- Sample Research

FREE 10+ Elementary Research Report Samples in PDF | MS Word

The book “ Practical Steps to the Research Process for Elementary School ” stated that elementary students usually feel bored in doing research projects. Due to the students being greatly influenced by streaming media, it appears to be really challenging for them to focus on doing educational tasks. Are you an elementary student who needs to accomplish a research report for your class? In this article, we have some informative guide and downloadable elementary research report templates to guide you in being successful in learning the processes of research. Keep on reading!
Elementary Research Report
Free 10+ elementary research report samples, 1. elementary research report template, 2. sample elementary research report, 3. elementary research report, 4. elementary research report in pdf template, 5. elementary grades research report, 6. elementary research report summary, 7. sample elementary school research report, 8. elementary students research report, 9. sample students research report, 10. basic elementary grades research report, 11. elementary research survey report, what is an elementary research report, how to write an elementary research report, 1. select a topic, 2. take some time to research important information, 3. organize and analyze your information, 4. develop an outline of methods and tasks, what is the format of the research report, what are different kinds of research skills, how do you make research fun, how do you teach elementary research skills.

Size: 174 KB

Size: 56 KB

Size: 15 MB

Size: 175 KB

Size: 311 KB

An elementary research report is a beneficial document made by the elementary or grade school students (typically in Grade 4-6), applying what they learned in performing basic research. This report appears to be a stepping stone for children in improving their skills and abilities to learn and process information, and promoting growth in their research study.
In this section, we provide you some easy-to-follow tips that indicate how to design an elementary report, as well as managing different kinds of phases in writing an effective research project report for elementary school students:
The most important step in the process of developing a plan for your report is selecting a topic. A good topic is both feasible and a little bit difficult to the student’s evaluated capabilities. Search for ideas or concepts in a specific list made by your teacher. or look for your grade-level textbooks or other library sources. Also, include several good subtopics that will help you to dig deeper on your primary topic.
The second step in your research work is taking some ample time to research important information that you will use for your report . Some examples of sources that you can use for research are books , references, magazines, newspapers, videos, internet, and many more. By doing effective research, your comprehension and evaluation skills may potentially improve.
Carefully read the entire materials or sources that you have chosen for your research work prior to selecting facts. Look for the significant points of your reading material. Then, organize the highlighted points you found, analyze them, and select key facts from each part to align your subtopics.
Last but not the least, you should develop a well-designed outline of specific actions or tasks for your elementary research report. Go back from your notes in your research study. Then, sort the notes into subtopic sections and arrange them in a basic outline order. Move the notes into a logical pattern for writing. Use numbers and bullets while arranging the methods and tasks.
The format of the research report contains a list of primary sections consisting page numbers, tables, illustrations, reference list, and appendices. Also, it provides an abstract that shows a clear overview of goals, methods, outcomes, and conclusions.
[/ns_row ]
There are different kinds of research skills such as analyzing information, asking questions, respecting ownership, using networks, and many more.
Make research fun by writing a quiz, creating a collage, going for a photo scavenger hunt, transforming research into art, and designing a magazine.
First, you need to identify the task significance for the research, look for top keywords, utilizing proper tools, taking notes, and collecting data.
Thus, elementary school students will fully benefit throughout their education by means of developing their research skills. This will help them instill an insight of academic research and establish a solid foundation for their future research projects when they enter middle school, high school, and college or university, especially when they got hired from work. Here are some of our downloadable and printable report samples available in different kinds of formats. Simply click the templates in this article and start downloading now!
Related Posts
Free 9+ case study analysis samples in pdf ms word, sample music lesson plan template, free 9+ sample elementary lesson plan templates in pdf, free 14+ biography writing samples and templates inpdf ms ..., free 5+ sample chapter summary templates in pdf ms word, free 5+ lesson learned samples in pdf ms word | excel, sample book review template, free 9+ survey templates in ms word pdf, free 20+ sample project proposals in pdf ms word | pages ..., free 63+ incident report examples in ms words pdf | pages, free 31 daily log templates in pdf ms word, free 9+ sample comparative market analysis templates in pdf ..., free 13+ sample parent survey templates in pdf ms word, free 8+ sample elementary lesson plan templates in pdf, sample soccer team roster, free 17+ sample student progress reports in pdf ms word ..., free 7+ sample news report templates in pdf, free 9+ sample middle school book reports in pdf ms word, free 20+ sample weekly activity reports in pdf ms word | apple ....
Bell Ringers
Independent research projects in upper elementary, independent research projects in upper elementary ela.
Every year, I plan to give my students more choice, voice, and independent project work. Of course, we also have to deal with state testing and loads of other requirements. However, giving your students independent research projects not only helps them demonstrate learning and mastery of standards, it also gives them some choices and ability to share their own unique voice! Here are some independent research projects in upper elementary ELA that your 4th through 6th graders will love!
Genius Hour
You may have heard of Genius Hour or Passion Projects. Genius Hour is considered project-based learning, and it starts with a question. Students choose their own research question about anything really, and they study it at least an hour a week. After reading/researching about their question, their final project can be something as simple as an explanatory slideshow or building their own dollhouse. The possibilities are endless.
Genius Hour can require some scaffolding at the beginning. For example, you may ask your students to research a question related to a certain topic. If you’re reading Watsons Go to Birmingham, for example, they may ask a question surrounding the Civil Rights Movement or the 1960s. The topics can be open-ended to give the students some choice but still have an overarching theme.
Once students get practice researching and coming up with their own final project, they can choose a Genius Hour topic about anything. Some example questions may include:
- How do I promote healthy eating in elementary school?
- How do I prepare for middle school?
- What is the best place to take a family vacation, and how can I plan one for my family?
- How do you start a small business as a student?
Genius Hour gives students choice and voice in the classroom, and you’ll love learning about their passions!
Author Studies

This is one of my favorite projects to use for upper elementary ELA students! I first implemented this project with fifth graders after state testing. This is the perfect time of year for an independent study, and it reinforces reading, writing, and research concepts used throughout the school year!
This project includes almost everything you need for your students to complete a research project on the author of their choosing . It sets them up to brainstorm, research, take notes, plan, and then complete a research paper on their selected authors. I have also made sure to leave some of the note-taking more generic so that you and your students can use as little or as many pages as they need.
Start by giving students the included list of possible authors to research or let them choose their own. This author may already be a favorite or one they want to know more about! Once the author is chosen, your job is to facilitate. Remind them of resources to use for research, note-taking skills and options, and let them learn and explore!
The author study resource includes everything your students need to get started. You’ll have the author examples, note sheets, rubrics, and an example research paper to help guide your instruction and student learning!
Differentiate by having students work in groups to research an author together or study different authors within the same genre. This is also a great way to culminate literature circles by having students research the author they read!
These independent research projects in upper elementary ELA are some of my favorites to provide choice while differentiating for all learners. What research projects have you tried in your ELA classroom?

- Read more about: Upper Elementary Reading
You might also like...

Reading and Writing Activities for Back to School in Middle School ELA

Teaching Reading Skills with Louis Sachar’s Holes

The Best Novels to Read with Sixth Grade
Get your free middle school ela pacing guides with completed scopes and sequences for the school year..

My ELA scope and sequence guides break down every single middle school ELA standard and concept for reading, writing, and language in 6th, 7th, and 8th grade. Use the guides and resources exactly as is or as inspiration for you own!
Meet Martina

I’m a Middle School ELA teacher committed to helping you improve your teaching & implement systems that help you get everything done during the school day!
Let's Connect
Member login.
PRIVACY POLICY
TERMS OF USE
WEBSITE DISCLAIMERS
MEMBERSHIP AGREEEMENT
© The Hungry Teacher • Website by KristenDoyle.co • Contact Martina

Elementary Research Report
Report generator.

Even at their young age, elementary kids should have an idea of how research works. They have to be ready when it’s their turn to make a research. They have to be able to know the important parts of the research so they can start conducting it themselves. As teachers, you can always make their lives a little easier. You can always give them an outline on how research is formulated. If you want to help them make their research reports, you can check some of our pre-made research report templates . Here are 10+ elementary research report templates for your kids.
10+ Elementary Research Report Examples
1. performance report template.

- Google Docs
Size: A4 & US Letter Sizes
As a teacher, it is your task to keep track of how your students are doing. you need to make sure they understand the topics from your lesson plan .You need to make sure that they are constantly learning new things and improving their skills while they are under your care. And when they are having a rough time, you need to be fully knowledgeable of their situation to know how to aid them. To help you keep track of their performance, you can use this performance report template. This template helps you record and present a written document when parents ask about their kids’ performance.
2. Summary Report Template

Do you need to summarize a class research or market research in a single report? Do you need an outline to help you create the perfect report? When summarizing your research paper, you need to make that you don’t forget the vital information. Maybe what you need is this summary report template. You can easily edit the labels of this template so that it fits your research. With this template, all you will need to do next is just fill in the spaces. You can even use this as an executive summary template for your business reports and proposals.
3. Test Report Template

5th graders love to do experiments. They get to see chemicals change color and use cool lab equipment. Lab experiments are great learning experiences because, not only do the kids have fun, they also gain new information. But with great fun comes great responsibility. After the experiments, the kids have to write a physics lab report . This helps teachers know if they did the experiment correctly and if they actually learned something. To make their lives a little easier, you can let them use this fully editable and printable lab report template. Download this template now!
4. Test Report Template

Does your research need testing? Do you want to make sure you don’t make any mistakes and forget the results of your test? Do you need a way to document your conditions, variables, and results to make assure that your final outcome and conclusion will be reliable? When testing something out for research, you need to be very careful. What you need for documentation is this test report template. This template lets you compile all your results for easy documentation. It’s easy to use, ready to print, and available in multiple formats.
5. Technical Report Template

- Editable PDF
School-aged kids will do everything to get their hands on the things they want. They will find ways to get some sort of income. From bake sales to lemonade stands, they get super excited when they have a creative business plan. It may seem a bit much, but at this age, you can also start teaching them about sales, marketing, and audit reports . To help them create a report on their new venture, you can have them try out this technical report template. It’s made by professionals but usable for kids. Go on, use thiis technical report to get them a head start on the industry.
6. Free Research Report Cover Page Template

