
- Benefits of Whole Brain® Thinking
- HBDI and Other Assessments
Team Effectiveness
- Innovation, Creativity and Change Management
- Management and Leadership Development
- Herrmann Platform Overview
- The Whole Brain® Methodology
- Work at Herrmann
- In the News
- Resource Library
- Whole Brain® Champions
- Whole Brain® Certified Practitioners
- Consultants, Coaches & Integrations


How to Use Problem-Solving Examples to Improve Team Performance
Effective problem-solving is an indispensable skill for high-performing teams, whether they’re overcoming complex challenges, streamlining processes, or fostering innovation. But there’s a difference between recognizing a problem and knowing how to address it. Teams need practical guidance and real-world problem-solving examples to help them get started.
Learn more about the importance of problem-solving, what this looks like in practice, and how Whole Brain® Thinking can help.
Why Problem-Solving Is Important in Every Organization
Successful organizations are good at implementing new ideas, and they’re also adept at recognizing and responding to problems efficiently. They see problems as opportunities, even when they are thorny or complicated. Instead of problems causing division, they unite teams as they work together to diagnose the issues, collaborate on potential solutions, and move forward.
To embed a culture of problem-solving into your organizations, it’s important to:
- Acknowledge and name the problem : Problem-solving starts with problem definition . Team members must understand that a problem exists and how it impacts the team and the business.
- Find the root cause : The goal of problem-solving is to create lasting solutions to causes, not just address symptoms.
- Work together to find solutions and test them : With the root cause in mind, teams can come together and test potential solutions. This step can be repeated as necessary, depending on the findings.
- Incorporate the new solution into your processes: If you can’t avoid the problem, you can often avoid a recurrence by applying the solution to your processes and habits.
Rarely are problems solved by one person; you need collaborative brainstorming to identify and resolve root causes. Problem-solving should be a structured process that instills organizational discipline while inviting employees to contribute their questions, experience, and ingenuity in a collaborative environment.
Common Skills for Effective Problem-Solving
There are countless types of workplace problems, and each might require a different set of skills, steps, and philosophies to address. That said, there are core skills that all leaders can develop in their teams to make the problem-solving process more structured and consistent.
Here are a few common skills that facilitate effective problem-solving in the workplace.
Active Listening
Active listening involves intentionally focusing on what the other person is saying without interruption or judgment. Engaging in active listening isn’t just about paying attention but also attempting to understand the meaning and intent of the speaker.
In the context of problem-solving, active listening helps you understand the other person’s intent as they describe a problem, its circumstances, and possible solutions. Active listening can help at every stage of problem-solving because it facilitates shared understanding and reduces miscommunication. When people listen deeply and with intent, they better understand the problem, what might be causing it, what action has been taken, and what might be tried next.
Put this skill into practice by asking open-ended questions, repeating or paraphrasing the speaker’s words back to ensure understanding, and being patient. This technique can feel time-consuming, but you ultimately save time by gaining clarity, avoiding confusion, and building rapport and trust.
Critical Thinking
Critical thinking is the ability to assess a situation objectively and logically, ultimately making decisions based on facts and evidence. It involves developing and evaluating hypotheses and analyzing data to draw conclusions to make informed decisions. It also involves considering the long-term implications of the decisions that result from this thinking process.
Critical thinking for problem-solving presents itself when teams are working to understand the problem and identify the most logical steps forward to resolve the challenge. This type of thinking typically involves good communication with team members, insightful questions, and tapping into analytical thinking.
Time Management
Time management helps teams break down problems into smaller steps and account for how long each step will take. This is especially helpful for problems that must be solved on a deadline or for project-based work, where progress depends on many contingencies across individuals, teams, or even departments.
Effective time management enables teams to prioritize tasks, allocate resources, and create accountability around deadlines. This approach also creates clear expectations for employees.
Information Processing
Information processing is a framework that involves recognizing patterns in data and using critical thinking to interpret and draw conclusions.
In the workplace, one way information processing can be used is to identify root causes by analyzing data such as customer feedback, financial records, or performance metrics.
.png?width=1200&height=627&name=InternalImageA_KeyProblemSolvingSkills%20%20(1).png)
How Whole Brain® Thinking Supports Problem-Solving
When teams understand how each person responds to challenging situations, they're better equipped to work together on mutually beneficial solutions. This is where Herrmann’s Whole Brain® Thinking framework and Herrmann Brain Dominance Instrument (HBDI®) assessment can be especially helpful.
The HBDI® assessment helps people discover their thinking preferences, and the Whole Brain® Thinking framework helps teams understand those thinking preferences in themselves and others. Whole Brain® Thinking categorizes thinking preferences into four quadrants: Analytical (Blue), Structural (Green), Relational (Red), and Experimental (Yellow).
People typically prefer one or two quadrants, but people use all four quadrants daily. No quadrant or combination of quadrants is superior to another.
Whole Brain® Thinking can help teams improve their problem-solving skills by asking these questions for problem-solving:
- What? Look at the relevant facts about the problem.
- How? Identify what processes, procedures, etc., could be causing the obstacle or situation.
- Who? Determine the people who are implementing those processes and procedures.
- Why? Look at why the problem is happening and whether there is another way to view the challenge or situation.
These problem-solving questions can help teams cut out unnecessary steps and find effective solutions quickly.
.png?width=1200&height=627&name=InternalImageB_3CreativeApproachestoProblemSolvingatWork%20(1).png)
3 Creative Approaches to Problem-Solving at Work
While there are many ways to solve problems, you can access many proven approaches to help your team get started. These methods often push participants to think differently and Whole Brain® Thinking to get outside the box when confronting complex or difficult problems.
Here are three creative problem-solving examples of problem-solving at work.
Design Thinking
Design thinking is a problem-solving approach that centers on deeply understanding users and their needs. It is an iterative process that involves five distinct stages: empathize, define, ideate, prototype, and test. This process helps teams to approach problems from a user-centric perspective and develop creative solutions.
Whole Brain® Thinking in design takes the four quadrants and asks foundational questions with design in mind. Modifying these questions for a problem-solving exercise might look like this:
- What is the end goal? (Blue)
- How are we getting there? (Green)
- Who’s helping solve the problem, and who could be affected by the solution? (Red)
- Why are you solving the problem (and in this way)? (Yellow)
Reverse Engineering
Reverse engineering is the process of taking an existing product, system, or object and deconstructing it to understand its functionality, components, and construction. This approach can be beneficial when solving problems because it breaks the challenge down into smaller parts.
Many problems can seem overwhelming at first glance — too big for any person or team to solve. The bigness of the problem can obscure possible causes, adding to the frustration and even creating feelings of helplessness. Reverse engineering is a way in, helping your team take apart the problem and examine it, one piece at a time.
The Whole Brain® Thinking framework complements reverse engineering by tapping into people’s skills and thinking preferences across the quadrants. As teams break down complex problems and collaborate on solutions, they access different types of thinking, some of which will feel more natural.
For example, analytical thinkers embrace logical, fact-based approaches. They can buy into identifying the elements of the problem and what they mean. The organization of reverse engineering is welcoming for structural thinkers. Taking this new perspective to the problem helps interpersonal thinkers overcome the emotions potentially triggered by the big, overwhelming original problem.
Finally, experimental thinkers are skilled at integrating and synthesizing information. Reverse engineering is a prime opportunity for them to assess the components and reconstruct them in a way that advances new ideas and potential solutions.
Mind Mapping
Mind mapping is a creative and visual way of organizing ideas and information. It’s often represented by a diagram that uses words and visuals to illustrate relationships between different concepts or ideas. Mind mapping can be an effective tool for group problem-solving because it helps people to brainstorm without losing track of ideas or strains of thought that might later prove useful.
Mind mapping is a powerful tool for Whole Brain® Thinking teams because it encourages open dialogue, close collaboration, and embracing different perspectives, experiences, and thinking styles.
Embrace Thinking to Make Problem-Solving More Effective
Every organization has to solve problems, but you don’t have to dread them. When you build a team of Whole Brain® Thinkers and adopt successful problem-solving techniques, you can turn problems into opportunities that impact the business and your customers.
Try these problem-solving examples in your team to see how people respond — and keep experimenting. Just like solving organizational problems can require multiple attempts, finding the best problem-solving strategies for your unique team can take time to perfect.
Explore more ways to help your team solve problems effectively .
Weekly LinkedIn Newsletter

