Home — Essay Samples — Sociology — Globalization — Globalization Pros And Cons

Globalization Pros and Cons
- Categories: Globalization
About this sample

Words: 570 |
Published: Jun 13, 2024
Words: 570 | Page: 1 | 3 min read
Table of contents
Pros of globalization, cons of globalization.

Cite this Essay
To export a reference to this article please select a referencing style below:
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Verified writer
- Expert in: Sociology

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
1 pages / 619 words
2 pages / 977 words
6 pages / 2622 words
4 pages / 2116 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online
Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on Globalization
The impact of globalization on employment is a multifaceted phenomenon that has brought about significant changes in the world of work. As economies and societies become increasingly interconnected, the dynamics of employment [...]
Globalization, a process characterized by the increasing interconnectedness and interdependence of the world's markets and businesses, has sparked extensive debate over its benefits and drawbacks. The phenomenon has transformed [...]
Globalization is the key word of having this huge world coming very small. It has changed the way many people think, behave, react, talk, dress and take actions in different fields. It made the international aspects from all [...]
European Commission. (2019). Voting and standing as a candidate in another EU country. Retrieved from 127-141.
In popular discourse, globalization is often synonymous with internationalization, referring to the growing interconnectedness and interdependence of people and institutions throughout the world. Although these terms have [...]
Globalisation and overseas ventures have made today’s workplace boundarlyless where no one works in isolation (Friedman, 2005). In fact today’s work environment is characterised as volatile, uncertain, complex, and ambiguous [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
Advantages And Disadvantages Of Globalization Essay
Adele Green
Globalization has been a transformative phenomenon in the modern world, shaping economies, cultures, and technologies in profound ways. As nations become more interconnected, barriers to trade, communication, and travel have significantly decreased. This essay aims to explore both the advantages and disadvantages of globalization, offering a balanced perspective on its multifaceted impact. One of the most significant advantages of globalization is economic growth. By opening up markets, nations can trade freely, leading to increased production and consumption worldwide. Companies can access a larger customer base, and consumers benefit from a greater variety of goods and services. Additionally, globalization often brings about more efficient allocation of resources due to comparative advantages, where countries specialize in producing goods they can create most efficiently. This can lead to lower prices and improved quality of life for people around the world. Furthermore, foreign direct investment increases as companies invest in different regions, spurring development and job creation in host countries. However, globalization is not without its disadvantages. One major concern is the economic disparity it can cause. While some countries and individuals thrive, others may find themselves left behind, exacerbating income inequality both within and between nations. Developing countries often face the brunt of this inequality, struggling to compete with more developed nations and multinational corporations. Additionally, globalization can lead to the exploitation of labor, with companies sometimes prioritizing profit over ethical labor practices. This can result in poor working conditions, low wages, and violation of workers’ rights, particularly in countries with lax labor regulations. Cultural homogenization is another drawback. As global brands and Western culture spread, local traditions and identities can be overshadowed. This can result in the loss of cultural diversity and heritage, diminishing the unique cultural landscapes that define different regions. Moreover, the dominance of a few languages, especially English, can undermine linguistic diversity, leading to the extinction of lesser-known languages. Environmental degradation is also a critical disadvantage of globalization. The increased production and consumption driven by globalization contribute to environmental challenges such as climate change, deforestation, and pollution. Industrial activities and global supply chains often prioritize economic gain over sustainability, exacerbating environmental issues. Countries with fewer resources to combat these problems may suffer the most, facing severe environmental and health consequences. In conclusion, globalization presents a complex array of advantages and disadvantages. While it promotes economic growth, enhances consumer choices, and encourages efficiency, it also risks increasing economic inequality, cultural loss, labor exploitation, and environmental degradation. A balanced approach to globalization is crucial, where its benefits can be maximized while mitigating its adverse effects. Policymakers, businesses, and individuals must work collaboratively to ensure that globalization becomes a force for good, fostering sustainable development and inclusive prosperity for all.
Say Goodbye to Annoying AI Checkers. Try These Undetectable AI Paraphrasers & Undetectable AI Essay Writers Below to Get Undetectable, Plagiarism-Free Essays >>
https://essaygpt.hix.ai/
Essay AI: AI Essay Writer - Essay Generator - Avoid AI Detection
Essayai is the ultimate undetectable ai essay writer to generate 100% human essays and papers. remove ai detection and….
https://bypassgpt.ai/
https://bypass.hix.ai/
AI Humanizer: Convert AI to Natural & Human-Like Text for Free
Use aihumanizer.ai to humanize ai text and make it undetectable. our ai humanizer empowers you to get 100% human score….
aihumanizer.ai

Written by Adele Green
Text to speech
- Lifestyles & Social Issues
- Philosophy & Religion
- Politics, Law & Government
- World History
- Health & Medicine
- Browse Biographies
- Birds, Reptiles & Other Vertebrates
- Bugs, Mollusks & Other Invertebrates
- Environment
- Fossils & Geologic Time
- Geography & Travel
- Entertainment & Pop Culture
- Sports & Recreation
- Visual Arts

globalization

globalization , integration of the world’s economies, politics, and cultures. German-born American economist Theodore Levitt has been credited with having coined the term globalization in a 1983 article titled “The Globalization of Markets.” The phenomenon is widely considered to have begun in the 19th century following the advent of the Industrial Revolution , but some scholars date it more specifically to about 1870, when exports became a much more significant share of some countries’ gross domestic product (GDP). Its continued escalation is largely attributable to the development of new technologies—particularly in the fields of communication and transportation—and to the adoption of liberal trade policies by countries around the world.
Social scientists have identified the central aspects of globalization as interconnection, intensification, time-space distanciation (conditions that allow time and space to be organized in a manner that connects presence and absence), supraterritoriality, time-space compression, action at a distance, and accelerating interdependence. Modern analysts also conceive of globalization as a long-term process of deterritorialization—that is, of social activities (economic, political, and cultural) occurring without regard for geographic location. Thus, globalization can be defined as the stretching of economic, political, and social relationships in space and time. A manufacturer assembling a product for a distant market , a country submitting to international law , and a language adopting a foreign loanword are all examples of globalization.
Of course history is filled with such occurrences: Chinese artisans once wove silk bound for the Roman Empire ( see Silk Road ); kingdoms in western Europe honoured dictates of the Roman Catholic Church ; and English adopted many Norman French words in the centuries after the Battle of Hastings . These interactions and others laid the groundwork for globalization and are now recognized by historians and economists as important predecessors of the modern phenomenon. Analysts have labeled the 15th to 18th century as a period of “proto-globalization,” when European explorers established maritime trade routes across the Atlantic and Pacific oceans and encountered new lands. Integration prior to this time has been characterized as “archaic globalization.”
What distinguishes the process of modern globalization from those forms of global integration that preceded it are its pace and extent. According to some academics, three distinct eras of modern globalization can be identified, each of them marked by points of sudden acceleration in international interaction. Under this scheme, the “first globalization” era refers to the period between approximately 1870 and 1914, during which new transportation and communication technology decreased or eliminated many of the drawbacks to distance. The “second globalization” era is said to have lasted from roughly 1944 to 1971, a period in which an international monetary system based on the value of the U.S. dollar facilitated a new level of trade between capitalist countries. And the “third globalization” era is thought to have begun with the revolutions of 1989–90, which opened the communist Eastern bloc to the flow of capital and coincided with the creation of the World Wide Web . Some scholars argue that a new period of globalization, the “fourth globalization,” is underway, but there is little consensus on when this era began or whether it is truly distinct enough to merit its own designation.

