questions GI tract enzyme groups hormones o Cephalic phase of digestion increase motility and secretions ps stimulation of salivary glands and enteric neurons system o Gastric phase of digestion Stimulus for secretion Increase parasympathetic increase gastric secretion increase gastric chime decrease pH Hormone Gastrin secretion by the G cells of the antrum of the stomach Target cells

UNCG BIO 277 - Final Exam Study Guide

Exam 4 Study Guide

Exam 3 Study Guide

Exam 2 Study Guide

Exam 1 Study Guide

Lecture 1 : Gene expression and proteins
Sign up for free to view:
- This document and 3 million+ documents and flashcards
- High quality study guides, lecture notes, practice exams
- Course Packets handpicked by editors offering a comprehensive review of your courses
- Better Grades Guaranteed
- Terms Of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Recent Documents
- Students with Disabilities
- Become a Note-Taker
Please select your school
Join to view Final Exam Study Guide and access 3M+ class-specific study document.
We couldn't create a GradeBuddy account using Facebook because there is no email address associated with your Facebook account.
Link an email address with your Facebook below or create a new account.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A) When a sodium channel is opened sodium leaves the cell because there is more sodium inside the cell than outside. B) When sodium channels open the membrane potential of the cell moves towards +60 mV. C) When a sodium channel is opened sodium enters the cell because there is more sodium outside the cell than inside.
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Use the information in your textbook and in the file "Neurobiology (Links to an external site.)" to answer the following question. Match the letters below to the description of the structure, region, or process., Which of the following statements about potassium is FALSE? A) Opening of potassium channels causes the membrane ...
Bio 277 Unit 3 - Homework Q's. Flashcards; Learn; Test; Match; Q-Chat; Get a hint. If the sodium channels open, which way will sodium move? It will move into the cell. 1 / 29. 1 / 29. Flashcards; Learn; Test; ... Health 28Lesson 2,3 Test. 28 terms. snw451. Preview. BIO Review questions 14-15. 24 terms. Davis_Tomlin. Preview. English 101 chapter ...
Studying BIO 277 Human Physiology at University of North Carolina at Greensboro? On Studocu you will find 33 lecture notes, practice materials, assignments, tutorial. ... IRAT 3 - quiz unit 3; IRAT 2 - quiz unit 2; Show 2 more documents Show all 10 documents... Assignments. Date Rating. year. Ratings. Lecture Exam 3 - Exam. 2 pages. 2022/2023 ...
Save. Share. IRAT 3 - quiz unit 3. Course: Human Physiology (BIO 277) 39Documents. Students shared 39 documents in this course. University: AI Chat. Info More info.
Unit 2 - unit 2 notes. Lecture exam 4 - Exam. IRAT 7 - Quiz unit 7. IRAT 6 - Quiz unit 6. IRAT 5a - Quiz unit 5a. Team Assignment Stress Axis. Exam name: greer my name on this graded work signifies that have completed it in accordance with the uncg academic integrity policy lecture test3 bio human.
Biology questions and answers. Bio 277L Spring 2020 Name: Critical Thinking Assignment 3: Sensory Physiology C G C II) 1. Using this diagram, label the following using the word bank below: (5 pts) The type of channel at A (ion and gating mechanisme) The type of channel at B (ion and galing mechanism The region at C The type of channel at Dion ...
UNCG BIO 277 - Exam 3 Study Guide School name The University of North Carolina at Greensboro Course Bio 277- Human Physiology Type Study Guide. Pages 5. This preview shows page 1-2 out of 5 pages. Save. View full document ...
The threshold for an action potential is at circled number: 3. Which circled number is closest to the resting membrane potential? 2. The membrane potential gets closet to the equilibrium potential for potassium at circled number? 8. A- Voltage-gated calcium channels open. B- synapse. C- ligand-gated ion channel.
Click the links below to view the Student Answer Keys in Microsoft Word format. Answer Key - Chapter 01 (23.0K) Answer Key - Chapter 02 (20.0K)
Unformatted text preview: Bio 277 1st Edition Exam 1 Study Guide Lectures 1 5 Lecture Test 1 General Overview Study Guide Unit 1 I II III IV Transmembrane trafficking a K Na ATPase maintains gradient in cell b Ca Na is higher outside cell c K proteins higher inside the cell d Types of transport define and give an example i Simple diffusion ii ...
Question: Bio 277L Spring 2020 3. Fill in the homeostasis loop to show what disturbance to ho blood. Include 2 effector tissues. (7 pts) Name: ice to homeostasis would result in elevated ANP in your Integrating center Correcting sinal Sensor Homeostasis loop for ANP Effector tissues) Controlled variable(s) Result(s) of effector tissue activity 4.
How do signals control tissues. Primary ligands, agonists and antagonists. Autocrine, paracrine and endocrine signaling. Lecture Exam 1 - Exam. Team Assignment Stress Axis. Quiz unit 5a tc makes ne name: collanyt et team individual readiness assurance test write the capital letter of the correct answer in the box. which letter.
Bio 277 Unit 8 Homework. Match the term on the left with the description on the right. Note that there are more descriptions than terms given so you will have to eliminate those that don't apply to any of the terms! - Secretin: This hormone is secreted in response to acidic chyme and acts as an enterogastrone.
This preview shows page 1-2 out of 5 pages. Unformatted text preview: BIO 277 1st Edition Final Exam Study Guide Work through all of the specific learning objectives for each unit 6 Questions Principles of biology and chemistry eg diffusion carrier mediated transport osmosis pH etc o Simple diffusion small lipid soluble steroids o Facilitated ...
BIO 277 Unit 8 Homework (Digestion and Metabolism) Match the term on the left with the description on the right. Note that there are more descriptions than terms given so you will have to eliminate those that don't apply to any of the terms! Click the card to flip 👆. Secretion- This refers to the movement of solutes from the intracellular ...
Human PhysiologyBIO 277. University of North Carolina at Greensboro. 41 Documents. Go to course. 2. Lecture exam 4 - Exam. Human Physiology 100% (4) 8. Unit 1 - unit 1 notes.
Primary ligands, agonists and antagonists. Autocrine, paracrine and endocrine signaling. Lecture Exam 3 - Exam. Lecture Exam 1 - Exam. IRAT 9 - Quiz unit 9. Team Assignment Stress Axis. Quiz unit 6 spring 2022 name: qcerc team eles: individual readiness assurance test circle or write clearly the correct answer in the box. the lungs? hich of the.