Physical Review Research

Subject Area and Category
- Physics and Astronomy (miscellaneous)
American Physical Society
Publication type
Information.
How to publish in this journal
The set of journals have been ranked according to their SJR and divided into four equal groups, four quartiles. Q1 (green) comprises the quarter of the journals with the highest values, Q2 (yellow) the second highest values, Q3 (orange) the third highest values and Q4 (red) the lowest values.
The SJR is a size-independent prestige indicator that ranks journals by their 'average prestige per article'. It is based on the idea that 'all citations are not created equal'. SJR is a measure of scientific influence of journals that accounts for both the number of citations received by a journal and the importance or prestige of the journals where such citations come from It measures the scientific influence of the average article in a journal, it expresses how central to the global scientific discussion an average article of the journal is.
Evolution of the number of published documents. All types of documents are considered, including citable and non citable documents.
This indicator counts the number of citations received by documents from a journal and divides them by the total number of documents published in that journal. The chart shows the evolution of the average number of times documents published in a journal in the past two, three and four years have been cited in the current year. The two years line is equivalent to journal impact factor ™ (Thomson Reuters) metric.
Evolution of the total number of citations and journal's self-citations received by a journal's published documents during the three previous years. Journal Self-citation is defined as the number of citation from a journal citing article to articles published by the same journal.
Evolution of the number of total citation per document and external citation per document (i.e. journal self-citations removed) received by a journal's published documents during the three previous years. External citations are calculated by subtracting the number of self-citations from the total number of citations received by the journal’s documents.
International Collaboration accounts for the articles that have been produced by researchers from several countries. The chart shows the ratio of a journal's documents signed by researchers from more than one country; that is including more than one country address.
Not every article in a journal is considered primary research and therefore "citable", this chart shows the ratio of a journal's articles including substantial research (research articles, conference papers and reviews) in three year windows vs. those documents other than research articles, reviews and conference papers.
Ratio of a journal's items, grouped in three years windows, that have been cited at least once vs. those not cited during the following year.
Evolution of the percentage of female authors.
Evolution of the number of documents cited by public policy documents according to Overton database.
Evolution of the number of documents related to Sustainable Development Goals defined by United Nations. Available from 2018 onwards.
Leave a comment
Name * Required
Email (will not be published) * Required
* Required Cancel
The users of Scimago Journal & Country Rank have the possibility to dialogue through comments linked to a specific journal. The purpose is to have a forum in which general doubts about the processes of publication in the journal, experiences and other issues derived from the publication of papers are resolved. For topics on particular articles, maintain the dialogue through the usual channels with your editor.

Follow us on @ScimagoJR Scimago Lab , Copyright 2007-2024. Data Source: Scopus®

Cookie settings
Cookie Policy
Legal Notice
Privacy Policy
Physical Review Research (PRResearch) is a fully open access, peer-reviewed journal welcoming the full spectrum of research topics of interest to the physics community and offering authors and readers the Physical Review experience and quality they value and trust.
Some content from Wikipedia , licensed under CC BY-SA
Physical Review Research
- Date 6 hours 12 hours 1 day 3 days all
- Rank Last day 1 week 1 month all
- LiveRank Last day 1 week 1 month all
- Popular Last day 1 week 1 month all

New framework uses games of chance to put 'price' on intangible assets
A new statistical model could help to address the age-old question of how to price non-physical, intangible goods like data, say scientists.
Mathematics
Nov 6, 2024

Quantum register reaches 1,200 neutral atoms in continuous operation
A team of physicists led by Johannes Zeiher, research group leader in Immanuel Bloch's Quantum Many-Body Systems department and co-founder of the MPQ spin-off planqc, has achieved significant progress in scaling up quantum ...
Optics & Photonics
Oct 9, 2024

Quantum research paves the way toward efficient, ultra-high-density optical memory storage
As our digital world generates massive amounts of data—more than 2 quintillion bytes of new content each day—yesterday's storage technologies are quickly reaching their limits. Optical memory devices, which use light ...
Oct 2, 2024

Exploiting quantum squeezing to enhance precision of measurements in systems with multiple factors
Quantum squeezing is a concept in quantum physics where the uncertainty in one aspect of a system is reduced while the uncertainty in another related aspect is increased.
Quantum Physics
Sep 27, 2024

New technology produces ultrashort ion pulses
TU Wien (Vienna) has succeeded in generating laser-synchronized ion pulses with a duration of well under 500 picoseconds, which can be used to observe chemical processes on material surfaces. The work has been published in ...
Sep 17, 2024

Researchers model physics of the pumping technique used to achieve air on a skateboard half-pipe
A team of engineers and mathematicians from ETH Zürich, working with colleagues from The Institute of Statistical Mathematics, and ATR Institute International, both in Japan, has successfully modeled the physics involved ...
General Physics
Aug 28, 2024

Bubbling, frothing and sloshing: Long-hypothesized plasma instabilities finally observed
Whether between galaxies or within doughnut-shaped fusion devices known as tokamaks, the electrically charged fourth state of matter known as plasma regularly encounters powerful magnetic fields, changing shape and sloshing ...
Plasma Physics
Aug 27, 2024

Chaos theory approach reveals long-distance relationship in seemingly random behavior of bowhead whales
Applying chaos theory to the movement of iconic arctic whales uncovered a 24-hour diving cycle and a long-range (~100 km) synchronization.
Aug 12, 2024

The structure of sound: Network insights into Bach's music
Even today, centuries after he lived, Johann Sebastian Bach remains one of the world's most popular composers. On Spotify, close to seven million people stream his music per month, and his listener count is higher than that ...
Aug 8, 2024

