MLA Citation Style 9th Edition: Quotations
- Core Elements
- Audio Materials
- Books & eBooks
- Encyclopedias & Dictionaries
- Government Documents
- Images, Infographics, Maps, Charts, & Tables
- Indigenous Elders and Knowledge Keepers (Oral Communication)
- Journal Articles
- Magazine Articles
- Newspaper Articles
- Personal Communications (including emails and interviews)
- Religious Works
- Social Media
- Theses & Dissertations
- Websites (including documents/PDFs posted on websites)
- Works in Another Language / Translations
- No Author/Date/Etc.
- Sample Paper
- Annotated Bib.

Quoting vs. Paraphrasing
There are two ways to integrate sources into your assignment: quoting directly or paraphrasing.
Quoting is copying a selection from someone else's work, phrasing it exactly as it was originally written. When quoting place quotation marks (" ") around the selected passage to show where the quote begins and where it ends. Make sure to include an in-text citation.
Paraphrasing is used to show that you understand what the author wrote. You must reword the passage, expressing the ideas in your own words, and not just change a few words here and there. Make sure to also include an in-text citation.
Quotation Examples
There are two basic formats that can be used when quoting a source:
Parenthetical Style:
Narrative Style:
Note: If there are no page numbers, as in a website, cite the author name only.
Long Quotations
A long or block quotation is a quotation which is 4 lines or more.
Rules for Long Quotations
- The line before your long quotation, when you're introducing the quote, usually ends with a colon.
- The long quotation is indented half an inch from the rest of the text, so it looks like a block of text.
- There are no quotation marks around the quotation.
- The period at the end of the quotation comes before your in-text citation as opposed to after , as it does with regular quotations.
Example of a Long Quotation
At the end of Lord of the Flies the boys are struck with the realization of their behaviour:
The tears began to flow and sobs shook him. He gave himself up to them now for the first time on the island; great, shuddering spasms of grief that seemed to wrench his whole body. His voice rose under the black smoke before the burning wreckage of the island; and infected by that emotion, the other little boys began to shake and sob too. (Golding 186)
Modifying Quotations
Sometimes you may want to make some modifications to the quote to fit your writing. Here are some MLA rules when changing quotes:
Changing Quotations
Omitting parts of a quotation
If you would like to exclude some words from a quotation, replace the words you are not including with an ellipsis: …
Adding words to a quote
If you are adding words that are not part of the original quote, enclose the additional words in square brackets: [XYZ]
- Using Quotations (The Learning Portal) Tip sheet on how and when to use quotations
- Paraphrasing (The Learning Portal) Tip sheet on paraphrasing information
- << Previous: No Author/Date/Etc.
- Next: Sample Paper >>
- Last Updated: Apr 5, 2024 4:43 PM
- URL: https://libguides.msubillings.edu/mla9
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
MLA Formatting and Style Guide