Size: A4 & US Sizes
When writing research, you want it to be memorable. From the introduction to the conclusion, your research should have no boring and unnecessary parts. It should excite and intrigue your teachers, professors, and reviewers. Your research paper should catch their eyes the second you show the cover page. Perhaps what you need is a skillfully made research cover page. Well, not to worry, we have something just for you. Check out this research report cover page template. This template is ready for you to print, just edit in the right data and you have your cover page for your class and business report .
7. Free Research Report Cover Page Template

- “Illustrator
- Editable PDF “
Do you need some sort of chart to keep track of your students’ project progress? Are you the leader of your group research and do you want to make sure everyone does their task? Are you working on multiple projects at a time and you need to make sure that you finish them all before the deadline? What you need is this project report template. This template can help you plot down all your projects for a smooth workflow and proper time management. It’s doesn’t take too much and to edit and it’s absolutely free! Get a copy now!
8. Free Daily Report Template
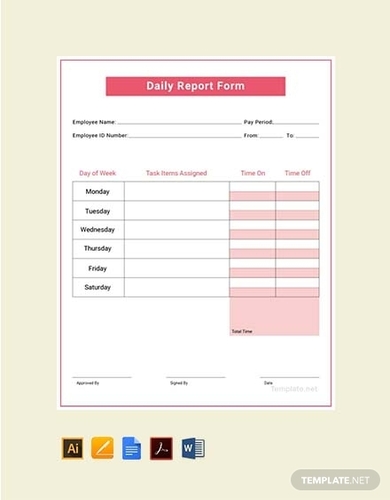
- Illustrator
If your kids are conducting an elementary research , it is your duty to make sure that they make time for it every day. You have to make sure that they have a time table for their daily input for their research. To help them keep up with their work, you could let them try this daily report template. It helps inform you of the students’ school progress and lets your students keep the deadline in mind. This template is professionally designed so you don’t have to worry about its quality. This daily report template can be used by elementary and high school students.
9. Free Book Report Template

Are your students making book reports as a form of research? Do you want to make sure that they don’t hand in lousy works? Are you worried they might not be able to cover the important details? If you want to help your students write outstanding book reports, we could give you an example. Why don’t you give this book report template a spin? This template is super editable, you can add in your own questions and labels for your students to answer and fill in. It’s free to download and ready to print.
10. Free Safety Report Template

Do you have students that say they want to be future engineers? Are they interested in building strong and tall infrastructures? Do you want to make sure they also learn about building safety and not just its methodology? Maybe you could have them research how to make a building safe and strong. This way, you can instill in them the importance of infrastructure safety and building inspections . To make things a little easier, you can make them use this safety report template. It’s customizable so you can make sure that their works look consistent and clean. You can even make them add an abstract if you want.
11. Sample Research Report

Size: 118.4 KB
Do you want to teach elementary kids what college research looks like? Do you want them to understand what MLA and APA are? Do you think giving them some advance lessons can help them in the near future, then you need an example that is easy to understand? And if you are a college kid who needs help making your own research paper, you should take a look at this. This sample research report is the perfect guide for you. It has the important parts of any research report so you don’t have to stress about making yours. With this you won’t have to cancel plan in your college planner .
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
Generate a report on the impact of technology in the classroom on student learning outcomes
Prepare a report analyzing the trends in student participation in sports and arts programs over the last five years at your school.
Step-by-Step Explanation of How to Write a Research Paper for Elementary Students
Sarah pickard.

Learning the basics of writing a research paper during elementary school will help students develop strong writing and research skills. Elementary level research papers can differ from those of high school or college levels in that the information presented is usually more general and the paper is shorter. The writing style may not be as strict for elementary students, but the concepts are just as important.
Explore this article
- Create a title for your paper
- Create an outline for your paper
- Gather your information
- Write the introduction to your paper
- Create the sub-topics or body
- Write two or three paragraphs or for each sub-topic
- Write a conclusion
- Create the bibliography
- Review the paper for any writing errors
1 Create a title for your paper
Create a title for your paper that tells the reader what topic that it is about. Keep the title short and easy to read.
2 Create an outline for your paper
Create an outline for your paper. This will be used as a road map for writing your paper. A research paper will include an introduction, three to four sub-topics, a conclusion and a bibliography.
3 Gather your information
Gather your information by going to your school of local public library and searching for keywords in an encyclopedia. Make notes of information that you would like to include in your paper.
4 Write the introduction to your paper
Write the introduction to your paper. This is a short paragraph that explains to the reader what the paper is about.
5 Create the sub-topics or body
Create the sub-topics or body of the paper. A sub-topic is something that falls under the main category of the paper. For instance, if you are writing about the city in which you live in, have such sub-topics as population, state symbols or history of the city. Elementary students should pick three to four sub-topics to talk about in their paper.
6 Write two or three paragraphs or for each sub-topic
Write two or three paragraphs for each sub-topic. Tell the reader the information that you found on each topic.
7 Write a conclusion
Write a conclusion, which is a paragraph that summarizes the information given in the paper without giving any new information.
8 Create the bibliography
Create the bibliography, which is a list of sources that were used for the information presented in the paper.
9 Review the paper for any writing errors
Review the paper for any writing errors, including misspelled words, incorrect punctuation and grammar mistakes. Correct the writing errors and check that the papers follows the outline.
- Understand what is expected of you and what your teacher wants in your paper. Always ask your teacher for help if you need it. Never copy information straight from a book or article; always use your own words.
About the Author
Writing out of Salt Lake City, Sarah Pickard started her freelance writing career in 2010. She graduated with a B.S. in psychology from the University of Utah. Pickard is a member of the American Psychological Association, as well as several honor societies.
Related Articles

How to Write an Essay About Education

How to Write a Suitable Objective Report

How to Address a Letter to a Mayor

How to Write & Reference an Essay

How to Make a Good Introduction Paragraph

Define MLA Writing Format

How to Write a Discussion for an APA Style Paper

How to Write Book Titles in an Essay

How to Create Foldables for the Classroom

How to Write Outlines for 9th Grade

How to Outline the Format for APA

Note Taking Sentence Method

How to Do a Research Paper Outline From Your Note Cards

What Is an Objective in a Synthesis Paper?

How to Use Lead-Ins for In-Text Citations in MLA

Format for Writing an Information Paper

How to Write an Informative/Explanatory Paper

How to Make a Content Outline

How to Write a Math Report

How to Write a Bachelor's Capstone Paper
Regardless of how old we are, we never stop learning. Classroom is the educational resource for people of all ages. Whether you’re studying times tables or applying to college, Classroom has the answers.
- Accessibility
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Copyright Policy
- Manage Preferences
© 2020 Leaf Group Ltd. / Leaf Group Media, All Rights Reserved. Based on the Word Net lexical database for the English Language. See disclaimer .
- Most Recent
- Free Silly Handwriting
- Easy Sub Plans Template
- Sprinkle Topped Shop
- My TpT Shop
- Amazon Favorites
- Free Video Series
The Sprinkle Topped Teacher

Research Project Template For Elementary Students
Hey teachers! Are you searching for one easy resource that keeps on giving, all year long? My Research Project Template for Elementary Students is perfect for you!
We all know that research skills are super important for students to have, but some of you may be wondering how best to fit research into a younger student’s curriculum. Typically when you think of research, you think of long hours in a college library and tons of citations. Well, it’s easier than you might think!
Seriously, you can do a simple research problem on pretty much anything. I’m talking bugs, states, countries, plants… you name it. And since younger kids are naturally super curious, they always get excited to embark on the quest to find out more about the things they like — and learning about completely new things, too!

It’s key for students to start to get some research experience while they are in elementary school because this will build their ability to question the world around them while they are young. It also helps them develop note taking skills and write out their ideas and observations, both of which are essential parts of good communication and good classroom habits. They will take these skills with them for the rest of their lives, so it’s never too early to start!
Here’s the good news: research projects for elementary students don’t have to get fancy at all. In fact, my Research Project Template is both incredibly simple for you to prep, and comprehensive on the students’ side of things. Plus, you can use it again and again all year round because it’s totally editable. Yay for reusable resources!


How does this Research Project Template for Elementary Students work?
It doesn’t get much easier for you and your students than this research project flip flap! All you have to do is print it for your students and you’re ready to roll. As easy as the prep is for you, students still get the opportunity to cut, color, and write about any research topic they’re assigned or that sparks their curiosity.
The research project template is a Powerpoint file, and complete instructions are included for you. This way, you can easily edit the text to suit your classroom’s needs!

Students will pick a topic that interests them, or you can assign a topic based on any unit your class is currently studying. Then, according to the topic, students will record their observations and more, including…
● 3 Interesting Facts
● Vocabulary word with pictures
● Illustrate what you learned
● Create a poem
● Can, Have, Are activity
The combination of writing, observations, and illustrations make this a comprehensive activity that covers ELA skills, STEM skills, and creative expression. And since it is customizable in the Powerpoint document, you can choose which sections to use and leave some out if they don’t best suit your lesson.

How can I use this Research Project Template in the classroom?
My favorite part about this research project template for elementary students is that you can reuse it in the classroom all school year long! Since it is a generic template and completely editable, it can easily fit with any kind of research project or activity you have in mind, from geography, to science, to art, and more.
Students can even pick their own topic they would like to research and complete their own mini project themselves! This option is great for centers. Flip flaps are amazing for centers because once students observe how to complete the flip flap once or twice, they can easily do it on their own in groups. You can assign a topic for the group to research or let students go their own way and work independently.
They can keep their research projects in their folders all year long if it’s important stuff to know, or they can bring them home and proudly show them off to their families. If you’d like, you could even have a research day where students present their findings to their classmates at the end of the day!