Artificial intelligence could help make quantum computers a reality
Could artificial intelligence help overcome one of quantum computing's biggest roadblocks?
Jul 12, 2024
E-mail newsletter
Physical Review Research - Impact Score, Ranking, SJR, h-index, Citescore, Rating, Publisher, ISSN, and Other Important Details
Published By: American Physical Society
Impact Score The impact Score or journal impact score (JIS) is equivalent to Impact Factor. The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a scientometric index calculated by Clarivate that reflects the yearly mean number of citations of articles published in the last two years in a given journal, as indexed by Clarivate's Web of Science. On the other hand, Impact Score is based on Scopus data.
Important details, about physical review research.
Physical Review Research is a journal published by American Physical Society . This journal covers the area[s] related to Physics and Astronomy (miscellaneous), etc . The coverage history of this journal is as follows: 2019-2022. The rank of this journal is 1538 . This journal's impact score, h-index, and SJR are 4.23, 53, and 1.824, respectively. The ISSN of this journal is/are as follows: 26431564 . The best quartile of Physical Review Research is Q1 . This journal has received a total of 15713 citations during the last three years (Preceding 2022).
Physical Review Research Impact Score 2022-2023
The impact score (IS), also denoted as the Journal impact score (JIS), of an academic journal is a measure of the yearly average number of citations to recent articles published in that journal. It is based on Scopus data.
Prediction of Physical Review Research Impact Score 2023
Impact Score 2022 of Physical Review Research is 4.23 . If a similar downward trend continues, IS may decrease in 2023 as well.
Impact Score Graph
Check below the impact score trends of physical review research. this is based on scopus data., physical review research h-index.
The h-index of Physical Review Research is 53 . By definition of the h-index, this journal has at least 53 published articles with more than 53 citations.
What is h-index?
The h-index (also known as the Hirsch index or Hirsh index) is a scientometric parameter used to evaluate the scientific impact of the publications and journals. It is defined as the maximum value of h such that the given Journal has published at least h papers and each has at least h citations.
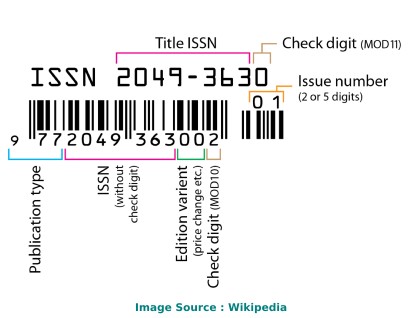
Physical Review Research ISSN
The International Standard Serial Number (ISSN) of Physical Review Research is/are as follows: 26431564 .
The ISSN is a unique 8-digit identifier for a specific publication like Magazine or Journal. The ISSN is used in the postal system and in the publishing world to identify the articles that are published in journals, magazines, newsletters, etc. This is the number assigned to your article by the publisher, and it is the one you will use to reference your article within the library catalogues.
ISSN code (also called as "ISSN structure" or "ISSN syntax") can be expressed as follows: NNNN-NNNC Here, N is in the set {0,1,2,3...,9}, a digit character, and C is in {0,1,2,3,...,9,X}
Physical Review Research Ranking and SCImago Journal Rank (SJR)
SCImago Journal Rank is an indicator, which measures the scientific influence of journals. It considers the number of citations received by a journal and the importance of the journals from where these citations come.
Physical Review Research Publisher
The publisher of Physical Review Research is American Physical Society . The publishing house of this journal is located in the United States . Its coverage history is as follows: 2019-2022 .
Call For Papers (CFPs)
Please check the official website of this journal to find out the complete details and Call For Papers (CFPs).
How to publish in Physical Review Research
If your area of research or discipline is related to Physics and Astronomy (miscellaneous), etc. , please check the journal's official website to understand the complete publication process.
Acceptance Rate
- Interest/demand of researchers/scientists for publishing in a specific journal/conference.
- The complexity of the peer review process and timeline.
- Time taken from draft submission to final publication.
- Number of submissions received and acceptance slots
- And Many More.
The simplest way to find out the acceptance rate or rejection rate of a Journal/Conference is to check with the journal's/conference's editorial team through emails or through the official website.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is the impact score of physical review research.
The latest impact score of Physical Review Research is 4.23. It is computed in the year 2023.
What is the h-index of Physical Review Research?
The latest h-index of Physical Review Research is 53. It is evaluated in the year 2023.
What is the SCImago Journal Rank (SJR) of Physical Review Research?
The latest SCImago Journal Rank (SJR) of Physical Review Research is 1.824. It is calculated in the year 2023.
What is the ranking of Physical Review Research?
The latest ranking of Physical Review Research is 1538. This ranking is among 27955 Journals, Conferences, and Book Series. It is computed in the year 2023.
Who is the publisher of Physical Review Research?
Physical Review Research is published by American Physical Society. The publication country of this journal is United States.
What is the abbreviation of Physical Review Research?
This standard abbreviation of Physical Review Research is .
Is "Physical Review Research" a Journal, Conference or Book Series?
Physical Review Research is a journal published by American Physical Society.
What is the scope of Physical Review Research?
- Physics and Astronomy (miscellaneous)
For detailed scope of Physical Review Research, check the official website of this journal.
What is the ISSN of Physical Review Research?
The International Standard Serial Number (ISSN) of Physical Review Research is/are as follows: 26431564.
What is the best quartile for Physical Review Research?
The best quartile for Physical Review Research is Q1.
What is the coverage history of Physical Review Research?
The coverage history of Physical Review Research is as follows 2019-2022.
Credits and Sources
- Scimago Journal & Country Rank (SJR), https://www.scimagojr.com/
- Journal Impact Factor, https://clarivate.com/
- Issn.org, https://www.issn.org/
- Scopus, https://www.scopus.com/
Note: The impact score shown here is equivalent to the average number of times documents published in a journal/conference in the past two years have been cited in the current year (i.e., Cites / Doc. (2 years)). It is based on Scopus data and can be a little higher or different compared to the impact factor (IF) produced by Journal Citation Report. Please refer to the Web of Science data source to check the exact journal impact factor ™ (Thomson Reuters) metric.

Impact Score, SJR, h-Index, and Other Important metrics of These Journals, Conferences, and Book Series
Check complete list
Physical Review Research Impact Score (IS) Trend
Top journals/conferences in physics and astronomy (miscellaneous).
Physical Review Research impact factor, indexing, ranking (2024)

