Now Available on Whatsapp:
+1 (888) 687-4420
Online 24/7
- College Essay
- Argumentative Essay
- Expository Essay
- Narrative Essay
- Descriptive Essay
- Scholarship Essay
- Admission Essay
- Reflective Essay
- Nursing Essay
- Economics Essay
Assignments
- Term Papers
- Research Papers
- Case Studies
- Dissertation
- Presentation
- Editing Help
- Cheap Essay Writing
- How to Order
Writing A Case Study
Types Of Case Study

Understand the Types of Case Study Here

People also read
A Complete Case Study Writing Guide With Examples
Simple Case Study Format for Students to Follow
Brilliant Case Study Examples and Templates For Your Help
Case studies are effective research methods that focus on one specific case over time. This gives a detailed view that's great for learning.
Writing a case study is a very useful form of study in the educational process. With real-life examples, students can learn more effectively.
A case study also has different types and forms. As a rule of thumb, all of them require a detailed and convincing answer based on a thorough analysis.
In this blog, we are going to discuss the different types of case study research methods in detail.
So, let’s dive right in!
- 1. Understanding Case Studies
- 2. What are the Types of Case Study?
- 3. Types of Subjects of Case Study
- 4. Benefits of Case Study for Students
Understanding Case Studies
Case studies are a type of research methodology. Case study research designs examine subjects, projects, or organizations to provide an analysis based on the evidence.
It allows you to get insight into what causes any subject’s decisions and actions. This makes case studies a great way for students to develop their research skills.
A case study focuses on a single project for an extended period, which allows students to explore the topic in depth.
What are the Types of Case Study?
Multiple case studies are used for different purposes. The main purpose of case studies is to analyze problems within the boundaries of a specific organization, environment, or situation.
Many aspects of a case study such as data collection and analysis, qualitative research questions, etc. are dependent on the researcher and what the study is looking to address.
Case studies can be divided into the following categories:
Illustrative Case Study
Exploratory case study, cumulative case study, critical instance case study, descriptive case study, intrinsic case study, instrumental case study.
Let’s take a look at the detailed description of each type of case study with examples.
An illustrative case study is used to examine a familiar case to help others understand it. It is one of the main types of case studies in research methodology and is primarily descriptive.
In this type of case study, usually, one or two instances are used to explain what a situation is like.
Here is an example to help you understand it better:
Illustrative Case Study Example
An exploratory case study is usually done before a larger-scale research. These types of case studies are very popular in the social sciences like political science and primarily focus on real-life contexts and situations.
This method is useful in identifying research questions and methods for a large and complex study.
Let’s take a look at this example to help you have a better understanding:
Exploratory Case Study Example
A cumulative case study is one of the main types of case studies in qualitative research. It is used to collect information from different sources at different times.
This case study aims to summarize the past studies without spending additional cost and time on new investigations.
Let’s take a look at the example below:
Cumulative Case Study Example
Critical instances case studies are used to determine the cause and consequence of an event.
The main reason for this type of case study is to investigate one or more sources with unique interests and sometimes with no interest in general.
Take a look at this example below:
Critical Instance Case Study Example
When you have a hypothesis, you can design a descriptive study. It aims to find connections between the subject being studied and a theory.