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
The following overview should help you better understand how to cite sources using MLA 9 th edition, including how to format the Works Cited page and in-text citations.
Please use the example at the bottom of this page to cite the Purdue OWL in MLA. See also our MLA vidcast series on the Purdue OWL YouTube Channel .
Creating a Works Cited list using the ninth edition
MLA is a style of documentation that may be applied to many different types of writing. Since texts have become increasingly digital, and the same document may often be found in several different sources, following a set of rigid rules no longer suffices.
Thus, the current system is based on a few guiding principles, rather than an extensive list of specific rules. While the handbook still describes how to cite sources, it is organized according to the process of documentation, rather than by the sources themselves. This gives writers a flexible method that is near-universally applicable.
Once you are familiar with the method, you can use it to document any type of source, for any type of paper, in any field.
Here is an overview of the process:
When deciding how to cite your source, start by consulting the list of core elements. These are the general pieces of information that MLA suggests including in each Works Cited entry. In your citation, the elements should be listed in the following order:
- Title of source.
- Title of container,
- Other contributors,
- Publication date,
Each element should be followed by the corresponding punctuation mark shown above. Earlier editions of the handbook included the place of publication and required different punctuation (such as journal editions in parentheses and colons after issue numbers) depending on the type of source. In the current version, punctuation is simpler (only commas and periods separate the elements), and information about the source is kept to the basics.
Begin the entry with the author’s last name, followed by a comma and the rest of the name, as presented in the work. End this element with a period.
Bhabha, Homi K. The Location of Culture. Routledge, 1994.
Title of source
The title of the source should follow the author’s name. Depending upon the type of source, it should be listed in italics or quotation marks.
A book should be in italics:
Henley, Patricia. The Hummingbird House . MacMurray, 1999.
An individual webpage should be in quotation marks. The name of the parent website, which MLA treats as a "container," should follow in italics:
Lundman, Susan. "How to Make Vegetarian Chili." eHow, www.ehow.com/how_10727_make-vegetarian-chili.html.*
A periodical (journal, magazine, newspaper) article should be in quotation marks:
Bagchi, Alaknanda. "Conflicting Nationalisms: The Voice of the Subaltern in Mahasweta Devi's Bashai Tudu." Tulsa Studies in Women's Literature , vol. 15, no. 1, 1996, pp. 41-50.
A song or piece of music on an album should be in quotation marks. The name of the album should then follow in italics:
Beyoncé. "Pray You Catch Me." Lemonade, Parkwood Entertainment, 2016, www.beyonce.com/album/lemonade-visual-album/.
*The MLA handbook recommends including URLs when citing online sources. For more information, see the “Optional Elements” section below.
Title of container
The eighth edition of the MLA handbook introduced what are referred to as "containers," which are the larger wholes in which the source is located. For example, if you want to cite a poem that is listed in a collection of poems, the individual poem is the source, while the larger collection is the container. The title of the container is usually italicized and followed by a comma, since the information that follows next describes the container.
Kincaid, Jamaica. "Girl." The Vintage Book of Contemporary American Short Stories, edited by Tobias Wolff, Vintage, 1994, pp. 306-07.
The container may also be a television series, which is made up of episodes.
“94 Meetings.” Parks and Recreation, created by Greg Daniels and Michael Schur, performance by Amy Poehler, season 2, episode 21, Deedle-Dee Productions and Universal Media Studios, 2010.
The container may also be a website, which contains articles, postings, and other works.
Wise, DeWanda. “Why TV Shows Make Me Feel Less Alone.” NAMI, 31 May 2019, www.nami.org/Blogs/NAMI-Blog/May-2019/How-TV-Shows-Make-Me-Feel-Less-Alone . Accessed 3 June 2019.
In some cases, a container might be within a larger container. You might have read a book of short stories on Google Books , or watched a television series on Netflix . You might have found the electronic version of a journal on JSTOR. It is important to cite these containers within containers so that your readers can find the exact source that you used.
“94 Meetings.” Parks and Recreation , season 2, episode 21, NBC , 29 Apr. 2010. Netflix, www.netflix.com/watch/70152031?trackId=200256157&tctx=0%2C20%2C0974d361-27cd-44de-9c2a-2d9d868b9f64-12120962.
Langhamer, Claire. “Love and Courtship in Mid-Twentieth-Century England.” Historical Journal , vol. 50, no. 1, 2007, pp. 173-96. ProQuest, doi:10.1017/S0018246X06005966. Accessed 27 May 2009.
Other contributors
In addition to the author, there may be other contributors to the source who should be credited, such as editors, illustrators, translators, etc. If their contributions are relevant to your research, or necessary to identify the source, include their names in your documentation.
Foucault, Michel. Madness and Civilization: A History of Insanity in the Age of Reason. Translated by Richard Howard , Vintage-Random House, 1988.
Woolf, Virginia. Jacob’s Room . Annotated and with an introduction by Vara Neverow, Harcourt, Inc., 2008.
If a source is listed as an edition or version of a work, include it in your citation.
The Bible . Authorized King James Version, Oxford UP, 1998.
Crowley, Sharon, and Debra Hawhee. Ancient Rhetorics for Contemporary Students. 3rd ed., Pearson, 2004.
If a source is part of a numbered sequence, such as a multi-volume book or journal with both volume and issue numbers, those numbers must be listed in your citation.
Dolby, Nadine. “Research in Youth Culture and Policy: Current Conditions and Future Directions.” Social Work and Society: The International Online-Only Journal, vol. 6, no. 2, 2008, www.socwork.net/sws/article/view/60/362. Accessed 20 May 2009.
Quintilian. Institutio Oratoria. Translated by H. E. Butler, vol. 2, Loeb-Harvard UP, 1980.
The publisher produces or distributes the source to the public. If there is more than one publisher, and they are all are relevant to your research, list them in your citation, separated by a forward slash (/).
Klee, Paul. Twittering Machine. 1922. Museum of Modern Art, New York. The Artchive, www.artchive.com/artchive/K/klee/twittering_machine.jpg.html. Accessed May 2006.
Women's Health: Problems of the Digestive System . American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, 2006.
Daniels, Greg and Michael Schur, creators. Parks and Recreation . Deedle-Dee Productions and Universal Media Studios, 2015.
Note : The publisher’s name need not be included in the following sources: periodicals, works published by their author or editor, websites whose titles are the same name as their publisher, websites that make works available but do not actually publish them (such as YouTube , WordPress , or JSTOR ).
Publication date
The same source may have been published on more than one date, such as an online version of an original source. For example, a television series might have aired on a broadcast network on one date, but released on Netflix on a different date. When the source has more than one date, it is sufficient to use the date that is most relevant to your writing. If you’re unsure about which date to use, go with the date of the source’s original publication.
In the following example, Mutant Enemy is the primary production company, and “Hush” was released in 1999. Below is a general citation for this television episode:
“Hush.” Buffy the Vampire Slayer , created by Joss Whedon, performance by Sarah Michelle Gellar, season 4, Mutant Enemy, 1999 .
However, if you are discussing, for example, the historical context in which the episode originally aired, you should cite the full date. Because you are specifying the date of airing, you would then use WB Television Network (rather than Mutant Enemy), because it was the network (rather than the production company) that aired the episode on the date you’re citing.
“Hush.” Buffy the Vampire Slayer, created by Joss Whedon, performance by Sarah Michelle Gellar, season 4, episode 10, WB Television Network, 14 Dec. 1999 .
You should be as specific as possible in identifying a work’s location.
An essay in a book or an article in a journal should include page numbers.
Adiche, Chimamanda Ngozi. “On Monday of Last Week.” The Thing around Your Neck, Alfred A. Knopf, 2009, pp. 74-94 .
The location of an online work should include a URL. Remove any "http://" or "https://" tag from the beginning of the URL.
Wheelis, Mark. "Investigating Disease Outbreaks Under a Protocol to the Biological and Toxin Weapons Convention." Emerging Infectious Diseases , vol. 6, no. 6, 2000, pp. 595-600, wwwnc.cdc.gov/eid/article/6/6/00-0607_article. Accessed 8 Feb. 2009.
When citing a physical object that you experienced firsthand, identify the place of location.
Matisse, Henri. The Swimming Pool. 1952, Museum of Modern Art, New York .
Optional elements
The ninth edition is designed to be as streamlined as possible. The author should include any information that helps readers easily identify the source, without including unnecessary information that may be distracting. The following is a list of optional elements that can be included in a documented source at the writer’s discretion.
Date of original publication:
If a source has been published on more than one date, the writer may want to include both dates if it will provide the reader with necessary or helpful information.
Erdrich, Louise. Love Medicine. 1984. Perennial-Harper, 1993.
City of publication:
The seventh edition handbook required the city in which a publisher is located, but the eighth edition states that this is only necessary in particular instances, such as in a work published before 1900. Since pre-1900 works were usually associated with the city in which they were published, your documentation may substitute the city name for the publisher’s name.
Thoreau, Henry David. Excursions . Boston, 1863.
Date of access:
When you cite an online source, the MLA Handbook recommends including a date of access on which you accessed the material, since an online work may change or move at any time.
Bernstein, Mark. "10 Tips on Writing the Living Web." A List Apart: For People Who Make Websites, 16 Aug. 2002, alistapart.com/article/writeliving. Accessed 4 May 2009.
As mentioned above, while the MLA handbook recommends including URLs when you cite online sources, you should always check with your instructor or editor and include URLs at their discretion.
A DOI, or digital object identifier, is a series of digits and letters that leads to the location of an online source. Articles in journals are often assigned DOIs to ensure that the source is locatable, even if the URL changes. If your source is listed with a DOI, use that instead of a URL.
Alonso, Alvaro, and Julio A. Camargo. "Toxicity of Nitrite to Three Species of Freshwater Invertebrates." Environmental Toxicology , vol. 21, no. 1, 3 Feb. 2006, pp. 90-94. Wiley Online Library, doi: 10.1002/tox.20155.
Creating in-text citations using the previous (eighth) edition
Although the MLA handbook is currently in its ninth edition, some information about citing in the text using the older (eighth) edition is being retained. The in-text citation is a brief reference within your text that indicates the source you consulted. It should properly attribute any ideas, paraphrases, or direct quotations to your source, and should direct readers to the entry in the Works Cited list. For the most part, an in-text citation is the author’s name and the page number (or just the page number, if the author is named in the sentence) in parentheses :
When creating in-text citations for media that has a runtime, such as a movie or podcast, include the range of hours, minutes and seconds you plan to reference. For example: (00:02:15-00:02:35).
Again, your goal is to attribute your source and provide a reference without interrupting your text. Your readers should be able to follow the flow of your argument without becoming distracted by extra information.
How to Cite the Purdue OWL in MLA
Entire Website
The Purdue OWL . Purdue U Writing Lab, 2019.
Individual Resources
Contributors' names. "Title of Resource." The Purdue OWL , Purdue U Writing Lab, Last edited date.
The new OWL no longer lists most pages' authors or publication dates. Thus, in most cases, citations will begin with the title of the resource, rather than the developer's name.
"MLA Formatting and Style Guide." The Purdue OWL, Purdue U Writing Lab. Accessed 18 Jun. 2018.
Pasco-Hernando State College
- MLA In-Text Citations
- Finding and Evaluating Sources (Critical Analysis)
- Synthesizing Information from Sources
- MLA Page Format
- MLA Works Cited
- APA Documentation
- Writing a Research Paper
Test Yourself
- MLA - Part A - Quiz
- MLA - Part B Quiz
- MLA Handout
- MLA Quick Citations
How to cite sources
One or two authors:.
See information below about using a page number. Sometimes, there is no page number to use.
Use the last name of the author and the page number. Note that there is nothing between the last name and page number.
(Anderson 50)
If there are two authors, use both last names even if both authors have the same last name.
(Sampson and Bernini) - Note that the word and is used and not an ampersand (&).
When there are two authors, note that even though both names are used to cite the source, it is still one source and should have a singular verb when used in a signal phrase: Sampson and Bernini says, not say. (The source - it - says.)
More than two people named as authors
Alvarez et al. (et al. is the Latin abbreviation for and others .). When more than two, individual names many not be listed even in the Works Cited. There is no longer a choice to list all the authors.
More than one source written by the same author
When you have more than one source from the same author, you must distinguish between them in the citation by adding the title: (Mirando, “Dinosaurs”) and (Mirando, “Jurassic Wilderness”).
If you name the author in the sentence, just put the title in parentheses in quotation marks:
According to Mirando, there are multiple theories for the extinction of the dinosaurs (“Dinosaurs”).
Different authors with the same last name
If you find two sources where the authors, have the same last name, obviously, using only the last name to cite the source will not clearly identify the source. In this case, use the first name as well: (Gonzalez, Jorge) or (Gonzalez, Marisol).
When no person named as author
Sometimes, a source has no person named as author. This is actually common in articles in encyclopedias and even newspapers, newswires, or news services such as The Associated Press. In that case, just use the title of the article or page, not the publication or website.
Occasionally, an organization or group is listed as the author: Mayo Clinic Staff. Then, the author is considered to be Mayo Clinic Staff. However, this applies only when a group or organization is actually listed as author. There are some special rule with government publications, but generally, the format applies. Start with the title of the publication when no specific agency is named as author. The agency will be listed as publisher.
Here is an example of using a title:
("Dinosaur Extinction")
Articles are considered short, published works, so titles of articles or pages from a website must be in quotation marks.
If the title to an article is longer than three or four words, shorten (don't use a key word or words) the title to the first noun. “Crime: Risks for Children of Non-Biological Parents Greater” should be shortened to “Crime.” “Organic Foods: Are They Really Healthier?” should be shortened to “Organic Foods” since Foods is the first noun . ( Note that the question mark is dropped on a shortened title.) An article with no author which is entitled "What Is Gene Therapy?" should be cited as "What Is Gene Therapy?" since it is not longer than three or four words, and the word therapy is the first noun anyway. The question mark is kept since the title is not shortened.) By retraining the first word(s), the reader can look alphabetically to the Works Cited list and easily find the source.
Don't forget to drop any period or comma that would ordinarily be next to a question mark or exclamation point. An example of dropping the comma is as follows: According to "What Is Gene Therapy?" there are several approaches. Ordinarily, there would be a comma after the introductory wording According to "What Is Gene Therapy?" However, since the grammar rule is to drop any comma or period next to a question mark or exclamation point, it would be dropped.
Also, the first letter of the first word and all other words in titles has to be capitalized in MLA style even if they are not so in the article itself except the following:
- articles (a, an, the),
- BOYFANS (but, or, yet, for, and, nor, so) – coordinating conjunctions, and
- prepositions (such as in, at, of, around, over, and so on).
Here’s an example of a title with words that should not start with a capital: “Genetic Manipulation of Food Has Some Scientists in the United States Worried”
Many sources are not in MLA style, so the titles are not following MLA format. Using capitals which are not capitals in the original is not a violation of the rule that you can’t change what’s in a quote. Using quotation marks for titles of short, published works is a different use of quotation marks than for quotes. (By the way, you can change a quote in quotation marks by putting brackets [ ] around your changes as previously mentioned.)