Aim and Scope
The Physical Review Research is a research journal that publishes research related to Physics and Astronomy . This journal is published by the American Physical Society. The ISSN of this journal is 26431564 . Based on the Scopus data, the SCImago Journal Rank (SJR) of physical review research is 1.824 .
Physical Review Research Ranking
The latest Impact Factor list (JCR) is released in June 2024.
The Impact Factor of Physical Review Research is 3.5.
The impact factor (IF) is a measure of the frequency with which the average article in a journal has been cited in a particular year. It is used to measure the importance or rank of a journal by calculating the times its articles are cited.
The impact factor was devised by Eugene Garfield, the founder of the Institute for Scientific Information (ISI) in Philadelphia. Impact factors began to be calculated yearly starting from 1975 for journals listed in the Journal Citation Reports (JCR). ISI was acquired by Thomson Scientific & Healthcare in 1992, and became known as Thomson ISI. In 2018, Thomson-Reuters spun off and sold ISI to Onex Corporation and Baring Private Equity Asia. They founded a new corporation, Clarivate , which is now the publisher of the JCR.
Important Metrics
The physical review research is indexed in:
- Web of Science (ESCI)
An indexed journal means that the journal has gone through and passed a review process of certain requirements done by a journal indexer.
The Web of Science Core Collection includes the Science Citation Index Expanded (SCIE), Social Sciences Citation Index (SSCI), Arts & Humanities Citation Index (AHCI), and Emerging Sources Citation Index (ESCI).
Note: ESCI journals donot come with an impact factor. However, ESCI journals are evaluated every year and those who qualified are transferred to SCIE.
Physical Review Research Impact Factor 2024
The latest impact factor of physical review research is 3.5 which is recently updated in June, 2024.
The impact factor (IF) is a measure of the frequency with which the average article in a journal has been cited in a particular year. It is used to measure the importance or rank of a journal by calculating the times it's articles are cited.
Note: Every year, The Clarivate releases the Journal Citation Report (JCR). The JCR provides information about academic journals including impact factor. The latest JCR was released in June, 2023. The JCR 2024 will be released in the June 2024.
The latest Quartile of physical review research is Q1 .
Each subject category of journals is divided into four quartiles: Q1, Q2, Q3, Q4. Q1 is occupied by the top 25% of journals in the list; Q2 is occupied by journals in the 25 to 50% group; Q3 is occupied by journals in the 50 to 75% group and Q4 is occupied by journals in the 75 to 100% group.
Publication fee
According to journal website, the publication fee of physical review research is around 2755 USD .
The physical review research has also Journal waiver policy (for developing countries, authors etc).
An article processing charge (APC), also known as a publication fee, is a fee which is sometimes charged to authors. Most commonly, it is involved in making a work available as open access (OA), in either a full OA journal or in a hybrid journal.
Journal Publication Time
The Journal Publication Time means the average number of weeks between article submission and publication. According to the journal website, the physical review research publishes research articles in 15 weeks on an average.
Call for Papers
Visit to the official website of the journal/ conference to check the details about call for papers.
How to publish in Physical Review Research?
If your research is related to Physics and Astronomy, then visit the official website of physical review research and send your manuscript.
Tips for publishing in Physical Review Research:
- Selection of research problem.
- Presenting a solution.
- Designing the paper.
- Make your manuscript publication worthy.
- Write an effective results section.
- Mind your references.
Acceptance Rate
Final summary.
- The impact factor of physical review research is 3.5.
- The physical review research is a reputed research journal.
- It is published by American Physical Society .
- The journal is indexed in UGC CARE, Scopus, ESCI, DOAJ .
- It is an open access journal .
- The (SJR) SCImago Journal Rank is 1.824 .
- The publication time (Average number of weeks between article submission and publication) of the journal is 15 weeks .
- The Publication fee (APC) of physical review research 2755 USD .
SIMILIAR JOURNALS
MODERN PHYSICS LETTERS A
CLASSICAL AND QUANTUM GRAVITY
GENERAL RELATIVITY AND GRAVITATION
PHYSICS LETTERS B
SCIENTIA SINICA-PHYSICA MECHANICA & ASTRONOMICA
ASTROPARTICLE PHYSICS
COMPTES RENDUS PHYSIQUE
JOURNAL OF COSMOLOGY AND ASTROPARTICLE PHYSICS
PHYSICAL REVIEW D
TOP RESEARCH JOURNALS
- Agricultural & Biological Sciences
- Arts & Humanities
- Business, Management and Accounting
- Computer Science
- Engineering
- Mathematics
- Social Sciences
Physical Review Research Impact Factor 2024-25

Physical Review Research (PRR) is a scholarly journal dedicated to publishing research in the field of Physics and Astronomy , and Published by American Physical Society . and its abbreviation is Phys Rev Res .
Physical Review Research Impact Factor List
The impact factor or journal impact factor of an academic journal is a scientometric index calculated by Clarivate that reflects the yearly mean number of citations of articles published in the last two years in a given journal, as indexed by Clarivate's Web of Science .
To know more about Physical Review Research visit click here
Advertisement
Physics and Astronomy Journals List
- Advanced Electromagnetics Physics and Astronomy Impact Factor, Indexing, Ranking
- Acta Physica Polonica B, Proceedings Supplement Physics and Astronomy Impact Factor, Indexing, Ranking
- Acta Mathematica Scientia Physics and Astronomy Impact Factor, Indexing, Ranking
- AAPPS Bulletin Physics and Astronomy Impact Factor, Indexing, Ranking
- ISA Transactions Physics and Astronomy Impact Factor, Indexing, Ranking
- Physical Review D Physics and Astronomy Impact Factor, Indexing, Ranking
- Microsystems and Nanoengineering Physics and Astronomy Impact Factor, Indexing, Ranking
- International Journal of Mechanical Sciences Physics and Astronomy Impact Factor, Indexing, Ranking
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia Physics and Astronomy Impact Factor, Indexing, Ranking
- Critical Reviews in Solid State and Materials Sciences Physics and Astronomy Impact Factor, Indexing, Ranking
Welcome to JournalsInsights!
JournalsInsights is a free journal search tool for authors. If you are an author, you can bookmark our website and ask any journal publication-related questions. Our team is here to assist you for free throughout your publication journey.
If you share our website and support us, it would be greatly appreciated. Please also share your feedback to help us improve our website.
You will be redirected to the journal's website in 20 seconds...
Need Help? Get Quick Services & Answers
Scientometrics
Citing bodies, physical review research, what is the 2023 impact factor of physical review research .
- Editage One platform for all researcher needs
- Paperpal AI-powered academic writing assistant
- R Discovery Your #1 AI companion for literature search
- Mind the Graph AI tool for graphics, illustrations, and artwork
- [email protected]
- Request a callback
Researcher.Life is built on Editage's in-depth understanding of what researchers need during publication and beyond, accumulated over 20 years.
Physical Review Research : Impact Factor & More
Check your submission readiness.
Find out how your manuscript stacks up against 24 technical compliance and 6 language quality checks.
Physical Review Research Key Metrics
Topics covered on physical review research, physical review research journal specifications.
Indexed in the following public directories
Planning to publish in Physical Review Research ?
Upload your Manuscript to get
- Degree of match
- Common matching concepts
- Additional journal recommendations