Download the No-Prep Research Template:
Click here to download a copy for your students.
This Research Project Template for younger students is totally worth returning to all year round! It’s super simple to prep, easy to edit, and can be used for any topic that you or your students want to cover. They will be able to practice their questioning, observational, note taking, and written communication skills, while everything stays low prep on your end. Have fun researching with your class, and enjoy!
What kinds of research do you like to do in your class? Do you plan on using this research project template? I’d love to hear from you all!
Share this:
You may also like, marshmallow stem activity – team building challenge, easy slime experiment for kids – scientific method, different ways teachers can use digital notebooks for google slides, student teacher mentor pack, growth mindset activity – craft and writing.
Primary School Education Research Paper

Sample Primary School Education Research Paper. Browse other research paper examples and check the list of research paper topics for more inspiration. If you need a research paper written according to all the academic standards, you can always turn to our experienced writers for help. This is how your paper can get an A! Feel free to contact our research paper writing service for professional assistance. We offer high-quality assignments for reasonable rates.
1. Introduction
The primary grades are the first few grades of elementary school, in which students aged approximately 5–8 are socialized into the student role and taught basic tool skills. Evolving views on what constitutes appropriate curriculum and instruction during these grades have been influenced by developments in theory and research on the needs, interests, capabilities, and other characteristics of children in this age range. Emphasis has shifted from maturation of generic stages of cognitive development to learning of domain-specific knowledge networks, so that readiness to learn is now seen as dependent more on relevant prior knowledge and experience than on age or developmental level.
Academic Writing, Editing, Proofreading, And Problem Solving Services
Get 10% off with 24start discount code, 2. from generic developmental stages to domain-specific learning.
The term ‘primary school education’ refers typically to the first two or three grades of elementary school, in which curriculum and instruction emphasize basic literacy and numeracy skills. These grades also emphasize socialization into the student role: teaching children to pay attention to lessons and to work persistently on assignments; to follow prescribed conventions for participating in whole-class activities (e.g., raise hand and wait to be called on); to collaborate productively with peers in pairs and small groups; and to take good care of personal possessions and classroom equipment. In many countries, formal schooling in the primary grades is preceded by a transitional year (called kindergarten in the USA). It is a year in which students are oriented to school routines, engaged in activities that feature artwork and other multisensory representations that call for listening, speaking, counting, building vocabulary, making visual discriminations, exercising fine motor skills, or in other ways developing readiness for the more formal academic learning emphasized in subsequent grades.
At all levels of schooling, curriculum development involves negotiating a reasonable balance among four general approaches: (a) equipping students with knowledge that is lasting, important, and fundamental to the human experience (emphasizing but not limited to the academic disciplines), (b) following the natural course of child development by matching content to students’ interests and learning needs at each grade level, (c) meeting society’s needs by preparing students to assume adult work roles and citizenship responsibilities, and (d) combating social injustice and promoting social change by addressing social policy issues (Kliebard 1994). The principle of meeting children’s developmental needs and interests has special relevance for the primary grades because substantial cognitive development occurs during these years. Children aged five–eight (especially five–six) are often considered to be not merely less knowledgeable, but qualitatively different in several respects from older children and adults. Philosophers traditionally have maintained that children reach the age of reason at about age seven, when developments in their understanding of cause-and-effect relationships, reciprocity and the Golden Rule, and other key concepts and principles enable them to distinguish right from wrong and engage in principled moral reasoning. Researchers studying children’s cognitive development speak of a Developmental shift that occurs between ages five and seven as children become less like animals and infants and more like older children and adults in their performance on a broad range of perceptual and cognitive tasks (Sameroff and Haith 1996).
Jean Piaget (1983) described children aged two– seven as egocentric in purview and unstable in their cognitive structures and thought patterns. Within his comprehensive stage theory of cognitive development, such children were labeled as preoperational because they had not yet acquired reversibility of thinking, conservation, classification, seriation, and other concrete operations that stabilize older children’s cognitive structures, and enable them to engage in systematic reasoning. Piaget’s work implied that progression from the preoperational to the concrete operational stage was determined primarily by maturation and thus not open to significant acceleration through educational interventions. Consequently, primary schooling models influenced by his ideas tended to emphasize play, exploration, discovery learning, and sensorimotor activities over more formally academic and verbally mediated instruction. Ideas drawn from Arnold Gesell, Maria Montressori, and others who emphasized developmental stages or the presumed special needs and characteristics of young children similarly led to early childhood and primary-grade education models that emphasize short and varied activities, hands-on learning, concrete and integrated topical units rather than systematic treatment of disciplinary content, and attempts to be responsive to children’s learning initiatives rather than to move them through preplanned curricula in lock-step fashion. Contemporary notions of developmentally appropriate practice continue this tradition (NAEYC 1991), as do the British Infant School model and the Italian Reggio Emilia model.
In recent years, the predominant theoretical emphasis in developmental psychology has shifted from the stage theory of Piaget to the sociocultural learning theory of Lev Vygotsky (1978), and research on children’s cognition has shifted emphasis from general developmental stages to domain and situation- specific learning. Findings indicate that many aspects of cultural learning, including much of what is taught in elementary school, can be acquired through instruction, in which teachers provide modeling and explanations for students and coach and ‘scaffold’ their learning efforts. Instead of emphasizing limitations in cognitive capacity, pending the unfolding of genetically programmed maturation of internal structures, contemporary thinking emphasizes connecting with and building on students’ prior knowledge in the domain. Instruction focuses on the zone of proximal Development: the range of knowledge and skills that students are not yet ready to learn on their own but can learn with help from teachers (Tharp and Gallimore 1988).
A related notion is that instead of being organized into hierarchical levels, knowledge is organized within networks structured around key ideas. This implies that, instead of having to begin with the lowest cognitive level (knowledge) and proceed systematically through successively higher levels (comprehension, application, analysis, synthesis, and evaluation), instruction can begin anywhere in the network and develop understandings from there. Initial possibilities will be limited by the extent of learners’ prior knowledge in the domain, but in principle, learners can accomplish any domain-related learning goals if they experience whatever instruction and learning opportunities may be required (without having to wait for supposed maturation of cognitive structures to occur).
Studies of children’s domain-specific knowledge have verified that children’s knowledge and learning capacities in many areas are much more advanced than previously suspected, although children find certain concepts difficult to grasp and certain misconceptions are commonly developed (e.g., that the sun rotates around the earth instead of vice-versa). It appears that Piaget’s notions about children’s learning capacities were too pessimistic and that his stage concepts are more applicable to developments in children’s mathematical and scientific thinking than to developments in their thinking about issues addressed in the humanities and social sciences. Children are able to understand historical and literary content that is encoded within narrative structures built around the goals and motives of central characters, as well as cultural comparisons or other social science content that focuses on food, clothing, shelter, transportation, or other cultural universals with which they have had personal experience (Downey and Levstik 1991).
Research supports the following generalizations about difficulty level of curriculum content: (a) difficulty increases with the number of items that must be addressed simultaneously (it is harder to compare or interpret three things than two things); (b) abstract content is more difficult than more concrete content; (c) fine distinctions are more difficult than gross ones; (d) learning from print alone is more difficult than learning from multiple media; (e) it is easier to develop skills in thinking about matters that students see as closely related to their own lives than about other matters; and (f ) providing structure, cues, and props makes thinking easier (Fair 1977)
In summary, much of what Piaget claimed about stage-related limitations in children’s cognitive capacities is incorrect or limited to certain knowledge domains. However, Piaget was correct in suggesting that young children are qualitatively different from older children and adults in certain respects, so that it is not possible (or at least, not cost effective) to teach them some of the more abstract and complex aspects of each school subject. Primary-grade children appear to be ready for certain forms of systematic instruction that go well beyond what usually are described as ‘developmentally appropriate practices,’ but not yet ready for discipline-based courses that emphasize abstract content organized conceptually.
3. Curriculum And Instruction In The Primary Grades
Children show the capacity for operational thinking at five or six, but usually do not become functionally operational (use operational thinking most of the time) until a year or two later. Thus, in effect, the preoperational period extends until second or third grade for most students. Preoperational students are ready to learn about familiar experiences and observable phenomena, especially through exploration and manipulation of concrete objects. They also learn basic literacy and mathematics skills and those aspects of content area knowledge that can be linked to their experience base. Instruction in basic skills should connect with knowledge about language, print, counting, and numbers that children develop through their preschool experiences. These tool skills should be taught in an integrated way that stresses explanations for meaningful understanding and opportunities for authentic applications (Adams 1990, Hiebert and Carpenter 1992, Hooper and DeFrain 1980). Execution of basic skills should gradually become automatized, but these skills should be learned as strategies, so that procedural knowledge (about what to do and how to do it) is developed in connection with related propositional knowledge (about the nature and purposes of the skill) and conditional knowledge (about when and why to use it).
Primary-grade students require demonstration and explanation of skills, guided practice with feedback, and frequent opportunities to develop mastery through application. Good demonstrations and visual aids provide concrete models for children to watch or imitate, so that they do not have to struggle to follow purely verbal instruction. Complex tasks are broken into subtasks that children can master in sequences that gradually connect until the ultimate task is learned. When they work on their own, they may need cues, reminders, or other learning scaffolds that will help them overcome their limited attention spans and difficulty in following spoken or written directions. Models of completed tasks can be placed in learning centers and worksheets can include features such as spacing and lines to keep things separate; boxes or arrows to indicate where responses should be placed or where to go next; and division of assignments into modular units that can be presented, reviewed, and discussed separately.
Teaching in subject areas other than basic skills should either emphasize familiar content or make the strange familiar by using concrete props or other media. Actual objects are best, but substitutes such as videos or photos are also useful. Because young children have limited experience and major gaps in their vocabularies, they may need such props to enable them to understand what the teacher is talking about. They are most likely to have difficulty when content is organized around the conceptual structures used in the academic disciplines rather than around their own emerging knowledge structures. Children tend to learn specifics first and build up abstract generalizations only gradually as they accumulate experience; they have trouble following the logical patterns (flowing from general rules to specific examples) that adults find helpful. They are predisposed to learn in various domains, and although they are inexperienced, they reason facilely with the knowledge they have (Bransford et al. 1999). However, it is important to focus instruction on familiar and observable events, or at least events that are easily assimilated into the students’ existing schemes. For example, children have an intuitive sense of the past and an interest in people that can provide a basis for instruction in history and social studies. However, such instruction has to reach the operative level rooted in students’ concrete experiences, e.g., by having them investigate their own family histories, explore the geography of the neighborhood, or examine photos and artifacts from another culture. If the instruction stays at a purely figurative level (associating tipis with Native Americans, sombreros with Mexicans, etc.), it will have little meaning or potential for inclusion in networks of knowledge structured around powerful ideas (and will engender stereotypes, rather than layered understandings).
There has been noteworthy cross-national variation in the age at which children begin school and in the scope of the primary-grade curriculum. As more has been learned about children’s knowledge and learning capacities, the trend has been towards earlier school initiation and more demanding curricula. Kindergarten classes in the USA, for example, now feature less sensorimotor play and more verbally mediated instruction than in the past. Even so, primary-grade teachers tend to be nurturant individuals who are oriented more toward teaching children than teaching subject matter, and who are concerned about supporting their students’ personal development and adjustment to school, along with meeting their academic learning needs. Subject matter specialization usually does not begin until at least the fourth grade, so primary-grade teachers tend to be generalists who stay with their home-room class all day and teach all subjects.
Some schools even use looping arrangements that keep intact classes together for two consecutive years with the same teacher, as part of a larger effort to provide emotionally safe and supportive classroom environments for young learners. The children often work in learning centers or sit together on a rug instead of always sitting at desks or in chairs. Teacher aides, adult volunteers, or older students often assist the teacher by working with individuals or small groups. Assessment is mostly informal, without emphasis on tests or grades. Curricula often present an idealistic and optimistic view of the world, sanitized to eliminate disturbing or depressing content, in an effort to ‘preserve childhood innocence’ by delaying confrontation with threatening realities. In general, most primary education approaches focus on orienting young children to school and equipping them with basic knowledge and skills, but within a relatively informal and highly supportive learning community. This ethos has persisted through developments from penpals to KIDSNET; from mathematics flash cards to number lines and manipulables; from penmanship drills to authentic writing and publishing; from fixed desks to flexibly arrangeable children’s chairs and tables, etc., apparently because it is well-suited to the educational needs and capacities of young students.
Bibliography:
- Adams M 1990 Beginning to Read: Thinking and Learning about Print. MIT Press, Cambridge, MA
- Bransford J, Brown A, Cocking R (eds.) 1999 How People Learn: Brain, Mind, Experience, and School. National Academy Press, Washington, DC
- Downey M, Levstik L 1991 Teaching and learning history. In: Shaver J (ed.) Handbook of Research on Social Studies Teaching and Learning. Macmillan, New York, pp. 400–10
- Fair J 1977 Skills in thinking. In: Kurfman D (ed.) Forty-seventh Yearbook: Developing Decision-making Skills. National Council for the Social Studies, Arlington, VA, pp. 29–68
- Hiebert J, Carpenter T 1992 Learning and teaching with understanding. In: Grouws D A (ed.) Handbook of Research on Mathematics Teaching and Learning. Macmillan, New York, pp. 65–97
- Hooper F, DeFrain J 1980 On delineating distinctly Piagetian contributions to education. Genetic Psychology Monographs 101: 151–81
- Kliebard H 1994 The Struggle for the American Curriculum 1893–1958, 2nd edn. Routledge, New York
- National Association for the Education of Young Children (NAEYC) 1991 Guidelines for appropriate curriculum content and assessment in programs serving children ages three through eight. Young Children 46(3): 21–38
- Piaget J 1983 Piaget’s theory. In: Mussen P (ed.) Handbook of Child Psychology, 4th edn. Wiley, New York, Vol. 1, pp. 703–32
- Sameroff A, Haith M 1996 The Fi e to Se en Year Shift: The Age of Reason and Responsibility. University of Chicago Press, Chicago
- Tharp R, Gallimore R 1988 Rousing Minds to Life: Teaching, Learning, and Schooling in Social Context. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK
- Vygotsky L 1978 In: Cole M, John-Steiner V, Scribner S, Souberman E (eds.) Mind in Society: The Development of Higher Psychological Processes. Harvard University Press, Cambridge
ORDER HIGH QUALITY CUSTOM PAPER