All caps are not used in MLA style except for some abbreviations such as NATO or AIDS. When there are all caps in a title, change to upper and lower case as otherwise appropriate
When you are using a specific article or page in a website, your source is the specific article or page and not the website.
If an article or page is in a website or newspaper and there is no author specifically named, use the title of the article or page as further described. The title of a source in a dictionary, encyclopedia, or other reference book is the word you are looking up. For example, if you are looking up the word sunspots, the title of the article is “sunspots” or “Sunspots,” however it is written in the source.
Here is an example of how to use the title to cite the source:
“The most accepted theory of dinosaur extinction is that a comet or asteroid hit the earth causing megatons of debris into the air blocking the sunlight” (“Dinosaur Extinction” 587).
The reference to the source could be in the sentence:
“Dinosaur Extinction” explains that “[t]he most accepted theory of dinosaur extinction is that a comet or asteroid hit the earth causing megatons of debris into the air blocking the sunlight” (587).
Punctuation and Quotes
Signal phrases (words that say who says the quote) with full sentence quotes.
There is no rule to use a comma to put a comma before or after words that are in quotation marks. Quoted words must follow the same rules for punctuation as words that are not in quotation marks. The only special rule there is to separate a signal phrase from a sentence quote with a comma.
Signal phrases are phrases that identify the source of a full sentence quote.
According to Anderson, “While tattoos may be popular today, few realize that tattooing was also popular in some ancient societies” (50).
The words According to Anderson are a signal phrase. Hernandez says, Khan states, and Dubrovsky agrees are all examples of signal phrases.
Note that there is a comma separating the signal phrase from the sentence quote and that the first letter of the first word of the quote starts with a capital since it is a sentence.
The signal phrase could be at the end of the sentence.
“While tattoos may be popular today, few realize that tattooing was also popular in some ancient societies,” according to Anderson (50).
See how there is still a comma to separate the signal phrase from the sentence quote.
Note that the comma goes before and not after the end quotation mark.
Also, see how the period follows the parentheses and does not go before the parentheses. Parenthetical documentation is part of the sentence.
The signal phrase could be in the middle of the sentence.
“While tattoos may be popular today,” according to Anderson, “few realize that tattooing was also popular in some ancient societies” (50).
Signal phrases are limited to words that identify the source of the quote such as the following: Jones says, According to Chan, “Dinosaur Extinction” claims.
The addition of other words such as the word that changes a signal phrase to just the beginning of a sentence that happens to contain some quoted words (even thought they might be a sentence) so what is in the quotation marks is a continuation of the sentence and is not considered a separate sentence. In these cases, there should not be a comma, and the first letter of the quote should not be capitalized since it is not considered to be the first word in a sentence. Here is an example:
Anderson says that “[w]hile tattoos may be popular today, few realize that tattooing was also popular in some ancient societies” (50).
Note that the re is no comma and no capital when the word that is used.
Partial sentence quotes; distinguishing a signal phrase
Sometimes a sentence includes words that identify the source or quoted words, but the quote is not a complete sentence. This is a partial sentence quote, and the words that identify the source are not considered a signal phrase to be separated by a comma. They are just part of a sentence that happens to begin outside the quote.
Anderson says that tattoos have been used "for thousands of years."
Remember that a signal phrase tells the source of a sentence quote. If there is not sentence quote, there is no signal phrase. Without a sentence quote, the words Anderson says (and other signal phrases wording) are just part of the sentence.
Anderson says that the interest in tattoos in the West has never been so popular.
See how there is no comma and no capital. The words Anderson says are the subject and verb of the sentence. Also see that the word that is used and not just Anderson says the interest....
More than one source with the same title and no person named as author
If you have more than one source with the same title, put the name of the publication in italics separated by a comma after the title of the article: “Farmed Salmon,” Aquaculture Journal and “Farmed Salmon,” Washington State Journal. The idea is to be sure they are distinguished from one another.
It is preferable not to include the word that after a signal phrase which introduces a sentence quote.
When the same information comes from more than one source
Sometimes, the same information is in more than one of your sources. If you are paraphrasing instead of quoting, just identify both sources separated by a semicolon in one parentheses: (“Dinosaur Extinction”; Jones).
(Note that the semicolon is placed after the end quotation mark whereas periods and commas are placed before the end quotation mark when there is supposed to be a period or comma next to an end quotation mark.)
Quoting a quote from a source (indirect quotations)
Sometimes, other people are quoted in your source. This is called an indirect quotation . When we use a quote that is quoted in the source, use the abbreviation qtd. in to let the reader know which source the quote you are quoting comes from. Say, for example, Jones wrote the article you found, but she quotes Herman Smith, and you want to use what Herman Smith says.
Say this is the wording in the source: Jones gives information provided by Professor Herman Smith. Smith says, "There are more dangers in the depth of the oceans that we know about."
Here’s a couple of ways to cite that information.
According to Smith, “There are more dangers in the depths of the oceans that we know about” (qtd. in Jones). This abbreviation qtd. in means that this quote is quoted in the article written by Jones. See how only Smith's words are actually quoted, so the quotation marks go around those words.
Here is another way Smith's words can be quoted.
"Smith says, 'There are more dangers in the depths of the oceans that we know about'" (qtd. in Jones).
In this phrasing, since the entire sentence is quoted, there is a quote within a quote. Single quotation marks must be used when you have to use quotation marks inside quotation marks. Note that there regular double quotation marks around all of the exact words from the source and single quotation marks around the exact words from Smith.
“There are more dangers in the depths of the oceans that we know about” (Herman Smith, qtd. in Jones). Here, the person who is quoted is named in the citation instead of in the sentence.
Including the name of the person being quoted is not required:
“There are more dangers in the depths of the oceans that we know about” (qtd. in Jones).
It is optional to include the name of the person quoted in the source in parentheses. If the name of the person quoted is used in the parentheses, then it should be the full name.
Use of the words qtd . in only applies when someone else is quoted in the source.
If there is no person named as author, use the title of the article or page to refer to the source. When you are using a specific article or page from a website, your source is the specific article or page and not the website. It’s like finding an article in a newspaper. Your source is the article, not the newspaper.
According to Smith, “Some earthquakes are caused by methane gas explosions” (qtd. in “Underwater Dangers”).
“Some earthquakes are caused by methane gas explosions” (Smith, qtd. in “Underwater Dangers”).
The reader has to be told which source your quote is coming from.
Length of quotations
Even though there is a sentence quote for these examples, sometimes more than one sentence is quoted. The method of documenting is still the same.
If, however, the quote is more than four lines from the source, you must indent the quote ten spaces (1”) from the left-hand margin. In this situation, quotation marks are not used, and the period goes before the parentheses. Here are more than four lines (not sentences) from a source:
“The theory that dinosaurs became extinct as a result of climate changes from a huge meteor impact has far reaching implications. There is always the possibility such an impact will happen again. There are many meteors that come close to earth’s gravitational pull. Scientists closely watch to identify potential problems. There is some discussion about an organized effort to launch a missile to either explode such meteors or defect them away from our orbit” (Jones).
Here is the quote indented ten spaces (1”) from the left margin:
The theory that dinosaurs became extinct as a result of climate changes from a huge meteor impact has far reaching implications. There is always the possibility such an impact will happen again. There are many meteors that come close to earth’s gravitational pull. Scientists closely watch to identify potential problems. There is some discussion about an organized effort to launch a missile to either explode such meteors or defect them away from our orbit. (Jones)
Paraphrasing and summarizing requires citations
Quoting is only one way of bringing information into a paper from a source. You can also paraphrase or summarize which is to put the source’s ideas into your own words. Quotation marks are not used, but you still have to give credit to the source the same way as with quotes. It is still plagiarism if you don’t use MLA or other documentation for paraphrased information. Each and every sentence with information from a source – whether you quote or paraphrase – must cite the source.
Use of Ellipsis (…) to show omitted words or sentences from a quote
You may remember seeing a series of three periods … in a quote. This is called an ellipsis and is used to represent an omission. Even though you may omit something from the beginning of a sentence you quote from, the general rule is not to use an ellipsis at the beginning of a quote. They are generally used in the middle of a quote to take out unnecessary words in a sentence or between sentences which are being quoted. You may use an ellipsis at the end of a quote if you don’t complete a sentence.
You may also use an ellipsis between quoted sentences to indicate that a sentence or sentences were omitted.
Identifying Internet sources
Increasingly, the Internet is being used for research. Because everything looks the same on the screen, it is important to figure out what exactly you are looking at. Sometimes, you are using information from a website that only has a couple of pages with no named author and which are clearly written for that website. In that case, your source is the website. Nowadays, these limited websites are not very common. Remember that the point of a citation system is to tell the reader where you found the information so that the reader can access the source. In a website that has more than a couple of pages, the reader would have difficulty finding the information.
When you are using an article or articles posted to a website or a specific page or pages in a website, your source is the particular article(s) or pages(s) just like an article in a newspaper and not the website. If there is a separate author, refer to the source by the author’s last name, just as with any other source. If there is no named author, refer to the source by the title of the article or page in quotation marks.
Page Numbers: When and how to use; When you don’t know the actual page number
The requirement to use a page number in MLA style refers to the actual page number in the original hard copy publication. The rule to use a page number does not apply to poetry or plays. See section below for details.
Sources created only for an online presentation do not have the type of page numbers to which the rule to use page numbers applies even when we have to click through a sequence of “pages.” The reason we should not use these website page numbers is that the pagination does not necessarily appear the same on everyone’s computer. What one person sees as page two could be page three on someone else’s computer.
When an article that was originally printed in a hard copy publication is posted, usually, there is no page number since it is an html format. If it is uploaded as a .pdf, the page number will appear.
When we don’t know the page number the particular information was printed on in the original hard copy publication, don’t use a page number.
If an Internet source numbers the paragraphs, you can use the paragraph number. However, if not numbered already in the web page, you should not start counting paragraphs to use a paragraph number.
The custom is that if you know a page number, you should not repeat the author’s name if you are using information from the same source in the same paragraph unless you use information from another source in between since you could just use the page number. However, if you don’t have a page number to use, you’ll have to repeat the author’s last name or title of the article (not the publication the article was printed in) for all references to that particular source.
When you have several sentences with information from a source, you should vary how you refer to the source: According to Jones, “Sasquatch is absolutely a real creature.” She goes on to say that they are intelligent enough to have hidden from humans. “The reason no skeletal remains have been found is that Sasquatch bury their dead” (Jones).
Since sometimes there is no page number or paragraph number to reference, you might not have a parentheses at all if the source is referred to as part of the sentence. The Internet has created situations where we don’t use parentheses even though MLA is called a parenthetical documentation system.
No Page Numbers: Poems and Plays
The MLA rule to use a page number for sources that were originally published in hard copy and for which we know the exact page number does not apply to poems.
In citing poetry, line numbers are used instead: (“Fire and Ice” 1). If the name of the poem is already mentioned in the sentence or it is clear that this quote is from this poem, use just the line number: (1).
When quoting two lines of poetry (not sentences), use a slash between the lines: “Some say the world will end in fire/Some say in ice” (1-2).
When quoting more than two lines, indent one inch from the left, write the lines as they appear in the poem (one under the other), do not use quotation marks, and the period goes before the parenthetical documentation:
Some say the world will end in fire
Some say in ice.
From what I’ve tasted of desire
I hold with those who favor fire. (“Fire and Ice” 1-4)
If the title is mentioned previously and it is clear the quote is from this poem, use just the line numbers.
If the poem is divided into sections such as chapters or parts, then identify in the citation: ( Odyssey 2.6) represent chapter or book 2, line 6.
The MLA rule to use a page number for sources that were originally published in hard copy and for which we know the exact page number does not apply to plays.
Cite the act , scene, and line number is used: Macbeth 2.1.13 referring to act. scene.line.
If lines from more than character are quoted, indent 10 spaced (1″) from the left starting a new line for each character, and indicate the character:
Mrs. Hale: ( stiffly ) There’s a great deal of work to be done on a farm.
County Attorney: To be sure. And yet ( with a little bow to her ) I know there
are some Dickson County farmhouses which do not have such roller towels.
Mrs. Hale: Those towels get dirty awful quick. Men’s hand aren’t always as
clear as they might be. ( Trifles 32-34)
Note that since this is a one-act play, only the line numbers are used.
Here is a quote from a play that has acts and scenes:
Hamlet: Methinks it is like a weasel.
Polonius: It is back’d like a weasel.
Hamlet: Or like a whale. ( Ham . 5.2.330-33)
Important Details:
- Use last name only when there is a person or persons listed as author(s) - no first name or p., pg., or other reference to the word page.
- Don't use the words source, article, or any other words to refer to a source other than the last name or the title of the article when no person listed as source.
- The page number refers to the page number the specific information was printed on in the original publication, not a page number assigned in a website. When the page number is not known, you just don’t list a page number. Sources posted to the Internet from a hard copy or pages on an web only site will not have a page number as part of the citation.
- The end quotation mark goes after the words quoted, not the parentheses. The parenthetical documentation is part of the sentence, but it is not part of the quote.
- There is no comma or period before the parentheses except for the end quotation mark. An exclamation point or question mark which is part of the quote is used.
- If you name the source in the sentence, you should not put the name in the parentheses.
- The source must be named in each and every sentence with information from a source whether you use exact words or put the information into your own words. If you don't, it is plagiarism. It is not all right to have more than one sentence from a source and then cite the source.The reader had no way of knowing how many, if any at all, of the previous sentences are from the source.
- Printer-friendly version