Compare Similar Journals with Physical Review Research
Physical review letters, nature communications, new journal of physics, physical review x, journal of physics condensed matter, nature physics, journal of the physical society of japan, physical review b, scientific reports.
SJR Ranking, Topics covered, Indexing Database, Publication Review Time, Publication Type, Article Processing Charges & Recently Published papers
Get detailed Journal comparison report on your email by signing up

Check if your research matches the topics covered in Physical Review Research?
Physical review research scite analysis.
7.2K articles received 72K citations see all
- 3,163 Supporting
- 68,436 Mentioning
- 206 Contrasting
Physical Review Research Editorial notices
- 1 Retractions
- 0 Withdrawals
- 59 Corrections
- 0 Expression of Concern
FAQs on Physical Review Research
How long has physical review research been actively publishing.
Physical Review Research has been in operation since 2019 till date.
What is the publishing frequency of Physical Review Research?
Physical Review Research published with a Quarterly frequency.
What is the eISSN & pISSN for Physical Review Research?
For Physical Review Research, eISSN is 2643-1564 and pISSN is 2643-1564.
What is Citescore for Physical Review Research?
Citescore for Physical Review Research is 4.6.
What is SNIP score for Physical Review Research?
SNIP score for Physical Review Research is 1.22.
Who is the publisher of Physical Review Research?
AMER PHYSICAL SOC is the publisher of Physical Review Research.
Copyright 2024 Cactus Communications. All rights reserved.
An official website of the United States government
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock Locked padlock icon ) or https:// means you've safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
- Publications
- Account settings
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
Relationship Between Loneliness, Psychiatric Disorders and Physical Health ? A Review on the Psychological Aspects of Loneliness
Raheel mushtaq, sheikh shoib, tabindah shah, sahil mushtaq.
- Author information
- Article notes
- Copyright and License information
NAME, ADDRESS, E-MAIL ID OF THE CORRESPONDING AUTHOR: Dr. Raheel Mushtaq, Senior Resident, Department of Psychiatry, Government Medical College, Srinagar, Jammu and Kashmir, India. Phone : +91 9596554343, E-mail : [email protected]
Received 2014 May 22; Revision requested 2014 Jun 28; Accepted 2014 Jul 17; Issue date 2014 Sep.
Human beings are social species which require safe and secure social surroundings to survive. Satisfying social relationships are essential for mental and physical well beings. Impaired social relationship can lead to loneliness. Since the time of dawn, loneliness is perceived as a global human phenomenon. Loneliness can lead to various psychiatric disorders like depression, alcohol abuse, child abuse, sleep problems, personality disorders and Alzheimer’s disease. It also leads to various physical disorders like diabetes, autoimmune disorders like rheumatoid arthritis, lupus and cardiovascular diseases like coronary heart disease, hypertension (HTN), obesity, physiological aging, cancer, poor hearing and poor health. Left untended, loneliness can have serious consequences for mental and physical health of people. Therefore it is important to intervene at the right time to prevent loneliness, so that physical and mental health of patients is maintained.
Keywords: Loneliness, Mental health, Physical health
Introduction
Loneliness is a painful universal phenomenon that has an evolutionary basis. Loneliness reminds us of the pain and warns us of the threat of becoming isolated. Loneliness is the absence of imperative social relations and lack of affection in current social relationships [ 1 ]. Loneliness is one of the main indicators of social well-being. Loneliness is caused not by being alone, but by being without some definite needed relationship or set of relationships. Research addressing loneliness has increased dramatically over the past 2 decades; however, despite the mental health risks associated with being lonely, the relationship between loneliness and psychiatric disorders has not been sufficiently explored [ 2 ].In India very little research has been done on psychological and physical affects of loneliness. There are just a few studies in India, in which relationship of loneliness with other psychiatric disorders has been studied .However most of these studies were done in elderly patients only [ 3 – 5 ].
Loneliness is a common experience with 80% of population below 18 years of age and 40% of population above 65 years of age report loneliness at least sometimes in their life [ 2 , 6 – 8 ]. Loneliness is generally reported more among adolescents and young children, contrary to the myth that it occurs more in elderly. The reason for this is that elder people have definite copying skills and can adjust accordingly to solitude, while as adolescents lack definite copying skills and adolescent period is the time of life when being accepted and loved is of such major importance to the formation of one’s identity. However elderly who have physical illness and disability report higher prevalence of loneliness, compared to elderly without physical illness and disability [ 1 , 9 , 10 ]. In India elderly patient population is increasing and their psychological problems are on a rise. India is destined to become the second largest population of elderly people in the coming years. Therefore it is necessary to intervene at the right time to prevent the psychological problems and physical disorders arising due to affects of loneliness in elderly population [ 3 ]. Further loneliness gradually diminishes through the middle adult years, and then again increases in old age (i.e., ≥70 years) [ 7 ].
Risk factors: The risk factors associated with loneliness include being female, being widowed, living alone, being aged, health factors, material resources and a limited number of ‘social’ resources [ 11 ].
Scales for measuring loneliness
Loneliness is measured by various scales like UCLA (University of California, Los Angeles) Loneliness Scale [ 12 ], Three-Item Loneliness Scale [ 12 ] and De Jong Gierveld Loneliness scale [ 13 ].
Types of loneliness
There are 3 types of loneliness i.e. situational loneliness, developmental loneliness and internal loneliness [ 14 ].
Situational Loneliness: The various factors associated with situational loneliness are environmental factors (unpleasant experiences, discrepancy between the levels of his/her needs), migration of people, inter personal conflicts, accidents and disasters, etc [ 14 ].