New levels of interconnectedness fostered by globalization are credited for numerous benefits to humanity. The spread of industrial technology and the resulting increase in productivity have contributed to a reduction in the percentage of the world’s population living in poverty. The sharing of medical knowledge has dramatically decreased the incidence of once-feared diseases and even eliminated smallpox. And economic interdependence among countries discourages war between them.
However, the implementation of globalization has been much criticized, leading to the development of the anti-globalization movement. Opponents of globalization—or at least, globalization in its present form ( see neoliberal globalization )—represent a variety of interests on both the political left and right. Labour unions disdain multinational companies’ ability to move their operations to countries with cheaper labour; Indigenous peoples rue the difficulty of maintaining their traditions; and leftists object to the neoliberal character of the new world economy, arguing that the capitalist logic on which they contend globalization is based leads to asymmetrical power relations (both internationally and domestically) and transforms every aspect of life into a commodity. Right-wing critics of globalization believe that it threatens both national economies and national identity. They advocate national control of a country’s economy and rigidly restricted immigration.

Globalization has also produced effects that are more universally worrisome. Expanded transportation networks facilitate not only increased trade but also the spread of diseases. Undesirable trade, such as human trafficking and poaching, has flourished alongside legitimate commerce. Moreover, the pollution generated by the world’s modernization has resulted in global warming and climate change , threatening Earth’s very habitability.

Whether globalization will adapt to these problems remains to be seen, but it is already changing again. For example, globalization began in the 19th century with an explosion in exports, but, even before the COVID-19 pandemic that swept through the world in 2020 resulted in global lockdowns, trade as a share of many countries’ GDP had fallen. It can be argued that the global supply chains today rely more on knowledge than on labour . And services now constitute a larger share of the global economy than goods. A “fourth globalization” might indeed be here—or at least on the way.
- Business Essentials
- Leadership & Management
- Credential of Leadership, Impact, and Management in Business (CLIMB)
- Entrepreneurship & Innovation
- Digital Transformation
- Finance & Accounting
- Business in Society
- For Organizations
- Support Portal
- Media Coverage
- Founding Donors
- Leadership Team

- Harvard Business School →
- HBS Online →
- Business Insights →
Business Insights
Harvard Business School Online's Business Insights Blog provides the career insights you need to achieve your goals and gain confidence in your business skills.
- Career Development
- Communication
- Decision-Making
- Earning Your MBA
- Negotiation
- News & Events
- Productivity
- Staff Spotlight
- Student Profiles
- Work-Life Balance
- AI Essentials for Business
- Alternative Investments
- Business Analytics
- Business Strategy
- Business and Climate Change
- Creating Brand Value
- Design Thinking and Innovation
- Digital Marketing Strategy
- Disruptive Strategy
- Economics for Managers
- Entrepreneurship Essentials
- Financial Accounting
- Global Business
- Launching Tech Ventures
- Leadership Principles
- Leadership, Ethics, and Corporate Accountability
- Leading Change and Organizational Renewal
- Leading with Finance
- Management Essentials
- Negotiation Mastery
- Organizational Leadership
- Power and Influence for Positive Impact
- Strategy Execution
- Sustainable Business Strategy
- Sustainable Investing
- Winning with Digital Platforms
6 Pros and Cons of Globalization in Business to Consider

- 01 Apr 2021
Throughout history, commerce and business have been limited by certain geographic constraints. In its earliest days, trade happened between neighboring tribes and city-states. As humans domesticated the horse and other animals, the distances they could travel to trade increased. These distances increased further with the development of seafaring capabilities.
Although humans have been using ships for centuries to transport goods, cargo, people, and ideas around the world, it wasn’t until the development of the airplane that the blueprint of a “globalized economy” was laid. This was for a simple reason: You can travel greater distances faster than ever before.
The development of the internet accelerated this process even more, making it easier to communicate and collaborate with others. Today, your international co-worker, business partner, customer, or friend is only a few taps or clicks away.
Globalization has had numerous effects—both positive and negative—on business and society at large. Here’s an overview of the pros and cons of globalization in business.
Access your free e-book today.
What Is Globalization?
Globalization is the increased flow of goods, services, capital, people, and ideas across international boundaries according to the online course Global Business , taught by Harvard Business School Professor Forest Reinhardt.
“We live in an age of globalization,” Reinhardt says in Global Business . “That is, national economies are even more tightly connected with one another than ever before.”
How Globalization Affects Daily Life
Globalization has had a significant impact on various aspects of daily life.
For example, it’s changed the way consumers shop for products and services. Today, 70 percent of Americans shop online. In 2022, there were 268 million digital buyers in the US and by 2025, this number is predicted to reach 285 million.
In addition, the globalized economy has opened up new job markets by making it more feasible to hire overseas workers. This has created a wide range of career opportunities for both job seekers and employers.
The emergence of remote work post-pandemic was also made possible by globalization. According to a survey from WFH Research , only seven percent of paid workdays in the US were remote in 2019. However, this number climbed to 29 percent by January 2024.
Check out the video below to learn more about globalization, and subscribe to our YouTube channel for more explainer content!
Advantages of Globalization
1. economic growth.
It’s widely believed that one of the benefits of globalization is greater economic growth for all parties. There are several reasons why this might be the case, including:
- Access to labor: Globalization gives all nations access to a wider labor pool. Developing nations with a shortage of knowledge workers might, for example, “import” labor to kickstart industry. Wealthier nations, on the other hand, might outsource low-skill work to developing nations with a lower cost of living to reduce the cost of goods sold and pass those savings on to the customer.
- Access to jobs: This point is directly related to labor. Through globalization, developing nations often gain access to jobs in the form of work that’s been outsourced by wealthier nations. While there are potential pitfalls to this (see “Disproportionate Growth” below), this work can significantly contribute to the local economy.
- Access to resources: One of the primary reasons nations trade is to gain access to resources they otherwise wouldn’t have. Without this flow of resources across borders, many modern luxuries would be impossible to manufacture or produce. Smartphones, for example, are dependent on rare earth metals found in limited areas around the world.
- The ability for nations to “specialize”: Global and regional cooperation allow nations to heavily lean into their economic strengths, knowing they can trade products for other resources. An example is a tropical nation that specializes in exporting a certain fruit. It’s been shown that when nations specialize in the production of goods or services in which they have an advantage, trade benefits both parties.

2. Increased Global Cooperation
For a globalized economy to exist, nations must be willing to put their differences aside and work together. Therefore, increased globalization has been linked to a reduction—though not an elimination—of conflict.
“Of course, as long as there have been nations, they've been connected with each other through the exchange of lethal force—through war and conquest—and this threat has never gone away,” Reinhardt says in Global Business . “The conventional wisdom has been that the increased intensity of these other flows—goods, services, capital, people, and so on—have reduced the probability that the world's nations will fall back into the catastrophe of war.”