- Our Mission
Getting First Graders Started With Research
Teaching academically honest research skills helps first graders learn how to collect, organize, and interpret information.

Earlier in my career, I was told two facts that I thought to be false: First graders can’t do research, because they aren’t old enough; and if facts are needed for a nonfiction text, the students can just make them up. Teachers I knew went along with this misinformation, as it seemed to make teaching and learning easier. I always felt differently, and now—having returned to teaching first grade 14 years after beginning my career with that age group—I wanted to prove that first graders can and should learn how to research.
A lot has changed over the years. Not only has the science of reading given teachers a much better understanding of how to teach reading skills , but we now exist in a culture abundant in information and misinformation. It’s imperative that we teach academically honest research skills to students as early as possible.
Use a Familiar Resource, and Pair it with a Planned Unit
How soon do you start research in first grade? Certainly not at the start of the year with the summer lapse in skills and knowledge and when new students aren’t yet able to read. By December of this school year, skills had either been recovered or established sufficiently that I thought we could launch into research. This also purposely coincided with a unit of writing on nonfiction—the perfect pairing.
The research needed an age-related focus to make it manageable, so I chose animals. I thought about taking an even safer route and have one whole class topic that we researched together, so that students could compare notes and skills. I referred back to my days working in inquiry-based curriculums (like the International Baccalaureate Primary Years Program) and had students choose which animal to study. Our school librarian recommended that we use Epic because the service has an abundance of excellent nonfiction animal texts of different levels.
Teach the Basics for Organized Research
I began with a conversation about academic honesty and why we don’t just copy information from books. We can’t say this is our knowledge if we do this; it belongs to the author. Instead, we read and learn. Then, we state what we learned in our own words. Once this concept is understood, I model how to do this by creating a basic step-by-step flowchart taught to me by my wife—a longtime first-grade and kindergarten teacher and firm believer in research skills.
- Read one sentence at a time.
- Turn the book over or the iPad around.
- Think about what you have learned. Can you remember the fact? Is the fact useful? Is it even a fact?
- If the answer is no, reread the sentence or move onto the next one.
- If the answer is yes, write the fact in your own words. Don’t worry about spelling. There are new, complex vocabulary words, so use your sounding-out/stretching-out strategies just like you would any other word. Write a whole sentence on a sticky note.
- Place the sticky note in your graphic organizer. Think about which section it goes in. If you aren’t sure, place it in the “other facts” section.
The key to collecting notes is the challenging skill of categorizing them. I created a graphic organizer that reflected the length and sections of the exemplar nonfiction text from our assessment materials for the writing unit. This meant it had five pages: an introduction, “what” the animal looks like, “where” the animal lives, “how” the animal behaved, and a last page for “other facts” that could become a general conclusion.
Our district’s literacy expert advised me not to hand out my premade graphic organizer too soon in this process because writing notes and categorizing are two different skills. This was my intention, but I forgot the good advice and handed out the organizer right away. This meant dedicating time for examining and organizing notes in each combined writing and reading lesson. A lot of one-on-one feedback was needed for some students, while others flourished and could do this work independently. The result was that the research had a built-in extension for those students who were already confident readers.
Focus on What Students Need to Practice
Research is an essential academic skill but one that needs to be tackled gradually. I insisted that my students use whole sentences rather than words or phrases because they’re at the stage of understanding what a complete sentence is and need regular practice. In this work, there’s no mention of citation language and vetting sources; in the past, I’ve introduced those concepts to students in fourth grade and used them regularly with my fifth-grade students. Finding texts that span the reading skill range of a first-grade class is a big enough task.
For some of the key shared scientific vocabulary around science concepts, such as animal groups (mammals, etc.) or eating habits (carnivore, etc.), I created class word lists, having first sounded out the words with the class and then asked students to attempt spelling them in their writing.
The Power of Research Can Facilitate Student Growth
I was delighted with the results of the research project. In one and a half weeks, every student had a graphic organizer with relevant notes, and many students had numerous notes. With my fourth- and fifth-grade students, I noticed that one of the biggest difficulties for them was taking notes and writing them in a way that showed a logical sequence. Therefore, we concluded our research by numbering the notes in each section to create a sequential order.
This activity took three lessons and also worked for my first graders. These organized notes created an internal structure that made the next step in the writing process, creating a first draft of their nonfiction teaching books, so much easier.
The overall result was that first graders were able to truly grasp the power of research and gathering accurate facts. I proved that young children can do this, especially when they work with topics that already fascinate them. Their love of learning motivated them to read higher-level and more sophisticated texts than they or I would normally pick, further proving how interest motivates readers to embrace complexity.
Research Topics & Ideas: Education
170+ Research Ideas To Fast-Track Your Project