MLA Citation Guide (9th Edition): In-Text Citation
- What Kind of Source Is This?
- Advertisements
- Books, eBooks & Pamphlets
- Book Reviews
- Class Handouts, Presentations, and Readings
- Encyclopedias & Dictionaries
- Government Documents
- Images, Artwork, Charts, Graphs & Tables
- Interviews and Emails (Personal Communications)
- Journal Articles
- Magazine Articles
- Newspaper Articles
- Primary Sources
- Religious Texts
- Social Media
- Videos & DVDs
- In-Text Citation
Works Quoted in Another Source
- No Author, No Date etc.
- Works Cited List & Sample Paper
- Annotated Bibliography
- Powerpoint Presentations
On This Page
About in-text citations, no known author, quoting directly, paraphrasing, no page numbers, repeated use of sources, in-text citation for more than one source, long quotations, quoting and paraphrasing: what's the difference, signal phrases, avoiding plagiarism when using sources.
T here are two ways to integrate others' research into your assignment: you can paraphrase or you can quote.
Paraphrasing is used to show that you understand what the author wrote. You must restate the meaning of the passage, expressing the ideas in your own words and voice, and not just change a few words here and there. Make sure to also include an in-text citation.
Quoting is copying the wording from someone else's work, keeping it exactly as it was originally written. When quoting, place quotation marks (" ") around the selected passage to show where the quote begins and where it ends. Make sure to include an in-text citation.
If you refer to the author's name in a sentence you do not have to include the name again as part of your in-text citation. Instead include the page number (if there is one) at the end of the quotation or paraphrased section.
Hunt explains that mother-infant attachment has been a leading topic of developmental research since John Bowlby found that "children raised in institutions were deficient in emotional and personality development" (358).
In MLA, in-text citations are inserted in the body of your research paper to briefly document the source of your information. Brief in-text citations point the reader to more complete information in the Works Cited list at the end of the paper.
| Number of Authors/Editors | Format of In-Text Citation |
|---|---|
| One | (Author's Last Name Page Number) Example: (Case 57) |
| Two | (Author's Last Name and Author's Last Name Page Number) Example: (Case and Daristotle 57) |
| Three or more | (Author's Last Name et al. Page Number) Example: (Case et al. 57) |
When a source has no known author, use the first one, two, or three words from the title instead of the author's last name. Don't count initial articles like "A", "An" or "The". You should provide enough words to make it clear which work you're referring to from your Works Cited list.
If the title in the Works Cited list is in italics, italicize the words from the title in the in-text citation.
( Cell Biology 12)
If the title in the Works Cited list is in quotation marks, put quotation marks around the words from the title in the in-text citation.
("Nursing" 12)
When you quote directly from a source, enclose the quoted section in quotation marks. Add an in-text citation at the end of the quote with the author name and page number, like this:
"Here's a direct quote" (Smith 8).
"Here's a direct quote" ("Trouble" 22).
Note: The period goes outside the brackets, at the end of your in-text citation.
Mother-infant attachment has been a leading topic of developmental research since John Bowlby found that "children raised in institutions were deficient in emotional and personality development" (Hunt 358).
When you write information or ideas from a source in your own words, cite the source by adding an in-text citation at the end of the paraphrased portion, like this:
This is a paraphrase (Smith 8).
This is a paraphrase ("Trouble" 22).
Mother-infant attachment became a leading topic of developmental research following the publication of John Bowlby's studies (Hunt 65).
Note: If the paraphrased information/idea summarizes several pages, include all of the page numbers.
Mother-infant attachment became a leading topic of developmental research following the publication of John Bowlby's studies (Hunt 50, 55, 65-71).
When you quote from electronic sources that do not provide page numbers (like webpages), cite the author name only. If there is no author, cite the first word or words from the title only.
"Three phases of the separation response: protest, despair, and detachment" (Garelli).
"Nutrition is a critical part of health and development" ("Nutrition").
Sources that are paraphrased or quoted in other sources are called indirect sources. MLA recommends you take information from the original source whenever possible.
If you must cite information from an indirect source, mention the author of the original source in the body of your text and place the name of the author of the source you actually consulted in your in-text citation. Begin your in-text citation with 'qtd. in.'
Kumashiro notes that lesbian and bisexual women of colour are often excluded from both queer communities and communities of colour (qtd. in Dua 188).
(You are reading an article by Dua that cites information from Kumashiro (the original source))
Note: In your Works Cited list, you only include a citation for the source you consulted, NOT the original source.
In the above example, your Works Cited list would include a citation for Dua's article, and NOT Kumashiro's.
If you're using information from a single source more than once in a row (with no other sources referred to in between), you can use a simplified in-text citation. The first time you use information from the source, use a full in-text citation. The second time, you only need to give the page number.
Cell biology is an area of science that focuses on the structure and function of cells (Smith 15). It revolves around the idea that the cell is a "fundamental unit of life" (17). Many important scientists have contributed to the evolution of cell biology. Mattias Jakob Schleiden and Theodor Schwann, for example, were scientists who formulated cell theory in 1838 (20).
Note: If using this simplified in-text citation creates ambiguity regarding the source being referred to, use the full in-text citation format.
If you would like to cite more than one source within the same in-text citation, simply record the in-text citations as normal and separate them with a semi-colon.
(Smith 42; Bennett 71).
( It Takes Two ; Brock 43).
Note: The sources within the in-text citation do not need to be in alphabetical order for MLA style.
What Is a Long Quotation?
If your quotation is longer than four lines, it is a considered a long quotation. This can also be referred to as a block quotation.
Rules for Long Quotations
There are 4 rules that apply to long quotations that are different from regular quotations:
- Place a colon at the end of the line that you write to introduce your long quotation.
- Indent the long quotation 0.5 inches from the rest of the text, so it looks like a block of text.
- Do not put quotation marks around the quotation.
- Place the period at the end of the quotation before your in-text citation instead of after , as with regular quotations.
Example of a Long Quotation
Vivian Gornick describes the process of maturing as a reader as a reckoning with human limitations:
Suddenly, literature, politics, and analysis came together, and I began to think more inclusively about the emotional
imprisonment of mind and spirit to which all human beings are heir. In the course of analytic time, it became apparent
that—with or without the burden of social justice—the effort required to attain any semblance of inner freedom was
extraordinary. Great literature, I then realized, is a record not of the achievement, but of the effort.
With this insight as my guiding light, I began to interpret the lives and work of women and men alike who had
spent their years making literature. (x-xi)
- << Previous: Websites
- Next: Works Quoted in Another Source >>
- Last Updated: Apr 15, 2024 11:24 AM
- URL: https://columbiacollege-ca.libguides.com/MLA9