3. Increased Cross-Border Investment
According to the course Global Business , globalization has led to an increase in cross-border investment. At the macroeconomic level, this international investment has been shown to enhance welfare on both sides of the equation.
The country that’s the source of the capital benefits because it can often earn a higher return abroad than domestically. The country that receives the inflow of capital benefits because that capital contributes to investment and, therefore, to productivity. Foreign investment also often comes with, or in the form of, technology, know-how, or access to distribution channels that can help the recipient nation.
Disadvantages of Globalization
1. increased competition.
When viewed as a whole, global free trade is beneficial to the entire system. Individual companies, organizations, and workers can be disadvantaged, however, by global competition. This is similar to how these parties might be disadvantaged by domestic competition: The pool has simply widened.
With this in mind, some firms, industries, and citizens may elect governments to pursue protectionist policies designed to buffer domestic firms or workers from foreign competition. Protectionism often takes the form of tariffs, quotas, or non-tariff barriers, such as quality or sanitation requirements that make it more difficult for a competing nation or business to justify doing business in the country. These efforts can often be detrimental to the overall economic performance of both parties.
“Although we live in an age of globalization, we also seem to be living in an age of anti-globalization,” Reinhardt says in Global Business . “Dissatisfaction with the results of freer trade, concern about foreign investment, and polarized views about immigration all seem to be playing important roles in rich-country politics in the United States and Europe. The threats in Western democracy to the post-war globalist consensus have never been stronger.”
2. Disproportionate Growth
Another issue of globalization is that it can introduce disproportionate growth both between and within nations. These effects must be carefully managed economically and morally.
Within countries, globalization often has the effect of increasing immigration. Macroeconomically, immigration increases gross domestic product (GDP), which can be an economic boon to the recipient nation. Immigration may, however, reduce GDP per capita in the short run if immigrants’ income is lower than the average income of those already living in the country.
Additionally, as with competition, immigration can benefit the country as a whole while imposing costs on people who may want their government to restrict immigration to protect them from those costs. These sentiments are often tied to and motivated—at least in part—by racism and xenophobia.
“Meanwhile, outside the rich world, hundreds of millions of people remain mired in poverty,” Reinhardt says in Global Business. “We don't seem to be able to agree about whether this is because of too much globalization or not enough.”
3. Environmental Concerns
Increased globalization has been linked to various environmental challenges, many of which are serious, including:
- Deforestation and loss of biodiversity caused by economic specialization and infrastructure development
- Greenhouse gas emissions and other forms of pollution caused by increased transportation of goods
- The introduction of potentially invasive species into new environments
While such issues are governed by existing or proposed laws and regulations, businesses have made climate change concerns and sustainability a priority by, for example, embracing the tenets of the triple bottom line and the idea of corporate social responsibility .

Managing the Risks of Globalization
The world is never going to abandon globalization. While it’s true that individual countries and regions put policies and practices in place that limit globalization, such as tariffs, it’s here to stay. The good news is that businesses and professionals willing to prepare for globalization’s challenges by developing strong social impact skills have the potential to benefit immensely.
Whether you’re a business owner, member of executive leadership, or an employee, understanding the impacts of globalization and how to identify its opportunities and risks can help you become more effective in your role and drive value for your organization.
Taking a course like Global Business is one path toward developing international business skills and gaining an understanding of the macroeconomic, political , and social conditions that continue to impact globalization.
Are you interested in breaking into a global market? Sharpen your knowledge of the international business world with Global Business , one of our online business in society courses . If you aren't sure which course is the right fit, download our free course flowchart .
This post was updated on February 26, 2024. It was originally published on April 15, 2021.

About the Author
Globalization: Concept, Advantages and Disadvantages Essay
Reasons for choosing the topic.
Globalization is the historical process of the world’s transformation into the unified system that would have the uniform characteristics. Each person in the global society is involved in this process and contributes to its development through his/her everyday life decisions and actions. Thus, the comprehension of factors influencing globalization, as well as the individual’s role in the process, is of significant interest.
The lecture examines globalization from multiple points of view: cultural/religious, economic, and historical. The historical and cultural analysis of globalization allows identification of causes and people’s motivation that underlie the process development. The lecture provokes the interest to the evaluation of the consequences of globalization.
The accumulation of the first experience has started with watching the different documentary and feature movies about the global and cultural integration such as The Cup , The Corporation , Mumbai Calling , and others. They tell the stories of individuals from different countries and depict the globalization as an inevitable process-affecting people live to a large extent.
Globalization has many implications: cultural, economic, national, and individual. Since each individual takes part in globalization, it is important for him/her to know about their responsibilities before the other people and the environment. Learning the information about the process of global integration may help to avoid negative impacts on various aspects of human life.
Understanding of globalization
Before the course, there was a little interest to the topic. The significance of globalization was evident – its impact on the social structure, environment, and economy is extensive.
The United Kingdom is involved in globalization to a large extent. The country is one of the main participants in the global trade, industrialisation, and urbanisation. Moreover, the UK society consists of many nationalities and ethnicities.
The investigation of the topic will allow becoming a good citizen of the country and world. It will support the conscious decision-making, consumption, and interactions.
Definitions
Globalization is ‘a contemporary term used in academic and nonacademic contexts to describe a late twentieth- and early twenty-first-century condition of economic, social, and political interdependence across cultures, societies, nations, and regions that has been precipitated by an unprecedented expansion of capitalism on a global scale’ (Lowe 2014).
Globalization is the increase in the influence of the external factors (economic, social and cultural) on the reproduction of all the nations involved in this process; the formation of a single world market (markets) without national barriers, and the creation of common legal terms for all countries (Matthews 2014).
Globalization is the process of the technological changes supporting the proliferation of the products and goods around the globe; the rapid development of the informational technologies and devices that helps to constrict the gaps between the people; and the formation of the global ideologies (cultures), such as ecologic and the human rights movement.
Advantages and disadvantages of globalization
Globalization by John Madeley. The author claims that globalization benefits the richer part of the world and, at the same time, doesn’t provide any advantages for the poorer half of the global society.
The issue of social and economic inequality is up-to-date. Thus, it is important to know all the potential causes of it.
‘The engine of globalization is free trade, liberalization, no restrictions to trade’ (Madeley 2009). However, these concepts do not benefit the poor citizens because of the inappropriate policies and lack of globalization’s regulation.
The provided information makes it clear that some changes at the governmental level should be made. It is important for the international community officials to undertake measures to improve the situation in the developing part of the world.
Ethical dilemmas
The ethical problems of globalization by Niadi Cernica. The study investigates the negative effects of globalization on the poor, underdeveloped countries.
Globalization implies multiple ethical and moral issues as its negative impacts on society and environment are observed.
The cultural integration that takes place in the modern world provokes the dissemination of values of material well-being and financial prosperity, as well as the standards of the high-quality life (Cernica 2011). At the same time, at the current stage of the social development, these values are unapproachable to the significant portion of people. Thus, globalization is considered unethical.
The balance between the ideological perfectionism and the real situation must be found.
Globalization and international communication
In Commentary: globalization and science communication , Susanna Horing Priest explores the beneficial effects of the global integration on the informational and cultural exchange, as well as the economic development.
The comprehension of the positive sides of globalization helps to consolidate and strengthen the beneficial effects on the social development.
Globalization provides the advantages of the international cooperation in business, science, and knowledge exchange. To a large extent, the process is provoked by the development of media and informational technologies (Priest 2000).
The intercultural communication, especially in the field of science, helps to enhance the technologic, medical, and business innovation and exploration. It increases the accessibility of science in the less developed countries.
Urbanization
The global urbanisation is stimulated by the economic and technological development, and the process gathers momentum – nowadays, more than a half of the world’s population lives in the urban areas.
The large urban community is diverse in many aspects: culture, socioeconomic status, ethnicity, education, etc. The population diversity creates difficulties in the social communication and interrelations. The issues of the social inequality, crime, and discrimination are up-to-date in the industrial cities.
Despite the fact that urbanisation provokes technological and economic progress, the environmental and social problems caused by the urban development indicate the inefficiency of the urban planning and lack of the environmental protection policies. The current issues prove that the changes in the government regulations are needed.
International trade
Globalization provoked the expansion of the goods distribution streams worldwide. As a result, the economy in many countries experiences the significant growth.
The liberalization of cross-national trade contributes to the development of relationships among the number of countries involved in these agreements. Globalization helps to remove the trade barriers between the nations, and it is expected that all the parties involved in the trade process attain the relevant economic benefits.
Negative impacts: increase of consumption and the deterioration of the natural environment.
Global warming caused by the extensive greenhouse gasses emissions during the transportation of goods is regarded as one of the most significant issues.. According to the recent statistics, since the end of the 20 th century, the emissions caused by the cross-national aviation has been increased to over 50%, and the further expansion of the international trade will provoke even greater increases (Abe, Hattori, & Kawagoshi, 2014, p. 468).
Primary research: effects of globalization on environmental state
The globalization processes including the international commercial cooperation, trade, transportation, and the global politics largely impact the environmental condition and the national ecological policies. The majority of the environmental problems are of the cross-national character, and the global community must be involved in their resolving.
Frequently, the environmental expenses are ignored in the international trade because the businessmen want to attain the financial benefits and attract the international investments (Abe, Hattori & Kawagoshi 2014). Moreover, the decrease of the ecological standards and the increase of the natural resources consumption take place. It leads to the environmental degradation.
Technologic advancement stimulated by globalization provokes the positive effects on the environment. The increase of the population income induces the environmental protection requirements.
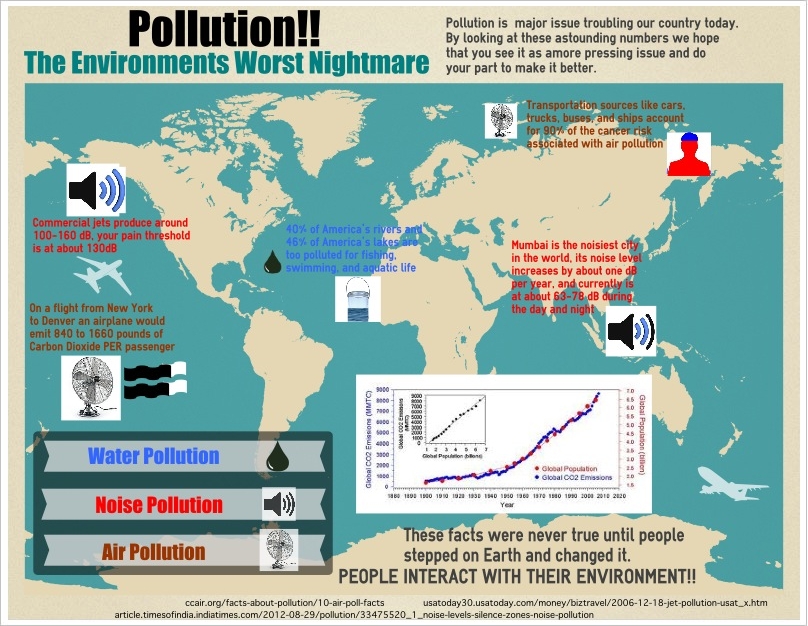
Understanding globalization after research
The research helped to understand the impacts of globalization more profoundly.
The global integration has both advantages (i.e. technology and science development) and disadvantages (i.e. environmental pollution and social inequality).
It is important to know about the negative and positive effects of globalization because only through the critical analysis it is possible to prevent the potentially disastrous outcomes or facilitate the achievement of better results.