Developmental Loneliness: The various factors associated with developmental loneliness are personal inadequacies, developmental deficits, significant separations, poverty, living arrangements, and physical/psychological disabilities [ 14 ].
Internal Loneliness: The various factors associated with internal loneliness are personality factors, locus of control, mental distress, low self-esteem, guilt feeling , and poor coping strategies with situations [ 14 ].
Further Weiss et al., reported 2 types of loneliness i.e. emotional and social loneliness. Emotional loneliness defined by the absence of an attachment figure and social isolation, characterized by the absence of a social network [ 15 ].
Psychiatric Disorders and Loneliness
Depression : Lonely people suffer from more depressive symptoms, as they have than been reported to be less happy, less satisfied and more pessimistic [ 16 ]. Further loneliness and depression share common symptoms like helplessness and pain. There is so much similarity in between loneliness and depression that many authors consider it a subset of depression. However the distinction can be made by the fact that loneliness is characterized by the hope that all would be fine, if the lonely person could be united with another longed for person [ 2 ]. In patients, who are both lonely and depressed, loneliness is positively correlated with negative feelings and negative judgment of personality attributes and negatively correlated with it .It has been seen that there is an association between insecure attachment styles and depression. Several studies further suggest insecure attachment styles increases vulnerability to depression. The vulnerability to depression can be due to the fact that insecurely attached have tendency to develop low self esteem, difficulty or inability in developing and maintaining relationships with others, poor problem solving skills, and an unstable self- concept [ 17 ]. In a study done by Singh A et al., of 55 elder persons in the age group of 60-80 in Delhi (India) based regions (living in various housing societies), found out an increase in level of depression with increase in level of loneliness. However no gender difference in elder males and females was found between loneliness and depression. The absence of significant gender difference is in contrast to the belief, as well as what has been reported in the literature that older females are more vulnerable to depression. The reason for this could be that all elderly females were not working women before 60 years of age. The transition in their lifestyle in their old age included breaking ties with their colleagues, friends and loss of status. However the transition in their lifestyle was slow, which could have prevented any change in mood [ 4 ]. In a study done by Bhatia SPS et al., found higher mean loneliness score in elderly women , compared to elderly males. He further concluded that older people, who were living alone were experiencing higher loneliness ,compared to who were living with their spouses or their families [ 5 ].
Alzheimer’s disease : Loneliness is associated with more then two fold risk of dementia, as loneliness is associated with loss of cognition in old age. In fact some authors signal it as prodromal stage of dementia [ 18 ]. In loneliness, there is more rapid decline in global cognition, semantic memory, perceptual speed, and visuospatial ability. The basis of association of loneliness with Alzheimer’s disease (AD) can be attributed to two possibilities. First possibility is that loneliness is a consequence of dementia, perhaps as a behavioral reaction to diminished cognition or as a direct result of the pathology contributing to dementia. Second possibility is that loneliness might somehow compromise neural systems underlying cognition and memory, thereby making lonely individuals more vulnerable to the deleterious effects of age-related neuropathology and thereby decreasing neural reserves [ 19 ]. In one study, the incidence of AD was predicted by degree of baseline loneliness, after adjusting for age, sex, and education. It was found that those in the top deciles of loneliness scores were 2.1 times more likely to develop AD than those in the bottom deciles of loneliness scores. The prevalence of AD is lower in India compared to other countries. There are wide variations in the incidence rates in community based as well as urban based studies in India. Various risk factors have been identified in the causation of AD in India. However, to the best of the knowledge of the author, there are no studies which assesses relationship of loneliness with AD [ 20 ].
Alcoholism: Loneliness is recognized as a contributing, maintaining and poor prognostic factor in the development of alcohol abuse. Further it is recognized as an essential risk factor in all the stages of alcoholism [ 21 – 24 ]. Various studies have demonstrated lonely people with heavy drinking are more vulnerable to alcohol related problems. The reasons attributed to this are due to lack of social support, and distinct perceptions of community pressure [ 22 – 24 ]. However presently in India as well as in the world, there are no studies which compares loneliness in alcoholics with loneliness in nonalcoholic [ 22 – 24 ].
Child abuse : Loneliness is more prevalent among child abusers and those who disregard than who take good care of their children. Women abused in the past were noted to be more lonely and had more negative network orientation, compared to women, who were not abused. Further in whom abuse lasted for a longer duration period and involving multiple incidents were more loneliness and had lower network orientation [ 8 , 25 , 26 ]. In a study conducted by Dhal A et al., of 110 adolescents of Delhi (India) found that two third of children reported higher level of loneliness and one third of children reported lower level of loneliness. Further low self esteem in the adolescents was associated with loneliness .The adolescents with low self esteem develop loneliness ,as they feel rejected.They also lacked confidence and skills in initiating and maintaining relationships. Psychological intervention like copying skills, talking with friends and maintaining relationships can benefit adolescents in dealing with psychological affects of loneliness [ 27 ].
Bereavement: Loneliness is expected when people grieve the loss of someone to whom they were closely attached. Widows express loneliness usually with the absence of a spouse or a social support. Various studies report 86% of widows experience loneliness, however the proportion decreases with increasing number of children and with the support system. It must be noted that loneliness in grief is associated with acute absence of an attachment figure, rather than absence of a social support. Further loneliness in bereavement is in itself a risk factor for the development of depression [ 2 ].