After making these connections, the study can be concluded. The results of the descriptive case study will usually suggest how to develop a theory further.
This example can help you understand the concept better:
Descriptive Case Study Example
Intrinsic studies are more commonly used in psychology, healthcare, or social work. So, if you were looking for types of case studies in sociology, or types of case studies in social research, this is it.
The focus of intrinsic studies is on the individual. The aim of such studies is not only to understand the subject better but also their history and how they interact with their environment.
Here is an example to help you understand;
Intrinsic Case Study Example
This type of case study is mostly used in qualitative research. In an instrumental case study, the specific case is selected to provide information about the research question.
It offers a lens through which researchers can explore complex concepts, theories, or generalizations.
Take a look at the example below to have a better understanding of the concepts:
Instrumental Case Study Example
Review some case study examples to help you understand how a specific case study is conducted.
Types of Subjects of Case Study
In general, there are 5 types of subjects that case studies address. Every case study fits into the following subject categories.
- Person: This type of study focuses on one subject or individual and can use several research methods to determine the outcome.
- Group: This type of study takes into account a group of individuals. This could be a group of friends, coworkers, or family.
- Location: The main focus of this type of study is the place. It also takes into account how and why people use the place.
- Organization: This study focuses on an organization or company. This could also include the company employees or people who work in an event at the organization.
- Event: This type of study focuses on a specific event. It could be societal or cultural and examines how it affects the surroundings.
Benefits of Case Study for Students
Here's a closer look at the multitude of benefits students can have with case studies:
Real-world Application
Case studies serve as a crucial link between theory and practice. By immersing themselves in real-world scenarios, students can apply theoretical knowledge to practical situations.
Critical Thinking Skills
Analyzing case studies demands critical thinking and informed decision-making. Students cultivate the ability to evaluate information, identify key factors, and develop well-reasoned solutions – essential skills in both academic and professional contexts.
Enhanced Problem-solving Abilities
Case studies often present complex problems that require creative and strategic solutions. Engaging with these challenges refines students' problem-solving skills, encouraging them to think innovatively and develop effective approaches.
Holistic Understanding
Going beyond theoretical concepts, case studies provide a holistic view of a subject. Students gain insights into the multifaceted aspects of a situation, helping them connect the dots and understand the broader context.
Exposure to Diverse Perspectives
Case studies often encompass a variety of industries, cultures, and situations. This exposure broadens students' perspectives, fostering a more comprehensive understanding of the world and the challenges faced by different entities.
So there you have it!
We have explored different types of case studies and their examples. Case studies act as the tools to understand and deal with the many challenges and opportunities around us.
Case studies are being used more and more in colleges and universities to help students understand how a hypothetical event can influence a person, group, or organization in real life.
Not everyone can handle the case study writing assignment easily. It is even scary to think that your time and work could be wasted if you don't do the case study paper right.
Buy a case study from us today to ease your stress and achieve success. We are here to make your academic journey easier!
Besides, if you're wondering, c an I pay someone to do my essay , the answer is yes! Let us worry about your assignment, while you get your important tasks done with peace of mind!