The four-color, four-quadrant graphic, HBDI® and Whole Brain® are trademarks of Herrmann Global, LLC.
You Might Find These Interesting

To Solve a Problem, First You Have to Define It
So much of work is about solving problems. When something breaks, how do you fix it? If a customer is upset, how do you assuage them? Falling behind competitors? Solve the problem through innovation....

How to Prevent Quiet Quitting With Performance Management
“Quiet quitting” might have started as a TikTok trend, but it’s become a major retention concern in recent years. Not only did millions of employees quit boldly during the Great Resignation, but now...

SOC 2 Type 2: Ensuring Your Company's Data Security with Herrmann
As businesses increasingly rely on cloud-based services and third-party vendors to manage critical data and systems, the need for reliable and secure information-handling practices has never been...
Bring Your Whole Brain® to Work with Our Weekly LinkedIn Newsletter
- Our Products
- Thinker Portal
- The Whole Brain® Blog
- Case Studies
- White Papers & Guides
- Webinars & Events
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Cookie Policy
- +1-800-432-4234
- Help Center
- Global Headquarters (US)
- Germany / DACH
- Southeast Asia
- UK & EMEA
- New Zealand

- Book a Demo
Are you looking to enhance your or your team’s problem-solving abilities? Engaging in activities specifically designed to stimulate your and your team’s critical thinking skills can be an excellent way to sharpen your problem-solving prowess. Whether you enjoy puzzles, brain teasers, or interactive challenges, these activities provide an opportunity to overcome obstacles and think creatively.
By immersing yourself in problem-solving activities, you can develop valuable strategies, improve your decision-making abilities, and boost your overall problem-solving IQ.
One key aspect of successful problem-solving is ensuring clear and effective communication, such as when teams use critical tools available online. For example, testing emails for deliverability and using an email spam checker to avoid spam filters can improve team efficiency. Try Maileroo’s free mail tester to validate your email campaigns effectively. Get ready to unlock your full potential and tackle any challenge that comes your way with these exciting activities for problem-solving.
In this article, we will explore activities for problem-solving that can help enhance your team’s problem-solving skills, allowing you to approach challenges with confidence and creativity.
What Are Problem Solving Activities?
Problem-solving activities or problem-solving exercises are interactive games requiring critical thinking to solve puzzles. They enhance teamwork & critical thinking. Examples include building towers, navigating simulated challenges, and fostering creativity and communication.
For instance, imagine a team working together to construct the tallest tower using limited materials. They strategize, communicate ideas, and problem-solve to create the best structure, promoting collaboration and inventive thinking among team members.
Some widely practiced problem-solving activities include:
- A Shrinking Vessel: Teams must fit into a shrinking space, testing their cooperation and adaptability.
- Marshmallow Spaghetti Tower: Participants build a tower using marshmallows and spaghetti, promoting creative engineering.
- Egg Drop: Protecting an egg from a fall challenges problem-solving skills.
- Desert Island Survival: Teams simulate survival scenarios, encouraging creative solutions.
- Rolling Dice: A simple yet effective game involving chance and decision-making.
- Build a Tower: Constructing a stable tower with limited resources fosters teamwork and innovation, etc.
13 Easy Activities For Problem-Solving Ideas to Enhance Team Collaboration
Team building activities offer a great opportunity to test problem-solving abilities and promote effective collaboration within a group to problem solving group activities. By engaging in these activities, teams can break the monotony of the workplace and create a more inclusive and welcoming environment.
Here are nine easy-to-implement activities that can bring substantial change to your team culture and overall workplace dynamics.
#1. Crossword Puzzles
Objective: To enhance problem-solving skills, vocabulary, and cognitive abilities through engaging crossword puzzles.
Estimated Time: 15-20 Minutes
Materials Needed:
- Crossword puzzle sheets
- Pens or pencils
- Distribute crossword puzzle sheets and pens/pencils to each participant.
- Explain the rules of crossword puzzles and the goal of completing as many clues as possible within the given time.
- Participants individually or in pairs work on solving the crossword puzzle by filling in the correct words.
- Encourage critical thinking, word association, and collaborative discussions for solving challenging clues.
- At the end of the time limit, review the answers and discuss any interesting or challenging clues as a group.
- Enhanced Problem-Solving: Participants engage in critical thinking while deciphering clues, promoting effective problem-solving skills.
- Vocabulary Expansion: Exposure to new words and phrases within the crossword improves vocabulary and comprehension.
- Cognitive Stimulation: The mental exercise of solving the puzzle stimulates the brain, enhancing cognitive abilities.
- Team Collaboration: If done in pairs, participants practice collaboration and communication to solve clues together.
- Achievement and Motivation: Successfully completing the crossword brings a sense of accomplishment and motivates individuals to explore more puzzles.
Tips for Facilitators:
- Provide varying levels of crossword puzzles to accommodate different skill levels.
- Encourage participants to share strategies for solving challenging clues.
- Emphasize the fun and educational aspects of the activity to keep participants engaged.
#2. A Shrinking Vessel