Stress, Immune system : Loneliness is not only a source of acute stress, but also chronic stress. Recently, there has been extensive research on psychosocial effects of stress on neuroendocrine and immune systems. Whether loneliness qualifies as stress may be debatable [ 2 , 20 , 28 ]. However there is ample data, which gives evidence of immune system getting involved in loneliness. Loneliness has been associated with impaired cellular immunity, as reflected by lower natural killer (NK) cell activity and higher antibody titers. In addition, loneliness among middle-age adults has been found associated with smaller increase in NK cell numbers ,in response to acute stress associated with various tasks [ 2 , 28 ].
Suicide: Research on suicide has revealed that there is a strong association between suicide ideation, parasuicide and loneliness .The prevalence of suicide ideation and parasuicide rises with the degree of loneliness. Further the peak season for loneliness has been reported to be winter and spring, the same season for which peak incidence of suicide has been reported [ 29 ]. However there is minimal differences in suicide between men and women related to loneliness [ 30 ]. SC Tiwari attributes loneliness as an important factor in etiology of suicide and parasuicide .He also considers loneliness as a disease and wants its place in classification of psychiatric disorders [ 14 ].
Personality disorder : The various personality disorders associated with loneliness include borderline personality disorder and schizoid personality disorder [ 31 , 32 ] Intolerance of aloneness is considered a core feature of borderline personality disorder (BPD). Loneliness also potentiates other symptoms associated with BPD. The various Theories of Aloneness in BPD are The Need for Time Alone, Signaling the Need, Development of the Capacity to be Alone, The Holding Environment and Internal Representation [ 31 , 32 ]. Several psychoanalytic theorists have suggested that emotional deprivation plays a critical role in the development of schizoid personality disorder. As a result of emotional deprivation and lack of ability to gain security, a lack of contentedness in interpersonal relationships has been observed as components in attachment distortion. Further contributing to the development of schizoid personality disorder is the maladaptive schema’s and attached cognitive behavior associated with emotional deprivation [ 32 ]. In India, there are no studies which assess relationship of personality disorders with loneliness. In future, research should be done in India, which focuses on psychological affects of loneliness on various personality disorders.
Sleep: Loneliness has been associated with poor sleep quality with daytime dysfunction like low energy, fatigue. However loneliness has no relationship with sleep duration. As greater daytime dysfunction is a marker of poor sleep quality, loneliness has been found associated with greater day time dysfunction. Numerous studies have demonstrated greater daytime dysfunction accompanied by more nightly micro-awakenings with loneliness, thus demonstrating a role of loneliness with poor sleep quality [ 20 ].
Physical illness and Loneliness: Loneliness related chronic stress can cause low- grade peripheral inflammation. The low- grade peripheral inflammation in turn has been linked to inflammatory diseases .The inflammatory diseases include diabetes ,autoimmune disorders like rheumatoid arthritis, lupus and cardiovascular diseases like coronary heart disease, hypertension (HTN) [ 30 ]. In a study conducted by Hawkley et al., of young adults, loneliness was found associated with elevated levels of total peripheral resistance (TPR).TPR is the primary determinant of SBP, which suggests that loneliness- related elevations in TPR may lead to higher blood pressure [ 17 ]. Loneliness related chronic stress can also cause low- grade peripheral inflammation. The low- grade peripheral inflammation in turn has been linked to cardiovascular disease like atherosclerosis etc [ 17 , 24 ]. There have been various studies, showing relationship of loneliness with obesity, physiological aging,cancer, poor hearing and poor health [ 17 , 24 ]. In a study by SK Mishra et al., in 380 HIV (Human immunodeficiency virus) patients of Andhra Pradesh (India) found that 66.57% of patients were found to be lonely and loneliness was associated with depression (71.84%) in them. He also concluded that in physical illnesses like HIV infection, the mental health indicators like loneliness and depression needs more stress in the continuum of care of patients [ 33 ].
Interventions for loneliness: Left untended, loneliness has serious consequences mental and physical well being of people. Therefore it is important to intervene at the right time to prevent loneliness. There are broadly 4 types of interventions. The four main types of interventions: (1) Developing social skills, (2) Giving social support, (3) Developing opportunities for social interaction, and (4) Recognizing maladaptive social cognition [ 17 ].
Loneliness is one of the main indicators of social well-being. Loneliness can lead to various psychiatric disorders and various physical disorders. Left untended, loneliness can have serious consequences for mental and physical health. In India, there are very few studies which assess relationship of psychiatric and physical disorders with loneliness. However most of these studies were done in elderly patients. In the near future, research should be done in India, which focuses on psychological and physical affects associated with loneliness. Therefore it is important to intervene at the right time to prevent loneliness, so that physical and mental health of patients is maintained.
Financial or Other Competing Interests
- [1]. Rubin A. Research and Therapy. New York: Wiley; 1982. Children without friends, in Peplau LA, Perlman D (eds): Loneliness: A Sourcebook of Current Theory; pp. 255–68. [ Google Scholar ]
- [2]. West Donald A, Kellner Robert, Moore-West Maggi. The Effects of Loneliness: A Review of the Literature. Comprehensive Psychiafry. 1986;27(4):351–83. doi: 10.1016/0010-440x(86)90011-8. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- [3]. Acharya A. Depression,Loneliness And Insecurity Feelings Among the Elderly Female Living in Old Age Homes of Agatala. Indian J of Gerontology. 2012;vol 26(4):524–36. [ Google Scholar ]