Reflection on learning experience
The globalization research assisted the expansion of knowledge regarding the issue. The knowledge became multidimensional and more detailed than before.
In a vast amount of information, sometimes it may be hard to find the reliable and valid sources.
The literature review and critical analysis of the previous study findings is one of the best tools of research.
It is better to avoid such methods of the information collection as watching documentaries or interviews. Although, the received information may be valuable, these methods are rather time-consuming.
Next time, a larger number of aspects related to the topic will be researched.
Further exploration
It would be useful to include the social and economic aspects of globalization in the further research. The positive effects of the cultural integration need some more focus.
The methods of the literature review will be implemented for the further exploration. The analysis of the academic articles or case studies may be regarded as reliable sources of information.
The issues of globalization affect each single person. Therefore, this topic of research is of significant interest.
The process of building knowledge requires the individual’s investment of mental strengths and abilities. It requires logical and rational approach, yet it is an exciting process. The comprehensive research of the information contributes to the knowledge development to the largest extent. The development of the skills in research may be regarded a step in the personal and professional growth.
The research should cover multiple aspects of the issue because understanding every single constituent of the problem leads to the generation of the holistic picture. The comprehension of the basic topical elements and the connections between them is essential in this regard.
Abe, K, Hattori, K & Kawagoshi, Y 2014, ‘Trade liberalization and environmental regulation on international transportation’, The Japanese Economic Review, vol. 65, no. 4, pp. 468-482.
Cernica, N 2011, ‘the ethical problems of globalization’, Euromentor Journal, vol. 2, no. 1, pp. 85-90.
Lowe, L 2014, ‘Globalization’, in B Burgett & G Hendler (eds.), Keywords for American cultural S tudies, New York University Press, New York, pp. 345-347.
Madeley, J 2009, “Globalization”, Appropriate Technology, vol. 36, no. 1, pp. 52-53.
Matthews, J 2014, Encyclopedia of environmental change , SAGE Publications, Thousand Oaks.
Priest, S H 2000, Commentary: globalization and science communication , Science Communication, vol. 21, no. 3, pp. 219-222.
- Our Global Neighborhood by Commission on Global Governance
- International Trading in the Global Economy
- Financial Globalization Advantages & Disadvantages
- Globalization: What Globalization Is and Its Impact
- Globalization Positive and Negative Impacts
- Global Communications: The Case of China
- West African Maritime Trade and Globalization
- How Is Globalization Affecting Rates of Disease
- International Business and Its Response to Institutional Voids
- Russia Economy and Recent News
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2022, November 12). Globalization: Concept, Advantages and Disadvantages. https://ivypanda.com/essays/globalization-concept-advantages-and-disadvantages/
"Globalization: Concept, Advantages and Disadvantages." IvyPanda , 12 Nov. 2022, ivypanda.com/essays/globalization-concept-advantages-and-disadvantages/.
IvyPanda . (2022) 'Globalization: Concept, Advantages and Disadvantages'. 12 November.
IvyPanda . 2022. "Globalization: Concept, Advantages and Disadvantages." November 12, 2022. https://ivypanda.com/essays/globalization-concept-advantages-and-disadvantages/.
1. IvyPanda . "Globalization: Concept, Advantages and Disadvantages." November 12, 2022. https://ivypanda.com/essays/globalization-concept-advantages-and-disadvantages/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Globalization: Concept, Advantages and Disadvantages." November 12, 2022. https://ivypanda.com/essays/globalization-concept-advantages-and-disadvantages/.
- To find inspiration for your paper and overcome writer’s block
- As a source of information (ensure proper referencing)
- As a template for you assignment
IvyPanda uses cookies and similar technologies to enhance your experience, enabling functionalities such as:
- Basic site functions
- Ensuring secure, safe transactions
- Secure account login
- Remembering account, browser, and regional preferences
- Remembering privacy and security settings
- Analyzing site traffic and usage
- Personalized search, content, and recommendations
- Displaying relevant, targeted ads on and off IvyPanda
Please refer to IvyPanda's Cookies Policy and Privacy Policy for detailed information.
Certain technologies we use are essential for critical functions such as security and site integrity, account authentication, security and privacy preferences, internal site usage and maintenance data, and ensuring the site operates correctly for browsing and transactions.
Cookies and similar technologies are used to enhance your experience by:
- Remembering general and regional preferences
- Personalizing content, search, recommendations, and offers
Some functions, such as personalized recommendations, account preferences, or localization, may not work correctly without these technologies. For more details, please refer to IvyPanda's Cookies Policy .
To enable personalized advertising (such as interest-based ads), we may share your data with our marketing and advertising partners using cookies and other technologies. These partners may have their own information collected about you. Turning off the personalized advertising setting won't stop you from seeing IvyPanda ads, but it may make the ads you see less relevant or more repetitive.
Personalized advertising may be considered a "sale" or "sharing" of the information under California and other state privacy laws, and you may have the right to opt out. Turning off personalized advertising allows you to exercise your right to opt out. Learn more in IvyPanda's Cookies Policy and Privacy Policy .
30 Globalization Pros and Cons