Citation Guide
- APA Style - 7th Edition
Introduction to MLA Style
Creating mla citations: examples, paper formatting guidelines & sample papers, in-text citations & the list of works cited, examples of works cited & in-text citations, software tools for mla style, works cited for this page.
- Chicago/Turabian Style
- Quoting, Paraphrasing, and Summarizing
- Tools for Managing Citations
- Citation Season!
What is MLA Style?
MLA stands for Modern Language Association. MLA Style is an established style for formatting your paper and giving credit to your sources.
This page provides resources for all the elements of a preparing a paper in MLA Style, including formatting, in-text citations, and the works cited list.
Disciplines at Caldwell that use MLA Style include English, history, theology, philosophy, and others.
MLA Quick Links
- Quoting and Paraphrasing in MLA Format This video course is all about quoting and paraphrasing sources in your paper! Learn rules of quoting and paraphrasing responsibly, and see examples of in-text citations in MLA format.
- Purdue OWL Guide to MLA Style Purdue OWL has resources about many citation styles. Here is their section on MLA

An Article from a Journal Found in a Library Database (a source in two containers)
from MLA Handbook chapter 5.100-103, The Three Most Common Types of Entries

A Chapter or Section of a Book Accessed through an Online Repository (a source with two containers)

An Episode of a TV Show Watched on an Online Platform (a source in two containers)

A Chapter or Section of a Print Book (a source in one container)

A Print Book (a source that is self-contained)
- Sample MLA Papers These sample student papers show MLA formatting for all details of a research paper. Look a the structure of the page, how quotes are incorporated, and how works are cited.
- Formatting Your Research Project (MLA Handbook, Ch. 1) Instructions for formatting your paper in MLA style, including margins, title, headers and footers, headings and subheadings, etc.
- The Writing Process Purdue OWL's Guide to academic writing in MLA Style, including grammar, mechanics, and punctuation.
- Mechanics of Prose (MLA Handbook, Ch. 2) Guidance on all the details of writing, such as spelling, grammar, punctuation, how format titles and names in your paper.
In-Text Citations
- In-Text Citations: The Basics Basic instructions from Purdue OWL about how to format in-text citations in MLA Style. This is how you credit your sources when you mention them in the text of your paper.
- Citing Sources in the Text (MLA Handbook, Ch. 6) This chapter starts with the basics of citing your sources in the text of your paper. It covers many situations you might encounter.
Works Cited Page
- MLA Style 101 This video course goes through each "element" of the MLA works cited page entry (like author, title, publisher) and shows how to identify what belongs in each element. This will help you create works cited page entries and know how to edit citations that a database generates!
- Interactive Practice Template Learn how to create citations for your Works Cited page!
- How to Cite Books This page from Purdue OWL covers the basics of citing books as well as what to do in a variety of situations. This page has guidance on multiple authors, an organization as author, translations, anthologies, and more.
- How to Cite Electronic Resources (aka things you found online) This page from Purdue OWL covers works cited page entries for most kinds of online sources, including scholarly journal articles in a library database, ebooks, government agency websites, online news, a YouTube video, personal email correspondence, and more.
- Citation Examples from the MLA Handbook This is a regularly updated list of citations for a wide variety of sources. It's organized by source, so scroll down or use ctrl-F to search the page for the kind of source you want to see, like "translated book" or "YouTube Video".
Journal Article Found in a Library Database
Works cited page entry.
Lorensen, Jutta. “Between Image and Word, Color, and Time: Jacob Lawrence’s The Migration Series.” African American Review , vol. 40, no. 3, 2006, pp. 571-86. Academic Search Premier, each.ebscohost.com/login.aspx? Drect=true&db=f5h&AN=24093790&site=eho st-live.

In-text citation
(Lorensen 577)
Newspaper Article Found in a Library Database
Fessenden, Ford, et al. "The Battle for New York's Key Voting Blocs in the Primaries." New York Times , 19 Apr. 2016, p. A 14. ProQuest Central , ezproxy.caldwell.edu:2048/login?url=http:// search.proquest.com/ docview/1781721245?accountid=26523.
(Fessenden et al. A14)
Article from an Online News Source
Chang, Kenneth. “NASA Will Send More Helicopters to Mars.” The New York Times , 27 July 2022, www.nytimes.com/2022/07/27/science/mars-sample-mission-nasa.html.
Dorris, Michael, and Louise Erdrich. The Crown of Columbus . HarperCollins Publishers, 1999.
(Dorris and Erdrich 110-12)
Article or Specific Chapter from a Book
Copeland, Edward. “Money.” The Cambridge Companion to Jane Austen , edited by Copeland and Juliet McMaster, Cambridge UP, 1997, pp. 131-48.
(Copeland 135)
Webpage on a Website
“Infographic: Benefits of Language Learning.” Modern Language Association , 2022, www.mla.org/Resources/Advocacy/Infographics/Infographic-Benefits-of-Language-Learning.
("Inforgraphic: Benefits of Language Learning")
Film on an App
Mamma Mia . Directed by Phyllida Lloyd, Universal Pictures, 2008. Netflix app.
( Mamma Mia ) or ( Mamma Mia 59:03-61:23) - cite a specific scene with timestamps in the page number spot
There are many tools that can help you create, manage, and organize your citations and your references page. Here are some that the library provides or recommends for students and faculty.
NoodleTools is an online tool that helps you take notes and correctly format citations. MLA, APA, and Chicago/Turabian citation styles are included. Use throughout your research project to track sources, take notes, create outlines, collaborate with classmates, and format bibliographies. Use this link to create an account.
- ZoteroBib ZoteroBib is a free service that helps you build a bibliography from any computer or device, without creating an account or installing any software. It's from the team behind the open source citation management app Zotero. ZBib can create a draft citation from a link or ISBN and has helpful templates for you to use to manually create citations. You can use it for MLA, APA, or Chicago Style.
The information on this page comes from the MLA Handbook, 9th Edition. This book can be cited in MLA style like this:
MLA Handbook. 9th ed., Modern Language Association of America, 2021.
The elements used here are: [2. Title of source] MLA Handbook. [5. Version] 9th ed., [7. Publisher] Modern Language Association of America, [8. Publication date] 2021. Because the publisher is an organization who is also the author, this organization - the Modern Language Association - is only listed once, as the publisher.
An in-text citation for this handbook could be ( MLA Handbook 45) to refer specifically to something on page 45.
- << Previous: APA Style - 7th Edition
- Next: Chicago/Turabian Style >>
- Last Updated: Jun 3, 2024 8:27 AM
- URL: https://libguides.caldwell.edu/citations
- Free Tools for Students
- MLA Citation Generator
Free MLA Citation Generator
Generate accurate citations in MLA format automatically, with MyBib!

😕 What is an MLA Citation Generator?
An MLA citation generator is a software tool designed to automatically create academic citations in the Modern Language Association (MLA) citation format. The generator will take information such as document titles, author, and URLs as in input, and output fully formatted citations that can be inserted into the Works Cited page of an MLA-compliant academic paper.
The citations on a Works Cited page show the external sources that were used to write the main body of the academic paper, either directly as references and quotes, or indirectly as ideas.
👩🎓 Who uses an MLA Citation Generator?
MLA style is most often used by middle school and high school students in preparation for transition to college and further education. Ironically, MLA style is not actually used all that often beyond middle and high school, with APA (American Psychological Association) style being the favored style at colleges across the country.
It is also important at this level to learn why it's critical to cite sources, not just how to cite them.
🙌 Why should I use a Citation Generator?
Writing citations manually is time consuming and error prone. Automating this process with a citation generator is easy, straightforward, and gives accurate results. It's also easier to keep citations organized and in the correct order.
The Works Cited page contributes to the overall grade of a paper, so it is important to produce accurately formatted citations that follow the guidelines in the official MLA Handbook .
⚙️ How do I use MyBib's MLA Citation Generator?
It's super easy to create MLA style citations with our MLA Citation Generator. Scroll back up to the generator at the top of the page and select the type of source you're citing. Books, journal articles, and webpages are all examples of the types of sources our generator can cite automatically. Then either search for the source, or enter the details manually in the citation form.
The generator will produce a formatted MLA citation that can be copied and pasted directly into your document, or saved to MyBib as part of your overall Works Cited page (which can be downloaded fully later!).
MyBib supports the following for MLA style:
| ⚙️ Styles | MLA 8 & MLA 9 |
|---|---|
| 📚 Sources | Websites, books, journals, newspapers |
| 🔎 Autocite | Yes |
| 📥 Download to | Microsoft Word, Google Docs |

Daniel is a qualified librarian, former teacher, and citation expert. He has been contributing to MyBib since 2018.

MLA Style: Writing & Citation
- Advertisements
- Books, eBooks & Pamphlets
- Class Notes & Presentations
- Encyclopedias & Dictionaries
- Government Documents
- Images, Charts, Graphs, Maps & Tables
- Interviews and Emails (Personal Communications)
- Journal Articles
- Magazine Articles
- Newspaper Articles
- Religious Texts
- Social Media
- Videos & DVDs
- When Information Is Missing
- Works Quoted in Another Source
- MLA Writing Style
- Unknown or Multiple Authors
- Paraphrasing
- Long Quotes
Block Quotations
- Repeated Sources
- In-Text Citation For More Than One Source
- Works Cited List & Sample Paper
- Annotated Bibliography
Need Help? Virtual Chat with a Librarian, 24/7
You Can Also:
What Is a Block Quotation?
If your quotation extends to more than four lines as you're typing your essay, it should be put into a 'block' format.
Rules for Block Quotations
There are 4 rules that apply to long quotations that are different from regular quotations:
- The line before your block quotation, when you're introducing the quote, ends with a colon.
- The bock quotation is indented half an inch from the rest of the text, so it looks like a block of text.
- There are no quotation marks needed when using block quotes.
- The period at the end of the quotation comes before your in-text citation as opposed to after , as it does with regular quotations.
Example of a Long Quotation
At the end of Lord of the Flies the boys are struck with the realization of their behaviour:
The tears began to flow and sobs shook him. He gave himself up to them now for the first time on the island; great, shuddering spasms of grief that seemed to wrench his whole body. His voice rose under the black smoke before the burning wreckage of the island; and infected by that emotion, the other little boys began to shake and sob too. (Golding 186)
- << Previous: Paraphrasing
- Next: Repeated Sources >>
- Last Updated: Jun 10, 2024 10:58 AM
- URL: https://libguides.gvltec.edu/CiteMLA
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- College University and Postgraduate
- Academic Writing
- Research Papers
How to Quote in a Research Paper
Last Updated: September 30, 2022 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Christopher Taylor, PhD . Christopher Taylor is an Adjunct Assistant Professor of English at Austin Community College in Texas. He received his PhD in English Literature and Medieval Studies from the University of Texas at Austin in 2014. There are 16 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 909,073 times.
A research paper can be made stronger through the use of quotations. You may use quotes when you need to cite a key piece of primary source material, strengthen your argument through another writer's work, or highlight a term of art. It is important to both use quotations effectively and cite them properly to write an effective paper and avoid plagiarizing.

