
Gurukul of Excellence
Classes for Physics, Chemistry and Mathematics by IITians

Category: Case Study Questions for Class 6 Science
Join our Telegram Channel for Free PDF Download
Case Study Questions for Class 6 Science Chapter 16 Garbage In Garbage Out
Case study questions for class 6 science chapter 15 air around us, case study questions for class 6 science chapter 14 water, case study questions for class 6 science chapter 13 fun with magnets, case study questions for class 6 science chapter 12 electricity and circuits, case study questions for class 6 science chapter 11 light shadow and reflection, case study questions for class 6 science chapter 10 motion and measurement, case study questions for class 6 science chapter 9 living organisms and their surroundings, case study questions for class 6 science chapter 8 body movements, case study questions for class 6 science chapter 7 getting to know plants, case study questions for class 6 science chapter 6 changes around us, case study questions for class 6 science chapter 5 separation of substances, case study questions for class 6 science chapter 4 sorting materials into groups, case study questions for class 6 science chapter 3 fibre to fabric, case study questions for class 6 science chapter 2 components of food, case study questions for class 6 science chapter 1 food – where does it come from.

Editable Study Materials for Your Institute - CBSE, ICSE, State Boards (Maharashtra & Karnataka), JEE, NEET, FOUNDATION, OLYMPIADS, PPTs
Class 6 Science Chapter 15 Air Around Us Extra Questions and Answers
CBSE Class 6 Science Chapter 15 Air Around Us Extra Questions and Answers is available here. Students can learn and download the PDF of these questions for free. These extra questions and answers are prepared by our expert teachers as per the latest NCERT textbook and guidelines. Learning these extra questions will help you to score excellent marks in the final exams.
Air Around Us Class 6 Science Extra Questions and Answers
Very short answer questions.
1. Name the main component of air. Answer: Nitrogen gas
2. What is the source of oxygen gas in air? Answer: Photosynthesis by green plants is source of oxygen gas in air.
3. What is the percentage of nitrogen in air? Answer: 78.1%
4. What is the percentage of oxygen in air? Answer: 20.9%
5. What is the source of carbon dioxide in air? Answer: Respiration by animals and plants and burning of fuel.
6. Mention one necessary condition for the combustion to take place. Answer: Presence of air.
7. Define atmosphere. Answer: The blanket of air that surrounds the earth is called atmosphere.
8. What is humidity? Answer: The amount of water vapour present in the air is called humidity.
9. Which gas is most abundant and is important for growth of plants and animals? Answer: Nitrogen
10. Name the component of air used by green plants to make their food. Answer: Carbon dioxide
11. Name any two musical instruments in which air plays an important role. Answer: Flute and saxophone
Short Answer Type Questions
1: What happens when air comes in contact with a cool surface?
Answer: When air comes in contact with a cool surface, it condenses and drops of water appear on cool surface.
2: Why do you think mountaineer carry oxygen cylinders with them, while climbing high mountains?
Answer: There is less oxygen at high places like mountains, so they carry oxygen cylinder with them to breathe there.
3: Why you feel suffocation in a closed room, where some material is burning?
Answer: Burning of some material releases smoke that contains few gases and fine dust particles that is harmful, thus we feel suffocation in a closed room, where some material is burning.
4: Why there are long chimneys in factories?
Answer: Chimneys take the harmful gases and smoke of factories away from our noses.
5: Air is necessary for combustion. Explain the statement.
Answer: Fix two candles in middle of a container containing water. Light both candles. Now cover the candles with an inverted transparent glass, you will observe that candles goes off. This happens because of absence of air. Thus, we can say that air is necessary for combustion.
6: Air occupies space. Explain the statement.
Answer: Blow a balloon, air from your body enters balloon at it gets bigger because air occupies space.
7: When the open mouth of an empty bottle is tilted in a bucket filled with water, we see bubbles coming out of it. Explain the phenomenon.
Answer: The bottle contains air so when it was titled air came out in the form of bubbles.
8: What is air made up of?
Answer: Air is made up of mixture of gases like – Nitrogen, oxygen, carbon dioxide, water vapour, dust particles and other gases.
9: Air contains dust particles, while inhaling air we also inhale dust particles. Give reason in support of the statement, whether it is true or false?
Answer: False, because our nose contains fine hair and mucus that trap all dust particles and prevent its entrance inside our body.
10: Why we should not breathe through our mouth?
Answer: If we will breathe through our mouth then dust particles present in air will enter our body and will cause harmful diseases.
11: Draw a diagram showing composition of air in atmosphere. Answer:
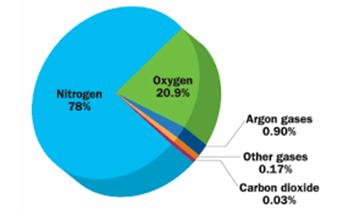
12: How does an organism living in soil breathe?
Answer: Through air present in soil.
13: How can you show that air is dissolved in water?
Answer: Take water in a pan and heat it. After sometimes just before it boils we can observe some bubbles at the inner surface of the pan. This is because of the air dissolved in water.
14: Why an animal living in soil does, comes out of soil for respiration in rainy season?
Answer: When it rains heavily, water fills up all the spaces occupied by the air in the soil. Therefore, organism living in soil has to come out for respiration.
15: Why does a lump of cotton wool shrink in water?
Answer: A lump of cotton wool shrinks in water because water filled up the empty space that the air has occupied.
16: List at least five activities that are possible due to the presence of air.
Answer: Respiration, burning, photosynthesis, movement of aeroplane and parachutes, generation of electricity by windmills.
17. Why is air considered as a mixture?
Answer: Air contains oxygen and nitrogen as its major constituents of air. These gases retain their properties in air. So, the air is called a mixture.
18. Name the major gas present in the (a) inhaled air (b) exhaled air.
Answer: (a) Oxygen (b) Carbon dioxide.
19. Write the necessary conditions for rusting of iron to take place.
Answer: Rusting of iron takes place in the presence of moisture and air. So, the presence of air and water vapour in air are two necessary conditions for rusting of iron.
20. Name a device which uses wind energy to generate electricity.
Answer: Windmills use the wind energy to convert wind energy into electrical energy
21: What is wind energy? Mention its two advantages.
Answer: Blowing air is called wind. Wind possesses kinetic energy. The kinetic energy possessed by wind is called wind energy.
Uses of Wind Energy are: (i) Wind energy is used to pump the ground water. (ii) Wind energy is used to generate electricity with the help of windmills.
22. Mention two uses of air.
Answer: The two uses of air are as below: (a) For respiration all organisms need air. (b) For burning of any substance air is needed.