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
Learn about our Editorial Process
Definition: Globalization refers to the increasing global interconnectedness of nations. It it not only economic integration. It also refers to cultural , technological , social , and political integration (Dincer et al., 2018). A good catch-all definition comes from Hodos (2016), who writes: “Globalization is defined as the process of becoming globally connected.”

| Pros of Globalization | Cons of Globalization |
|---|---|
Globalization Pros and Cons
The advantages of globalization, 1. increased economic growth.

Globalization facilitates technology, knowledge, and goods transfer, which in turn boosts economic growth (Erixon, 2018).
Through globalization, countries can now purchase the newest technologies and import the most productive machinery from other countries.
This means every country now has access to the most productive machineries, making the whole world more productive. Productivity means more output, which means more economic growth.
2. Cultural exchange and diversity
Globalization facilitates cultural exchange and diversity by increasing interactions among people from different parts of the world through trade, travel, and communication.
This exposure leads to the sharing of ideas, traditions, languages, and values across borders, enriching the cultural landscape of participating societies.
Such interactions often lead to the fusion of cuisines, music, art, and fashion, creating new, hybrid forms of cultural expression.
3. Improvement in global communication

Globalization is both caused by and a catalyst for the expansion of global technology and telecommunications. For example, the internet helps facilitate global trade, and demand for a fast and reliable global internet has stimulated its technological development.
The resulting interconnectedness allows for real-time communication across different countries, breaking down geographical and temporal barriers. The result is a more integrated world where cultural and professional exchanges occur more seamlessly.
4. Greater access to foreign investment

Globalization leads to greater access to foreign investment. With broken-down financial barriers, businesses can now source overseas investors for funds. This helps push down the cost of investment and stimulate local business (Erixon, 2018).
It’s also good for investors. They can diversify their portfolios by investing in different countries, and developing countries can benefit from foreign capital to fund growth and development projects.
This influx of foreign investment can lead to economic growth, technological advancements, and increased employment opportunities in the recipient countries.
5. Access to new markets for businesses

200 years ago, everyday small businesspeople could generally only trade with nearby communities. They had to get goods to market via horse and cart and anything perishable had to be consumed fast. There were no refigerators!
Today, with global supply chains, refrigerators, and free trade agreements, even small businesspeople have access to global markets.
Companies can therefore expand their operations and customer base beyond their domestic markets, tapping into demand in different countries (Erixon, 2018).
6. Increased migration opportunities

Globalization has opened up global labor markets. Nowadays, it takes less than 24 hours to move anywhere across the world. No more 3-month boat rides! This has allowed highly-skilled professionals to cross the world and get jobs exactly where there is market demand.
This mobility benefits migrants through better opportunities, the companies by linking them up with the best possible employees, and also contributes to the cultural and economic dynamism of the host countries (Dumont, Rayp & Willemé, 2012).
7. Reduction in prices of goods and services

Globalization leads to a reduction in prices of goods and services by allowing countries to specialize in producing goods where they have a comparative advantage, leading to more efficient production and lower costs (Mir, Hassan & Qadri, 2014).
The removal of trade barriers and the increased competition in global markets drive down prices, making products more affordable for consumers (Erixon, 2018).
Additionally, the global supply chain means consumers have access to a wider variety of goods and services from different parts of the world.
8. Increased competition leading to innovation

Globalization leads to increased competition because you’re no longer just competing with Bob down the road. Businesses are now competing with other businesses from the other side of the world (Erixon, 2018).
While at first this competition sounds bad, it tends to have positive effects. For example, it spurs innovation as companies strive to maintain their competitive edge in a global market.
The exposure to different market needs and technological advancements across borders encourages businesses to innovate and improve their products and services.
This competition not only drives technological advancement but also leads to better quality and diverse options for consumers.
9. Opportunity for developing countries to develop faster

Developing countries need foreign investment and access to foreign markets in order to grow. Globalization provides this access (Mir, Hassan & Qadri, 2014).
This exposure to global markets and capital can accelerate economic growth, create jobs, and promote infrastructure development.
Furthermore, the exchange of knowledge and best practices with developed nations can enhance the skills and capacities of the workforce in developing countries, leading to sustainable development.
10. Spread of democratic values

Some argue that globalization has led to the spread of democratic values. Arjun Appadurai calls this the “ideoscape” of globalization.
The global spread of media and the internet allows for the rapid dissemination of democratic ideals and human rights concepts.
We saw this, for example, during the Arab Spring of 2011, where activist groups multiple countries in the Arab world collaborated via social media to demand democratic reforms.
11. Global talent pool for employment

Globalization leads to a global talent pool for employment as businesses and organizations have access to a wider range of skills and expertise from around the world (Dumont, Rayp & Willemé, 2012).
Enhanced mobility and interconnectedness allow employers to recruit talent from different countries, enabling them to meet specific skill requirements more effectively.
This global workforce diversifies the workplace, fosters innovation, and enhances competitiveness by bringing together diverse perspectives and experiences.
12. Enhanced opportunities for high-skilled workers

Globalization leads to enhanced opportunities for high-skilled workers as it opens up a vast array of international job opportunities in various sectors, including technology, finance, and healthcare (Dumont, Rayp & Willemé, 2012).
These workers can leverage their specialized skills in a broader market, often finding better employment prospects, higher salaries, and advanced career development options globally.
Moreover, the exchange of expertise and knowledge across borders contributes to professional growth and the advancement of specialized fields.
13. Enhanced global cooperation and peace

Globalization could also, in an optimistic scenario, lead to enhanced global cooperation and peace. This is based on the theory that increasing economic interdependence among nations encourages diplomatic relations and collaboration rather than war (Baldwin, 2008).
The shared interests in maintaining stable trade and investment environments promote peaceful interactions and reduce the likelihood of conflicts.
Furthermore, international institutions and agreements foster a platform for dialogue and conflict resolution, contributing to global stability and peace.
14. Widening networking opportunities