Using Different Types of Quotes

- Use a complete sentence to incorporate a dropped quote. Ex: As Rembrandt’s skill developed, he began painting landscapes that are “romantic and visionary” (Wallace 96).
- Use a short phrase to incorporate a dropped quote: Rembrandt’s landscapes are “romantic and visionary” (Wallace 96).

- Use a complete sentence to introduce a full sentence quote. Ex: Over the course of time Rembrandt’s work began to change and focus on different themes, but as Wallace points out: "Rembrandt’s great gift as an etcher lay in preserving a sense of spontaneity while scrupulously attending to close detail” (142).
- Use a signal phrase to introduce your full sentence quote. Ex: As Wallace states, “Rembrandt’s great gift as an etcher lay in preserving a sense of spontaneity while scrupulously attending to close detail” (142).

- Introduce your block quote with a colon. Ex: According to Wallace: (add a line break here, and then indent the entire quote).
- Block quotes do not use quotation marks. You have already stated who the author is/what is being referred to in the introduction sentence. Add the in-text parenthetical citation after the period at the end of the quote, though.
- If your block quote is inside a paragraph, you don’t have to start a new paragraph at the end of it. Simply add another line break and begin writing along the left margin (with no indent). [4] X Research source However, you will need to indent the second paragraph by an extra 0.25 in (0.64 cm) if you are citing more than 1 paragraph. [5] X Trustworthy Source Purdue Online Writing Lab Trusted resource for writing and citation guidelines Go to source

- Change the structure of the sentence by moving clauses around. Aim to change at least half of the sentence into a new structure, but also make sure that the grammar is correct and the meaning of the sentence is still clear. You can use a thesaurus to exchange words with synonyms.
- Paraphrasing should only be done if you are certain that you understand the content you are copying. If you are unclear as to the meaning of the quote, you won’t be able to put it adequately into your own words.
- When you write your paraphrase, don’t look at the quote. Keep the meaning in your head and create a new sentence to match. [7] X Research source
Formatting Your Quotes

- To use a comma, you might structure the quote with in sentence like this: “Yogurt provides beneficial bacteria to your gut,” so it is good to include 1 serving per day in your diet.
- To use a period, you might structure the quote like this: “Carrots are a valuable source of vitamin A.”

- Example of a quotation that comes with a question mark: Alice said “but where will I go?” (24).
- Example of asking a question about a quotation: With so much contention, will literary scholars ever agree on “the dream-like quality of Alice’s adventure” (39)?
- Example of a question about a quoted question: At this point in the story, readers communally ask “but where will I go?” (24).

- Ellipses can be used in the center of a quote to leave out words that you feel add unnecessary length to the statement without adding value. For example: As the man stated, “reading the book was...enlightening and life-changing.” This is done rather than: As the man stated, “reading the book over the last few weeks was not only incredibly enjoyable, but also enlightening and life-changing.”
- Ellipses should be used only before or after a quote, not both. If you are only use a part of a quote from the center of a selection, it is just a partial or dropped quote. However, keep in mind that ellipses rarely come at the beginning of a quotation. [11] X Research source

- For example: As scholars have noted, “Rembrandt’s portrait of her [Henrickje, his mistress] was both accurate and emotion-filled” (Wallace 49).

- Ex: As Dormer has noted, “his work is much more valuable now then [sic] it was at the time of its creation.”
Quoting in Different Styles

- Ex: We can therefore ascertain that “Rembrandt’s decline in popularity may have been his dedication to Biblical painting” (Wallace 112).
- Ex: According to some, “another reason for Rembrandt’s decline in popularity may have been his dedication to Biblical painting” (Wallace 112), but not everyone agree on this matter.
- Ex: Wallace states that “another reason for Rembrandt’s decline in popularity may have been his dedication to Biblical painting” (112). [15] X Research source

- Ex: As Billy’s character is described, we learn “Billy wasn’t a Catholic, even though he grew up with a ghastly crucifix on his wall” (Vonnegut 1969).
- Ex: Vonnegut gives a factual statement with a clear opinion thrown in when he says “Billy wasn’t a Catholic, even though he grew up with a ghastly crucifix on his wall” (1969).
- Ex: With the knowledge that “Billy wasn’t a Catholic, even though he grew up with a ghastly crucifix on his wall” (Vonnegut 1969), we begin to understand his philosophical standings.

Quoting Successfully

Community Q&A
- Keep a list of quotations as you take research notes, and star your favorites to return later. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0
- Watch for quotations that are quoted by other researchers again and again. Often secondary material will give you hints to finding the best parts of the primary sources. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0
- Quote the opposition so that you can directly pick apart their argument. It's easier to argue against someone if you're using exactly what they said and pointing out its flaws. Otherwise, the opposition can claim that you simply twisted their meaning. Rely on their words and attack directly. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0

- Don't let a research paper become a sea of he-said, she-said. While you want to set up the arguments that have been made on both sides in the past, you also want to make a compelling argument for yourself. Rephrasing, re-organizing an argument, and synthesizing different arguments in your own words makes it clear that you understand what you've researched and makes the paper interesting to read. The reader is searching for a new way to understand the research or a new idea. Too many quotes tend to bury the lead. Thanks Helpful 1 Not Helpful 0
- Don't rely too heavily on one source. It's easy to fall in love with a single book when doing research, particularly if there aren't a lot of books on the subject and one author particularly agrees with you. Try to limit how much you quote that author, particularly if a lot of your argument is relying on his or her groundwork already. Look for quotations that complement or challenge that person, and provide your own analysis. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0
- Don't be a sloppy note-taker. Unfortunately, accidental plagiarism is all too common, and it has serious consequences. You may not have meant to plagiarize, but if you write someone else's words down without indicating that you are using a direct quotation, you are plagiarizing whether it was intentional or not (after all, merely relying on lecture notes and not on your own research is lazy and not acknowledging direct quotes as you take notes from texts reflects poor organization). Always indicate quotations in your notes. It's also better to write down a lot of quotations and then paraphrase them later than to write down a paraphrased version. The danger here, particularly if you don't alter the quote much, is that you'll unwittingly change it back to the quotation later, in revision. It's better to have the original right in front of you. If you find yourself unable to choose better language, just quote it properly. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0
You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://midway.libguides.com/c.php?g=1100261&p=8025172
- ↑ https://facultyweb.ivcc.edu/rrambo/eng1001/quotes.htm
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/research_and_citation/mla_style/mla_formatting_and_style_guide/mla_formatting_quotations.html
- ↑ http://public.wsu.edu/~campbelld/engl402/cited.htm
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/general_writing/punctuation/quotation_marks/index.html
- ↑ http://writing.wisc.edu/Handbook/QPA_paraphrase2.html
- ↑ http://www.thepunctuationguide.com/ellipses.html
- ↑ https://www.unr.edu/writing-speaking-center/student-resources/writing-speaking-resources/mla-quotation-punctuation
- ↑ https://guides.libraries.psu.edu/mlacitation/intext
- ↑ http://owl.english.purdue.edu/owl/resource/747/03/
- ↑ https://apastyle.apa.org/style-grammar-guidelines/citations/quotations
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/research_and_citation/chicago_manual_17th_edition/cmos_formatting_and_style_guide/general_format.html
- ↑ https://writingcenter.uagc.edu/quoting-paraphrasing-summarizing
- ↑ https://writingcenter.unc.edu/tips-and-tools/quotations/
- ↑ https://academicguides.waldenu.edu/writingcenter/evidence/quotation
About This Article

To quote in a research paper in APA style, use in-text parenthetical citations at the end of quotes that have the author's last name and the year the text was published. If you mention the author's name in the sentence with the quote, just include the year the text was published in the citation. If you're citing a quote in MLA style, do the same thing you would for APA style, but use the page number instead of the year the text was published. To learn how to quote a research paper in Chicago style, scroll down! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Dec 27, 2021
Did this article help you?
Mar 5, 2018
Apr 10, 2018
Dec 10, 2017