If you’re just starting out exploring education-related topics for your dissertation, thesis or research project, you’ve come to the right place. In this post, we’ll help kickstart your research topic ideation process by providing a hearty list of research topics and ideas , including examples from actual dissertations and theses..
PS – This is just the start…
We know it’s exciting to run through a list of research topics, but please keep in mind that this list is just a starting point . To develop a suitable education-related research topic, you’ll need to identify a clear and convincing research gap , and a viable plan of action to fill that gap.
If this sounds foreign to you, check out our free research topic webinar that explores how to find and refine a high-quality research topic, from scratch. Alternatively, if you’d like hands-on help, consider our 1-on-1 coaching service .
Overview: Education Research Topics
- How to find a research topic (video)
- List of 50+ education-related research topics/ideas
- List of 120+ level-specific research topics
- Examples of actual dissertation topics in education
- Tips to fast-track your topic ideation (video)
- Free Webinar : Topic Ideation 101
- Where to get extra help
Education-Related Research Topics & Ideas
Below you’ll find a list of education-related research topics and idea kickstarters. These are fairly broad and flexible to various contexts, so keep in mind that you will need to refine them a little. Nevertheless, they should inspire some ideas for your project.
- The impact of school funding on student achievement
- The effects of social and emotional learning on student well-being
- The effects of parental involvement on student behaviour
- The impact of teacher training on student learning
- The impact of classroom design on student learning
- The impact of poverty on education
- The use of student data to inform instruction
- The role of parental involvement in education
- The effects of mindfulness practices in the classroom
- The use of technology in the classroom
- The role of critical thinking in education
- The use of formative and summative assessments in the classroom
- The use of differentiated instruction in the classroom
- The use of gamification in education
- The effects of teacher burnout on student learning
- The impact of school leadership on student achievement
- The effects of teacher diversity on student outcomes
- The role of teacher collaboration in improving student outcomes
- The implementation of blended and online learning
- The effects of teacher accountability on student achievement
- The effects of standardized testing on student learning
- The effects of classroom management on student behaviour
- The effects of school culture on student achievement
- The use of student-centred learning in the classroom
- The impact of teacher-student relationships on student outcomes
- The achievement gap in minority and low-income students
- The use of culturally responsive teaching in the classroom
- The impact of teacher professional development on student learning
- The use of project-based learning in the classroom
- The effects of teacher expectations on student achievement
- The use of adaptive learning technology in the classroom
- The impact of teacher turnover on student learning
- The effects of teacher recruitment and retention on student learning
- The impact of early childhood education on later academic success
- The impact of parental involvement on student engagement
- The use of positive reinforcement in education
- The impact of school climate on student engagement
- The role of STEM education in preparing students for the workforce
- The effects of school choice on student achievement
- The use of technology in the form of online tutoring
Level-Specific Research Topics
Looking for research topics for a specific level of education? We’ve got you covered. Below you can find research topic ideas for primary, secondary and tertiary-level education contexts. Click the relevant level to view the respective list.
Research Topics: Pick An Education Level
Primary education.
- Investigating the effects of peer tutoring on academic achievement in primary school
- Exploring the benefits of mindfulness practices in primary school classrooms
- Examining the effects of different teaching strategies on primary school students’ problem-solving skills
- The use of storytelling as a teaching strategy in primary school literacy instruction
- The role of cultural diversity in promoting tolerance and understanding in primary schools
- The impact of character education programs on moral development in primary school students
- Investigating the use of technology in enhancing primary school mathematics education
- The impact of inclusive curriculum on promoting equity and diversity in primary schools
- The impact of outdoor education programs on environmental awareness in primary school students
- The influence of school climate on student motivation and engagement in primary schools
- Investigating the effects of early literacy interventions on reading comprehension in primary school students
- The impact of parental involvement in school decision-making processes on student achievement in primary schools
- Exploring the benefits of inclusive education for students with special needs in primary schools
- Investigating the effects of teacher-student feedback on academic motivation in primary schools
- The role of technology in developing digital literacy skills in primary school students
- Effective strategies for fostering a growth mindset in primary school students
- Investigating the role of parental support in reducing academic stress in primary school children
- The role of arts education in fostering creativity and self-expression in primary school students
- Examining the effects of early childhood education programs on primary school readiness
- Examining the effects of homework on primary school students’ academic performance
- The role of formative assessment in improving learning outcomes in primary school classrooms
- The impact of teacher-student relationships on academic outcomes in primary school
- Investigating the effects of classroom environment on student behavior and learning outcomes in primary schools
- Investigating the role of creativity and imagination in primary school curriculum
- The impact of nutrition and healthy eating programs on academic performance in primary schools
- The impact of social-emotional learning programs on primary school students’ well-being and academic performance
- The role of parental involvement in academic achievement of primary school children
- Examining the effects of classroom management strategies on student behavior in primary school
- The role of school leadership in creating a positive school climate Exploring the benefits of bilingual education in primary schools
- The effectiveness of project-based learning in developing critical thinking skills in primary school students
- The role of inquiry-based learning in fostering curiosity and critical thinking in primary school students
- The effects of class size on student engagement and achievement in primary schools
- Investigating the effects of recess and physical activity breaks on attention and learning in primary school
- Exploring the benefits of outdoor play in developing gross motor skills in primary school children
- The effects of educational field trips on knowledge retention in primary school students
- Examining the effects of inclusive classroom practices on students’ attitudes towards diversity in primary schools
- The impact of parental involvement in homework on primary school students’ academic achievement
- Investigating the effectiveness of different assessment methods in primary school classrooms
- The influence of physical activity and exercise on cognitive development in primary school children
- Exploring the benefits of cooperative learning in promoting social skills in primary school students
Secondary Education
- Investigating the effects of school discipline policies on student behavior and academic success in secondary education
- The role of social media in enhancing communication and collaboration among secondary school students
- The impact of school leadership on teacher effectiveness and student outcomes in secondary schools
- Investigating the effects of technology integration on teaching and learning in secondary education
- Exploring the benefits of interdisciplinary instruction in promoting critical thinking skills in secondary schools
- The impact of arts education on creativity and self-expression in secondary school students
- The effectiveness of flipped classrooms in promoting student learning in secondary education
- The role of career guidance programs in preparing secondary school students for future employment
- Investigating the effects of student-centered learning approaches on student autonomy and academic success in secondary schools
- The impact of socio-economic factors on educational attainment in secondary education
- Investigating the impact of project-based learning on student engagement and academic achievement in secondary schools
- Investigating the effects of multicultural education on cultural understanding and tolerance in secondary schools
- The influence of standardized testing on teaching practices and student learning in secondary education
- Investigating the effects of classroom management strategies on student behavior and academic engagement in secondary education
- The influence of teacher professional development on instructional practices and student outcomes in secondary schools
- The role of extracurricular activities in promoting holistic development and well-roundedness in secondary school students
- Investigating the effects of blended learning models on student engagement and achievement in secondary education
- The role of physical education in promoting physical health and well-being among secondary school students
- Investigating the effects of gender on academic achievement and career aspirations in secondary education
- Exploring the benefits of multicultural literature in promoting cultural awareness and empathy among secondary school students
- The impact of school counseling services on student mental health and well-being in secondary schools
- Exploring the benefits of vocational education and training in preparing secondary school students for the workforce
- The role of digital literacy in preparing secondary school students for the digital age
- The influence of parental involvement on academic success and well-being of secondary school students
- The impact of social-emotional learning programs on secondary school students’ well-being and academic success
- The role of character education in fostering ethical and responsible behavior in secondary school students
- Examining the effects of digital citizenship education on responsible and ethical technology use among secondary school students
- The impact of parental involvement in school decision-making processes on student outcomes in secondary schools
- The role of educational technology in promoting personalized learning experiences in secondary schools
- The impact of inclusive education on the social and academic outcomes of students with disabilities in secondary schools
- The influence of parental support on academic motivation and achievement in secondary education
- The role of school climate in promoting positive behavior and well-being among secondary school students
- Examining the effects of peer mentoring programs on academic achievement and social-emotional development in secondary schools
- Examining the effects of teacher-student relationships on student motivation and achievement in secondary schools
- Exploring the benefits of service-learning programs in promoting civic engagement among secondary school students
- The impact of educational policies on educational equity and access in secondary education
- Examining the effects of homework on academic achievement and student well-being in secondary education
- Investigating the effects of different assessment methods on student performance in secondary schools
- Examining the effects of single-sex education on academic performance and gender stereotypes in secondary schools
- The role of mentoring programs in supporting the transition from secondary to post-secondary education
Tertiary Education
- The role of student support services in promoting academic success and well-being in higher education
- The impact of internationalization initiatives on students’ intercultural competence and global perspectives in tertiary education
- Investigating the effects of active learning classrooms and learning spaces on student engagement and learning outcomes in tertiary education
- Exploring the benefits of service-learning experiences in fostering civic engagement and social responsibility in higher education
- The influence of learning communities and collaborative learning environments on student academic and social integration in higher education
- Exploring the benefits of undergraduate research experiences in fostering critical thinking and scientific inquiry skills
- Investigating the effects of academic advising and mentoring on student retention and degree completion in higher education
- The role of student engagement and involvement in co-curricular activities on holistic student development in higher education
- The impact of multicultural education on fostering cultural competence and diversity appreciation in higher education
- The role of internships and work-integrated learning experiences in enhancing students’ employability and career outcomes
- Examining the effects of assessment and feedback practices on student learning and academic achievement in tertiary education
- The influence of faculty professional development on instructional practices and student outcomes in tertiary education
- The influence of faculty-student relationships on student success and well-being in tertiary education
- The impact of college transition programs on students’ academic and social adjustment to higher education
- The impact of online learning platforms on student learning outcomes in higher education
- The impact of financial aid and scholarships on access and persistence in higher education
- The influence of student leadership and involvement in extracurricular activities on personal development and campus engagement
- Exploring the benefits of competency-based education in developing job-specific skills in tertiary students
- Examining the effects of flipped classroom models on student learning and retention in higher education
- Exploring the benefits of online collaboration and virtual team projects in developing teamwork skills in tertiary students
- Investigating the effects of diversity and inclusion initiatives on campus climate and student experiences in tertiary education
- The influence of study abroad programs on intercultural competence and global perspectives of college students
- Investigating the effects of peer mentoring and tutoring programs on student retention and academic performance in tertiary education
- Investigating the effectiveness of active learning strategies in promoting student engagement and achievement in tertiary education
- Investigating the effects of blended learning models and hybrid courses on student learning and satisfaction in higher education
- The role of digital literacy and information literacy skills in supporting student success in the digital age
- Investigating the effects of experiential learning opportunities on career readiness and employability of college students
- The impact of e-portfolios on student reflection, self-assessment, and showcasing of learning in higher education
- The role of technology in enhancing collaborative learning experiences in tertiary classrooms
- The impact of research opportunities on undergraduate student engagement and pursuit of advanced degrees
- Examining the effects of competency-based assessment on measuring student learning and achievement in tertiary education
- Examining the effects of interdisciplinary programs and courses on critical thinking and problem-solving skills in college students
- The role of inclusive education and accessibility in promoting equitable learning experiences for diverse student populations
- The role of career counseling and guidance in supporting students’ career decision-making in tertiary education
- The influence of faculty diversity and representation on student success and inclusive learning environments in higher education

Education-Related Dissertations & Theses
While the ideas we’ve presented above are a decent starting point for finding a research topic in education, they are fairly generic and non-specific. So, it helps to look at actual dissertations and theses in the education space to see how this all comes together in practice.
Below, we’ve included a selection of education-related research projects to help refine your thinking. These are actual dissertations and theses, written as part of Master’s and PhD-level programs, so they can provide some useful insight as to what a research topic looks like in practice.
- From Rural to Urban: Education Conditions of Migrant Children in China (Wang, 2019)
- Energy Renovation While Learning English: A Guidebook for Elementary ESL Teachers (Yang, 2019)
- A Reanalyses of Intercorrelational Matrices of Visual and Verbal Learners’ Abilities, Cognitive Styles, and Learning Preferences (Fox, 2020)
- A study of the elementary math program utilized by a mid-Missouri school district (Barabas, 2020)
- Instructor formative assessment practices in virtual learning environments : a posthumanist sociomaterial perspective (Burcks, 2019)
- Higher education students services: a qualitative study of two mid-size universities’ direct exchange programs (Kinde, 2020)
- Exploring editorial leadership : a qualitative study of scholastic journalism advisers teaching leadership in Missouri secondary schools (Lewis, 2020)
- Selling the virtual university: a multimodal discourse analysis of marketing for online learning (Ludwig, 2020)
- Advocacy and accountability in school counselling: assessing the use of data as related to professional self-efficacy (Matthews, 2020)
- The use of an application screening assessment as a predictor of teaching retention at a midwestern, K-12, public school district (Scarbrough, 2020)
- Core values driving sustained elite performance cultures (Beiner, 2020)
- Educative features of upper elementary Eureka math curriculum (Dwiggins, 2020)
- How female principals nurture adult learning opportunities in successful high schools with challenging student demographics (Woodward, 2020)
- The disproportionality of Black Males in Special Education: A Case Study Analysis of Educator Perceptions in a Southeastern Urban High School (McCrae, 2021)
As you can see, these research topics are a lot more focused than the generic topic ideas we presented earlier. So, in order for you to develop a high-quality research topic, you’ll need to get specific and laser-focused on a specific context with specific variables of interest. In the video below, we explore some other important things you’ll need to consider when crafting your research topic.
Get 1-On-1 Help
If you’re still unsure about how to find a quality research topic within education, check out our Research Topic Kickstarter service, which is the perfect starting point for developing a unique, well-justified research topic.