Write Essay Within 60 Seconds!

Dr. Barbara is a highly experienced writer and author who holds a Ph.D. degree in public health from an Ivy League school. She has worked in the medical field for many years, conducting extensive research on various health topics. Her writing has been featured in several top-tier publications.
Struggling With Your Paper?
Get a custom paper written at
With a FREE Turnitin report, and a 100% money-back guarantee
LIMITED TIME ONLY!
Keep reading
OFFER EXPIRES SOON!
- Privacy Policy

Home » Case Study – Methods, Examples and Guide
Case Study – Methods, Examples and Guide
Table of Contents
A case study is an in-depth examination of a single case or a few selected cases within a real-world context. Case study research is widely used across disciplines such as psychology, sociology, business, and education to explore complex phenomena in detail. Unlike other research methods that aim for broad generalizations, case studies offer an intensive understanding of a specific individual, group, event, or situation.

A case study is a research method that involves a detailed examination of a subject (the “case”) within its real-life context. Case studies are used to explore the causes of underlying principles, behaviors, or outcomes, providing insights into the nuances of the studied phenomena. This approach allows researchers to capture a wide array of factors and interactions that may not be visible in other methods, such as experiments or surveys.
Key Characteristics of Case Studies :
- Focus on a specific case, individual, or event.
- Provide in-depth analysis and contextual understanding.
- Useful for exploring new or complex phenomena.
- Generate rich qualitative data that contributes to theory building.
Types of Case Studies
Case studies can be classified into different types depending on their purpose and methodology. Common types include exploratory , descriptive , explanatory , intrinsic , and instrumental case studies.
1. Exploratory Case Study
Definition : An exploratory case study investigates an area where little is known. It helps to identify questions, variables, and hypotheses for future research.
Characteristics :
- Often used in the early stages of research.
- Focuses on discovery and hypothesis generation.
- Helps clarify research questions.
Example : Examining how remote work affects team dynamics in an organization that has recently transitioned to a work-from-home model.
2. Descriptive Case Study
Definition : A descriptive case study provides a detailed account of a particular case, describing it within its context. The goal is to provide a complete and accurate depiction without necessarily exploring underlying causes.
- Focuses on describing the case in detail.
- Provides comprehensive data to paint a clear picture of the phenomenon.
- Helps understand “what” happened without delving into “why.”
Example : Documenting the process and outcomes of a corporate restructuring within a company, describing the actions taken and their immediate effects.
3. Explanatory Case Study
Definition : An explanatory case study aims to explain the cause-and-effect relationships of a particular case. It focuses on understanding “how” or “why” something happened.
- Useful for causal analysis.
- Aims to provide insights into mechanisms and processes.
- Often used in social sciences and psychology to study behavior and interactions.
Example : Investigating why a school’s test scores improved significantly after implementing a new teaching method.
4. Intrinsic Case Study
Definition : An intrinsic case study focuses on a unique or interesting case, not because of what it represents but because of its intrinsic value. The researcher’s interest lies in understanding the case itself.
- Driven by the researcher’s interest in the particular case.
- Not meant to generalize findings to broader contexts.
- Focuses on gaining a deep understanding of the specific case.
Example : Studying a particularly successful start-up to understand its founder’s unique leadership style.
5. Instrumental Case Study
Definition : An instrumental case study examines a particular case to gain insights into a broader issue. The case serves as a tool for understanding something more general.
- The case itself is not the focus; rather, it is a vehicle for exploring broader principles or theories.
- Helps apply findings to similar situations or cases.
- Useful for theory testing or development.
Example : Studying a well-known patient’s therapy process to understand the general principles of effective psychological treatment.
Methods of Conducting a Case Study
Case studies can involve various research methods to collect data and analyze the case comprehensively. The primary methods include interviews , observations , document analysis , and surveys .