Estimated Time: 10-15 Minutes
- Materials Needed: A rope and a ball of yarn
- Prepare the Setting: Lay a rope on the floor in a shape that allows all team members to stand comfortably inside it. For larger teams, multiple ropes can be used, dividing them into smaller groups.
- Enter the Circle: Have all team members stand inside the rope, ensuring that nobody steps outside its boundaries.
- Shrinking the Circle: Begin gradually shrinking the rope’s size, reducing the available space inside the circle.
- Adapt and Maintain Balance: As the circle shrinks, team members must make subtle adjustments to maintain their positions and balance within the shrinking area.
- The Challenge: The objective for the team is to collectively brainstorm and find innovative ways to keep every team member inside the circle without anyone stepping outside.
- Collaboration and Communication: The activity promotes teamwork and open communication as participants strategize to stay within the shrinking circle.
- Adaptability: Team members learn to adapt swiftly to changing circumstances, fostering agility and flexibility.
- Creative Problem-Solving: The challenge encourages inventive thinking and brainstorming to find unique solutions.
- Trust Building: By relying on each other’s actions, participants build trust and cohesion among team members.
- Time-Efficient: The short duration makes it an ideal icebreaker or energizer during meetings or workshops.
- Observe and Facilitate: Monitor the team’s dynamics and offer guidance to encourage equal participation and effective problem-solving.
- Encourage Verbalization: Prompt participants to voice their ideas and collaborate vocally, aiding in real-time adjustments.
- Debrief Thoughtfully: Engage the team in a discussion afterward, reflecting on strategies employed and lessons learned.
- Emphasize Adaptability: Highlight the transferable skill of adaptability and its significance in both professional and personal contexts.

#3. Human Knots
- Objective: Improving Collaboration & enhancing Communication Skills
Estimated Time: 15-20 minutes
- Materials: None required
Procedure:
- Organize your team into a compact circle. For more sizable teams, subdivide them into smaller clusters, with each cluster forming its own circle.
- Direct each individual to grasp the hands of two other people in the circle, with the exception of those positioned directly adjacent to them. This action will result in the formation of a complex “human knot” within the circle.
- Present the challenge to the group: to unravel themselves from this entanglement while maintaining their hold on each other’s hands. If preferred, you can establish a specific time limit.
- Observe the team members collaborating to unravel the knot, witnessing their collective effort to devise solutions and free themselves from the intricate puzzle.
- Team Cohesion: The activity encourages team members to interact closely, promoting bonding and understanding among participants.
- Effective Communication: Participants practice clear and concise communication as they coordinate movements to untangle the knot.
- Problem-Solving: The challenge stimulates creative thinking and problem-solving skills as individuals work collectively to find the optimal path for untangling.
- Adaptability: Participants learn to adapt their actions based on the evolving dynamics of the human knot, fostering adaptability.
- Trust Building: As individuals rely on each other to navigate the intricate knot, trust and cooperation naturally develop.
- Set a Positive Tone: Create an inclusive and supportive atmosphere, emphasizing that the focus is on collaboration rather than competition.
- Encourage Verbalization: Urge participants to articulate their intentions and listen to others’ suggestions, promoting effective teamwork.
- Observe Group Dynamics: Monitor interactions and step in if needed to ensure everyone is actively engaged and included.
- Reflect and Share: Conclude the activity with a debriefing session, allowing participants to share their experiences, strategies, and key takeaways.
- Vary Grouping: Change group compositions for subsequent rounds to enhance interactions among different team members.
#4. Egg Drop

Helps With: Decision Making, Collaboration
- A carton of eggs
- Construction materials (balloons, rubber bands, straws, tape, plastic wrap, etc.)
- A suitable location for the activity
- Assign each team a single egg and random construction materials.
- Teams must create a carrier to protect the egg from breaking.
- Drop the carriers one by one and increase the height if necessary to determine the most durable carrier.
- The winning team is the one with the carrier that survives the highest drop.
- Decision Making: Participants engage in critical decision-making processes as they select construction materials and determine carrier designs.
- Collaboration: The activity necessitates collaboration and coordination among team members to construct an effective carrier.
- Problem-Solving: Teams apply creative problem-solving skills to devise innovative methods for safeguarding the egg.
- Risk Management: Participants learn to assess potential risks and consequences while making design choices to prevent egg breakage.
- Celebrating Success: The victorious team experiences a sense of accomplishment, boosting morale and promoting a positive team spirit.
- Provide Diverse Materials: Offer a wide range of construction materials to stimulate creativity and allow teams to explore various design options.
- Set Safety Guidelines: Prioritize safety by specifying a safe drop height and ensuring participants follow safety protocols during construction.
- Encourage Brainstorming: Prompt teams to brainstorm multiple carrier ideas before finalizing their designs, fostering diverse perspectives.
- Facilitate Reflection: After the activity, lead a discussion where teams share their design strategies, challenges faced, and lessons learned.
- Highlight Collaboration: Emphasize the significance of teamwork in achieving success, acknowledging effective communication and cooperation.
As a teamwork activity, Egg Drop can help team members solve problems through collaboration and communication.
Each team can design and customize their own balloons and can display their team logo, slogan, or elements related to team culture through custom balloons . Awards can also be set up, such as the most creative balloon design, the strongest frangipani structure, etc., to increase the motivation for competition and participation.
After the activity, team sharing and feedback can be conducted to allow everyone to share their learning experience and feelings about teamwork.
This combination allows team members to experience the importance of teamwork in creativity and practice, and strengthen team cohesion by completing challenges and sharing experiences.
#5. Marshmallow Spaghetti Tower
Helps With: Collaboration
Estimated Time: 20-30 Minutes
Materials Needed (per team):
- Raw spaghetti: 20 sticks
- Marshmallow: 1
- String: 1 yard
- Masking tape: 1 roll
- Tower Construction: Instruct teams to collaborate and utilize the provided materials to construct the tallest tower possible within a designated time frame.
- Marshmallow Support: Emphasize that the tower must be capable of standing independently and supporting a marshmallow at its highest point.
- Prototype and Iterate: Encourage teams to engage in prototyping and iteration, testing different design approaches and refining their tower structures.
- T eamwork and Communication: Promote effective teamwork and communication as team members coordinate their efforts to build a stable and tall tower.
- Evaluation Criteria: Evaluate each tower based on its height, stability, and the successful placement of the marshmallow at the top.
- Collaboration: Participants collaborate closely, sharing ideas and working together to design and construct the tower.
- Innovative Thinking: The activity encourages innovative thinking as teams experiment with different strategies to build a stable tower.
- Time Management: Teams practice time management skills as they work within a specified time limit to complete the task.
- Problem-Solving: Participants engage in creative problem-solving to address challenges such as balancing the marshmallow and constructing a sturdy tower.
- Adaptability: Teams adapt their approaches based on trial and error, learning from each iteration to improve their tower designs.
- Set Clear Guidelines: Clearly explain the materials, objectives, and evaluation criteria to ensure teams understand the task.
- Foster Creativity: Encourage teams to think outside the box and explore unconventional methods for constructing their towers.
- Emphasize Collaboration: Highlight the importance of effective communication and teamwork to accomplish the task successfully.
- Time Management: Remind teams of the time limit and encourage them to allocate their time wisely between planning and construction.
- Reflect and Share: Facilitate a discussion after the activity, allowing teams to share their design choices, challenges faced, and lessons learned.