23. What happens if the percentage of oxygen in the air reaches to 70%?
Answer: If any substance catches fire it will become difficult to extinguish the fire, as oxygen supports combustion.
24. Why is carbon-dioxide gas used to extinguish fire?
Answer: It is because carbon-dioxide does not support combustion. When sprayed on burning object it stops the supply of oxygen and extinguishes fire.
25. How will you prove that soil contains air in it?
Answer: Take a glass tumbler add some soil in it, then pour some water on the soil slowly, the air-bubbles comes out of the soil. This proves that soil holds air in it.
26. Why do we see the sky and air clear and clean after rainfall?
Answer: The dust particles which remain suspended in air get loaded and come down on the ground due to rainfall, this is the reason that the sky and the air look clean and clear after rainfall.
27. Explain why mountaineers carry oxygen cylinders with them?
Answer: As you go up, above the sea-level the atmospheric pressure goes on decreasing and the amount of oxygen also decreases at higher altitude.
28. Explain why during an incident of fire, one is advised to wrap a woollen blanket over a burning object.
Answer: Blanket cuts the supply of oxygen to the object that is burning, thereby prevents it from further burning.
29. Why does the transparent glass of windows, if not wiped off regularly, appears hazy?
Answer: Air contains dust and smoke along with the gases. These gets deposited on the glass windows and make them appear hazy.
30. Why during an incident of fire, one is advised to wrap a woollen blanket over a burning object?
Answer: For combustion to take place, oxygen is required. When a woollen blanket is wrapped over a burning object, fire loses contact with oxygen and, therefore, stops burning after sometime.
31. Why do you think, mountaineers carry oxygen cylinders with them, while climbing high mountains?
Answer: As we go higher on the mountains, the air becomes thinner. The amount of oxygen decreases and it becomes hard to breath. Therefore, mountaineers carry oxygen cylinders with them.
32. How do the organisms living in soil get the air they need, for respiration?
Answer: The spaces between the soil particles are filled with air. This air is taken up by plants and animals for respiration.
33. Why are factories fitted with tall chimneys?
Answer: Burning of fuel and materials produce smoke and other harmful gases which are released out of the factories by the chimneys.
Long Answer Type Questions
1: How do plants and animals help each other in the exchange of gases in the atmosphere?
Answer: Plants and animals help each other in the exchange of gases in the atmosphere Plants take carbon dioxide to prepare food and release oxygen during daytime. This oxygen is taken in by animals and carbon dioxide is released. Thus, plants and animals help in maintaining balance of oxygen and carbon dioxide.
2: Explain the role played by air in the life of human, animals and plants.
Answer: Living things cannot live without air. We can survive on planet earth because of atmosphere only. Plants cook their food by the process of photosynthesis because of air only. They use carbon dioxide gas of air and releases oxygen that is utilized by human and animals to breathe in. Air is necessary for combustion, flying of aeroplanes and birds. Thus, it is well said Air is life.
3. Describe balance of oxygen in the air.
Answer: The oxygen in air is used by the organisms present in air, water or soil or on earth for their respiration. During respiration carbon dioxide gas is released to air. But green plants during photosynthesis use carbon dioxide of air for preparing food and they release oxygen gas in the air. Thus, the balance of oxygen in air is maintained.
4. What happens if the percentage of carbon-dioxide increases in the air?
Answer: The increased percentage of carbon-dioxide will cause green house effect, i.e. it will not allow the hot rays of sun to escape from the atmosphere after reflection once they enter the earth’s atmosphere, thereby increasing the temperature of earth, ice on mountains will melt and water level will rise.
5. You must have seen during rainy season, when it rains the animals like earthworm, snakes, snails etc. are commonly seen. Explain why?
Answer: All these animals live in underground burrows or remain buried in the soil. They get oxygen from air that enters into the burrow through entrance of burrow or through pores in the soil. But when it rains, the water gets filled in their dwelling places and pores of the soil. So, they come out in search of air.
6. Why all the oxygen of atmosphere does not get used up though a large number of organisms are consuming it?
Answer: A large number of organisms take up oxygen for respiration and release carbon dioxide. Plants take up this carbon dioxide and release oxygen in the atmosphere. Therefore, this balance is maintained.
7. How will you prove that oxygen supports burning? Answer:
- Take three candles, two glass jars that can cover two candles but of different sizes and a watch.
- Light all the three candles at one time after fixing them on the table. Cover two candles with the jars. Leave one candle uncovered. Switch off the fan and close doors and windows. This will stop wind from blowing off the candles.
- After some time the candle covered with the small jar goes off first. Then the one with a bigger jar goes off. The candle in the open continues to burn. Thus, air supports burning.
8. How will you show that air is dissolved in water? Answer:
- Take some water in a glass vessel. Look carefully at the inner surface of the vessel.
- There are tiny bubbles on the inside of the vessel. These bubbles come from the air dissolved in water.
- Heat the water slowly on a tripod stand.
- We see the air dissolved in it escapes. On further heating, the water itself turns into vapour and finally begins to boil.
Thus, the animals living in water use the dissolved oxygen in water.
9. How is the level of oxygen maintained in the atmosphere?
Answer: The level of oxygen is maintained in the atmosphere by planting more and more trees and by avoiding excessive burning of fuels. The plants will take up the carbon dioxide in the atmosphere to make their food and in turn will release oxygen. This oxygen is taken up by animals, including humans, for respiration and in turn release carbon dioxide.