- [4]. Singh A, Misralnd N. Loneliness, depression and sociability in old age. Indian J of Psychiatry. 2009;18(1):51–55. doi: 10.4103/0972-6748.57861. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- [5]. Bhatia SPS, Swami HM, Thakur JS, Bhatia V. Astudy of health problems and loneliness among the elderly in Chandigarh. Indian J of Community Medicine. 2007;32(4):255–58. [ Google Scholar ]
- [6]. Berguno G, Leroux P, McAinsh K, Shaikh S. Children’s experience of loneliness at school and its relation to bullying and the quality of teacher interventions. Qualitative Report. 2004;9:483–99. [ Google Scholar ]
- [7]. Pinquart M, Sorensen S. Influences on loneliness in older adults: A meta-analysis. Basic and Applied Social Psychology. 2001;23:245–66. [ Google Scholar ]
- [8]. Weeks DJ. A review of loneliness concepts, with particular reference to old age. International Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry. 1994;9:345–55. [ Google Scholar ]
- [9]. Brennan T. Research and Therapy. New York: Wiley; 1982. Loneliness at adolescence, in Peplau LA, Perlman D (eds): Loneliness: A Sourcebook of Current Theory; p. 273. [ Google Scholar ]
- [10]. Brennan T, Auslander N: Adolescent Loneliness: An Exploratory Study of Social and Psychological Predispositions and Theory, 1979 vol 1. Prepared for the National Institute of Mental Health, Juvenile Problems Division, Behavioral Research Institute.
- [11]. Victo Christina R, Scambler Sasha J, Bowling Ann, John The prevalence of, and risk factors for, loneliness in later life: a survey of older people in Great Britain BOND. Cambridge University Press Ageing & Society. 2005;25:357–75. [ Google Scholar ]
- [12]. Hughes M E, Waite L J, Hawkley L C, Cacioppo J T. A Short Scale for Measuring Loneliness in Large Surveys Results From Two Population-Based Studies. Research on aging. Res Aging. 2004;26(6):655–72. doi: 10.1177/0164027504268574. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- [13]. Gierveld Jong J D, Tilburg T V. A 6-Item Scale for Overall, Emotional, and Social Loneliness Confirmatory Tests on. Research on Survey Data. 2006;28(5):582–98. [ Google Scholar ]
- [14]. Tiwari SC. Loneliness: A disease? Indian J of Psychiatry. 2013;55(4):320–22. doi: 10.4103/0019-5545.120536. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- [15]. Weiss R. Loneliness: The Experience of Emotional and Social Isolation. Cambridge, Mass: MIT Press; 1973. p. 17. [ Google Scholar ]
- [16]. Singh B, Kiran U V. Loneliness among elderly women. International Journal of Humanities and Social Science Invention. 2013;2(2):10–14. [ Google Scholar ]
- [17]. Daniel K. Loneliness and Depression among University Students in Kenya ? Global Journal of Human Social Science. 2013;4(1.0) Online ISSN: 2249-460x. [ Google Scholar ]
- [18]. Holwerda1 TJ, Deeg J H D, Beekman T F A, Van Tilburg T G, Stek M L, Jonker Cees, Schoevers Robert A. Feelings of loneliness, but not social isolation, predict dementia onset: results from the Amsterdam Study of the Elderly (AMSTEL) J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry dec. 2012 doi: 10.1136/jnnp-2012-302755. doi:10.1136/jnnp-2012-302755. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- [19]. Wilson Robert S, Krueger Kristin R, Arnold Steven E, Schneider Julie A, Kelly Jeremiah F, Barnes Lisa L, Tang Yuxiao, Bennett David A. Loneliness and Risk of Alzheimer Disease. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2007;64:234–40. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.64.2.234. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- [20]. Raina SK, Raina S, Chander V, Grover A, Singh S, Bhardwaj A. Idientifying risk for ementia across population:A study on the prevalence of dementia in tribal elderly population of Himalayan region in Northern India. Ann Indian Acad Neurol. 2013;16(4):640–44. doi: 10.4103/0972-2327.120494. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- [21]. Hawkley LC, Cacioppo JT. Loneliness matters: a theoretical and empirical review of consequences and mechanisms. Ann Behav Med. 2010;14:218–27. doi: 10.1007/s12160-010-9210-8. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- [22]. Sadava S. W, Thompson M. M. Loneliness, social drinking, and vulnerability to alcohol prob1lems. Canadian Journal of Behavioural Science. 1986;18(2):19. [ Google Scholar ]
- [23]. Kim OS. The effects of loneliness on Alcohol Drinking, Smoking, and Health Perception in College Students. J Korean Acad Nurs. 1999;29(1):107–16. [ Google Scholar ]
- [24]. Akerlind Hörnquist JO. Loneliness and alcohol abuse: a review of evidences of an interplay. Soc Sci Med. 1992;34(4):405–14. doi: 10.1016/0277-9536(92)90300-f. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- [25]. Gibson Rebecca L, Hartshorne Timothy S. Childhood Sexual abuse and adult loneliness and network. Childabuse & Neglect. 1996;20(11):1087–93. doi: 10.1016/0145-2134(96)00097-x. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- [26]. Seidman B T, Marshall W. L, Hudson S M, Robertson P J. An Examination of Intimacy and Loneliness in Sex Offenders. Journal of Interpersonal Violence. 1994;Vol 9(4):518–34. [ Google Scholar ]
- [27]. Dhal A, Bhatia S, Sharma V, Gupta P. Adolescents Self esteem, Attachment and Loneliness. J Indian Assoc. Child Adolesc. Ment. Health. 2007;3(3):61–63. [ Google Scholar ]
- [28]. Cacioppo JT, et al. Lonely traits and concomitant physiological processes:The MacArthur Social Neuroscience Studies. Int. J Psychophys. 2000;35:143. doi: 10.1016/s0167-8760(99)00049-5. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- [29]. Stravynski A, Boyer R. Loneliness in Relation to Suicide Ideation and Parasuicide: A Population-Wide Study. The American Association for Suicidology Issue Suicide and Life- Threatening Behavior. 2001;31(1):32–40. doi: 10.1521/suli.31.1.32.21312. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- [30]. Wenz Friedrich V. Seasonal suicide attempts and forms of loneliness. Psychological Reports. 1977;40:807–10. doi: 10.2466/pr0.1977.40.3.807. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- [31]. Richman NE, Sokolove RL. The experience of aloneness, object representation, and evocative memory in borderline and neurotic patients. Psychoanalytic Psychology. 1992;9:77–91. [ Google Scholar ]
- [32]. Martens Willem H.J. Schizoid personality disorder linked to unbearable and inescapable loneliness. Eur. J. Psychiat. 2010;24(38-45):24 N.1. [ Google Scholar ]
- [33]. Mishra SK, Behera UK, Jena SK. Assessment and Evaluation of Depression and Loneliness among People Living with HIV in Selected Places of Coastal Andhra Pradesh. Indian J of Public Health Research and Development. 2013;4(3):261–66. [ Google Scholar ]
- View on publisher site
- PDF (72.3 KB)
- Collections
Similar articles
Cited by other articles, links to ncbi databases.
- Download .nbib .nbib
- Format: AMA APA MLA NLM
Add to Collections