You Might Also Like:

66 Comments
This is an helpful tool 🙏
Special education
Really appreciated by this . It is the best platform for research related items
Research title related to school of students
How are you
I think this platform is actually good enough.
Research title related to students
My field is research measurement and evaluation. Need dissertation topics in the field
Assalam o Alaikum I’m a student Bs educational Resarch and evaluation I’m confused to choose My thesis title please help me in choose the thesis title
Good idea I’m going to teach my colleagues
You can find our list of nursing-related research topic ideas here: https://gradcoach.com/research-topics-nursing/
Write on action research topic, using guidance and counseling to address unwanted teenage pregnancy in school
Thanks a lot
I learned a lot from this site, thank you so much!
Thank you for the information.. I would like to request a topic based on school major in social studies
parental involvement and students academic performance
Science education topics?
plz tell me if you got some good topics, im here for finding research topic for masters degree
How about School management and supervision pls.?
Hi i am an Deputy Principal in a primary school. My wish is to srudy foe Master’s degree in Education.Please advice me on which topic can be relevant for me. Thanks.
Every topic proposed above on primary education is a starting point for me. I appreciate immensely the team that has sat down to make a detail of these selected topics just for beginners like us. Be blessed.
Kindly help me with the research questions on the topic” Effects of workplace conflict on the employees’ job performance”. The effects can be applicable in every institution,enterprise or organisation.
Greetings, I am a student majoring in Sociology and minoring in Public Administration. I’m considering any recommended research topic in the field of Sociology.
I’m a student pursuing Mphil in Basic education and I’m considering any recommended research proposal topic in my field of study
Research Defense for students in senior high
Kindly help me with a research topic in educational psychology. Ph.D level. Thank you.
Project-based learning is a teaching/learning type,if well applied in a classroom setting will yield serious positive impact. What can a teacher do to implement this in a disadvantaged zone like “North West Region of Cameroon ( hinterland) where war has brought about prolonged and untold sufferings on the indegins?
I wish to get help on topics of research on educational administration
I wish to get help on topics of research on educational administration PhD level
I am also looking for such type of title
I am a student of undergraduate, doing research on how to use guidance and counseling to address unwanted teenage pregnancy in school
the topics are very good regarding research & education .
Can i request your suggestion topic for my Thesis about Teachers as an OFW. thanx you
Would like to request for suggestions on a topic in Economics of education,PhD level
Would like to request for suggestions on a topic in Economics of education
Hi 👋 I request that you help me with a written research proposal about education the format
Am offering degree in education senior high School Accounting. I want a topic for my project work
l would like to request suggestions on a topic in managing teaching and learning, PhD level (educational leadership and management)
request suggestions on a topic in managing teaching and learning, PhD level (educational leadership and management)
I would to inquire on research topics on Educational psychology, Masters degree
I am PhD student, I am searching my Research topic, It should be innovative,my area of interest is online education,use of technology in education
request suggestion on topic in masters in medical education .
Look at British Library as they keep a copy of all PhDs in the UK Core.ac.uk to access Open University and 6 other university e-archives, pdf downloads mostly available, all free.
May I also ask for a topic based on mathematics education for college teaching, please?
Please I am a masters student of the department of Teacher Education, Faculty of Education Please I am in need of proposed project topics to help with my final year thesis
Am a PhD student in Educational Foundations would like a sociological topic. Thank
please i need a proposed thesis project regardging computer science
Greetings and Regards I am a doctoral student in the field of philosophy of education. I am looking for a new topic for my thesis. Because of my work in the elementary school, I am looking for a topic that is from the field of elementary education and is related to the philosophy of education.
Masters student in the field of curriculum, any ideas of a research topic on low achiever students
In the field of curriculum any ideas of a research topic on deconalization in contextualization of digital teaching and learning through in higher education
Amazing guidelines
I am a graduate with two masters. 1) Master of arts in religious studies and 2) Master in education in foundations of education. I intend to do a Ph.D. on my second master’s, however, I need to bring both masters together through my Ph.D. research. can I do something like, ” The contribution of Philosophy of education for a quality religion education in Kenya”? kindly, assist and be free to suggest a similar topic that will bring together the two masters. thanks in advance
Hi, I am an Early childhood trainer as well as a researcher, I need more support on this topic: The impact of early childhood education on later academic success.
I’m a student in upper level secondary school and I need your support in this research topics: “Impact of incorporating project -based learning in teaching English language skills in secondary schools”.
Although research activities and topics should stem from reflection on one’s practice, I found this site valuable as it effectively addressed many issues we have been experiencing as practitioners.
Your style is unique in comparison to other folks I’ve read stuff from. Thanks for posting when you have the opportunity, Guess I will just book mark this site.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
Home — Essay Samples — Education — Educational System — Elementary School
Essay Types and Topics
Argumentative essay.
- Should students have homework over the weekend?
- Is social media beneficial or harmful to society?
- Should school uniforms be mandatory?
Paragraph Example: In today's digital age, the impact of social media on our society has become a topic of great debate. As we navigate through the pros and cons of social media, it is essential to understand its potential benefits and drawbacks.
Paragraph Example: While social media has its pitfalls, its ability to connect people globally and disseminate information cannot be overlooked. It is imperative for us to approach social media with a critical eye and use it responsibly.
Compare and Contrast Essay
- Public School vs. Homeschooling
- City Life vs. Suburban Life
- Traditional Learning vs. Online Learning
Descriptive Essay
- A Memorable School Field Trip
- My Favorite Childhood Toy
- The Perfect Day at the Park
Persuasive Essay
- Why Reading is Important for Children
- The Benefits of Volunteering in the Community
- The Importance of Physical Education in Schools
Narrative Essay
- My First Day of Elementary School
- An Unforgettable Family Vacation
- A Lesson Learned from Failure
Engagement and Creativity
Essay writing is not just about meeting academic requirements; it's an opportunity to explore your interests and critical thinking skills. Embrace the chance to express your unique perspective and engage your readers through compelling storytelling and persuasive arguments.
Educational Value
Each essay type offers a unique opportunity for you to develop essential skills. Argumentative essays enhance your analytical thinking, compare and contrast essays improve your critical analysis, descriptive essays hone your descriptive abilities, persuasive essays strengthen your ability to persuade, and narrative essays help you master the art of storytelling.
My Experience in Elementary School
Teaching unplugged in elementary classroom, made-to-order essay as fast as you need it.
Each essay is customized to cater to your unique preferences
+ experts online
Reflection on School Days and Feeling Like an Underdog because of The Racial Difference
My elementary years and the bullying that came with them, capstone project: exploring student performance, let us write you an essay from scratch.
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Relevant topics
- Middle School
- High School
- Single Sex Schools
- Extracurricular Activities
- Homeschooling
- Online Vs. Traditional Classes
- Indian Education
- Special Education
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
Fall 2024 Semester
Undergraduate courses.
Composition courses that offer many sections (ENGL 101, 201, 277 and 379) are not listed on this schedule unless they are tailored to specific thematic content or particularly appropriate for specific programs and majors.
- 100-200 level
ENGL 151.S01: Introduction to English Studies
Tuesday and Thursday, 11 a.m.-12:15 p.m.
Sharon Smith
ENGL 151 serves as an introduction to both the English major and the discipline of English studies. In this class, you will develop the thinking, reading, writing and research practices that define both the major and the discipline. Much of the semester will be devoted to honing your literary analysis skills, and we will study and discuss texts from several different genres—poetry, short fiction, the novel, drama and film—as well as some literary criticism. As we do so, we will explore the language of the discipline, and you will learn a variety of key literary terms and concepts. In addition, you will develop your skills as both a writer and researcher within the discipline of English.
ENGL 201.ST1 Composition II: The Mind/Body Connection
In this section of English 201, students will use research and writing to learn more about problems that are important to them and articulate ways to address those problems. The course will focus specifically on issues related to the mind, the body and the relationship between them. The topics we will discuss during the course will include the correlation between social media and body image; the efficacy of sex education programs; the degree to which beliefs about race and gender influence school dress codes; and the unique mental and physical challenges faced by college students today. In this course, you will be learning about different approaches to argumentation, analyzing the arguments of others and constructing your own arguments. At the same time, you will be honing your skills as a researcher and developing your abilities as a persuasive and effective writer.
ENGL 201.S10 Composition II: Environmental Writing
Monday/Wednesday/Friday 1-1:50 p.m.
Gwen Horsley
English 201 will help students develop the ability to think critically and analytically and to write effectively for other university courses and careers. This course will provide opportunities to develop analytical skills that will help students become critical readers and effective writers. Specifically, in this class, students will:
- Focus on the relationships between world environments, land, animals and humankind.
- Read various essays by environmental, conservational and regional authors.
- Produce student writings.
Students will improve their writing skills by reading essays and applying techniques they witness in others’ work and those learned in class. This class is also a course in logical and creative thought. Students will write about humankind’s place in the world and our influence on the land and animals, places that hold special meaning to them or have influenced their lives and stories of their own families and their places and passions in the world. Students will practice writing in an informed and persuasive manner, in language that engages and enlivens readers by using vivid verbs and avoiding unnecessary passives, nominalizations and expletive constructions.
Students will prepare writing assignments based on readings and discussions of essays included in "Literature and the Environment " and other sources. They may use "The St. Martin’s Handbook," as well as other sources, to review grammar, punctuation, mechanics and usage as needed.
ENGL 201.13 Composition II: Writing the Environment
Tuesday and Thursday 9:30-10:45 a.m.
Paul Baggett
For generations, environmentalists have relied on the power of prose to change the minds and habits of their contemporaries. In the wake of fires, floods, storms and droughts, environmental writing has gained a new sense of urgency, with authors joining activists in their efforts to educate the public about the grim realities of climate change. But do they make a difference? Have reports of present and future disasters so saturated our airwaves that we no longer hear them? How do writers make us care about the planet amidst all the noise? In this course, students will examine the various rhetorical strategies employed by some of today’s leading environmental writers and filmmakers. And while analyzing their different arguments, students also will strengthen their own strategies of argumentation as they research and develop essays that explore a range of environmental concerns.
ENGL 201 Composition II: Food Writing
S17 Tuesday and Thursday 12:30-1:45 p.m.
S18 Tuesday and Thursday 2-3:15 p.m.
Jodi Andrews
In this composition class, students will critically analyze essays about food, food systems and environments, food cultures, the intersections of personal choice, market forces and policy and the values underneath these forces. Students will learn to better read like writers, noting authors’ purpose, audience organizational moves, sentence-level punctuation and diction. We will read a variety of essays including research-intensive arguments and personal narratives which intersect with one of our most primal needs as humans: food consumption. Students will rhetorically analyze texts, conduct advanced research, reflect on the writing process and write essays utilizing intentional rhetorical strategies. Through doing this work, students will practice the writing moves valued in every discipline: argument, evidence, concision, engaging prose and the essential research skills for the 21st century.
ENGL 221.S01 British Literature I
Michael S. Nagy
English 221 is a survey of early British literature from its inception in the Old English period with works such as "Beowulf" and the “Battle of Maldon,” through the Middle Ages and the incomparable writings of Geoffrey Chaucer and the Gawain - poet, to the Renaissance and beyond. Students will explore the historical and cultural contexts in which all assigned reading materials were written, and they will bring that information to bear on class discussion. Likely themes that this class will cover include heroism, humor, honor, religion, heresy and moral relativity. Students will write one research paper in this class and sit for two formal exams: a midterm covering everything up to that point in the semester, and a comprehensive final. Probable texts include the following:
- The Norton Anthology of English Literature: The Middle Ages. Ed. Alfred David, M. H. Abrams, and Stephen Greenblatt. 9th ed. New York: W. W. Norton & Company, 2012.
- The Norton Anthology of English Literature: The Sixteenth Century and Early Seventeenth Century. Ed. George M. Logan, Stephen Greenblatt, Barbara K Lewalski, and M. H. Abrams. 9th ed. New York: W. W. Norton & Company, 2012.
- The Norton Anthology of English Literature: The Restoration and the Eighteenth Century. Ed. George M. Logan, Stephen Greenblatt, Barbara K Lewalski, and M. H. Abrams. 9th ed. New York: W. W. Norton & Company, 2012.
- Gibaldi, Joseph. The MLA Handbook for Writers of Research Papers. 6th ed. New York: The Modern Language Association of America, 2003.