- School Solutions
- Star Program
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Physics
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Chemistry
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Commerce
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Economics
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Accountancy
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Physics
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Chemistry
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Biology
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Commerce
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Accountancy
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Statistics
- NCERT Solutions Class 10 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 10 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 10 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 Social Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 8 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 8 Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 8 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 8 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 8 Social Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 7 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 7 Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 7 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 7 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 7 Social Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 6 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 6 Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 6 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 6 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 6 Social Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 5 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 5 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 5 EVS
- NCERT Solutions Class 4 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 4 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 4 EVS
- NCERT Solutions Class 4 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 3 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 3 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 3 EVS
- NCERT Solutions Class 3 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 2 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 2 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 2 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 1 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 1 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 1 Hindi
- NCERT Books Class 12
- NCERT Books Class 11
- NCERT Books Class 10
- NCERT Books Class 9
- NCERT Books Class 8
- NCERT Books Class 7
- NCERT Books Class 6
- NCERT Books Class 5
- NCERT Books Class 4
- NCERT Books Class 3
- NCERT Books Class 2
- NCERT Books Class 1
- Important Questions Class 12
- Important Questions Class 11
- Important Questions Class 10
- Important Questions Class 9
- Important Questions Class 8
- Important Questions Class 7
- important questions class 6
- CBSE Class 12 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 11 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 10 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 9 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 8 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 7 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 6 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 12 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 11 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 10 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 9 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 8 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 7 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 6 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 5 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 4 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 3 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 2 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 1 Syllabus
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 12
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 11
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 10
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 9
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 8
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 7
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 6
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 5
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 4
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 3
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 2
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 1
- CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 12
- CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 10
- Extra Questions For Class 8 Maths
- Extra Questions For Class 8 Science
- Extra Questions For Class 9 Maths
- Extra Questions For Class 9 Science
- Extra Questions For Class 10 Maths
- Extra Questions For Class 10 Science
- NEET 2021 Question Paper
- NEET 2020 Question Paper
- NEET 2019 Question Paper
- NEET 2018 Question Paper
- NEET 2017 Question Paper
- NEET 2016 Question Paper
- NEET 2015 Question Paper
- NEET Physics Questions
- NEET Chemistry Questions
- NEET Biology Questions
- NEET Sample Papers
- NEET Physics Syllabus
- NEET Chemistry Syllabus
- NEET Biology Syllabus
- NEET Mock Test
- NEET Eligibility Criteria
- JEE Main 2021 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2020 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2019 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2018 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2017 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2016 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2015 Question Paper
- JEE Main Sample Papers
- JEE Main Physics Syllabus
- JEE Main Chemistry Syllabus
- JEE Main Maths Syllabus
- JEE Main Physics Questions
- JEE Main Chemistry Questions
- JEE Main Maths Questions
- JEE main revision notes
- JEE Main Mock Test
- JEE Advanced Physics Questions
- JEE Advanced Chemistry Questions
- JEE Advanced Maths Questions
- JEE Advanced 2021 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2020 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2019 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2018 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2017 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2016 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2015 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced Physics Syllabus
- JEE Advanced Chemistry Syllabus
- JEE Advanced Maths Syllabus
- JEE Advanced Mock Test
- ISC Class 12 Syllabus
- ISC Class 11 Syllabus
- ICSE Class 10 Syllabus
- ICSE Class 9 Syllabus
- ICSE Class 8 Syllabus
- ICSE Class 7 Syllabus
- ICSE Class 6 Syllabus
- ISC Sample Question Papers for Class 12
- ISC Sample Question Papers for Class 11
- ICSE Sample Question Papers for Class 10
- ICSE Sample Question Papers for Class 9
- ICSE Sample Question Papers for Class 8
- ICSE Sample Question Papers for Class 7
- ICSE Sample Question Papers for Class 6
- ICSE Class 10 Revision Notes
- ICSE Class 9 Revision Notes
- ISC Important Questions for Class 12
- ISC Important Questions for Class 11
- ICSE Important Questions for Class 10
- ICSE Important Questions for Class 9
- ICSE Important Questions for Class 8
- ICSE Important Questions for Class 7
- ICSE Important Questions for Class 6
- ISC Class 12 Question Paper
- ICSE Class 10 Question Paper
- Maharashtra Board Syllabus
- Maharashtra Board Sample Question Paper
- Maharashtra Board Previous Year Question Paper
- AP Board Syllabus
- AP Board Sample Question Paper
- AP Board Previous Year Question Paper
- Tamilnadu Board Syllabus
- Tamilnadu Board Sample Question Paper
- Tamilnadu Board Previous Year Question Paper
- Telangana Board Syllabus
- Telangana Board Sample Question Paper
- Telangana Board Previous Year Question Paper
- Karnataka Board Syllabus
- Karnataka Board Sample Question Paper
- Karnataka Board Previous Year Question Paper
- Examination Full Forms
- Physics Full Forms
- Chemistry Full Forms
- Biology Full Forms
- Educational Full Form
- CUET Eligibility Criteria
- CUET Exam Pattern
- CUET Cutoff
- CUET Syllabus
- CUET Admit Card
- CUET Counselling
- CUET Previous Year Question Papers
- CUET Application Form
- CUET Sample Papers
- CUET Exam Centers
- CUET Exam Dates
- CUET Results
- Physics Formulas
- Chemistry Formulas
- Math Formulas
- Algebra Formulas
- Geometry Formulas
- Trigonometry Formulas
- Subscription
Important Questions Class 6 Science Chapter 15
Home » CBSE » Important Questions Class 6 Science Chapter 15

- CBSE Important Questions
- Important Questions Class 6
- CBSE Previous Year Question Papers
- CBSE Revision Notes
- CBSE Syllabus
- CBSE Extra Questions
- CBSE Sample Papers
- ISC & ICSE Syllabus
- ICSE Syllabus Class 9
- ICSE Syllabus Class 8
- ICSE Syllabus Class 7
- ICSE Syllabus Class 6
- ICSE Syllabus Class 10
- ICSE Question Paper
- ICSE Sample Question Papers
- ISC Sample Question Papers For Class 12
- ISC Sample Question Papers For Class 11
- ICSE Sample Question Papers For Class 10
- ICSE Sample Question Papers For Class 9
- ICSE Sample Question Papers For Class 8
- ICSE Sample Question Papers For Class 7
- ICSE Sample Question Papers For Class 6
- ICSE Revision Notes
- ICSE Important Questions
- ISC Important Questions For Class 12
- ISC Important Questions For Class 11
- ICSE Important Questions For Class 10
- ICSE Important Questions For Class 9
- ICSE Important Questions For Class 8
- ICSE Important Questions For Class 7
- ICSE Important Questions For Class 6
- Maharashtra board
- Rajasthan-Board
- Andhrapradesh Board
- AP Board syllabus
- Telangana Board
- Tamilnadu Board
- Tamilnadu Sample Question Paper
- Tamilnadu Syllabus
- Tamilnadu Previous Year Question Paper
- NCERT Solutions Class 12
- NCERT Solutions Class 10
- NCERT Solutions Class 11
- NCERT Solutions Class 9
- NCERT Solutions Class 8
- NCERT Solutions Class 7
- NCERT Solutions Class 6
- NCERT Solutions Class 5
- NCERT Solutions Class 4
- NCERT Solutions Class 3
- NCERT Solutions Class 2
- NCERT Solutions Class 1
- JEE Main Question Papers
- JEE Main Syllabus
- JEE Main Questions
- JEE Main Revision Notes
- JEE Advanced Question Papers
- JEE Advanced Syllabus
- JEE Advanced Questions
- JEE Advanced Sample Papers
- NEET Question Papers
- Neet 2021 Question Paper
- Neet 2020 Question Paper
- Neet 2019 Question Paper
- Neet 2018 Question Paper
- Neet 2017 Question Paper
- Neet 2016 Question Paper
- Neet 2015 Question Paper
- NEET Syllabus
Important Questions Class 6 Science Chapter 15 – Air Around Us
Studying Science is a very demanding concept requiring students to follow through thoroughly at every step. For a good exam score, students must understand the theory and its working principles.Understanding concepts alone is not sufficient.They must practise questions regularly to improve their theoretical and practical application of learned concepts.