Objective: To engage participants in the strategic and analytical world of Sudoku, enhancing logical thinking and problem-solving abilities.
Estimated Time: 20-25 Minutes
- Sudoku puzzle sheets
- Pencils with erasers
- Distribute Sudoku puzzle sheets and pencils to each participant.
- Familiarize participants with the rules and mechanics of Sudoku puzzles.
- Explain the goal: to fill in the empty cells with numbers from 1 to 9 while adhering to the rules of no repetition in rows, columns, or subgrids.
- Encourage participants to analyze the puzzle’s layout, identify potential numbers, and strategically fill in cells.
- Emphasize the importance of logical deduction and step-by-step approach in solving the puzzle.
- Provide hints or guidance if needed, ensuring participants remain engaged and challenged.
- Logical Thinking: Sudoku challenges participants’ logical and deductive reasoning, fostering analytical skills.
- Problem-Solving: The intricate interplay of numbers and constraints hones problem-solving abilities.
- Focus and Patience: Participants practice patience and attention to detail while gradually unveiling the solution.
- Pattern Recognition: Identifying number patterns and possibilities contributes to enhanced pattern recognition skills.
- Personal Achievement: Successfully completing a Sudoku puzzle provides a sense of accomplishment and boosts confidence.
- Offer varying levels of Sudoku puzzles to cater to different skill levels.
- Encourage participants to share strategies and techniques for solving specific challenges.
- Highlight the mental workout Sudoku provides and its transferable skills to real-life problem-solving.

Helps With: Communication, Problem-solving, & Management
- A lockable room
- 5-10 puzzles or clues
- Hide the key and a set of clues around the room.
- Lock the room and provide team members with a specific time limit to find the key and escape.
- Instruct the team to work together, solving the puzzles and deciphering the clues to locate the key.
- Encourage efficient communication and effective problem-solving under time pressure.
- Communication Skills: Participants enhance their communication abilities by sharing observations, ideas, and findings to collectively solve puzzles.
- Problem-solving Proficiency: The activity challenges teams to think critically, apply logical reasoning, and collaboratively tackle intricate challenges.
- Team Management: The experience promotes effective team management as members assign tasks, prioritize efforts, and coordinate actions.
- Time Management: The imposed time limit sharpens time management skills as teams strategize and allocate time wisely.
- Adaptability: Teams learn to adapt and adjust strategies based on progress, evolving clues, and time constraints.
- Clear Introduction: Provide a concise overview of the activity, emphasizing the importance of communication, problem-solving, and time management.
- Diverse Challenges: Offer a mix of puzzles and clues to engage various problem-solving skills, catering to different team strengths.
- Supportive Role: Act as a facilitator, offering subtle guidance if needed while allowing teams to independently explore and solve challenges.
- Debriefing Session: Organize a debriefing session afterward to discuss the experience, highlight successful strategies, and identify areas for improvement.
- Encourage Reflection: Encourage participants to reflect on their teamwork, communication effectiveness, and problem-solving approach.
#8. Frostbite for Group Problem Solving Activities
Helps With: Decision Making, Trust, Leadership
- An electric fan
- Construction materials (toothpicks, cardstock, rubber bands, sticky notes, etc.)
- Divide the team into groups of 4-5 people, each with a designated leader.
- Blindfold team members and prohibit leaders from using their hands.
- Provide teams with construction materials and challenge them to build a tent within 30 minutes.
- Test the tents using the fan to see which can withstand high winds.
- Decision-Making Proficiency: Participants are exposed to critical decision-making situations under constraints, allowing them to practice effective and efficient decision-making.
- Trust Development: Blindfolding team members and relying on the designated leaders fosters trust and collaboration among team members.
- Leadership Skills: Designated leaders navigate the challenge without hands-on involvement, enhancing their leadership and communication skills.
- Creative Problem Solving: Teams employ creative thinking and resourcefulness to construct stable tents with limited sensory input.
- Team Cohesion: The shared task and unique constraints promote team cohesion and mutual understanding.
- Role of the Facilitator: Act as an observer, allowing teams to navigate the challenge with minimal intervention. Offer assistance only when necessary.
- Clarity in Instructions: Provide clear instructions regarding blindfolding, leader restrictions, and time limits to ensure a consistent experience.
- Debriefing Session: After the activity, conduct a debriefing session to discuss team dynamics, leadership approaches, and decision-making strategies.
- Encourage Communication: Emphasize the importance of effective communication within teams to ensure smooth coordination and successful tent construction.
- Acknowledge Creativity: Celebrate creative solutions and innovative approaches exhibited by teams during the tent-building process.
#9. Dumbest Idea First