Globalization leads to widening networking opportunities as it connects people from different cultures and professional backgrounds through international business, education, and social media platforms.
These connections facilitate the exchange of ideas, collaboration on projects, and the formation of global communities with shared interests and goals.
This extensive networking can lead to new business opportunities, partnerships, and innovations, benefiting individuals and organizations alike (Dumont, Rayp & Willemé, 2012).
15. Access to more goods for consumers

Globalization leads to access to more goods for consumers by breaking down trade barriers and enabling the efficient flow of products across borders (Mir, Hassan & Qadri, 2014).
Amazon Canada doesn’t have the product? No problem, try Amazon UK instead!
This results in a wider variety of goods available in the market, often at lower prices due to increased competition and economies of scale in production.
Consumers benefit from the improved quality, variety, and affordability of products, enhancing their purchasing choices and overall quality of life.
Disadvantages of Globalization
1. widening of economic disparities.

While the above positives sound good, many like Naomi Klein argue that globalization can lead to the widening of economic disparities as it often benefits developed nations and those with competitive advantages, while less developed countries may struggle to keep up.
This can result in increased wealth for certain regions and sectors, while others may experience stagnation or decline in economic growth. The result is a growing gap between the rich and the poor, both within and between countries.
2. Cultural Homogenization (Loss of local cultures)

There is an argument that globalization can lead to the loss of local cultures and identities as global brands and Western media dominate, overshadowing local traditions, languages, and practices.
We call this ‘ cultural homogenization ‘.
The spread of a homogenized global culture can dilute the uniqueness of local cultures, leading to a decrease in cultural diversity. People may adopt global trends at the expense of traditional values and customs, leading to a loss of cultural heritage.
Others dispute this claim, arguing instead that globalization leads to a process called glocalization .
3. Exploitation of labor in developing countries

Globalization can lead to the exploitation of labor in developing countries (Sharma, 2014). Multinational companies may seek to minimize costs by relocating production to regions where labor is cheaper and regulations are less stringent (e.g. opening up factories in Mexico and China instead of midwestern USA).
This can result in poor working conditions, low wages, and a lack of labor rights, exploiting the workforce in these countries. The pursuit of profit by global corporations can overshadow the need for ethical labor practices, leading to exploitation.
4. Environmental degradation

Environmentalists are often concerned that globalization is exacerbating environmental degradation. Increased industrial activity and international transportation contribute to pollution and natural resource depletion (Mir, Hassan & Qadri, 2014).
The global demand for goods encourages mass production, often without adequate environmental safeguards, leading to habitat destruction, loss of biodiversity, and climate change.
The focus on economic growth and consumerism can overshadow the need for sustainable environmental practices, exacerbating global environmental challenges.
5. Increased risk of financial contagion

Globalization leads to an increased risk of financial contagion as economies become more interconnected, meaning that financial crises can quickly spread from one country to another (Mendoza & Quadrini, 2010; Mir, Hassan & Qadri, 2014).
This interdependence is due to global investment and the intertwined nature of banking and financial markets.
A financial problem in one country can lead to investor panic and a loss of confidence, triggering a domino effect that impacts economies worldwide.
6. Over-dependence on global markets
Globalization leads to concerns that countries are over-dependent on foreign markets for essential supplies.
This dependence can make economies vulnerable when supply chains break down. When a major global shock occurs, countries heavily reliant on that market for exports or investment can experience significant economic disruptions (Mendoza & Quadrini, 2010).
For example, most nations in the world are reliant on Taiwan for computer chips. If Taiwan were suddenly invaded by China, the rest of the world won’t be able to produce sufficient computers!
7. Threat to local businesses and industries

In a globalized marketplace, local businesses face intense competition from larger multinational corporations.
These multinationals often have greater resources, technology, and access to larger markets, which can overshadow local enterprises (Burlacu, Gutu & Matei, 2018).
This intense competition can lead to the closure of local businesses, loss of traditional industries, and a decrease in domestic job opportunities.
8. Erosion of national sovereignty

National sovereignty is threatened by a globalized world. Governments may be compelled to alter their policies and regulations to attract global investment and remain competitive in the international market, locking themselves into international trade agreements that require compromise and cooperation (Burlacu, Gutu & Matei, 2018).
This can result in countries losing control over their economic, social, and environmental policies, potentially prioritizing international interests over national priorities.
9. Downward pressure on wages

Globalization can lead to downward pressure on wages as businesses seek to reduce costs by outsourcing jobs to countries where labor is cheaper (Mir, Hassan & Qadri, 2014).
This competition for lower-cost labor markets can result in wage stagnation or decreases in higher-wage countries.
Additionally, the influx of workers willing to accept lower wages can suppress wage growth even in sectors not directly exposed to international competition.
10. Spread of Political Ideologies

While earlier I noted that globalization may have sped up the spread of democracy, the opposite may occur.
While democracy may have been promoted by globalization – especially in the 20th Century – the same could happen with anti-democratic ideologies . For example, recently we have seen the spread of authoritarianism and “illiberal democracy” across the world.
11. Brain drain in developing countries

Globalization leads to brain drain in developing countries as highly educated and skilled professionals migrate to developed countries in search of better job opportunities, salaries, and living conditions (Dumont, Rayp & Willemé, 2012).
This migration of talent results in a significant loss of skilled labor for the originating countries, impacting their development and economic growth.
The departure of these key individuals can also lead to a shortage of expertise necessary for local advancement and innovation.
12. Spread of diseases across borders
Globalization leads to the spread of diseases across borders as increased international travel and trade facilitate the rapid movement of people and goods around the world.
This mobility can enable pathogens to cross geographical boundaries more easily, leading to the faster spread of infectious diseases.
Outbreaks that might have been contained within a region in the past can now quickly escalate into global health emergencies.
13. Vulnerability to global economic fluctuations

A globalized nation may be vulnerable to global economic fluctuations as economies become increasingly interconnected through trade, investment, and financial markets (Mendoza & Quadrini, 2010).
This interconnectedness means that economic issues in one country or region can have ripple effects globally, impacting economies that might not be directly related to the initial problem.
As a result, even local economies can be significantly affected by economic downturns or crises occurring in distant markets.
14. Concentration of corporate power

Some argue that globalization leads to the concentration of corporate power as large multinational corporations expand their reach and influence across multiple countries (Cowling & Tomlinson, 2005).
These corporations can dominate markets, overshadowing smaller local businesses and potentially manipulating markets to their advantage.
This concentration of power can lead to reduced competition, influence over political and economic policies, and an unequal distribution of economic benefits.
15. Potential for global monopolies and oligopolies