1. Interviews
Definition : Interviews allow researchers to gather in-depth information from individuals involved in the case. These interviews can be structured, semi-structured, or unstructured, depending on the study’s goals.
- Develop a list of open-ended questions aligned with the study’s objectives.
- Conduct interviews with individuals directly or indirectly involved in the case.
- Record, transcribe, and analyze the responses to identify key themes.
Example : Interviewing employees, managers, and clients in a company to understand the effects of a new business strategy.
2. Observations
Definition : Observations involve watching and recording behaviors, actions, and events within the case’s natural setting. This method provides first-hand data on interactions, routines, and environmental factors.
- Define the behaviors and interactions to observe.
- Conduct observations systematically, noting relevant details.
- Analyze patterns and connections in the observed data.
Example : Observing interactions between teachers and students in a classroom to evaluate the effectiveness of a teaching method.
3. Document Analysis
Definition : Document analysis involves reviewing existing documents related to the case, such as reports, emails, memos, policies, or archival records. This provides historical and contextual data that can complement other data sources.
- Identify relevant documents that offer insights into the case.
- Systematically review and code the documents for themes or categories.
- Compare document findings with data from interviews and observations.
Example : Analyzing company policies, performance reports, and emails to study the process of implementing a new organizational structure.
Definition : Surveys are structured questionnaires administered to a group of people involved in the case. Surveys are especially useful for gathering quantitative data that supports or complements qualitative findings.
- Design survey questions that align with the research goals.
- Distribute the survey to a sample of participants.
- Analyze the survey responses, often using statistical methods.
Example : Conducting a survey among customers to measure satisfaction levels after a service redesign.
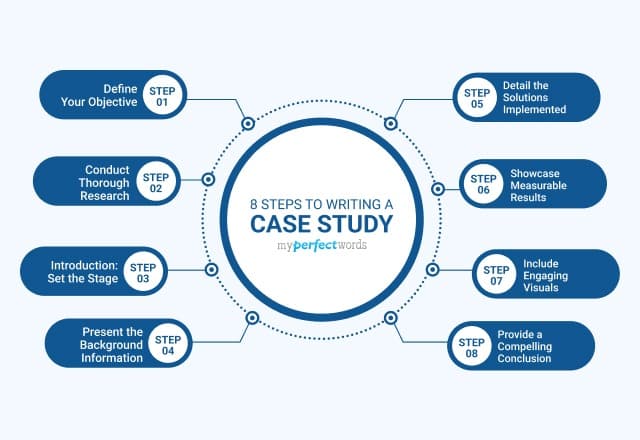
Case Study Guide: Step-by-Step Process
Step 1: define the research questions.
- Clearly outline what you aim to understand or explain.
- Define specific questions that the case study will answer, such as “What factors led to X outcome?”
Step 2: Select the Case(s)
- Choose a case (or cases) that are relevant to your research question.
- Ensure that the case is feasible to study, accessible, and likely to yield meaningful data.
Step 3: Determine the Data Collection Methods
- Decide which methods (e.g., interviews, observations, document analysis) will best capture the information needed.
- Consider combining multiple methods to gather rich, well-rounded data.
Step 4: Collect Data
- Gather data using your chosen methods, following ethical guidelines such as informed consent and confidentiality.
- Take comprehensive notes and record interviews or observations when possible.
Step 5: Analyze the Data
- Organize the data into themes, patterns, or categories.
- Use qualitative or quantitative analysis methods, depending on the nature of the data.
- Compare findings across data sources to identify consistencies and discrepancies.
Step 6: Interpret Findings
- Draw conclusions based on the analysis, relating the findings to your research questions.
- Consider alternative explanations and assess the generalizability of your findings.
Step 7: Report Results
- Write a detailed report that presents your findings and explains their implications.
- Discuss the limitations of the case study and potential directions for future research.
Examples of Case Study Applications
- Objective : To understand the success factors of a high-growth tech company.
- Methods : Interviews with key executives, analysis of internal reports, and customer satisfaction surveys.
- Outcome : Insights into unique management practices and customer engagement strategies.
- Objective : To examine the impact of project-based learning on student engagement.
- Methods : Observations in classrooms, interviews with teachers, and analysis of student performance data.
- Outcome : Evidence of increased engagement and enhanced critical thinking skills among students.
- Objective : To explore the effectiveness of a new mental health intervention.
- Methods : Interviews with patients, assessment of clinical outcomes, and reviews of therapist notes.
- Outcome : Identification of factors that contribute to successful treatment outcomes.
- Objective : To assess the impact of urban development on local wildlife.
- Methods : Observations of wildlife, analysis of environmental data, and interviews with residents.
- Outcome : Findings showing the effects of urban sprawl on species distribution and biodiversity.
Case studies are valuable for in-depth exploration and understanding of complex phenomena within their real-life contexts. By using methods such as interviews, observations, document analysis, and surveys, researchers can obtain comprehensive data and generate insights that are specific to the case. Whether exploratory, descriptive, or explanatory, case studies offer unique opportunities for understanding and discovering practical applications for theories.
- Baxter, P., & Jack, S. (2008). Qualitative Case Study Methodology: Study Design and Implementation for Novice Researchers . The Qualitative Report, 13(4), 544–559.
- Creswell, J. W., & Poth, C. N. (2017). Qualitative Inquiry and Research Design: Choosing Among Five Approaches (4th ed.). SAGE Publications.
- Stake, R. E. (1995). The Art of Case Study Research . SAGE Publications.
- Yin, R. K. (2018). Case Study Research and Applications: Design and Methods (6th ed.). SAGE Publications.
- Thomas, G. (2016). How to Do Your Case Study (2nd ed.). SAGE Publications.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Correlational Research – Methods, Types and...

Applied Research – Types, Methods and Examples

Explanatory Research – Types, Methods, Guide

Textual Analysis – Types, Examples and Guide

Qualitative Research Methods

Phenomenology – Methods, Examples and Guide

IMAGES
VIDEO