Helps With: Critical Thinking & Creative Problem Solving Activity
Estimated Time: 15-20 Minutes
Materials Needed: A piece of paper, pen, and pencil
- Problem Presentation: Introduce a specific problem to the team, either a real-world challenge or a hypothetical scenario that requires a solution.
- Brainstorming Dumb Ideas: Instruct team members to quickly generate and jot down the most unconventional and seemingly “dumb” ideas they can think of to address the problem.
- Idea Sharing: Encourage each participant to share their generated ideas with the group, fostering a relaxed and open atmosphere for creative expression.
- Viability Assessment: As a team, review and evaluate each idea, considering potential benefits and drawbacks. Emphasize the goal of identifying unconventional approaches.
- Selecting Promising Solutions: Identify which seemingly “dumb” ideas could hold hidden potential or innovative insights. Discuss how these ideas could be adapted into workable solutions.
- Divergent Thinking: Participants engage in divergent thinking, pushing beyond conventional boundaries to explore unconventional solutions.
- Creative Exploration: The activity sparks creative exploration by encouraging participants to let go of inhibitions and embrace imaginative thinking.
- Critical Analysis: Through evaluating each idea, participants practice critical analysis and learn to identify unique angles and aspects of potential solutions.
- Open Communication: The lighthearted approach of sharing “dumb” ideas fosters open communication, reducing fear of judgment and promoting active participation.
- Solution Adaptation: Identifying elements of seemingly “dumb” ideas that have merit encourages participants to adapt and refine their approaches creatively.
- Safe Environment: Foster a safe and non-judgmental environment where participants feel comfortable sharing unconventional ideas.
- Time Management: Set clear time limits for idea generation and sharing to maintain the activity’s energetic pace.
- Encourage Wild Ideas: Emphasize that the goal is to explore the unconventional, urging participants to push the boundaries of creativity.
- Facilitator Participation: Participate in idea generation to demonstrate an open-minded approach and encourage involvement.
- Debriefing Discussion: After the activity, facilitate a discussion on how seemingly “dumb” ideas can inspire innovative solutions and stimulate fresh thinking.
This activity encourages out-of-the-box thinking and creative problem-solving. It allows teams to explore unconventional ideas that may lead to unexpected, yet effective, solutions.
#10: Legoman
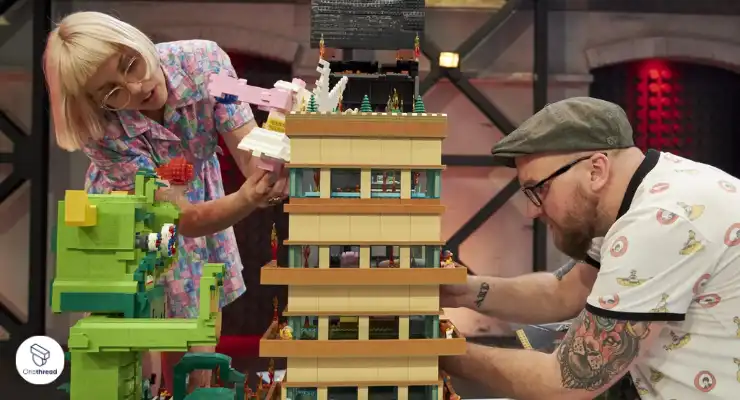

Helps With: Foster teamwork, communication, and creativity through a collaborative Lego-building activity.
Estimated Time: 20-30 minutes
- Lego bricks
- Lego instruction manuals
Procedure :
- Divide participants into small teams of 3-5 members.
- Provide each team with an equal set of Lego bricks and a Lego instruction manual.
- Explain that the goal is for teams to work together to construct the Lego model shown in the manual.
- Set a time limit for the building activity based on model complexity.
- Allow teams to self-organize, build, and collaborate to complete the model within the time limit.
- Evaluate each team’s final model compared to the manual’s original design.
- Enhanced Communication: Participants must communicate clearly and listen actively to collaborate effectively.
- Strengthened Teamwork: Combining efforts toward a shared goal promotes camaraderie and team cohesion.
- Creative Problem-Solving: Teams must creatively problem-solve if pieces are missing or instructions unclear.
- Planning and Resource Allocation: Following instructions fosters planning skills and efficient use of resources.
- Sense of Achievement: Completing a challenging build provides a sense of collective accomplishment.
- Encourage Participation: Urge quieter members to contribute ideas and take an active role.
- Highlight Teamwork: Emphasize how cooperation and task coordination are key to success.
- Ensure Equal Engagement: Monitor group dynamics to ensure all members are engaged.
- Allow Creativity: Permit modifications if teams lack exact pieces or wish to get creative.
- Focus on Enjoyment: Create a lively atmosphere so the activity remains energizing and fun.
#11: Minefield
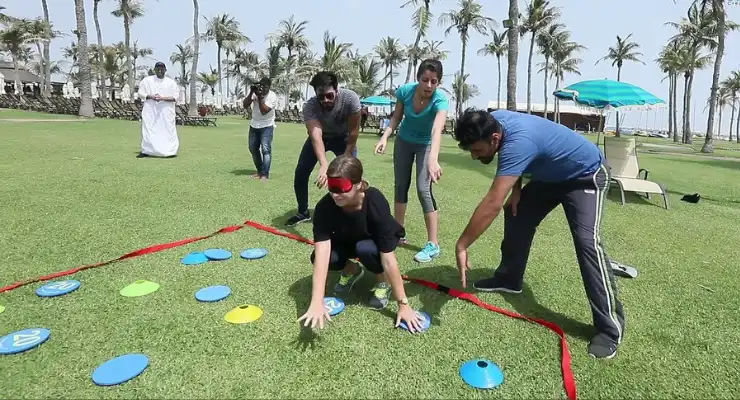

Helps With: Trust, Communication, Patience
Materials Needed: Open space, blindfolds
- Mark a “minefield” on the ground using ropes, cones, or tape. Add toy mines or paper cups.
- Pair up participants and blindfold one partner.
- Position blindfolded partners at the start of the minefield. Direct seeing partners to verbally guide them through to the other side without hitting “mines.”
- Partners switch roles once finished and repeat.
- Time partnerships and provide prizes for the fastest safe crossing.
- Trust Building: Blindfolded partners must trust their partner’s instructions.
- Effective Communication: Giving clear, specific directions is essential for navigating the minefield.
- Active Listening: Partners must listen closely and follow directions precisely.
- Patience & Support: The exercise requires patience and encouraging guidance between partners.
- Team Coordination: Partners must work in sync, coordinating movements and communication.
- Test Boundaries: Ensure the minefield’s size accommodates safe movement and communication.
- Monitor Interactions: Watch for dominant guidance and ensure both partners participate fully.
- Time Strategically: Adjust time limits based on the minefield size and difficulty.
- Add Obstacles: Introduce additional non-mine objects to increase challenge and communication needs.
- Foster Discussion: Debrief afterward to discuss communication approaches and trust-building takeaways.
#12: Reverse Pyramid
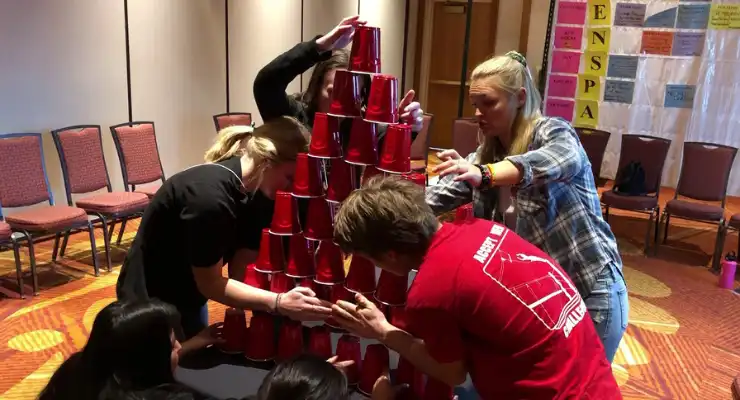