Quick Links
Chapter 15 of Science Class 6 deals with the air present around us. It introduces students to various topics, which are given below as stated:
- Presence of air
- Composition of air
- Oxygen’s importance
- Oxygen cycle
This chapter is essential for students as it teaches them about the basic need for survival: air. For decades, the air was not studied. However, time and research efforts proved that air is a mixture of a lot of gases like water vapour, oxygen, carbon dioxide, nitrogen, and pollutants like smoke and dust. Scientists have revealed more details about the atmosphere and air as science and technology progressed.Most of the advanced topics will be discussed in higher classes.
For overall preparation for exams, students must solve questions regularly and as much as possible. Extramarks, an educational platform that provides study materials for exams, provides question banks like Important Questions Class 6 Science Chapter 15 to help students practise and overcome their fear of exams. Furthermore, students are advised to solve Chapter 15 Class 6 Science Important Questions for a better understanding of concepts.
Get Access to CBSE Class 6 Science Important Questions with Solutions
Also, get access to CBSE Class 6 Science Important Questions for other chapters too:
Important Questions Class 6 Science Chapter 15 – With Solutions
Solving Important Questions Class 6 Science Chapter 15 helps students in revising important concepts and retaining all the important sections of the chapter. Important Questions Class 6 Science Chapter 15
Extramarks question bank are curated by subject experts.
Solving Class 6 Science Chapter 15 Important Questions prior to exams will help students review the entire chapter in one sitting.Given below is a list of all the Important Questions Chapter 15, Class 6
Question 1: What is the composition of air?
Answer 1: Atmospheric air comprises oxygen(21%), nitrogen(78%), carbon dioxide, water vapour and pollutants(1%) like dust and smoke.
Question 2: Why does a lump of cotton wool shrink in water?
Answer 2: A lump of cotton wool shrinks in water as air pockets are present in the cotton. When it is dipped in water, air pockets are replaced with water, making the cotton fabric stick together. This causes the cotton wool lump to shrink in water.
Question 3: Which are the five processes that require the presence of air?
Answer 3: Processes which require the presence of air are:
- Cloud formation
- Respiration
- Transpiration
- Photosynthesis
Question 4: How do plants and animals help each other in the exchange of gases in the atmosphere?
Answer 4: Two processes, respiration and photosynthesis, help plants and animals exchange the gases in the atmosphere. In respiration, plants and animals take in oxygen and give out carbon oxide.
Plants, during the day, take in carbon dioxide and synthesise food, giving out oxygen into the atmosphere as a byproduct. Thus, plants and animals help each other in the exchange of gases and maintain the balance of gases in the atmosphere.
Question 5: The blanket of air surrounding the earth is known as ________.
Answer 5: The blanket of air surrounding the earth is known as the atmosphere.
Question 6: The component of air used to make food by green plants is ___________.
Answer 6: The component of air used to make food by green plants is carbon dioxide.
Question 7: Solve the following multiple-choice questions given below.
(i) Wind does not help in the movement of which of the following?
(a)Weathercock
(b) Sailing yacht
(c) Ceiling fan
Answer (i): ( c) Ceiling fan
A ceiling fan runs on electricity; hence, wind doesn’t help in the movement of the fan.
(ii) What is not true about the air?
(a) It helps in the movements of aeroplanes.
(b) Birds can fly due to the presence of air.
(c)It makes the windmill rotate.
(d) It has no role in the water cycle.
Answer (ii): (d) It has no role in the water cycle.
Air plays the biggest role in the water cycle as water vapours rise to form clouds.
(iii) Why do mountaineers need to carry oxygen cylinders with them? Because
(a) there is no oxygen in high mountains
(b) there is a lot of deficiency of oxygen in the mountains at high altitudes
(c) oxygen keeps them warm at low temperatures.
(d) oxygen is used for cooking
Answer (iii): (b) there is a lot of deficiency of oxygen in the mountains at high altitudes.
Mountaineers carry oxygen cylinders with them because there is a deficiency of oxygen in the mountains at high altitudes. As we go higher in altitude, the atmosphere gets thinner, and the oxygen supply decreases. Therefore while climbing mountains, it makes breathing difficult. Hence, mountaineers carry oxygen cylinders with them.
(iv) In our atmosphere, which components of the air are present in the largest amount?
(a) Nitrogen
(b) Water vapour
(d) Carbon dioxide
Answer (iv): (a) Nitrogen
The atmosphere is composed of so many different gases, but the gas present in the largest amount is nitrogen, which is 78%. Other gases found in the atmosphere include oxygen (21%), and carbon dioxide (1%).
(v)Anya took a lump of dry soil in a glass beaker and added water to it until the soil was completely immersed. She observed bubbles coming out of the soil. The bubbles contain
(a) only oxygen gas
(b) water vapour
(d) none of these.
Answer (v): (c ) air
When water is poured into dry soil, the soil absorbs the water, and the air pockets present in the soil escape and form bubbles.
Question 7: Explain the reasons for the following statements:
(a) A firki does not rotate in a closed area.
(b) The arrow of the weathercock points towards a particular direction at a particular moment.
(c) An empty glass, in fact, is not empty.
(d) Breathing through the mouth may harm you.
- There is a lack of air movement in a closed area, which prevents firki rotation. Because of the moving air all around, a firki usually rotates when placed in an open area.
- A weathercock is a device that indicates the direction of the wind. It is made up of an arrow that is mounted at its centre of gravity and can freely rotate around a vertical axis. As a result, the arrow points in a specific direction at a specific time to indicate the most recent direction of the wind’s movement.
- An empty glass is not empty; it contains air. It can be demonstrated by using a simple experiment. Place an empty bottle upside down in a beaker that is filled with water. Water does not enter the bottle when pushed inverted because there is no space for the air to escape.When the bottle is tilted, the air escapes as bubbles, and the empty space is filled with water. This demonstrates that even an empty glass contains air.
- Yes, breathing through our mouths can be harmful. The air may contain gases, water vapour, and dust particles. When we breathe in through our nostrils, the fine hair and mucus in our nose keep dust particles from entering our respiratory tract. However, if we breathe through our mouths, harmful dust particles may enter our bodies and make us sick. As a result, breathing through the mouth may be harmful.