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A Journal Impact Factor of 1.0 means that, on average, the articles published one or two years ago have been cited one time. A Journal Impact Factor of 2.5 means that, on average, the articles published one or two years ago have been cited two and a half times. The citing works may be articles published in the same journal.
The American Physical Society is conducting an international search for a new Lead Editor of Physical Review Research, our fully open access, ... 2023 Journal Impact Factors June 21, 2024. Clarivate Analytics has released the 2023 Journal Citation Reports, which provides journal impact factors and rankings for over 11,000 scholarly journals. ...
The Impact IF 2023 of Physical Review Research is 3.77, which is computed in 2024 as per its definition. Physical Review Research IF is decreased by a factor of 0.46 and approximate percentage change is -10.87% when compared to preceding year 2022, which shows a falling trend.
Physical Review Research. Physical Review Research (PRResearch) is a fully open access, ... 2023 Impact Factor* 1,159. Total Articles Published in 2023. 19,343. Total Citations in 2023. 1. 2023 Immediacy Index* 0.06129. 2023 Eigenfactor®* 2022 h5-index** * 2023 Journal Citation Reports (Clarivate Analytics, 2024).
Scope. Physical Review Research welcomes papers from the full spectrum of research topics of interest to the physics community. Research coverage in the journal comprises: fundamental and applied; theoretical and experimental, including technical and methodological advances; and interdisciplinary and newly emerging areas.
Physical Review is a peer-reviewed scientific journal established in 1893 by Edward Nichols.It publishes original research as well as scientific and literature reviews on all aspects of physics.It is published by the American Physical Society (APS). The journal is in its third series, and is split in several sub-journals each covering a particular field of physics.
Physical Review Research (PRResearch) is a fully open access, peer-reviewed journal welcoming the full spectrum of research topics of interest to the physics community and offering authors and ...
The latest impact score (IS) of the Physical Review Research is 4.23.It is computed in the year 2023 as per its definition and based on Scopus data. 4.23 It is decreased by a factor of around 0.18, and the percentage change is -4.08% compared to the preceding year 2021, indicating a falling trend.The impact score (IS), also denoted as the Journal impact score (JIS), of an academic journal is a ...
Physical Review Research Impact Factor 2024 . The latest impact factor of physical review research is 3.5 which is recently updated in June, 2024. The impact factor (IF) is a measure of the frequency with which the average article in a journal has been cited in a particular year. It is used to measure the importance or rank of a journal by ...
» Physical Review Research. Abbreviation: PHYS REV RES ISSN: N/A eISSN: 2643-1564 Category: PHYSICS, MULTIDISCIPLINARY - ESCI. WoS Core Citation Indexes: ESCI - Emerging Sources Citation Index. Journal Impact Factor (JIF): 3.5 5-year Impact Factor: 3.8 Best ranking: PHYSICS, MULTIDISCIPLINARY (Q1) ― Percentage rank: 77.3% . Open Access Support:
Physical Review Research (PRR) is a scholarly journal dedicated to publishing research in the field of Physics and Astronomy, and Published by American Physical Society. and its abbreviation is Phys Rev Res. The latest Impact Factor of the Physical Review Research for 2024-2025 is 4.2. The Publicaiton fees (APC) is $2755.
Physical Review Research (PRR) is a scholarly journal dedicated to publishing research in the field of Physics and Astronomy, and Published by American Physical Society. and its abbreviation is Phys Rev Res. The latest Impact Factor of the Physical Review Research for 2024-2025 is 4.2.
The 2023 impact factor of Physical Review Research is 3.562. This impact factor has been calculated by dividing the number of citations in the year 2023 to the articles published in 2021 and 2022. Physical Review Research published 1,237 and 1,180 articles in the years 2021 and 2022, which have received 4,622 and 3,988 citations in 2023 ...
Quantum-enhanced sensing promises to improve the performance of sensing tasks using nonclassical probes and measurements that require far fewer scene-modulated photons than the best classical schemes, thereby granting previously inaccessible information about a wide range of physical systems. We propose a generalized distributed sensing framework that uses an entangled quantum probe to ...
Physical Review Physics Education Research, the only APS publication indexed in the Social Sciences Citation Index as well as the Science Citation Index Expanded received its highest-ever Journal Impact Factor (3.1). Physical Review Accelerators and Beams, which this year celebrates 25 years of publication, was one of the first open access ...
Physical Review Research publishes original research contributions in the field of General Engineering and Technology, General Materials Science and General Physics. The journal is targeted at scholars, practitioners and scientists who are interested in such subjects of academic research. Physical Review Research features original scientific ...
Get access to Physical Review Research details, impact factor, Journal Ranking, H-Index, ISSN, Citescore, Scimago Journal Rank (SJR). Check top authors, submission guidelines, Acceptance Rate, Review Speed, Scope, Publication Fees, Submission Guidelines at one place. ... Physical Review Research : Impact Factor & More . eISSN: 2643-1564 pISSN ...
APS clearly intends for Physical Review Research to be less selective than PRL/PRX, as they elucidated in two volume 1 editorials: M. Thoennessen: "Editorial: Introducing Physical Review Research". We are launching Physical Review Research to achieve three main objectives: (1) to cover the entire range of topics in physics and related fields, including interdisciplinary and newly emerging ...
Aug 7, 2020. #4. f95toli. Science Advisor. Gold Member. 3,508. 1,068. Phys rev B is a very good journal. Phys rev A, B, App etc are often the "default" journals for high-quality basic research aimed at a specialised audience so it is going to be one of the journals your peers will be keeping an eye on. .
Clarivate Analytics has released the 2023 Journal Citation Reports, which provides journal impact factors and rankings for over 11,000 scholarly journals. The Physical Review journals continue to hold its world-leading positions among titles publishing high quality, peer-reviewed research in physics and related areas of research.
In a randomized, controlled trial of 52 obese men (BMI 31.3 ± 2.0 kg/m 2), Ross et al. demonstrated a body weight decrease of 7.5 kg over 3 months in the exercise-only group (16 men) that was comparable to that of the calorie-restricted group. Duration of exercise was based on the goal of a daily 700-calorie energy expenditure (∼60 min/day ...
As has been discussed in this review, various factors, for example, hormones, neuroendocrine mediators, peptides, and neurotransmitters are involved in the body's response to stress. ... Harris G, Reichlin S. The effect of emotional and physical stress on thyroid activity in the rabbit. J Physiol. 1954;126:29-40. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1954 ...
The impact of life stressors has also been studied within the context of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) spectrum disease. Leserman et al. (2000) followed men with HIV for up to 7.5 years and found that faster progression to AIDS was associated with higher cumulative stressful life events, use of denial as a coping mechanism, lower ...
Therefore, ED is typically linked to a web of closely interrelated cardiovascular risk factors such as physical inactivity, obesity, hypertension, and metabolic syndrome. Physical activity (PA) has proved to be a protective factor against erectile problems, and it has been shown to improve erectile function for men affected by vascular ED.
3.2.2. Physical Activity. An extensive body of literature documents the impacts of access to green spaces or surrounding greenness on physical activity in children and adults. Proximity to green spaces may promote physical activity by providing a space for walking, running, cycling, and other activities.
4.3. Physical Activity and Exercise as It Pertains to Sleep throughout the Lifespan. In a variety of conditions such as cardiovascular disease, type 2 diabetes, depression, some cancers, and arthritis, physical activity and exercise are advocated as effective interventions for the treatment of disordered sleeping [26-28]. How exercise should ...
The dearth of literature in the Indian context also indicated that more research was needed to evaluate and implement interventions for physical activity tailored to the Indian context. Keywords: anxiety, depression, morbidity, mental health, physical activity. Introduction and background. Physical activity has its origins in ancient history.
Research addressing loneliness has increased dramatically over the past 2 decades; however, despite the mental health risks associated with being lonely, the relationship between loneliness and psychiatric disorders has not been sufficiently explored .In India very little research has been done on psychological and physical affects of loneliness.