Helps With: Teamwork, Communication, Creativity
Materials Needed: 36 cups per group, tables
- Form small groups of 5-7 participants.
- Provide each group with a stack of 36 cups and a designated building area.
- Explain the objective: Build the tallest pyramid starting with just one cup on top.
- Place the first cup on the table, and anyone in the group can add two cups beneath it to form the second row.
- From this point, only the bottom row can be lifted to add the next row underneath.
- Cups in the pyramid can only be touched or supported by index fingers.
- If the structure falls, start over from one cup.
- Offer more cups if a group uses all provided.
- Allow 15 minutes for building.
Teamwork: Collaborate to construct the pyramid.
Communication: Discuss and execute the building strategy.
Creativity: Find innovative ways to build a tall, stable pyramid.
Clarify Expectations: Emphasize the definition of a pyramid with each row having one less cup.
Encourage Perseverance: Motivate groups to continue despite challenges.
Promote Consensus: Encourage groups to work together and help each other.
Reflect on Failure: Use collapses as a metaphor for overcoming obstacles and improving.
Consider Competitions: Modify the activity for competitive teams and scoring.
#13: Stranded
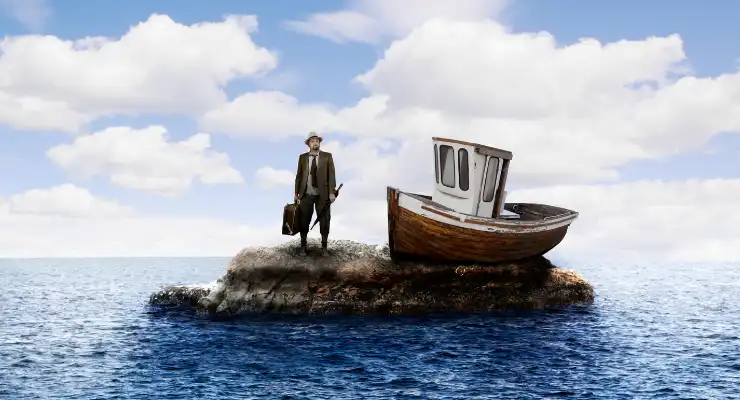