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
wikiHow Tech Help Pro:
Develop the tech skills you need for work and life
Generate accurate MLA citations for free
- Knowledge Base
- MLA format for academic papers and essays
MLA Format | Complete Guidelines & Free Template
Published on December 11, 2019 by Raimo Streefkerk . Revised on May 6, 2024 by Jack Caulfield.
The MLA Handbook provides guidelines for creating MLA citations and formatting academic papers. This includes advice on structuring parenthetical citations, the Works Cited page, and tables and figures. This quick guide will help you set up your MLA format paper in no time.
Cite your MLA source
Start by applying these MLA format guidelines to your document:
- Use an easily readable font like 12 pt Times New Roman
- Set 1 inch page margins
- Use double line spacing
- Include a ½” indent for new paragraphs
- Include a four-line MLA heading on the first page
- Center the paper’s title
- Use title case capitalization for headings
- Cite your sources with MLA in-text citations
- List all sources cited on a Works Cited page at the end
Alternatively, you can automatically apply the formatting with our MLA docx or Google Docs template.
Table of contents
How to set up mla format in google docs, header and title, running head, works cited page, creating mla style citations, headings and subheadings, tables and figures, frequently asked questions about mla format.
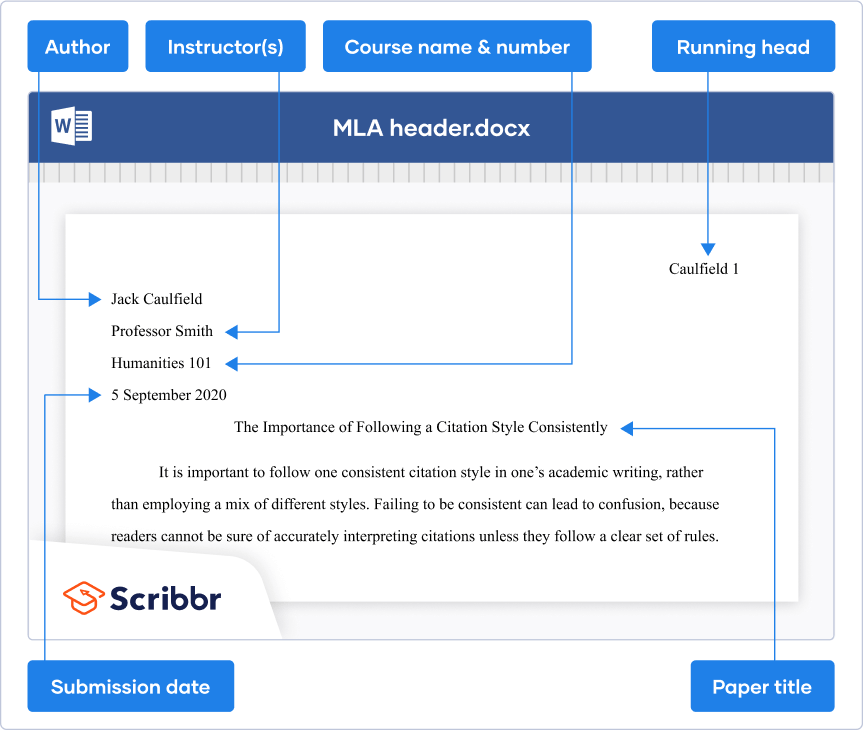
The header in MLA format is left-aligned on the first page of your paper. It includes
- Your full name
- Your instructor’s or supervisor’s name
- The course name or number
- The due date of the assignment
After the MLA header, press ENTER once and type your paper title. Center the title and don’t forget to apply title-case capitalization. Read our article on writing strong titles that are informative, striking and appropriate.
For a paper with multiple authors, it’s better to use a separate title page instead.
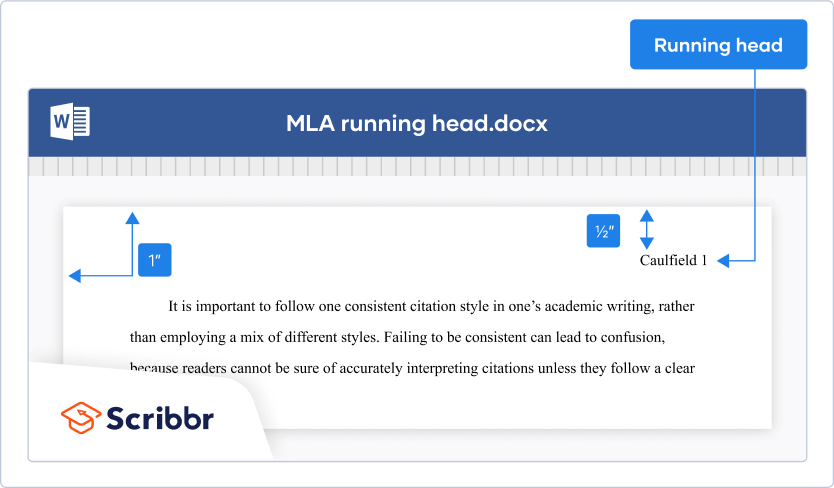
At the top of every page, including the first page, you need to include your last name and the page number. This is called the “running head.” Follow these steps to set up the MLA running head in your Word or Google Docs document:
- Double-click at the top of a page
- Type your last name
- Insert automatic page numbering
- Align the content to the right
The running head should look like this:
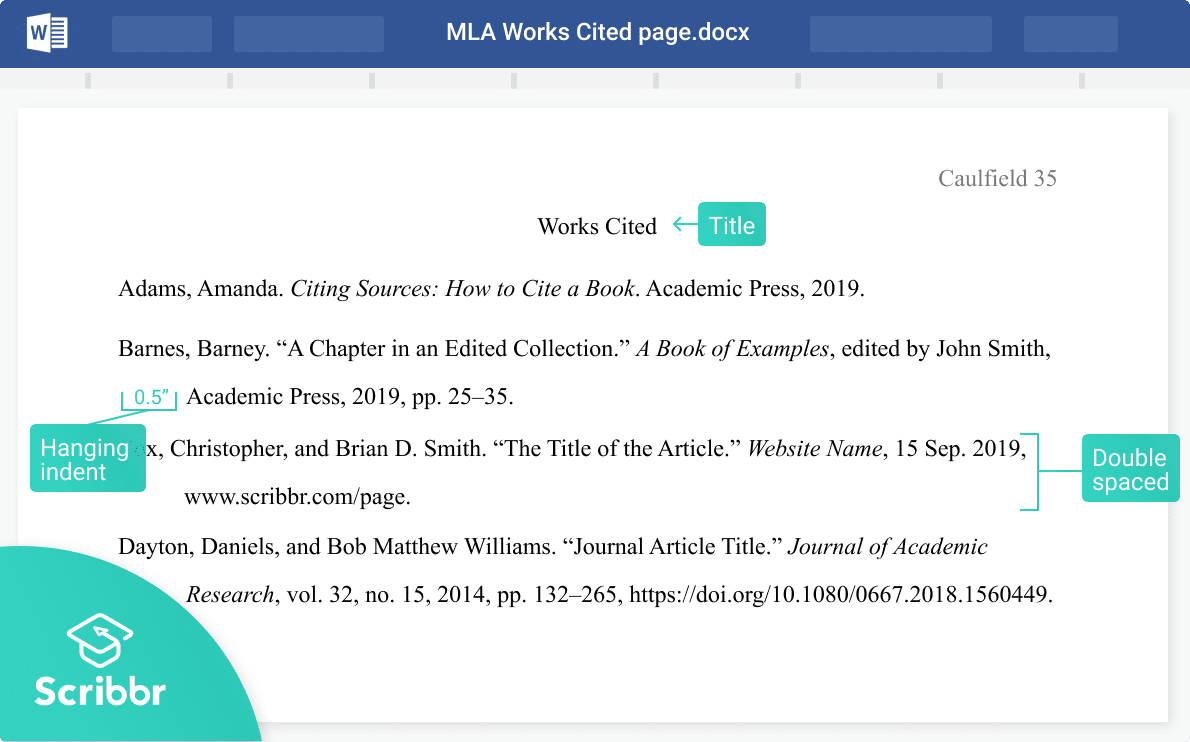
The Works Cited list is included on a separate page at the end of your paper. You list all the sources you referenced in your paper in alphabetical order. Don’t include sources that weren’t cited in the paper, except potentially in an MLA annotated bibliography assignment.
Place the title “Works Cited” in the center at the top of the page. After the title, press ENTER once and insert your MLA references.
If a reference entry is longer than one line, each line after the first should be indented ½ inch (called a hanging indent ). All entries are double spaced, just like the rest of the text.
Generate accurate MLA citations with Scribbr
Prefer to cite your sources manually? Use the interactive example below to see what the Works Cited entry and MLA in-text citation look like for different source types.
Headings and subheadings are not mandatory, but they can help you organize and structure your paper, especially in longer assignments.
MLA has only a few formatting requirements for headings. They should
- Be written in title case
- Be left-aligned
- Not end in a period
We recommend keeping the font and size the same as the body text and applying title case capitalization. In general, boldface indicates greater prominence, while italics are appropriate for subordinate headings.
Chapter Title
Section Heading
Tip: Both Google Docs and Microsoft Word allow you to create heading levels that help you to keep your headings consistent.
Tables and other illustrations (referred to as “figures”) should be placed as close to the relevant part of text as possible. MLA also provides guidelines for presenting them.
MLA format for tables
Tables are labeled and numbered, along with a descriptive title. The label and title are placed above the table on separate lines; the label and number appear in bold.
A caption providing information about the source appears below the table; you don’t need one if the table is your own work.
Below this, any explanatory notes appear, marked on the relevant part of the table with a superscript letter. The first line of each note is indented; your word processor should apply this formatting automatically.
Just like in the rest of the paper, the text is double spaced and you should use title case capitalization for the title (but not for the caption or notes).
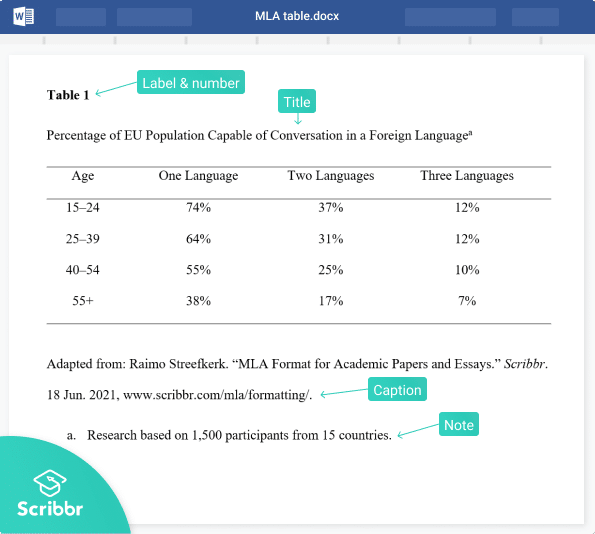
MLA format for figures
Figures (any image included in your paper that isn’t a table) are also labeled and numbered, but here, this is integrated into the caption below the image. The caption in this case is also centered.
The label “Figure” is abbreviated to “Fig.” and followed by the figure number and a period. The rest of the caption gives either full source information, or (as in the example here) just basic descriptive information about the image (author, title, publication year).