- Any Standard College Dictionary.
ENGL 240.S01 Juvenile Literature Elementary-5th Grade
Monday, Wednesday and Friday noon-12:50 p.m.
April Myrick
A survey of the history of literature written for children and adolescents, and a consideration of the various types of juvenile literature. Text selection will focus on the themes of imagination and breaking boundaries.
ENGL 240.ST1 Juvenile Literature Elementary-5th Grade
Randi Anderson
In English 240 students will develop the skills to interpret and evaluate various genres of literature for juvenile readers. This particular section will focus on various works of literature at approximately the K-5 grade level. We will read a large range of works that fall into this category, as well as information on the history, development and genre of juvenile literature.
Readings for this course include classical works such as "Hatchet," "Little Women", "The Lion, the Witch and the Wardrobe" and "Brown Girl Dreaming," as well as newer works like "Storm in the Barn," "Anne Frank’s Diary: A Graphic Adaptation," "Lumberjanes," and a variety of picture books. These readings will be paired with chapters from "Reading Children’s Literature: A Critical Introduction " to help develop understanding of various genres, themes and concepts that are both related to juvenile literature and also present in our readings.
In addition to exposing students to various genres of writing (poetry, historical fiction, non-fiction, fantasy, picture books, graphic novels, etc.) this course will also allow students to engage in a discussion of larger themes present in these works such as censorship, race and gender. Students’ understanding of these works and concepts will be developed through readings, research, discussion posts, exams and writing assignments designed to get students to practice analyzing poetry, picture books, informational books and transitional/easy readers.
ENGL 241.S01: American Literature I
Tuesday and Thursday 12:30-1:45 p.m.
This course provides a broad, historical survey of American literature from the early colonial period to the Civil War. Ranging across historical periods and literary genres—including early accounts of contact and discovery, narratives of captivity and slavery, poetry of revolution, essays on gender equality and stories of industrial exploitation—this class examines how subjects such as colonialism, nationhood, religion, slavery, westward expansion, race, gender and democracy continue to influence how Americans see themselves and their society.
Required Texts
- The Norton Anthology of American Literature: Package 1, Volumes A and B Beginnings to 1865, Ninth Edition. (ISBN 978-0-393-26454-8)
ENGL 283.S01 Introduction to Creative Writing
Steven Wingate
Students will explore the various forms of creative writing (fiction, nonfiction and poetry) not one at a time in a survey format—as if there were decisive walls of separation between then—but as intensely related genres that share much of their creative DNA. Through close reading and work on personal texts, students will address the decisions that writers in any genre must face on voice, rhetorical position, relationship to audience, etc. Students will produce and revise portfolios of original creative work developed from prompts and research. This course fulfills the same SGR #2 requirements ENGL 201; note that the course will involve a research project. Successful completion of ENGL 101 (including by test or dual credit) is a prerequisite.
ENGL 283.S02 Introduction to Creative Writing
Jodilyn Andrews
This course introduces students to the craft of writing, with readings and practice in at least two genres (including fiction, poetry and drama).
ENGL 283.ST1 Introduction to Creative Writing
Amber Jensen, M.A., M.F.A.
This course explores creative writing as a way of encountering the world, research as a component of the creative writing process, elements of craft and their rhetorical effect and drafting, workshop and revision as integral parts of writing polished literary creative work. Student writers will engage in the research practices that inform the writing of literature and in the composing strategies and writing process writers use to create literary texts. Through their reading and writing of fiction, poetry and creative nonfiction, students will learn about craft elements, find examples of those craft elements in published works and apply these elements in their own creative work, developed through weekly writing activities, small group and large group workshop and conferences with the instructor. Work will be submitted, along with a learning reflection and revision plan in each genre and will then be revised and submitted as a final portfolio at the end of the semester to demonstrate continued growth in the creation of polished literary writing.
- 300-400 level
ENGL 424.S01 Language Arts Methods grades 7-12
Tuesday 6-8:50 p.m.
Danielle Harms
Techniques, materials and resources for teaching English language and literature to middle and secondary school students. Required of students in the English education option.
AIS/ENGL 447.S01: American Indian Literature of the Present
Thursdays 3-6 p.m.
This course introduces students to contemporary works by authors from various Indigenous nations. Students examine these works to enhance their historical understanding of Indigenous peoples, discover the variety of literary forms used by those who identify as Indigenous writers, and consider the cultural and political significance of these varieties of expression. Topics and questions to be explored include:
- Genre: What makes Indigenous literature indigenous?
- Political and Cultural Sovereignty: Why have an emphasis on tribal specificity and calls for “literary separatism” emerged in recent decades, and what are some of the critical conversations surrounding such particularized perspectives?
- Gender and Sexuality: What are the intersecting concerns of Indigenous Studies and Women, Gender and Sexuality Studies, and how might these research fields inform one another?
- Trans-Indigeneity: What might we learn by comparing works across different Indigenous traditions, and what challenges do such comparisons present?
- Aesthetics: How do Indigenous writers understand the dynamics between tradition and creativity?
- Visual Forms: What questions or concerns do visual representations (television and film) by or about Indigenous peoples present?
Possible Texts
- Akiwenzie-Damm, Kateri and Josie Douglas (eds), Skins: Contemporary Indigenous Writing. IAD Press, 2000. (978-1864650327)
- Erdrich, Louise, The Sentence. Harper, 2021 (978-0062671127)
- Harjo, Joy, Poet Warrior: A Memoir. Norton, 2021 (978-0393248524)
- Harjo, Sterlin and Taika Waititi, Reservation Dogs (selected episodes)
- Talty, Morgan. Night of the Living Rez, 2022, Tin House (978-1953534187)
- Wall Kimmerer, Robin. Braiding Sweet Grass, Milkweed Editions (978-1571313560)
- Wilson, Diane. The Seed Keeper: A Novel. Milkweed Editions (978-1571311375)
- Critical essays by Alexie, Allen, Cohen, Cox, King, Kroeber, Ortiz, Piatote, Ross and Sexton, Smith, Taylor, Teuton, Treuer, Vizenor, and Womack.
ENGL 472.S01: Film Criticism
Tuesdays 2-4:50 p.m.
Jason McEntee
Do you have an appreciation for, and enjoy watching, movies? Do you want to study movies in a genre-oriented format (such as those we typically call the Western, the screwball comedy, the science fiction or the crime/gangster, to name a few)? Do you want to explore the different critical approaches for talking and writing about movies (such as auteur, feminist, genre or reception)?
In this class, you will examine movies through viewing and defining different genres while, at the same time, studying and utilizing different styles of film criticism. You will share your discoveries in both class discussions and short writings. The final project will be a formal written piece of film criticism based on our work throughout the semester. The course satisfies requirements and electives for all English majors and minors, including both the Film Studies and Professional Writing minors. (Note: Viewing of movies outside of class required and may require rental and/or streaming service fees.)
ENGL 476.ST1: Fiction
In this workshop-based creative writing course, students will develop original fiction based on strong attention to the fundamentals of literary storytelling: full-bodied characters, robust story lines, palpable environments and unique voices. We will pay particular attention to process awareness, to the integrity of the sentence, and to authors' commitments to their characters and the places in which their stories unfold. Some workshop experience is helpful, as student peer critique will be an important element of the class.
ENGL 479.01 Capstone: The Gothic
Wednesday 3-5:50 p.m.
With the publication of Horace Walpole’s "The Castle of Otranto " in 1764, the Gothic officially came into being. Dark tales of physical violence and psychological terror, the Gothic incorporates elements such as distressed heroes and heroines pursued by tyrannical villains; gloomy estates with dark corridors, secret passageways and mysterious chambers; haunting dreams, troubling prophecies and disturbing premonitions; abduction, imprisonment and murder; and a varied assortment of corpses, apparitions and “monsters.” In this course, we will trace the development of Gothic literature—and some film—from the eighteenth-century to the present time. As we do so, we will consider how the Gothic engages philosophical beliefs about the beautiful and sublime; shapes psychological understandings of human beings’ encounters with horror, terror, the fantastic and the uncanny; and intervenes in the social and historical contexts in which it was written. We’ll consider, for example, how the Gothic undermines ideals related to domesticity and marriage through representations of domestic abuse, toxicity and gaslighting. In addition, we’ll discuss Gothic texts that center the injustices of slavery and racism. As many Gothic texts suggest, the true horrors of human existence often have less to do with inexplicable supernatural phenomena than with the realities of the world in which we live.
ENGL 485.S01: Undergraduate Writing Center Learning Assistants
Flexible Scheduling
Nathan Serfling
Since their beginnings in the 1920s and 30s, writing centers have come to serve numerous functions: as hubs for writing across the curriculum initiatives, sites to develop and deliver workshops and resource centers for faculty as well as students, among other functions. But the primary function of writing centers has necessarily and rightfully remained the tutoring of student writers. This course will immerse you in that function in two parts. During the first four weeks, you will explore writing center praxis—that is, the dialogic interplay of theory and practice related to writing center work. This part of the course will orient you to writing center history, key theoretical tenets and practical aspects of writing center tutoring. Once we have developed and practiced this foundation, you will begin work in the writing center as a tutor, responsible for assisting a wide variety of student clients with numerous writing tasks. Through this work, you will learn to actively engage with student clients in the revision of a text, respond to different student needs and abilities, work with a variety of writing tasks and rhetorical situations, and develop a richer sense of writing as a complex and negotiated social process.
Graduate Courses
Engl 572.s01: film criticism, engl 576.st1 fiction.
In this workshop-based creative writing course, students will develop original fiction based on strong attention to the fundamentals of literary storytelling: full-bodied characters, robust story lines, palpable environments and unique voices. We will pay particular attention to process awareness, to the integrity of the sentence and to authors' commitments to their characters and the places in which their stories unfold. Some workshop experience is helpful, as student peer critique will be an important element of the class.
ENGL 605.S01 Seminar in Teaching Composition
Thursdays 1-3:50 p.m.
This course will provide you with a foundation in the pedagogies and theories (and their attendant histories) of writing instruction, a foundation that will prepare you to teach your own writing courses at SDSU and elsewhere. As you will discover through our course, though, writing instruction does not come with any prescribed set of “best” practices. Rather, writing pedagogies stem from and continue to evolve because of various and largely unsettled conversations about what constitutes effective writing and effective writing instruction. Part of becoming a practicing writing instructor, then, is studying these conversations to develop a sense of what “good writing” and “effective writing instruction” might mean for you in our particular program and how you might adapt that understanding to different programs and contexts.
As we read about, discuss and research writing instruction, we will address a variety of practical and theoretical topics. The practical focus will allow us to attend to topics relevant to your immediate classroom practices: designing a curriculum and various types of assignments, delivering the course content and assessing student work, among others. Our theoretical topics will begin to reveal the underpinnings of these various practical matters, including their historical, rhetorical, social and political contexts. In other words, we will investigate the praxis—the dialogic interaction of practice and theory—of writing pedagogy. As a result, this course aims to prepare you not only as a writing teacher but also as a nascent writing studies/writing pedagogy scholar.
At the end of this course, you should be able to engage effectively in the classroom practices described above and participate in academic conversations about writing pedagogy, both orally and in writing. Assessment of these outcomes will be based primarily on the various writing assignments you submit and to a smaller degree on your participation in class discussions and activities.
ENGL 726.S01: The New Woman, 1880–1900s
Thursdays 3–5:50 p.m.
Katherine Malone
This course explores the rise of the New Woman at the end of the nineteenth century. The label New Woman referred to independent women who rebelled against social conventions. Often depicted riding bicycles, smoking cigarettes and wearing masculine clothing, these early feminists challenged gender roles and sought broader opportunities for women’s employment and self-determination. We will read provocative fiction and nonfiction by New Women writers and their critics, including authors such as Sarah Grand, Mona Caird, George Egerton, Amy Levy, Ella Hepworth Dixon, Grant Allen and George Gissing. We will analyze these exciting texts through a range of critical lenses and within the historical context of imperialism, scientific and technological innovation, the growth of the periodical press and discourse about race, class and gender. In addition to writing an argumentative seminar paper, students will complete short research assignments and lead discussion.
ENGL 792.ST1 Women in War: Female Authors and Characters in Contemporary War Lit
In this course, we will explore the voices of female authors and characters in contemporary literature of war. Drawing from various literary theories, our readings and discussion will explore the contributions of these voices to the evolving literature of war through archetypal and feminist criticism. We will read a variety of short works (both theoretical and creative) and complete works such as (selections subject to change): "Eyes Right" by Tracy Crow, "Plenty of Time When We Get Home" by Kayla Williams, "You Know When the Men are Gone" by Siobhan Fallon, "Still, Come Home" by Katie Schultz and "The Fine Art of Camouflage" by Lauren Johnson.