Question 8: Explain why burning a fire in an enclosed room causes people to suffocate.
Answer 8: Any burning substance requires oxygen to burn and releases carbon dioxide. In a closed room, there is limited oxygen supply, and the carbon dioxide released cannot be accumulated nor expelled.As a result, in a closed room with fire, humans have less oxygen to breathe and later start inhaling the carbon dioxide released. Carbon dioxide is harmful to humans as it combines with haemoglobin present in the blood faster than oxygen. Resulting in asphyxia which proves to be fatal.
Question 9: Why should we breathe through our nose and not our mouth?
Answer 9: The human nose has two nostrils, each coated with a dense layer of tiny nostrils and a thick layer of mucus. The tiny hairs act as filters, removing smoke particles and dust, allowing air free of dangerous airborne particles to enter our respiratory system. As our mouth lacks all these filters, it is not advised to breathe through the mouth.
Question 10: State whether the following statements are true or false.
- Air is always stationary.
Answer: False.
Air can flow, and flowing air is called wind.
- Air is present everywhere.
Answer: True.
- Air occupies space.
- Air is coloured.
Answer: False.
Air is transparent, colourless, and odourless.
- The layer of air surrounding the earth is called oxygen.
The layer of air surrounding the earth like a blanket is called the atmosphere.
- Nitrogen does not support burning.
- Plants use oxygen for respiration and carbon dioxide for photosynthesis.
- Dust particles are present in the air.
- Oxygen cannot be dissolved in water.
Oxygen can be dissolved in water.
- Windmills require electricity to function.
Windmills generate electricity by harnessing the power of the wind.
Benefits of Solving Important Questions Class 6 Science Chapter 15
Important Questions Class 6 Science Chapter 15 is specially designed by professionals at Extramarks. It helps students score well in exams by giving them an extra edge in writing answers. This question bank is prepared by experts and includes important questions with a higher likelihood of appearing in exams. Hence, students are advised to solve Important Questions Class 6 Science Chapter 15 before appearing in exams.
Listed below are a few benefits of solving Important Questions Class 6 Science Chapter 15:
- Important Questions Class 6 Science Chapter 15 contains questions from the NCERT textbook, NCERT Exemplars, and references. It also consists of all formats of questions, like Multiple Choice Questions [MCQs], very short answers, short answer type, and long answer type questions.
- By solving such questions regularly, students get practice for real exams. Hence, it helps students to score good marks in exams as it helps in understanding the concept and improving the application of the concept.
- The question bank Important Questions Class 6 Science Chapter 15 not only is a combination of all the important questions but also includes a detailed step-by-step solution to each question, which aids in students’ preparation for exams.’
- Important Questions, Class 6 Science Chapter 15, aids in students’ self-evaluation by highlighting weak areas of the student or topics that were missed by the student.By solving Important Questions Class 6 Science Chapter 15, students get ample time to recognise and work on their weak points.
Extramarks is an online educational platform trusted by thousands of teachers and millions of students. It provides comprehensive study material to students who desire to score higher in exams. Their motto is to provide quality education material to all students helping them score good marks.
Given below are links to all of the resources provided at Extramarks:
- NCERT Books
- Important Formula
- CBSE Past Years’ Question Paper
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)
Chapter 1 - Food: Where Does It Come From?

Chapter 2 - Components of Food
Chapter 3 - fibre to fabric, chapter 4 - sorting materials into groups, chapter 5 - separation of substances, chapter 6 - changes around us, chapter 7 - getting to know plants, chapter 8 - body movements, chapter 9 - the living organisms and their surroundings, chapter 10 - motion and measurement of distances, chapter 11 - light, shadows and reflections, chapter 12 - electricity and circuits, chapter 13 - fun with magnets, chapter 14 - water, chapter 16 - garbage in, garbage out, faqs (frequently asked questions), 1. what are the chapter names in science class 6.
There are 16 chapters present in Science Class 6. Extramarks provides a question bank for all the chapters, including Science Class 6 Chapter 13 Important Questions. The names of all the chapters in Class 6 Science are mentioned below:
- Chapter 1- Food Where Does It Come From
- Chapter 2- Components Of Food
- Chapter 3- Fibre To Fabric
- Chapter 4- Sorting Materials Groups
- Chapter 5- Separation Of Substances
- Chapter 6- Changes Around Us
- Chapter 7- Getting To Know Plants
- Chapter 8- Body Movements
- Chapter 9- The Living Organisms and Their Surroundings
- Chapter 10- Motion And Measurement Of Distances
- Chapter 11- Light Shadow And Reflection
- Chapter 13- Fun With Magnets
- Chapter 14- Water
- Chapter 15- Air Around Us
- Chapter 16- Garbage
2. How can students access educational resources at Extramarks?
Students must sign up at the Extramarks website. After registering themselves at the Extramarks website, students can get unlimited access to all the educational resources.
CBSE Related Links


Fill this form to view question paper
Otp verification.
- NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Class 6
- NCERT Class 6 Science
- Chapter 15: Air Around Us
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 15 Air Around Us
Ncert solutions class 6 science chapter 15 – free pdf download.
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 15 Air Around Us benefits the students in understanding the concepts thoroughly. These NCERT Solutions are prepared by subject-matter experts at BYJU’S as per the 2022-23 CBSE syllabus. This chapter gives knowledge on air, constituents of air, wind, air present in soil and its importance, oxygen and its importance for living organisms, atmosphere and its importance and the importance of plants for our survival.
The questions with their detailed answers will help students to comprehend the concepts and ideas covered in this chapter. Hence, to score good marks in the examinations, students are advised to study NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science . These NCERT Solutions are really helpful in getting a better understanding of the concepts of air. Moreover, these solutions will help them prepare well and attempt the annual exam confidently.
- Chapter 1 Food: Where Does It Come From?
- Chapter 2 Components of Food
- Chapter 3 Fibre to Fabric
- Chapter 4 Sorting Materials into Groups
- Chapter 5 Separation of Substances
- Chapter 6 Changes Around Us
- Chapter 7 Getting to Know Plants
- Chapter 8 Body Movements
- Chapter 9 The Living Organisms and Their Surroundings
- Chapter 10 Motion and Measurement of Distances
- Chapter 11 Light, Shadows and Reflection
- Chapter 12 Electricity and Circuits
- Chapter 13 Fun with Magnets
- Chapter 14 Water
- Chapter 15 Air Around Us
- Chapter 16 Garbage In, Garbage Out
carouselExampleControls112

Previous Next

Access Answers to NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 15 Air Around Us
Exercise Questions
1. What is the composition of air?
Air comprises water vapour, oxygen, nitrogen, carbon dioxide, dust and smoke.