Source information in table and figure captions
If the caption of your table or figure includes full source information and that source is not otherwise cited in the text, you don’t need to include it in your Works Cited list.
Give full source information in a caption in the same format as you would in the Works Cited list, but without inverting the author name (i.e. John Smith, not Smith, John).
MLA recommends using 12-point Times New Roman , since it’s easy to read and installed on every computer. Other standard fonts such as Arial or Georgia are also acceptable. If in doubt, check with your supervisor which font you should be using.
The main guidelines for formatting a paper in MLA style are as follows:
- Apply double line spacing
- Indent every new paragraph ½ inch
The fastest and most accurate way to create MLA citations is by using Scribbr’s MLA Citation Generator .
Search by book title, page URL, or journal DOI to automatically generate flawless citations, or cite manually using the simple citation forms.
The MLA Handbook is currently in its 9th edition , published in 2021.
This quick guide to MLA style explains the latest guidelines for citing sources and formatting papers according to MLA.
Usually, no title page is needed in an MLA paper . A header is generally included at the top of the first page instead. The exceptions are when:
- Your instructor requires one, or
- Your paper is a group project
In those cases, you should use a title page instead of a header, listing the same information but on a separate page.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Streefkerk, R. (2024, May 06). MLA Format | Complete Guidelines & Free Template. Scribbr. Retrieved June 26, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/mla/formatting/
Is this article helpful?
Raimo Streefkerk
Other students also liked, creating an mla header, block quoting in mla style, how to format your mla works cited page, get unlimited documents corrected.
✔ Free APA citation check included ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts
popular searches
- Request Info
Suggested Ways to Introduce Quotations
When you quote another writer's words, it's best to introduce or contextualize the quote.
How To Quote In An Essay?
To introduce a quote in an essay, don't forget to include author's last name and page number (MLA) or author, date, and page number (APA) in your citation. Shown below are some possible ways to introduce quotations. The examples use MLA format.
Use A Full Sentence Followed by A Colon To Introduce A Quotation
- The setting emphasizes deception: "Nothing is as it appears" (Smith 1).
- Piercy ends the poem on an ironic note: "To every woman a happy ending" (25).
Begin A Sentence with Your Own Words, Then Complete It with Quoted Words
Note that in the second example below, a slash with a space on either side ( / ) marks a line break in the original poem.
- Hamlet's task is to avenge a "foul and most unnatural murder" (Shakespeare 925).
- The speaker is mystified by her sleeping baby, whose "moth-breath / flickers among the flat pink roses" (Plath 17).
Use An Introductory Phrase Naming The Source, Followed By A Comma to Quote A Critic or Researcher
Note that the first letter after the quotation marks should be upper case. According to MLA guidelines, if you change the case of a letter from the original, you must indicate this with brackets. APA format doesn't require brackets.
- According to Smith, "[W]riting is fun" (215).
- In Smith's words, " . . .
- In Smith's view, " . . .
Use A Descriptive Verb, Followed by A Comma To Introduce A Critic's Words
Avoid using says unless the words were originally spoken aloud, for instance, during an interview.
- Smith states, "This book is terrific" (102).
- Smith remarks, " . . .
- Smith writes, " . . .
- Smith notes, " . . .
- Smith comments, " . . .
- Smith observes, " . . .
- Smith concludes, " . . .
- Smith reports, " . . .
- Smith maintains, " . . .
- Smith adds, " . . .
Don't Follow It with A Comma If Your Lead into The Quotation Ends in That or As
The first letter of the quotation should be lower case.
- Smith points out that "millions of students would like to burn this book" (53).
- Smith emphasizes that " . . .
- Smith interprets the hand washing in MacBeth as "an attempt at absolution" (106).
- Smith describes the novel as "a celebration of human experience" (233).
Other Writing Resources
Enhance your academic writing skills by exploring our additional writing resources that will help you craft compelling essays, research papers, and more.

Your New Chapter Starts Wherever You Are
The support you need and education you deserve, no matter where life leads.
because a future built by you is a future built for you.
Too many people have been made to feel that higher education isn’t a place for them— that it is someone else’s dream. But we change all that. With individualized attention and ongoing support, we help you write a new story for the future where you play the starring role.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
MLA (Modern Language Association) style is most commonly used to write papers and cite sources within the liberal arts and humanities. This resource, updated to reflect the MLA Handbook (8th ed.), offers examples for the general format of MLA research papers, in-text citations, endnotes/footnotes, and the Works Cited page.
Citing a quote in APA Style. To cite a direct quote in APA, you must include the author's last name, the year, and a page number, all separated by commas. If the quote appears on a single page, use "p."; if it spans a page range, use "pp.". An APA in-text citation can be parenthetical or narrative.
MLA (Modern Language Association) style is most commonly used to write papers and cite sources within the liberal arts and humanities. This resource, updated to reflect the MLA Handbook (9th ed.), offers examples for the general format of MLA research papers, in-text citations, endnotes/footnotes, and the Works Cited page.
Revised on March 5, 2024. An MLA in-text citation provides the author's last name and a page number in parentheses. If a source has two authors, name both. If a source has more than two authors, name only the first author, followed by " et al. ". If the part you're citing spans multiple pages, include the full page range.
The nine core elements of MLA citations. 1. Author. Begin each source entry with the name of the author (s) or creator (s). The name of the first author is always inverted (Last name, First name). When a source has two authors, the second author's name is shown in the normal order (First name Last name).
In-Text Citations: An Overview. In-text citations are brief, unobtrusive references that direct readers to the works-cited-list entries for the sources you consulted and, where relevant, to the location in the source being cited. An in-text citation begins with the shortest piece of information that directs your reader to the entry in the ...
A long or block quotation is a quotation which is 4 lines or more. Rules for Long Quotations. The line before your long quotation, when you're introducing the quote, usually ends with a colon. The long quotation is indented half an inch from the rest of the text, so it looks like a block of text. There are no quotation marks around the ...
MLA (Modern Language Association) style is most commonly used to write papers and cite sources within the liberal arts and humanities. This resource, updated to reflect the MLA Handbook (9th ed.), offers examples for the general format of MLA research papers, in-text citations, endnotes/footnotes, and the Works Cited page.
Quoting a quote from a source (indirect quotations) Sometimes, other people are quoted in your source. This is called an indirect quotation. When we use a quote that is quoted in the source, use the abbreviation qtd. in to let the reader know which source the quote you are quoting comes from. Say, for example, Jones wrote the article you found ...
In MLA, in-text citations are inserted in the body of your research paper to briefly document the source of your information. Brief in-text citations point the reader to more complete information in the Works Cited list at the end of the paper. Number of Authors/Editors. Format of In-Text Citation. One.
An in-text citation can be included in one of two ways as shown below: 1. Put all the citation information at the end of the sentence: 2. Include author name as part of the sentence (if author name unavailable, include title of work): Each source cited in-text must also be listed on your Works Cited page. RefWorks includes a citation builder ...
1. Make a free-standing blockquote for quotes longer than 4 lines. Start the quote on a new line and type the quote exactly as it appears in the source text, including punctuation. Do not enclose blockquotes in double quotation marks. [6] The entire blockquote is indented .5 inches (1.3 cm) from the left margin.
When you cite a direct quote in MLA, the parenthetical format is (author's last name page number) or (Smith 7). The narrative format includes the author's name in the sentence, with the page number after the quote in parentheses. There is no punctuation within a set of parentheses. As in APA style, the final punctuation is placed after the ...
Do not use a period after your title or after any heading in the paper (e.g., Works Cited). Begin your text on a new, double-spaced line after the title, indenting the first line of the paragraph half an inch from the left margin. Fig. 1. The top of the first page of a research paper.
At college level, you must properly cite your sources in all essays, research papers, and other academic texts (except exams and in-class exercises). Add a citation whenever you quote, paraphrase, or summarize information or ideas from a source. You should also give full source details in a bibliography or reference list at the end of your text.
This page provides resources for all the elements of a preparing a paper in MLA Style, including formatting, in-text citations, and the works cited list. ... These sample student papers show MLA formatting for all details of a research paper. Look a the structure of the page, how quotes are incorporated, and how works are cited. Formatting Your ...
Scroll back up to the generator at the top of the page and select the type of source you're citing. Books, journal articles, and webpages are all examples of the types of sources our generator can cite automatically. Then either search for the source, or enter the details manually in the citation form. The generator will produce a formatted MLA ...
There are 4 rules that apply to long quotations that are different from regular quotations: The line before your block quotation, when you're introducing the quote, ends with a colon. The bock quotation is indented half an inch from the rest of the text, so it looks like a block of text. There are no quotation marks needed when using block ...
1. Know where to place commas and periods. When you're placing a quote inside your essay, you'll likely have to use a comma or period at the end. If you're quoting without giving a citation (because your entire essay is about a single work, for example) commas and periods go inside the quotations marks.
Revised on March 5, 2024. When you include a long quote in an MLA paper, you have to format it as a block quote. MLA style (8th edition) requires block quote formatting for: An MLA block quote is set on a new line, indented 0.5 inches, with no quotation marks. The MLA in-text citation goes after the period at the end of the block quote.
How to format and when to use a block quote in an MLA 9 research paper.
Cite your MLA source. Start by applying these MLA format guidelines to your document: Use an easily readable font like 12 pt Times New Roman. Set 1 inch page margins. Use double line spacing. Include a ½" indent for new paragraphs. Include a four-line MLA heading on the first page. Center the paper's title.
Use An Introductory Phrase Naming The Source, Followed By A Comma to Quote A Critic or Researcher. Note that the first letter after the quotation marks should be upper case. According to MLA guidelines, if you change the case of a letter from the original, you must indicate this with brackets. APA format doesn't require brackets.