COMMENTS
Elementary education research paper topics can span a wide range of areas, including teaching methods, learning styles, the impact of technology on learning, educational policies, classroom management, and many more. Choosing a research topic in this field requires careful consideration of various factors, including your interests, the ...
This video series will teach you how to write a research paper or report. Each episode leads you through each step of the writing process. In this video, you...
Appendix F: Sample Research Paper. Below are sample research papers written by William Beanes Elementary School students. These samples are meant to help illustrate the 5 parts to be included in the research paper. Notes inside of balloons, are added to the papers to highlight special parts of the paper.
ABOUT THE JOURNAL Frequency: 4 issues/year ISSN: 0013-5984 E-ISSN: 1554-8279 2022 CiteScore*: 2.5 Ranked #583 out of 1,469 "Education" journals. The Elementary School Journal has served researchers, teacher educators, and practitioners in the elementary and middle school education for more than one hundred years.ESJ publishes peer-reviewed articles that pertain to both education theory and ...
A research paper at the elementary school level meets many of the writing standards of the National Council of Teachers of English. A research paper allows students to read both print and nonprint texts, fiction and nonfiction, classic and contemporary works. Students are also asked to comprehend, interpret, evaluate and appreciate resources.
opinions of the 4th, 5th, 6th and 7th grade elementary school students taking the social studies course on learning environments. Method In this study, since it is aimed to examine some factors associated with learning environments of elementary school students taking social studies course, the model used in the study falls within the scope of
An elementary research report is a beneficial document made by the elementary or grade school students (typically in Grade 4-6), applying what they learned in performing basic research. This report appears to be a stepping stone for children in improving their skills and abilities to learn and process information, and promoting growth in their ...
Author Studies. This is one of my favorite projects to use for upper elementary ELA students! I first implemented this project with fifth graders after state testing. This is the perfect time of year for an independent study, and it reinforces reading, writing, and research concepts used throughout the school year!
The objectives of this study are to locate recent writings on success ful. pedagogy for elementary schools and to emphasize their themes in instru ctional contexts. 15 recen t journal papers were ...
Research reports are common assignments for students everywhere, and you will probably write your first research report in elementary school. If you learn the steps for writing a quality research report while you are in elementary school, the skill will serve you well in the rest of your educational journey.
It helps inform you of the students' school progress and lets your students keep the deadline in mind. This template is professionally designed so you don't have to worry about its quality. This daily report template can be used by elementary and high school students. 9. Free Book Report Template.
Learning the basics of writing a research paper during elementary school will help students develop strong writing and research skills. Elementary level research papers can differ from those of high school or college levels in that the information presented is usually more general and the paper is shorter. The writing ...
For example, the review of research on elementary mathematics programs by Slavin and Lake (2008), mentioned earlier, required that studies use random assignment or quasi-experimental designs, excluded measures overaligned with the treatment, and required a minimum duration of 12 weeks and a minimum sample size of 30 students in each treatment ...
The 10 Most Significant Education Studies of 2021. From reframing our notion of "good" schools to mining the magic of expert teachers, here's a curated list of must-read research from 2021. By Youki Terada, Stephen Merrill, Sarah Gonser. December 9, 2021. It was a year of unprecedented hardship for teachers and school leaders.
Elementary School Research Paper Examples - Free download as PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free. elementary school research paper examples
The research project template is a Powerpoint file, and complete instructions are included for you. This way, you can easily edit the text to suit your classroom's needs! Students will pick a topic that interests them, or you can assign a topic based on any unit your class is currently studying. Then, according to the topic, students will ...
STEM education. brings a myriad of positives to the elementary school classroom but comes with some challenges. This research found that STEM education, as was the case at higher grade levels, provides students with higher levels of in class engagement, increases student collaboration, and.
Feel free to contact our research paper writing service for professional assistance. We offer high-quality assignments for reasonable rates. 1. Introduction. The primary grades are the first few grades of elementary school, in which students aged approximately 5-8 are socialized into the student role and taught basic tool skills.
Theorem 1.2.1. A homogenous system of linear equations with more unknowns than equations always has infinitely many solutions. The definition of matrix multiplication requires that the number of columns of the first factor A be the same as the number of rows of the second factor B in order to form the product AB.
Teaching academically honest research skills helps first graders learn how to collect, organize, and interpret information. Earlier in my career, I was told two facts that I thought to be false: First graders can't do research, because they aren't old enough; and if facts are needed for a nonfiction text, the students can just make them up.
Below you'll find a list of education-related research topics and idea kickstarters. These are fairly broad and flexible to various contexts, so keep in mind that you will need to refine them a little. Nevertheless, they should inspire some ideas for your project. The impact of school funding on student achievement.
Research Paper Example Elementary School - Free download as PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free. Crafting a thesis, especially for elementary school research papers, is a complex process that requires meticulous research, critical analysis skills, and the ability to effectively communicate ideas. Many students struggle with meeting the academic demands of writing a high ...
2 pages / 703 words. When I walked into my classroom on the first day of elementary school, all I saw was white. White walls. White desks. White people. My caramel skin and curly hair stood out amongst the fair-skinned students with light straight hair.
Tuesday and Thursday, 11 a.m.-12:15 p.m. Sharon Smith. ENGL 151 serves as an introduction to both the English major and the discipline of English studies. In this class, you will develop the thinking, reading, writing and research practices that define both the major and the discipline. Much of the semester will be devoted to honing your ...