Similarly, globalization could lead to the potential for global monopolies and oligopolies as dominant corporations expand their reach across international borders (Burlacu, Gutu & Matei, 2018).
These entities can gain excessive market control, limiting competition and potentially leading to higher prices and fewer choices for consumers.
The global scale of these companies makes it challenging for new entrants to compete, and their influence can extend to shaping market regulations and policies in their favor.
Baldwin, R. (2008). EU institutional reform: Evidence on globalization and international cooperation. American Economic Review, 98(2), 127-132.
Burlacu, S., Gutu, C., & Matei, F. O. (2018). Globalization–pros and cons. Calitatea , 19 (S1), 122-125.
Cowling, K., & Tomlinson, P. R. (2005). Globalisation and corporate power . Contributions to Political Economy , 24 (1), 33-54.
Dincer, H., Yüksel, S., & Hacioglu, Ü. (Eds.). (2018). Strategic Design and Innovative Thinking in Business Operations: The Role of Business Culture and Risk Management . Springer International Publishing.
Dumont, M., Rayp, G., & Willemé, P. (2012). The bargaining position of low-skilled and high-skilled workers in a globalising world . Labour Economics , 19 (3), 312-319.
Erixon, F. (2018). The economic benefits of globalization for business and consumers. European Centre for International Political Economy .
Hodos, T. (Ed.). (2016). The Routledge Handbook of Archaeology and Globalization. Taylor & Francis.
Mendoza, E. G., & Quadrini, V. (2010). Financial globalization, financial crises and contagion . Journal of monetary economics , 57 (1), 24-39.
Mir, U. R., Hassan, S. M., & Qadri, M. M. (2014). Understanding globalization and its future: An analysis. Pakistan Journal of Social Sciences , 34 (2), 607-624.
Sharma, N. K. (2013). Globalization and its impact on the third world economy. Crossing the Border: International Journal of Interdisciplinary Studies , 1 (1), 21-28.

- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 10 Reasons you’re Perpetually Single
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 20 Montessori Toddler Bedrooms (Design Inspiration)
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 21 Montessori Homeschool Setups
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 101 Hidden Talents Examples
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
- Cultural Globalization as the Americanization of the World’s Cultures Words: 1925
- Globalization Advantages and Negative Cultural Impact Words: 970
- Ways of Eating Around the World: Impact of Globalization Words: 2208
- Interconnection of Globalization and Culture Words: 628
- The Impact of Racism on Globalization Words: 4995
- Globalization: Impact and Consequences Words: 599
- Evaluating Cultural Dimensions of Globalization Words: 3304
- Globalization and Its Pros and Cons Words: 615
- Is Globalization a Threat or an Opportunity to Developing Countries? Words: 1603
- Globalization and its Impact on the World Words: 583
- The Effects of Globalization on Sports Words: 2364
- History of Globalization and World Integration Words: 1432
- Globalization: More Positive Effects Than Negative Ones Words: 1643
- Impacts of Globalization on the Developing Countries Words: 2315
- Globalization and Businesses in New Economies Words: 2055
- Globalization: Managing Across Cultures Words: 3025
- Globalization, Its Defenders and Critics Words: 903
- Globalization Impacts on Trade and Employment Words: 1723
The Advantages of Globalization
Introduction, accessibility of technology, choice of culture, diverse culture products, sharing knowledge, reference list.
The world is fast becoming a global village, seemingly smaller than it was a decade ago. This scenario has resulted from the development of trade and transport systems, thus making it conducive for movement of people, goods, services, and ideas and creating diversity in social, economic, political, and cultural views across the world. The technological revolution has also played a critical role in advancing globalization.
Globalization is an age-old concept, even though it has elicited great discourses in contemporary times as compared in the past where the idea of a global village seemed farfetched. Globalization is the process of growth and interconnection of world economies and cultures, which are aided by transport and trade. This process has been in progress for hundreds of years although at a much slower pace than in recent years as aforementioned.
It affects the cultural, economic, and social spheres of society. As with every thing else, globalization has both advantages and disadvantages. This paper highlights some of the positive effects that globalization has on all spheres of human interaction including the sharing of cultural products such as music, sports, and movies, knowledge, technology, and foods from different cultures.
A few decades ago, the majority of the contemporary technology was non-existent in most developing countries. People had to do almost everything manually including basic tasks such as doing laundry, cleaning floors, and cooking. However, this scenario was different in most developed countries as they already had some of the technology needed to carry out such tasks with ease.
However, with the improvement and advancement in modes of transport in developing countries, developed countries found new markets in most parts of Africa and Asia and products such as vacuum cleaners, microwaves, and washing machines found their way to developing countries. The main advantage of this development is that it has drastically improved the quality of work done while reducing the amount of time spent doing the same.
This aspect consequently improves the lifestyles of the people using the machines (Rifkin, 2003, Spiritual Perspectives on Globalization, p.176). Nevertheless, western countries are constantly modifying these products and making them more efficient. Today, it does not take a decade for any new technology to be available to consumers in developing countries.
Globalization has opened boundaries across the world, and a new technology in the United States will only take a few months before hitting the market in developing countries. Also, the transport systems have drastically evolved from the use of steam engines and ships to using electric trains and airplanes.
Communication is also easier now with the introduction of hi-tech mobile telephones that connect people both in the same country and with people in different continents at the touch of a button (. The ultimate result of such developments is that people in different areas of the world are in a position to enjoy the benefits of products not ordinarily available to them in their own countries and have expansive markets in other parts of the world.
Marketing forums like Amazon, e-Bay and many other online trading forums enable consumers to purchase goods and services online regardless of one’s location (Pew Global Attitudes Project, 2007, p.177-178).
Globalization has led to the introduction of diverse cultural practices in places where originally there existed only one practice. A century ago, a certain culture was a specific aspect unique to a certain society. For instance, the Chinese culture was specific to people and residents of China, European culture was specific to people living in Europe and African culture specific to Africa.
However, ease of trade and travel has changed this dynamic by making most societies multicultural, with everyone having the freedom to embrace his or her culture of preference rather than being restricted to the culture of birth. For instance, it is Chinese culture that children should not buy food with their own money.
This cultural pursuit seeks to encourage children to eat whatever that their parents place before them, consequently encouraging healthy eating. Nevertheless, since the McDonalds opened its first branch in Beijing in 1992, this cultural requirement has changed drastically.
McDonald’s services, which include hosting birthday parties, appealed to children regardless of the fact that birthdays are not culturally celebrated in China either (The Levin Institute, n.d. Globalization and Culture: Globalization and local culture, p.180).
Also, the introduction of Starbucks, an American coffee retail enterprise, in Italy has given the people of Italy a choice between maintaining their culture of drinking coffee in small and relaxed establishments and ordering coffee at Starbucks to drink on the go at their convenience. There are also other restaurants established for the sole purpose of selling food associated with specific cultures.
There are restaurants that only make Italian cuisine, Chinese cuisine, Japanese cuisine, and French cuisine to mention but a few, while others take pride in being inclusive and serving cuisines from different cultures (Hastings, Thiel & Thomas, 2003, The deadly noodle, p.180). This aspect gives every individual a chance to either try something new or stick to what is familiar.
Another good example is fashion and how different cultures influence their trends. For instance, people associate the Kenyan Maasai kikoi with East Africa and the Ankara with West Africa. Therefore, a person may use any of the two fabrics or use them together to give an African feel to his or her outfit. The beauty of the freedom to choose elements from different cultures is that it creates diversity and nurtures an appreciation for different cultures.
It also creates opportunities to develop new and unique cultures made from the combination of cultures from different societies as well as a means to celebrate similarities. Sports are one such similarity, which is celebrated worldwide through the organization of events that bring different countries together to compete in various disciplines. The Olympics and the FIFA World Cup are examples of such events.
During these events, people from different cultures meet and exchange ideas and practices. Also, some sports are specific to some countries; for instance, the Chinese acrobatics, and through such events, other countries get to learn about these sports, which are specific to some cultures.
Apart from increasing the availability of consumer goods, globalization has increased production and trade of culture products and services such as music and movies. Cultural products and services are products and services that echo the lifestyles and cultural background of a given society. For instance, movies vary depending on the part of the world they come from and the culture in force in that particular part of the world.
For example, the United States developed the ‘Hollywood’ trademark for outstanding movies and other artistic displays that best defined what the culture is like in that part of the world(The Levin Institute, n.d. Globalization and Culture: Globalization and local culture, p.180). They packaged these performances and sold them as a commodity within the American borders.
As globalization progressed, other parts of the world such as Asia and Africa provided a ready market for this commodity. It also created a platform for different cultures around the world to share their experiences whether political, social-cultural, or economical.
It did not take long for Asia and Africa to start producing movies using the knowledge gained from the commodity they bought and incorporating their own cultural experiences into the stories.
Bollywood is the Asian version of this commodity while the Nollywood is the African version produced in the West African region.
Just like the example given earlier on regarding the choice of a culture where people establish restaurants serving specific foods from different parts of the world, the IMAX Company based in the United States is recorded to have opened six hundred and ninety-seven (697) movie theaters in fifty-two countries worldwide by September of 2012.
These theaters provide an avenue for people to enjoy the American movie-watching culture in an authentic American environment (The Levin Institute, n.d. Globalization and Culture: Globalization and local culture, p.180).
Air transportation has made it possible for people to leave one part of the world to learn and gain knowledge in another part of the world.
The Internet and by extension the social media platforms such as Facebook and Twitter have made haring of information, and consequently, knowledge easier and faster as information is relayed in real time to people all over the world (Knickerbocker, 2004, If Poor Get Richer; Does the World See Progress? page 185-186).
The Internet burst has facilitated knowledge sharing by a great margin, and even now, people in developing countries can undertake online studies offered in learning institutions in developing countries. Thanks to globalization, people can have cures to most of the diseases across the world.
A cure discovered in one part of the world now means a cure for the rest of the world. For instance, courtesy of the efforts of Dr. Jonas Salk in the early 1950s who invented the Polio vaccine the disease is now preventable. However, this achievement would not be possible without means of sharing information.
This information-sharing aspect is not only important in issues regarding medicine, but also in political, social, environmental and economic issues. As long as there is an interconnection of interests, through trade, for instance, it is crucial to ensure that there is a flow of information and knowledge.
A good example of why this element is important is the global financial meltdown that occurred throughout the world like a ripple effect to a credit crisis in Europe. Had there been information regarding the credit crunch on the onset, most of the countries with financial links to credit institutions in Europe would have taken necessary measures to prevent a global meltdown.
World leaders hold conventions in different places at different times of the year all over the world to discuss various ways of ensuring conservation and sustainability of the environment because what happens in one part of the world affects the rest of the world.
Carbon emissions, for example, affect the o-zone layer thus causing global warming across the world, regardless of the origin of the emissions (Knickerbocker, 2004, If Poor Get Richer; Does the World See Progress?, page 185-186).
Since every element has a negative side, globalization has numerous positive aspects that have changed the lives of many individuals across the world. The process is continuous and finds new ways of linking various parts of the world together.
Through globalization, culture has defied territorial boundaries, thus allowing the sharing of life-changing knowledge coupled with the development and sharing of technology. Globalization has created diversity in every part of the world and made people to appreciate both what is within and outside their territorial borders.
Hastings, M., Thiel, S., & Thomas, D. (2003). The deadly noodle. Newsweek, 141 (3), 180-182.
Knickerbocker, B. (2004). Globalization and sustainability: If Poor Get Richer, Does World See Progress? The Christian Science Monitor . Web.
Pew Global Attitudes Project. (2007). World publics welcome global trade-But not immigration.
Rifkin, I. (2003). Framing articles: What is globalization: Spiritual Perspectives on Globalization. Woodstock, VT: Skylight Paths Publishers.
The Levin Institute State University. (n.d.). Globalization and Culture: Globalization and local culture. Web.
Cite this paper
- Chicago (N-B)
- Chicago (A-D)
StudyCorgi. (2020, April 16). The Advantages of Globalization. https://studycorgi.com/the-advantages-of-globalization/
"The Advantages of Globalization." StudyCorgi , 16 Apr. 2020, studycorgi.com/the-advantages-of-globalization/.
StudyCorgi . (2020) 'The Advantages of Globalization'. 16 April.
1. StudyCorgi . "The Advantages of Globalization." April 16, 2020. https://studycorgi.com/the-advantages-of-globalization/.
Bibliography
StudyCorgi . "The Advantages of Globalization." April 16, 2020. https://studycorgi.com/the-advantages-of-globalization/.
StudyCorgi . 2020. "The Advantages of Globalization." April 16, 2020. https://studycorgi.com/the-advantages-of-globalization/.
This paper, “The Advantages of Globalization”, was written and voluntary submitted to our free essay database by a straight-A student. Please ensure you properly reference the paper if you're using it to write your assignment.
Before publication, the StudyCorgi editorial team proofread and checked the paper to make sure it meets the highest standards in terms of grammar, punctuation, style, fact accuracy, copyright issues, and inclusive language. Last updated: January 27, 2022 .
If you are the author of this paper and no longer wish to have it published on StudyCorgi, request the removal . Please use the “ Donate your paper ” form to submit an essay.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
This paper discusses the advantages and disadvantages of globalization using evidence from academic sources. The report also suggests how governments and companies may implement to reduce the negative impact of the process.
The advantages of globalization are actually much like the advantages of technological improvement. They have very similar effects: they raise output in countries, raise productivity, create more jobs, raise wages, and lower prices of products in the world economy.
Globalization: The Pros and Cons Essay. Exclusively available on IvyPanda®. Updated: Apr 6th, 2024. There are multiple arguments for and against globalization, each referring to the difference in the impact it has on the economy of individual state and their societies.
While globalization has brought about significant economic growth and cultural exchange, it has also been criticized for exacerbating inequalities and eroding local cultures. This essay aims to explore both the positive and negative aspects of globalization.
This essay aims to explore both the advantages and disadvantages of globalization, offering a balanced perspective on its multifaceted impact.
Thus, globalization can be defined as the stretching of economic, political, and social relationships in space and time. A manufacturer assembling a product for a distant market, a country submitting to international law, and a language adopting a foreign loanword are all examples of globalization.
Advantages of Globalization 1. Economic Growth. It’s widely believed that one of the benefits of globalization is greater economic growth for all parties. There are several reasons why this might be the case, including: Access to labor: Globalization gives all nations access to a wider labor pool. Developing nations with a shortage of ...
The comprehension of the positive sides of globalization helps to consolidate and strengthen the beneficial effects on the social development. Globalization provides the advantages of the international cooperation in business, science, and knowledge exchange.
The Advantages of Globalization. 1. Increased Economic Growth. Globalization facilitates technology, knowledge, and goods transfer, which in turn boosts economic growth (Erixon, 2018). Through globalization, countries can now purchase the newest technologies and import the most productive machinery from other countries.
This paper highlights some of the positive effects that globalization has on all spheres of human interaction including the sharing of cultural products such as music, sports, and movies, knowledge, technology, and foods from different cultures.