Helps With: Decision-making, Prioritization, Teamwork
Materials Needed: List of salvaged items, paper, pens
- Present a scenario where teams are stranded and must prioritize items salvaged from a plane crash.
- Provide teams with the same list of ~15 salvaged items.
- Instruct teams to agree on an item ranking with #1 being the most important for survival.
- Teams share and compare their prioritized lists. Identify differences in approach.
- Discuss what factors influenced decisions and how teams worked together to agree on priorities.
- Critical Thinking: Weighing item importance requires analytical thinking and discussion.
- Team Decision-Making: Coming to a consensus fosters team decision-making capabilities.
- Prioritization Skills: Ranking items strengthen prioritization and justification abilities.
- Perspective-Taking: Understanding different prioritizations builds perspective-taking skills.
- Team Cohesion: Collaborating toward a shared goal brings teams closer together.
- Encourage Discussion: Urge teams to discuss all ideas rather than allow single members to dominate.
- Be Engaged: Circulate to listen in on team discussions and pose thought-provoking questions.
- Add Complexity: Introduce scenarios with additional constraints to expand critical thinking.
- Highlight Disagreements: When priorities differ, facilitate constructive discussions on influencing factors.
- Recognize Collaboration: Acknowledge teams that demonstrate exceptional teamwork and communication.
Now let’s look at some common types of problem-solving activities.
Types of Problem-Solving Activities
The most common types of problem-solving activities/exercises are:
- Creative problem-solving activities
- Group problem-solving activities
- Individual problem-solving activities
- Fun problem-solving activities, etc.
In the next segments, we’ll be discussing these types of problem-solving activities in detail. So, keep reading!
Creative Problem-Solving Activities
Creative problem solving (CPS) means using creativity to find new solutions. It involves thinking creatively at first and then evaluating ideas later. For example, think of it like brainstorming fun game ideas, discussing them, and then picking the best one to play.
Some of the most common creative problem-solving activities include:
- Legoman: Building creative structures with LEGO.
- Escape: Solving puzzles to escape a room.
- Frostbite: Finding solutions in challenging situations.
- Minefield: Navigating a field of obstacles.
Group Problem-Solving Activities
Group problem-solving activities are challenges that make teams work together to solve puzzles or overcome obstacles. They enhance teamwork and critical thinking.
For instance, think of a puzzle-solving game where a group must find hidden clues to escape a locked room.
Here are the most common group problem-solving activities you can try in groups:
- A Shrinking Vessel
- Marshmallow Spaghetti Tower
- Cardboard Boat Building Challenge
- Clue Murder Mystery
- Escape Room: Jewel Heist
- Escape Room: Virtual Team Building
- Scavenger Hunt
- Dumbest Idea First
Individual Problem-Solving Activities
As the name suggests, individual problem-solving activities are the tasks that you need to play alone to boost your critical thinking ability. They help you solve problems and stay calm while facing challenges in real life. Like puzzles, they make your brain sharper. Imagine it’s like training your brain muscles to handle tricky situations.
Here are some of the most common individual problem-solving activities:
- Puzzles (jigsaw, crossword, sudoku, etc.)
- Brain teasers
- Logic problems
- Optical illusions
- “Escape room” style games
Fun Problem-Solving Activities
Fun problem-solving activities are enjoyable games that sharpen your critical thinking skills while having a blast. Think of activities like the Legoman challenge, escape rooms, or rolling dice games – they make problem-solving exciting and engaging!
And to be frank, all of the mentioned problem-solving activities are fun if you know how to play and enjoy them as all of them are game-like activities.
Team Problems You Can Address Through Problem Solving Activities
Fun problem-solving activities serve as dynamic tools to address a range of challenges that teams often encounter. These engaging activities foster an environment of collaboration, creativity, and critical thinking, enabling teams to tackle various problems head-on. Here are some common team problems that can be effectively addressed through these activities:
- Communication Breakdowns:
Activities like “Escape,” “A Shrinking Vessel,” and “Human Knots” emphasize the importance of clear and effective communication. They require teams to work together, exchange ideas, and devise strategies to accomplish a shared goal. By engaging in these activities, team members learn to communicate more efficiently, enhancing overall team communication in real-world situations.
- Lack of Trust and Cohesion:
Problem-solving activities promote trust and cohesiveness within teams. For instance, “Frostbite” and “Marshmallow Spaghetti Tower” require teams to collaborate closely, trust each other’s ideas, and rely on each member’s strengths. These activities build a sense of unity and trust, which can translate into improved teamwork and collaboration.
- Innovative Thinking:
“Dumbest Idea First” and “Egg Drop” encourage teams to think outside the box and explore unconventional solutions. These activities challenge teams to be creative and innovative in their problem-solving approaches, fostering a culture of thinking beyond traditional boundaries when faced with complex issues.
- Decision-Making Challenges:
Activities like “Onethread” facilitate group decision-making by providing a platform for open discussions and collaborative choices. Problem-solving activities require teams to make decisions collectively, teaching them to weigh options, consider different viewpoints, and arrive at informed conclusions—a skill that is transferable to real-world decision-making scenarios.
- Leadership and Role Clarification:
Activities such as “Frostbite” and “Egg Drop” designate team leaders and roles within groups. This provides an opportunity for team members to practice leadership, delegation, and role-specific tasks. By experiencing leadership dynamics in a controlled setting, teams can improve their leadership skills and better understand their roles in actual projects.
- Problem-Solving Strategies:
All of the problem-solving activities involve the application of different strategies. Teams learn to analyze problems, break them down into manageable components, and develop systematic approaches for resolution. These strategies can be adapted to real-world challenges, enabling teams to approach complex issues with confidence.
- Team Morale and Engagement:
Participating in engaging and enjoyable activities boosts team morale and engagement. These activities provide a break from routine tasks, energize team members, and create a positive and fun atmosphere. Elevated team morale can lead to increased motivation and productivity.
The incentives of event prizes can further stimulate the enthusiasm and participation of team members. The choice of prizes is crucial, as it can directly affect the attractiveness and participation of the event. Among them, Medals are essential prizes.
Medals are symbols of honor awarded to winners and represent the value and achievement of an event.
Medals also have a motivational effect, they encourage team members to pursue higher achievements and progress.
Medals are artistic and aesthetic. They are usually designed by designers according to different occasions and themes and have high collection value.