2. Which gas in the atmosphere is essential for respiration?
Oxygen in the atmosphere is essential for respiration.
3. How will you prove that air supports burning?
Place two candles of the same length on a table. Light both candles. Cover one of the candles with an inverted glass tumbler. We can observe that the candle covered with the glass tumbler got extinguished after some time, whereas the other candle continued burning. The candle gets extinguished because the air component inside of the glass tumbler, which supports burning, is limited. Most of the component is used up by the burning candle. However, the other candle is getting a continuous supply of air. This component of air, which supports burning, is known as oxygen.
4. How will you show that air is dissolved in water?
Take some water in a container. Heat it slowly on a tripod stand. Before the water begins to boil, look at the inner surface of the container. We observe tiny bubbles inside.
These bubbles come from the air dissolved in water. When you heat the water, to begin with, the air dissolved in it escapes. This experiment concludes that air is present in the water.
5. Why does a lump of cotton wool shrink in water?
The lump of cotton wool shrink in water because the air inside the cotton lumps is replaced by water which makes the layer stick together.
6. The layer of air around the earth is known as ___________.
The layer of air around the earth is known as the atmosphere .
7. The component of air used by green plants to make their food is ___________.
The component of air used by green plants to make their food is carbon dioxide .
8. List five activities that are possible due to the presence of air.
The five activities that are possible due to air are as follows:
- Photosynthesis
- Cloud formation
- Respiration
- Transpiration
9. How do plants and animals help each other in the exchange of gases in the atmosphere?
During the process of respiration, animals and plants consume oxygen from the air and release carbon dioxide gas into the air. Besides, green plants also release oxygen gas by utilising carbon dioxide during the process of photosynthesis. Hence, in this way, plants and animals help each other in the exchange of gases in the atmosphere.
Topics Covered in NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 15 Air Around Us
- Is air present everywhere around us?
- What is air made up of?
- How does oxygen become available to animals and plants living in water and soil?
- How is the oxygen in the atmosphere replaced?
To score good marks in the examination, students should solve the previous year question papers and sample papers. This will significantly help them understand the difficulty level of the questions and the marking scheme. Keep visiting BYJU’S, for the latest CBSE updates and notifications. Also, download BYJU’S – The Learning App for an effective learning experience.
Frequently Asked Questions on NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 15
List out the concepts discussed in chapter 15 of ncert solutions for class 6 science., how will you prove that air supports burning, covered in chapter 15 of ncert solutions for class 6 science, list five activities that are possible due to the presence of air from chapter 15 of ncert solutions for class 6 science., leave a comment cancel reply.
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
This is very good app thanks for helping me 😊
This is very useful app and good app thank you very much
You make very very good app
Bestest website to study I love this all in one
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.
Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
- NCERT Exemplar for Class 6 Science Solutions Chapter 15 Air Around Us
- Textbook Solutions

Class 6 Science NCERT Exemplar Solutions Chapter 15 Air Around Us
Free PDF download of NCERT Exemplar for Class 6 Science Chapter 15 Air Around Us solved by expert Science teachers on Vedantu.com as per NCERT (CBSE) Book guidelines. All Chapter 15 Air Around Us exercises questions with solutions to help you to revise the complete syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
You can also Download NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science to help you to revise the complete Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Access NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 15- Air Around Us
Multiple Choice Questions
1. Which of the following statements is incorrect?
(a) All living things require air to breathe.
(b) We can feel air but we cannot see it.
(c) Moving air makes it possible to fly a kite.
(d) Air is present everywhere but not in soil.
Ans: d) Air is present everywhere but not in soil.
Air is omnipresent and is present in soil too. This can be inferred by adding water to a pot filled with a lump of soil. After adding water it can be observed that the soil absorbs all the water and air bubbles are formed. These air bubbles show the escaping air.
2. Wind does not help in the movement of which of the following?
(a) Firki
(b) Weather cock
(c) Ceiling fan
(d) Sailing yacht
Ans: c) Ceiling fan
Wind does not help in the movement of ceiling fan because it moves by electricity.
3. What is not true about air?
(a) It makes the windmill rotate.
(b) It helps in the movements of aeroplanes.
(c) Birds can fly due to presence of air.
(d) It has no role in water cycle.
Ans: d) it has no role in water cycle.
During the process of evaporation, the vapours of water are risen up by air to form clouds.
4. Mountaineers carry oxygen cylinders with them because
(a) There is no oxygen on high mountains
(b) There is deficiency of oxygen on mountains at high altitude
(c) Oxygen is used for cooking
(d) Oxygen keeps them warm at low temperature.
Ans: b) there is deficiency of oxygen on mountains at high altitude.
With increase in altitude, the atmosphere gets thinner and levels of oxygen decreases. This makes it difficult to breathe in higher altitudes as oxygen supply is reduced.
5. Boojho took an empty plastic bottle turned it upside down and dipped its open mouth into a bucket filled with water. He then tilted the bottle slightly and made the following observations.
i. Bubbles of air came out from the bottle.
ii. Some water entered the bottle.
iii. Nitrogen gas came out in the form of bubbles and oxygen got dissolved in water.
iv. No bubbles formed, only water entered the bottle.
Which observations is/are correct?
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (iv) only
(c) (iii) and (iv)
(d) (i) only
Ans: a) (i) and (ii)
When we dip an empty bottle in a bucket filled with water, the air trapped in the bottle starts escaping and tiny air bubbles are formed. Also, when he tilted the bottle, some water entered it because when the air escaped there was empty space left.
6. Which of the following components of air is present in the largest amount in the atmosphere?
(a) Nitrogen
(b) Oxygen
(c) Water vapour
(d) Carbon dioxide
Ans: a) Nitrogen
Atmospheric air contains all the four mentioned components but the component with the largest amount present in the air is nitrogen, which constitutes $78\% $ of the atmospheric air whereas oxygen constitutes $21\% $ and remaining $1\% $ is formed by water vapour, carbon dioxide, few other gases and dust particles.
7. The components of air which are harmful to living beings are
(a) Nitrogen and carbon dioxide.
(b) Dust and water vapour.
(c) Dust and smoke.
(d) Smoke and water vapour.
Ans: c) Dust and smoke
Dust and smoke are harmful to living beings because if they enter our body, they can cause respiratory problems.