By incorporating these fun problem-solving activities, teams can address a variety of challenges, foster skill development, and build a more cohesive and effective working environment. As teams learn to collaborate, communicate, innovate, and make decisions collectively, they are better equipped to overcome obstacles and achieve shared goals.
The Benefits of Problem Solving Activities for Your Team
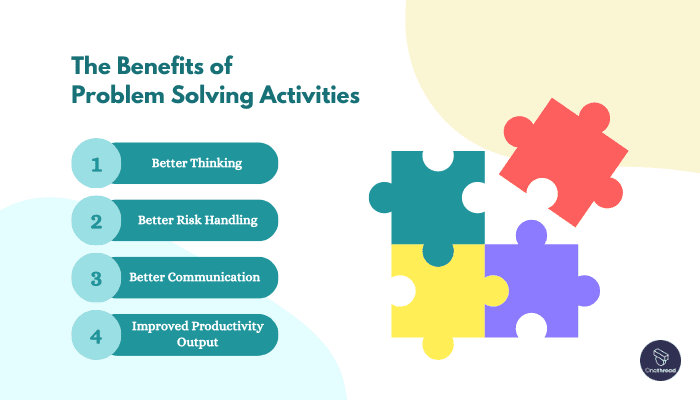
#1 Better Thinking
Problem-solving activities bring out the best in team members by encouraging them to contribute their unique ideas. This stimulates better thinking as team managers evaluate different solutions and choose the most suitable ones.
For example, a remote team struggling with communication benefited from quick thinking and the sharing of ideas, leading to the adoption of various communication modes for improved collaboration.
#2 Better Risk Handling
Team building problem solving activities condition individuals to handle risks more effectively. By engaging in challenging situations and finding solutions, team members develop the ability to respond better to stressful circumstances.
#3 Better Communication
Regular communication among team members is crucial for efficient problem-solving. Engaging in problem-solving activities fosters cooperation and communication within the team, resulting in better understanding and collaboration. Using tools like OneThread can further enhance team communication and accountability.
#4 Improved Productivity Output
When teams work cohesively, overall productivity improves, leading to enhanced profit margins for the company or organization. Involving managers and team members in problem-solving activities can positively impact the company’s growth and profitability.
How Onethread Enhances the Effect of Problem Solving Activities
Problem-solving activities within teams thrive on collaborative efforts and shared perspectives. Onethread emerges as a potent facilitator, enabling teams to collectively tackle challenges and harness diverse viewpoints with precision. Here’s a comprehensive view of how Onethread amplifies team collaboration in problem-solving initiatives:
Open Channels for Discussion:
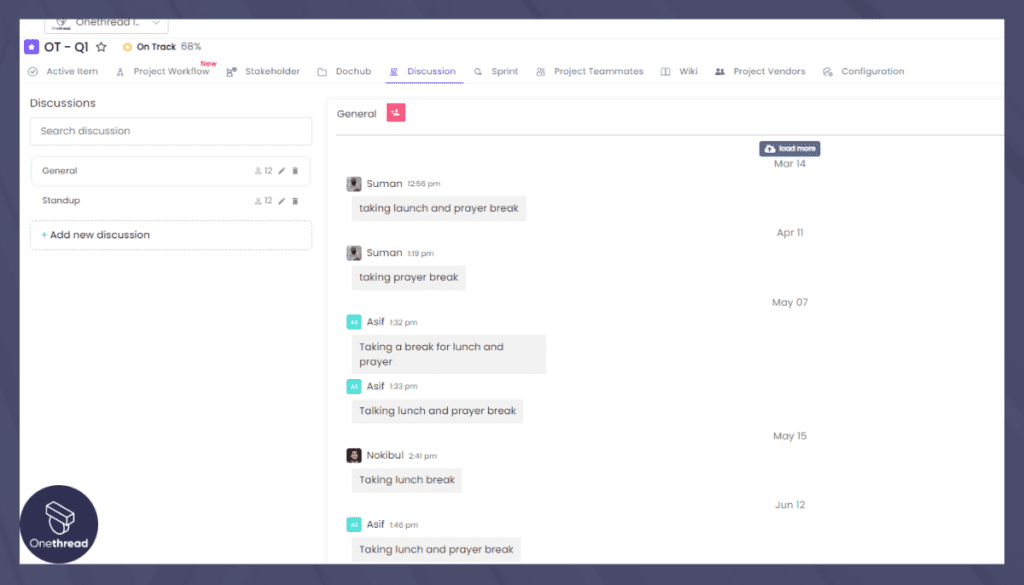
Onethread’s real-time messaging feature serves as a dedicated hub for open and seamless discussions. Teams can engage in brainstorming sessions, share insightful observations, and propose innovative solutions within a flexible environment. Asynchronous communication empowers members to contribute their insights at their convenience, fostering comprehensive problem analysis with ample deliberation.
Centralized Sharing of Resources:
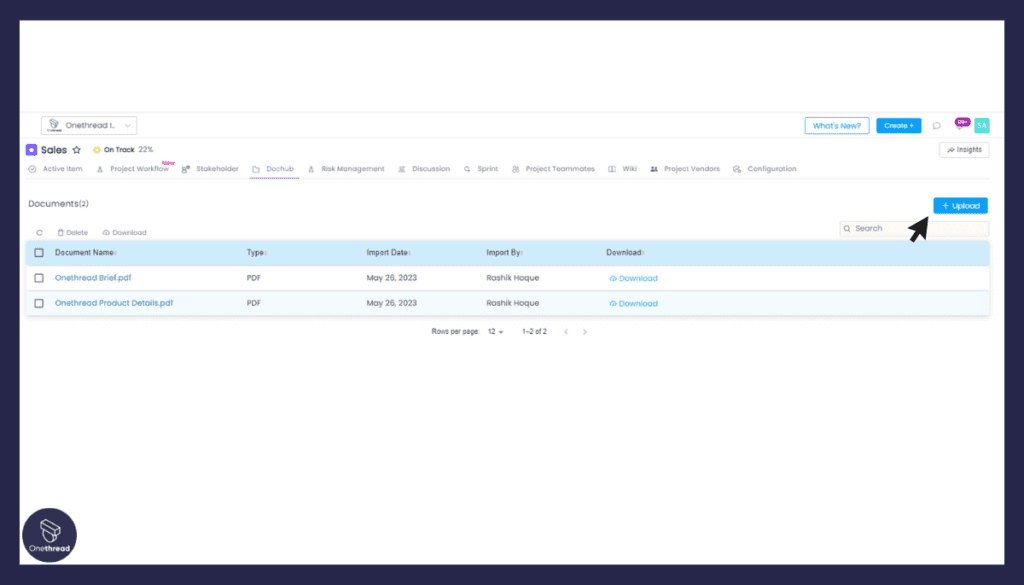
Effective problem-solving often hinges on access to pertinent resources. Onethread’s document sharing functionality ensures that critical information, references, and research findings are centralized and readily accessible. This eradicates the need for cumbersome email attachments and enables team members to collaborate with precise and up-to-date data.
Efficient Task Allocation and Monitoring:
Problem-solving journeys comprise a series of tasks and actions. Onethread’s task management capability streamlines the delegation of specific responsibilities to team members. Assign tasks related to research, data analysis, or solution implementation and monitor progress in real time. This cultivates a sense of accountability and guarantees comprehensive coverage of every facet of the problem-solving process.
Facilitated Collaborative Decision-Making: Navigating intricate problems often demands collective decision-making. Onethread’s collaborative ecosystem empowers teams to deliberate over potential solutions, assess pros and cons, and make well-informed choices. Transparent discussions ensure that decisions are comprehensively comprehended and supported by the entire team.
Seamless Documentation and Insights Sharing:
As the problem-solving journey unfolds, the accumulation of insights and conclusions becomes pivotal. Onethread’s collaborative document editing feature empowers teams to document their discoveries, chronicle the steps undertaken, and showcase successful solutions. This shared repository of documentation serves as a valuable resource for future reference and continuous learning.
With Onethread orchestrating the backdrop, team collaboration during problem-solving activities transforms into a harmonious fusion of insights, ideas, and actionable steps.
What are the 5 problem-solving skills?
The top 5 problem-solving skills in 2023 are critical thinking, creativity, emotional intelligence, adaptability, and data literacy. Most employers seek these skills in their workforce.
What are the steps of problem-solving?
Problem-solving steps are as follows: 1. Define the problem clearly. 2. Analyze the issue in detail. 3. Generate potential solutions. 4. Evaluate these options. 5. Choose the best solution. 6. Put the chosen solution into action. 7. Measure the outcomes to assess effectiveness and improvements made. These sequential steps assist in efficient and effective problem resolution.
How do you teach problem-solving skills?
Teaching problem-solving involves modelling effective methods within a context, helping students grasp the problem, dedicating ample time, asking guiding questions, and giving suggestions. Connect errors to misconceptions to enhance understanding, fostering a straightforward approach to building problem-solving skills.
So here is all about “activities for problem solving”.No matter which activity you choose, engaging in problem-solving activities not only provides entertainment but also helps enhance cognitive abilities such as critical thinking, decision making, and creativity. So why not make problem solving a regular part of your routine?
Take some time each day or week to engage in these activities and watch as your problem-solving skills grow stronger. Plus, it’s an enjoyable way to pass the time and challenge yourself mentally.
So go ahead, grab a puzzle or gather some friends for a game night – get ready to have fun while sharpening your problem-solving skills!
Let's Get Started with Onethread
Onethread empowers you to plan, organise, and track projects with ease, ensuring you meet deadlines, allocate resources efficiently, and keep progress transparent.
By subscribing you agree to our Privacy Policy .
Giving modern marketing teams superpowers with short links that stand out.
- Live Product Demo
© Copyright 2023 Onethread, Inc

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Definition and ImportanceProblem solving is the process of finding solutions to obstacles or challenges you encounter in your life or work. It is a skill that allo…
Problem-solving is the ability to identify a problem, prioritize based on gravity and urgency, analyze the root cause, gather relevant information, develop and evaluate viable …
Problem-solving skills are skills that enable people to handle unexpected situations or difficult challenges at work. Organisations need people who can accurately …
When you build a team of Whole Brain® Thinkers and adopt successful problem-solving techniques, you can turn problems into opportunities that impact the business and your customers. Try these problem-solving examples in your …
Define the problem. Diagnose the situation so that your focus is on the problem, not just its symptoms. Helpful problem-solving techniques include using flowcharts to identify the expected steps of a process and cause-and-effect …
Problem-solving is an essential and marketable soft skill in the workplace. So, how can you improve your problem-solving and show employers you have this valuable skill? In this guide, we’ll cover: Problem-Solving Skills …
Problem-solving activities or problem-solving exercises are interactive games requiring critical thinking to solve puzzles. They enhance teamwork & critical thinking. Examples include building towers, navigating …