8. Usha took a lump of dry soil in a glass and added water to it till it was completely immersed. She observed bubbles coming out. The bubbles contain
(a) water vapour
(b) only oxygen gas
(c) air
(d) none of these
Ans: c) Air
When Usha poured water on the lump of soil, the air trapped in it got displaced and air bubbles were formed.
Very Short Answer Questions
9. State whether the following statements are true or false. If false, correct them.
(a) Plants consume oxygen for respiration.
(b) Plants produce oxygen during the process of making their own food.
(c) Air helps in the movements of sailing yachts and glider but plays no role in the flight of birds and aeroplanes.
Ans: False because air helps in the flight of birds and aeroplanes.
(d) Air does not occupy any space.
Ans: False because air occupies space.
10. In a number of musical instruments, air plays an important role. Can you name some such instruments?
Ans: Such instruments are flute, mouth organ, trumpet, shehnai and harmonium.
11: In the boxes of Column I the letters of some words got jumbled. Arrange them in proper form in the boxes given in Column II.
12. Make sentences using the given set of words.
(a) 99%, oxygen, nitrogen, air, together
Ans: Nitrogen and oxygen together make up $99\% $ of the air.
(b) Respiration, dissolved, animals, air, aquatic
Ans: Aquatic animals use dissolved air for respiration.
(c) Air, wind, motion, called
Ans: Air in motion is called wind.
Short Answer Questions
13. A list of words is given in a box. Use appropriate words to fill up the blanks in the following statements.
Air, oxygen, wind, water vapour, mixture, combination, direction, road, bottles, cylinders.
(a) The ______ makes the windmill rotate.
(b) Air is a ______ of some gases.
Ans: Mixture
(c) A weather cock shows the ______ in which the air is moving at that place.
Ans: Direction
(d) Mountaineers carry oxygen ______ with them, while climbing high mountains.
Ans: Cylinders
14. Observe the picture given in Fig. $15.1$ carefully and answer the following questions.
(a) What is covering the nose and mouth of the police man?
Ans: A mask is covering his nose and mouth.
(b) Why is he putting a cover on his nose?
Ans: The mask is protecting him from dirt, pollution and exhaust of vehicles which are harmful elements. If these enter his body, he can suffer from respiratory disorders.
(c) Can you comment on air quality of the place shown in the Fig. $15.1$ ?
Ans: The exhaust from vehicles is polluting the environment and deteriorating the air quality making it difficult to breathe clean air.
15. Garima observed that when she left her tightly capped bottle full of water in the open sunlight, tiny bubbles were formed all around inside the bottle. Help Garima to know why it so happened?
Ans: We know that air is present in water in the form of oxygen. Due to heating from the sunlight, the air that was dissolved in water started escaping. This escape of air resulted in tiny bubbles formed all around inside the water filled bottle.
Question 16: Match the items of Column I with the items of Column II.
Ans: The correct match is given below.
Long Answer Questions
17. Explain the following observations very briefly
(a) A firki does not rotate in a closed area.
Ans: A firki rotates due to the air movement present in the surrounding and a closed area doesn’t support air movement. Hence, a firki will rotate only when placed in an open area due to the presence of moving air all around.
(b) The arrow of weather cock points towards a particular direction at a particular moment.
Ans: A weather cock is an instrument which is used to indicate the direction in which air is moving. It consists of an arrow, mounted at its centre of gravity so it can move freely about a vertical axis.
(c) An empty glass in fact is not empty.
Ans: In an empty glass there is always air present which covers up the space therefore, it cannot be said empty. Air is transparent, weightless and doesn’t have a definite shape or volume, thus, we cannot see it.
(d) Breathing through mouth may harm you.
Ans: There are many dust particles, gases and water vapours present in the air that we breathe. When we inhale through nostrils, the entry of these harmful particles is prevented by the fine hair and mucus present in the nose as they filter the air but when we breathe through the mouth there’s no such filtering of particles. Thus, they enter our body, reach the respiratory tract and make us ill.
18. Write just a few sentences for an imaginary situation if any of the following gases disappear from the atmosphere
(a) Oxygen
Ans: Almost all the living organisms present on earth inhale oxygen or use oxygen in the food making processes (plants use oxygen for photosynthesis). Hence, it is obvious that oxygen is an essential element for survival and there will be no life in the absence of oxygen.
(b) Nitrogen
Ans: Nitrogen constitutes major part i.e. $78\% $ of the atmosphere. Nitrogen is a gas that hinders burning. So, if nitrogen disappeared completely from earth, things will burn at a faster rate. Also, in the lack of nitrogen there are increased chances of dehydration. Nitrogen is a necessity for growth of plants. Although plants does not absorb nitrogen directly through air but they consume it in soluble forms. So, no nitrogen will disturb the plant cycle.
(c) Carbon dioxide
Ans: The ecosystem in which we live, all organisms are interdependent on each other. In this cycle of interdependence, carbon dioxide is produced by animals. During photosynthesis plants intake carbon dioxide and give us oxygen (which many other organisms require for respiration). In the absence of carbon dioxide plants will not be able to perform photosynthesis and will die eventually, also organisms which depend on plants for food will be left with no food at all and it will disturb the carbon dioxide – oxygen ratio. If there is no carbon dioxide, oxygen level will decrease simultaneously and we know there is no life without oxygen on earth.
19. Paheli kept some water in a beaker for heating. She observed that tiny bubbles appeared before the water started to boil. She boiled the water for about 5 minutes and filled it in a bottle up to the brim and kept the bottle air tight till it cooled down to room temperature.
(a) Why did the tiny bubbles appeared?
Ans: The tiny bubbles appeared when the water started boiling because of the air dissolved in water. When she started boiling the water, the air that was dissolved in the water escaped in the form of bubbles.
(b) Do you think tiny bubbles will appear on heating the water taken out from the bottle? Justify your answer.
Ans: No, tiny bubbles will not appear because when Paheli boiled the water, the air from the water escaped out so there is no dissolved air in this water. Hence, the cooled boiled water will not make any tiny bubbles.
20. On a Sunday morning Paheli’s friend visited her home. She wanted to see some flowering plants in the nearby garden. Both of them went to the garden. While returning from the garden they also observed some flowering plants on the road side. But to their surprise they found that the leaves and flowers of these roadside plants were comparatively very dull. Can you help them to know why?
Ans: The air quality present in the atmosphere which includes dust and soot particles released from vehicles, factories and chimneys makes the appearance of leaves and flowers dull which are planted on the roadside areas. The dust particles present in the air get deposited on the leaves and flowers and make them look dull.
NCERT Exemplar Class 6 Science Solutions Chapter 15 Air Around Us
The NCERT Exemplar Class 6 Science Solutions Chapter 15 Air Around Us is one of the best study materials for revision. It comprises different types of questions related to all the important concepts from the chapter Class 6 Science Chapter 15 Air Around Us. These questions are quite important for practice as they follow the same pattern as your exam question paper. Many of the questions in your exam will be picked from the NCERT Exemplar Class 6 Science Solutions Chapter 15 Air Around Us. So, revising from the NCERT Exemplar Class 6 Science Solutions Chapter 15 Air Around Us will prove to be quite helpful for you. With this PDF, you can secure a remarkable score in your exams and get ahead of your peers. It is available free of cost only on Vedantu’s official website and mobile application.
Significance of the NCERT Exemplar Class 6 Science Solutions Chapter 15 Air Around Us
The NCERT Exemplar Class 6 Science Solutions Chapter 15 Air Around Us is a significant part of your revision. It has answers to all the important questions from the Class 6 Science Chapter 15, which is a vital topic of your syllabus. Once you go through the NCERT Exemplar Class 6 Science Solutions Chapter 15 Air Around Us thoroughly, you will be able to attempt any question in the exam.
FAQs on NCERT Exemplar for Class 6 Science Solutions Chapter 15 Air Around Us
1. How to get access to the NCERT Exemplar Class 6 Science Solutions Chapter 15 Air Around Us?
You can get access to the NCERT Exemplar Class 6 Science Solutions Chapter 15 Air Around Us from Vedantu’s website. It is also available on Vedantu’s mobile application that you can download from the app store or play store. The NCERT Exemplar Class 6 Science Solutions Chapter 15 Air Around Us PDF is free to download on our website. There are other study materials for Class 6 available on the website. You can register and create your account on Vedantu.com and download the content you need for your exam preparations.
2. How will the NCERT Exemplar Class 6 Science Solutions Chapter 15 Air Around Us help me?
The NCERT Exemplar Class 6 Science Solutions Chapter 15 Air Around Us will come in handy for your exam preparations. It contains plenty of questions for you to practice and gain more knowledge about the concepts that come under this chapter. The answers available in the PDF are prepared by our teachers who have years of experience. So, you can rely on these solutions to revise the chapter. Moreover, all the questions in the PDF are based on the same exam pattern as your Class 6 Science exam. It will give you an idea of the types of questions that will be asked in your exam.
3. Is it necessary to practise the NCERT Exemplar Class 6 Science Solutions Chapter 15 Air Around Us?
Yes, it is necessary to practise the questions provided in the NCERT Exemplar Class 6 Science Solutions Chapter 15 Air Around Us. Once you are done with the textbook questions, the NCERT Exemplar Class 6 Science Solutions Chapter 15 Air Around Us PDF will provide you with other important questions. The textbook questions may not be enough to fully understand Class 6 Science Chapter 15. That is why you will need the NCERT Exemplar Class 6 Science Solutions Chapter 15 Air Around Us to explore more questions and become fully prepared for the exam.
4. Does the NCERT Exemplar Class 6 Science Solutions Chapter 15 Air Around Us cover all concepts?
The NCERT Exemplar Class 6 Science Solutions Chapter 15 Air Around Us contains questions that cover all the important concepts of the chapter. After you have completed studying from the NCERT textbook and revision notes, you can revise the entire chapter again using the PDF file of the NCERT Exemplar Class 6 Science Solutions Chapter 15 Air Around Us. The answers provided in the NCERT Exemplar Class 6 Science Solutions Chapter 15 Air Around Us are explained in detail to strengthen your grasp of the topics.
5. What are the types of questions in NCERT Exemplar Class 6 Science Solutions Chapter 15 Air Around Us?
The NCERT Exemplar Class 6 Science Solutions Chapter 15 Air Around Us PDF features around 20 questions. There are Multiple Choice Questions, Very Short Answer Questions, Short Answer Questions, and Long Answer Questions in this PDF file. All these questions will be enough for you to revise the entire chapter. The NCERT Exemplar Class 6 Science Solutions Chapter 15 Air Around Us also provides explanations to the MCQ answers to help you understand why that option was chosen.


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Solve practice questions: Look for practice questions or sample case study questions specifically designed for class 6 Science. Solve these questions to apply your knowledge, practice your analytical skills, and familiarize yourself with the format of case study questions.
Case Study Questions for Class 6 Science Chapter 4 Sorting Materials into Groups.
NCERT Extra Questions for Class 6 Science Chapter 15 Air Around Us. Is Air Present Everywhere Around Us? Question 1. What are the properties of air? Answer: Air occupies space. Air is present everywhere around us. Air has no colour and one can see through it. It is transparent. Question 2. What is atmosphere? Answer:
CBSE Class 6 Science Chapter 15 Air Around Us Extra Questions and Answers is available here. Students can learn and download the PDF of these questions for free. These extra questions and answers are prepared by our expert teachers as per the latest NCERT textbook and guidelines.
Get Access to Important Questions for CBSE Class 6 Science Chapter 15 Air Around Us prepared by subject experts from the latest edition. Practicing this set of questions for Class 6 Science will help you understand every aspect of the chapter and help you score well in your exams.
Access Answers to NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 15 Air Around Us. Exercise Questions. 1. What is the composition of air? Solution: Air comprises water vapour, oxygen, nitrogen, carbon dioxide, dust and smoke. 2. Which gas in the atmosphere is essential for respiration? Solution: Oxygen in the atmosphere is essential for ...
Extra Questions for Class 6 Science Chapter 15 Air Around Us with Answers Solutions. Air Around Us Class 6 Extra Questions Very Short Answer Type. Question 1. Name some musical instruments in which air plays an important role. Answer: Flute, saxophone, trumpet, horn, etc. Question 2. What do human beings release during respiration? Answer: Co2.
Question 1. Which of the following statements is incorrect? (a) All living things require air to breathe. (b) We can feel air but we cannot see it. (c) Moving air makes it possible to fly a kite. (d) Air is present everywhere but not in soil. Solution: (d): Air is omnipresent and is present in the soil also.
Class 6 Science Chapter 15 LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS. 1. What is air? Name the major constituents of air. Also give their volume proportions in air. Ans: Air is a mixture of gases. The major constituents of air are nitrogen, oxygen, carbon dioxide and argon. The percentage composition of constituents of air are as given below:
Sample Papers. Syllabus. Textbook Solutions. Class 6 Science NCERT Exemplar Solutions Chapter 15 Air Around Us. Free PDF download of NCERT Exemplar for Class 6 Science Chapter 15 Air Around Us solved by expert Science teachers on Vedantu.com as per NCERT (CBSE) Book guidelines.